Unit 4 Muscular System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Muscular System
The body’s “flesh”
The typical body contains approximately 640 muscles
Span a joint and taper at each end into a fibrous tendon anchored to a bone
Muscle Functions (all muscle types)
Producing Movement
Result of muscle contractions
Muscle Functions (skeletal muscle only)
Maintains posture
Maintain an erect or seated posture despite the downward pull of gravity
Stabilizes joints
Muscle tendons reinforce and stabilize joints
Generates heat
By-product of muscle activity
Vital in maintaining normal body temperature
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Cardiac muscle
Skeletal muscle
Smooth muscle
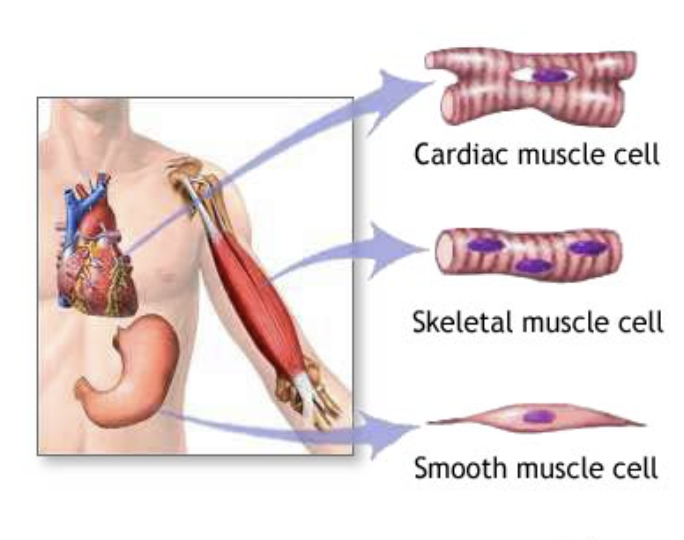
What are skeletal muscles?
Attached to bones or, for some facial muscles, to skin
Largest of the muscle fibre types
Multinucleated cells
Striated (ridges)
Voluntary muscles (can consciously control)
What is smooth muscle?
No striations (ridges)
Involuntary (cannot consciously control it)
Found in the walls of the visceral organs (stomach, urinary bladder and respiratory passages)
What is cardiac muscle?
Only found in the heart
Striated
involuntary
What are tendons?
Tough, fibrous cords that link skeletal muscle to bones
What are myofibres?
Densely packed groups of elongated muscle fibres
In skeletal muscle
Grouped into bundles called fascicules
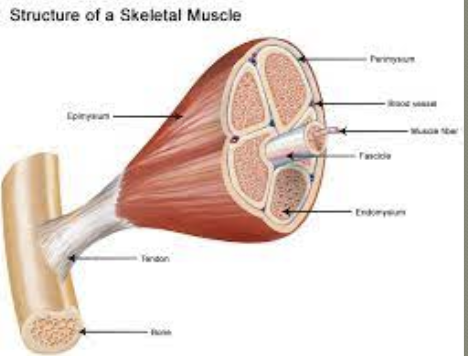
What are myofibrils?
Narrower structures that make muscle fibres
Contain thick and thin contractile ligaments made up of the proteins myosin and actin
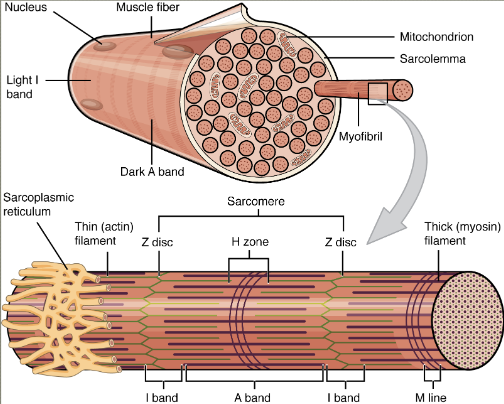
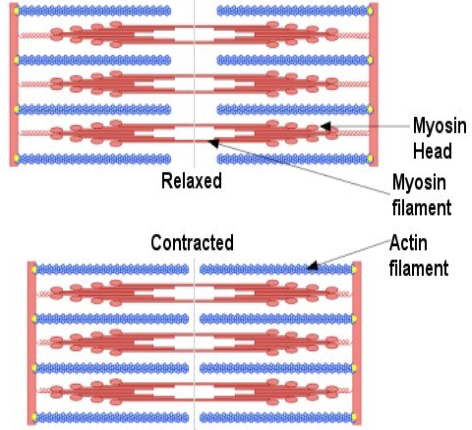
How do muscles contract?
In relaxed muscles, myofilaments only partly overlap
When contracted, the myosin filaments slide between the actin filaments shortening myofibril and muscle fibre
Contraction amount depend on how many muscle fibres shorten overall
How do we move?
Skeletal muscles, attached to bone by tendons, produce movement by bending the skeleton at moveable joints
The connecting tendon closest to the body of head is called the proximal attachment
This is termed by the origin of the muscle
The distal attachment is called the insertion
During contraction the origin remains stationary and the insertion moves
What is origin?
More stable attachment site
Usually the centre of the body
Doesn’t move during contraction
What is insertion?
Other attachment site
Towards the body’s periphery (outer area)
Moves more during contraction
What are agonists?
Prime movers
When two muscles work together by producing the same movements or by reducing undesirable movement
Example:
Biceps
Rotator cuff
What are antagonists?
Specialized synergists that hold bone still or stabilize the origin of a prime mover so all the tension can be used to move the insertion bone
Example:
Triceps
Biceps Brachii and brachioradialis
What is muscle tone?
The state of continuous partial contractions
Even when muscle is voluntarily relaxed, some of its fibres are contracting
Keeps muscles firm, healthy and constantly ready for action
What effect does exercise have on the muscle?
Regular exercise increases muscle strength, size and endurance
Aerobic (endurance) exercise result in stronger more flexible muscles with greater resistance to fatigue
Resistance (isometric) exercises results in an increase in muscle size and strength
What are contractures?
The lack of joint mobility caused by an abnormal shortening of a muscle
The contracted muscle is fixed into position, is deformed and cannot stretch
May be a result of immobilization from injury or disease; nerve injury, such as spinal cord damage and stroke; or muscle, tendon, or ligament disease
Permanent deformity and disability
Where are common sites of contractures?
Fingers
Wrists
Elbows
Toes
Ankles
Knees
Hips
What is muscular atrophy?
Muscle inactivity leads to muscle weakness and wasting
If nerve supply to a muscle is destroyed (as in an accident), the muscle is no longer stimulated, and it loses its tone and becomes paralyzed. Soon after it becomes flaccid, or soft and begins to atrophy (waste away)
What is atrophy?
The decrease in size or the wasting of tissue
What is hypertrophy?
An increase and growth of muscle cells
What is muscular dystrophy?
A group of disorders characterized by progressive degeneration and loss of muscle tissue
These disorders are distinguished from each other by the type of gene mutation (sex-linked, dominant gene, recessive gene), the age when the symptoms appear, and the types of symptoms that develop
It is an inherited disorder, so family history is a factor
What is ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) aka Lou Gehrig’s Disease?
A fatal type of motor neuron disease
Affects voluntary control of arms and legs, and leads to trouble breathing