1.4 Cells
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
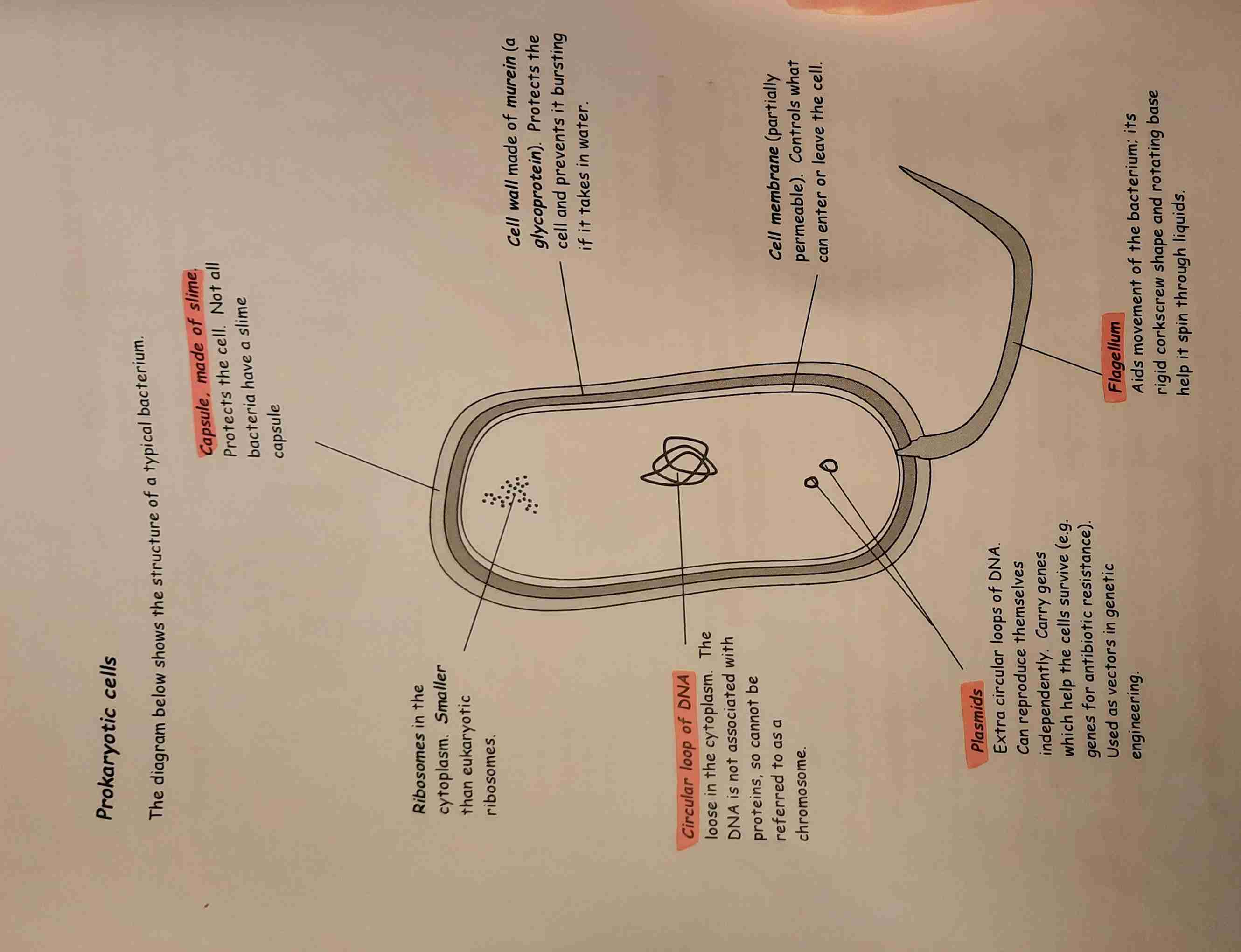
Prokaryotic cells
An example would be bacteria
CONTAINS NO:
• Nuclei
• Mitochondria
• Endoplasmic reticulum
CONTAINS:
• Naked, circular DNA
• Small ribosomes
• Sometimes plasmids
• Cell wall
• Capsule made of slime
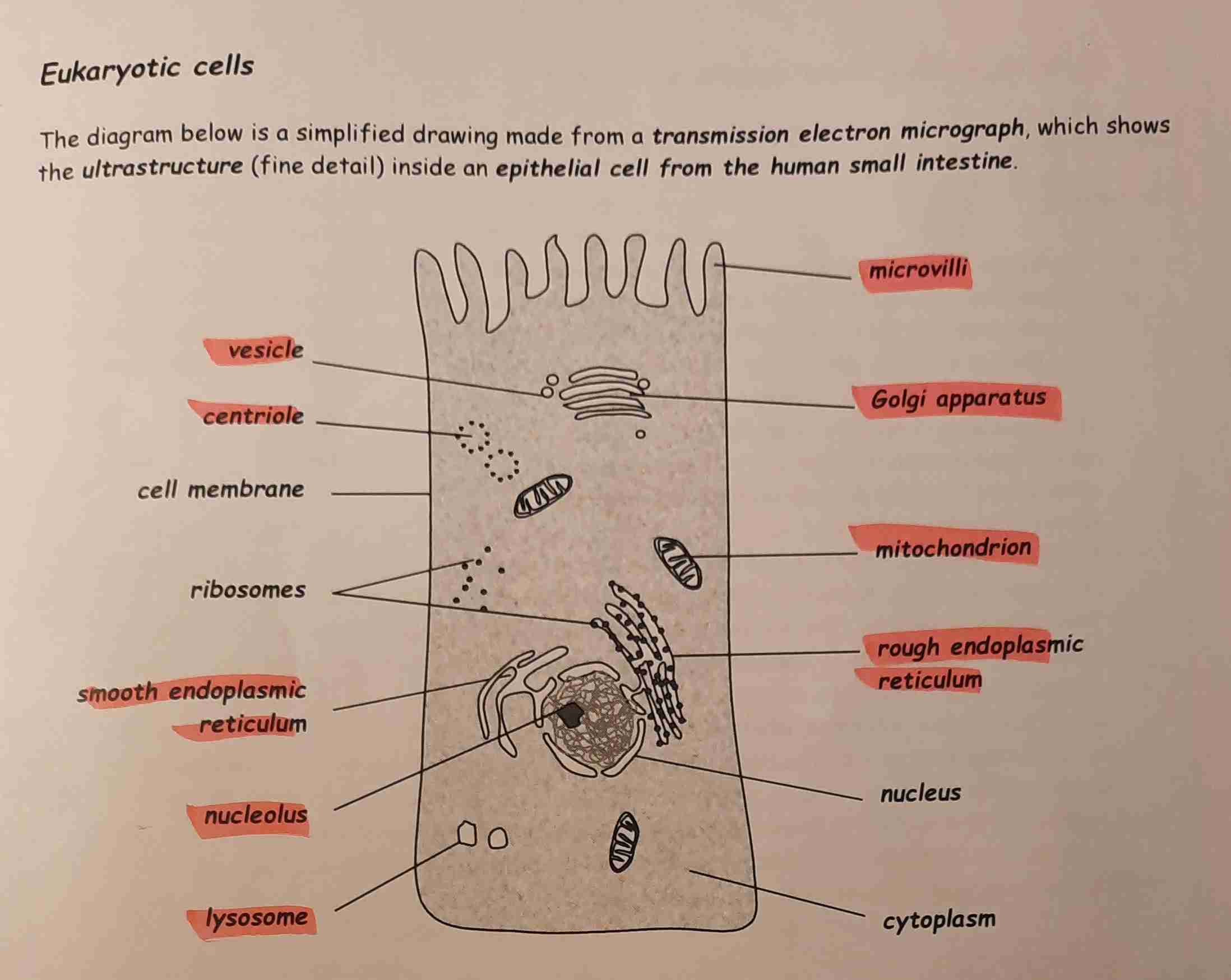
Eukaryotic cells
CONTAINS:
• Membrane bound nucleus
• Chromosomes (helical DNA with a histone protein coat)
• Mitochondria
• Endoplasmic reticulum
• Ribosomes
• Golgi apparatus
• Vesicles
• Lysosomes
• Microtubules
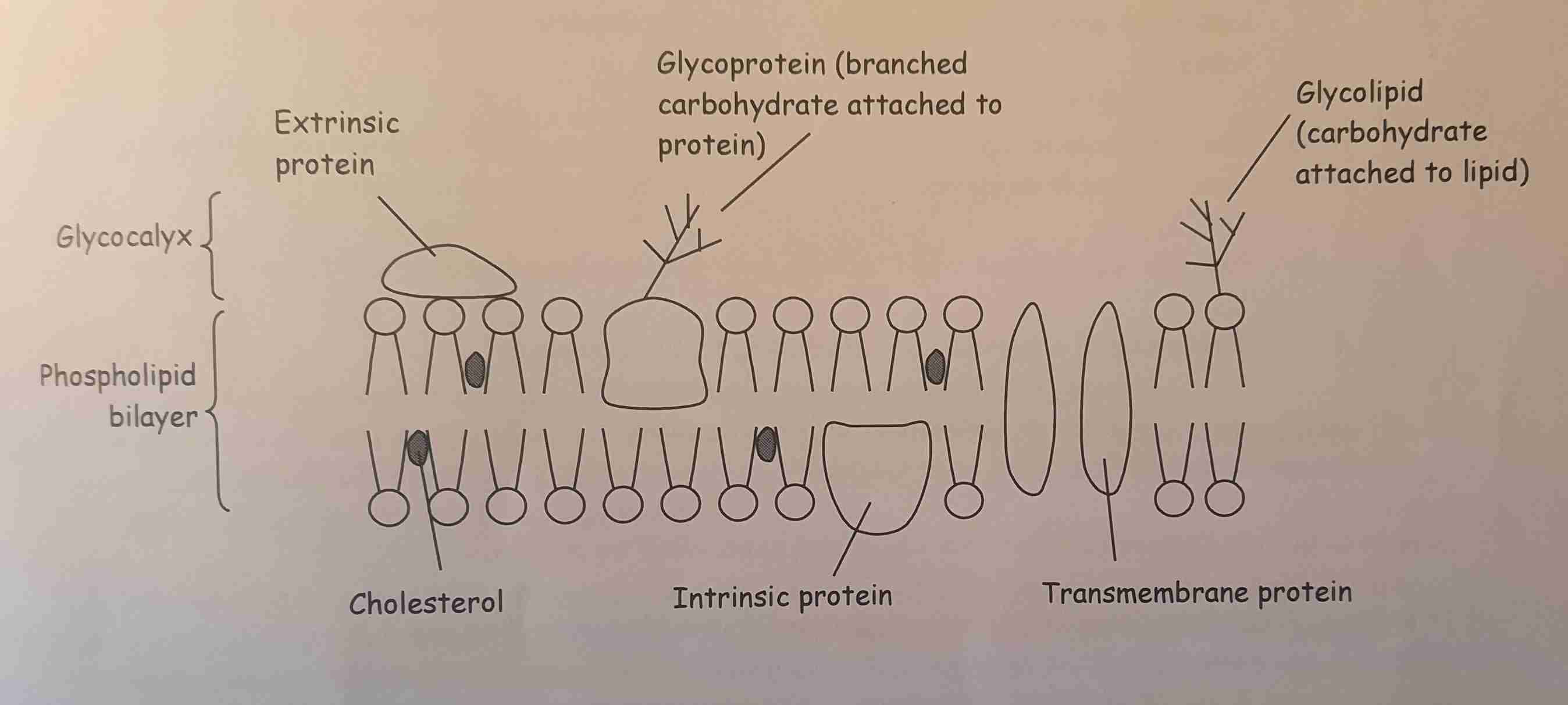
Molecules in a Cell Membrame
• Phospholipid bilayer
• Proteins
• Glycocalyx
• Glycoproteins
• Glycolipids
• Cholesterol (in animals)
• Receptors
• Enzymes
• Antigens
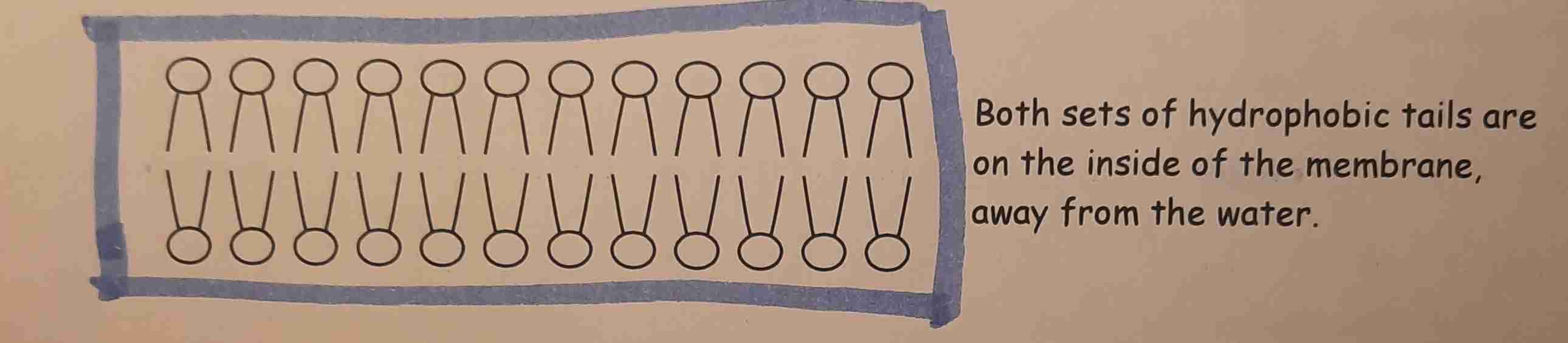
Phospholipid bilayer
Makes up cell surface membrane
• Hydrophillic head
• Hydrophobic tail
In a cell surface membrane, there’s water on both sides. Forcing the phospholipids to form a bilayer
Functions of phosphlipid bilayers
• Allow lipid soluble substances to enter kr leave the cell
• Prevent water soluble substances entering & leaving the cell
• Make the membrane flexible
Proteins & cell membranes
Extrinsic protein: On surface of phospholipid bilayer
Intrinsic protein: embedded into the membrane
Functions of proteins in cell membranes
• Structural support & stability to the cell
• Acts as a channel for movement of water soluble molecules across the membrane. Protein creates a hydrophilic channel so polar molecules can bypass the hydrophobic centre of the membrane
• Allow active transport
• Form recognition sites for identification of cells
• Helps cells stick together
• Act as receptors
• Act as enzymes
Glycocalyx
Contains polysaccharides bound to glycoproteins or glycolipids
• Acts as a barrier for a cell from its surroundings- providing protection
Cholesterol
Lies between phospholipid tails.
Provides stability by restricting sideways movement of phospholipids at high temps.
At low temps cholesterol helps stop adjacent phospholipid molecules sticking together
Function of Emzymes in Cell Membranes
Membrane provides attached enzymes with more stability
Cell Recognition & Cell Receptors
Glycocalyx allows cells to recognise each other & group to form tissues
Glycoprotein receptors & signalling molecules fit together because they have complementary shape
What is a cell membrane?
Structures surrounding cells and contributing to their internal structures
Defines the boundaries of organelles within the cytoplasm
Components of Eukaryotic (animal) cells
• Nucleus
• Endoplasmic reticulum
• Ribosomes
• Golgi apparatus
• Lysosomes
• Mitochondria
• Microtubules
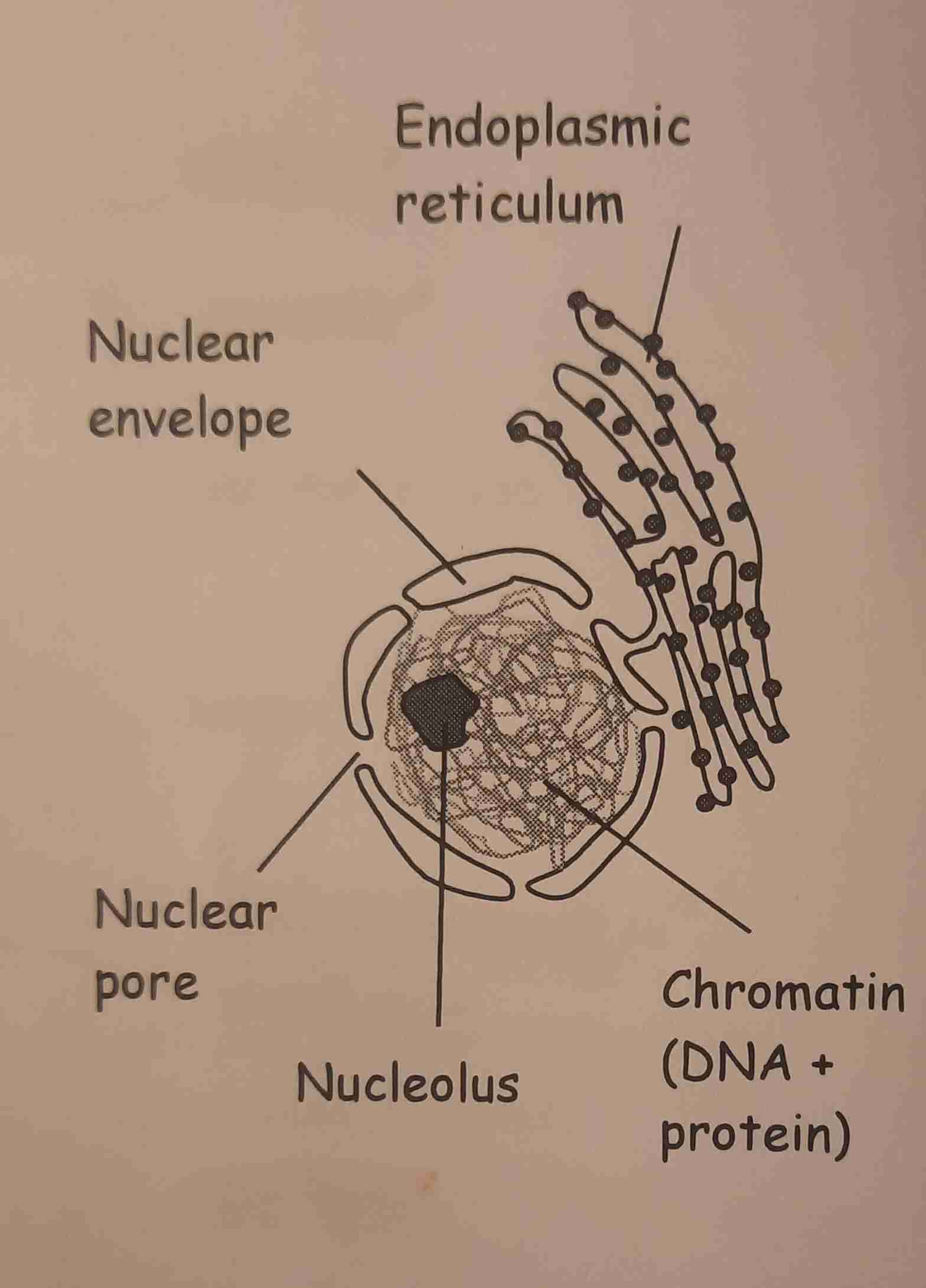
Components of the Nucleus
Contains DNA & histones in the form of chromosomes
Nucleolus- dark staining area where DNA codes for ribosomal RNA
Nuclear envelope- A perforated double membrane, separating contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Also provides structure to nucleus
Nuclear pore- allows molecules to enter/leave the nucleus
Outer membrane of the envelope is encrusted with ribosomes & is the site of origin of rough Endoplasmic reticulum
What is the function of the nucleus?
Protein synthesis
Carries the code for all the proteins a cell needs to make
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum has RIBOSOMES on the outside - provides scaffolding for ribosomes to make protein & the e.r. acts as a distribution network for the proteins- common in cells making a lot of protein
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum does NOT have ribosomes attached - synthesis of cholesterol, metabolises lipids & distributes them
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis
Found free in cytoplasm or attached to r.e.r.
Made from protein & ribosomal DNA
Golgi apparatus
Series of cisternae lined by a membrane
Has vesicles from ER joining it
Mitochondria
• Enclosed in a double membrane
• Matrix- thick juice filling the mitochondria
• The inner membrane is folded into cristae which project into the matrix - giving the inner membrane greater SA. Thus increasing number of enzymes embedded in membrane
Lysosomes
Vesicles produced by Golgi that have hydrolytic enzymes