Chemistry - Medconnect Practice Papers
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
atomic size across periodic table
atomic size gradually decrease from left to right
because within period electrons are added
does shape influence the polarity of the molecule
yes
when does pressure affect rate of reaction
in a reaction of gases
it does not however influence the rate of reaction of solids and liquids
oxidation-reduction (redox)
reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two species
electrolysis
A process by which an electric current breaks chemical bonds.
electrochemical series
A list of elements in decreasing order of ease with which they lose electrons.
why won't Copper reach with acids to liberate hydrogen
it is below hydrogen in the electrochemical series
sublimation is the
phase transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase
S + O2
SO2
1 mole reacts with 1 mole
Markovnikov's Rule
hydrogen will add to the least substituted carbon of the double bond
H attaches to least stable
sodium hydroxide and alcohols
do not react hence no salt is produced
naming esters
attached to c=o forms oate end portion
peptides are
polyamides of amino acids not polyesters
acronym to remember reactivity series
please stop calling me a careless zebra instead try learning how copper saves gold
(displacement)
s equilibrium aq
nacl aq solution must be
saturated
saturated chemistry definition
single bonds only
concentrated
HCO3-
this species in water can function as both bronsted acid and bronsted base
HNO3
-is strong oxidising agent
-highly corrosive
-reacts with CaO
-salts are NOT called nitrites BUT ACTUALLY CALLED NITRATES
which hydrogen is most easily abstracted in a radical bromination
the most stable hydrogen
bonded to the carbon that has the most c-c bonds
isobars are atoms that hav
the same mass but different atomic numbers
boiling point is determined
by intermolecular bonds
a product of neutralization of strong acid and strong base
KI
which substance releases hydrogen when it reacts with steam
Al Li CH3OH H2S
Li
most alkali metals +h2o
produce hydrogen expect beryllium
g1 and g2
prefix of the first member in alkene or alkyne
eth
primary amines react with carbonyl compounds
products obtained are called imines
reagent that can be used to distinguish between pentanal and pentanone
Ag2O
Tollens test
reagent carboxylic acid to alkyl halide
reaction of alcohols with Pcl5 or PCl3 yields an alkyl halide RCl
H2O bonding
both polar covalent and hydrogen
Which of the following solutions of equal concentration will have a 2-fold higher osmotic pressure than that of a sucrose solution of the same concentration?
KCl
K2SO4
AlCl3
K3PO4
KCl will have a higher osmotic pressure than sucrose. Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in water by osmosis
measure of the tendency of a solution to take in water by osmosis
osmotic pressure
if the pH value of a salt solution is 7, most likely this is a solution of
Complete neutralisation of a strong acid and a strong base will form a neutral salt and water. HCl is a strong acid and KOH is a strong base. So when they are reacted together, they form a solution with a pH of 7.
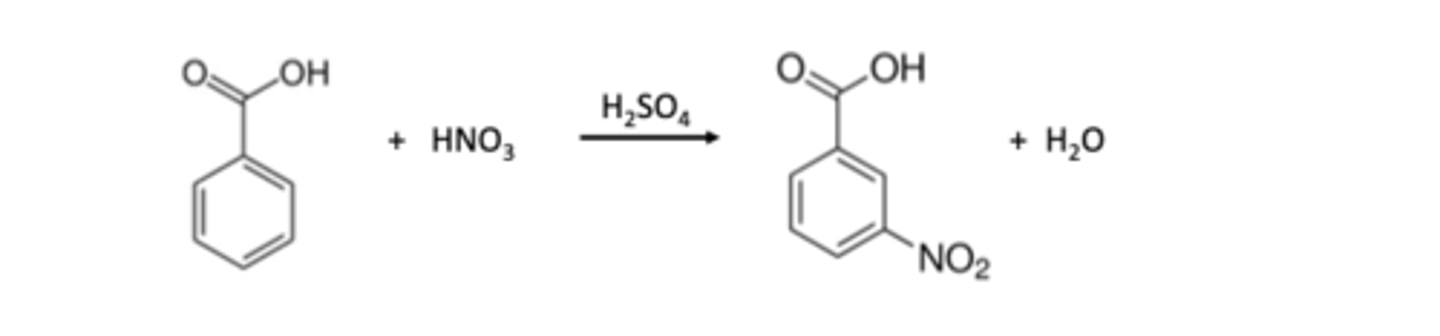
product if benzoic acid nitration
1 c between COOH and N2O
All of the substances listed below are natural polymers except:
proteins nucleic acids polysaccharides and lipids
lipids
max number of covalent bonds formed by nitrogen
( normal, not dative)
3
the aq solution of glycerol and water
the aq solution of glycerol freezes at a lower temperature than that of water
rate law
an expression relating the rate of a reaction to the concentration of the reactants
REACTANTS
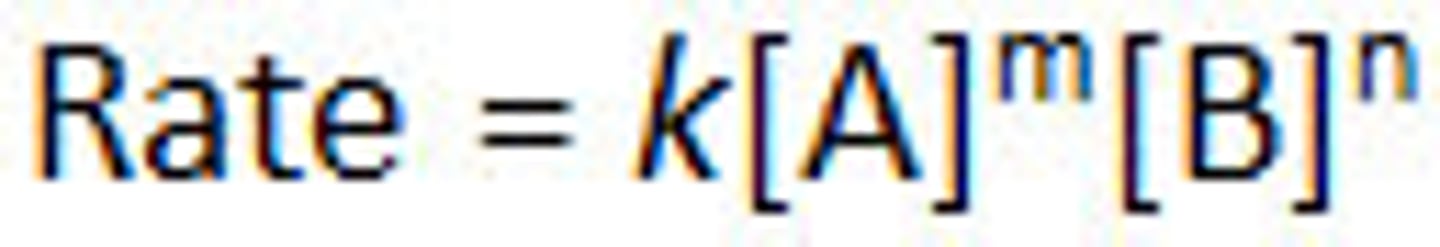
under similar conditions which of the following is the best reducing agent :
F Br Cl I
Br
To be a reducing agent you transfer electrons onto something else, ie the halide ion loses electrons. Down the group shielding increases and atomic radius , therefore weaker nuclear attraction. The reducing agent, its reducing something else and is actually being oxidised itself.[if it is the agent of something the thing it is the agent of is the effect of its friend]
metal that doesn't give H2 on treatment with HCl
Zn, Fe, Ag, Ca
Ag
unreactive metal ( Cu Ag Au)
molarity
moles of solute/litres of solution
why is Al(OH)3 a weaker base than LiOH
Al is a group 3 metal
are metals reducing or oxidising agents
metals, as solid materials often are reducing agents
metal ions are the oxidized form and act as oxidizing agents already lost e- relatively low electronegativity
isomer questions remember
cyclo molecules can be formed with alkene molecular formulas
chain isomerism
the same molecular formula, but a different arrangement of carbon atoms in the chain
positional isomerism
the same molecular formula, but the functional group in a different position
functional group isomerism
same molecular formula but different functional group
metamerism isomerism definition
Metamerism is a type of structural isomerism in which different alkyl groups are attached to the same functional group.
C6H5-CO-CH3
acetophenone
simplest aromatic ketone
Monosaccharide fructose is classified as an:
ketohexose
COOH + NaOH aq
carboxylate salt
COO-Na+
*LOOK OUT FOR FG IN COMPLEX MOLECULES
phenol + NaOH aq
phenolate salt
O-Na+
The alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produces
glycerol and soap
when triglycerides react with NaOH or Koh they are converted into soap and glycerol
alkaline hydrolysis of esters
saponification
structure of aspirin
benzene ring
COOH at C1
COOCH3 at C2
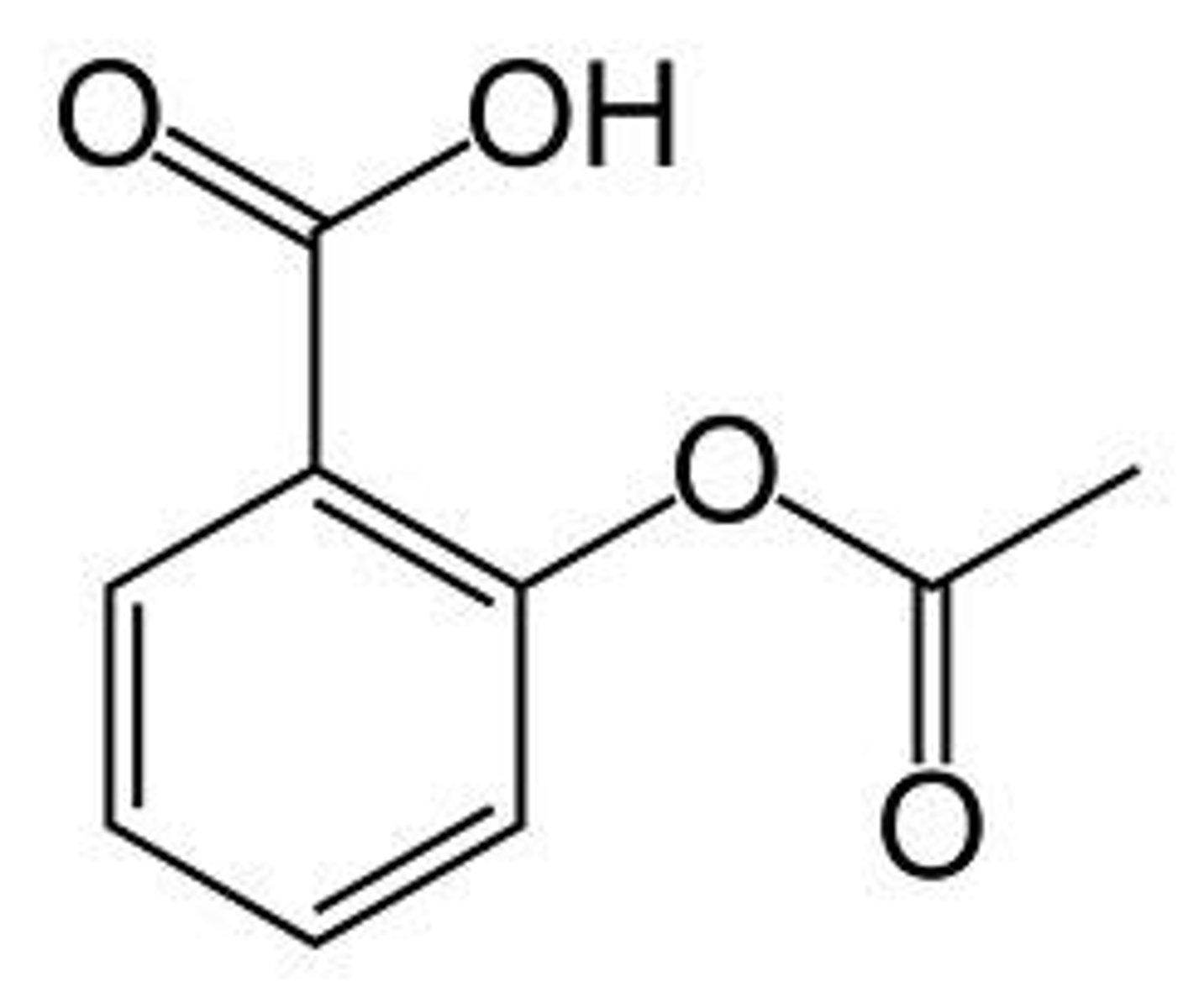
acetyl group
COCH3
glucose
C6H12O6
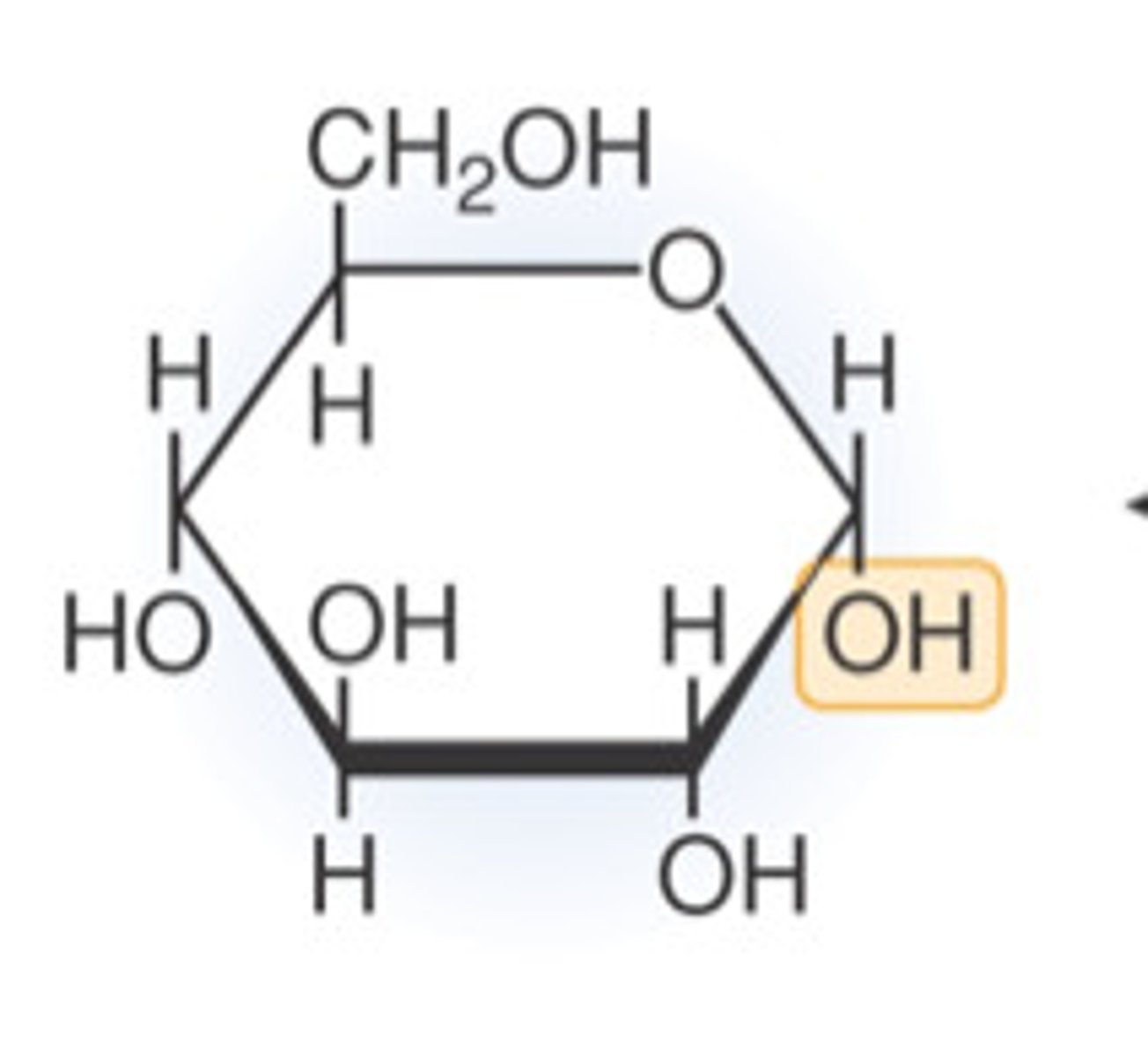
fructose
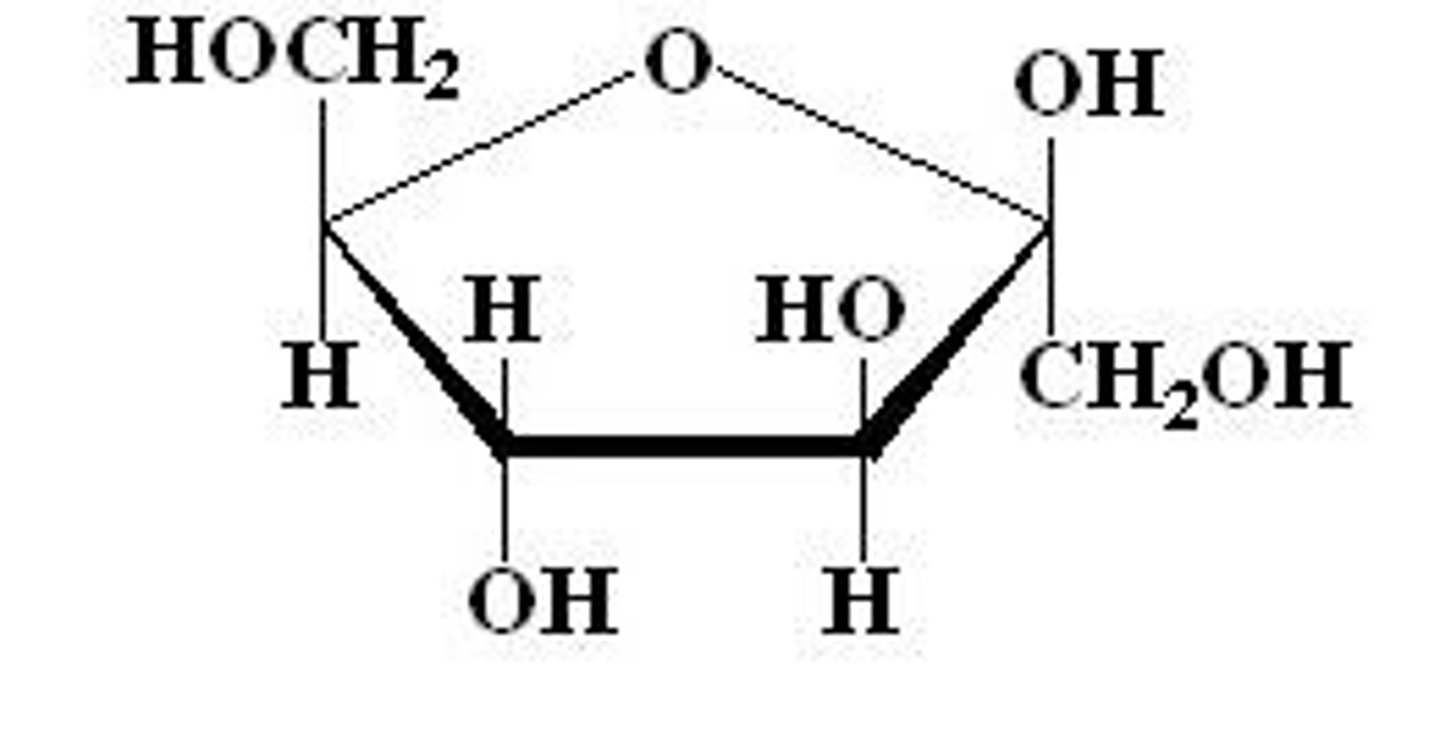
common reducing agetns
H2SO4 conc, KmnO4, K2Cr2O7, MnO2, Cl2, H2O2
common oxidizing agents
H2, Zn, C CO, LiAlH4, NaBH4
are solids included in the rate equations
no
their ability to react depends only on the surface at which particles collide, surface remains constant and erosion takes place after the initial phase of the reaction, so a time in the reaction not relates to the rate law
factors effecting deprotonation
-polarity of H-A bond
-size of atom A
-acid strength also depends in the stability of conjugate base
water solution of which compound has the lowest pH
NaHCO3 H2S HBr HCN
HBr
most acidic
Br larger than S
I2 + 10 HNO3 2 HIO3 + 10 NO2 + 4 H2O iodine is `
a reductant and reduces nitrogen
reductant - loses electrons
Acid + alkali
salt + water
reacts with Na but not with NaOH
an alcohol
Na+ and OH- are mobile in NaOH so unable to react with alcohol
(covalent and ionic)
nitrile
RCN
nitro
NO2-
benzene and NaOH
is impossible
benzene is very stable due to its ring structure and pi bonds and only has C and H ie no groups for NaOH to react with
Methylbenzene + Br2
possible
benzanoic acid + NaOH
possible
benzene + H2
possible
tollens reagent
AgNO3 + NH3
glucose is
aldohexose
aldohexose
a hexose with an aldehyde group on one end.
reagent that can be used to distinguish between pentanal and pentanone
Cu(OH)2
litmus paper test
Acid/ ammonia gas: red
Base: blue
type of bonds in KH
ionic
Henry's law states that
the volume of gas that will dissolve in a solvent is proportional to the solubility of the gas and the gas pressure
not apply to solubility of CO2
Exceptions to Henry's Law
CO2
or very dilute
(NH4)2SO4
ammonia sulfate
litmus colour to red
ammonia damp universal indicator
blue
pH of KCN
11
pH value with lowest conc of H+
14
Na2O and Ca(OH)2
do not react as they are 2 bases
metal oxides and metal hydroxides
are both bases
obtain sulfuric acid
dissolving SO3 in water
[make sure its a 3 not 2]
acid+ metal
salt + hydrogen
[BIPRODUCTS]
elimination reaction
The removal of a molecule from a saturated molecule to make an unsaturated molecule
intramolecular dehydration
addition reaction for alcohol, one reactant
alcohol to alkene
triol
glycerol
glucose has a keto group
false
gulcose dissolves in water
yes it dissolves
phenylamine and acetic acid
will not form a salt
benzene and amino group
amino benzene
acetic acid
CH3COOH
total hydrolysis of cellulose produces
glucose
osmotic pressure
pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane
osmotic pressure equation
II=iMRT
i: # of particles in solution
M: molarity
R: gas constant
T: tempt in Kelvins
Dissolution (chemical)
minerals dissolved by water or acids. Ex: halite/calcite, carbonates dissolve faster
characteristics of dissolution
-reversible process
-depends on temperature
-depends on the nature of the solvent and solute
equimolar
Containing moles at a ratio equal to the stoichiometric ratio.