2. Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
hematocrit
The percentage of total blood volume occupied by RBCs
47%
Average normal hematocrit for males is about
42%
Average normal hematocrit for females is about
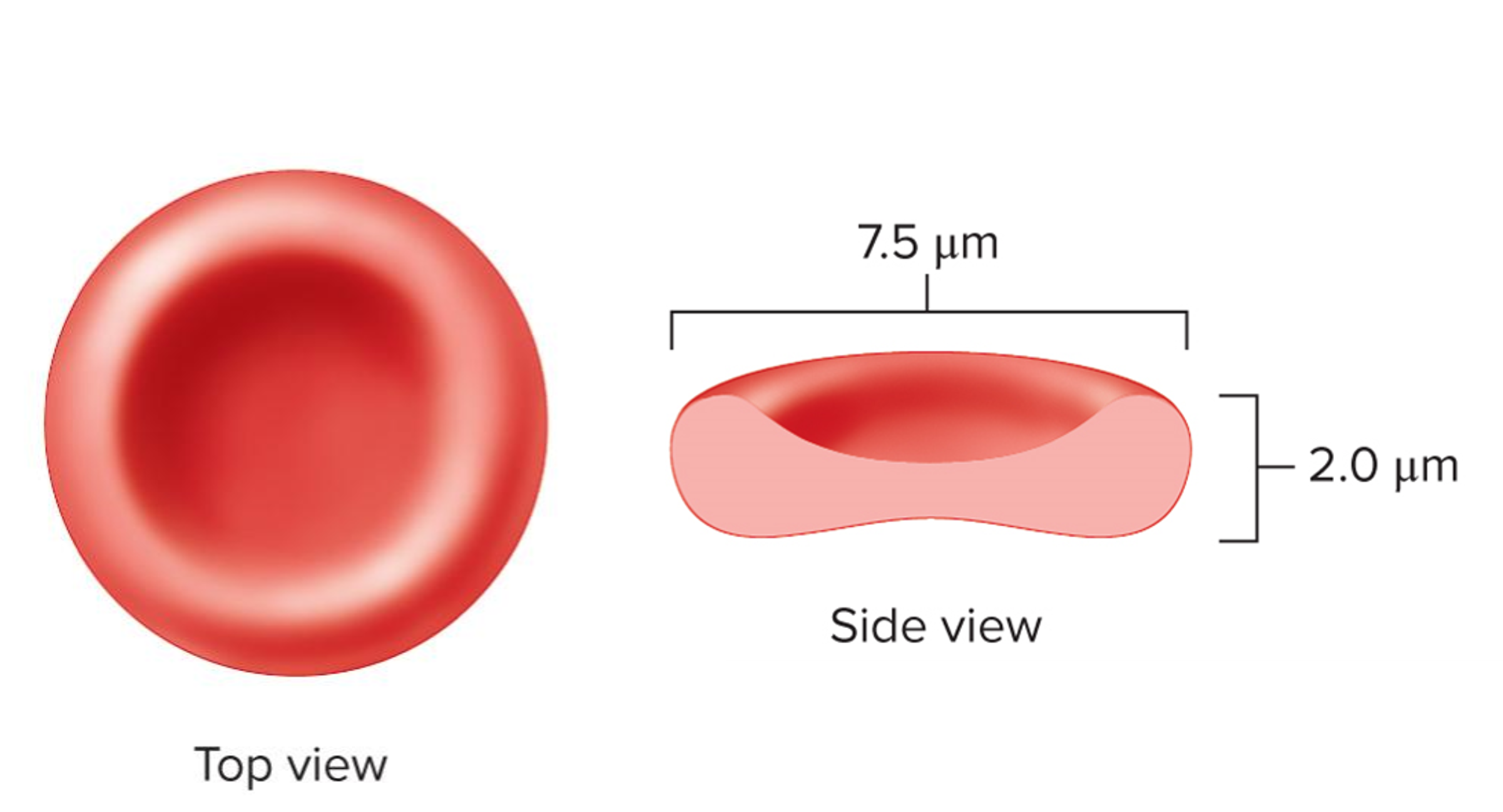
erythrocyte structure
Biconcave disc shape
No nucleus = anucleate
Very flexible – allows them to pass through small vessels easily
Contain the protein hemoglobin, lipids, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and carbonic anhydrase
oxygen and carbon dioxide
erythrocytes transport the respiratory gases…
hemoglobin (Hb)
Red iron-containing pigment protein
globins
Composed of four polypeptide chains called [term] – the part of the hemoglobin that carries carbon dioxide
![<p>Composed of four polypeptide chains called [term] – the part of the hemoglobin that carries carbon dioxide</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f330b75d-3fa2-41a2-ac0c-6e5bf3919739.png)
heme
Within each globin, there is an iron-containing group called [term] – the part of the hemoglobin that carries oxygen
1 molecule of oxygen can bind to 1 [term] group
4 [term] groups per hemoglobin = max of 4 oxygen molecules per hemoglobin
![<p>Within each globin, there is an iron-containing group called [term] – the part of the hemoglobin that carries oxygen</p><ul><li><p>1 molecule of oxygen can bind to 1 [term] group</p></li><li><p>4 [term] groups per hemoglobin = max of 4 oxygen molecules per hemoglobin</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9cb5ec33-a1b0-4fbe-b59c-f7ab9c8e5771.png)
oxyhemoglobin
Hb when it’s bound to oxygen
Unsaturated = 1-3 oxygen bound
Saturated = 4 oxygen bound
Appears bright red in color
deoxyhemoglobin
Hb when it is not bound to oxygen
appears dark red in color
Carbaminohemoglobin
Hb when it is bound to carbon dioxide
erythropoiesis
production of red blood cells
Stimulates red blood cell production in bone marrow
erythropoietin
hormone that regulates erythropoiesis
released slowly by the liver under normal conditions
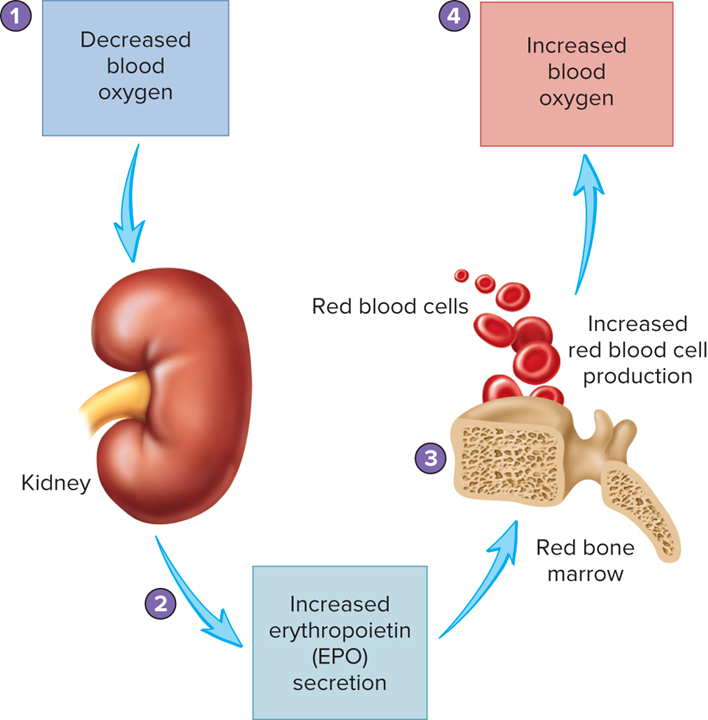
kidneys
Low blood oxygen levels stimulate the [term] to release erythropoietin, which promotes red blood cell production in the bone marrow
![<p>Low blood oxygen levels stimulate the [term] to release erythropoietin, which promotes red blood cell production in the bone marrow</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3e89bbdf-2a60-4a1a-9325-3c96be7d5e40.png)
Reticulocyte “retic” count
indicates the rate of RBC production
anemia
condition in which the ability of blood to carry oxygen is reduced
caused by a decrease in the amount of RBC or hemoglobin in the blood
erythrocyte life span
RBC last about 110-120 days in circulation
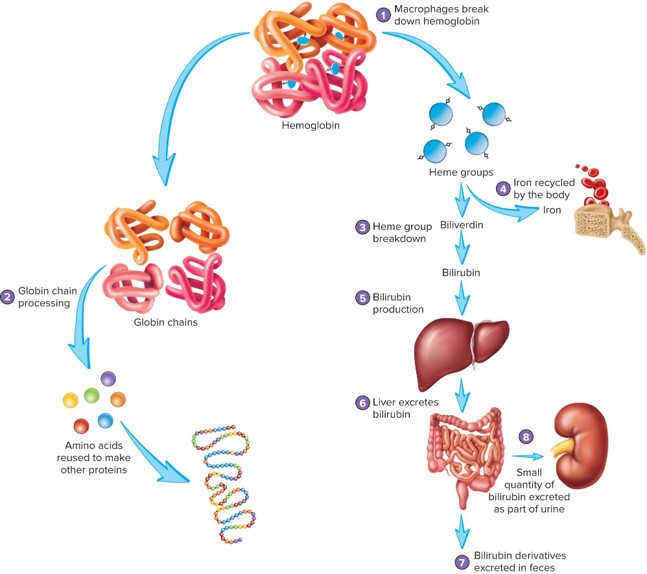
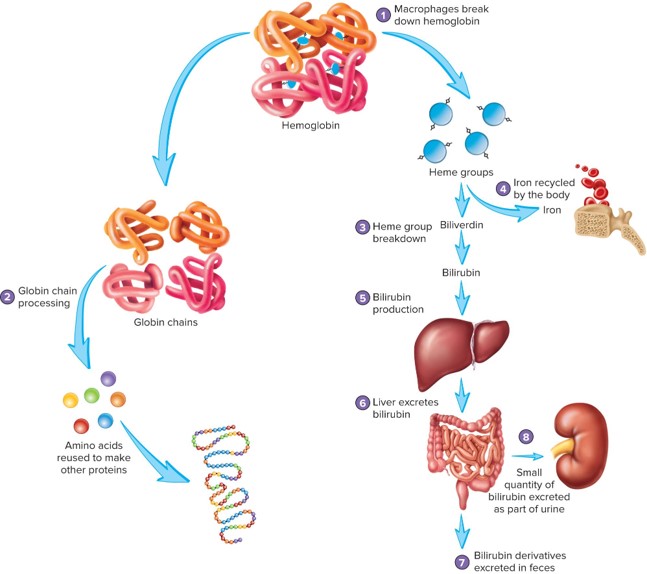
hemolysis
the breakdown of red blood cells (erythrocytes) in the bloodstream
hemoglobin breakdown
RBCs will rupture (hemolysis) at the end of their life and the hemoglobin is broken down by macrophages – occurs largely in the spleen