AP Biology Unit 5 - Heredity Flashcards (WIP)
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A flashcard set for AP Biology's Unit 5 - Hereditary. This set mostly focuses on vocabulary but touches on the unit's concepts as well. I tried to make this set as well as I could... if you found this set useful, please give 5 stars :) Also, it's REVERSIBLE! You can train either definition OR term :D
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Recombinant (Chromosome)
Product of recombination or “crossing over.” The chromosome has been “mixed up” with other alleles.
This results in [this] which differs from those found in the parents.
![<p>Product of recombination or “crossing over.” The chromosome has been “mixed up” with other alleles.</p><p>This results in [this] which differs from those found in the parents.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/061c748c-1970-4414-8d23-808287970b81.png)
Recombination / “Crossing over”
The exchange of genetic material (of same genes) between different chromosomes or chromatids (between homologous chromosomes) leading to new allele combinations. The chromosomes get “mixed up.”
Law of Independent Assortment (“Second law”)
Mendelian principle stating that alleles for different traits segregate independently of one another during gamete formation.
Parental Chromosomes (in respect to “crossing over”)
The chromosomes before recombination/making the recombinants.
Autosomes
All chromosomes except for sex chromosomes.
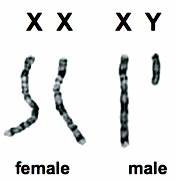
Sex Chromosomes
The chromosomes that determine the sex of an organism, typically referred to as X and Y chromosomes in mammals. Not Autosomes.
Haploid Cell
A cell that contains one set of chromosomes (two “strands”), typically found in gametes.
[These] have half the number of chromosomes compared to diploid cells, which contain two sets.
(n)
![<p>A cell that contains one set of chromosomes (two “strands”), typically found in gametes. </p><p>[These] have half the number of chromosomes compared to diploid cells, which contain two sets. </p><p>(n)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f8792da0-a4d5-4412-89a0-bdc081de99f4.png)
Diploid Cell
A cell that contains two complete sets (pairs) of chromosomes, one from each parent, typically found in somatic cells.
(2n)

Goal of Mitosis
Goal is to replicate the parent cell. Key in asexual reproduction.
Goal of Meiosis
Goal is to create genetic diversity and mutation. Key in sexual reproduction.
Stages in Meiosis
Two rounds of division: [this] I and [this] II, which include prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase in each round, resulting in four genetically diverse haploid cells.
The first stage of division breaks apart chromosomes, while the second stage breaks apart chromatids.
Stages of Mitosis
Interphase > Prophase > Metaphase > Anaphase > Telophase > Cytokinesis/Daughter cells
Interphase
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
When an organism is “true-breeding” for a trait, that means that the organism is…
homozygous for that trait, consistently producing offspring with the same phenotype.
Phenotypic plasticity
The ability of one genotype to produce more than one phenotype when exposed to different environments. (For adaptability.)
Dihybrid Cross
A “violation” of the Law of Assortment
Linked traits violate [this] Mendelian law.
Law of Segregation (“First law”)
Law of Dominance (“Third law”)