Muscle material for Lab & midterm 2
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What are the 3 specific types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
What is skeletal muscle?
(multicell nuclei) per cell
Striated, voluntary
attached to bone fascia & other muscle
appear long &cylindrical in shape
Fxn: body movement, helps posture, makes heat
What is cardiac muscle?
(single nucleus) per cell
Striated, involuntary
Found in the heart
Fxn: to pump blood throughout the body, maintaining circulation.
What is smooth muscle?
(single nucleus) per cell, spindle shape
Non-striated, involuntary
Found in walls of hollow organs( stomach, intestines, blood vessels, skin)
Fxn: regulates flow of substances, maintains internal pressure
Whats a muscle?
an organ, consist of skeletal muscle tissue & CT; muscle has belly & tendons at each end
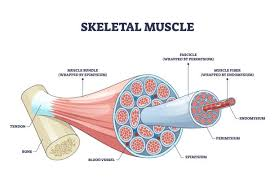
What is a Fasicle?
A bundle of muscle fibers surrounded by connective tissue, contributing to the overall structure of a muscle
visible to unaided eye
What is a muscle fiber?
A single cell of skeletal muscle, capable of contraction
containing multiple nuclei and organized into fascicles.
What is a myofibril?
Threadlike structures (organelles) in muscle cells
Visible in light microscope , run parallel to cell axis
Striated apprearance
What is the hierarchy arrangement of muscles?
Muscle > Fascicle > Muscle fiber > Myofibril> Myofilament > Muscle proteins
What is Sarcolemma?
Plasma mbn
The thin membrane that surrounds a muscle cell, playing a key role in transmitting electrical impulses and maintaining the cell's integrity
What is Sacroplasm?
Cytoplasm of a muscle cell, containing various organelles, myoglobin, and nutrients essential for muscle function
What is Sarcoplasmic Reticulum?
(modified) endoplasmic reticulum, stores calcium
What are Myofilaments?
composed of muscle proteins: filaments slide past eachotherduring contraction
Proteins are actin( thin filaments, light), Myosin (thick filaments, dark)
Titin - anchors to thick filaments of Z discs
What is sarcomere?
functional unit of muscle fiber, short segment of myofilament
Smallest functional unit of the muscle fiber
What does the Sarcomere organization include?
Z discs, A band(dark), I band(light), M lines(middle)
How are a bands formed?
Array of thick filaments , region of thick and thin filament overlap
What is the Sliding Filament theory of contraction?
explains how muscles contract
Myosin heads attach to actin, forming cross-bridges
Myosin pulls actin toward the center of the sarcomere, shortening the muscle
ATP (from mitochondria) is needed to detach and reset myosin heads
Result: muscle shortens and produces force
What is the function of Muscle tissue?
Motion- relies on integrated function of bones, joints& muscles
Movement- of substances within body( Heart, vessels, GI, urine, sperm, ova
Maint of posture- Stabilizes body posture
Heat Production- Working muscles convert 75% E to heat, only 25% to motion
Support soft tissues- abdominal wall & pelvic floor
Guard entrances/ exits- mouth, bladder, anus
Tendon of orgin:
Attaches to least moveable bone, most proximal bone(can be more than 1)
Tendon of insertion:
Attaches to most moveable, most distal bone(only 1)
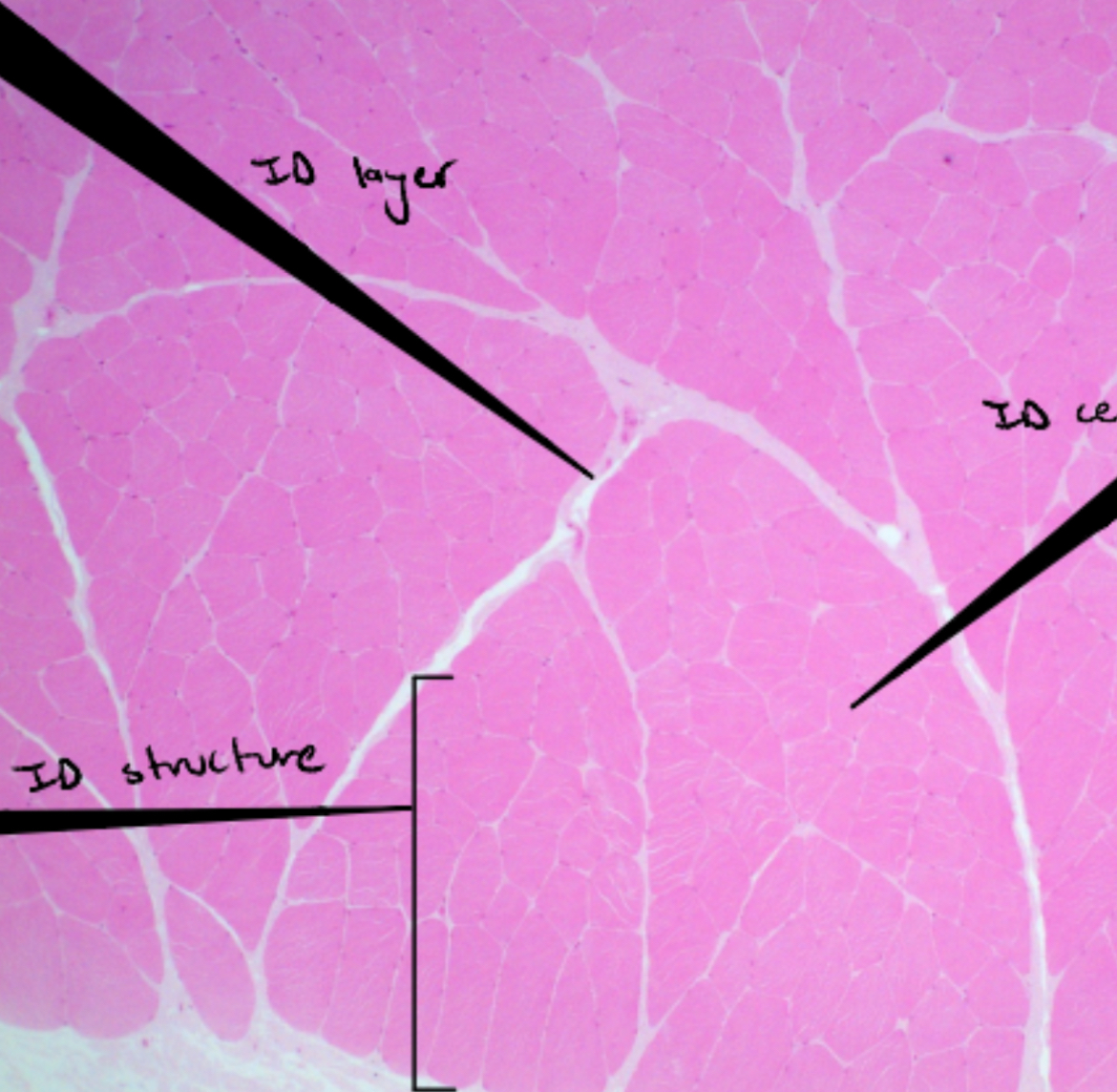
Endomysium:
Areolar CT, surrounds each muscle fiber, contains capillaries
Neuromuscular Junction:
site where neuron interfaces with Sarcolemma of muscle fiber
can be seen with light microscope
Consist of Axon terminal, synaptic cleft, motor end plate
is the synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. It enables the transmission of impulses that stimulate muscle contraction
Motor end plate=
Hold receptors for neurotransmitters
Light =
I Bad, contains only parts of thin filaments, made of actin
Dark =
A Band, contains all of thick filaments, made of myosin and ends of thin filaments
Perimysium=
Dense regular CT surrounds bundles of 10/100 fibers= fasicles ( loaded with blood supply)
Fascia=
sheet or broad band of fibrous CT deep to skin or around muscles or other organs
Superficial fascia=
-subq layer, areolar CT w/ adipose (under skin)
fxn: insulate fat storage, protection, pathway for AVLN to enter & exit muscles
Deep fascia=
Dense irregular CT, lines of body wall holds muscles together separates them into functional groups
M line is made of
protein that holds thick filaments is found in the middle of H zone
Myoepithelial cells
in some exocrine glands, facilitate secretion
Myofibroblasts=
In CT, participate in wound contraction
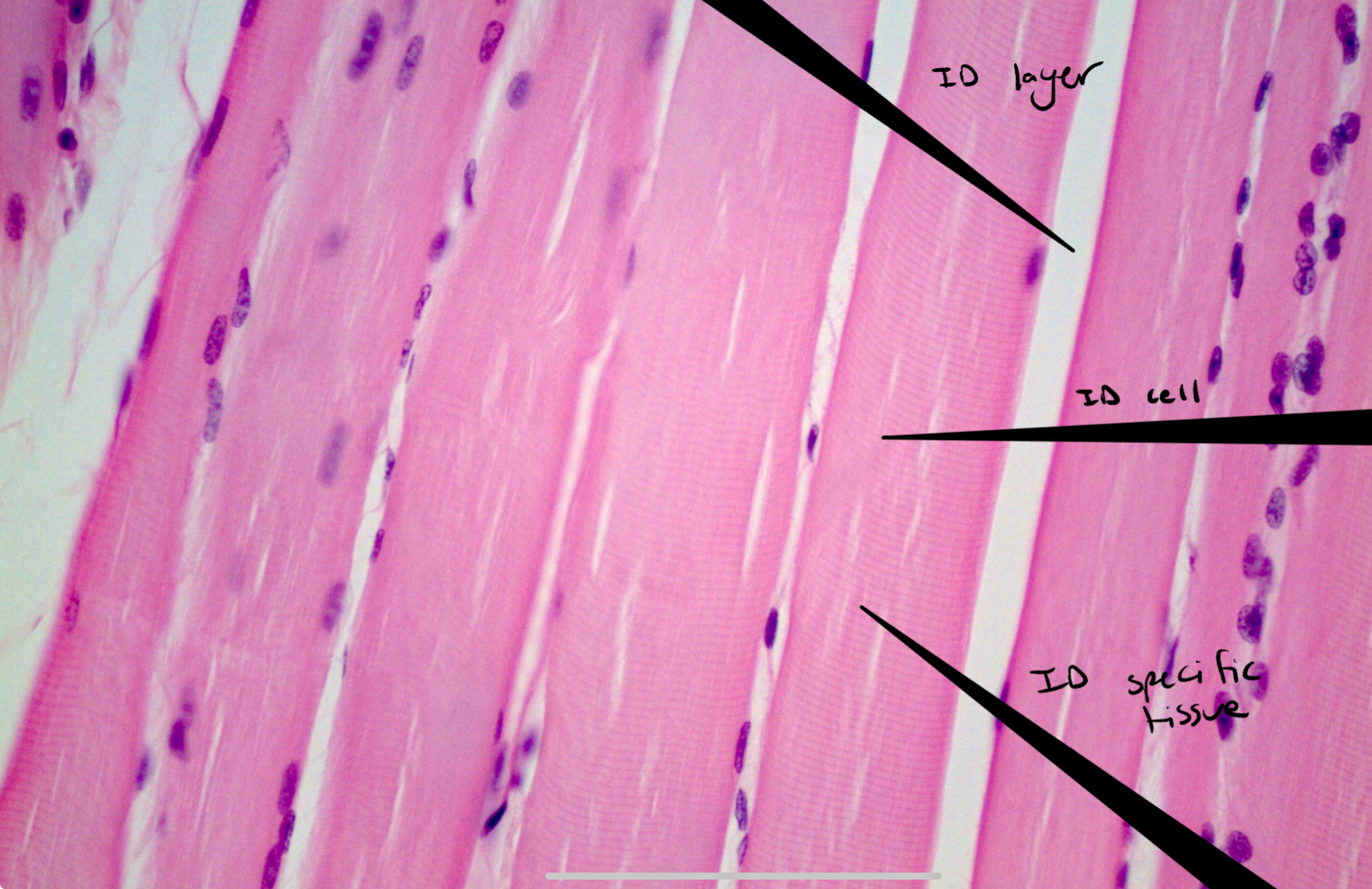
Identify this image
Skeletal muscle tissue
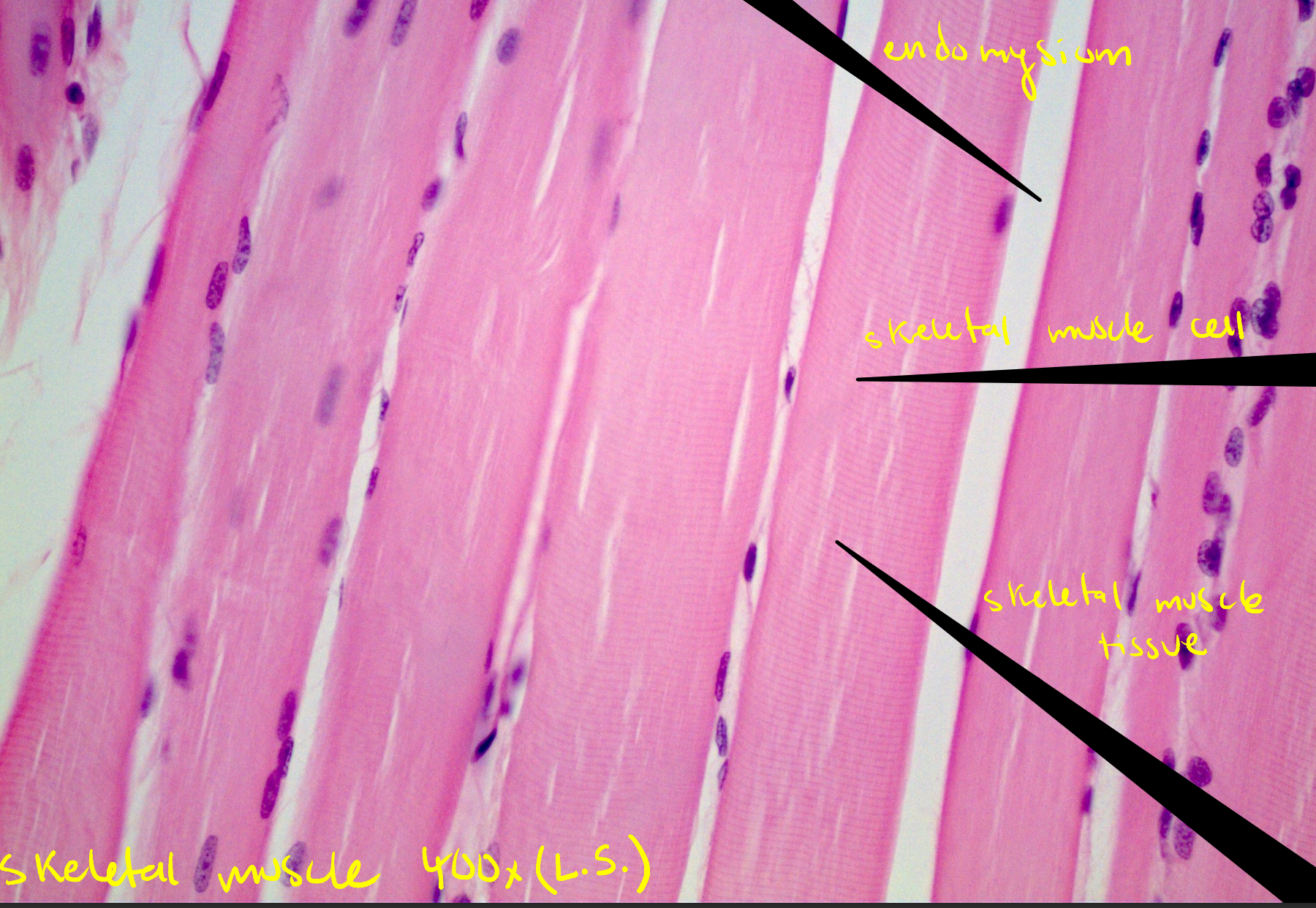
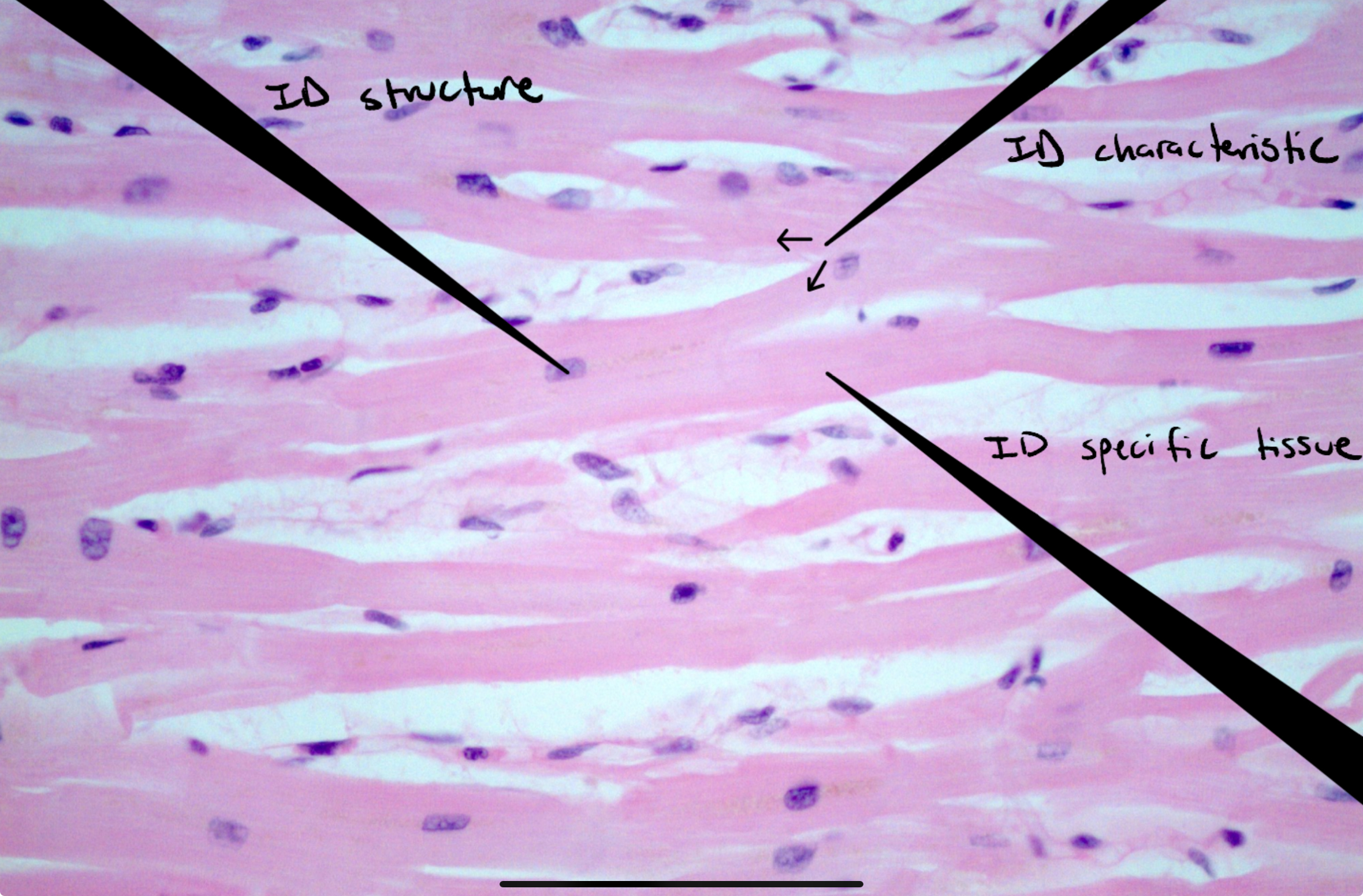
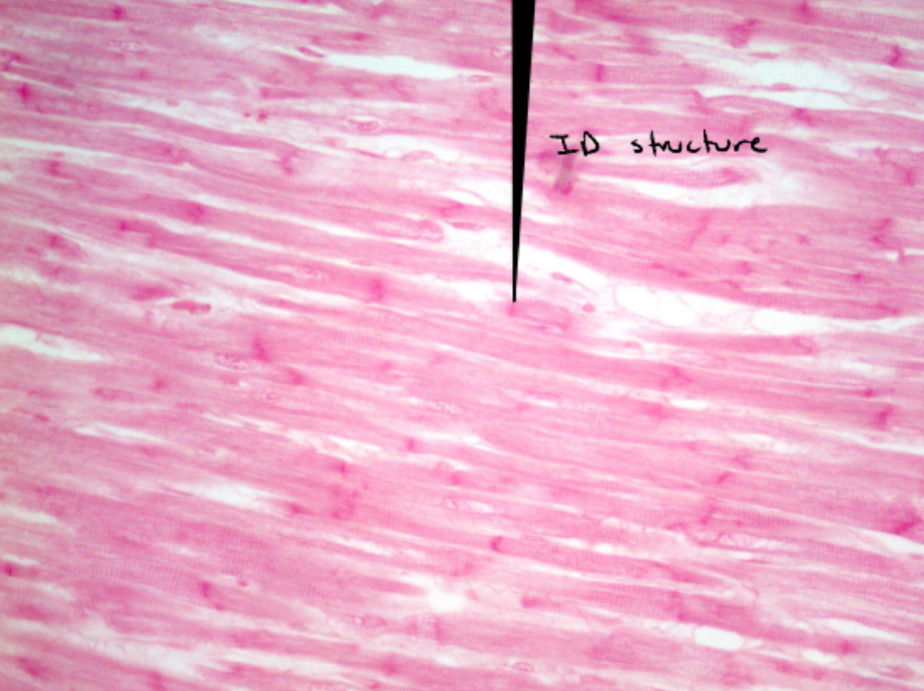
Identify this image
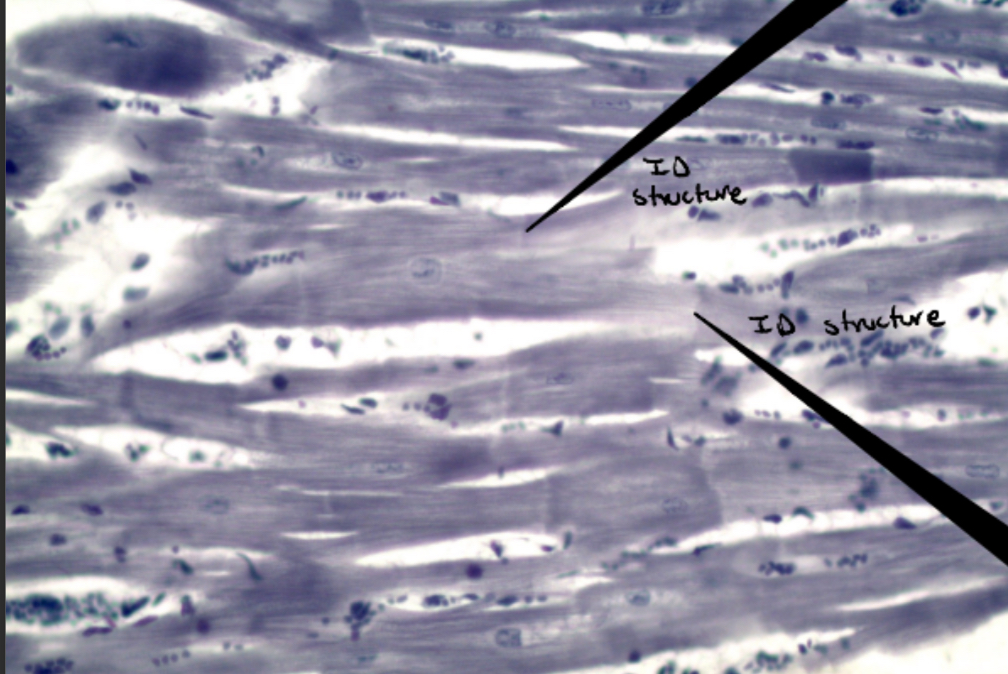
Identify this image
Cardiac muscle
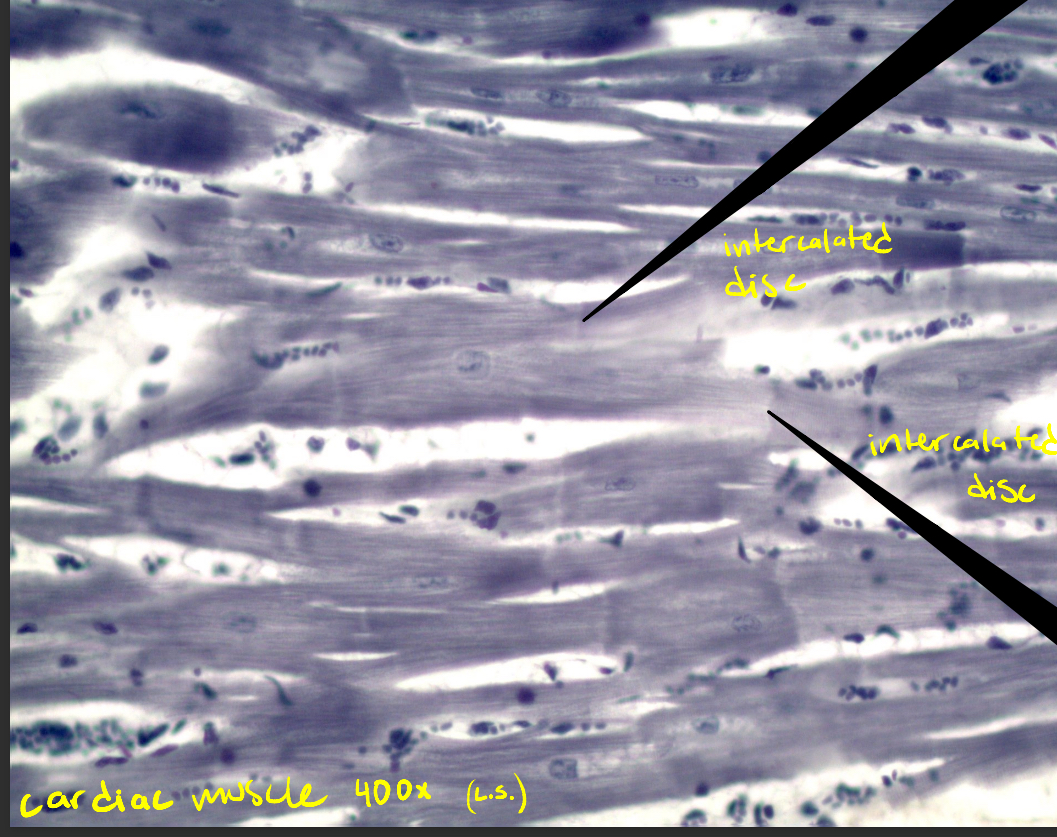
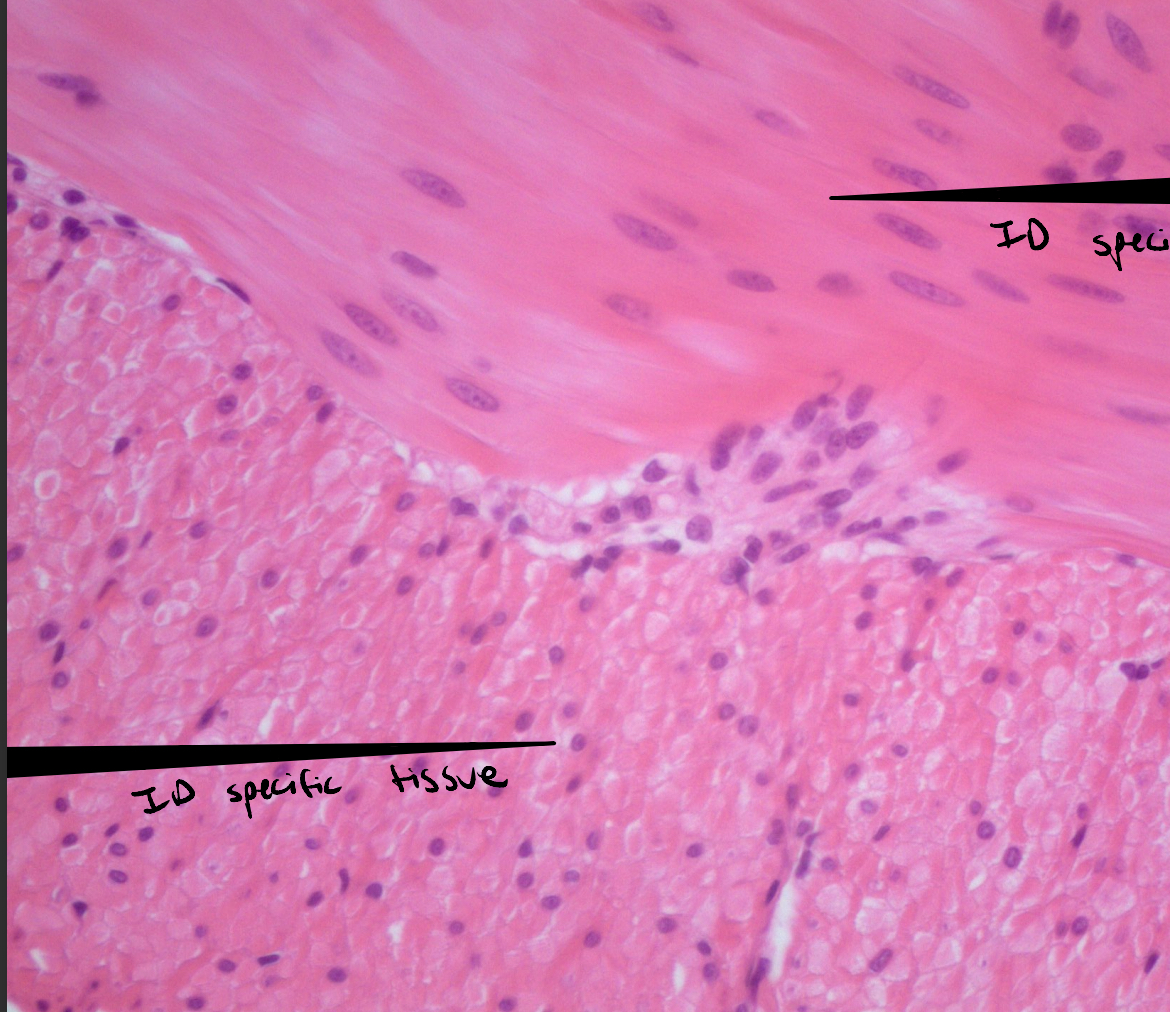

Rotator Cuff (SITS)
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
Quadriceps Femoris
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedius
Hamstring Muscles
Biceps femoris
Semimembranosus
Semitendinosus
All of the following are true of the movement capabilities of joints except
The strength of the joint is determined by the strength of the muscles that attach to it and its joint capsule
Which of the following is not a fxn of synovial fluid
Increase osmotic pressure within the joint
A joint in which the articular surfaces can slide in any direction?
Multiaxial
A twisting motion of the foot that turns the sole inward is:
Inversion
The ligaments that limit the anterior and posterior movement of the femur and maintain the alignment of the femoral and tibial condyles are the …
Cruciate ligaments
Each of the following changes in skeletal muscles is a consequence of aging except
A. muscle fibers become smaller in diameter
B. Muscles become less elastic
C. Muscle fibers increase their reserves of glycogen
D. The number of myosatellite cells decreases
C. Muscle fibers increase their reserves of glycogen
The fxn of neuromuscular synapse is ..
To facilitate chemical communication between a neuron and a muscle fiber
The direct energy supply produced by the skeletal muscles in order to enable them to contract is
ATP
Another name for the muscle that is the prime mover is
Agonist
The bundle of collagen fibers at the end of a skeleton muscle that attaches the muscle to bone is called a(n)
A. Fascicle
B. Myofibril
C. Motor Unit
D. None of the above
None of the above
Which of the following is not a muscle of the rotator cuff?
A. Supraspinatus
B. Subclavius
C. Subscapularis
D. Teres Minor
Subclavius
Which of the following muscles is a flexor of the elbow?