Price elasticity of demand (PED)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the PED formula?
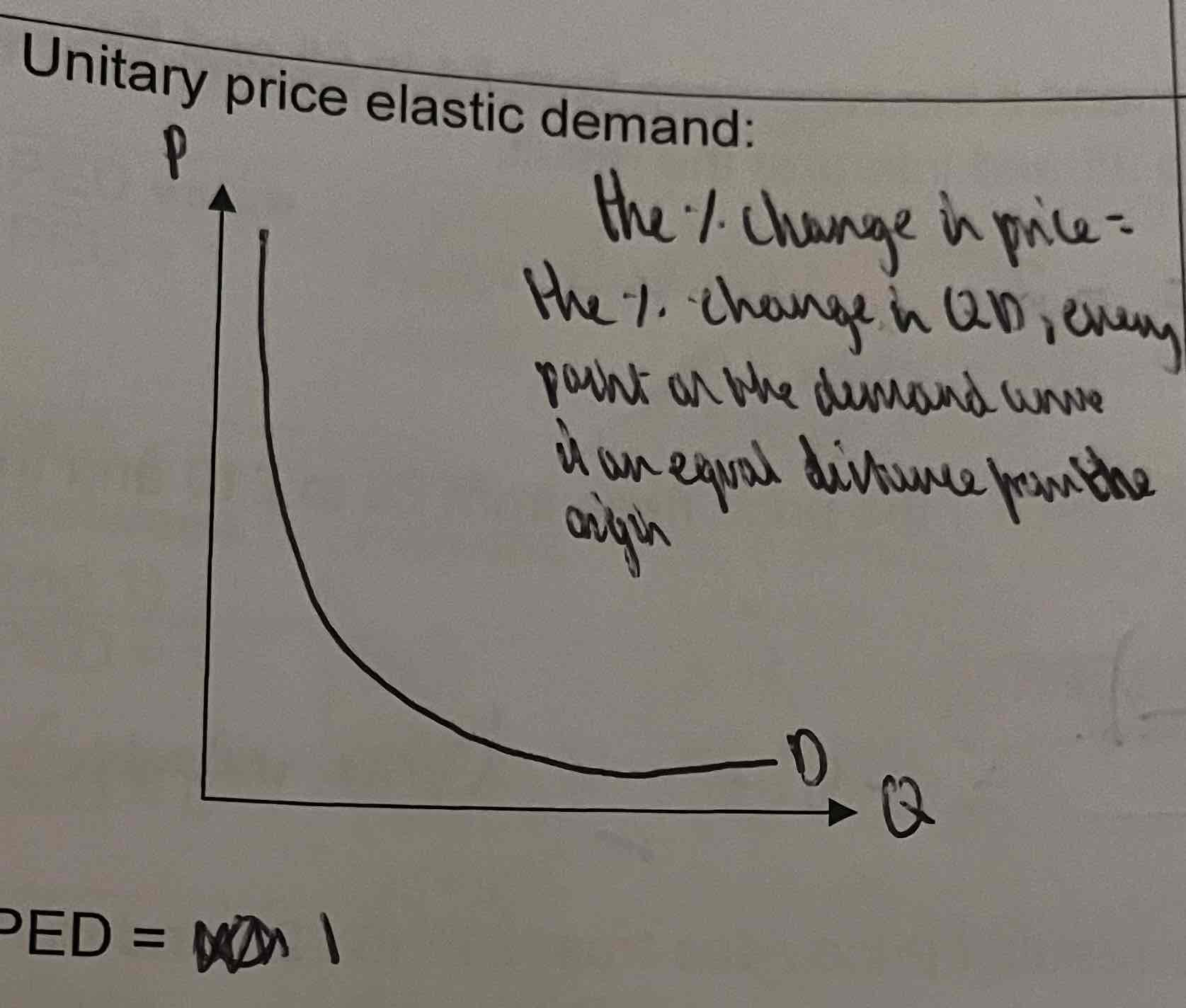
%change in Quantity demanded/ % in price change
When is the PED elastic?
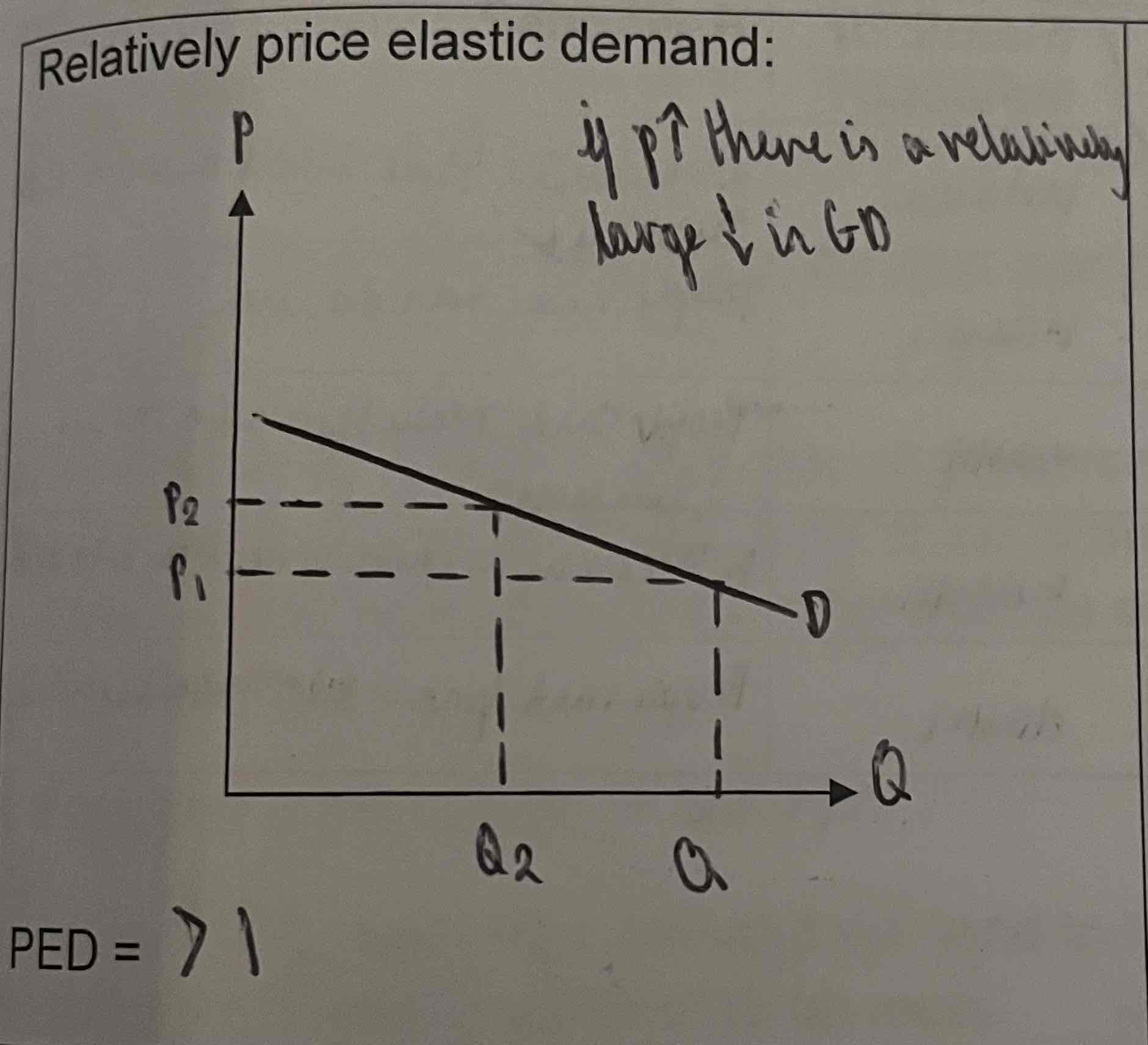
If the % change in quantity demanded is greater than the % change in price, then the PED is greater than 1.
When is PED inelastic?
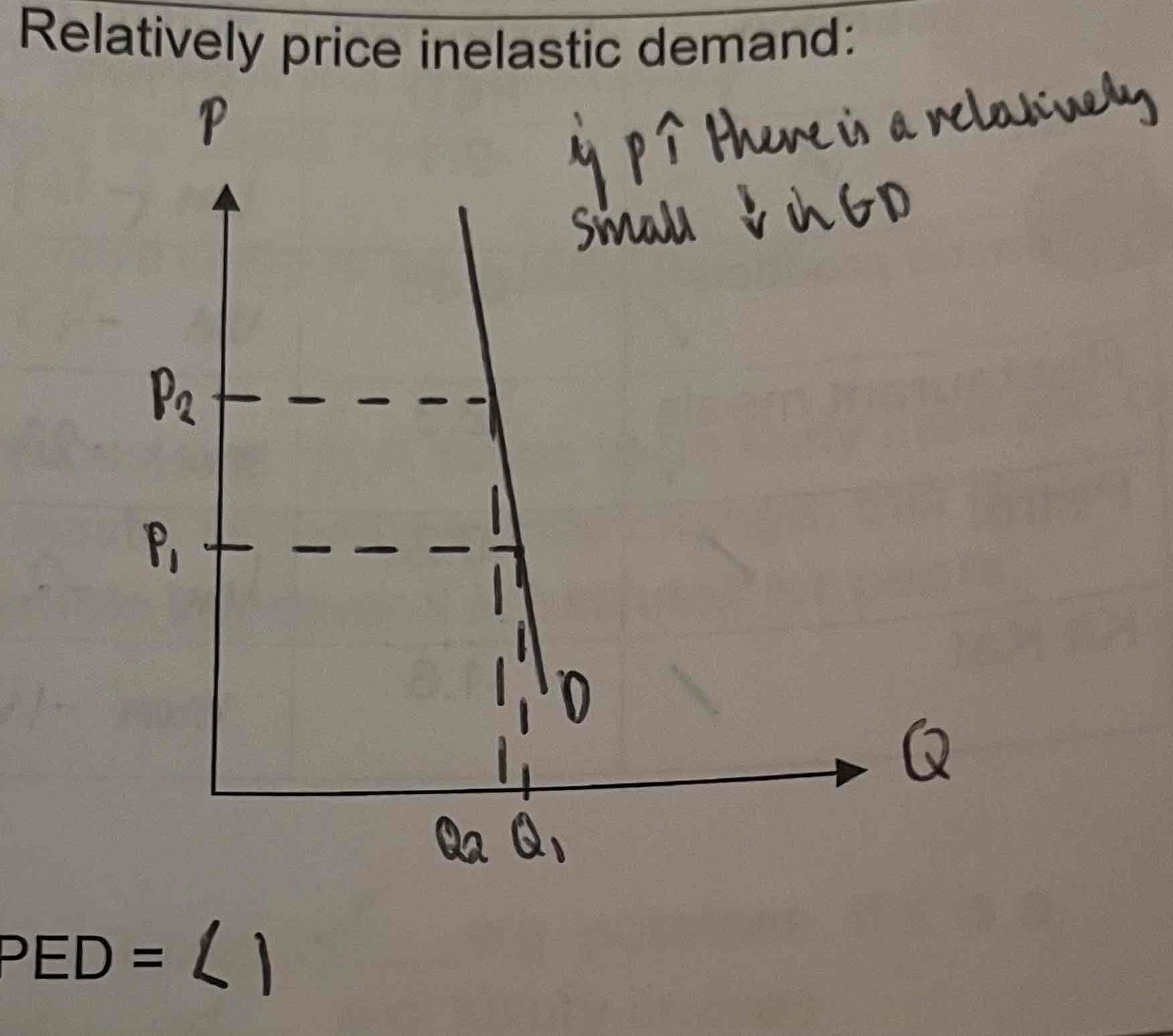
If the % change in price is more than the % change in quantity, then the PED is less than 1.
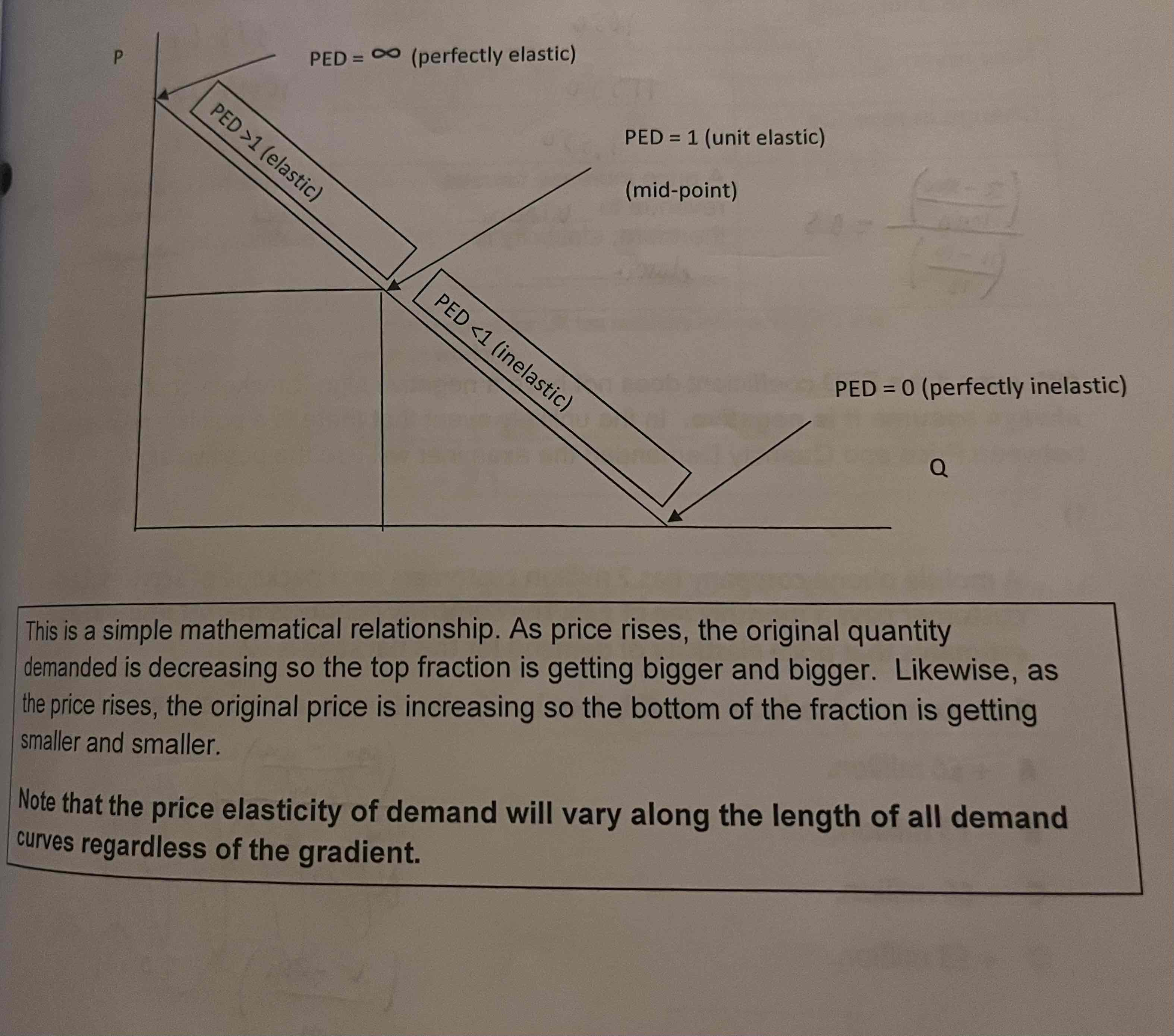
When is the PED>1?
=Price elastic
The % change in price will lead to a greater proportionate change in QD
Consumers are sensitive to price changes
When is PED<1
=price in elastic
The % change in price will lead to a smaller proportionate change in QD
Consumers insensitive to price changes
When does PED= 1?
=Unit elastic
a % change in price will lead to the same % change in QD
Consumers are neutral to price changes
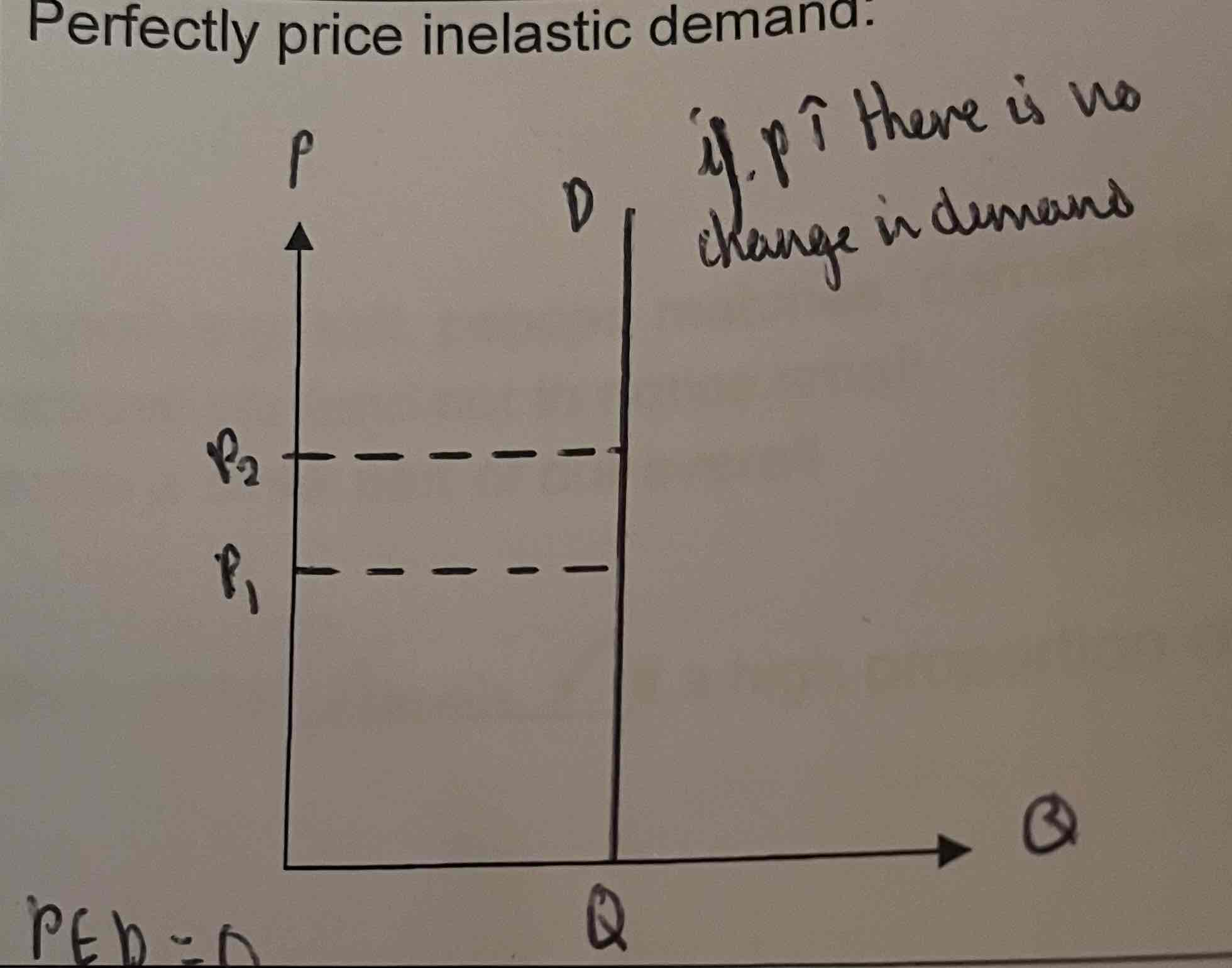
When does P=0?
= perfectly inelastic
the % change in price will lead to no change in QD
Consumers are completely insensitive to price changes
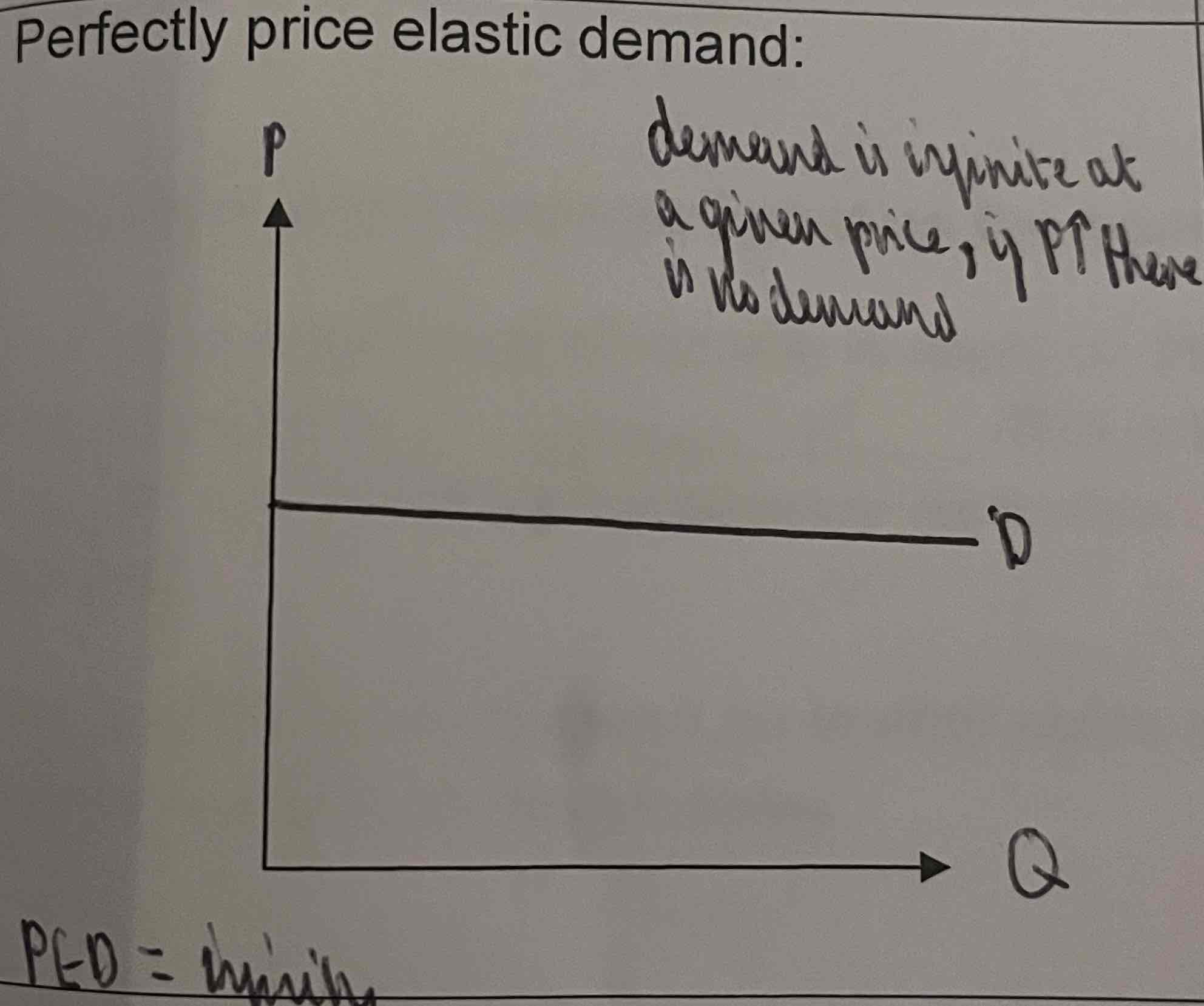
When does PED= infinity?
= perfectly elastic
QD is infinite at a particular price
Consumers are extremely sensitive to price chanhes
When you write PED do you use negative numbers?
No, you must ignore the negative sign
What does the relatively price elastic demand graph look like?
What does the relatively price inelastic demand graph look like?
What does a perfectly price elastic demand graph look like?
What does the perfectly price inelastic demand curve look like?
What does a unitary price elastic demand curve look like?
Is demand more likely to be elastic or inelastic if there are many substitutions?
Elastic- customers can switch
e.g if the price of apples rises, they might buy Paris instead, so the quantity demanded for pears rises
How does broad categories of goods compare to specific goods in elasticity?
Broad categories e.g fruit tends to be fairly inelastic (few substitutes) but specific fruits are more likely to be elastic
If the good is a necessity will it be inelastic or elastic?
Demand will be in inelastic e.g potatoes but luxury items are more elastic
what is the elasticity of a good if only a small amount of income is spent on it?
e.g salt- demand is likely to be price inelastic because we tend not to notice small changes in price which only forms a small part of our overall spending.
Demand for leather sofas is likely to be elastic if a high proportion of income is spent on leather sofas.
What are habit forming goods elasticity?
products like alcohol and tobacco tend to be price in elastic as buyers find it hard to stop buying even when prices rise
What is the elasticity of branded goods?
Demand tends to be more inelastic for branded goods as customers see a brand as a unique product without alternatives like Nike trainers
What is the price elasticity for the short or long run?
The price elasticity of demand is likely to change over time
in the short run, we tend to stay with current suppliers- our demand is usually fairly inelastic
In the long run we have time to source alternative suppliers and adjust our spending habits, so demand is more elsstic
What is revenue?
The income gained from selling a product
What is the revenue formula?
Price x quantity
What is the relationship between price elasticity of demand and revenue?

What happens with elasticity within firms?
When PED is inelastic, a firm should increase their prices because customers reduce consumption by a disproportionately small amount at the higher price, therefore, the firm’s total revenue would rise. (However, if they lower price, total revenue would fall)
When PED is elastic, a firm should decrease their prices because demand would rise by a larger proportional amount than the price fall and total revenue would increase. (However, if they increase price, total revenue would fall).
What is the relationship between PED and revenue of its elastic?
If PED is elastic, a fall in price leads to an increase in total revenue. If price rises, there will be a decrease in total revenue.
What is the relationship between PED and revenue of its inelastic?
If PED is inelastic, a fall in price leads to a fall in total revenue. If price rises, there will be an increase in total revenue.
What are the elasticities along the demand curve?
What are all the factors that affect the PED?
availability of substitutes
Necessity or luxury?
Proportion of income spent on good
Habit forming goods
Brand
Short or long run?