Ch. 22 - Nutrition and Energy for Life
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Macronutrients
Substances that are needed by the body in large amounts
Include carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
Micronutrients
Substances that are needed by the body only in small amounts
Classified as either vitamins or minerals
Some are utilized in enzymes
Other Essential Nutrients
Water
Constitutes 45%–75% of the human body mass
Fiber -
Prevents or relieves constipation by absorbing water and softening the stool for easier elimination
Nutrition Labeling and Education Act of 1990
brought changes to the regulations that define what is required on a food label
includes creation of daily values (DVs)
Daily Values (DVs)
Reference values developed by the FDA specifically for use on food labels
includes:
Reference Daily Intakes (RDIs): Standards for protein, vitamins, and minerals used on food labels
Daily Reference Values (DRVs): Standards for nutrients and food components such as fat and fiber that are important for health
FDA
The Food and Drug Administration
they finalized the Nutrition Facts label for packaged foods, which lets consumers make better informed food choices
Uses 2000 Calories as a standard for energy intake when calculating DRVs
Reviews and revises the guidelines every 5 years
1 nutritional Calorie is equivalent to…
1 kcal of energy
USDA
U.S. Department of Agriculture
issued the MyPlate food guide to replace the MyPyramid posters with new recommendations
Carbohydrates
Main dietary source of energy
Provide useful materials for the synthesis of cell and tissue components
Considered to be fattening
Excess calories are bc of high-calorie foods eaten with the carbs
Ex) Bread is eaten with butter, a high-energy lipid
Simple vs. Complex Carbs
Simple:
includes monosaccharides and disaccharides, aka sugars
Complex:
Include the polysaccharide starch, composed of amylose and amylopectin
Cellulose has a non-nutritive role as fiber bc it cannot be digested by humans
Lipids
About 95% of lipids in the body and in foods are triglycerides
Provides more than twice the energy of a carbohydrate
Contain some fat-soluble vitamins and help carry them through the body
Include essential fatty acids, which must come from diet
Improves the texture of foods and absorbs and retains flavors
Prolongs satiety as they are digested more slowly than other foods
Lipids in Diet
research shows a correlation between the consumption of too much fat and the wrong type of fat and obesity and cardiovascular disease
Moderate amount of fat is needed in a diet
Many people consume more fat than required
monounsaturated fats are better fats for your health
Proteins
Proteins are the only macronutrients with an established RDI (Reference Daily Intake)
Used in the body to aid in:
Production of new tissue as the body grows
Maintenance and repair of cells
Production of enzymes, hormones, and other important N-containing compounds of the body
Supplies energy (4 calories/gram)
Broken down to individual amino acids that are absorbed into the body's amino acid pool
What makes something a complete protein?
if they contain all the essential amino acids in the proportions needed by the body
How does the RDI for protein for pregnant women differ from the average adult
Average protein intake for adult is 50g
it is higher for pregnant and nursing mothers
The Essential Amino Acids:
9 of them
have to get these from our diet because our body doesn’t make enough of them
not every amino acid is essential
Vitamins
Organic compounds that cannot be produced by the body in the amounts needed for good health
2 Types:
Water soluble
Fat soluble
Water-Soluble Vitamins
Highly polar in nature
Function as coenzymes, minus vitamin C
Excess is excreted through the kidneys
go through body faster than fat soluble vitamins
includes Vitamin C, B1, B2, B6, B12, and niacin, folic acid, pantothenic acid, and biotin
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Have nonpolar molecular structures
Function like hormones
Excess accumulation in body tissues can lead to toxic effects
stay in body longer than water-soluble vitamins
Includes Vitamin A, D, E, and K
Minerals
Metals or nonmetals used in the body in the form of ions or compounds
includes major minerals and trace minerals
Major Minerals
Found in the body in quantities greater than 5g
Examples
Calcium and Phosphorus - Primary inorganic structural components of bones and teeth
Na, K, Cl, and Mg - Ions distributed throughout the body’s fluids
Sulfur
Trace Minerals
Found in the body in quantities less than 5g
Components of vitamins, enzymes, hormones, or specialized proteins
Examples : Fe, Mn, Cu, and I
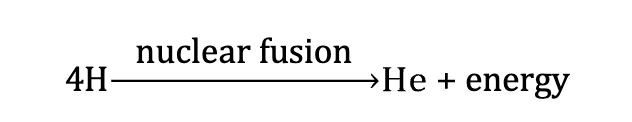
What is the ultimate source of energy used in all biological processes?
the sun
What does the enormous energy output from the sun come from?
the fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium atoms
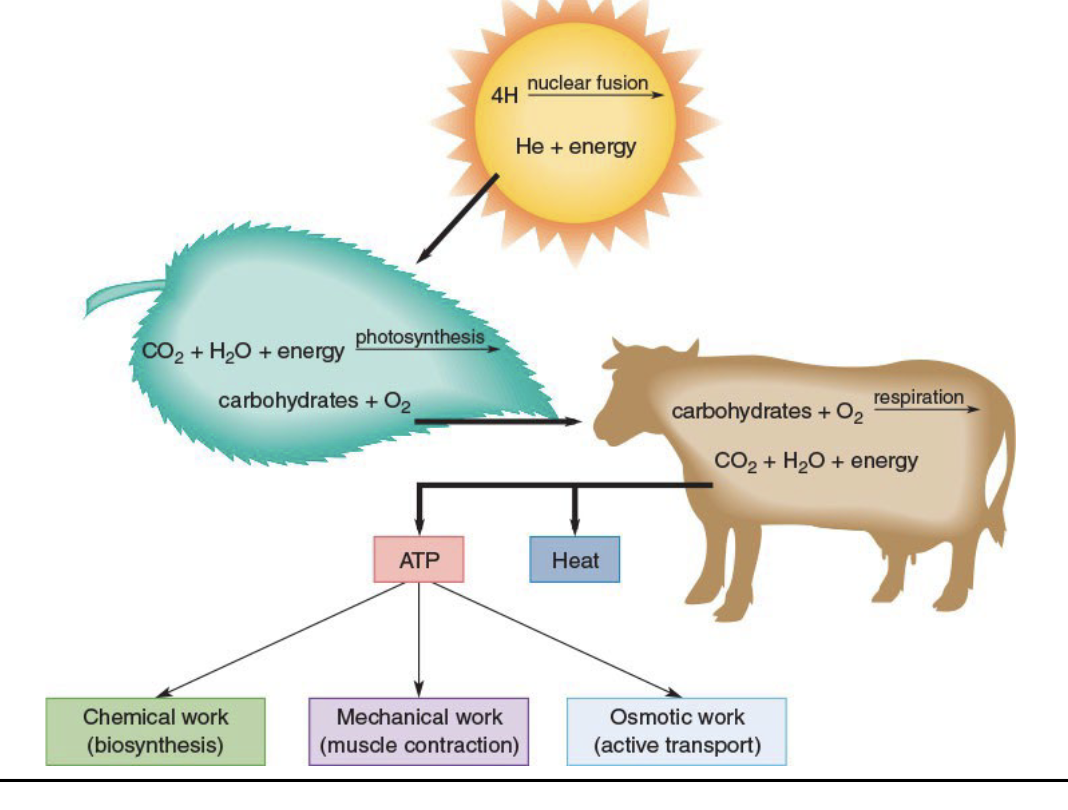
Role of the sun in plants:
A portion of the liberated energy reaches the Earth’s surface and is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments in the plants
Big part of photosynthesis
Energy stored in plants is obtained by all animals directly or indirectly
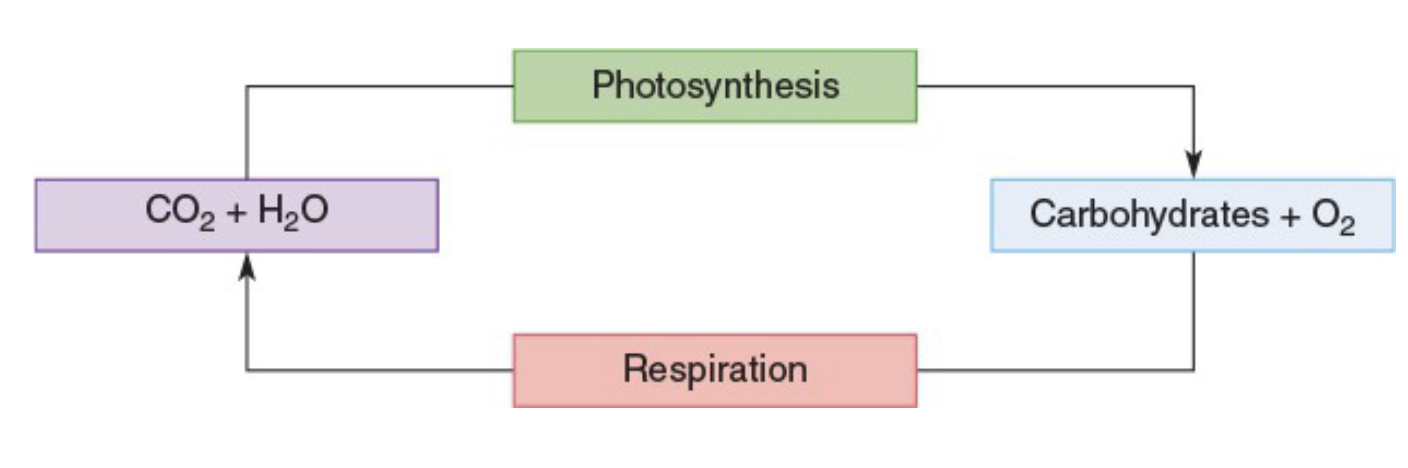
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis converts CO 2 and H2O into glucose, and then into starch, triglycerides, and other storage forms of energy

Cellular Respiration
plants and animals combine energy-rich compounds with oxygen from the air to produce CO 2 and H 2O and release energy
Portion of energy released is ATP
Remainder of the energy is released as heat
Energy Flow Chart
Nuclear fusion from the sun
Photosynthesis
Cellular Respiration
Production of ATP and heat
ATP either synthesizes biomolecules, muscle contraction, or active transport
Carbon Cycle
Some of Earth’s carbon compounds are repeatedly recycled by living organisms
Metabolism
sum of all reactions involved in maintaining a living cell
Categories
Catabolism
Anabolism
Catabolism
All reactions that lead to the breakdown of
biomolecules
releases energy
Anabolism
All reactions involved in the creation of
biomolecules
requires energy
Metabolic Pathway
Sequence of reactions used to produce one product or accomplish one process
Ex) - Citric acid cycle and ETC
Catabolism of Food - Stage 1
Large molecules are digested into smaller ones via hydrolysis
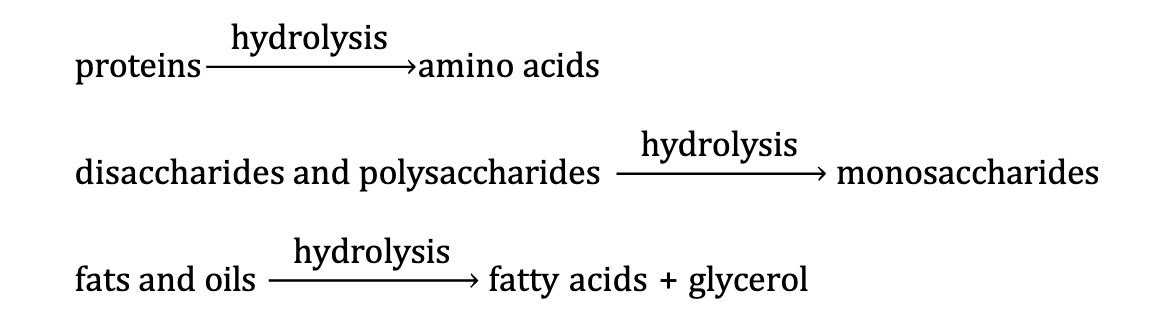
Catabolism of Food - Stage 2
Small molecules are broken down into simpler units, primarily the two-carbon acetyl portion of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
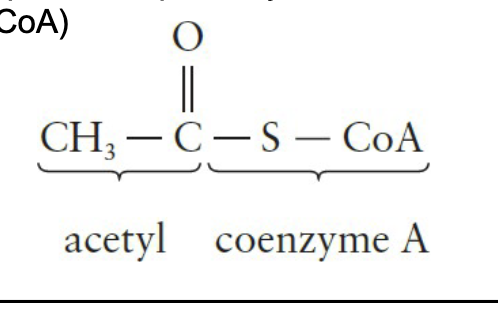
Catabolism of Food - Stage 3
Common catabolic pathway
Reactions of the CAC plus the ETC and oxidative phosphorylation
Purpose is to convert chemical energy in foods to ATP molecules
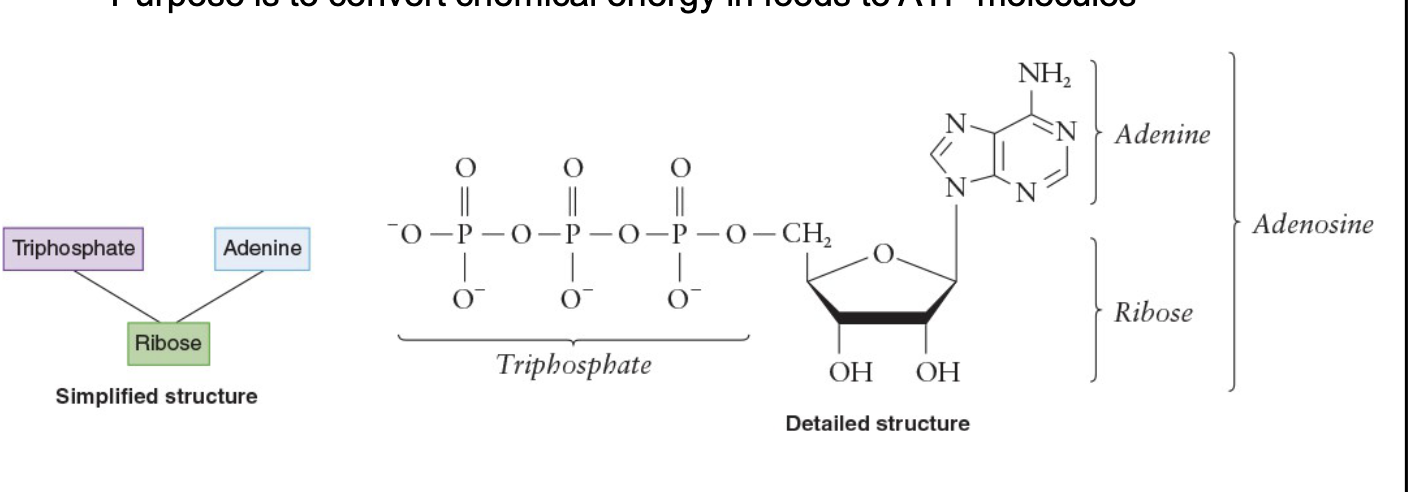
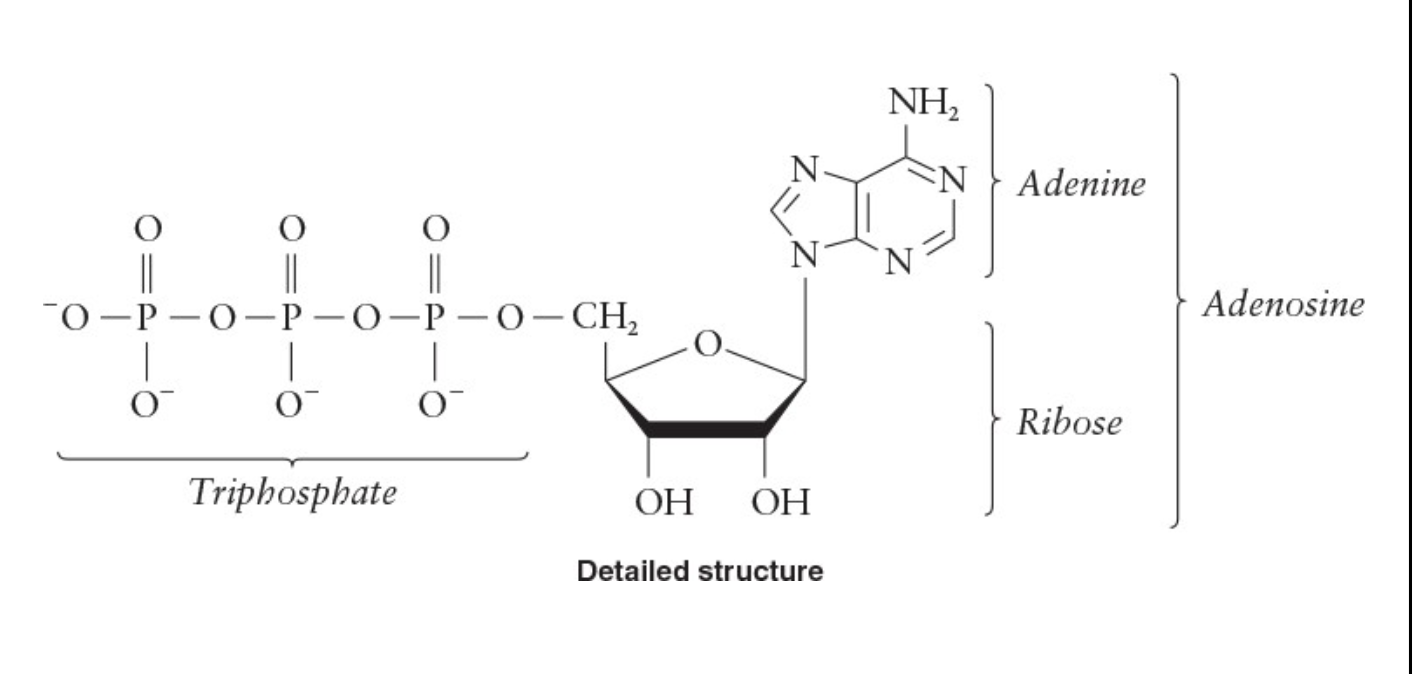
Structure of ATP
Adenosine portion has adenine bonded to a ribose
Triphosphate portion is bonded to the ribose
ATP molecule has a charge of –4
ATP is complexed with Mg 2+ in a 1:1 ratio
Net charge of complex is –2
Triphosphate end is essential in the transfer of biochemical energy
Is used quickly once it is formed
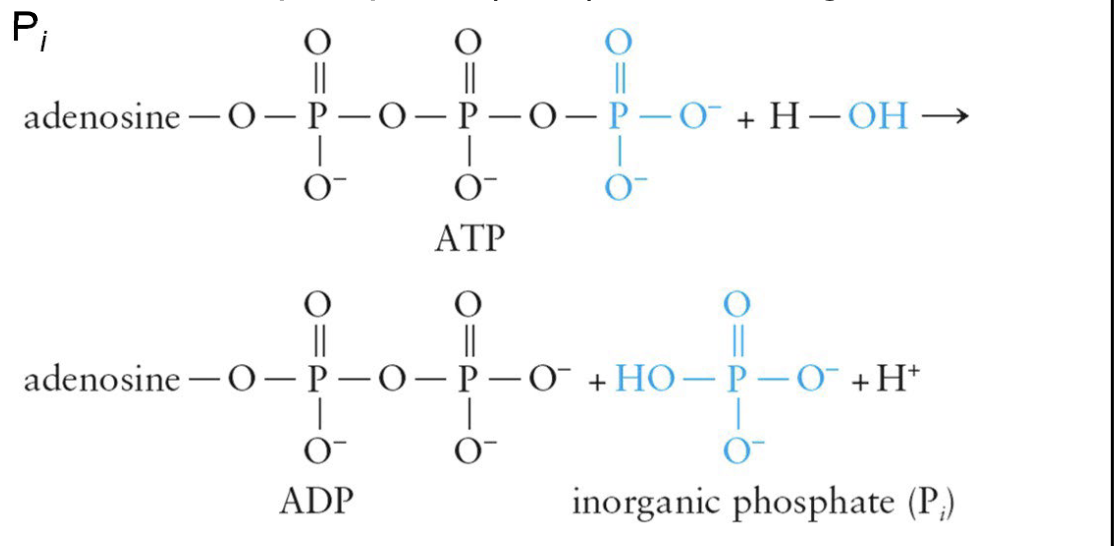
Hydrolysis of ATP in water:
Results in the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to water
Products are adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate, Pi
reaction releases free energy (ΔG), which is used in cellular processes that require input of energy
ATP is a high-energy compound
generates a great amount of free energy during hydrolysis
ΔG
has a positive value when energy is absorbed and a negative value when energy is released
Represented by ∆G° when measured under standard conditions
Represented by ∆G°′ when measured at body conditions
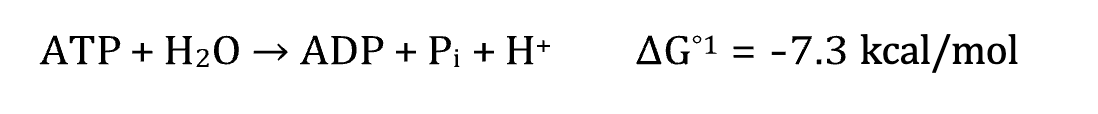
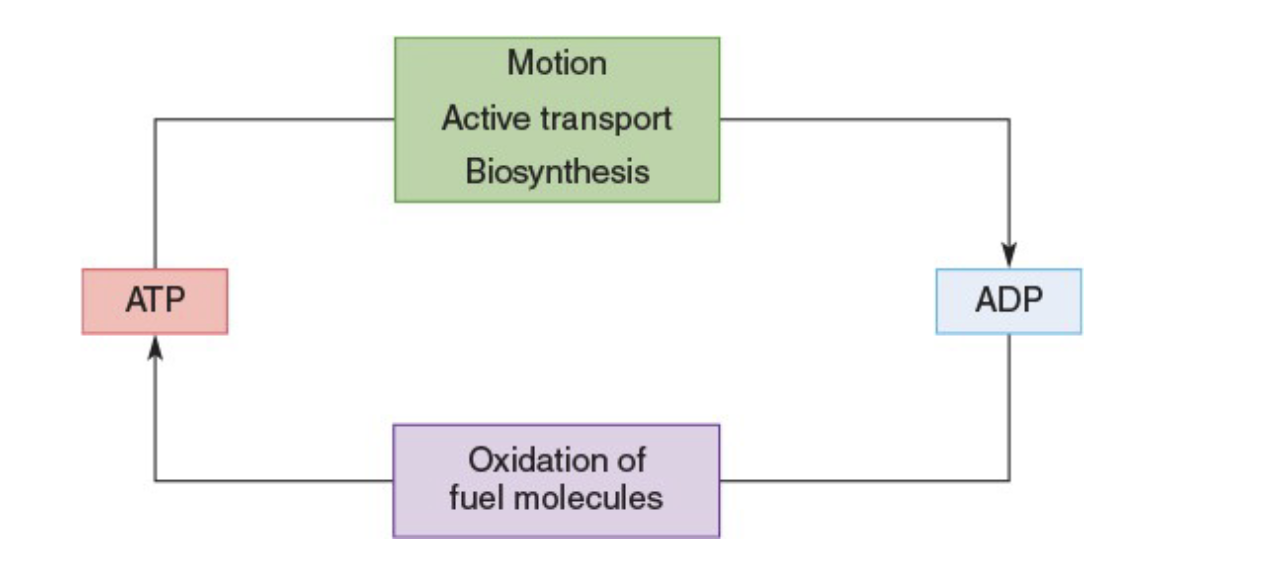
The ATP-ADP Cycle
Plays a central role in linking energy production with energy utilization
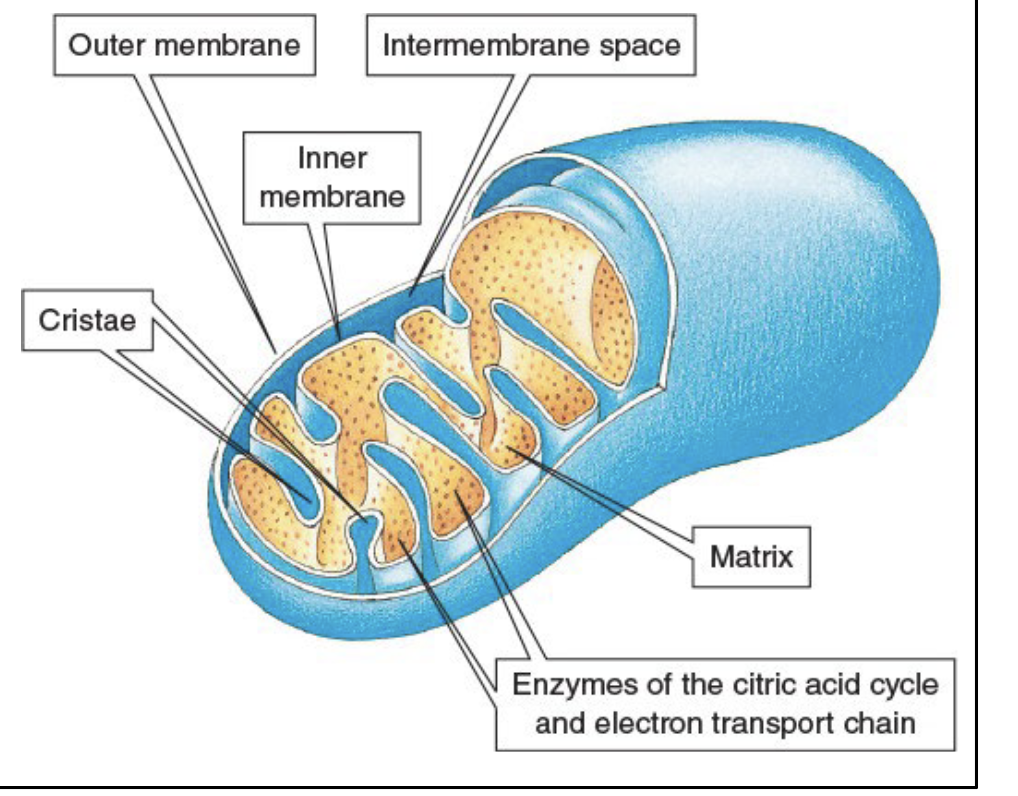
Mitochondria
organelles where reactions of the common catabolic pathway occur
Known as cellular power stations
Contain both inner and outer membranes
Folds of the inner membrane are called cristae
Gel-filled space that surrounds the cristae is called the matrix
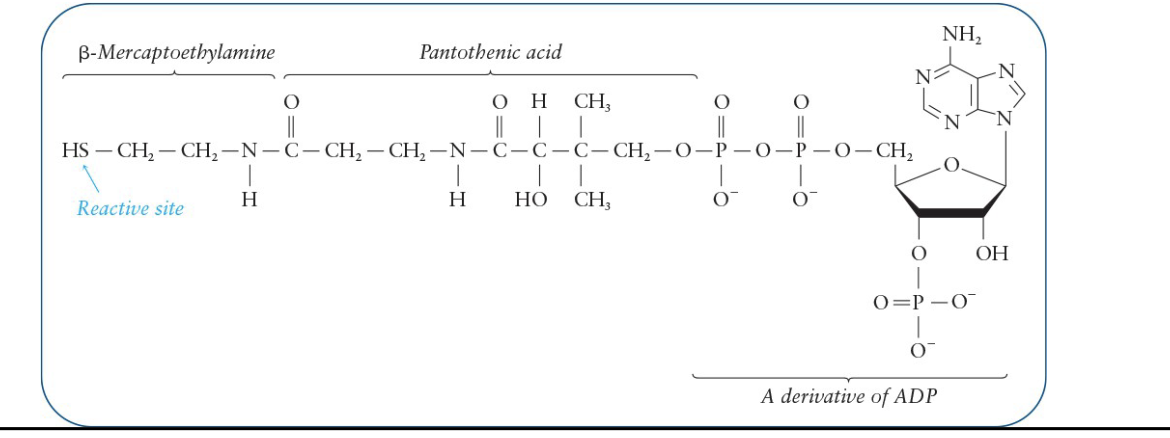
Coenzyme A (CoA)
Central compound in metabolism and is a part of acetyl CoA
Derived from the B vitamin pantothenic acid (B5)
Contains:
Phosphate derivative of ADP
b-mercaptoethylamine
sulfhydryl group (—SH)
transfers acyl groups
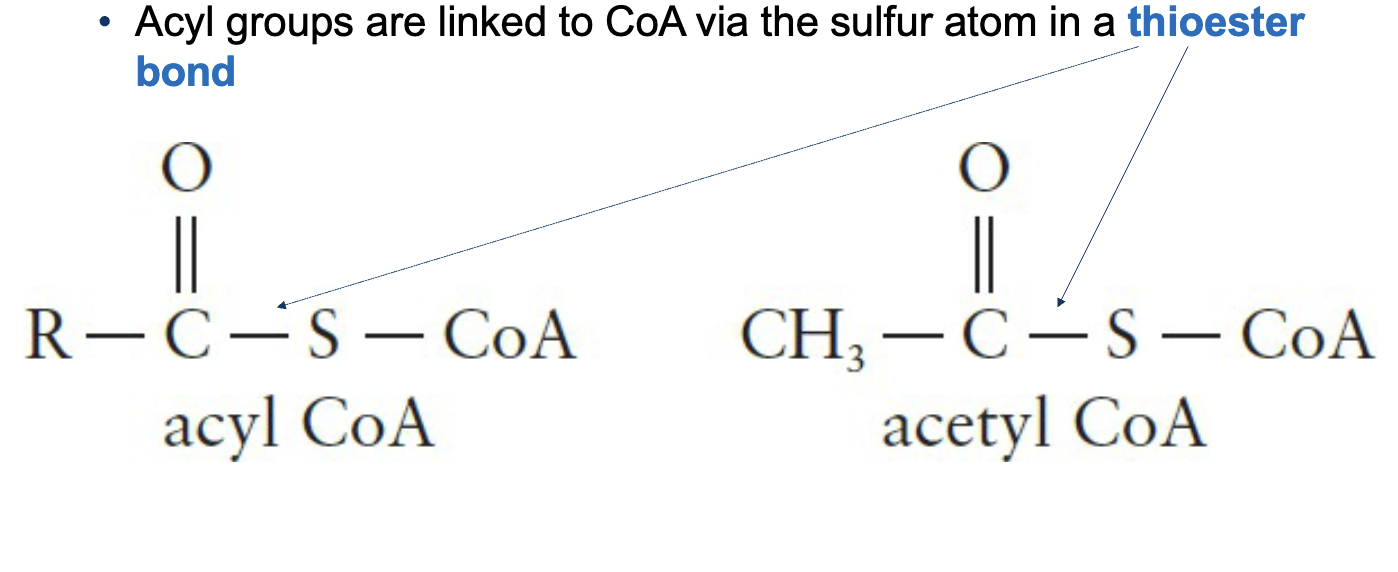
Acyl groups are linked to CoA by the sulfur atom in a thioester bond
Thioester bond
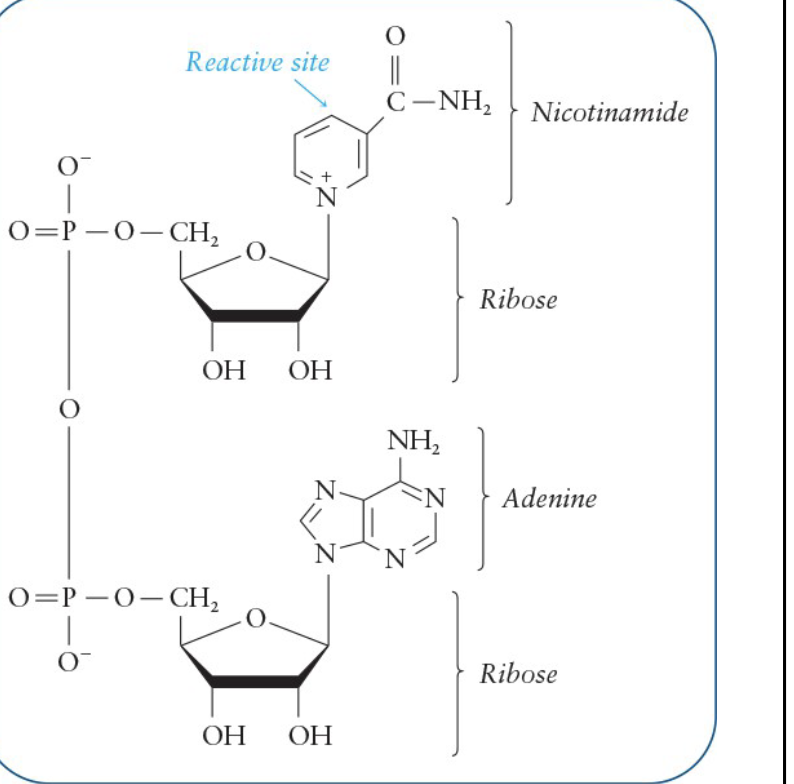
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+ )
Derivative of ADP and the vitamin nicotinamide
Reactive site is located in the nicotinamide portion
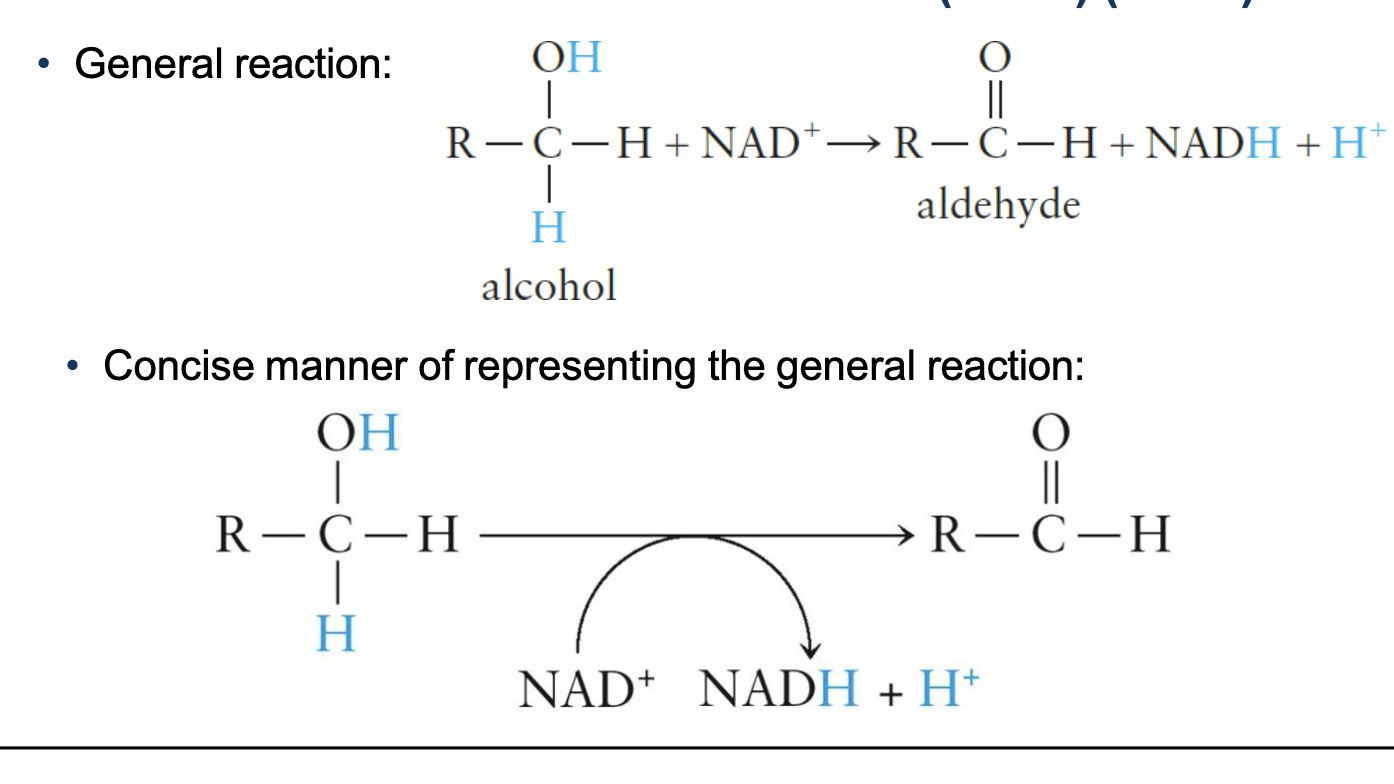
Acts as an electron acceptor
accepts 2 electrons and 1 proton during oxidation of a substrate, which forms NADH
How NAD+ accepts electrons:
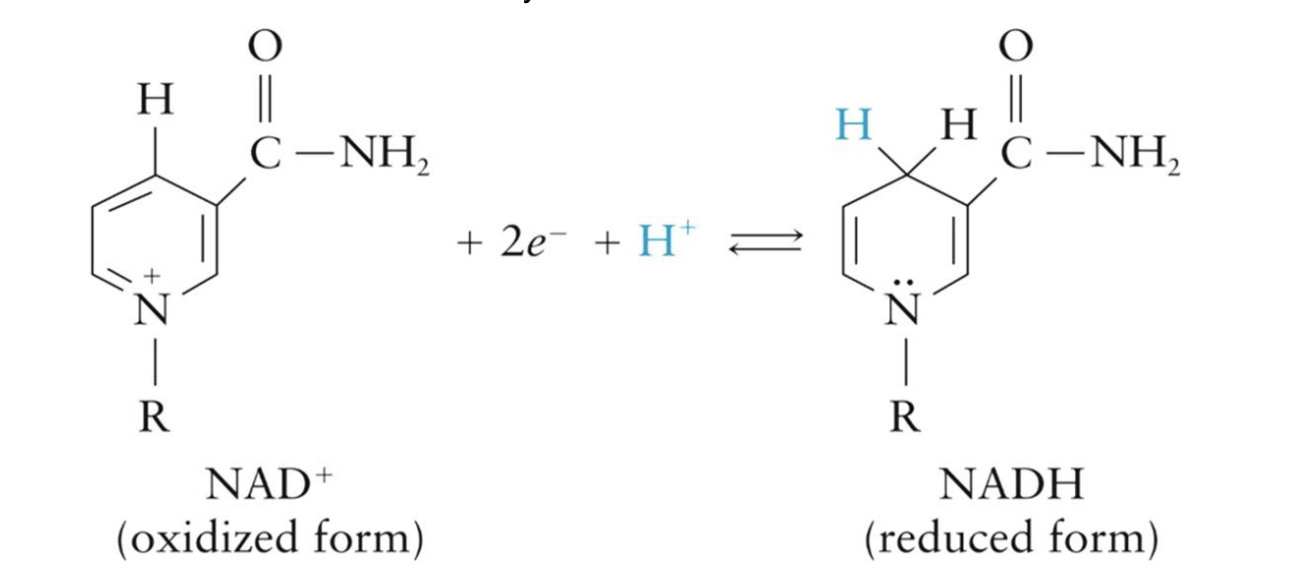
NAD+ Reaction
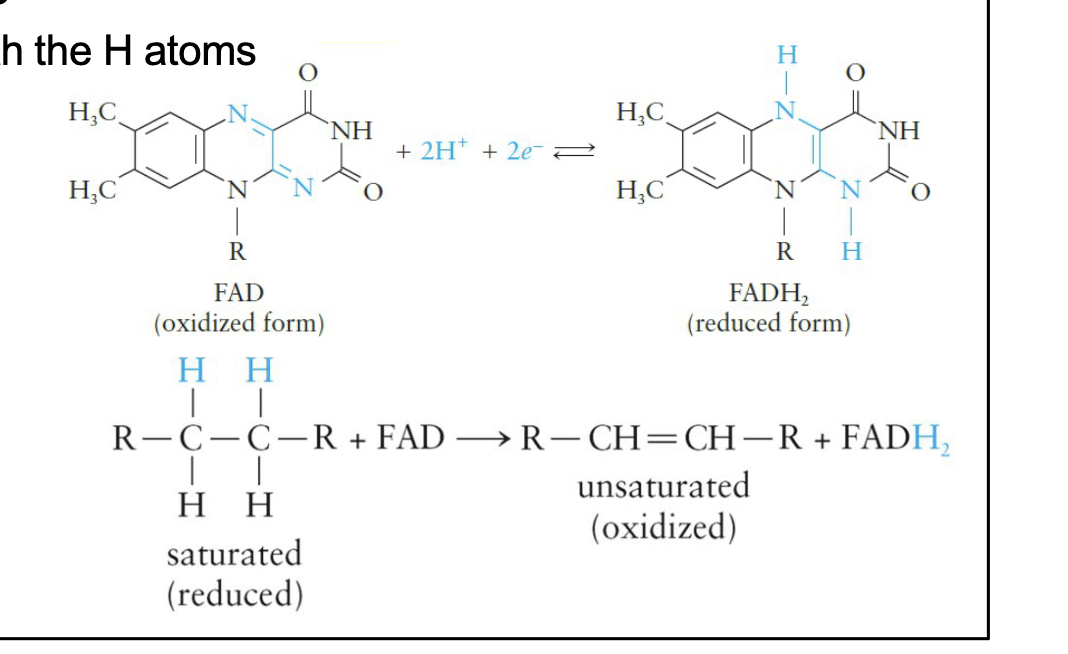
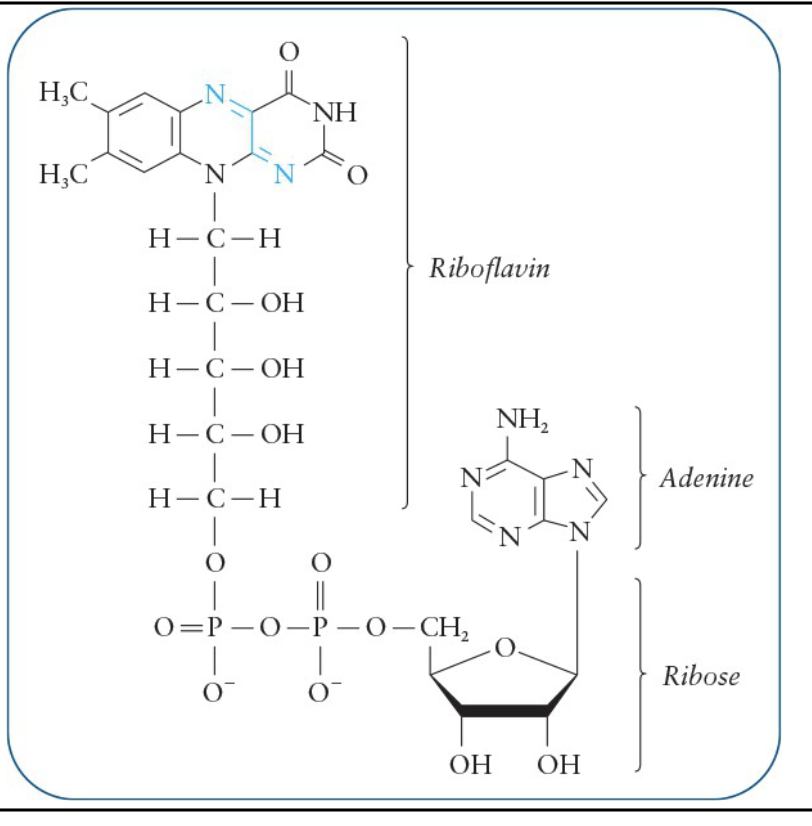
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD)
Derived from ADP and the vitamin riboflavin
Reactive site is located within the riboflavin ring system
Substrates of enzymes that use FAD as the coenzyme give up two electrons
FAD accepts both the H atoms Involved in the reactions in which a —CH2—CH2— portion of the substrate is oxidized to a double bond
FAD Reactions