Foundations of Nursing - Exam 3
breast subjective data
pain, lump, and discharge
rash, swelling, trauma
history of breast disease
surgery or radiation
medications
mammogram
self breast examination
SBE
self breast examination
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
breast subjective data
pain, lump, and discharge
rash, swelling, trauma
history of breast disease
surgery or radiation
medications
mammogram
self breast examination
SBE
self breast examination
45 to 50
annual mammography should be performed at from ages _____ to _____
55
biannual mammography or continuation of annual mammography should be performed over age _____
breast cancer
_______ ______ is the 2nd major cause of death from cancer in women
99%
what is the 5 year survival rate of breast cancer in the US today?
85%
what is the 5 year survival rate of breast cancer in the US today, if spread regionally?
relative risk
RR, if RR > 1 there is an indication of a higher likelihood of an occurrence among exposed then unexposed persons
nipples
these usually protrude although some are flat or inverted
supernumerary nipple
also known as extra nipples
common minor birth defect where a person has one or more nipples in addition to their normal two
typically harmless and often unnoticed until puberty or hormonal changes cause them to become more noticeable
lymph nodes
these can be found in the axillae but should be non palpable, if they are palpable, they should be small, soft, and nontender
circular method
examine the breast starting at the nipple and moving in a circular motion outwards
wedge method
examine the breast starting at the nipple and dividing the breast into wedges or pizza slices and feeling each wedge using a systemic approach
vertical strip method
examine the breasts starting at one side of the breast moving in an up and down moving moving your way across the breast to the opposite side
ask, advise, assess, assist, arrange
5 A’s counseling method (smoking)
3
the right lung has ___ lobes
2
the left lung has ___ lobes
vesicular lung sounds
normal lung sounds
soft, low-pitched, rustling sounds
heard during inspiration and fade quickly during expiration
indicate that the airways are clear and free from obstruction or inflammation
bronchovesicular lung sounds
normal lung sounds
medium pitch
heard during both inhalation and exhalation
considered intermediate between bronchial and vesicular sounds
typically located in the mid-chest area and posterior chest between the scapulae
reflect a mixture of bronchial and vesicular components, with equal inspiratory and expiratory phases.
bronchial lung sounds
loud, high-pitched, and hollow sounds
heard over the large airways, particularly the trachea and bronchi, when auscultating the chest
normal over these areas but can be abnormal if heard in other lung regions
characterized by a distinct pause between inspiration and expiration, and the expiratory phase is typically longer than the inspiratory phase
crackles, wheezes, rhonchi
3 examples of adventitious breath sounds
fine crackles
high pitched, soft, brief crackling sounds
can be stimulated by rolling a strand of hair near the ear or stethoscope
course crackles
low pitched, moist longer crackling sounds
sounds similar to velcro be separated slowly
wheezing
high pitched musical sounds heard primarily during inspiration
may be audible in severe asthma or bronchitis
sputum color - clear
rhonchi
low pitched snoring or gurgling sound
may clear with coughing
pleural friction rub
loud, course, and low pitched grating or creaking sound
similar to a squeaky door opening
heard during inspiration and expiration
TRIPOD position
commonly found in people experiencing respiratory distress, ex. COPD
tachypnea
breathing greater than 24 breaths per minute
bradypnea
breathing less than 10 breaths per minute
stridor
a loud, high-pitched crowing or honking sound (seal) from the upper airway - EMERGENCY
chronic hypoxia
clubbing indicates…
barrel chest
the term that coins a 1:1 anteroposterior and lateral diameter of thorax, common in COPD patients
S1
sound heard best at the apex (bottom) of the heart
occurs with the closure of the AV valves
signals the beginning of systole
S2
sound heard best at the base (top) of the heart
occurs with the closure of the semilunar valves
signals the end of systole
aortic component slightly precedes pulmonic component
S3
can be common in patients with heart failure or high BP
occurs when ventricles are resistant to filling during early rapid filling phase
occurs immediately after S2, when the AV valves open and atrial blood first pours into the ventricles
S4
commonly found in patients with thickening of the heart tissue
occurs at the end of diastole, at presystole, when the ventricles are resistant to filling
this occurs just before S1
heart murmur
an abnormal sound as a result of turbulent blood flow, often due to valve dysfunction or other cardiac anomalies
described as a gentle, blowing or swooshing sound that can be heard on the chest wall
can be a result of increased blood velocity or viscosity or valve structural defects
dyspnea
shortness of breath
angina
chest pain
orthopnea
short of breath when laying down
fluid overload or right sided heart failure
jugular venous distention may be a possible indication of this
aortic
2nd intercostal space, right sternal border
pulmonic
2nd intercostal space, left sternal border
erb’s point
3rd intercostal space, left sternal border
tricuspid
4th intercostal space, left sternal border
mitral
5th intercostal space, mid clavicular line
heart disease
this is the leading cause of death in both men and women worldwide
peripheral arterial disease
PAD
affects non coronary vessels and refers to arteries affecting the limbs
leads to reduced blood flow limiting oxygen in tissues
smoking, age, obesity, and diabetes are all risk factors
lymphatics
a separate vessel system which retrieves excess fluid and plasma proteins from the interstitial spaces and returns it to the bloodstream
small, soft, mobile, nontender
what are considered normal findings of lymph nodes?
enlarged lymph nodes
also called lymphadenopathy
nodes larger than 1 cm
may be tender, hard, or fixed
may indicated infection, inflammation, or malignancy
tender nodes
finding in lymph nodes that usually indicates infection or inflammation in the region that the node drains
hard/fixed nodes
finding that may indicate lymph node malignancy
generalized lymphadenopathy
enlargement of lymph nodes in multiple areas
can indicate a systemic infection, autoimmune diseases, or cancers like lymphoma
spleen
located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen
destroys old red blood cells
produces antibodies
stores red blood cells
filters microorganisms from blood
tonsils
includes palatine, adenoid, and linguil
located at the entrance to the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts
responds to local inflammation
thymus
flat, pink-grey gland located in the superior mediastinum behind the sternum and in front of the aorta
responsible for T-cells
pitting edema scale
+1 - 2mm depth
+2 - 4mm depth
+3 - 6mm depth
+4 - 8mm depth
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
pica
ingestion of non-food items…includes ice, toilet paper, drywall, ashes
constipation
this is not a physiological consequence of aging
can be cause by several factors: decreased physical activity, dehydration, low fiber diet, medication side effects, bowel obstruction, hypothyroidism, difficulty ambulating to toilet
contour, symmetry, umbilicus, skin
key components to look at when inspecting the abdomen
inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation
order of abdominal assessment
begin in the RLQ
when auscultating for bowel sounds in the abdomen…
normal bowel sounds
5-30 per minute
hypoactive bowel sounds
< 5 gurgles per minute
hyperactive bowel sounds
> 30 gurgles per minute
borborygmus
the name for the sound of stomach growling (hyperperistalsis)
absent
you must listen for 5 minutes in every quadrant to determine if the bowel sounds are _______
CVA
costovertebral angle tenderness
positive finding indicates inflammation of the kidney
to assess, place one hand over the 12th rib and hit that hand with your fist, repeat with the other side
light palpation of abdomen
use 4 fingers
depress skin about 1 cm
make a gentle rotary motion, moving clockwise
deep palpation of abdomen
use 2 hands
depress skin 5-8 cm (2-3 in)
used to detect masses or abnormal organ sizes
ascites
buildup of fluid in the abdomen
osteoporosis screenings
this is important for post-menopausal women
remind them to also focus on implementing weight bearing exercises
inspection, palpation, range of motion
order of musculoskeletal assessment
GALS assessment
locomotor screening
assesses gait, arms, legs, and spine
patient performs 11 tasks and the examiner asks two questions…do you have any pain or stiffness anywhere? do you have any difficulty washing, dressing, or climbing stairs?
lordosis
exaggerated inward curve of lumbar spine
scoliosis
lateral/sideways curve of the spine
kyphosis
enhanced curvature of the thoracic spine, “humpback“
ankylosis
abnormal stiffness of a joint due to the fusion of bone, occurs in severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis
contractures
permanent tightening of muscles, tendons, ligaments, or skin that restricts movement and/or felxibility
bursitis
inflammation of a bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between muscles or bones…prominent in shoulders, elbows, and hips
tendinitis
inflammation of a tendon due to overuse or injury
osteoarthritis
also called degenerative joint disease
the pain worsens with activity and improves with rest
can have hard, bony protrusions
limited ROM
rheumatoid arthritis
symmetrical joint involvement
common on the hands and feet
pain is worse in the morning
carpal tunnel
pain in the wrists
can cause finger numbness and tingling
caused by lots of repetitive movement
acute gout
crystals caught in joint
due to increased levels of uric acid in the blood
dietary restrictions are helpful in alleviating symptoms
LOC
level of consciousness
glascow coma scale
used to objectively describe the extent of impaired consciousness in all types of acute medical and trauma patients
assesses eye opening response, verbal response, and motor response
desired score of 15
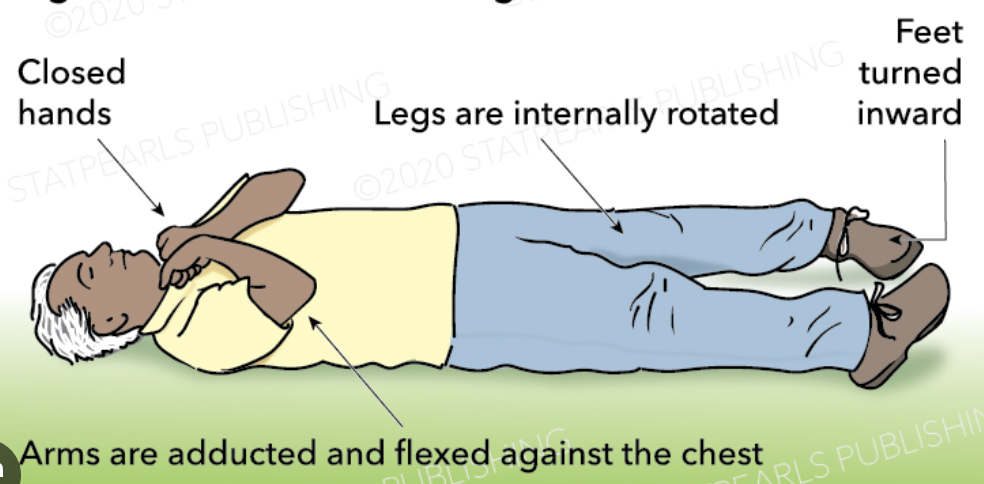
decorticate rigidity
flexion in upper extremities
extension and internal rotation in lower extremities
**indicates hemispheric lesion…bleeding**
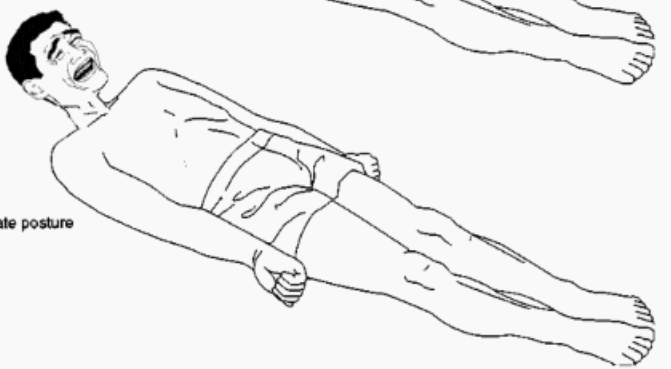
decerebrate rigidity
stiffly extended upper extremities
palms pronated
flexed wrists
stiffly extended lower extremities
**indicates lesion in brainstem*
flaccid quadriplegia
complete loss of muscle tone and paralysis of all four extremities
indicating nonfunctional brainstem
opisthotonos
prolonged arching of the back with head and heels bent backwards
indicates meningeal irritation
AVPU
A - Alert and conscious
V - Responds to verbal stimulus
P - Responds to painful stimulus
U - Unresponsive to any form of stimulus
lethargic
drowsy, sluggish
obtunded
difficult to arouse
stuporous
requires rigorous stimulation
comatose
no response
gait
this should be smooth, rhythmic, and effortless
opposing arms should swing accordingly
turns should be smooth
step length should be about 15 inches from heel to heel
ataxia
unsteady/uncoordinated gait