Protists: Diversity, Characteristics, and Roles in Ecosystems
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Protists
Any eukaryotic organism which is not a plant, fungi or animal.
Most protists prefer ______ or _______locations if they are terrestrial.
Aquatic or moist Locations
Autotrophic
Can produce their own food, often through photosynthesis.
Photoautotroph
Organisms that have chlorophyll and can perform photosynthesis.
Heterotrophic
Organisms that obtain their food by consuming other organisms.
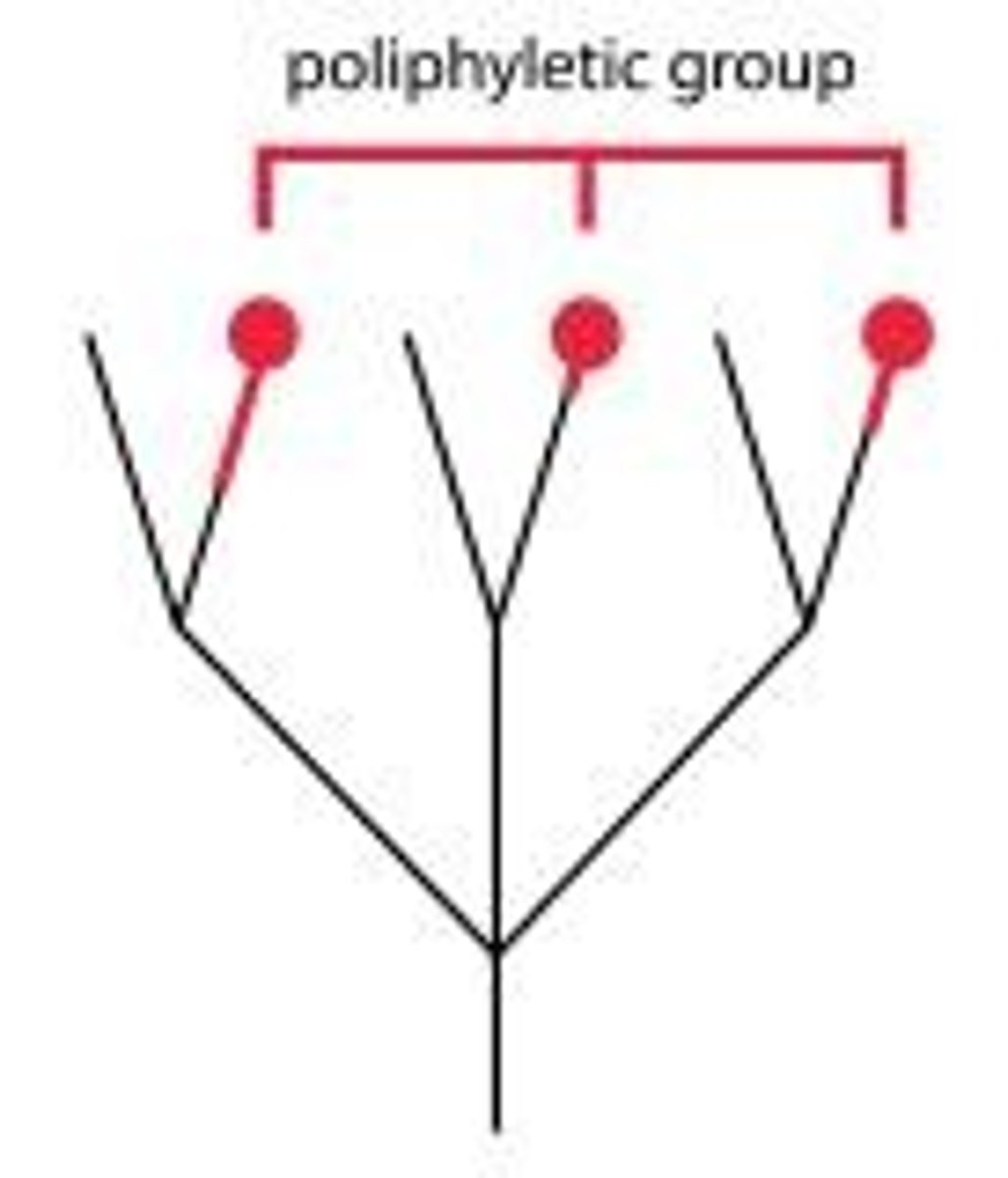
Polyphyletic
A group that is derived from more than one common evolutionary ancestor.
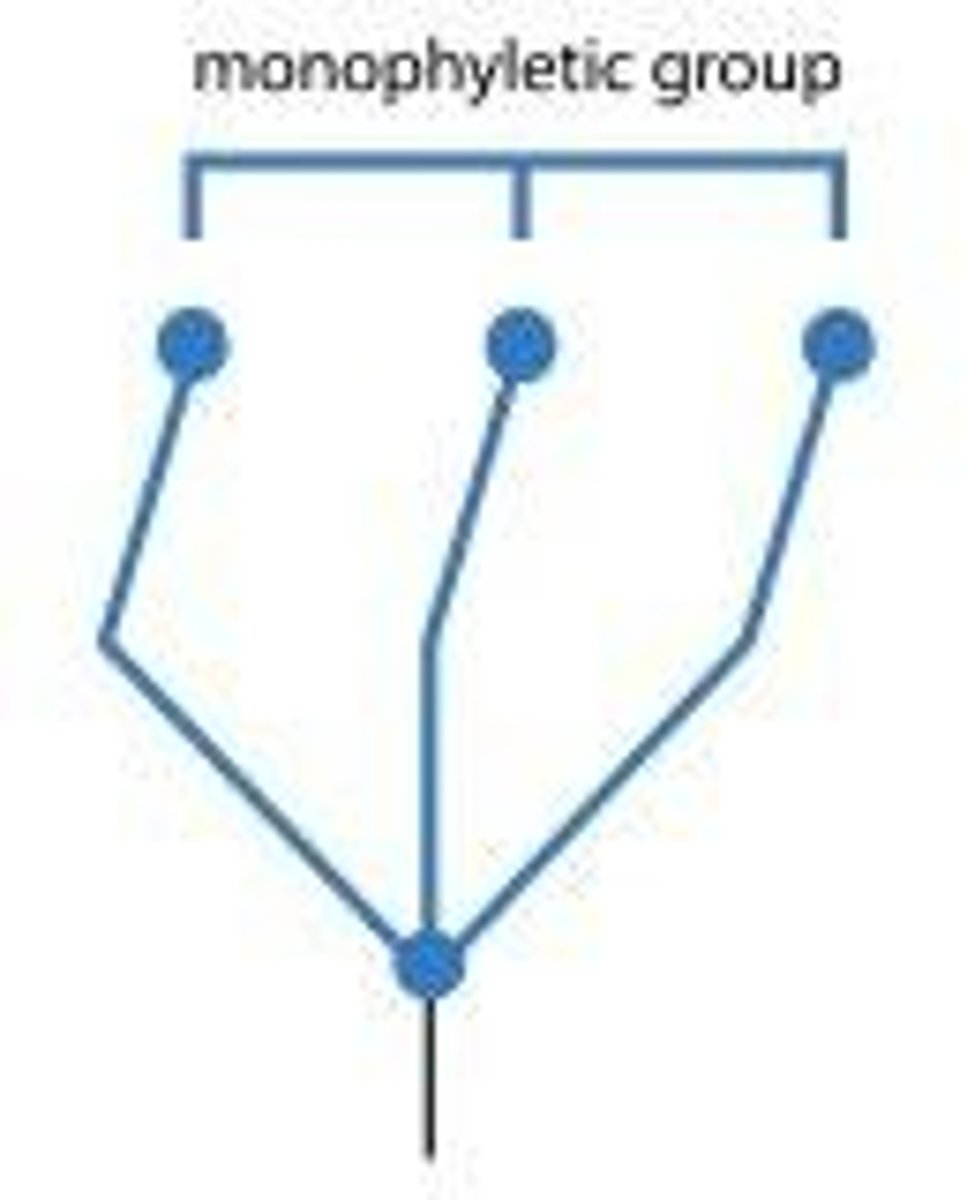
Monophyletic
A group that consists of all the descendants of a common ancestor.
Chytridiomycota
Fungi-like single-celled eukaryotic microbes that are ancestors of fungi.
Choanoflagellates
Single-celled eukaryotic microbes that are ancestors of animals.
Chlorophytes
Single-celled photosynthetic eukaryotic microbes that are ancestors of plants.
Algae
Diverse and polyphyletic protists that can be multicellular or unicellular.
Sargassum
A genus of large brown seaweed that floats in island-like masses.
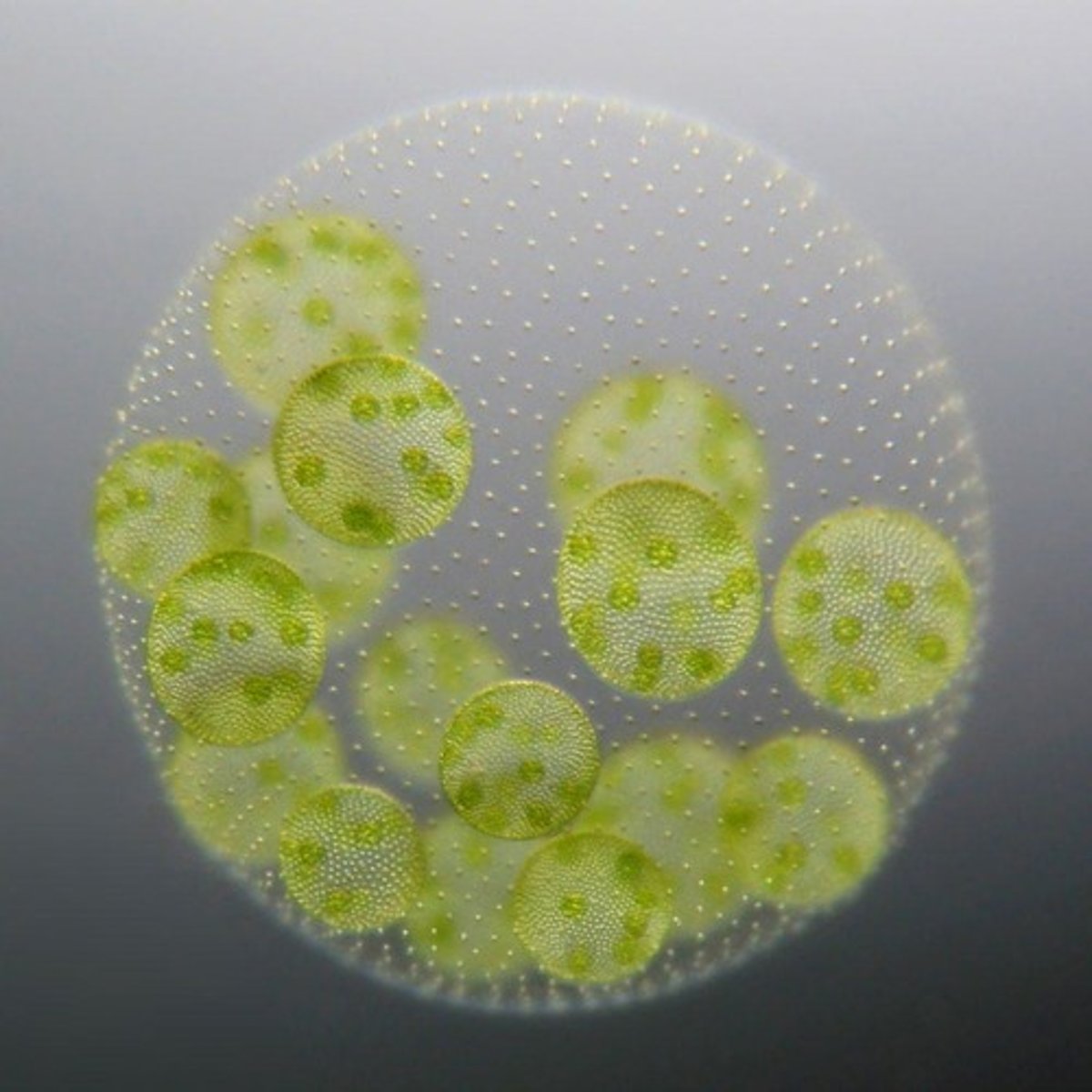
Chlorella
A genus of photosynthetic single-cell green algae that can multiply rapidly.
Volvox
A single-celled genus that forms spherical colonies and is capable of sexual reproduction.

Ciliates
Protists with specialized hair-like organelles called 'cilia' used for motility.
Cilia
Short, numerous hair-like structures used for motility in ciliates.
Micronucleus
One of the two nuclei in ciliates, responsible for reproduction and is diploid.
Macronucleus
One of the two nuclei in ciliates, responsible for cell regulation and is ampliploid.
Fission
A method of reproduction used by ciliates.
Conjugation
A process ciliates can perform in addition to fission for reproduction.
Contractile Vacuole
An organelle in ciliates used for osmotic balance.
ampliploid
Reproduce using fission (but different forms) and can also perform conjugation. Heterotrophs, feed through phagocytosis.
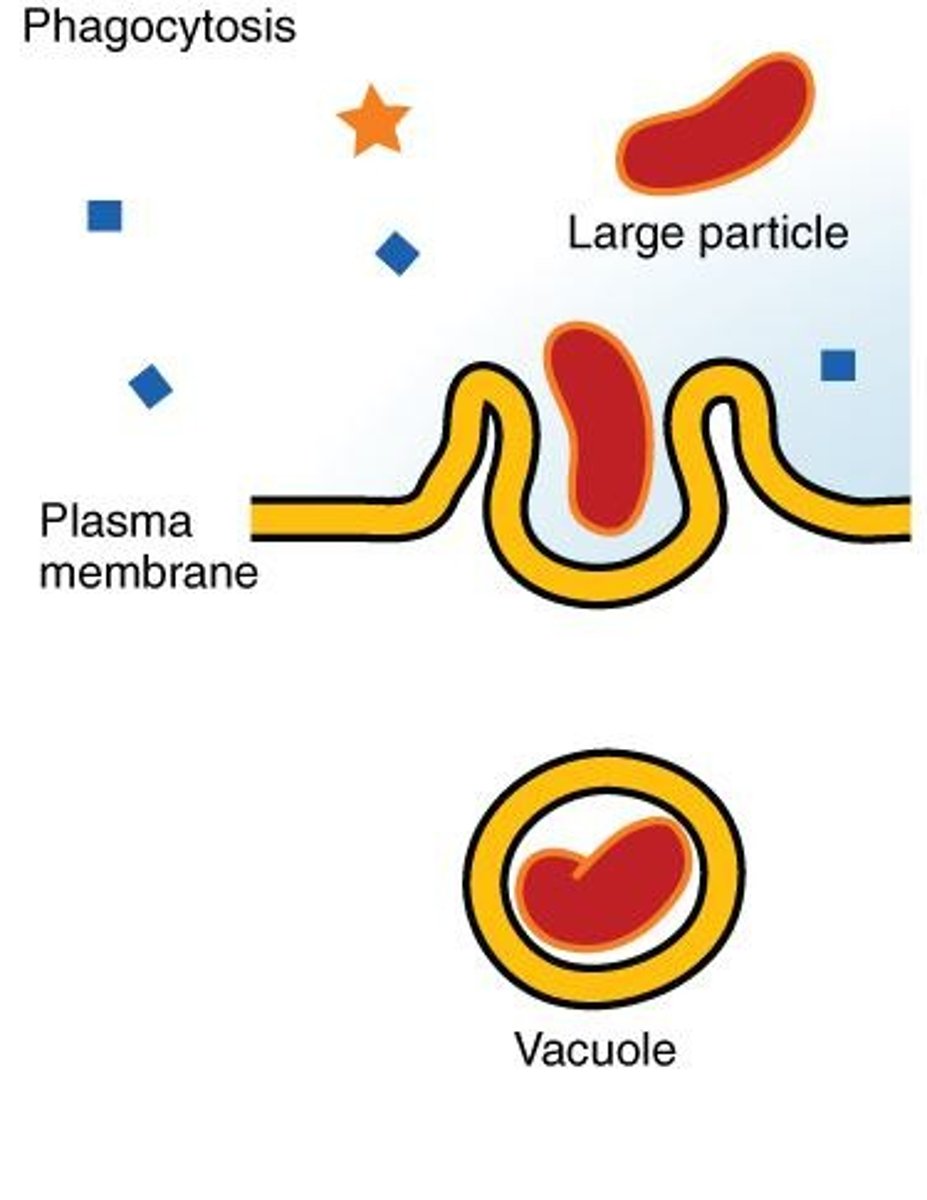
Phagocytosis
A form of endocytosis where cells engulf particles using the plasma membrane. Many protists use this as a way to 'feed', giving rise to an internal compartment 'phagosome' which can merge with lysosomes for digestion.
Paramecium
The platonic ideal of a ciliate.
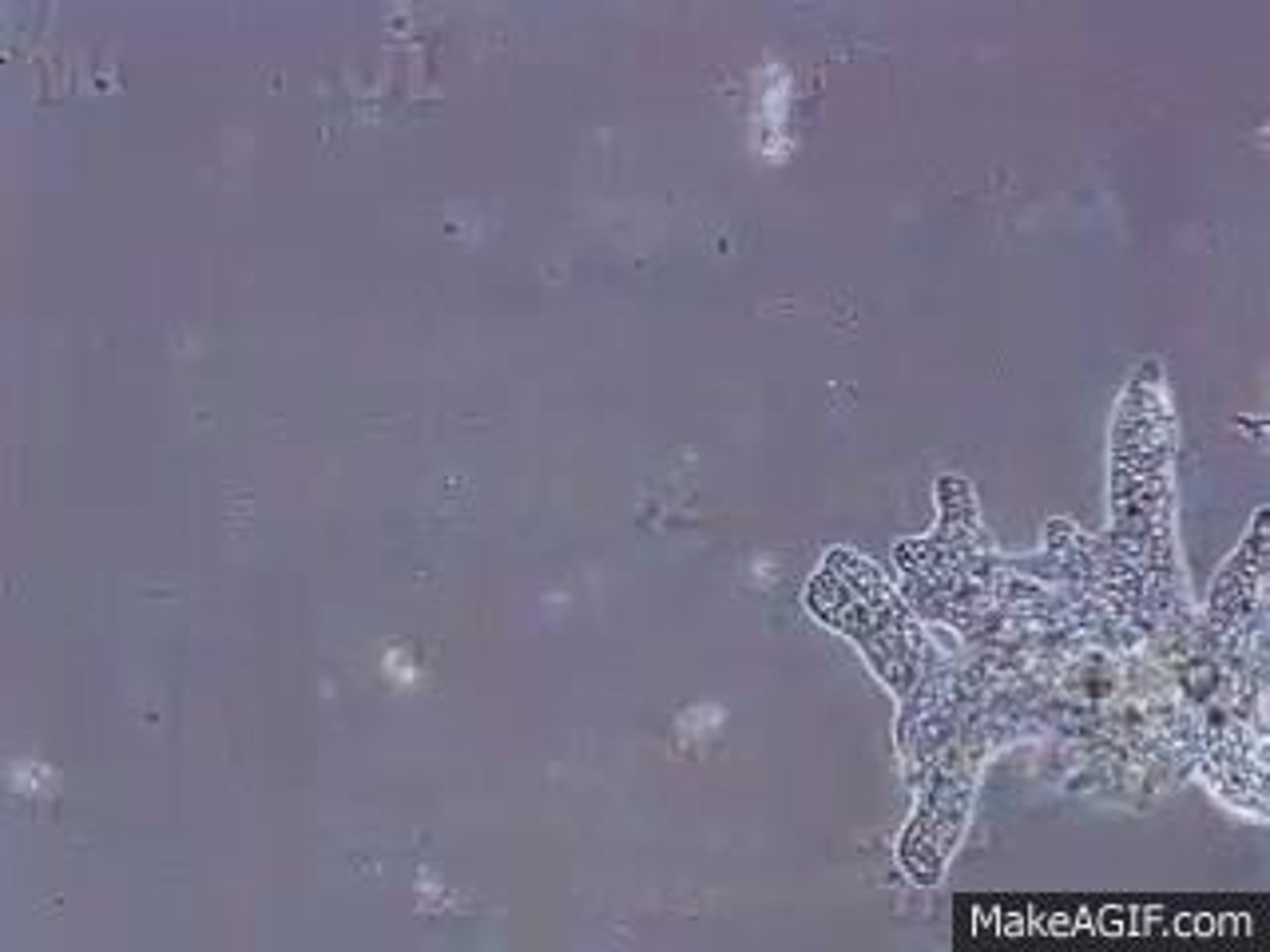
Amoeba
Unicellular, polyphyletic organisms that have 'pseudopods', which are temporary 'arm like' projections of the cell membrane used for motility and ingestion, allowing the cells to change shape. Example: Amoeba proteus.

Chaos carolinense
A single celled amoeba that can reach 5mm (visible to the naked eye) and can have up to 1000 nuclei in a cell.
Slime moulds
Once thought to be fungi but now recognized as several separate groups (polyphyletic). Most are microscopic and have a life cycle that includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores for reproduction. They play important roles in the decomposition of organic matter.
Plasmodial slime moulds
These slime moulds start off as amoeba-like cells but change into plasmodium after mating with other compatible slime moulds. A plasmodium is a living structure of cytoplasm that contains many nuclei but is not divided into individual cells. The unicellular amoebae are commonly haploid and feed on microorganisms such as bacteria, yeasts, and fungal spores. Plasmodium forms are diploid.
Cellular slime moulds
Exist as single celled amoeba-like organisms when conditions are favorable. If nutrient sources become scarce, they congregate and start moving as a single body, which allows them to better detect chemical signals to find food sources. They will also form fruiting bodies and release spores.
Diatoms
Large group of genera containing microalgae
Dinoflagellates
Monophyletic group - all contained within the Dinoflagellata phylum
Amoebas
Have pseudopods filled with cytoplasm or microtubules that they shoot in the direction of movement
Diatoms movement
Mostly move passively, only male gametes of some diatoms possess flagella
Dinoflagellates movement
Two flagella, one to act as propulsion and one for steering
Ciliates reproduction
Ciliates have two nuclei and contractile vacuoles. They feed through phagocytosis and reproduce through binary fission. Can also perform conjugation as a form of sexual reproduction.
Autogamy
A form of sexual reproduction where a single organism undergoes meiosis and recombination internally.
Binary fission
Asexual reproduction method where a cell divides into two genetically identical cells.
Cytostome
Specialized cell structure in ciliates where phagocytosis occurs.
Dinokaryon
A specialized nucleus in dinoflagellates with chromosomes attached to the nuclear membrane.
Endocytosis
Cellular process of engulfing external particles via the plasma membrane.
Flagella
Long, whip-like structures used for movement in some protists like dinoflagellates.
Mixotroph
Organism that combines autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
Multinucleate
Having multiple nuclei within a single cell or structure.
Phagosome
Vesicle formed around a particle engulfed by phagocytosis.
Protist
Any eukaryotic organism that is not a plant, animal, or fungus.
Pseudopod
Temporary projection of the cell membrane used by amoebas for movement and feeding.