Cartilage and Bone
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Characteristics of Cartilage
semirigid, flexible yet resilient due to elastic fibers, collagen fibers, and a gel-like ground substance, avascular
Functions of cartilage
support soft tissues, articular surfaces for joints, provide a model for endochondral bone formation
Chondroblasts
cells that produce cartilage matrix and are essential for cartilage growth and repair.
Chondrocytes
the mature cells of cartilage that maintain the cartilage matrix.
Extracellular Matrix of cartilage
protein fibers embedded in a gel-like ground substance
perichondrium
dense irregular connective tissue
Types of cartilage
hyaline (flexible but resilient), fibrocartilage (contains thick collagen fibers, shock absorber), elastic (contains elastic fibers, provides flexibility)
Organic component of bone matrix
Called osteoid and contains collagen and other proteins
Inorganic component of bone matrix
called hydroxyapatite and contains calcium phosphate and calcium hydroxide
Classification by structure of bones
long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid
Structure of flat bones
compact/cortical bone (lined by periosteum and composed of osteons)
spongy/cancellous bone (lined by endosteum, composed of trabeculae, often contains red bone marrow)
Osteocyte
a mature bone cell that maintains the bone matrix and communicates with other bone cells through canaliculi.
Osteoblast
a bone-forming cell responsible for the synthesis of the bone matrix and aids in mineralization.
Osteogenic cell
a stem cell that differentiates into osteoblasts and is involved in bone formation.
Osteoclast
a large multinucleated cell that breaks down bone tissue, playing a crucial role in bone remodeling.
Structure of compact bone
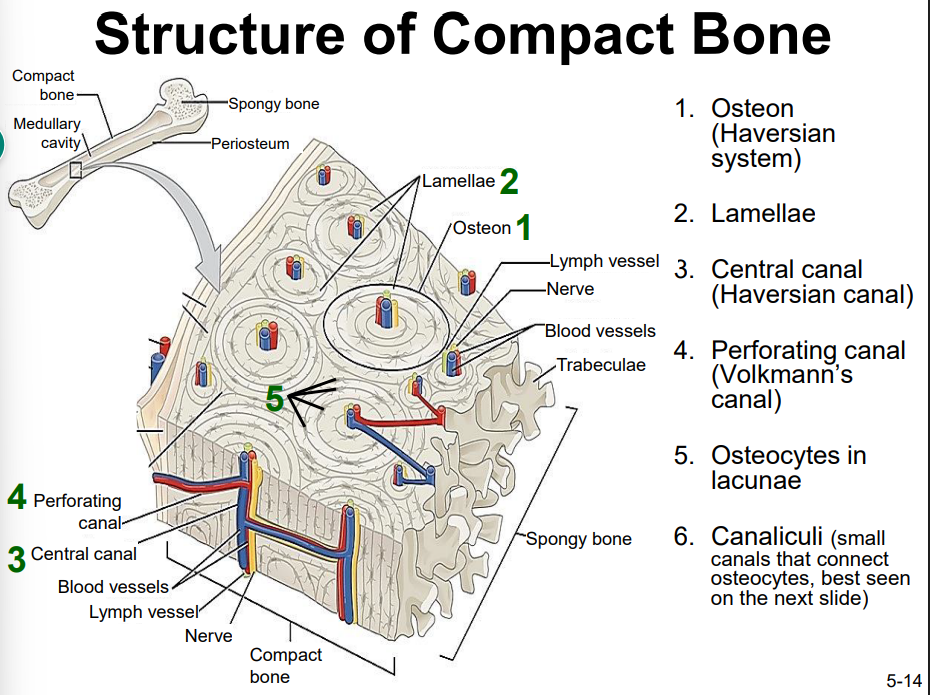
Ossification
the process of bone tissue formation, where cartilage is gradually replaced by bone.
Intramembranous Ossification
bone growth within a membrane. Form flat bones of skull, some facial, mandible, and clavicle
Endrochondral Ossification
Bone growth within cartilage, turns fetal framework of hyaline cartilage into bone, formation of most bones
Osteomalacia (rickets)
a disorder characterized by the softening of bones due to a deficiency of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate, leading to weakened bones and increased fracture risk.
Osteoporosis
Excessive bone resorption, aged and post-menopause