2.3 Adaptations for transport
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is an open circulatory system?
blood bathed over tissues directly
moved by muscular movements
no respiratory pigment
Open circulatory system example
insects
blood moves in spaces called haemocoel
dorsal tube shape heart
What is a closed circulatory system and example?
blood remains in blood vessels
moved by heart pumps
organs not in direct contact with blood
respiratory pigment to carry gases
e.g. earthworm
What is a single circulatory system and example?
blood passes through heart once in a complete circulation
e.g. fish
What is a double circulatory system and example?
blood passes through heart twice in complete circuit
e.g. mammals
Systems in double circulatory system
pulmonary - to lungs
systemic - to body
Double circulatory system advantages
maintains higher pressure
oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separated
blood constantly delivered to cells
Blood vessel structure
Tunica externa - collagen to resist stretching
Tunica media - elastic fibers to sustain pressure
Endothelium - thin/smooth to reduce friction
Lumen
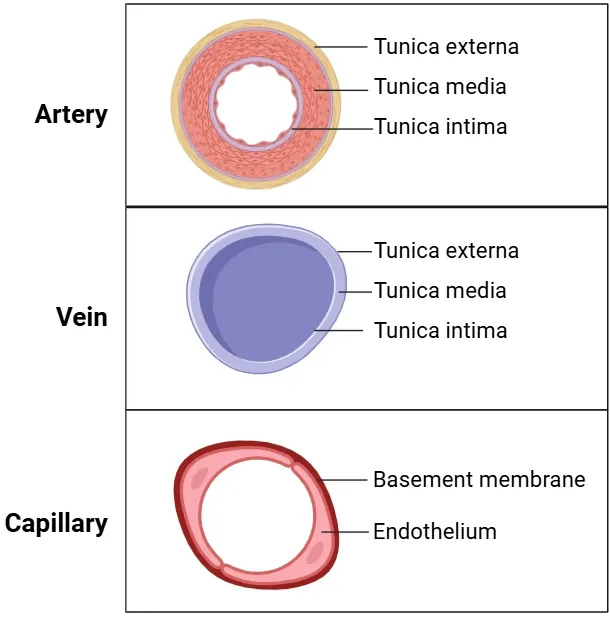
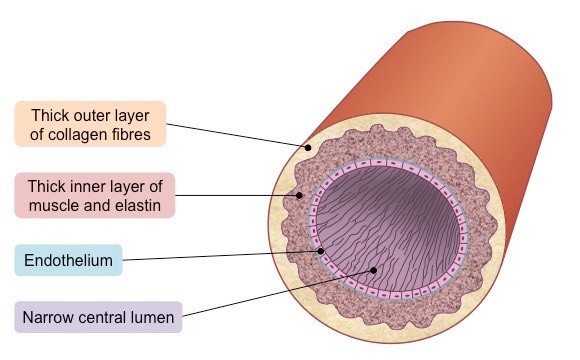
Arteries
usually carry oxygenated blood away from heart
thicker tunica media to allow recoil
smaller branches called arterioles
high pressure
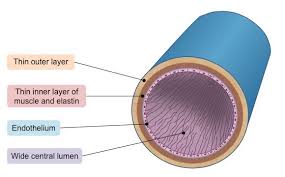
Veins
usually carry deoxygenated blood to heart
valves prevent back flow
large lumen for increased volume
smaller branches called venules
low pressure
Capillaries
connect arteries and veins
close contact with cells
endothelium for short diffusion path
exchanges substances
Heart pathway
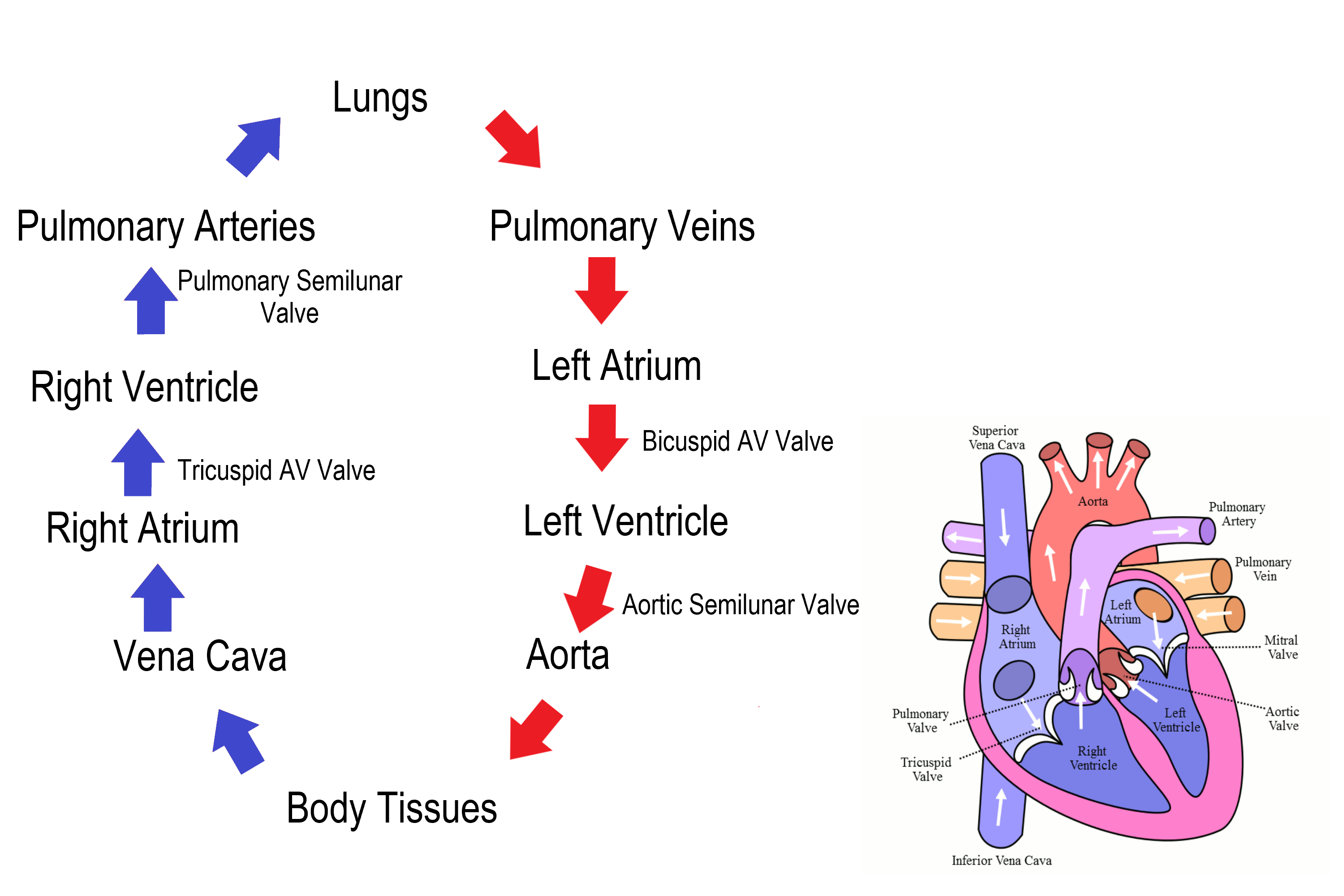
Heart structure
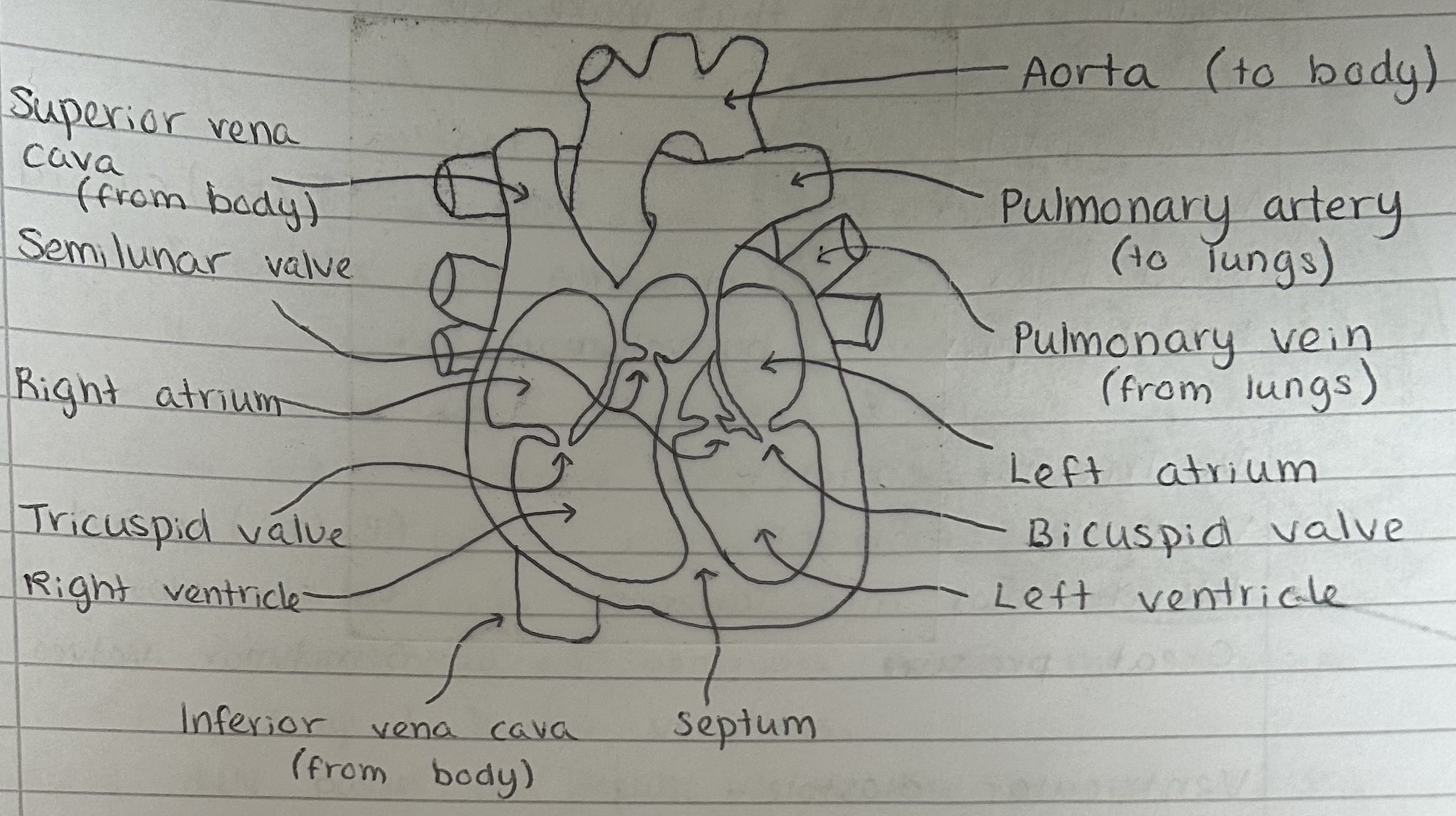
What vessels surround the outer heart?
Coronary arteries
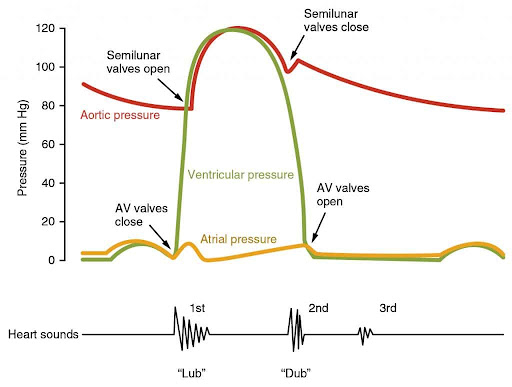
Atrial systole
atria contract
bi/tri cuspid valves open
blood flows into ventricles
Ventricular systole
ventricles contract
bi/tri cuspid valves close
semilunar valves open
blood flows into arteries
great pressure
Ventricular diastole
heart muscle relaxes
pressure decreases in ventricles
semilunar valves close
Diastole
whole heart relaxes
blood flow into atria
cardiac cycle begins again
What happens at sino-atrial node
stimulus to contract comes from sino-atrial node, found in right atrium
electrical impulse from SAN cause the two atria to contract
a thin layer of tissue prevents stimulus spreading to ventricles
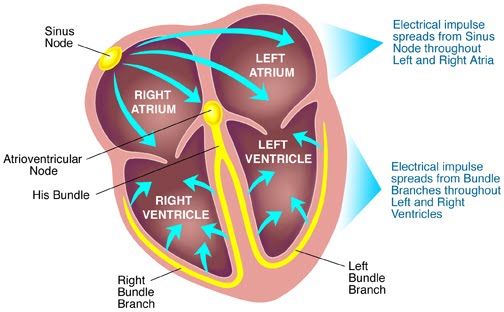
What happens at atrio-ventricular node?
the atrio-ventricular node found between atria and ventricles delays the impulse before passing it onto ventricles
the AVN passes the impulse down the bundle of HIS which has branches of Purkinje fibers
the impulses are conveyed upwards along the Purkinje fibers which cause a wave of ventricular contraction from the bottom of the ventricle to the top
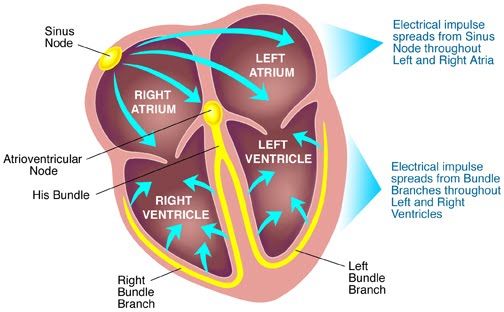
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
P - atrial systole
Q,R,S - ventricle depolarisation (contract after spike)
T - ventricular diastole
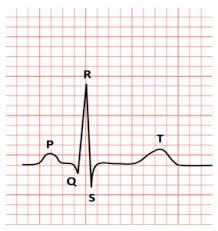
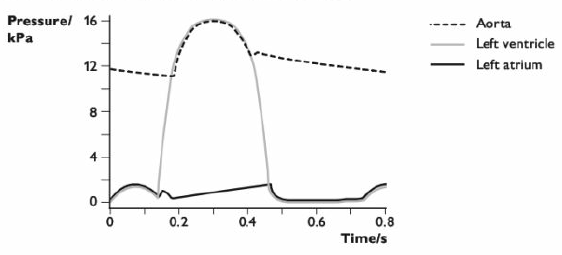
Pressure changes around heart
Red blood cells
carry 4 oxygen molecules a time
made of haemoglobin
made in bone marrow
no nucleus
biconcave disc shape - large SA
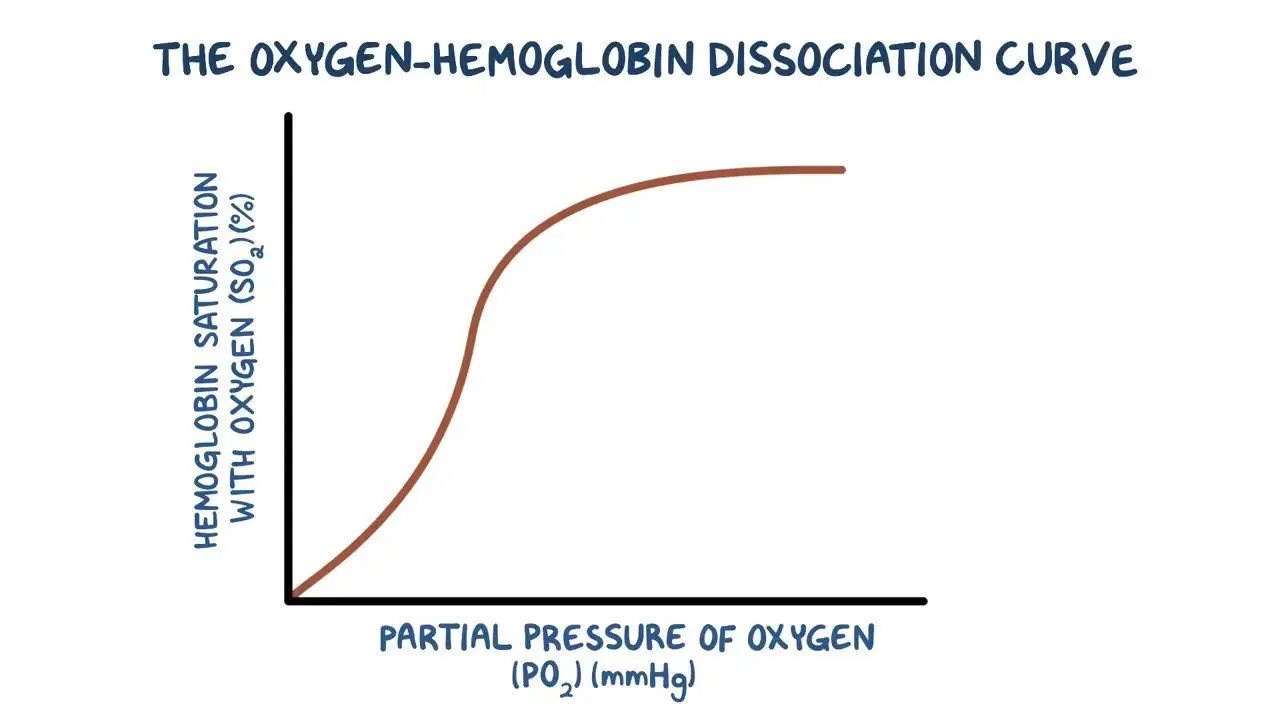
Bohr effect on oxygen dissociation curve
more carbon dioxide
shifts to right
lower affinity for oxygen so more oxygen released
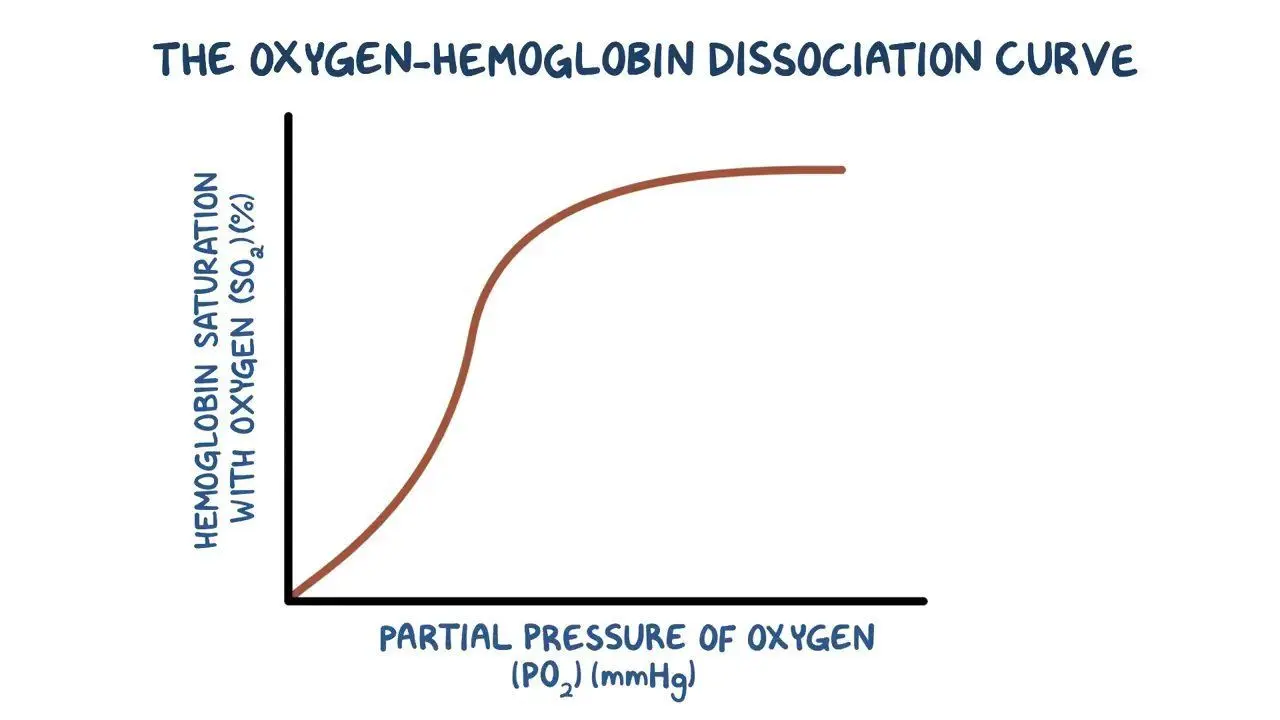
Foetal effect on oxygen dissociation curve
cant mix with mothers
shifts to left
greater affinity for oxygen so more picked up
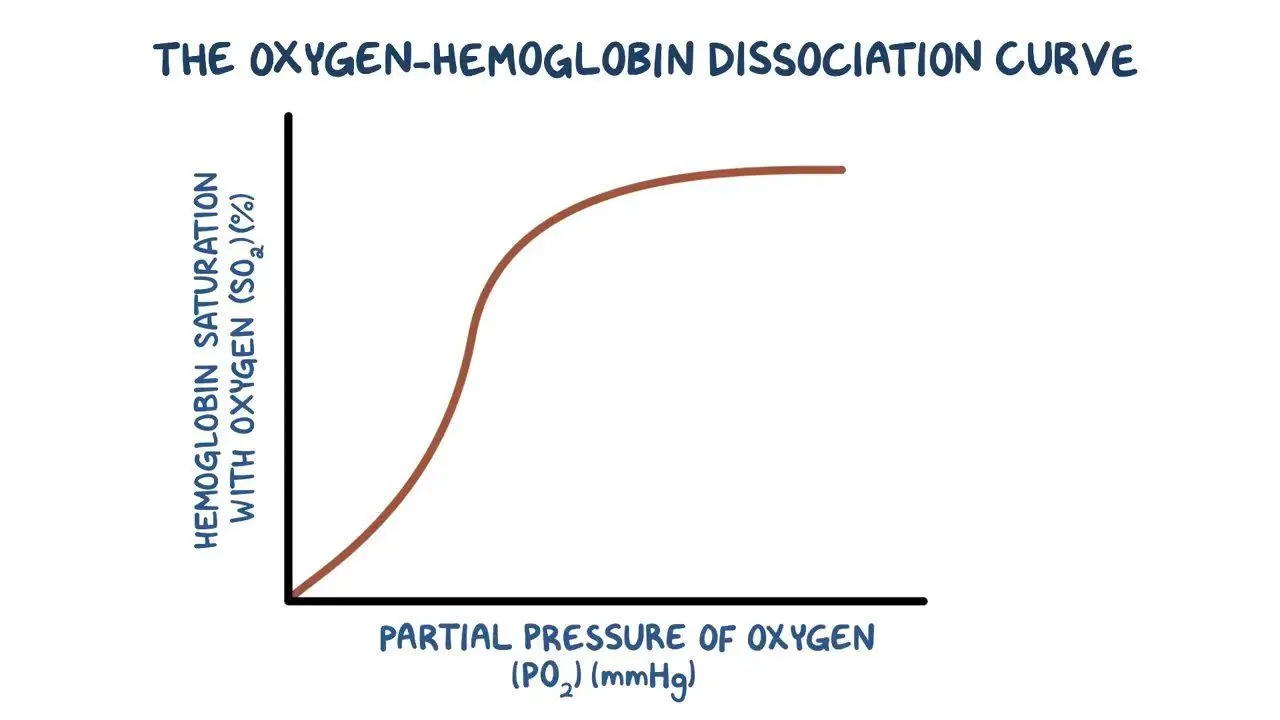
Low oxygen level effect on oxygen dissociation curve
e.g. lugworm and llama
shifts to left
greater affinity for oxygen so more picked up
Chloride shift
Carbon dioxide produced by respiring tissues diffuses into fluid and cell
Carbonic Anhydrase catalyses the reaction between Carbon Dioxide and Water to form Carbonic Acid
Carbonic Acid dissociates to form H+ and HCO3- ions
HCO3- ions diffuse out and Cl- ions diffuse in to maintain electrochemical neutrality
Oxyhaemoglobin and H+ ions form Haemoglobinic acid and Oxygen (buffering effect to maintain pH)
Oxygen diffuses out of cell into fluid and respiring tissue
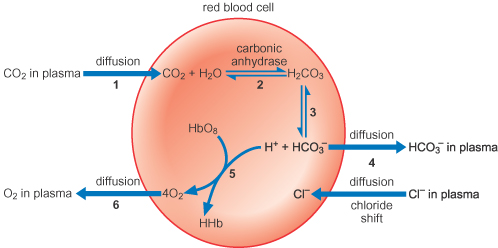
When is chloride shift opposite way?
Lungs
How can Carbon dioxide be transported?
chloride shift
in solution in plasma
bound to haemoglobin
Tissue fluid
blood coming into arteriole end is under high hydrostatic pressure so small molecules are forced out of capillary walls into tissue fluid
this is opposed by reduced water potential of blood due to plasma proteins not diffusing out
at the venous end blood hydrostatic pressure is lower so water passes into capillaries via osmosis
carbon dioxide and other excretory substances diffuse back into capillaries
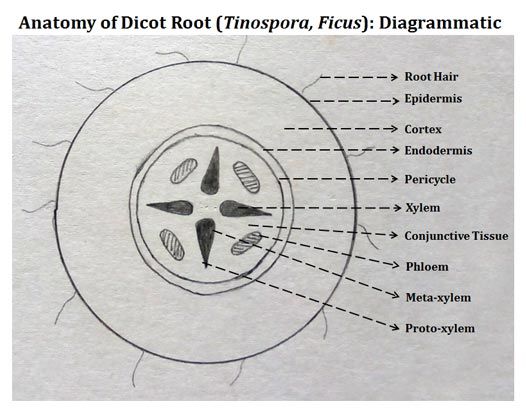
Structure of TS root
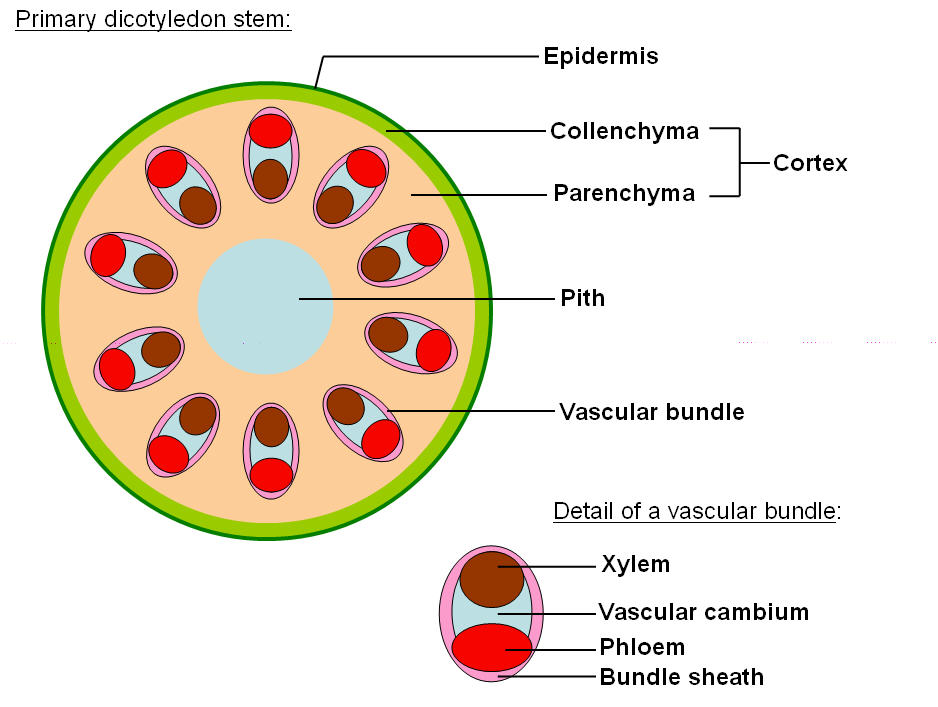
Structure of TS stem
Root hair cell structure and functions
water absorption
mineral absorption by active transport
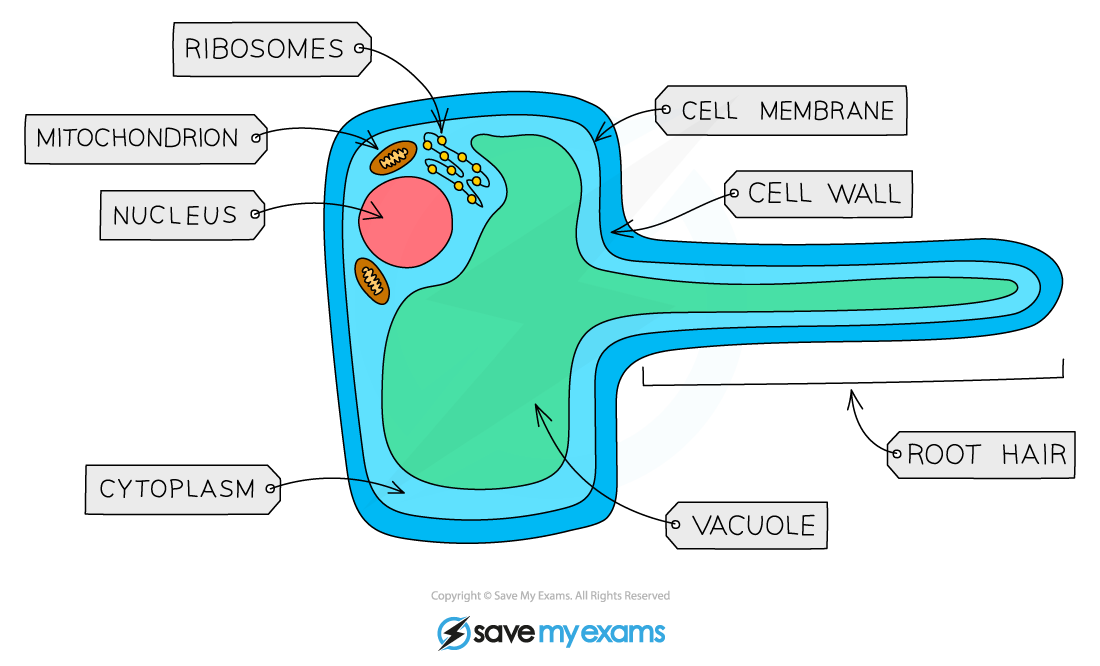
Adaptations of root hair cell
extended cell wall + vacuole = large SA
thin cell wall
mitochondria for active transport
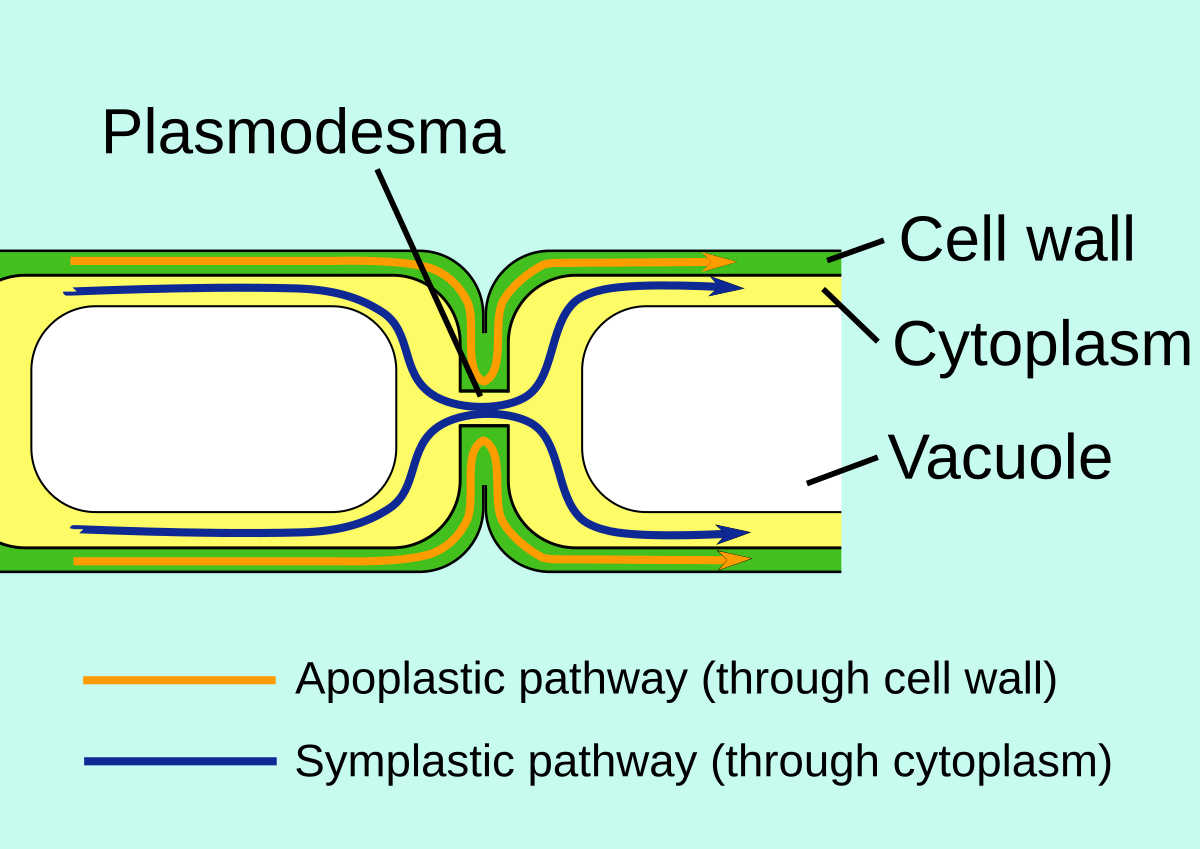
Apoplast water movement
through cell walls
after endodermis, goes symplast route
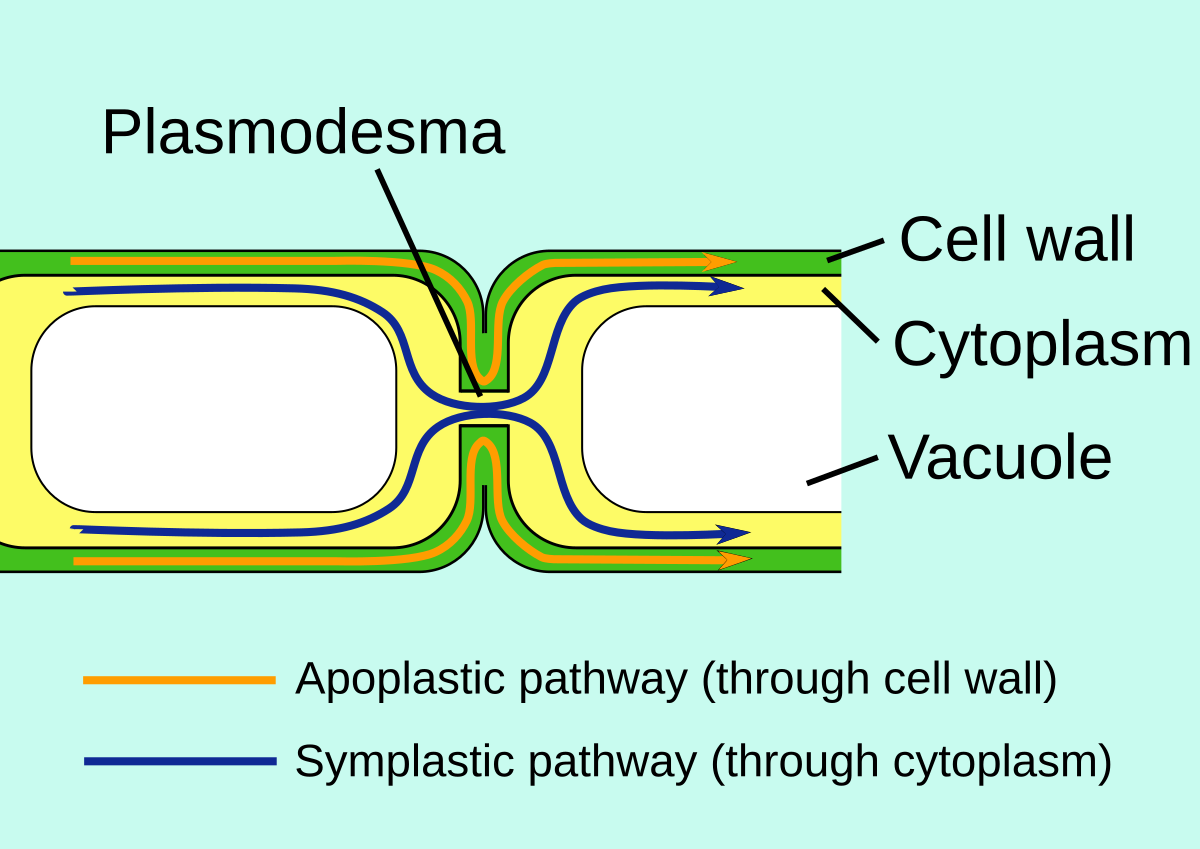
Symplast water movement
through cytoplasm and plasmodesmarta
Vacuolar water movement
through vacuole
Endodermis
Contains a Casparian strip which controls the flow of water as it is waterproof due to the suberin in it
Slows apoplast flow
Xylem structure
4 cells; vessels, tracheids, fibres, parenchyma
vessels, tracheids, fibres dead as lignin is deposited in cell wall so impermeable to water
parenchyma store water for support
contains pitted walls and vessels
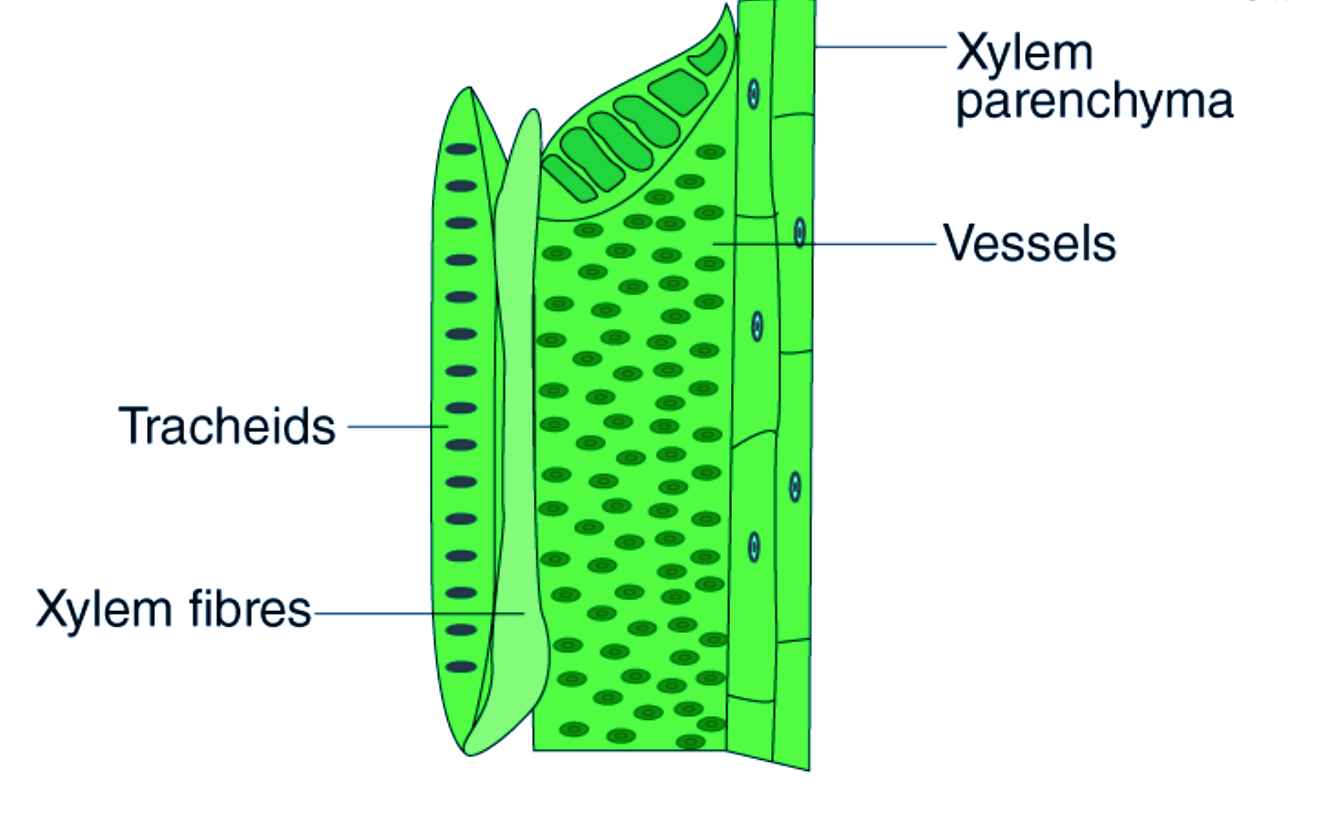
Xylem adaptations
small diameter
pit vessles so water moves laterally
lignified for strength
What is root pressure
osmotic pressure that build up within root cells forcing water up xylem
nutrients pumped into xylem cause water to follow via osmosis
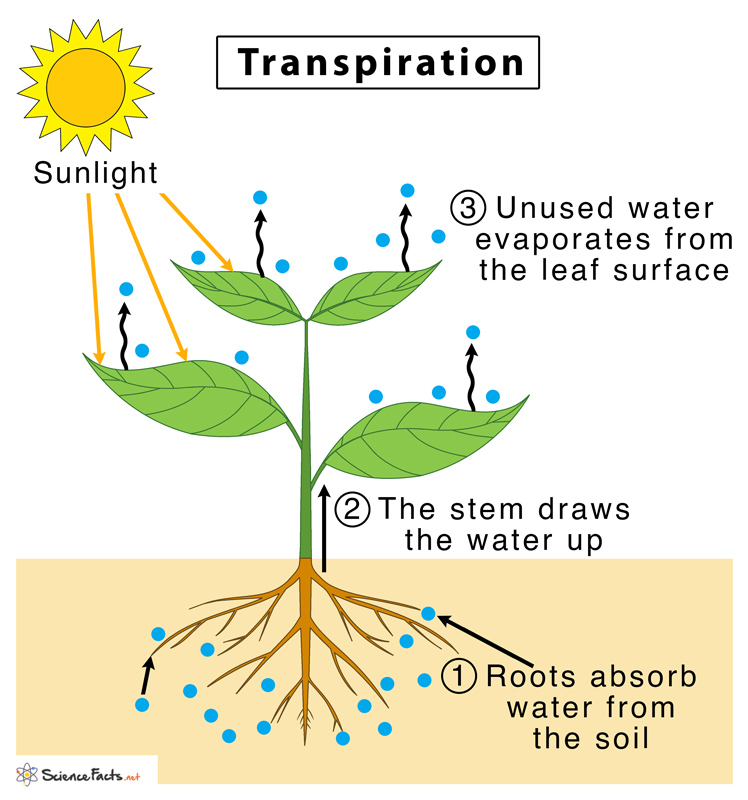
Transpiration
root > xylem > evaporation through stomata
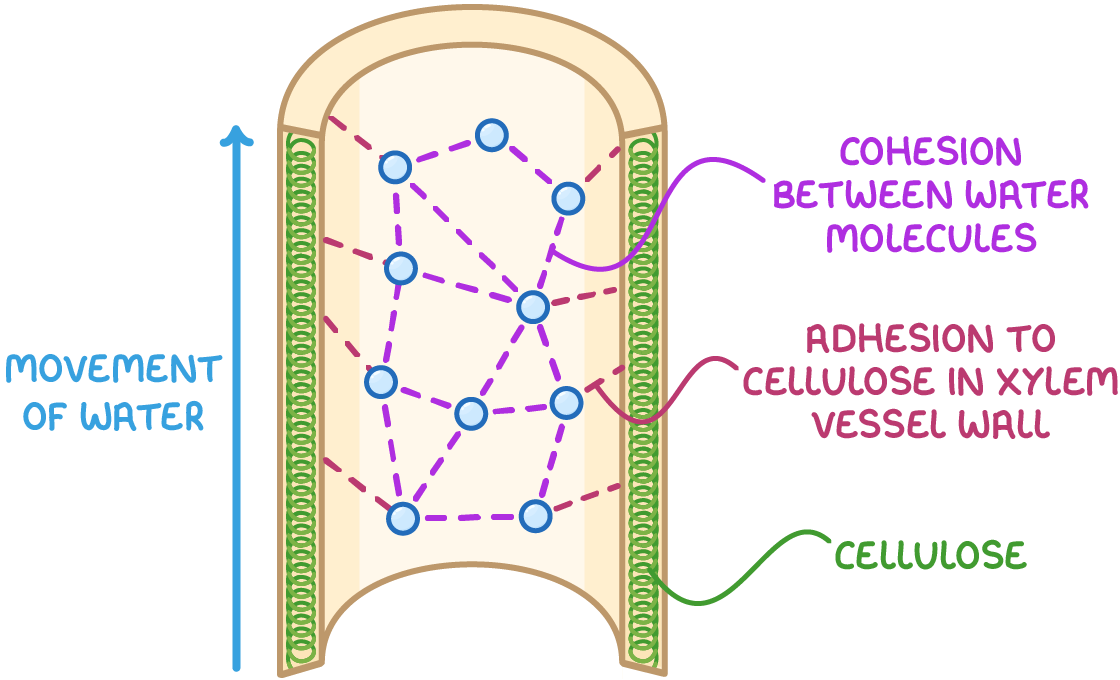
Cohesion-tension theory
Cohesion - hydrogen bonds
Adhesion - stick to xylem walls
How does humidity affect transpiration
decrease rate of evaporation
lower concentration gradient
How does wind speed affect transpiration
increase rate of evaporation
wind removes water
maintains concentration gradient
How does temperature affect transpiration
increase rate of evaporation
more kinetic energy
too high will close stomata and stop evaporation