Edexcel IGCSE Physics : 3 Waves
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves ?
longitudinal waves vibrate parallel to the direction the wave travels
Transverse waves vibrate perpendicular to the direction the wave travels
Define the term amplitude
the maximum distance moved by a vibrating object from its equilibrium position
Define the term wavefront
an imaginary surface which shows the position of particles at different phases of the wave, it is made by overlapping lots of different waves
a wavefront is a line where all the vibrations are in phase and the same distance from the source
Define the term frequency
the number of waves passing a point per second, measured in Hertz
Define the term wavelength
the distance from one point on a wave to the corresponding point on the next wave
Define the term time period
the time needed to make one complete wave or vibration, measured in seconds
What is a wave?
(a disturbance) that transfers energy and information without transferring matter
State the relationship between speed, frequency and wavelength
Wave Speed = Frequency x Wavelength
v = f × λ
State the relationship between frequency and time period
Frequency = 1 / Time Period
f = 1/T
What is the doppler effect ?
the change in frequency caused by the relative movement of the source of the waves or the observer
( wavefronts squash or stretch, changing wavelength and frequency )
What are some similarities between all waves ?
all waves can be reflected and refracted
all waves transfer energy and information without transferring matter
What spectrum is light in ?
Electromagnetic Spectrum
What properties are shared by EM waves?
all EM waves travel at the same speed in free space
State the order of the EM spectrum in terms of decreasing wavelength ?
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible light
ultraviolet
x-rays
gamma rays
State the order of the EM spectrum in terms of increasing frequency ?
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible light
ultraviolet
x-rays
gamma rays
What are the uses of radio waves?
broadcasting and communications
What are the uses of microwaves?
cooking and satellite transmissions
What are the uses of infrared waves?
heaters and night-vision equipment
What are the uses of visible light ?
optical fibres and photography
What are the uses of ultraviolet ?
fluorescent lamps
What are the uses of x-rays ?
Observing the internal structure of objects and materials and medical applications (medical imaging and treatments)
What are the uses of gamma rays?
Sterilising food and medical equipment
What are the dangers of microwaves and how can we prevent this?
internal heating of body tissue
Microwave ovens have a metal grill over the door which reflects back microwaves into the oven to protect users
What are the dangers of infrared waves and how can we prevent this?
skin burns
take care when using sources of infrared waves, e.g. move heater away from body
What are the dangers of ultraviolet waves and how can we prevent this?
damage to surface cells ( sunburn) blindness
wear sun-cream, stay in shade
wear UV absorbing sunglasses
don't use tanning beds for too long
What are the dangers of gamma rays and how can we prevent this?
can cause cancer and cell mutations
wear photographic film badges , if they turn dark when developed a person has too much radiation and must stop working/ being around them
What are the properties of light waves?
transverse waves that can be reflected and refracted
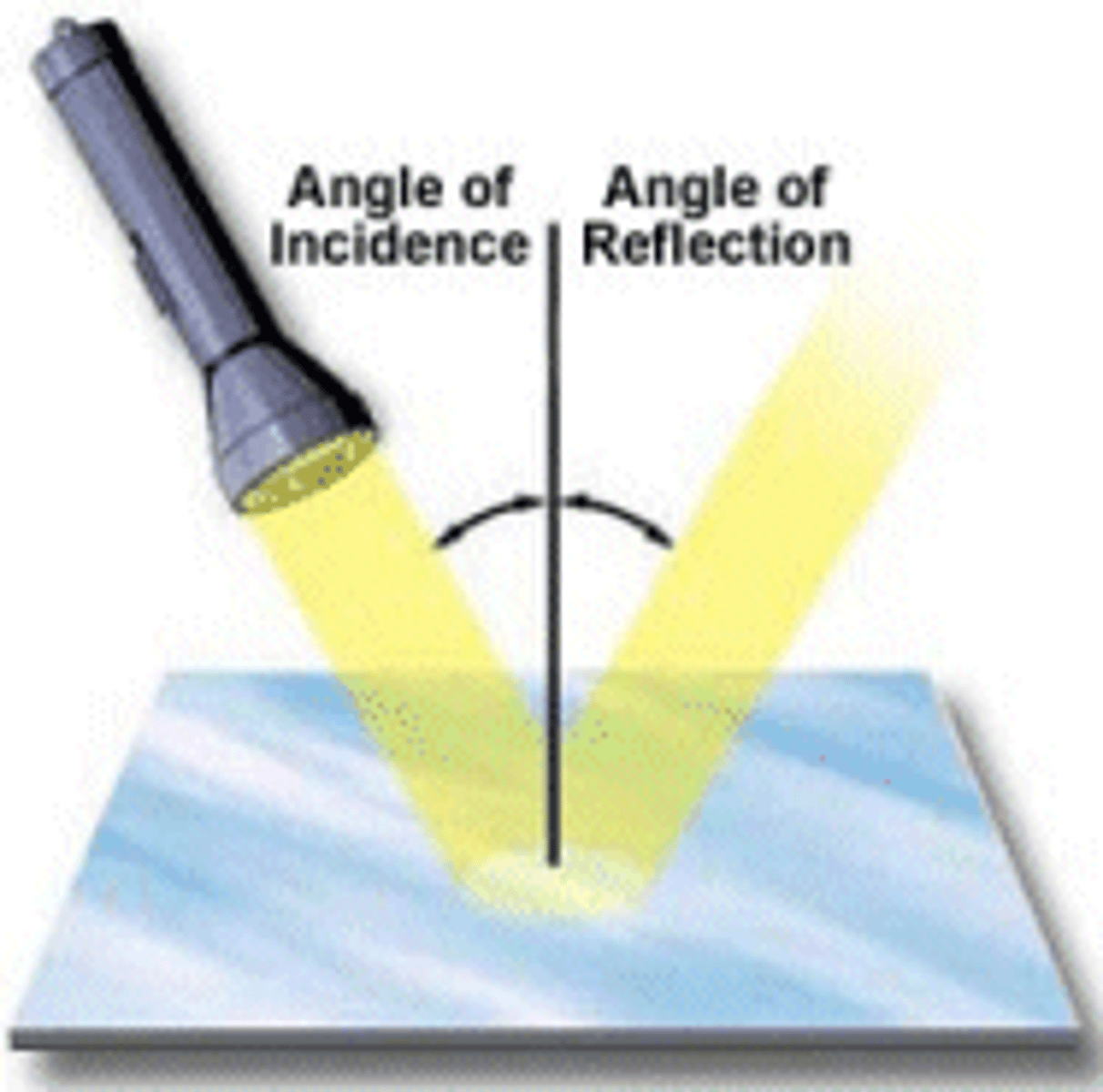
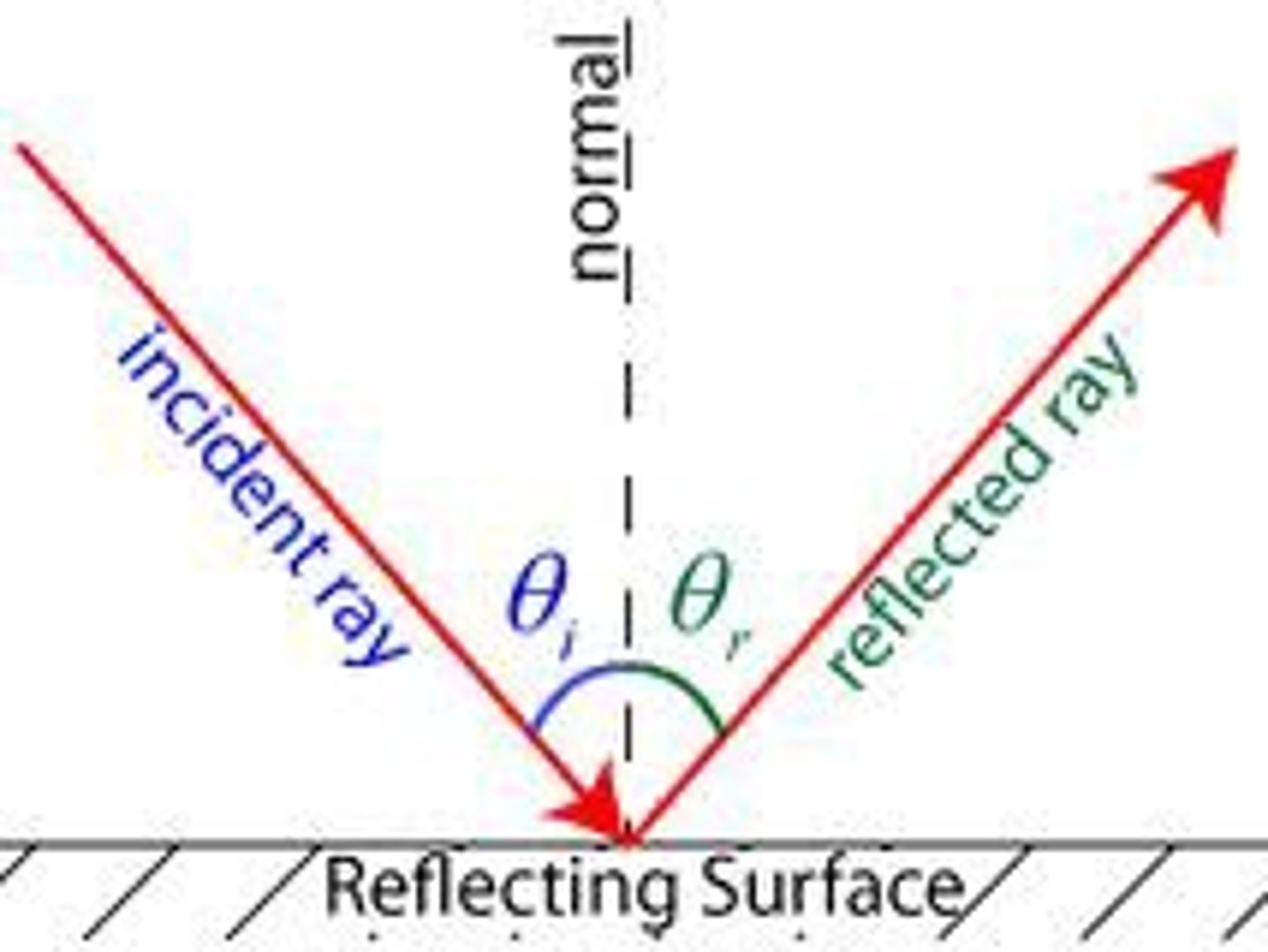
How do you use the law of reflection ?
the law of reflection states that the angle of incidence = the angle of reflection
so when given one of these angles you can find the other
How do you draw ray diagrams of reflection and refraction ?
you draw arrows in the direction which light travels
whenever light changes direction/ goes through a material draw a normal at 90 degrees
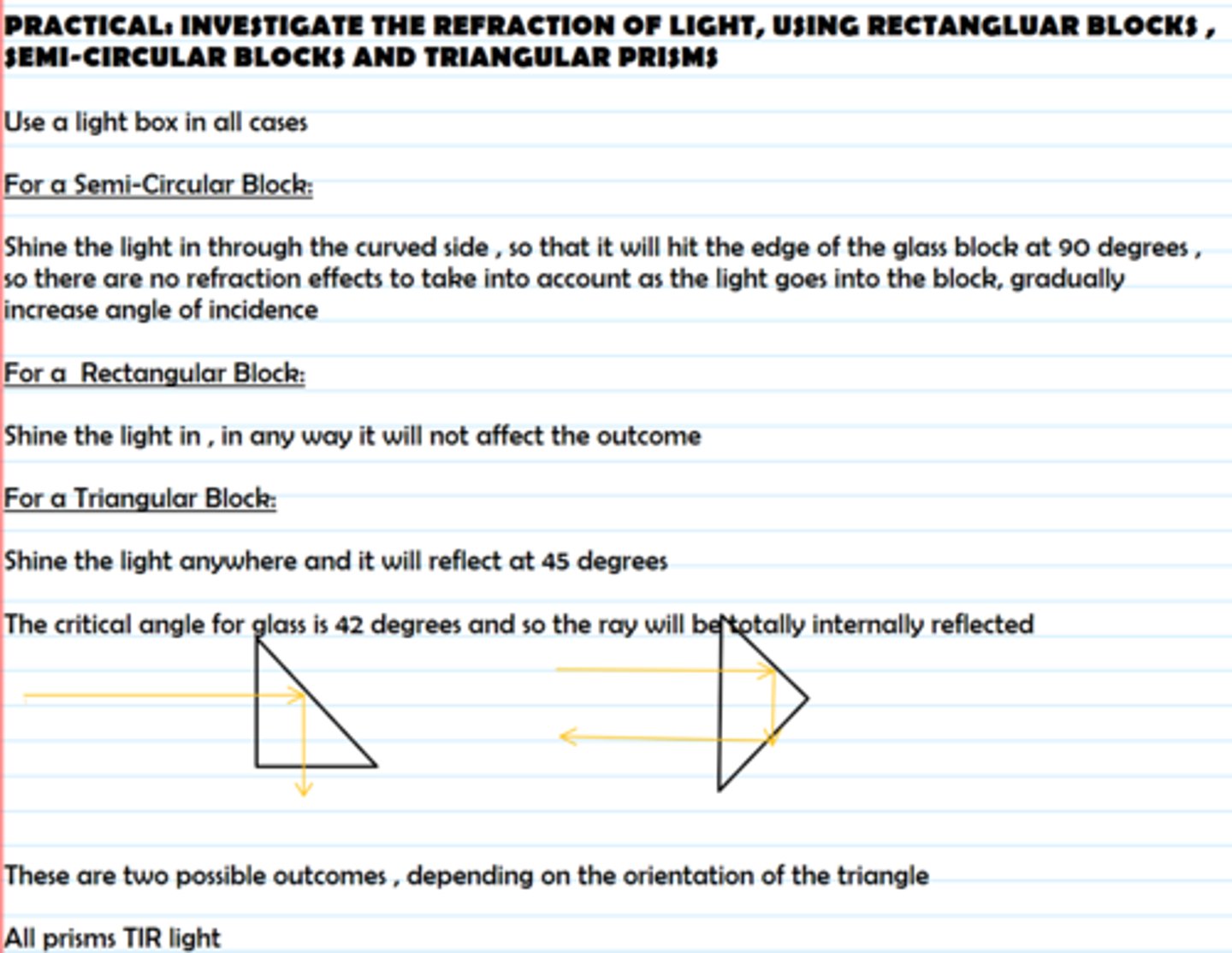
Practical: investigate the refraction of light, using rectangular blocks, semi-circular blocks and triangular prisms
state the relationship between , refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction
refractive index = (sin angle of incidence ) / (sin angle of refraction)
Practical: investigate the refractive index of glass, using a glass block

How can total internal reflection be used to transmit information in optical fibres and prisms ?
thin glass fibres are bent so that the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
so when light his the fibre TIR will occur and no light will be refracted until it reaches the end of the optical fibre
What is total internal reflection ?

Define the term critical angle
the smallest possible angle of incidence at which light rays are totally internally reflected
State the relationship between critical angle and refractive index
sin critical angle = 1 / refractive index
sin c = 1/n
What are the properties of sound waves ?
longitudinal waves that can be reflected and refracted
What is the range of frequency for human hearing ?
20-20,000 Hz
Practical: investigate the speed of sound in air

How can an oscilloscope and microphone be used to display a sound waves ?
a microphone is connected to an oscilloscope
the microphone converts sound energy into electrical energy
the oscilloscope displays the patterns of sound waves
Practical: investigate the frequency of a sound wave using an oscilloscope
to measure the frequency of a sound wave:
count how may squares across from one point on the first wave to the corresponding point on the next wave
multiply this number by the time base to get time period
then divide the time period by 1 to get frequency
How is the pitch of a sound related to its frequency of vibration of the source?
the pitch of a sound is directly proportional to the frequency
the higher the frequency the higher the pitch
How is the loudness of a sound related to the amplitude of vibration of the source ?
the loudness of a sound is directly proportional to the amplitude
the higher the amplitude the higher the volume/loudness