Exam
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms

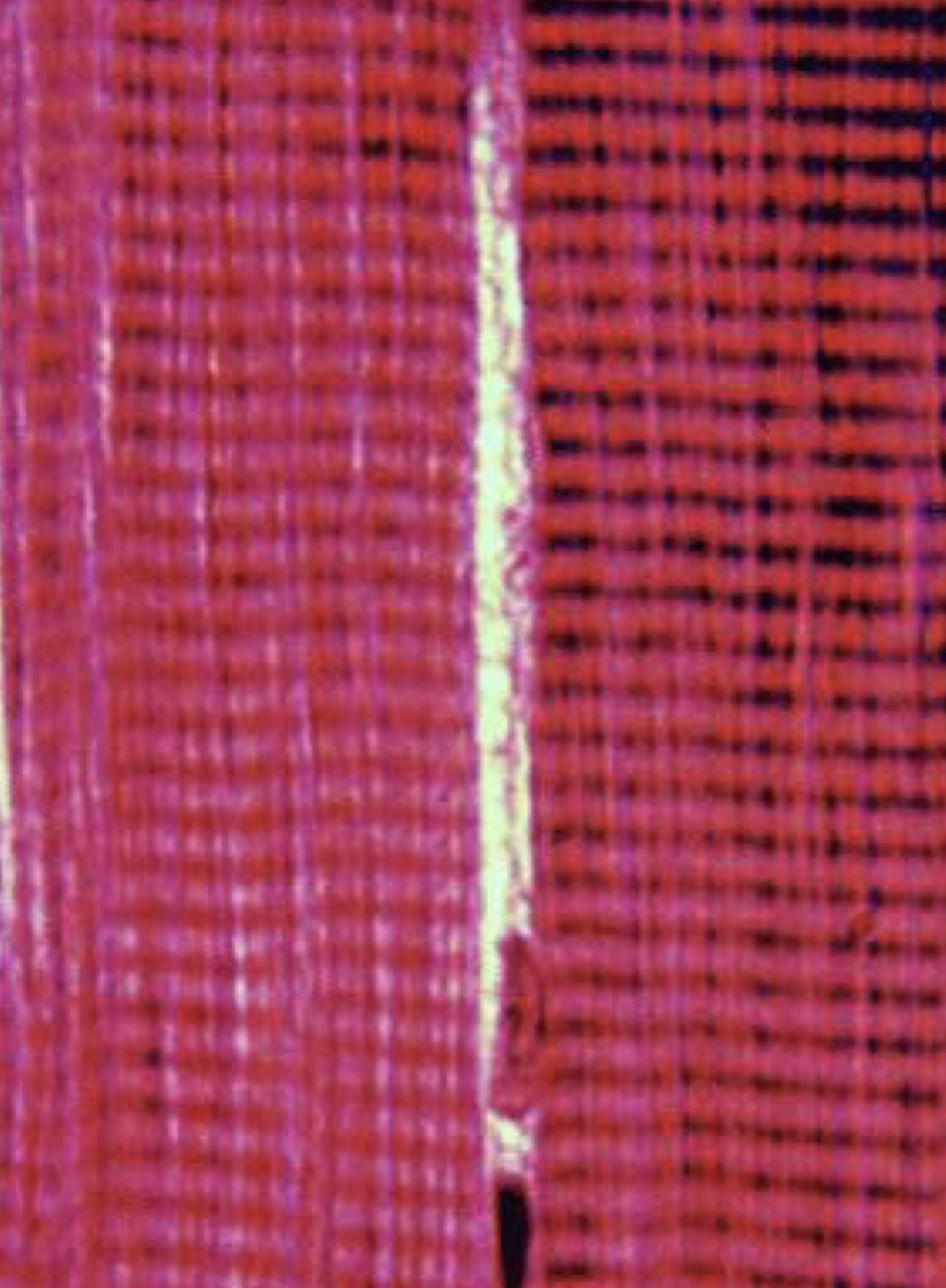
What type of muscle
Skeletal muscle
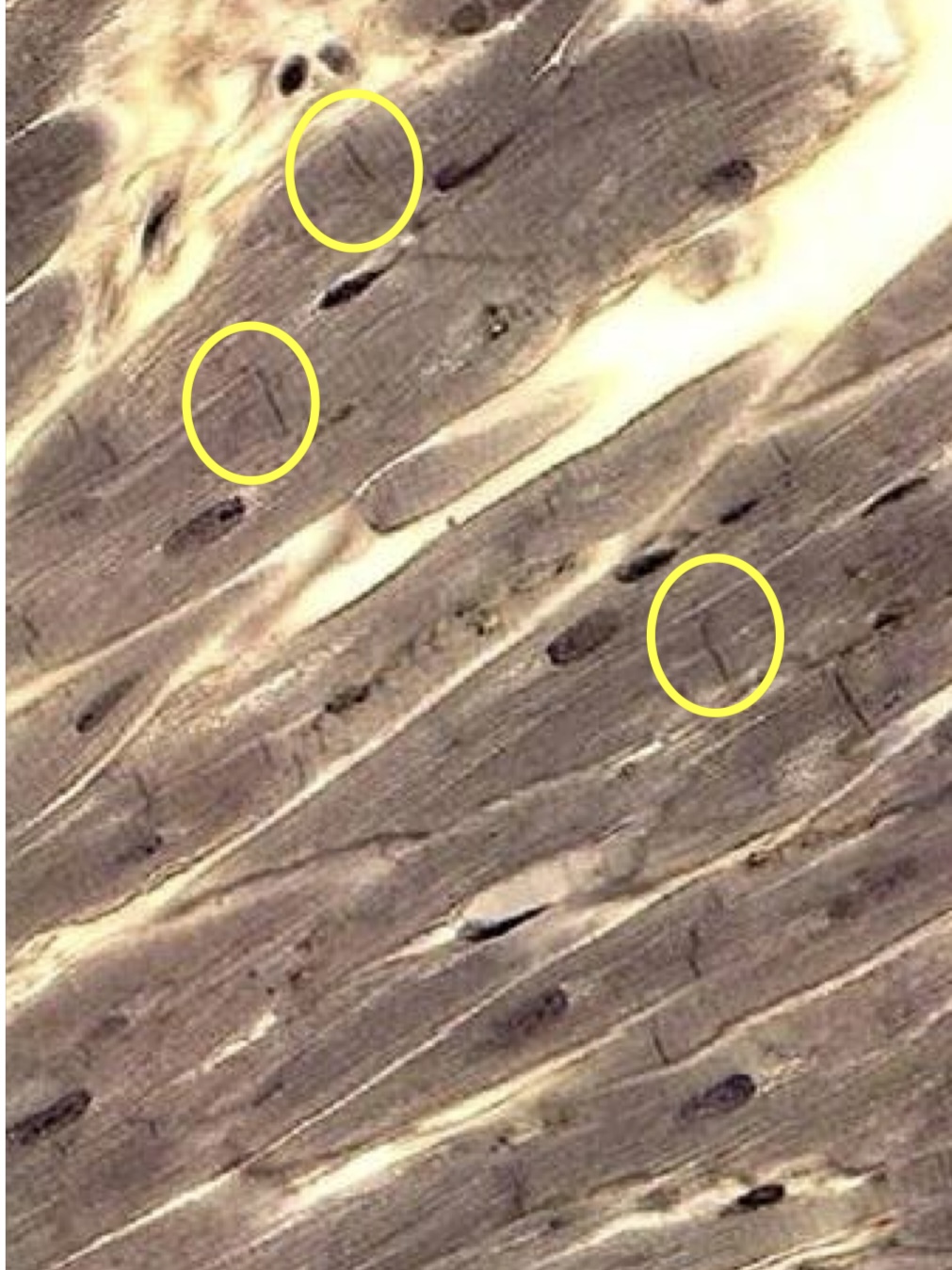
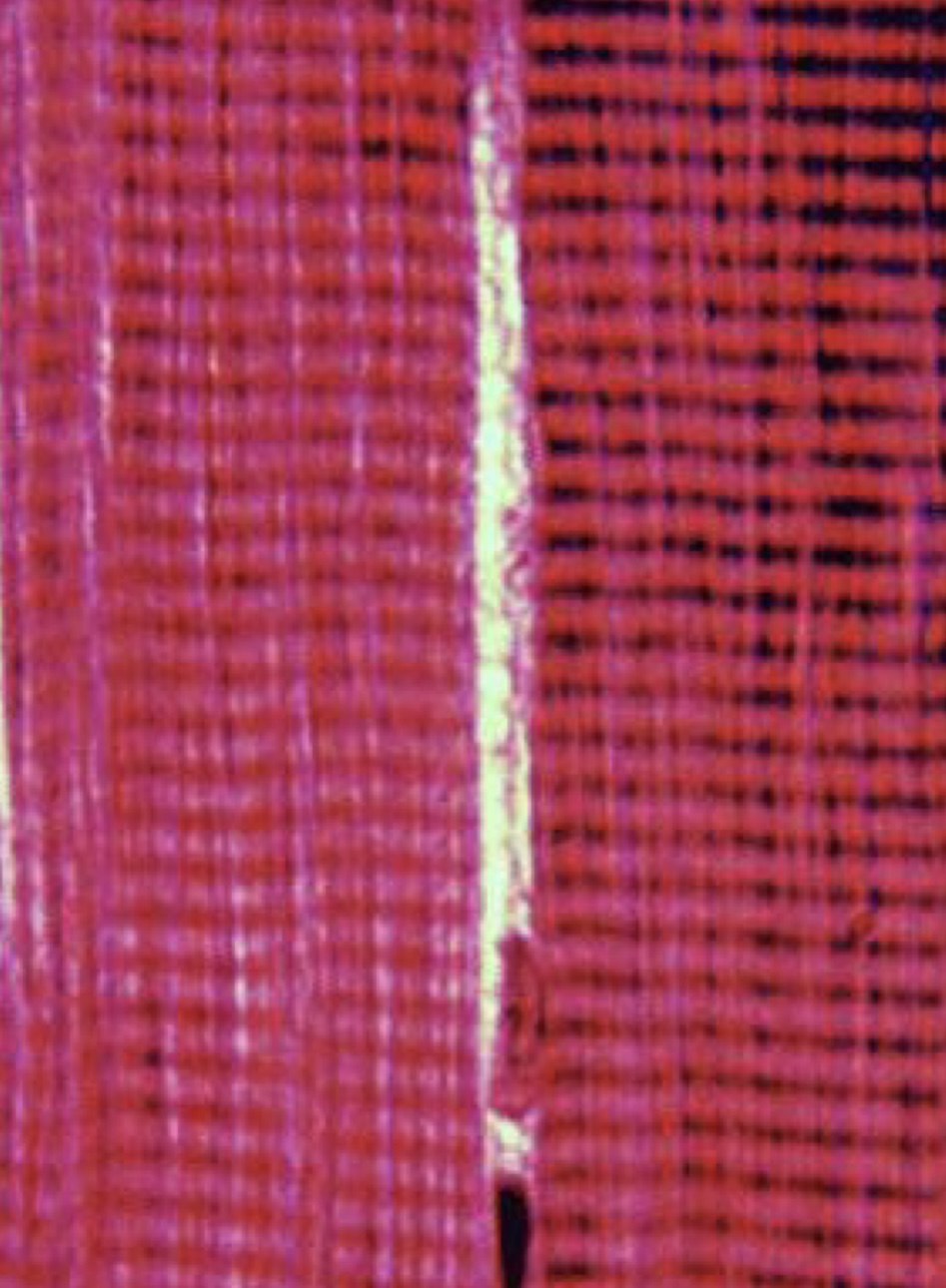
What type of muscle
Cardiac muscle
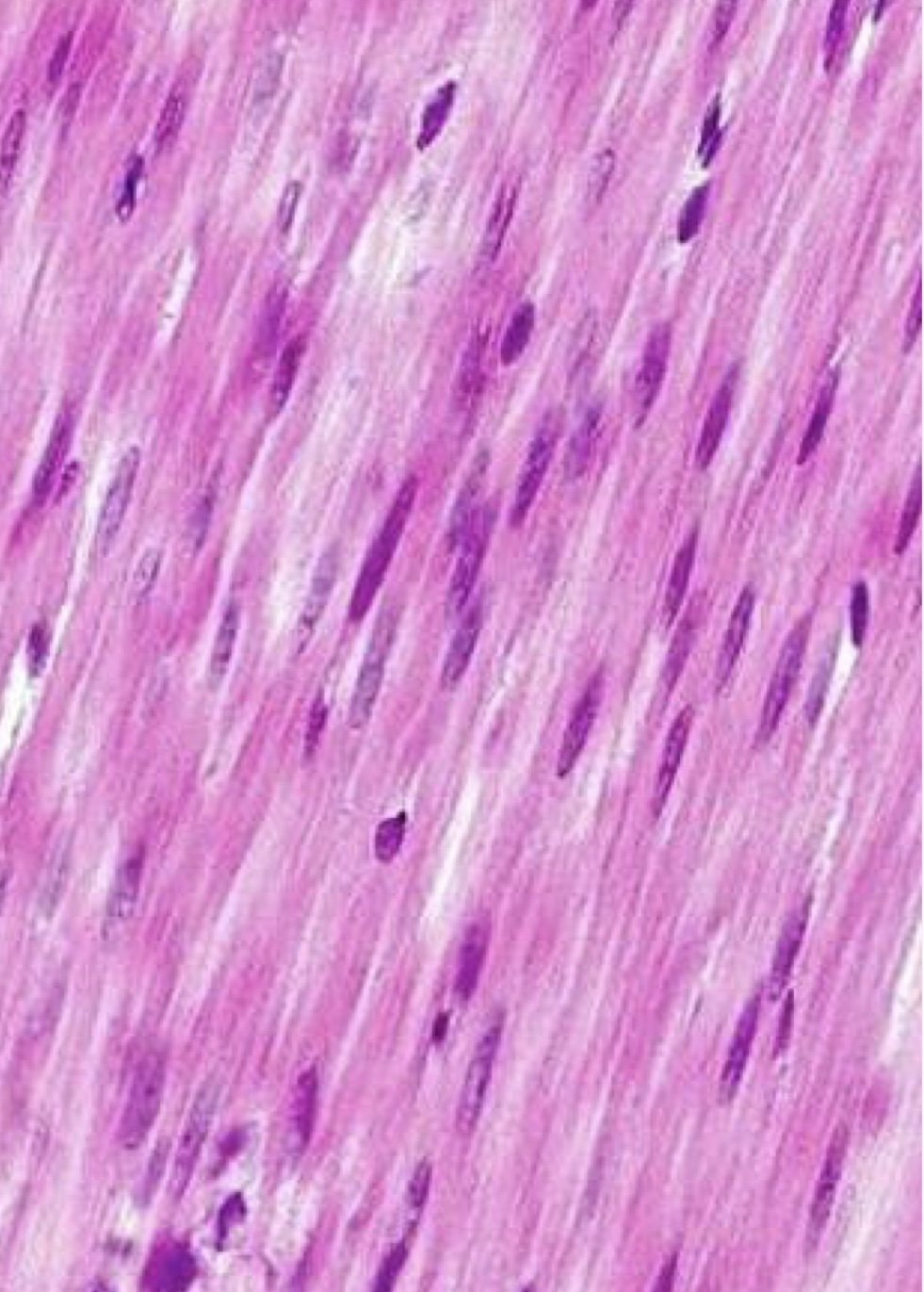
What type of muscle
Smooth muscle

Skeletal muscle
Striated
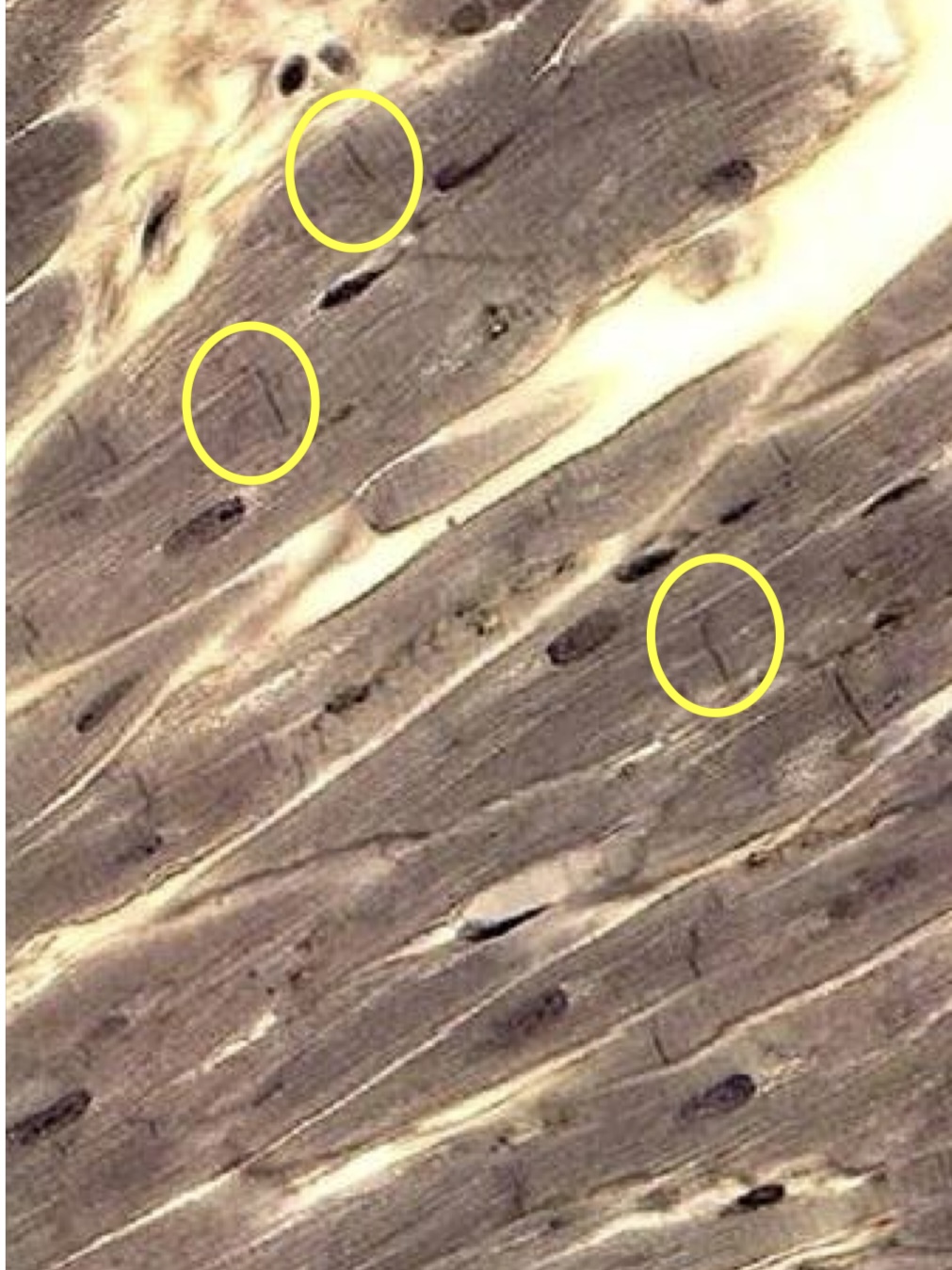
Cardiac muscle
Also striated, but intercalated discs give it a bamboo- like appearance
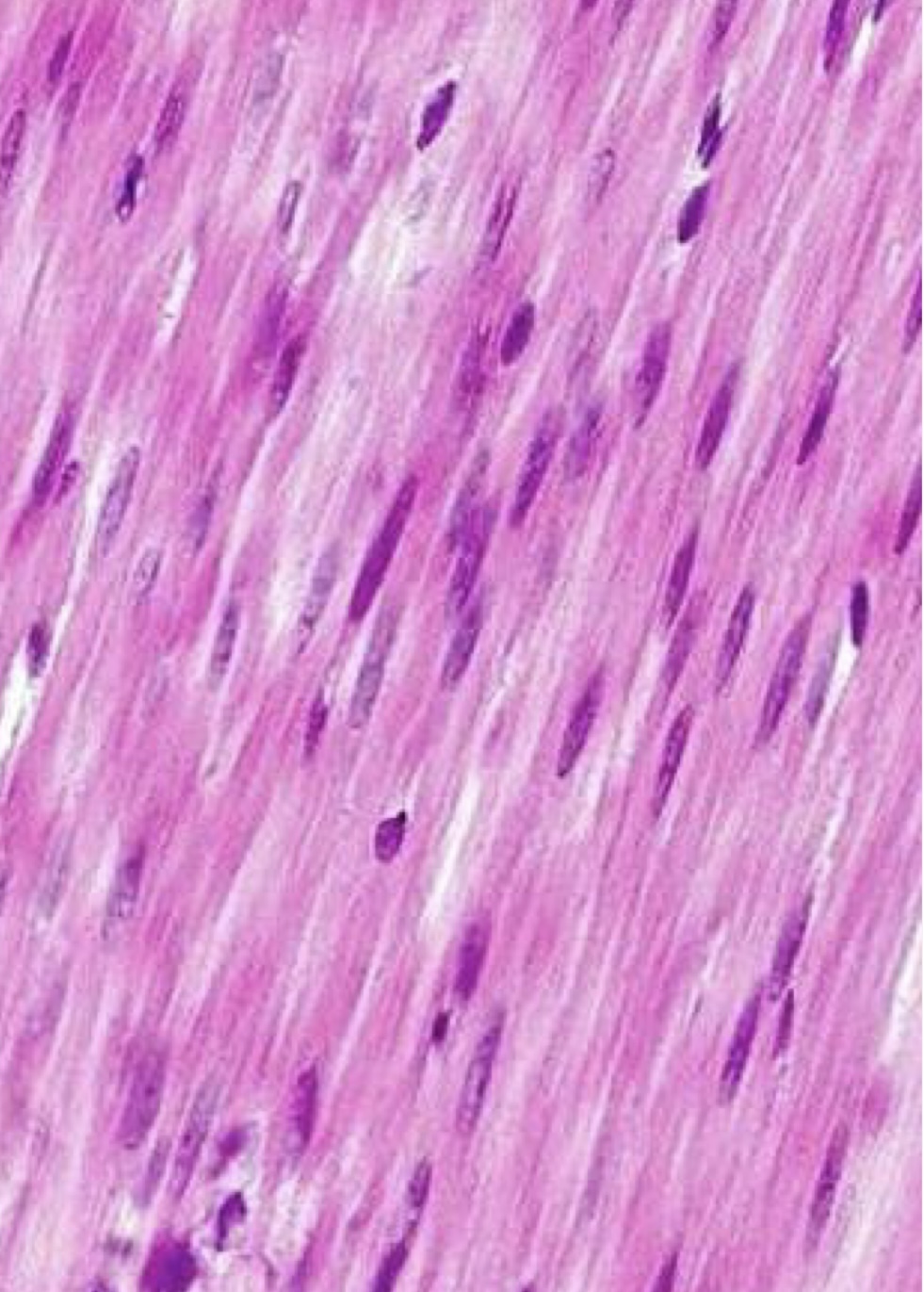
Smooth muscle
Cell appear “smeared”
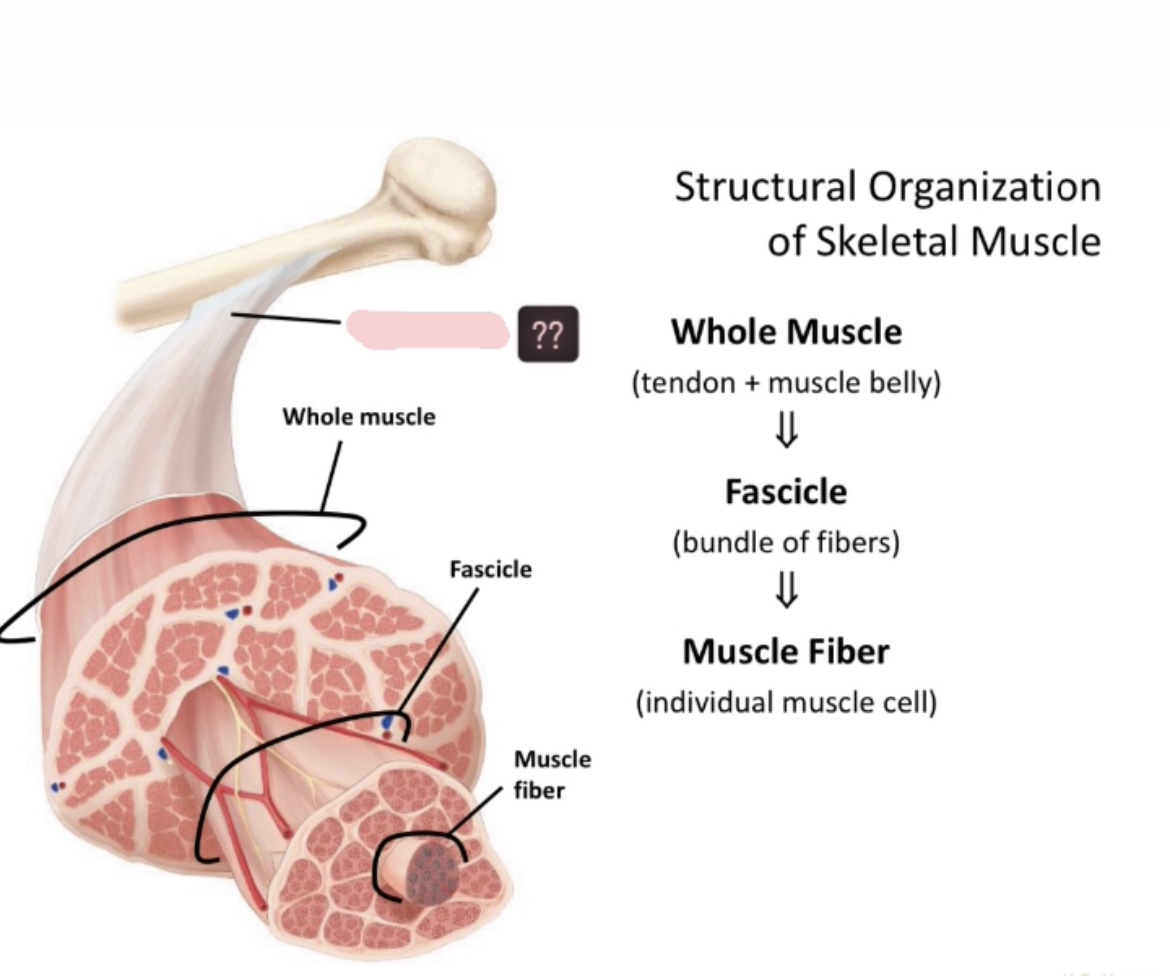
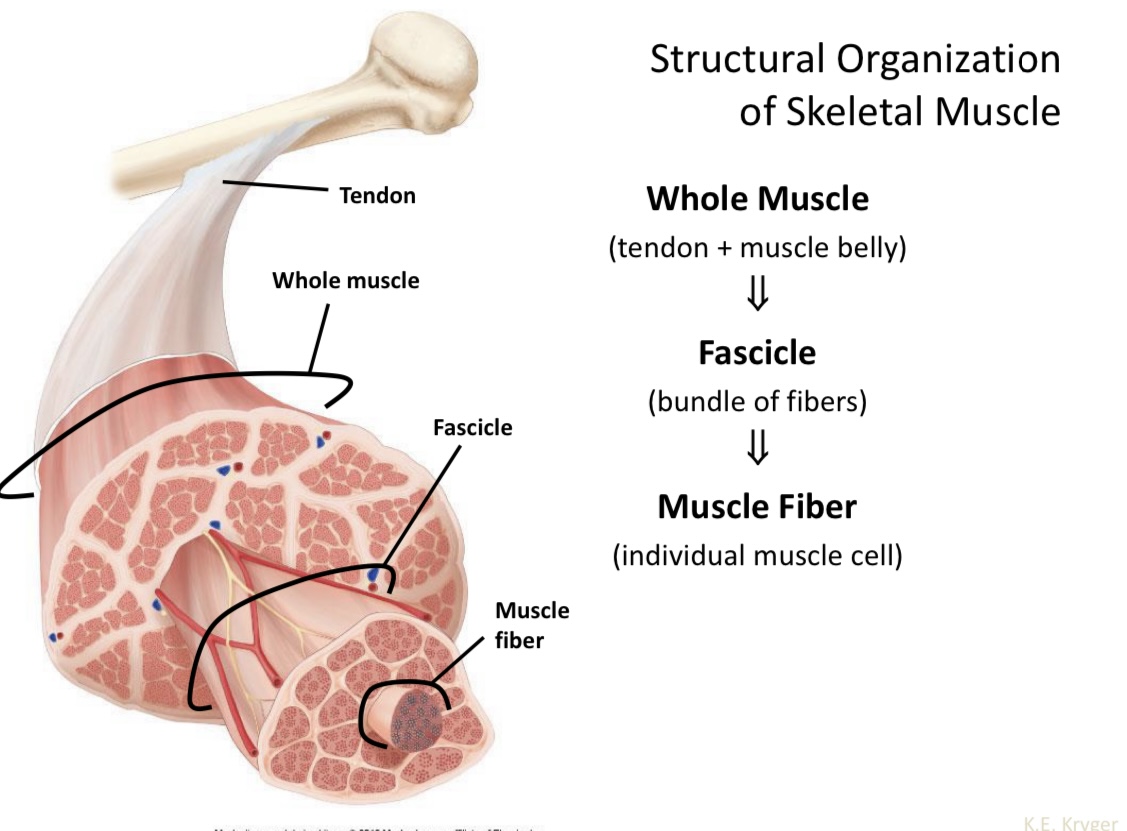
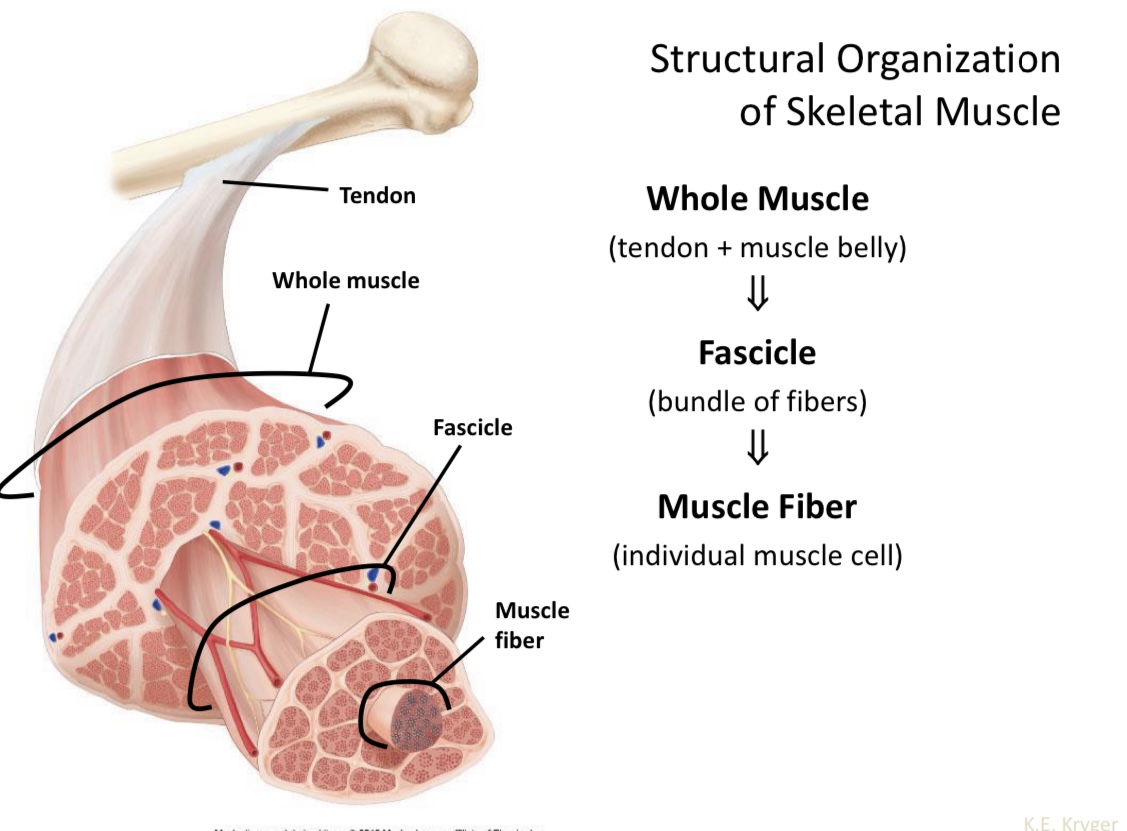
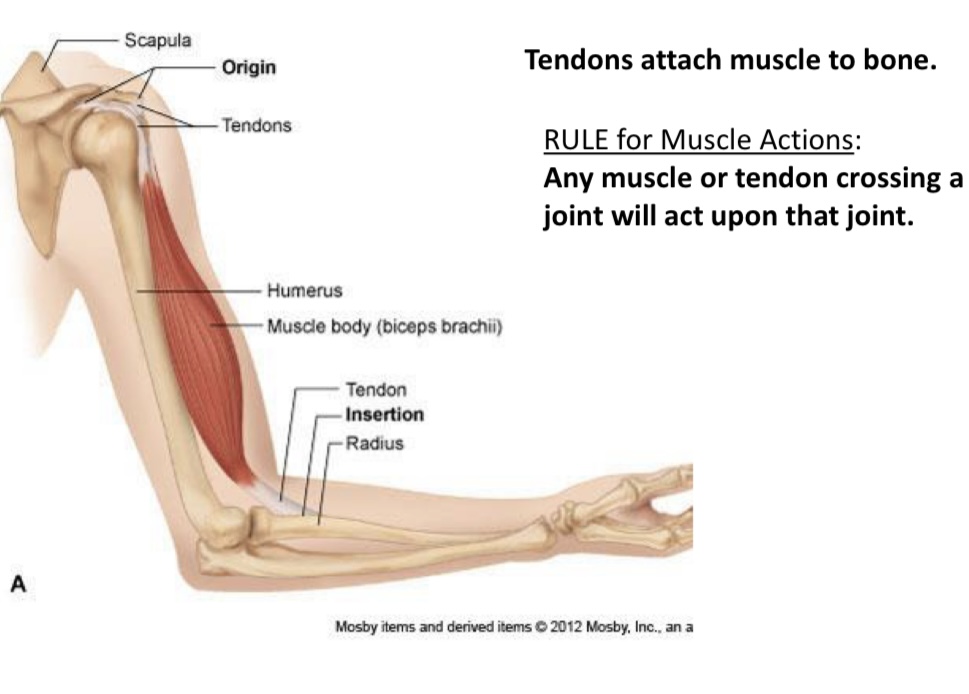
Name the structure of skeletal muscle
Tendon
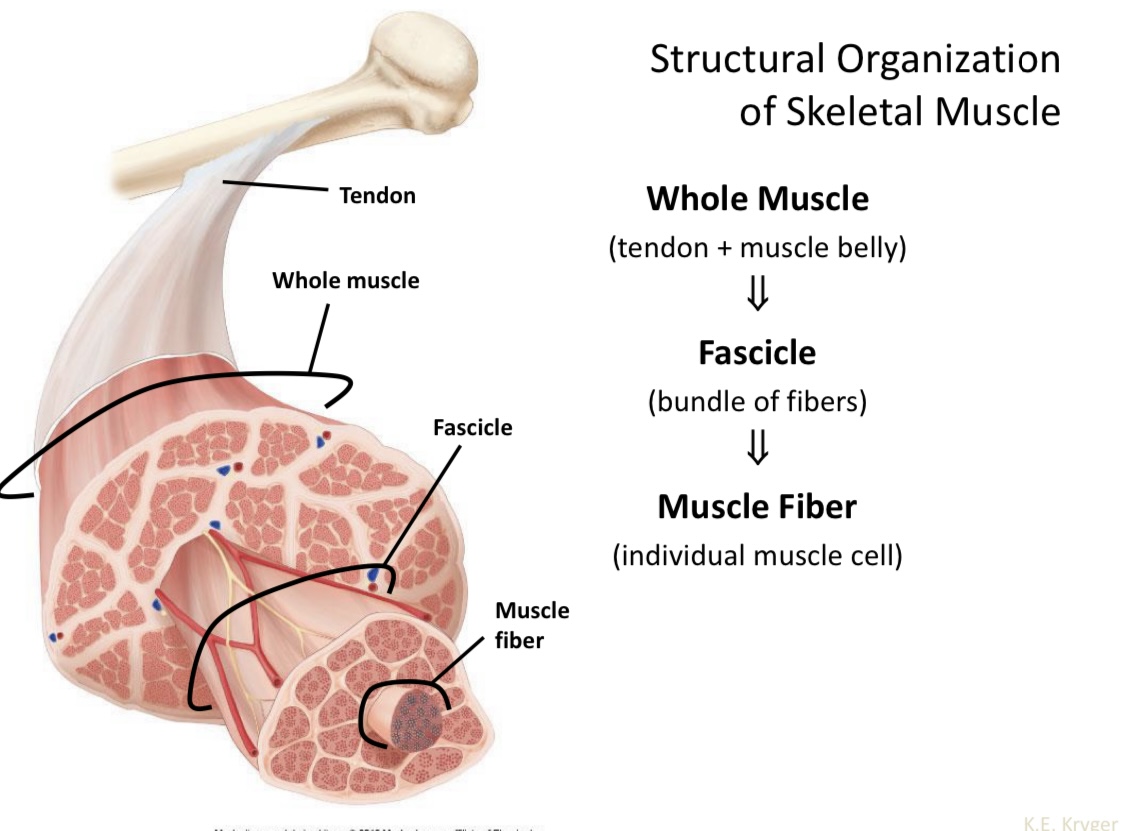
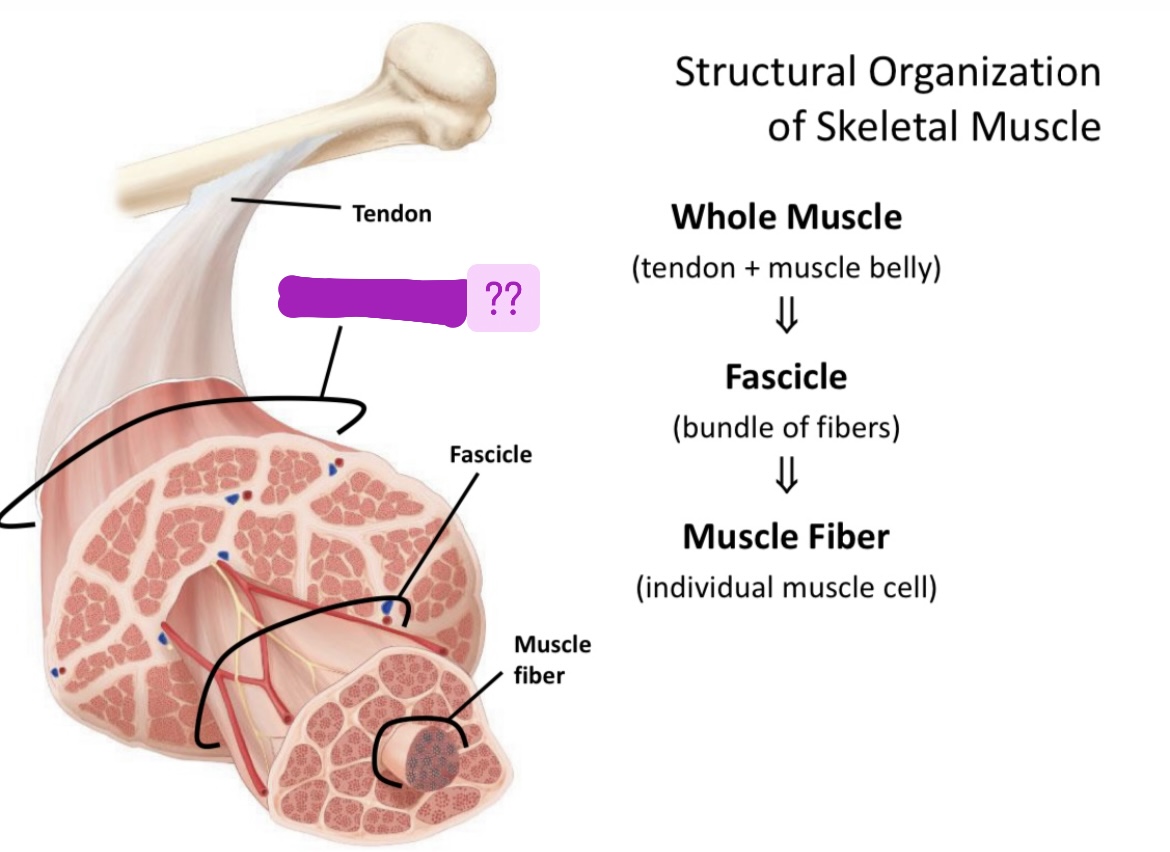
Name structural organization of skeletal muscle
Whole muscle
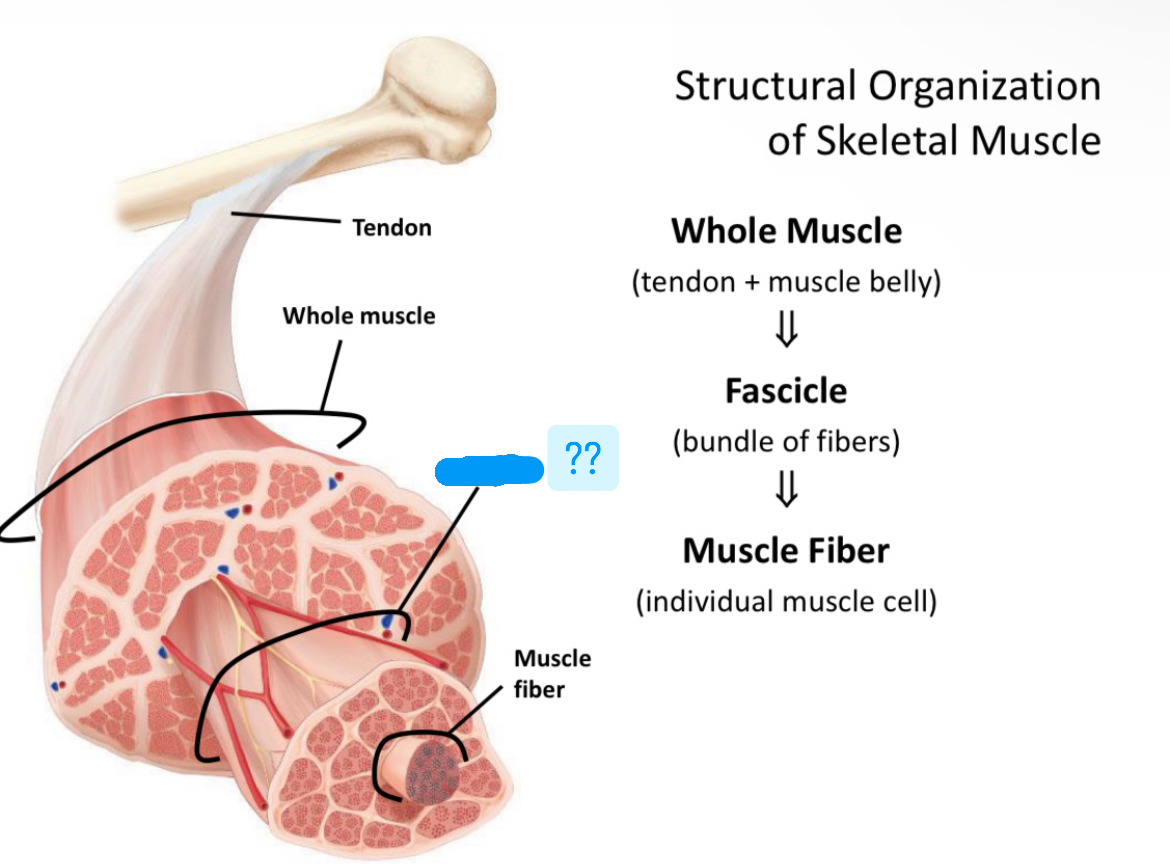
Name structural organization of skeletal muscle
Fascicle
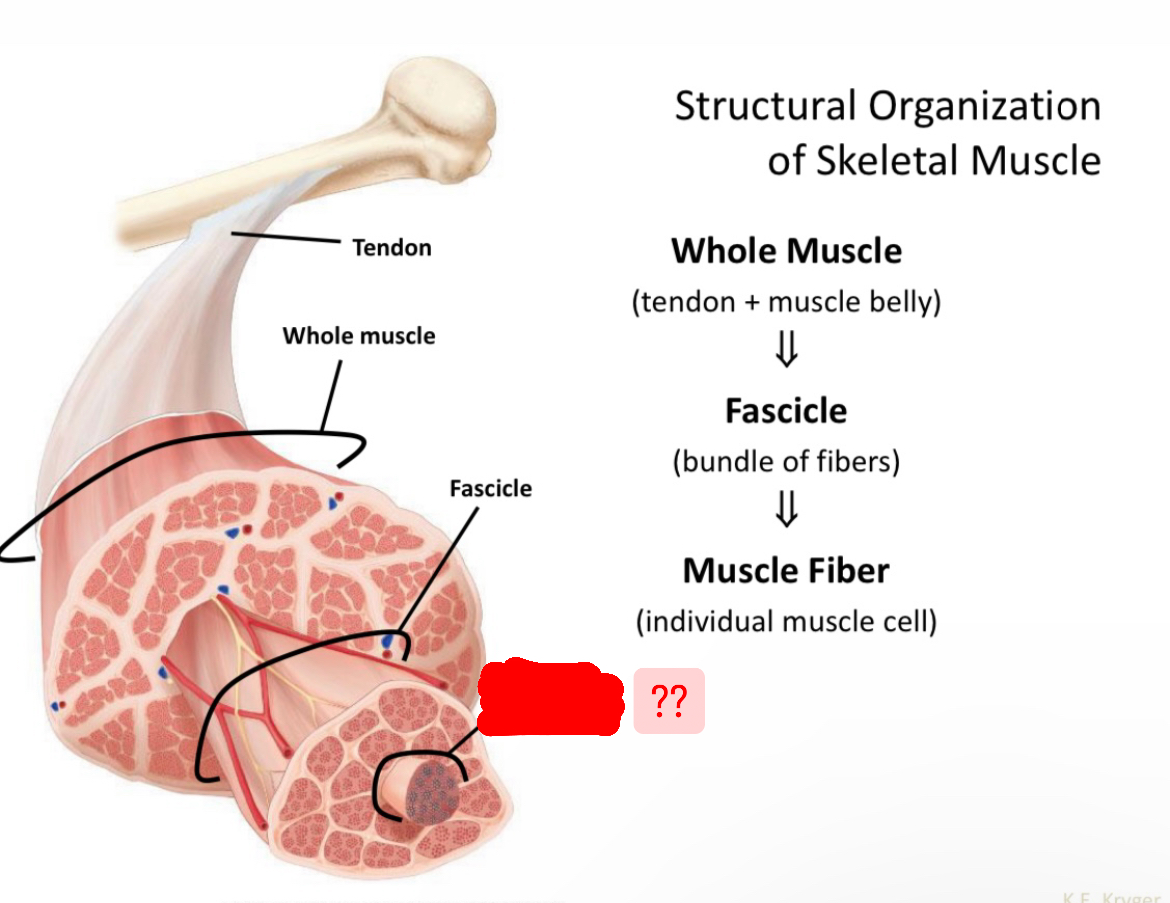
Name structural organization of skeletal muscle
Muscle fiber
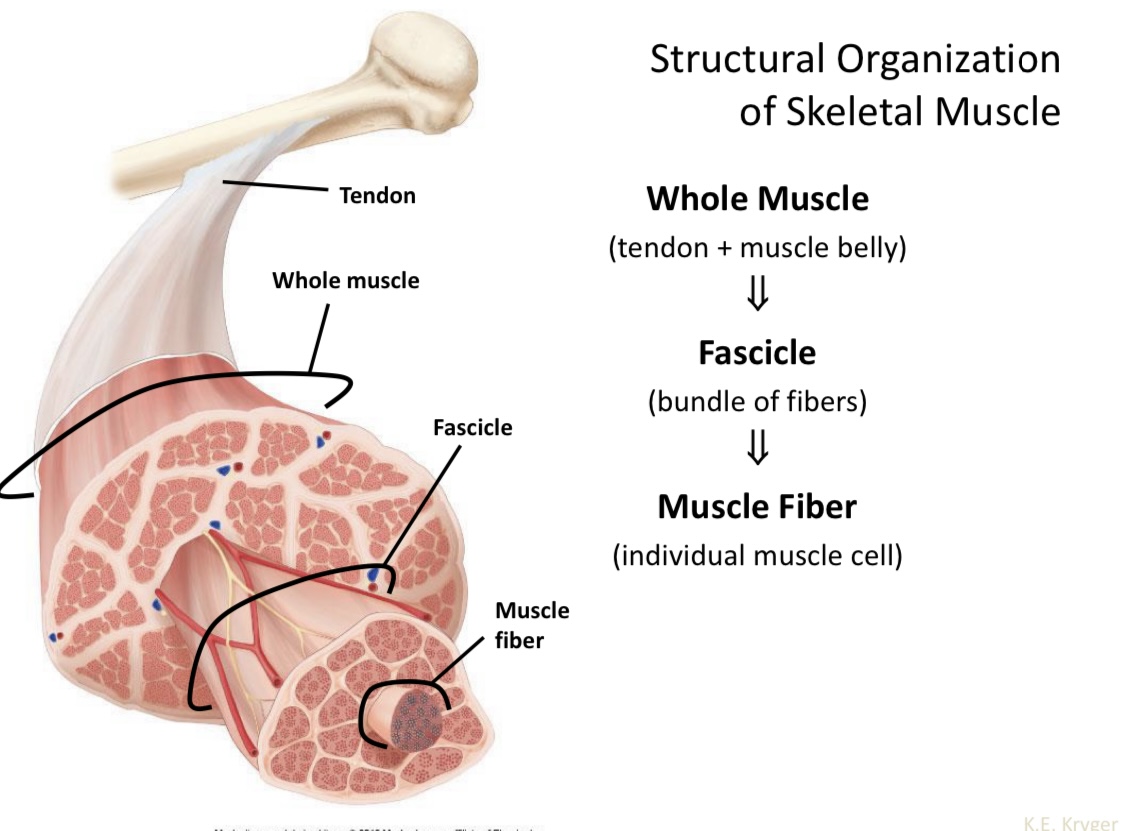
Whole muscle
Tendon + muscle belly
Fascicle
Bundle of fibers
Muscle fiber
Individual muscle cell
Epimusium
Surrounds the muscle belly (Epi=upon)
Perimysium
Surrounds each fascicle (Peri = around)
Endomysium
Surrounds each muscle fiber (Endo= within)
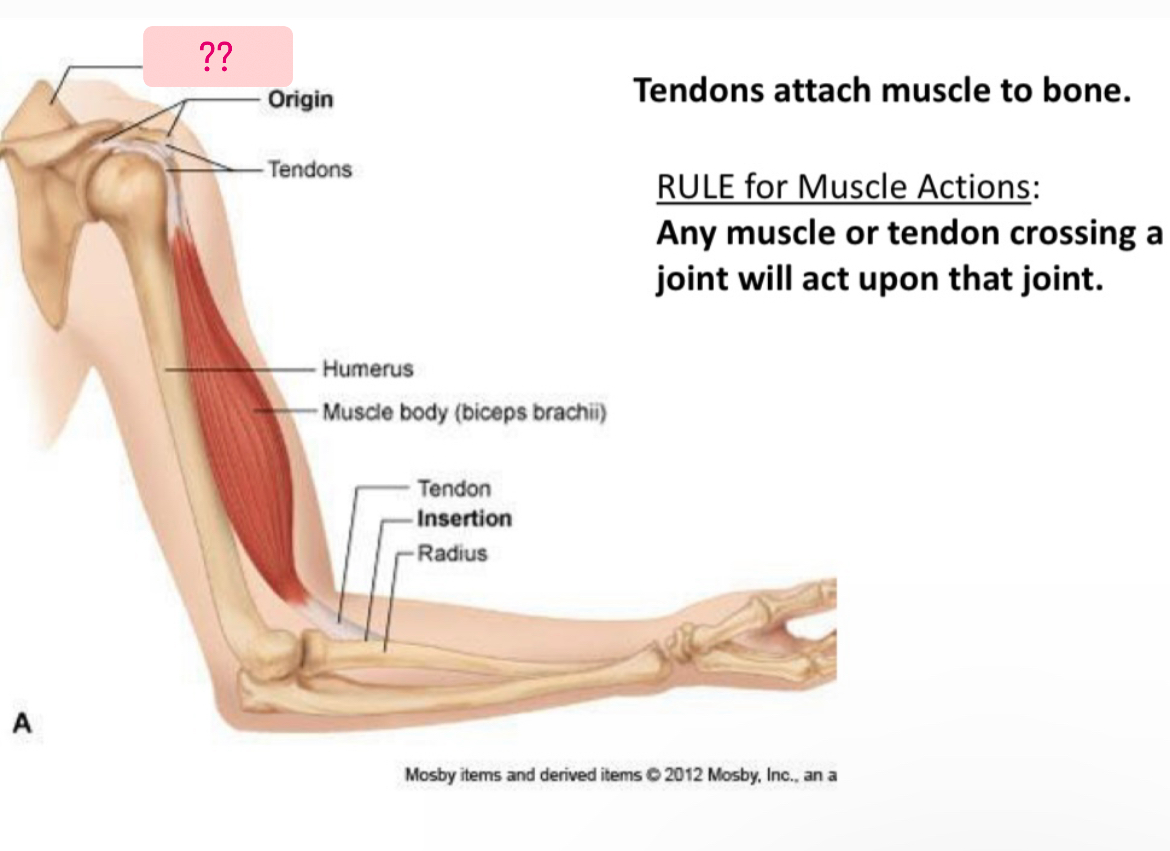
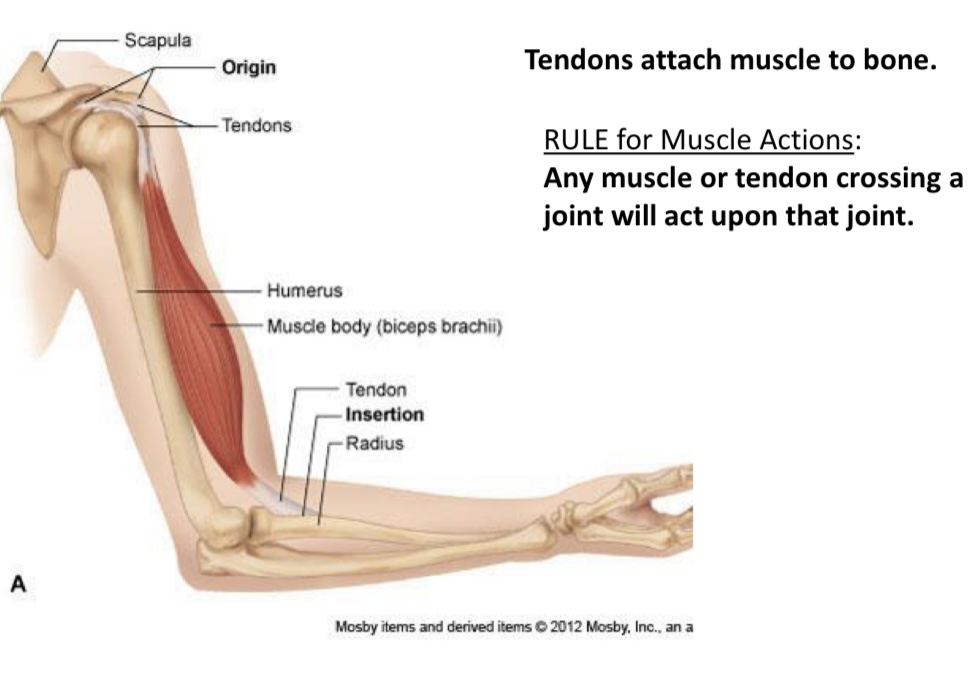
What is it called??
Scapula
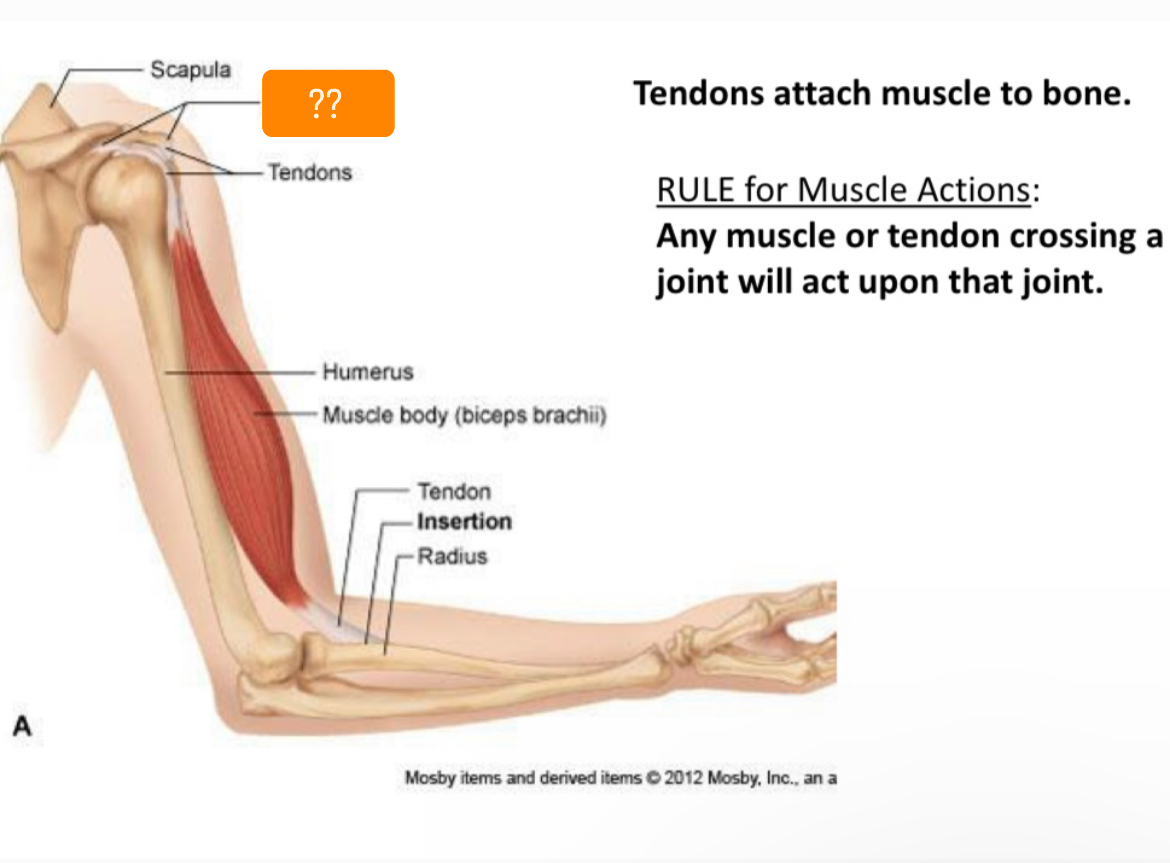
What is it called??
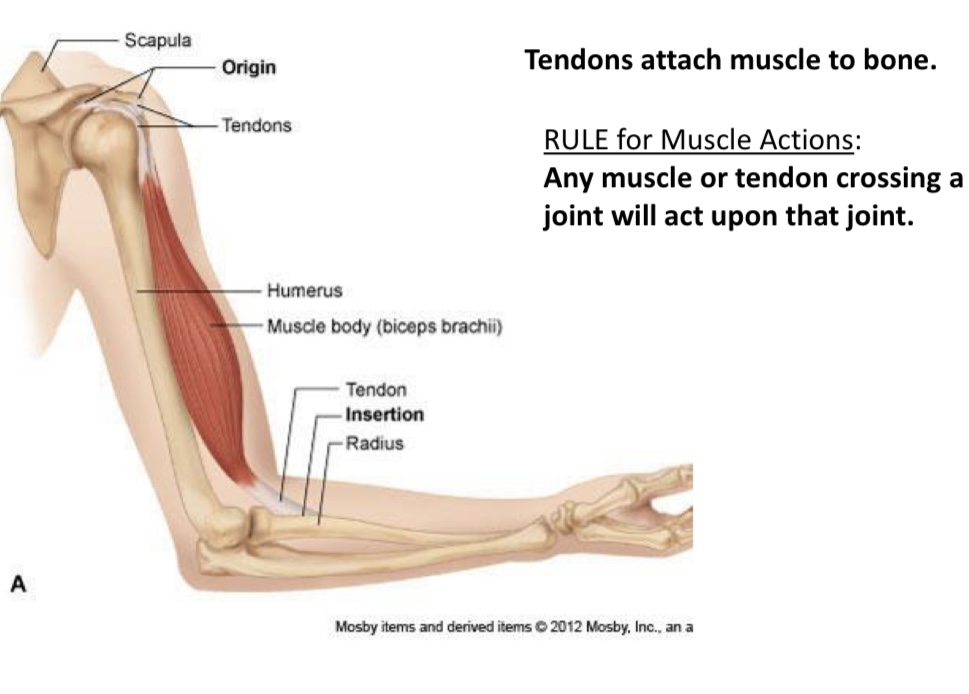
Origin
What is it called??
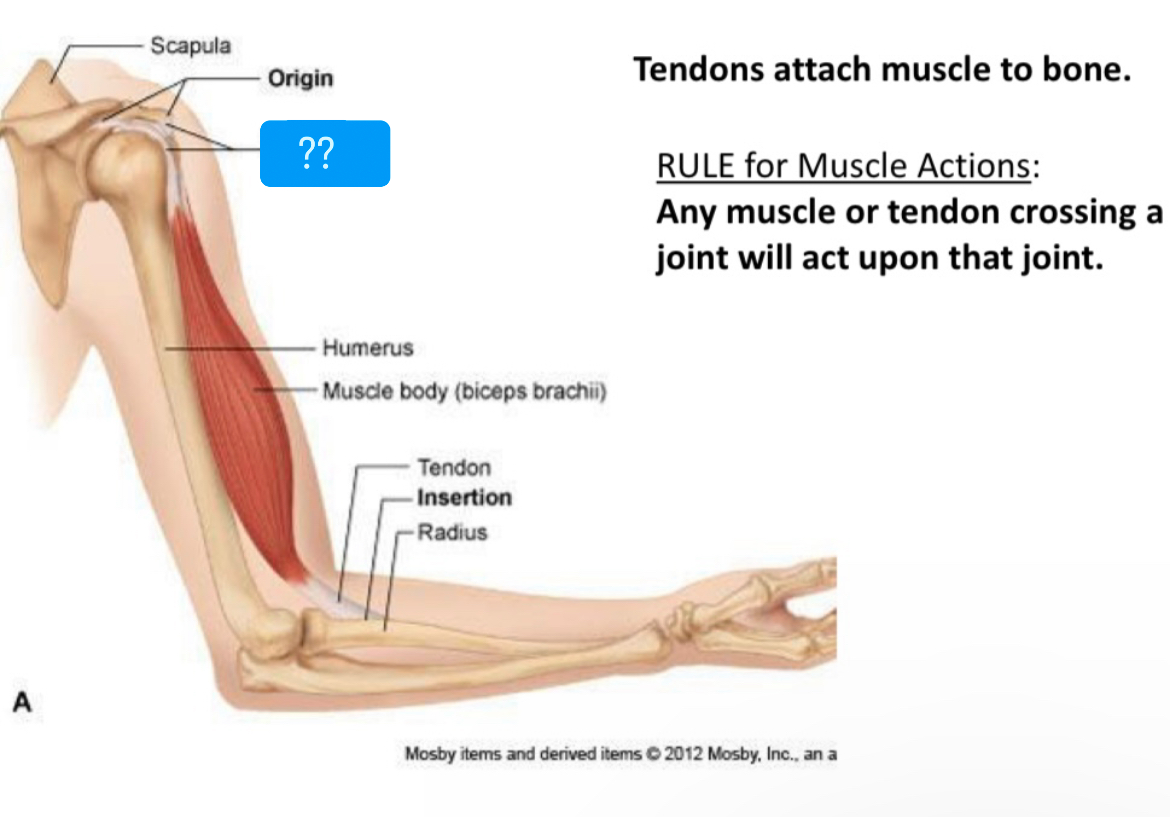
Tendons
What is it called?
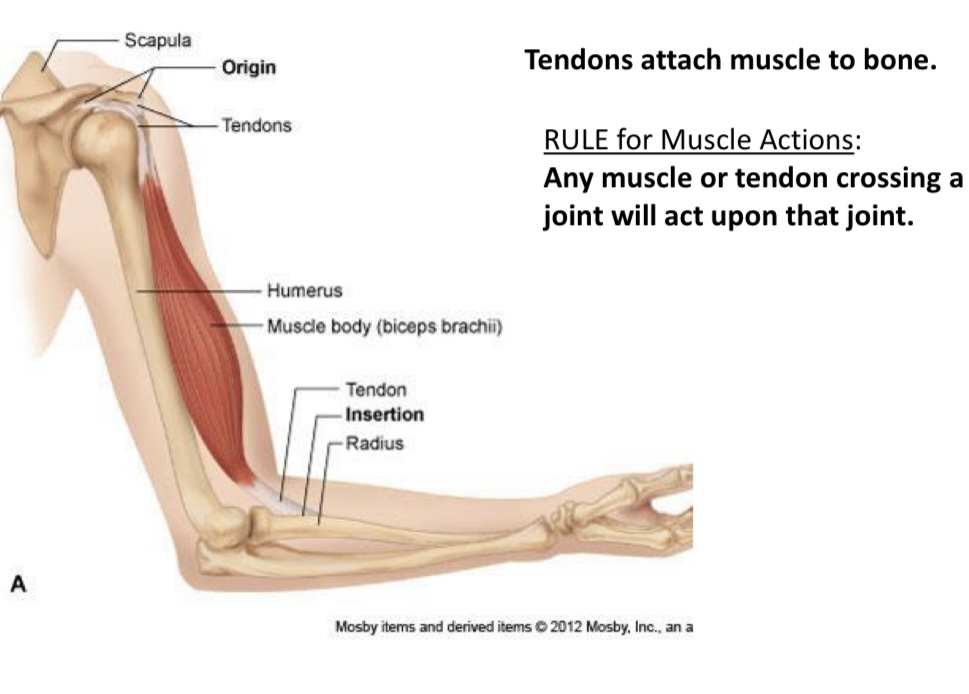
Humerus
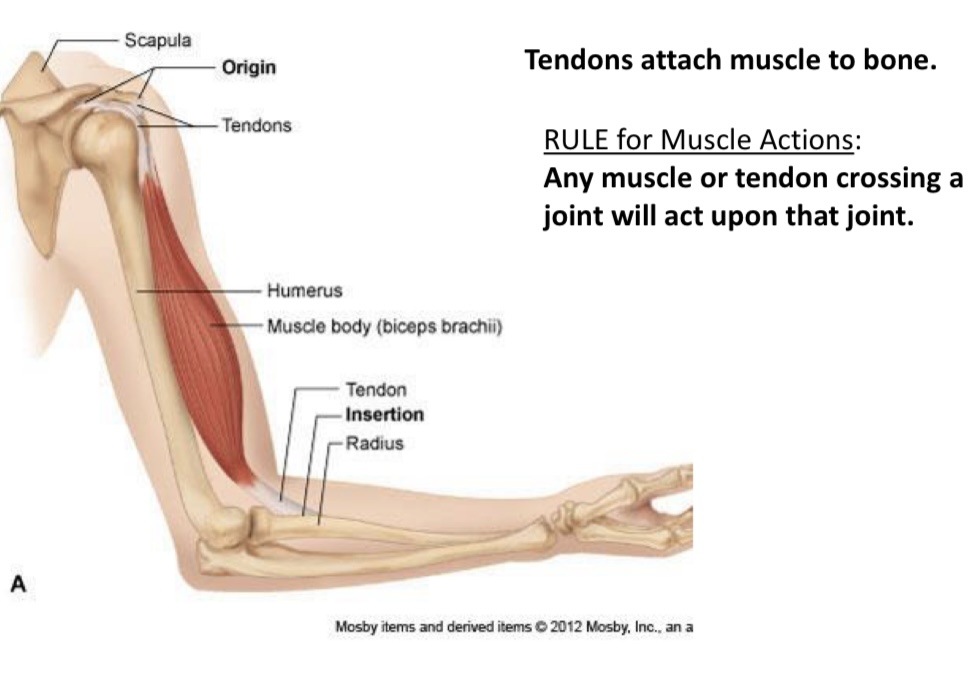
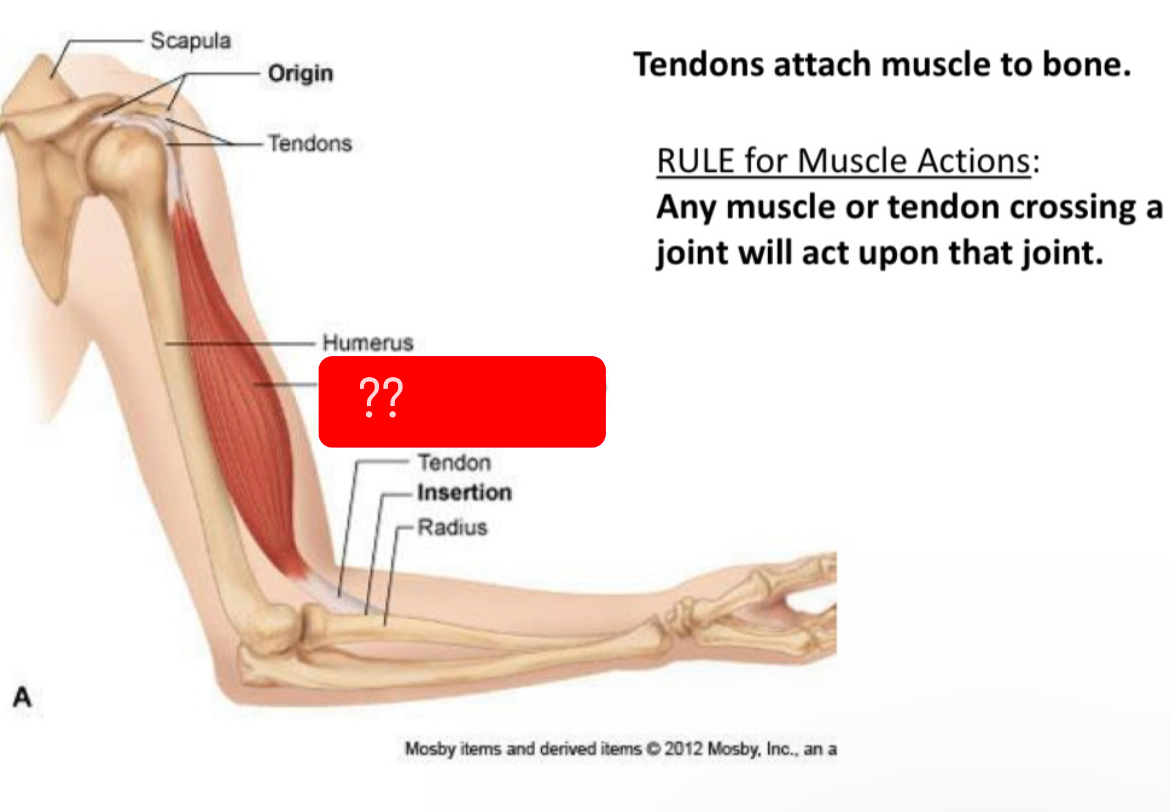
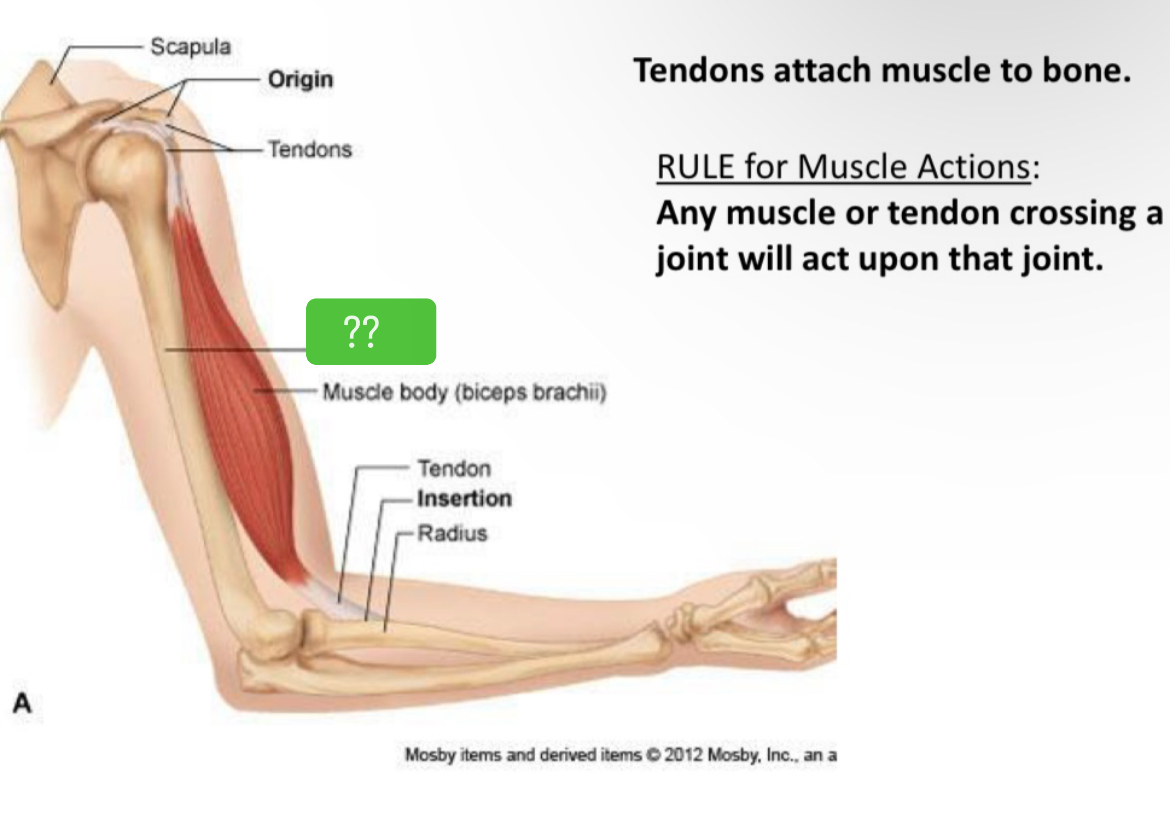
What is this called
Muscle body(biceps brachii)
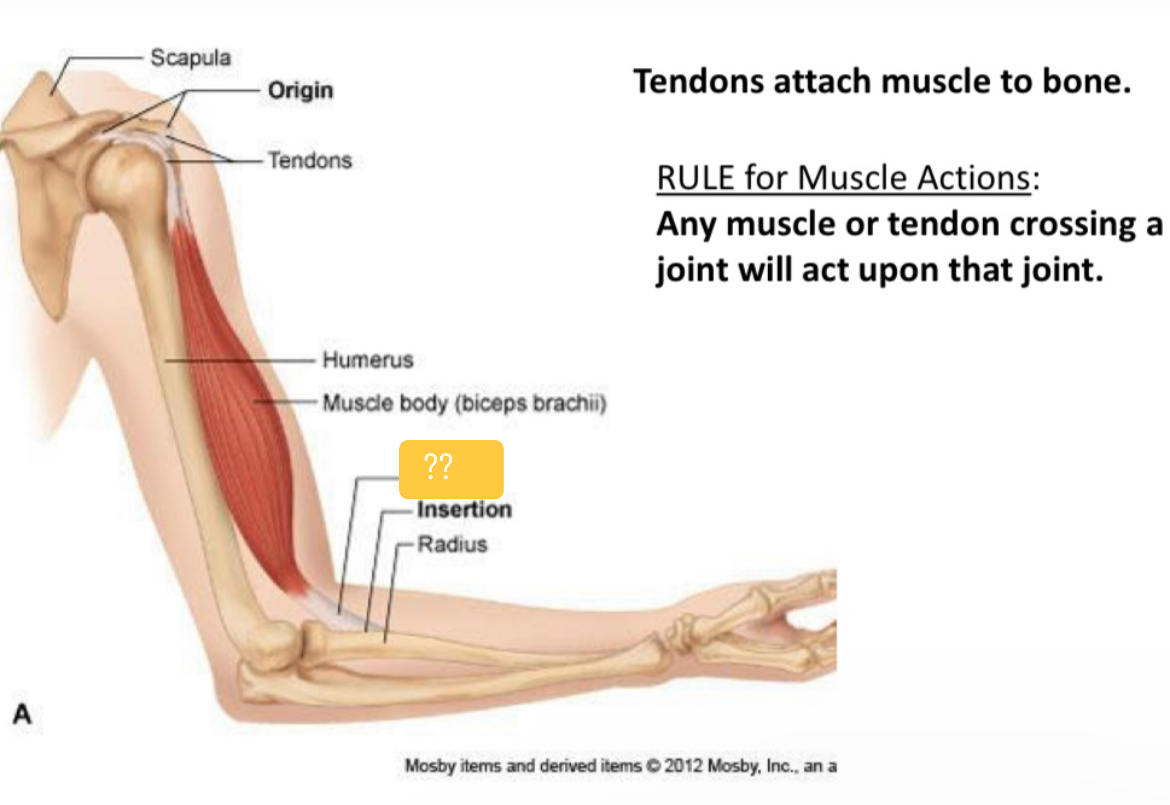
What is it called?
Tendon
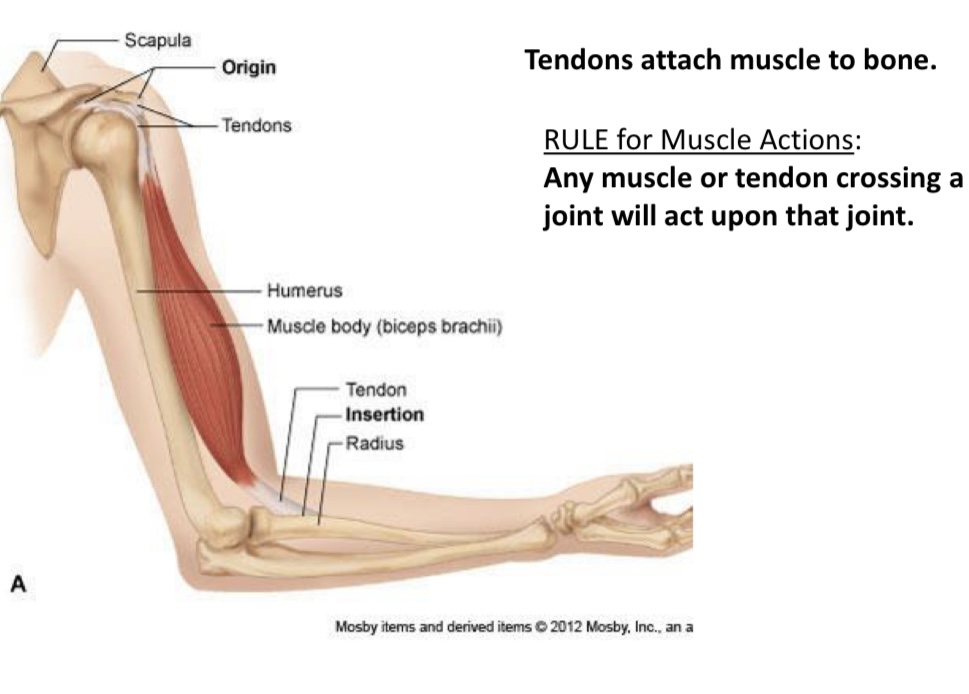
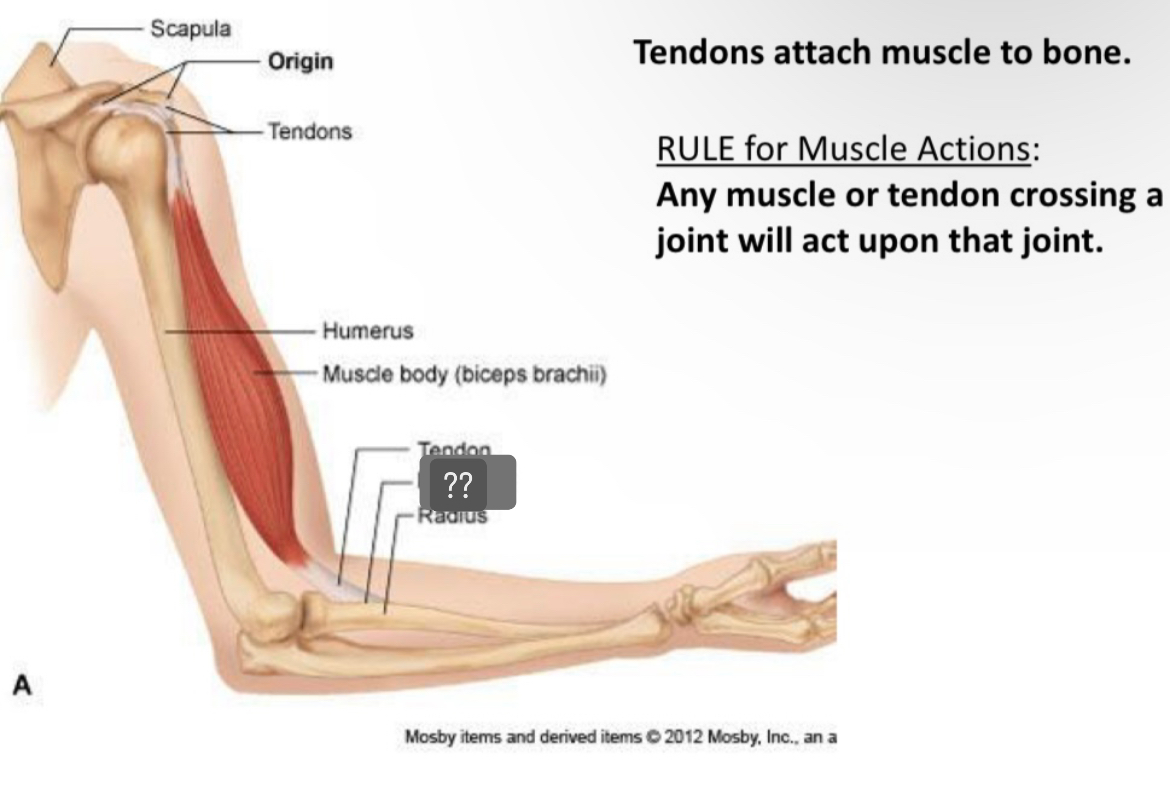
What is it called?
Insertion
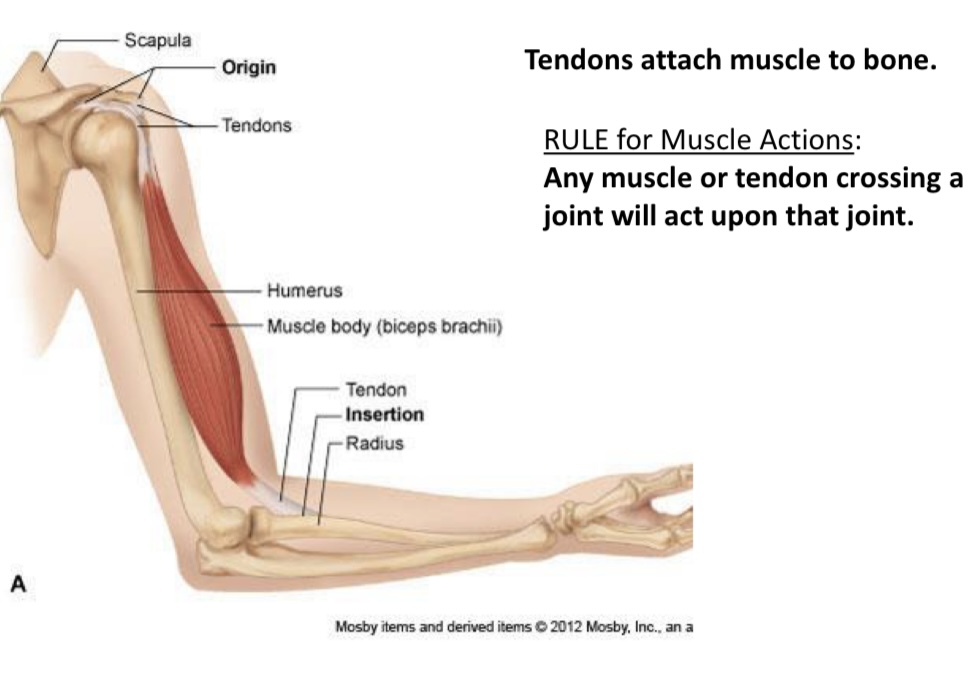
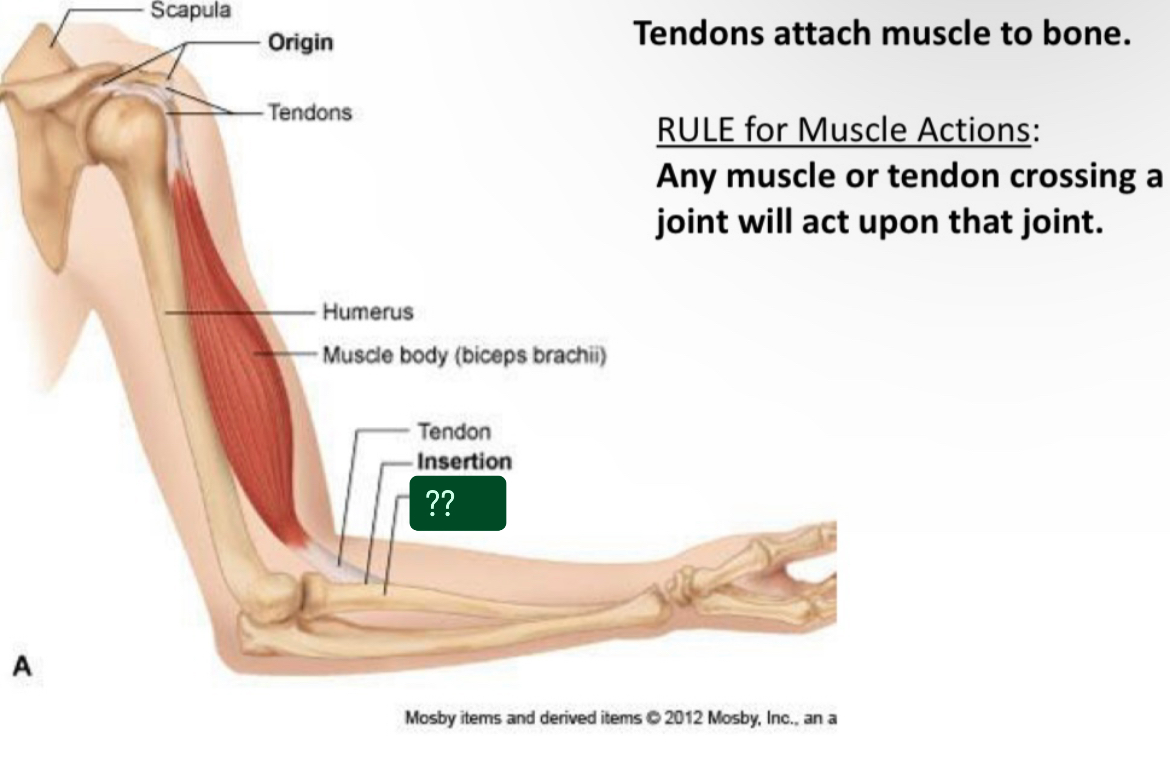
What is this called?
Radius
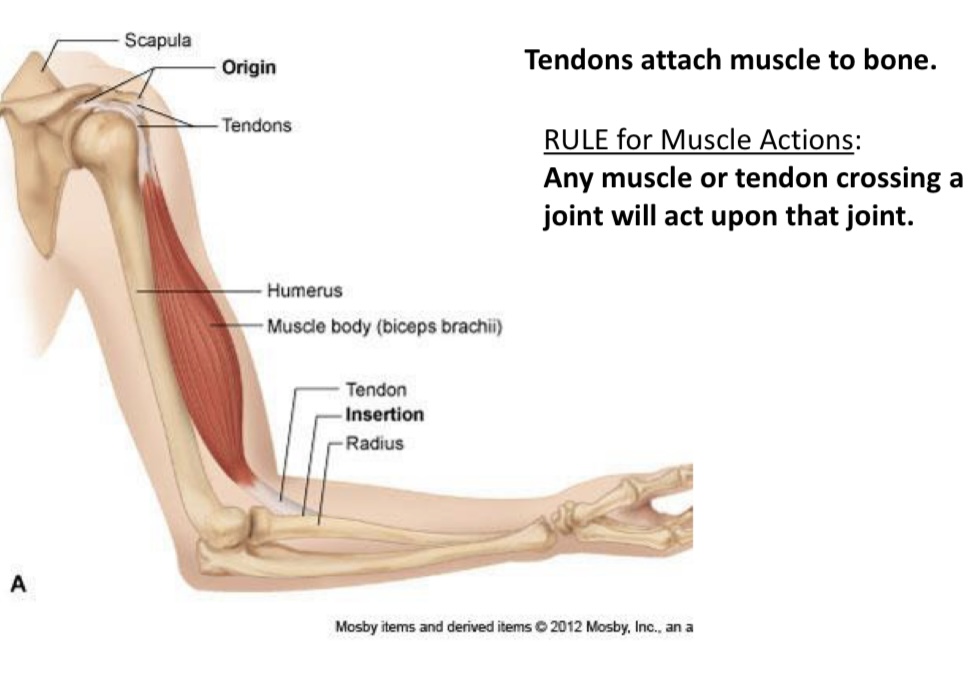
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone
Muscle belly
Contractile portion
Origin(O)
Fixed end
Insertion(I)
Moveable end
During contraction, muscle shortens which results in an ______
During contraction, muscle shortens which results in an action
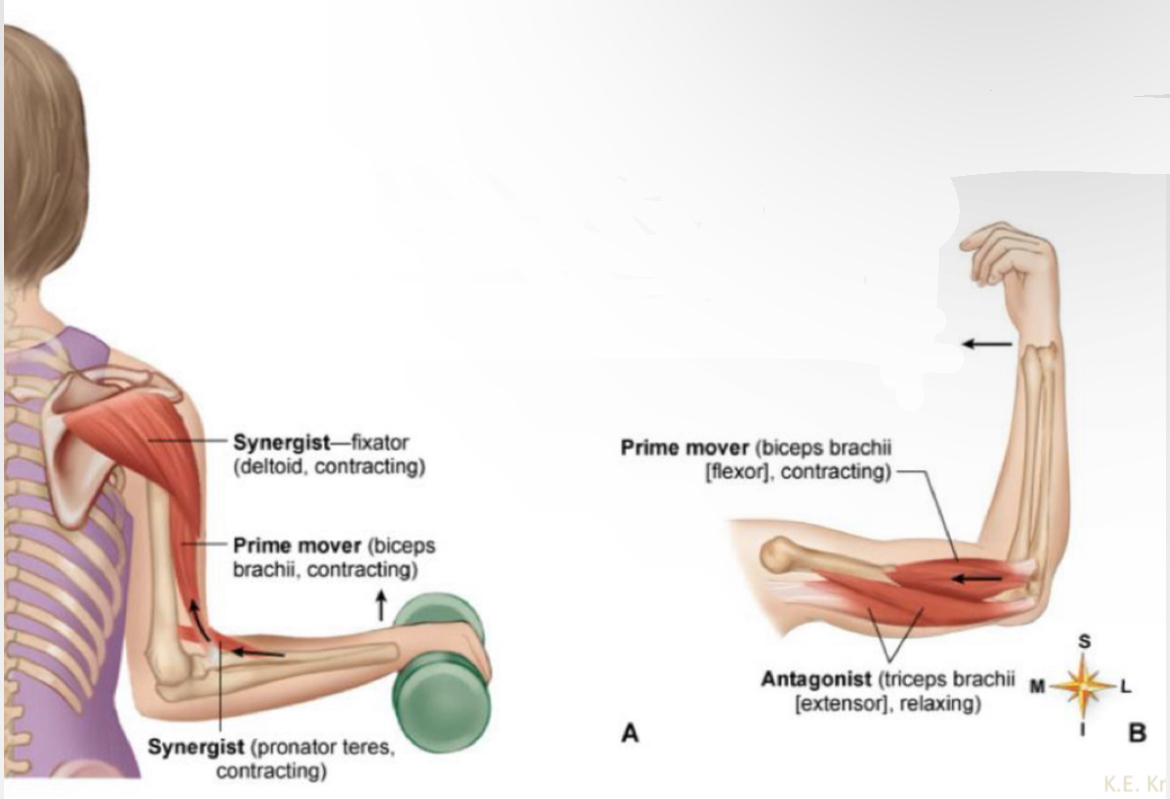
Prime mover
Main muscle performing the movement
Synergist
Muscle(s) that aid the prime mover
Fixator
Muscles that stabilize a joint
Antagonist
Main muscle opposing the movement
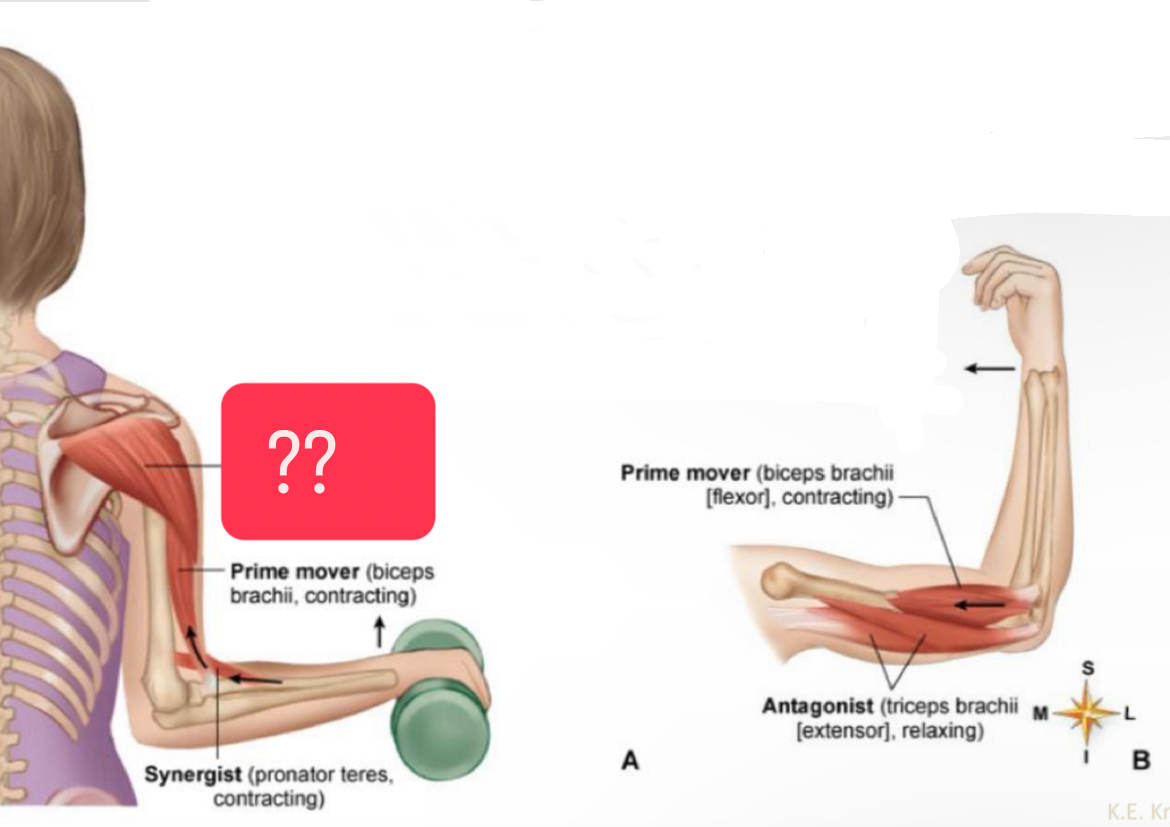
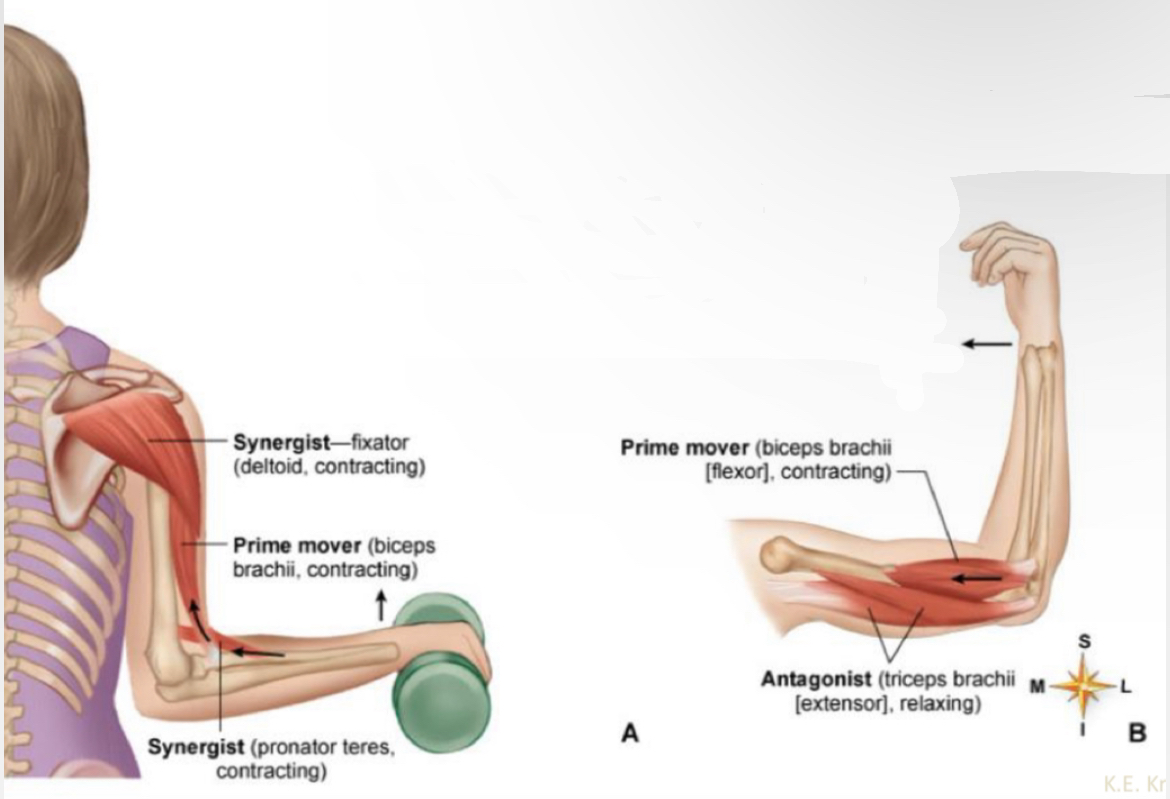
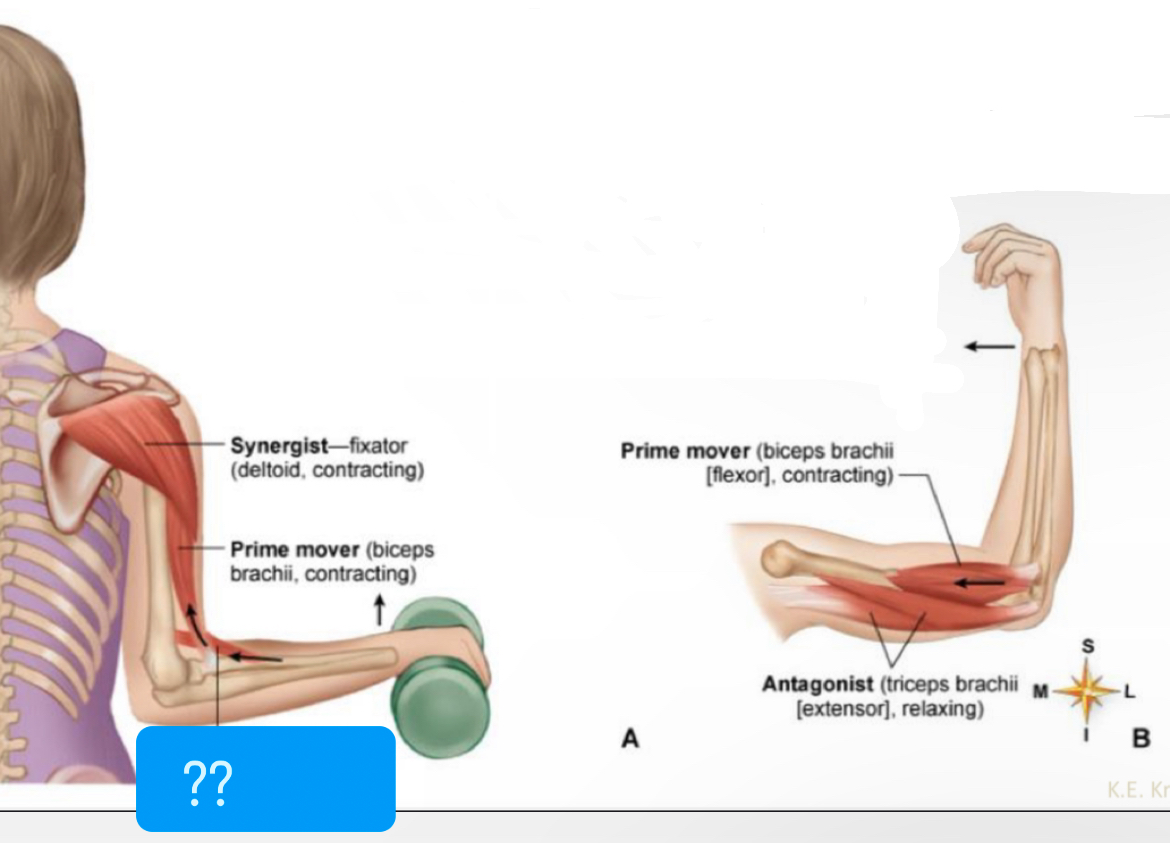
What muscle?
Synergist - fixator (deltoid, contracting)
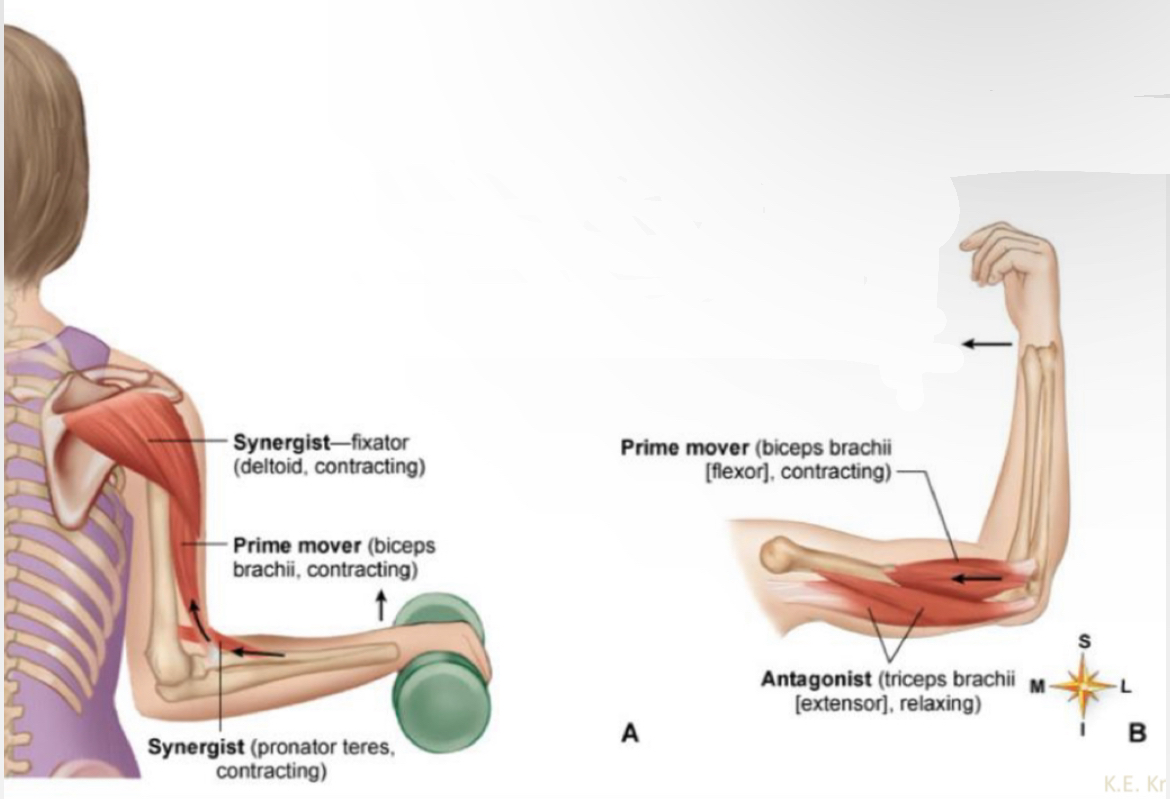
what muscle?
Prime mover (biceps brachii, contracting)
What muscle?
Synergist ( pronator teres, contracting?
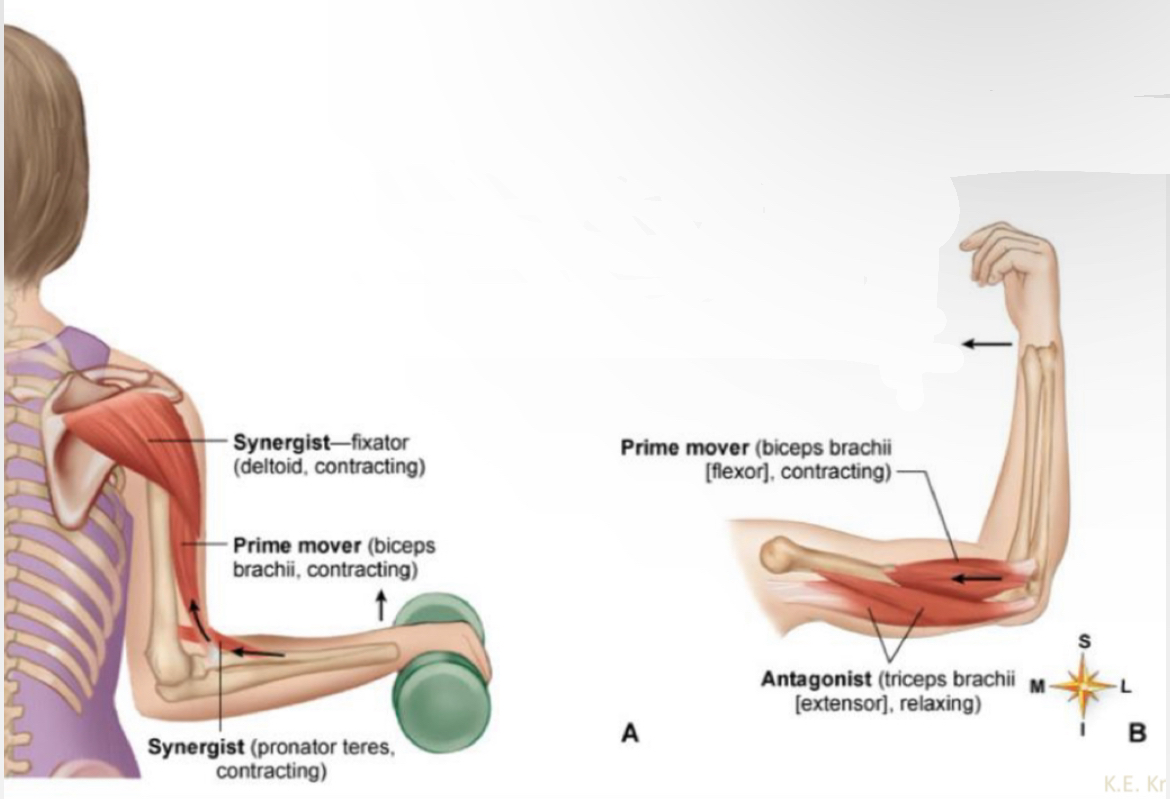
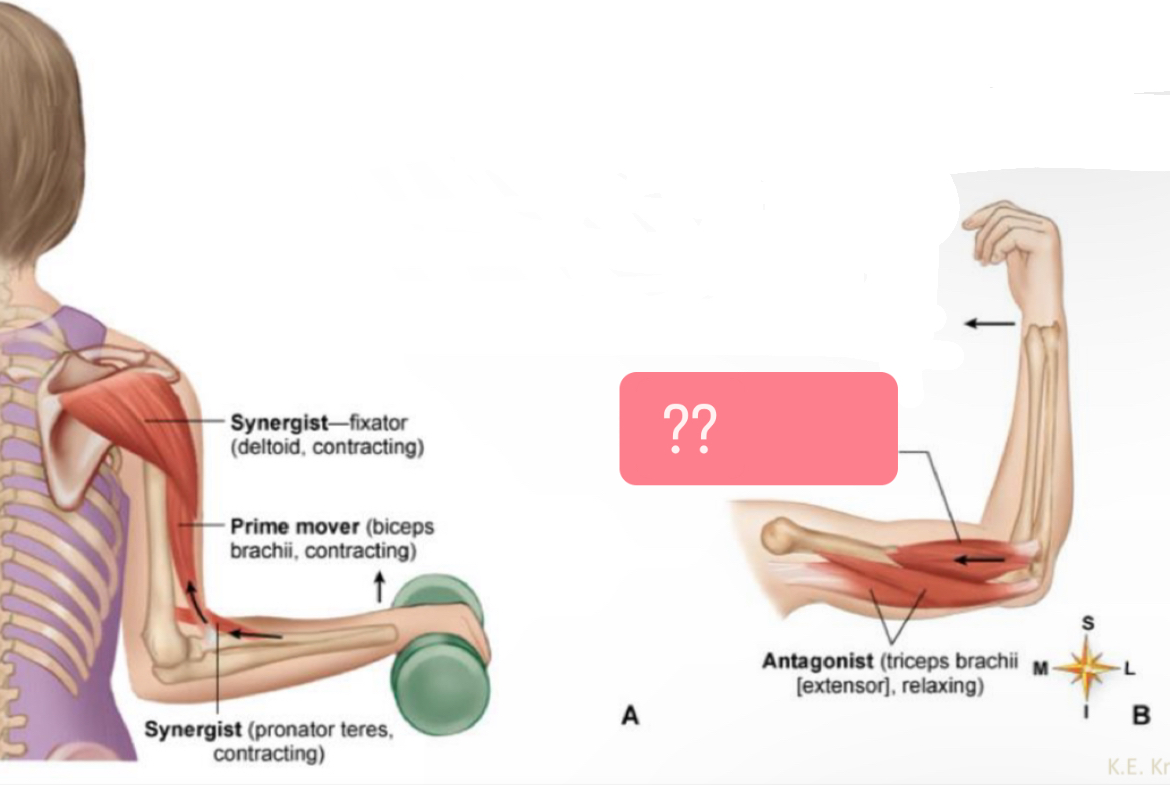
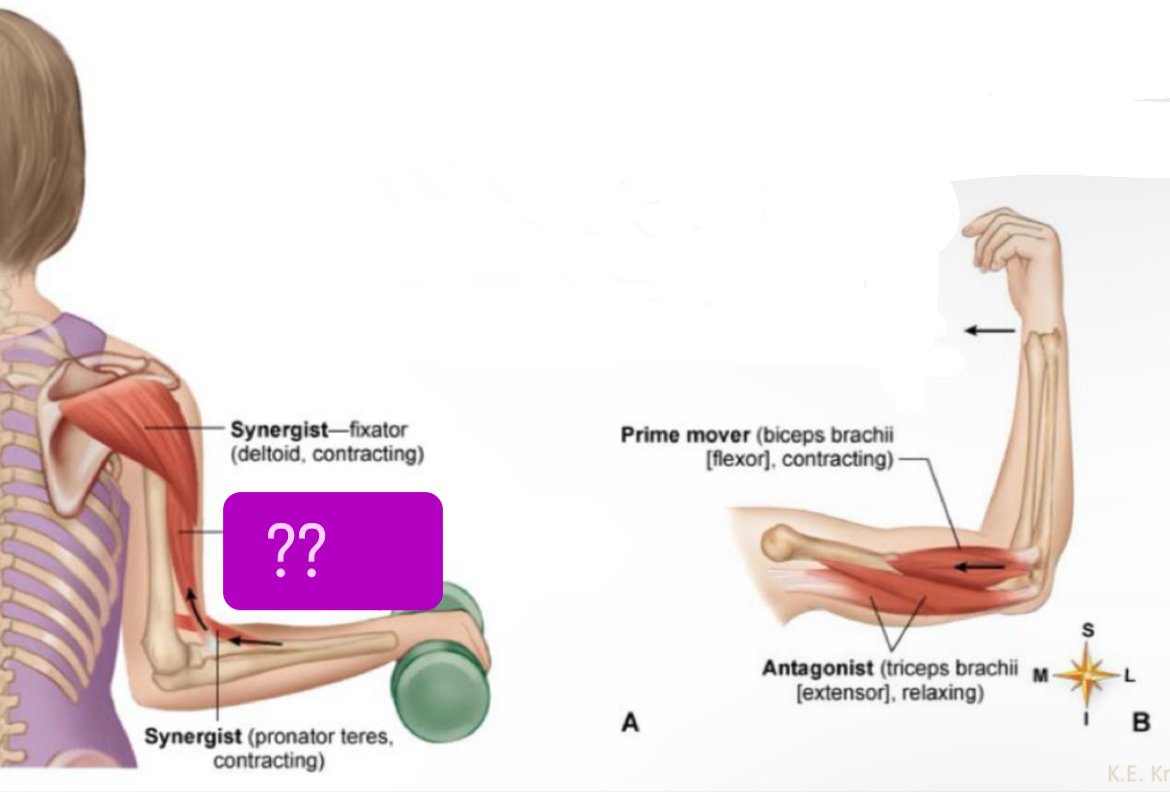
What muscle?
Prime mover (biceps brachii(flexor), contracting)
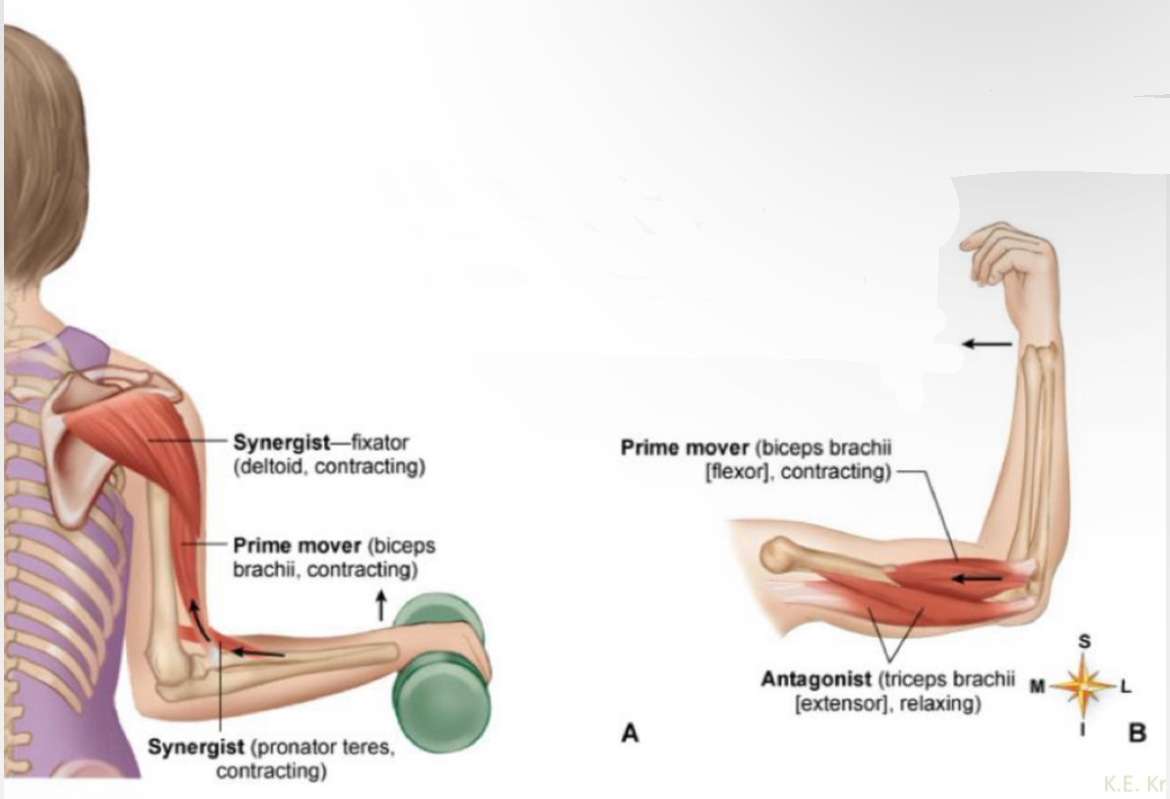
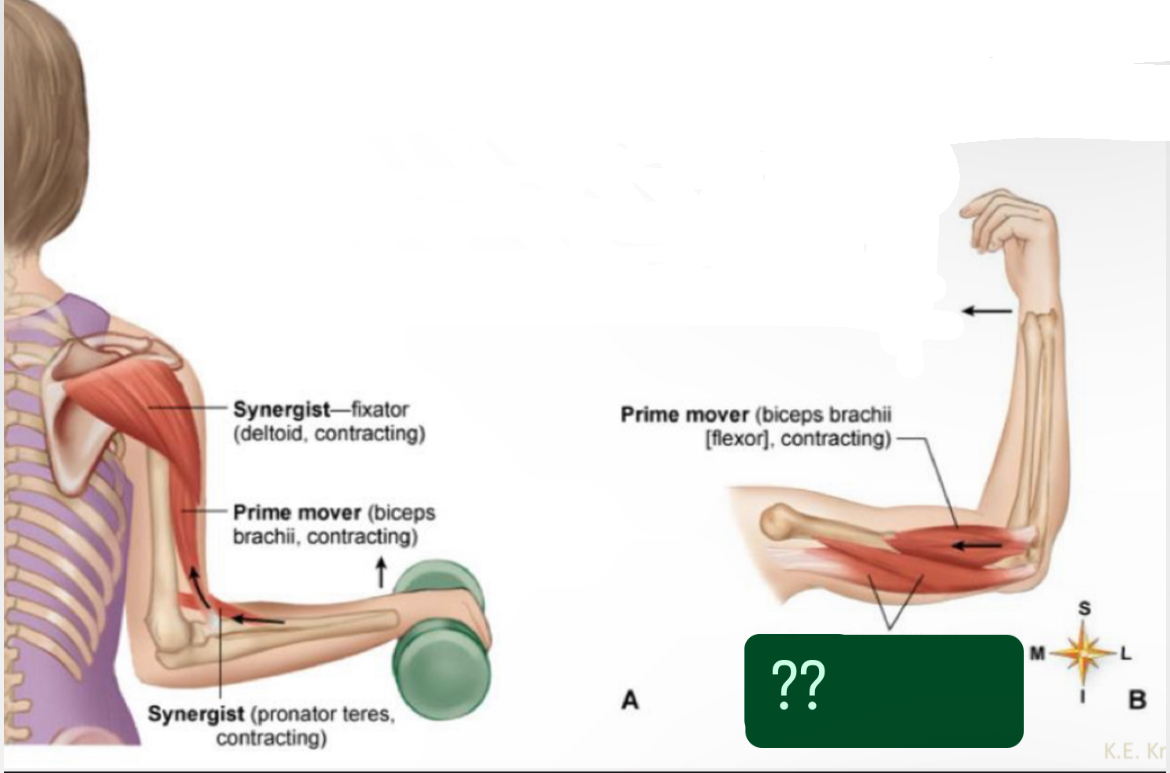
What muscle?
Antagonist ( triceps brachii(extensor), relaxing)

Flexors vs. Extension
Flexors touch the tree
Extensors do not!!!!
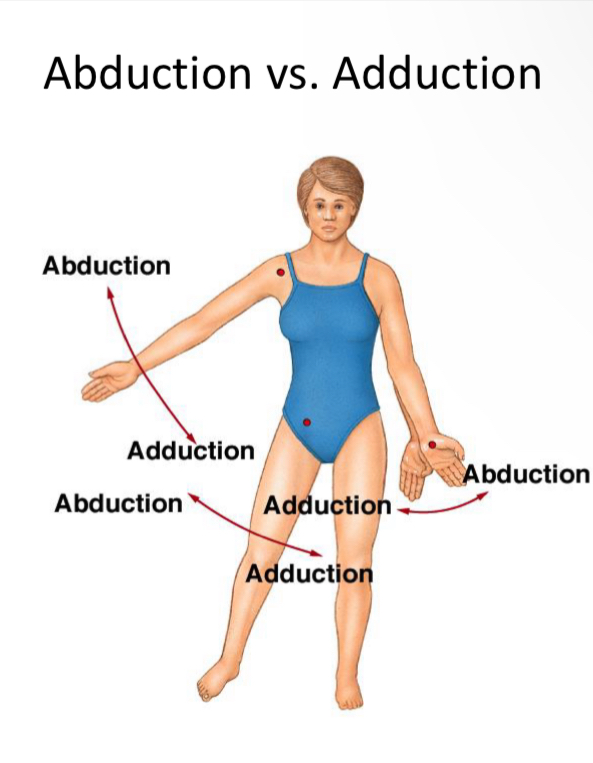
Abduction
“Help someone abducted my child!”
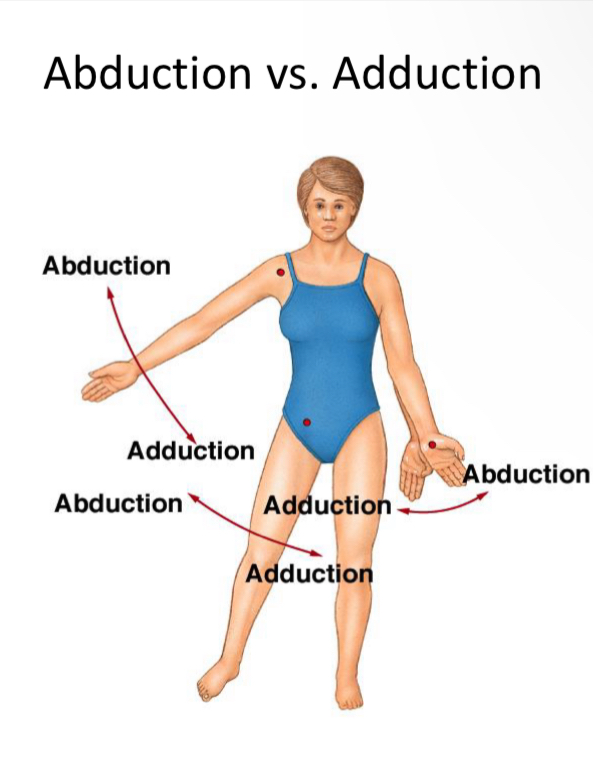
Addiction
“ Add to the midline”
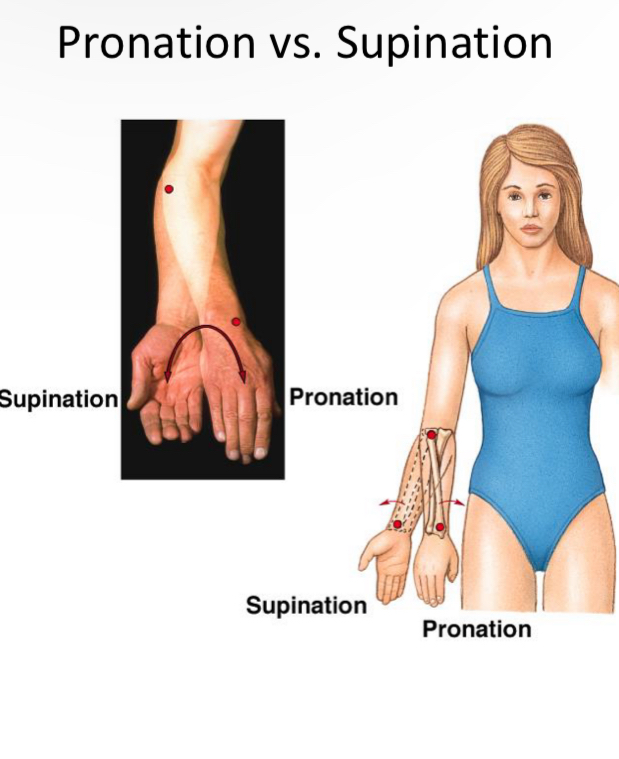
Supination
Carry a bowl of soup
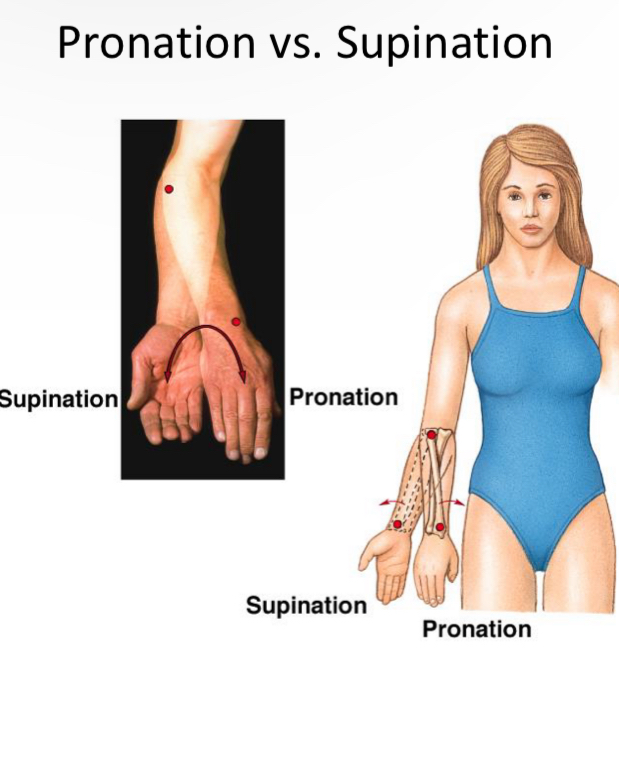
Probation
Pour it out
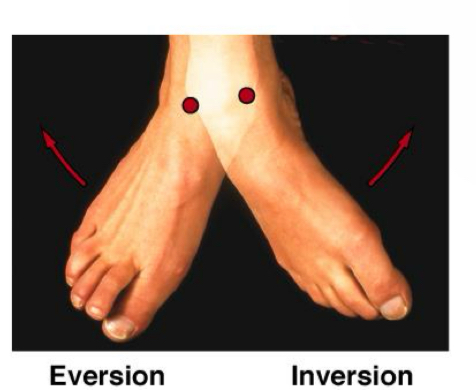
Inversion & eversion occur at the _____ think soccer!
Inversion & eversion occur at the ankle think soccer!
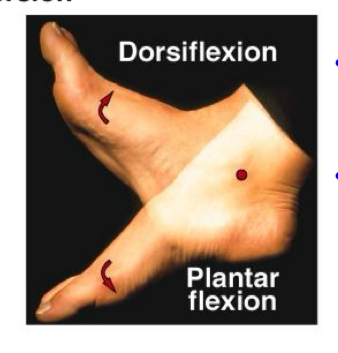
Plantarflexion
Push on gas pedal
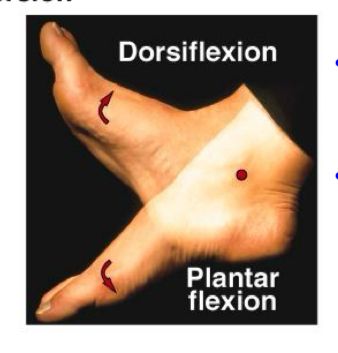
Dorsiflexion
Easing off the gas pedal
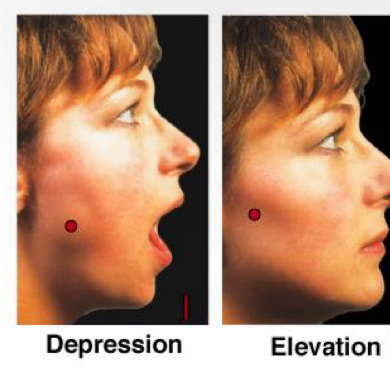
Elevation
“Elevators go up”
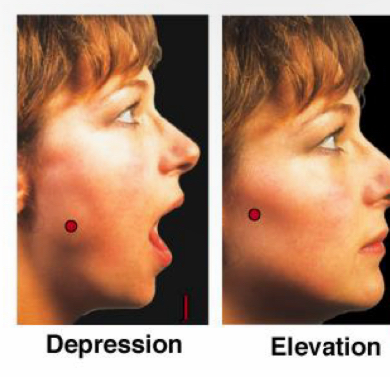
Depression
“Depression drags people down”
Anterior group
Extends the knee
Posterior group
Flexes the knee
Medial group
Addicted the thigh
Sartorius
Separates the anterior compartment from the medial compartment
Central Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Spinal nerves (31 pairs)
Cranial nerves (12 pairs)
Neuron
Basic functional unit of nervous system
Neuroglia
(glial cells)- support cells
Which cells conduct action potentials (nerve impulses)?
Neurons
What’s is the relationship between neurons and nerves?
A nerve is a bundle of neurons
Implication: A nerve’s function is determined by the types of neurons it carries
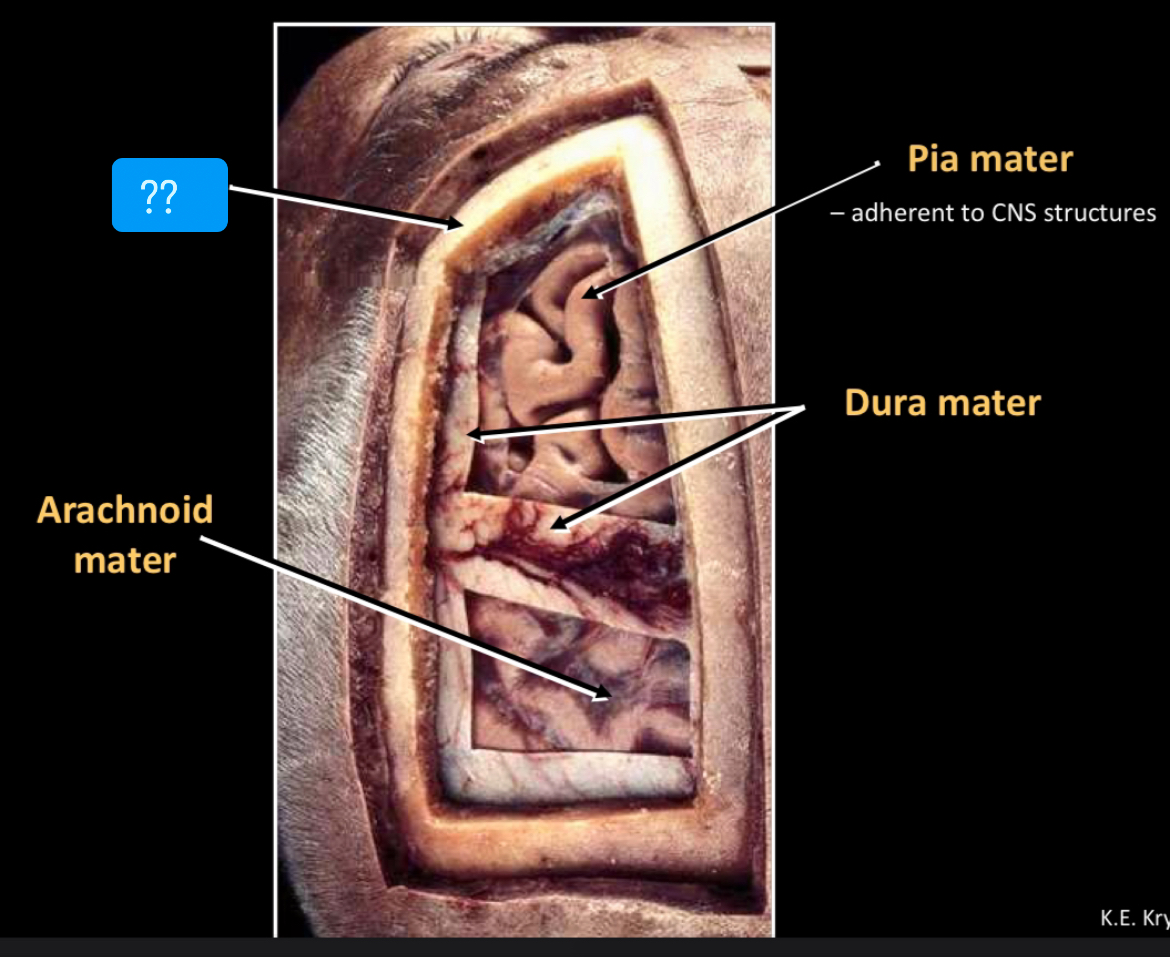
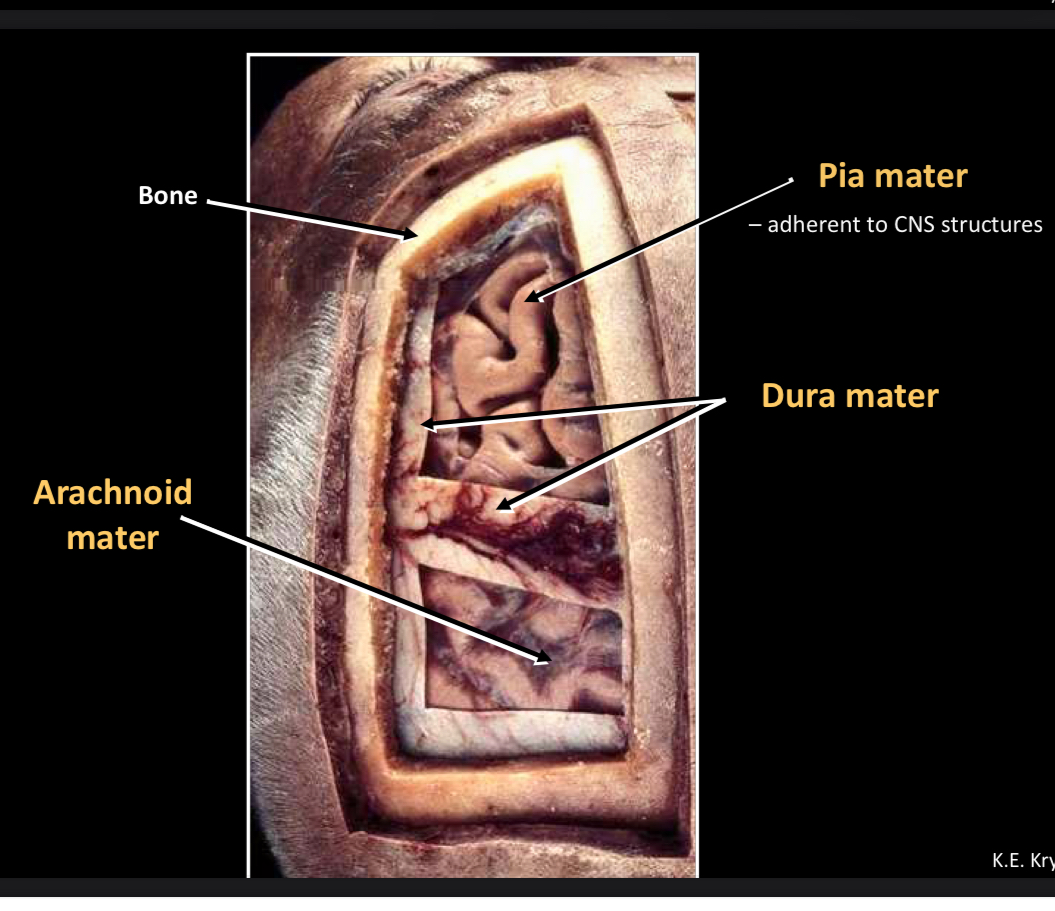
What is this?
Bone
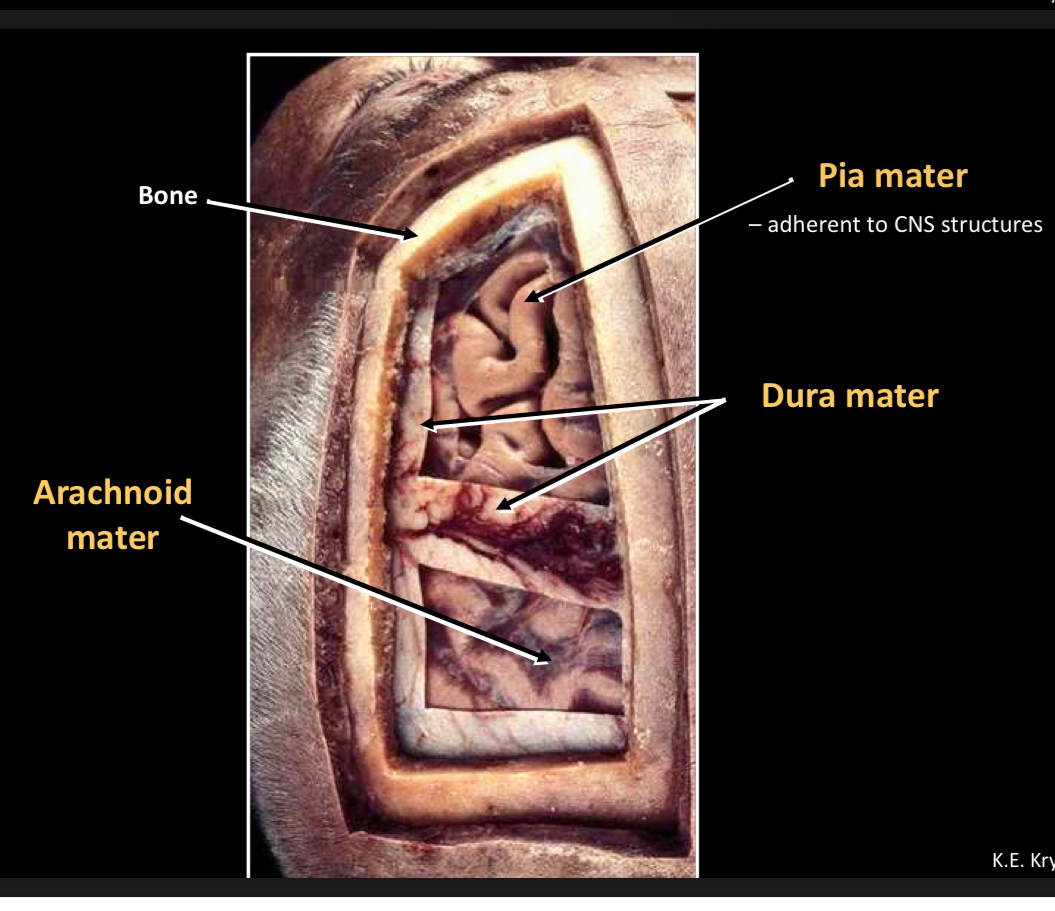
What is this?
Arachnoid mater
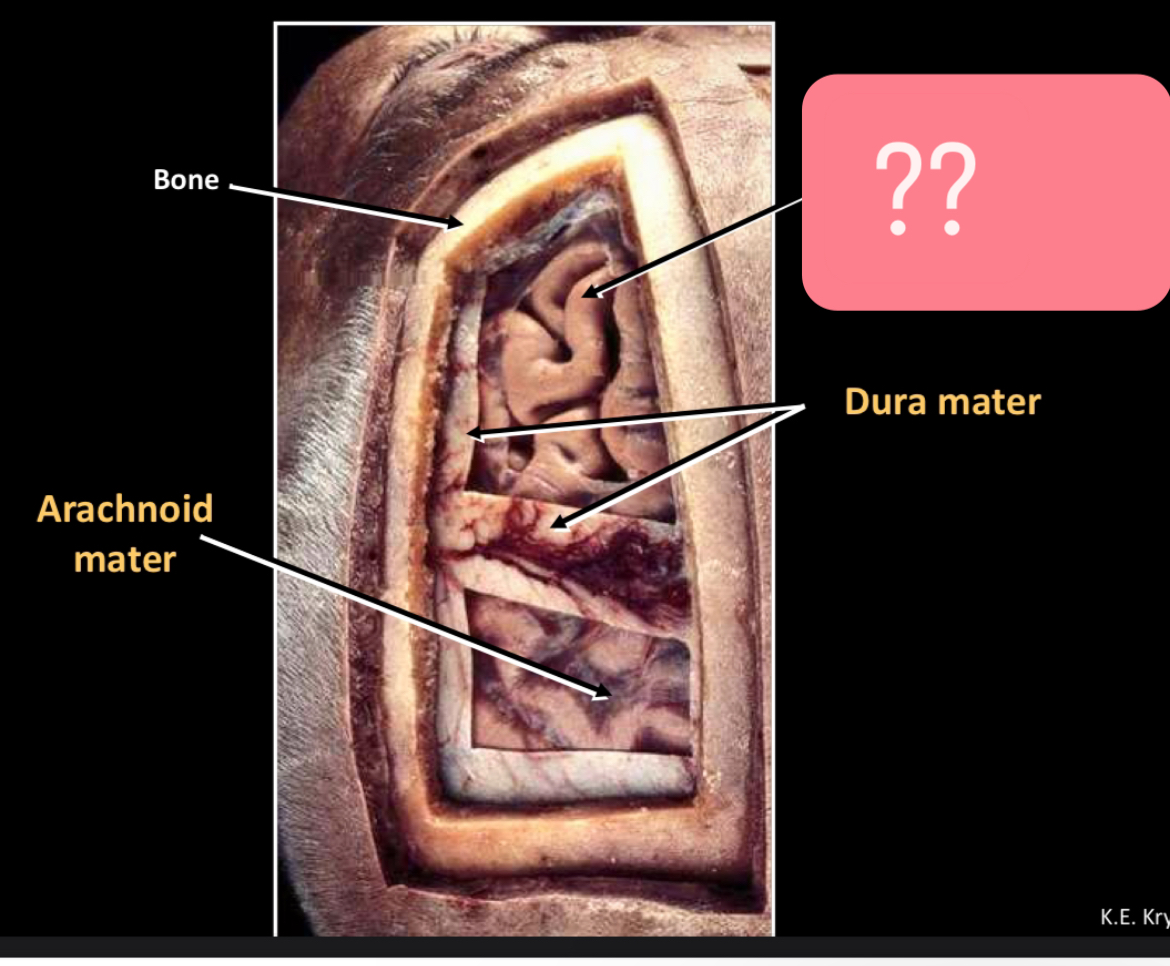
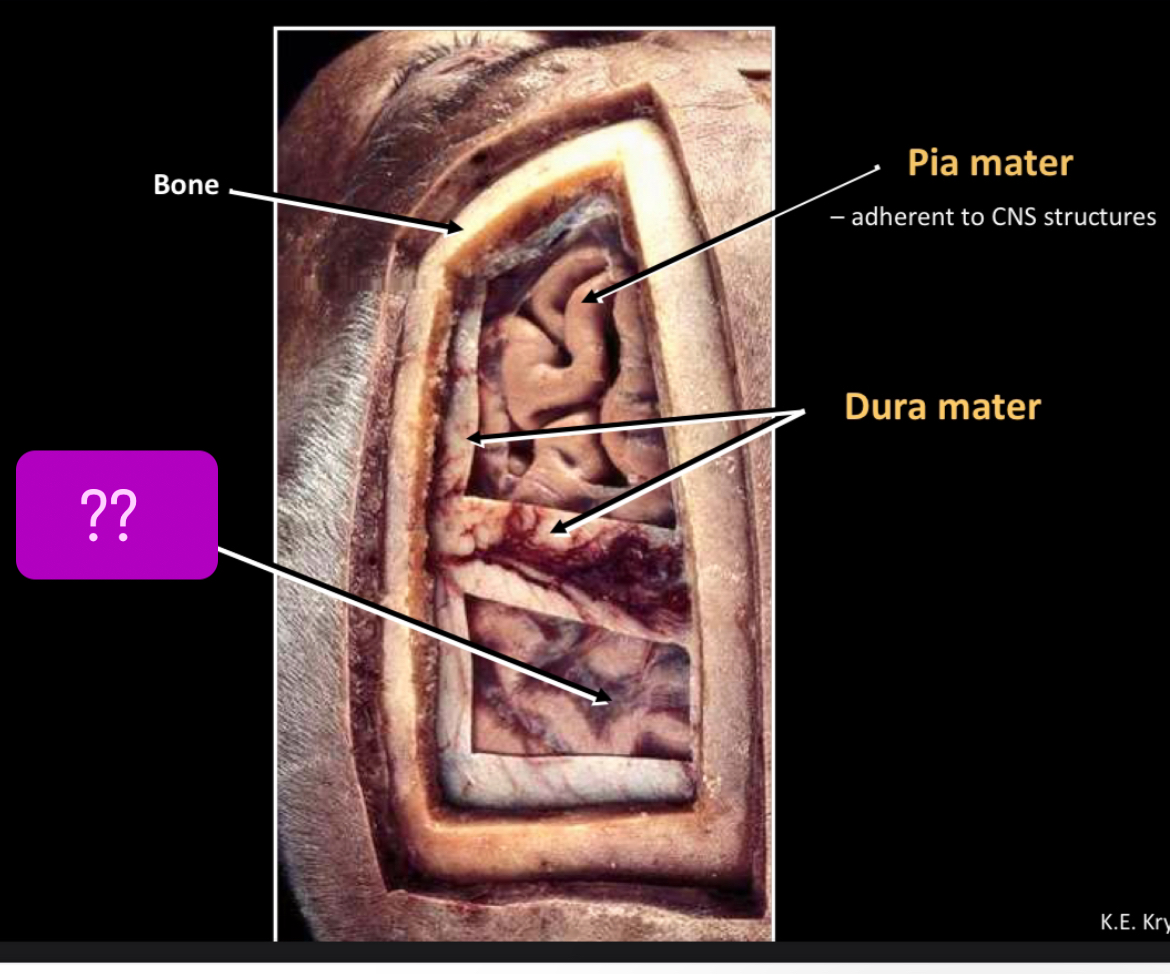
What is this?
Pia mater -adherent to CNS structures
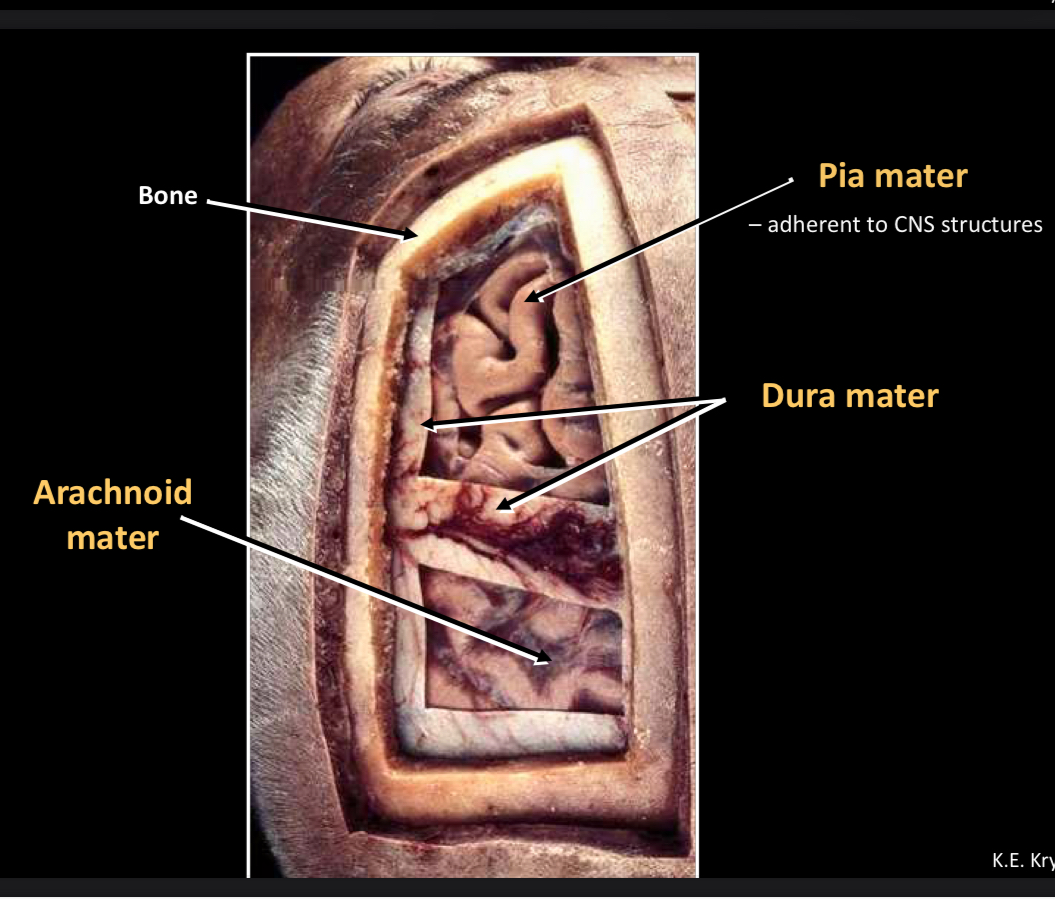
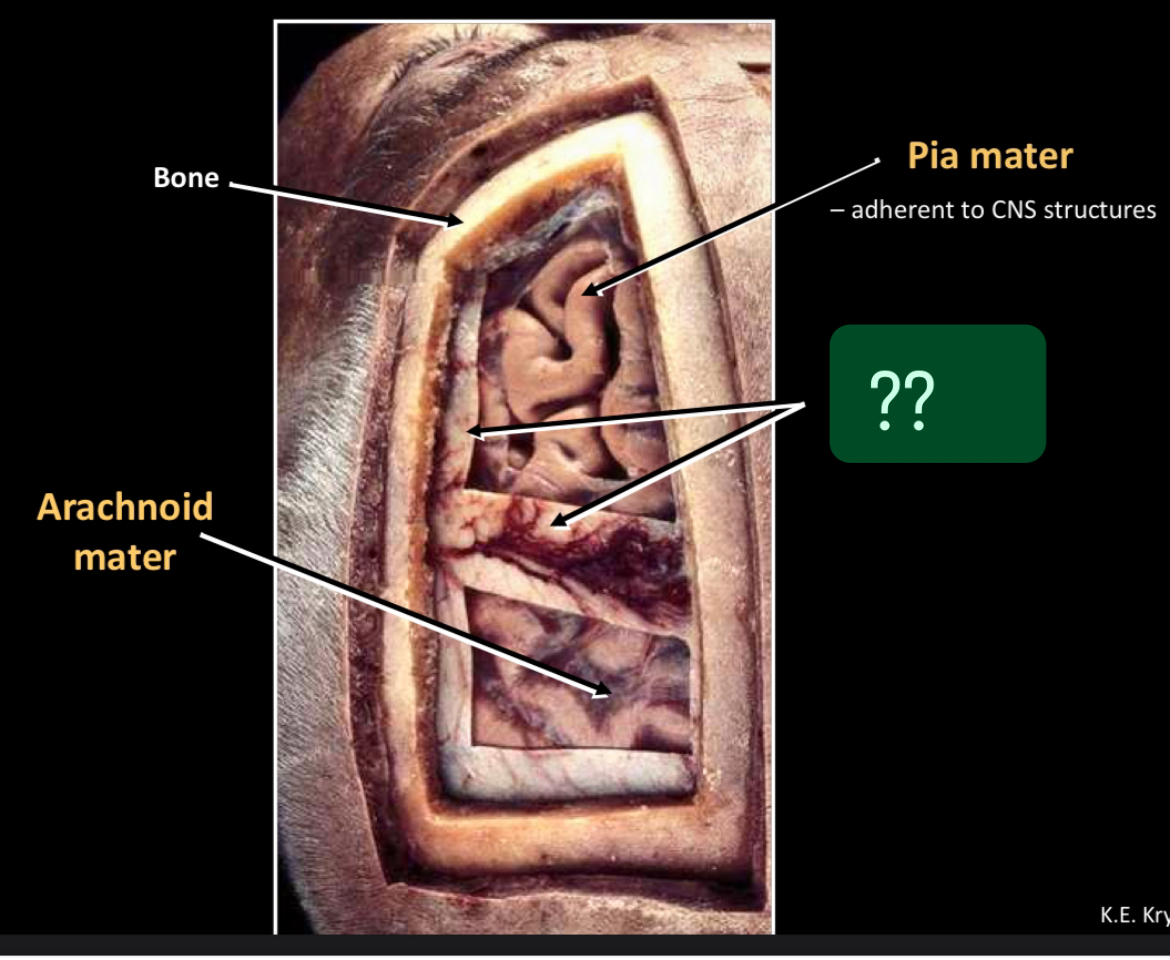
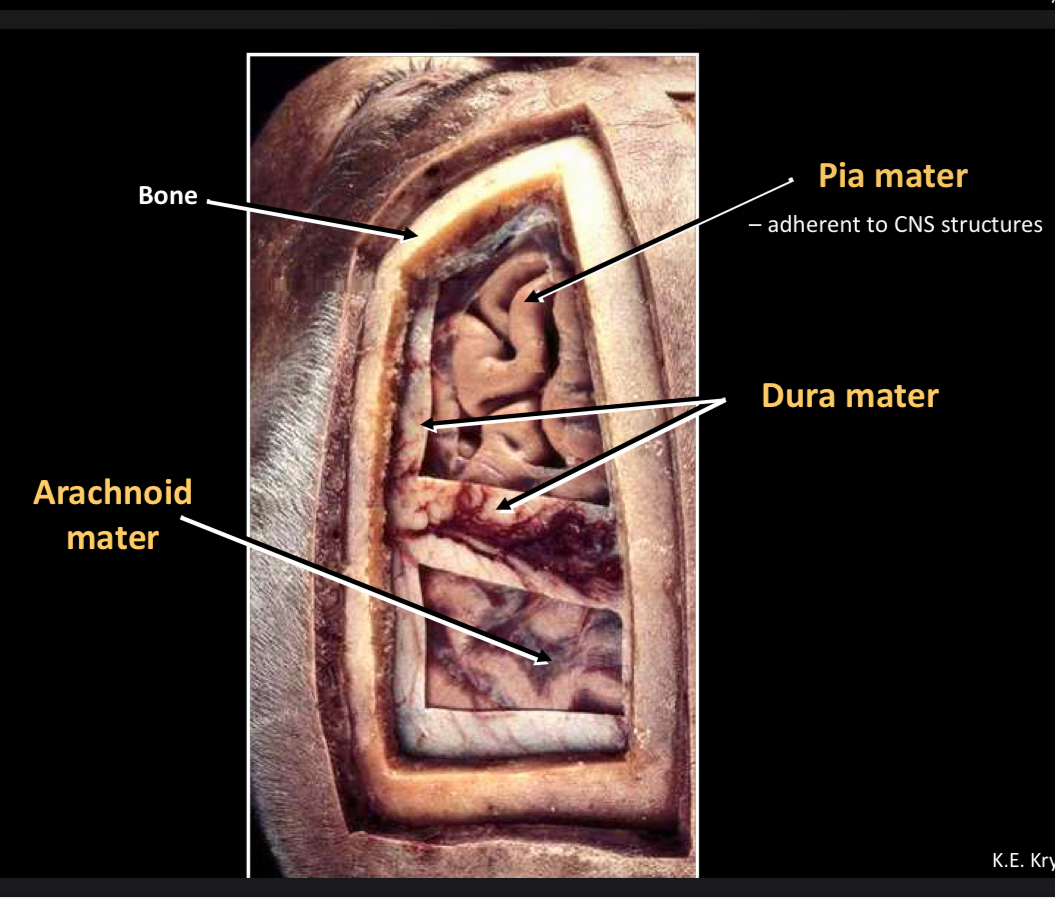
What is this?
Dura mater