BMS1062 - W10: Recombination, Repair and Mutations
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is a conservative mutation?
Mutations which result in the same kind of amino acid
e.g. original amino acid = Glu. Mutated amino acid = Asp. Both are Acidic Amino acids.
What is a non conservative mutation?
Mutation where new amino acid is of a different type to the original amino acid
What is a mutation?
Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA
What are germline mutations?
Inherited mutations
Mutations inherited form parents
present in all nucleated cells of the body (including germ cells)
responsible for single gene disorders (e.g. cystic fibrosis)
may or may not be present in multifactorial disorders (cancer, heart disease, diabetes, etc.)
What are somatic mutations?
Non-inherited mutations
affect only the mutant somatic cell and its descendants
will not be transmitted to offspring
contribute to multifactorial disorders (e.g. cancer, heart disease, alzheimer’s)
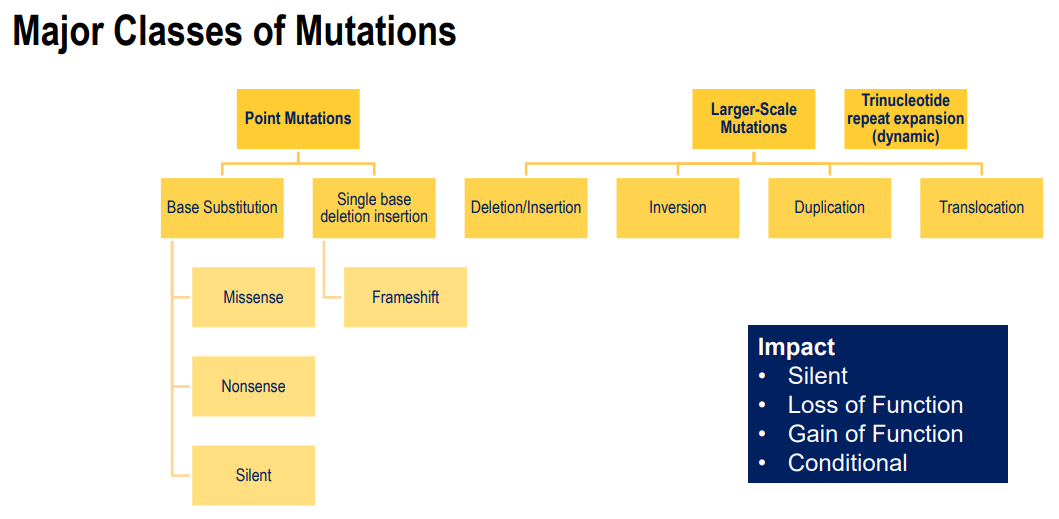
Point mutations:
Occur usually in a single base (base substitution or base deletion/ insertion)
missense mutation - change in an amino acid
Nonsense mutation - causes a stop codon
Silent mutation - does not change the amino acid
frameshift - changes the reading frame
Effects:
silent
loss of function
gain of function - overactive or cannot be turned off
conditional - some enzymes only active under certain conditions, mutation can change these conditions
What is a disease resulting from a missense mutation (point mutation)?
Sickle Cell Anaemia
A→T
Glu→Val
results in clumped haemoglobin, instead of globular
affects shape of red blood cells
high risk of blood clotting
What is a disease resulting from a nonsense mutation (point mutation)?
Dopa-responsive dystonia and depiapterin reductase
A→T
Lys→stop
affects muscle contraction (stiffness, tremors, coordination etc.)
What is a disease resulting from a deletion/ insertion mutation (point mutation)?
A little info: e.g. can result from a depurinated A base
Wild type - results in premature stop codon
Frameshift - results in a change of reading frame
Disease: Duchenne (DMD) and Becker Muscular Dystrophies (BMD)
progressive muscle wasting due to mutations in 79-exon
Dystrophin connects muscle cytoskeleton to ECM
Duchenne is much more severe than Becker
Duchenne - frameshift mutation that often results in premature stop codon
Becker - 3 codon in frame deletion
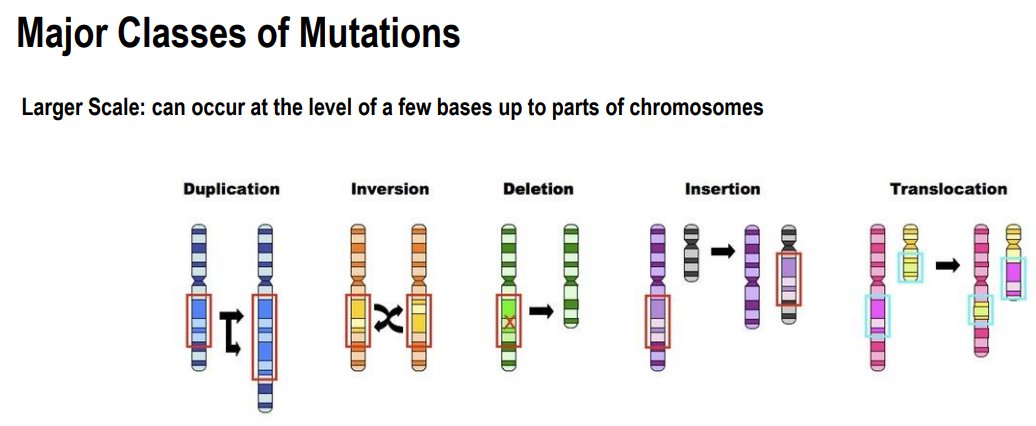
Large-Scale mutations:
occur at chromosomal level
Duplication:
large sections of chromosome is duplicated
often occur during replication
Inversion
a segment of chromosome is inverted
Deletions:
large scale deletions
Insertions:
Large scale insertions
Translocation:
swap of DNA between 2 different chromosomes
What is a disease resulting from a deletion mutation (Large Scale)?
DiGeorge Syndrome
deletion in part of chromosome 22
delayed development
congenital heart defects
reduced immune function
cleft palate
What is a disease resulting from a translocation mutation (Large Scale)?
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
translocation from chromosome 8
results in increased activity of c-myc (transcription facto involved in regulation of proliferative gene)
results in lymph node tumours
What causes mutations?
Spontaneous - occur naturally
arise in all cells at low frequency
error sin DNA replication
spontaneous lesions/ damage
Induced - require a mutagen
chemical (e.g. base analogues)
radiation (e.g. UV light)
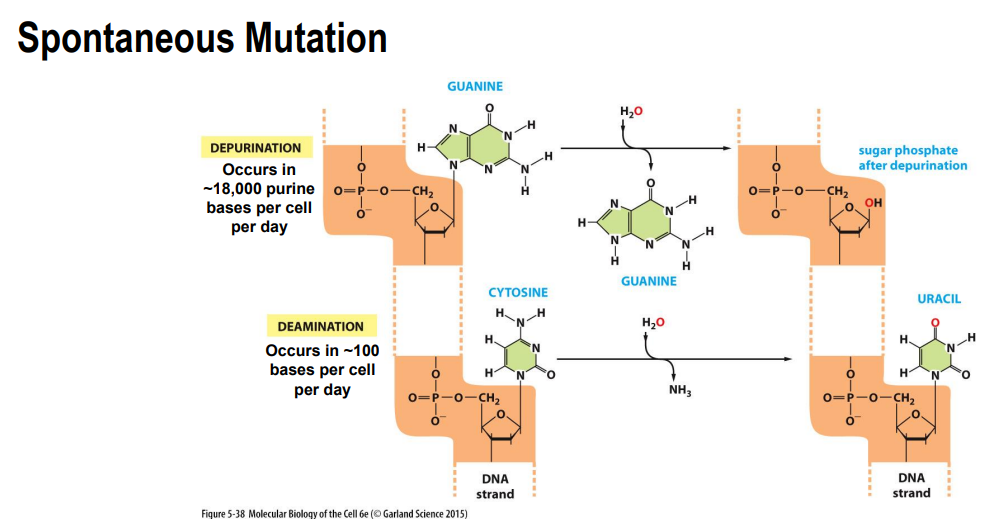
Spontaneous mutations:
Depurination
purine bases can be lost from the sequence
Deamination:
deamination of cytosine → Uracil
Tautomeric forms of DNA bases:
bases can be incorporated inro DNA in their rare tautomeric forms
allows different base pairing
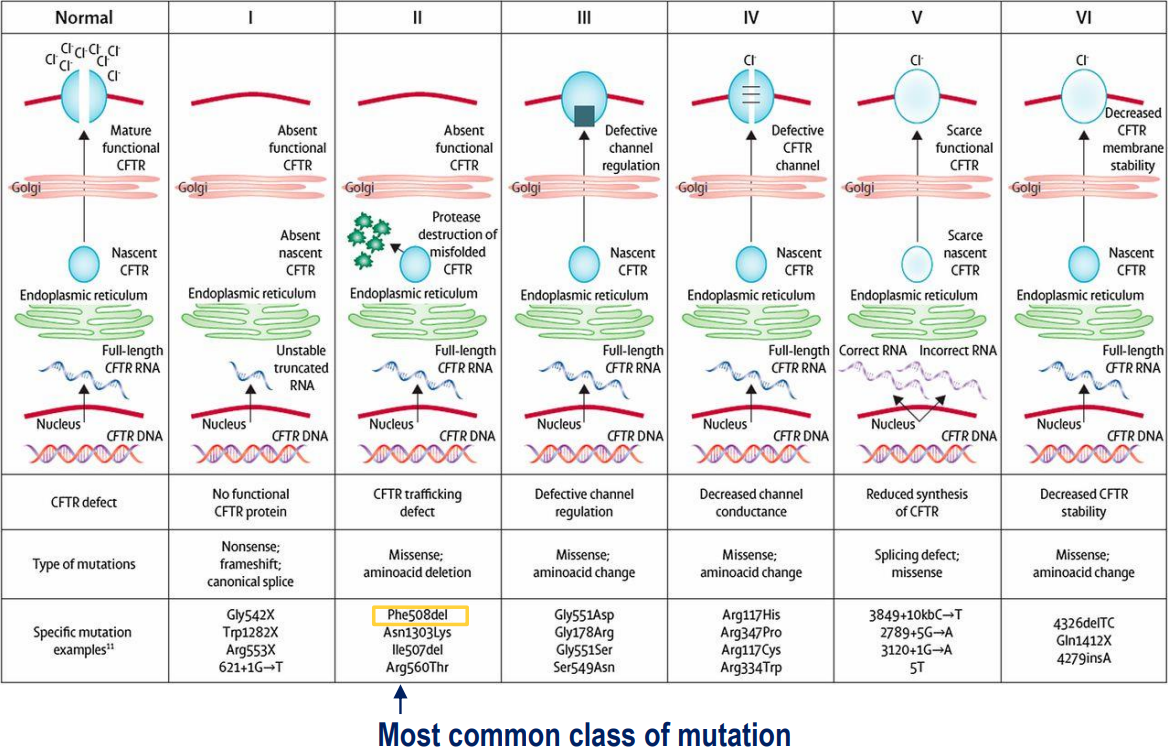
Cystic Fibrosis:
Different CFTR mutations have different consequences on the protein
CFTR encodes for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (a protein that sits within the cell membrane and is a chloride channel - important for epithelial fluid transport between cell and external environment)
cystic fibrosis results in dysregulation of epithelial fluid transport (prevents fluid from leaving the cell, resulting in buildup inside the cell)
What is human variation?
humans have variation in their genes
arise from mutations (e.g. ACE gene II, ID, DD)
majority of differences occur in non-coding regions of our DNA
Are mutations bad?
Can be bad (disease) or bad (evolution)
Mutations in evolution:
Good mutations give us a selective advantage (advantageous trait which helps us thrive)
E.g. high altitude adaptation: animals and people who lived in high altitudes had bigger chests and greater lung capacity
E.g. CCR5 receptor helps HIV-1 enter cells
people who carry a particular mutation in the CCR5 receptor are protected against HIV-1 (32 bp deletion on CCR5 gene)
reduces amount of receptor on immune cell (which HIV binds to)
What are neutral mutations?
Neither advantageous nor disadvantageous
don’t actually affect the protein (silent mutation)
majority of mutations are neutral
can also spread in a population
can be useful for forensic testing and paternity tests
Disease mutations:
Why do many disease-causing mutations persist in the population?
Many genetic diseases require 2 inherited mutated copies of the same gene
recessive inheritance
but many people are heterozygous (carriers of the disease without presenting symptoms)
if mutation confers some selective advantage to heterozygous people, it may be maintained in the population by natural selection
E.g. Sickle cell anemia
heterozygous people (Aa) have one good copy (so have enough red blood cells so they only have mild symptoms sickle cell. But they have protection from malaria.
How can new genes/ DNA be introduced into a genome?
mutation - particularly if this mutation presents with some advantage
duplication - can happen during replication
DNA segment shuffling - can occur during replication (translocations happening between the genes)
horizontal gene transfer - transformation, conjugation and transduction (bacterial cells)
Gene families:
Genes that are related
E.g. Globin family
consists of both an alpha and beta version of the globin protein and gene. This forms haemoglobin.
these related proteins all evolved from the same original ancestral gene
results of an initial gene duplication, translocation and then subsequent mutations
What is the effect of mutation/ inactivation of DNA repair genes?
increase rate of mutation
because there is no longer the proteins to repair the DNA
What are some mechanisms to prevent replication errors?
Proofreading polymerase (fixing majority of errors)
errors occur usually in 1:100,000 to 1:1,000,000 bases
with proofreading 1:100,000,000 bases
fixes up to 99% of errors
3’-5’ exonuclease activity of the polymerase removes several bases (including the incorrect one) → then replication resumes in 5’ to 3’ direction
occurs during S phase (replication)
Mismatch repair system
mismatch repair enzyme recognises and removes/ replaces the nucleotide
identifies errors in the secondary structure (e.g. tautomeric bases)
mismatch repair enzymes recognize this and bind to base (MutS)
MutL scan DNA to find nick
region between mismatch and nick will be removed by endonucleases and DNA polymerase fills in the gap
occurs mostly in S phase
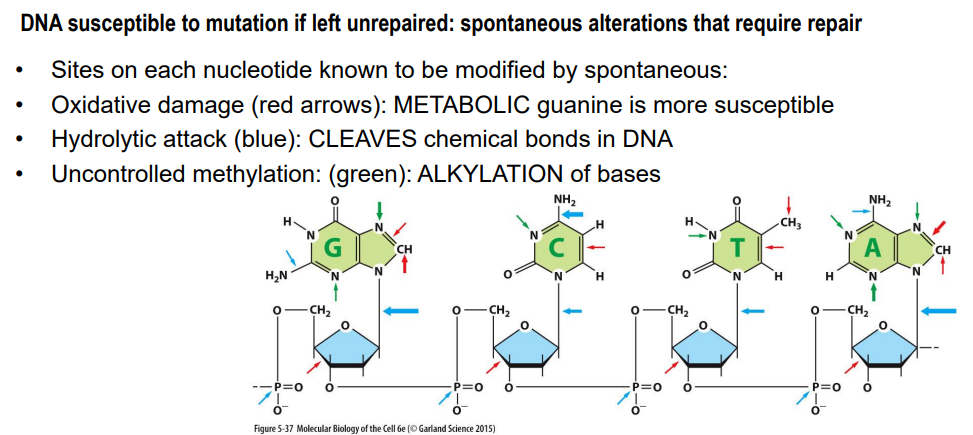
DNA damage: What are some types of DNA damage that can occur?
Oxidative damage:
guanine is more susceptible
Hydrolytic attack:
cleave chemical bonds in DNA
can result in removal of a base or deamination
Uncontrolled methylation:
alkylation of bases
can change the base pairing
DNA damage by hydrolysis (hydrolytic attack):
repairable damage
Depurination = spontaneous loss of purine bases (adenine and guanine) by hydrolysis
backbone remains intact but base is lost
can result in a deletion (frameshift)
after several rounds of replication, this mutation becomes incorporated into daughter cells
Deamination = spontaneous conversion of a cytosine to uracil (which have different base pairing) by hydrolysis
mismatch occurs (no longer pairs with guanine)
DNA damage by alkylation/ methylation:
Guanine particularly susceptible (alkyling event → methyl group attached to oxygen atom on guanine)
affects base pairing (methyl guanine pairs with thymine, not cytosine)
result in base substitution
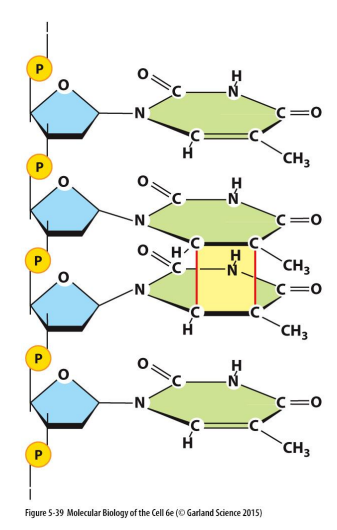
DNA damage by UV Irradiation:
Covalent linkage between two adjacent pyrimidine bases
caused by UVB radiation from the sun
Thymine dimers: covalent linkages on the C-C bonds from lesions
can occur between any two neighboring pyrimidine bases (T or C)
if left unrepaired, end up with permanent damage
e.g. melanoma
can be repaired (when one strand is damaged, the complementary strand remains intact and can be used to restore correct nucleotides to damaged strands)
DNA damage repair pathways: Base lesions - single or double
Base excision repair (BER)
Nucleotide excision repair (NER)
for both of these, damage is excised (physically excise and remove damaged nucleotide/ string or nucleotides). Original sequence then restored using undamaged complementary strand.
Enzymes involved: DNA polymerase (to restore) and DNA ligase (to seal them up)
Direct reversal repair (DR)
Direct removal of lesion
no cleavage or ligation
Base Excision Repair (BER):
What is it?
What events does it respond to (what types of mutation)?
What are the enzymes involved?
Repairs damage to a single base
occurs when an event like deamination or depurination has occurred (damage to the base rather than whole nucleotide)
A set of enzymes acting sequentially:
DNA glycosylases:
scan DNA and identify DNA to single bases (such as deamination or depurination)
recognise specific type of altered base by ‘flipping out’ from helix
excise/ remove base via hydrolysis (breaking bonds attaching the base - does not break backbone)
AP endonucleases (AP = apurinic or apyrimidinic):
recognise the phosphodiester bond which is missing a base
cut the phosphodiester backbone
DNA polymerase:
adds a new nuclotide
DNA ligase:
seals up the nick
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER):
Repairs larger changes to DNA helix: 2 or more bases damaged
entire nucleotides removed
can be used to repair pyrimidine dimers (induced by UV radiation)
What are the enzymes involved:
Multicomplex enzyme (scans for DNA distortion)
several enzymes apart of this multicomplex enzyme
this complex cleaves the phosphodiester backbone of abnormal strand on both sides of distortion
DNA helicase:
unwinds the region of DNA
stretch of oligonucleotides removed from either side of lesion (a few extra bases also removed)
DNA polymerase:
fills gaps
DNA ligase:
seals
Example of disease:
Xeroderma pigmentosum
recessive genetic defect
enzymes required for nucleotide excision repair are mutated
makes them very sensitive to UV (sunlight)
high risk of developing skin cancer
Transcription coupled DNA repair:
Occurs during transcription
Ensures cell’s most important DNA is efficiently repaired
Links excision repair system with RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase stalls at DNA lesions and directs repair machinery to these sites
targets repair to genes that are actively being transcribed into mRNA (making it efficient)
Disease where this doesn’t work:
Cockayne syndrome
recessive congenital disorder
the RNA polymerase that would stall lesion is permanently stalled/ unable to return to polymerization = high level of apoptosis (programmed cell death) = more cell death
Direct Reversal Repair (DR):
Most efficient form of DNA repair
rapid removal of certain highly mutagenic or cytotoxic lesions (e.g. alkylation lesion 6-O-methylguanine)
does not require any removal of bases or nucleotides
used to repair alkylation/ methylation
Enzyme involved:
methyltransferase (MTase) protein:
accepts methyl group on cysteine residue from alkylated guanine nucleotide.
This corrects chance of pairing with wrong base
restores normal guanine
MTase then inactivated
No DNA cleavage or ligation
Emergency repair of heavily damaged DNA:
Regular DNA polymerase (Pol III) stalls when it encounters DNA damage and release DNA (highly accurate)
In emergencies, they employ less accurate back-up polymerases to replicate through the DNA damage - translesion polymerase (Pol V)
can continue polymerisation despite DNA damage
doesn’t have proofreading activity (instead just keeps going)
but it falls off (doesn’t bound that long) then Pol III continues.
Risky for cell as it incorporates mutations
not preferred form of repair (not even really repair just allows replication to continue)
When does DNA repiar occur?
Proofreading and mismatch occurs during S phase (DNA replication)
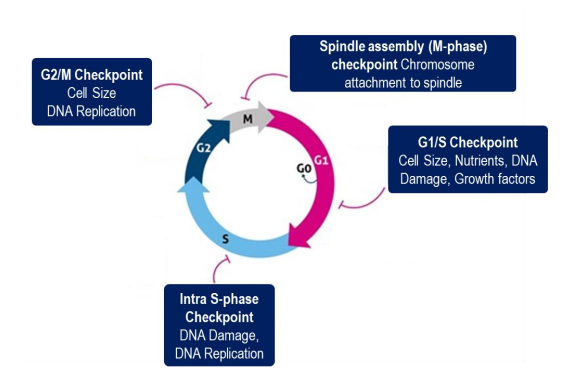
Checkpoints:
M phase Checkpoint
G1/S phase checkpoint:
G2/M phase checkpoint:
Intra- S-phase checkpoint:
Cell cycle stops if damaged DNA is detected
In mammalian cells, the presence of DNA damage can:
block entry from G1 to S phase (checkpoint)
slow S phase (replication) once it has begun
block transition from G2 phase to M phase (checkpoint)
Some proteins involved in regulating the cell cycle:
ATM protein:
large kinase (phosphorylates proteins) that signals intracellularly to delay the cell cycle in response to DNA damage
Individuals with ataxia telangiectasia (AT) (defects in ATM protein) suffer from effects of unrepaired DNA lesions (neurodegeneration, genome instability etc)
p53: ‘Guardian of the genome’
arrests the cell cycle at G1/S checkpoint until damage is repaired
activates DNA repair enzymes
can initiate apoptosis is damage is too great (if arrested too long)
huge implication in cancer - mutations in P53 can prevent apoptosis = cancer
CHK1: Kinase
cycle arrest at S and G2/M checkpoints
DNA repair or cell death