Microbio Exam 1
1/361
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 314
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
362 Terms
Microbiology
The study of small organisms
Why should we study microbiology?
Helps us understand/develop vaccines, treatments, foods, and drinks
What percent of microbes are pathogenic?
Less than 5 percent
Normal flora
All of the microbes on or in your body (aka helpers)
Pathogenicity
Potential to cause disease
Virulence
Severity of disease caused
How can normal flora become pathogenic?
If placed in the wrong place or if host is immunocompromised.
What are opportunistic pathogens?
Infections that take advantage of immunocompromised people
Nosocomial Infections
Hospital Acquired Infections such as spesis
What is the first step for pathogenic microbes?
Enter the body/cell
What is the second step for pathogenic microbes?
Stay in!
What is the 3rd step for pathogenic microbes?
Defeat the host’s defenses
What is the 4th step for pathogenic microbes?
Cause damage
What is the 5th step for pathogenic microbes?
Transmit to a new host
What domain of life do fungi fall into?
Eukarya
What is the coccus bacteria shape?
Sphere
What is the bacillus arrangement of bacteria?
Rod
What is the spirillum arrangement of bacteria?
Spiral
What is the Strep arrangement of bacteria?
Chain
What is the Staph arrangement of bacteria?
Cluster
What is the name for 2 cells?
Diplo
What is the name for 4 cells?
Tetrad
What is peptidoglycan also known as?
Murein
What is the primary component of bacterial cell walls?
Peptidoglycan
What are peptidoglycan meshes made of?
Sugars & amino acids
How big is/are the layer(s) of peptidoglycan in gram positive bacteria?
Only 1 layer; it’s a thick layer
How big is/are the layer(s) of peptidoglycan in gram negative bacteria?
Two thin layers; one outer one inner
Teichoic acid
Sugar phosphate molecules
Describe the concentration of teichoic acids & lipids in gram positive bacteria
Lots of teichoic acids; little to no lipids
Describe the concentration of teichoic acids & lipids in gram negative bacteria
No teichoic acid; lots of lipids
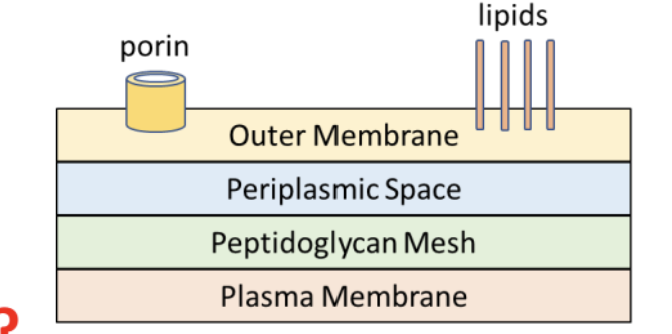
Is this gram positive or gram negative?
Gram negative
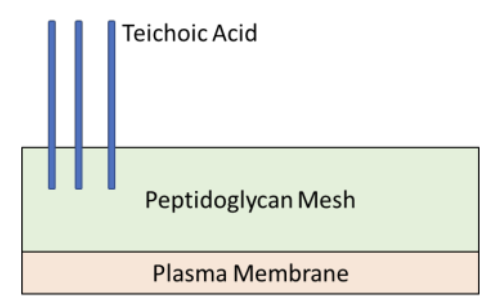
Is this gram positive or negative?
Gram positive
Which gram configuration is harder to treat and why?
Gram negative because it has more layers and selective porins.
exotoxins
Continually released
Endotoxins
only released upon cell death
What type of toxins do gram positive bacteria have?
exotoxins
What type of toxins do gram negative bacteria have?
endotoxins
What is the purpose of teichoic acid in nosocomial infections?
They help with attachment
What happens when a gram positive cell dies?
Teichoic acids are released, triggering immune response and inflammation
What is the benefit of having an outer membrane for a bacterium?
More protection
What is the Lipid A anchor of LPS?
It’s a toxin released during gram negative cell death
What does the release of endotoxins in gram negative cell death lead to?
Stomach issues and a host immune system overreaction
What is distinct about mycoplasma?
It has no cell wall and is the smallest known bacteria
What does the lack of a cell wall mean for mycoplasma?
Antibiotics targeting the cell wall will be ineffective
What does mycoplasma cause?
Walking pneumonia
What is a glycocalyx
A structure outside a cell wall that some bacteria have. It helps with protection, attachment, and nutrients.
What are the 3 structures that some bacteria have outside their cell wall that help with adherence?
Glycocalyx, fimbriae, and pili.
What are the 3 structures that some bacteria have outside their cell wall that help with movement?
Pili, flagella, and axial filaments
What are the two different types of glycocalyx?
Capsules and slime layers
Capsules
Tightly attached to cells and gelatinous
Slime layers
Loosely attached to the cell
Monotrichious flagella
One flagella
Lophotrichous flagella
Lots of flagella
Amphitrichous flagella
2-sided flagella (flagella attached on each end)
Peritrichous flagella
Flagella all around the bacterium
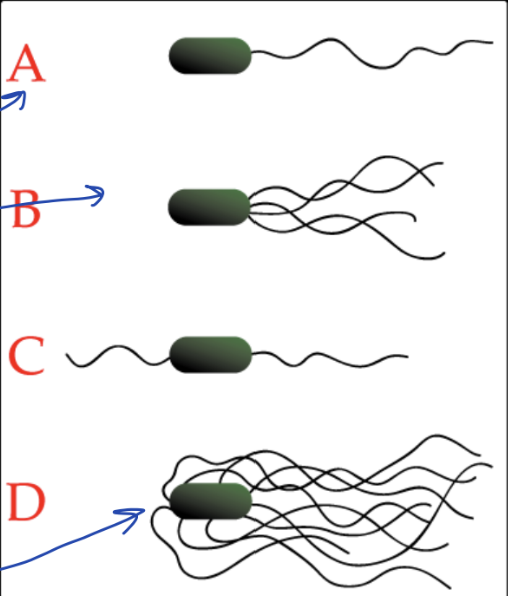
What type of flagella is A?
Monotrichious flagella
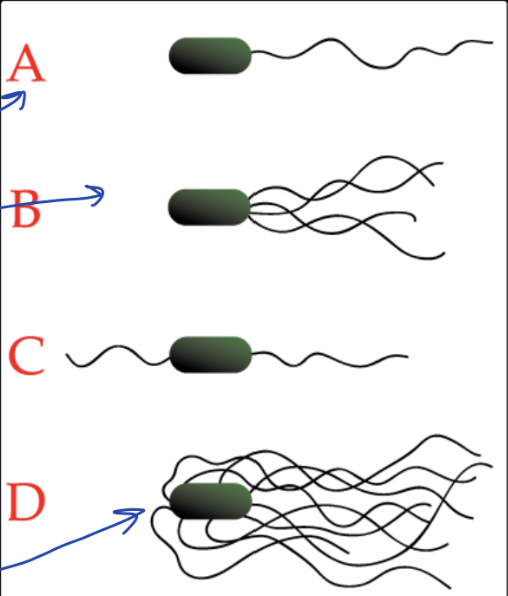
What type of flagella is B?
Lophotrichous flagella
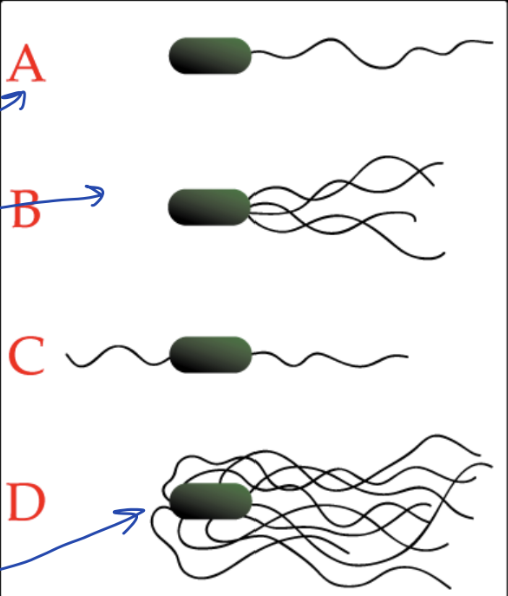
What type of flagella is C?
Amphitrichous flagella
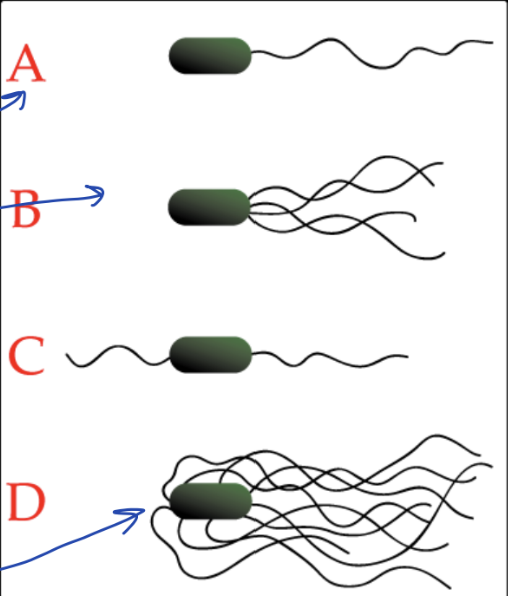
What type of flagella is D?
Peritrichous flagella
What do axial filaments allow for in terms of motion?
Corkscrew motions to screw into host
What is a medical infection example of axial filaments?
Syphilis
Gliding motility
Secretes large amounts of slime to glide over cell surfaces WITHOUT having to use flagella
What is a simple stain?
A single dye that can determine shape, arrangement, and size of bacteria
What is a differential stain?
When you use 2 or more dyes
What can a differential stain uncover?
Cell structures or cell types
What is gram staining?
It distinguishes gram positive and gram negative bacteria based on the composition of their cell wall
What is the first stain in the gram staining process?
Crystal violet
What type of stain is crystal violet?
A primary stain
What is the 2nd stain in gram staining?
Iodine
What does iodine achieve in gram staining?
It traps the primary stains
What is the 3rd stain in gram staining?
Alcohol
What is the significance of the alcohol wash in gram staining?
It dissolves lipids because it is a lipid solvent
What is the 4th stain in gram staining?
Safranin
After gram staining, what are purple cells?
Gram positive cells
After gram staining, what are pink and/or red cells?
Gram negative cells
What is osmosis?
The passive movement of H20 across a cell membrane
In osmosis, what direction does water flow?
From high concentration to low concentration
What happens to a hypotonic cell?
It swells due to too much water
What happens to a hypertonic cell?
It shrivels due to too much salt/not enough water
What is an isotonic cell
In equilibrium
What is passive transport?
No energy is used; molecules move WITH the gradient from high to low concentration
WHat is active transport?
ATP energy is needed to move molecules AGAINST the gradient from low to high concentration
What is sporulation
When a bacterium goes into a protective pod
When does sporulation occur
In harsh environments
How does a sporulated bacterium exit the state of dormancy?
When environmental conditions are better, the cell(s) take in water and become active “germinates”.
How can you kill endospores?
By autoclaving them (high heat and pressure)
What is cytosol?
The liquid inside the cell
What is the cytoplasm?
The space inside the cell
What is the function of the cytoskeleton?
It maintains the shape and support of the cell
What type of cells have a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells
What type of cells have a nucleoid?
Prokaryotic cells
What is the difference between a nucleus and nucleoid?
A nucleoid has no internal membrane around it
What advantage can plasmids provide bacteria?
antibiotic resistance
What is a nucleoprotein?
A combination of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Why is it significant when a structure is a nucleoprotein?
It can grab nucleic acids
What do inclusions do?
They hold things such as enzymes and ATP
What is the endomembrane system?
A class of organelles that communicate with each other via membrane channels or vesicles
What are some examples of the endomembrane system?
The nuclear envelope, golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum
What are examples of energy-related organelles?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts
What are energy-related organelles?
Energy independent and self-sufficient organelles