carbohydrates 1.1
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
what are monomers
smaller repeating units from which larger molecules are made
what are polymers
molecules made from many similar monomer molecules
condensation reaction
joins monomers together and forms a chemical bond and releases water
hydrolysis reaction
2 monomers separated,
breaks a chemical bond
and uses water
carbohydrates
What are monosaccharides? Give 3 common examples
● Monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made
● Glucose, fructose, galactose
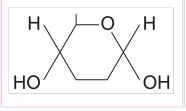
α-glucose
beta glucose
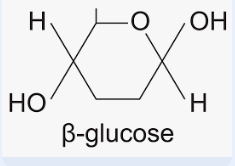
Describe the difference between the structure of α-glucose and β-glucose
● Isomers - same molecular formula but differently arranged atoms
● OH group is below carbon 1 in α-glucose but above carbon 1 in β-glucose
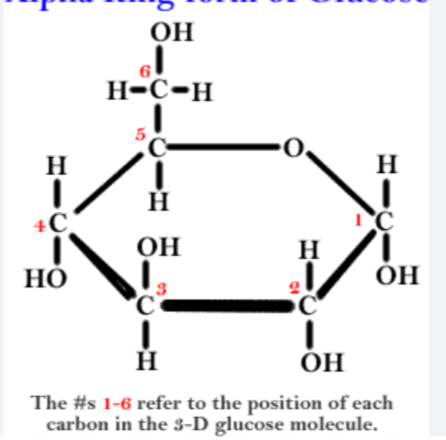
What are disaccharides and how are they formed?
● Two monosaccharides joined together with a glycosidic bond
● Formed by a condensation reaction, releasing a water molecule
List 3 common disaccharides & monosaccharides from which they’re made
gm
gl
fs
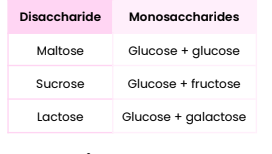
Draw a diagram to show how two monosaccharides are joined together
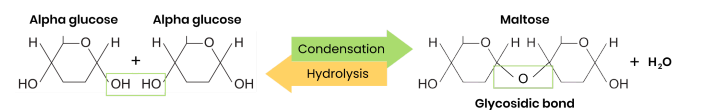
What are polysaccharides and how are they formed?
● Many monosaccharides joined together with glycosidic bonds
● Formed by many condensation reactions, releasing many water molecules
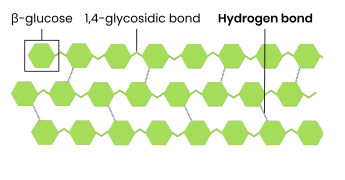
Basic function of cellulose
FUNCTION:
provides strength and structural support to plants/algae cell walls
STRUCTURE
cellulose is made of beta-glucose by condensation reaction (monomer)
has a straight chain
has only 1-4 glycosidic bonds
how does the structure of cellulose relates to it function
Every other β-glucose molecule is inverted
1. Long and straight chains;
2. Become linked together by many hydrogen bonds to form fibrils;
3. Provide strength (to cell wall)
1.basic function of starch and 2.structure
1.energy store in plant cells
2. - polysaccharide of alpha-glucose
amylose has 1,4-glycosidic bonds so is unbranched
amylopectin has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bond so is branched
how does the structure of starch relate to its function
insoluble —→ so dosent affect water potential
helical ——> compact
large molecule —→ cannot leave cell
branched —→ so makes molecule compact
polymer of alpha glucose —> so provides glucose for respiration
branched ——> more ends for fast breakdown/hydrolysis
basic function and structure of glycogen
function - energy store for animal cells
structure:
polysaccharide of alpha glucose
branched
has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
coiled
suggest how glycogen acts as a source of energy
hydrolysed to glucose
glucose used in respiration
describe how the structure of glycogen relates to its function
insoluble —> dosent affect water potential
branched —→ so makes molecule compact
polymer of alpha- glucose —→ so provides glucose for respiration
branched —→more ends for fast breakdown /hydrolysis
large - cant cross/leave cell membrane
which are reducing and non-reducing sugars
reducing sugars:
all monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose)
maltose
lactose
non - reducing sugar:
sucrose
TEST FOR REDUCING SUGARS
add benedicts solution to the sample
heat in boiling water bath
+ve result —→ green/yellow/orange/ red precipitate

TEST FOR NON- REDUCING SUGAR
do benedicts test and it remains blue/ -ve
heat in a boiling water bath with acid
neutralise with alkali
heat in a boiling water bath with benedicts solution
+ve —→ green/yellow/orange/ red precipitate
TEST FOR STARCH
add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide and stir it
+ve result —> blue-black
Use of a colorimeter in a investigation would improve the repeatability of the student’s results.
quantitative
strandises the method