Molecular and Cell Biology Lecture 13
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What does the basigin gene code for?
2 isoforms
both isoforms are ___________
transmembrane glycoproteins
What are isoforms?
protein variants
What are transmembrane glycoproteins?
embedded proteins that extend from the inner to the outer surfaces of the plasma membrane
What are glycoproteins?
protein that is attached to a carbohydrate
What are cell adhesion molecules?
proteins embedded in the plasma membrane that help cells stick to each other and to the surrounding extracellular matrix
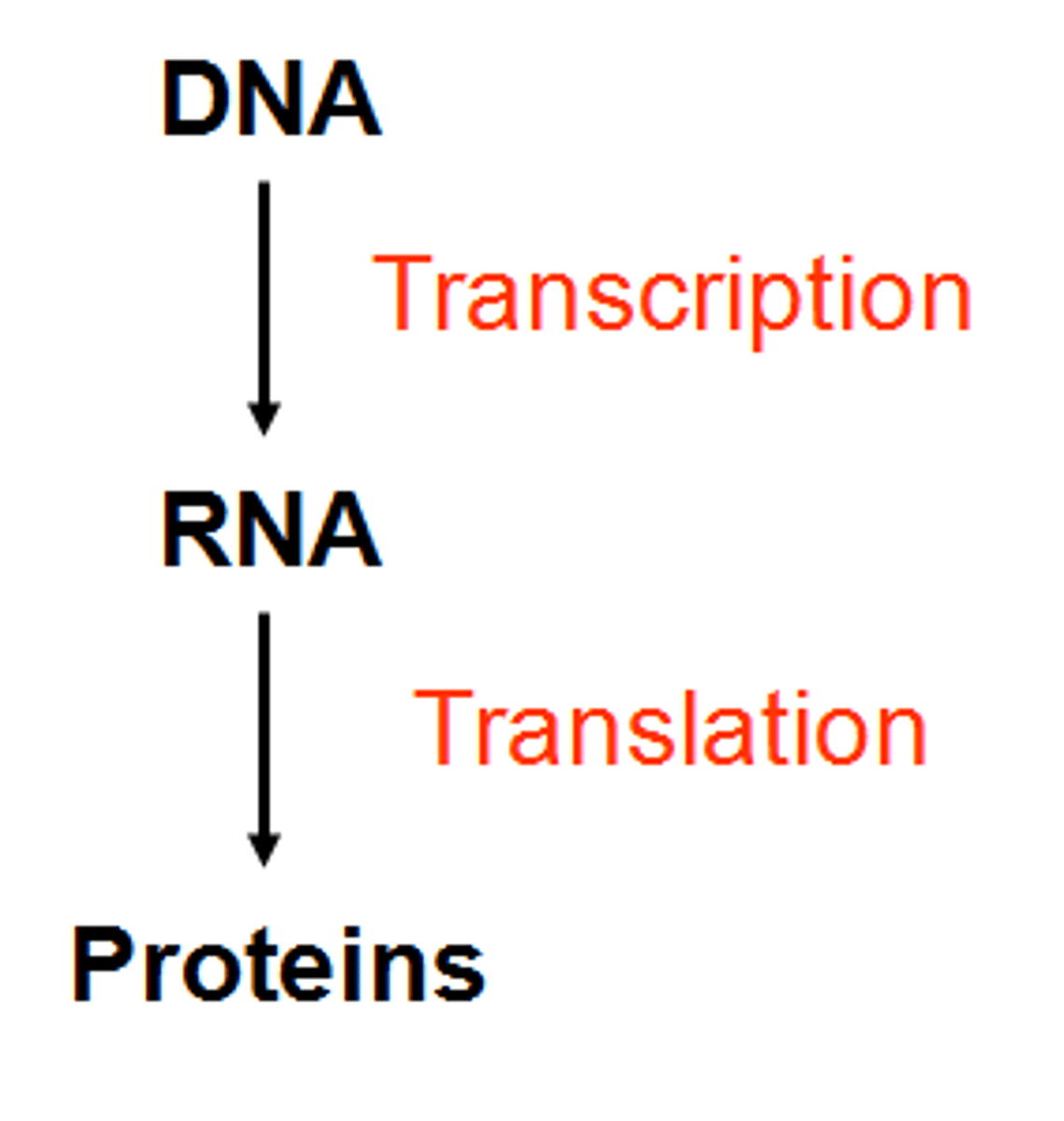
What is the order of the central dogma (flow of genetic information)?
Genes are made of DNA, DNA is transcribed into mRNA, mRNA is translated into protein.
Transcription
process through which mRNA forms on a template of DNA
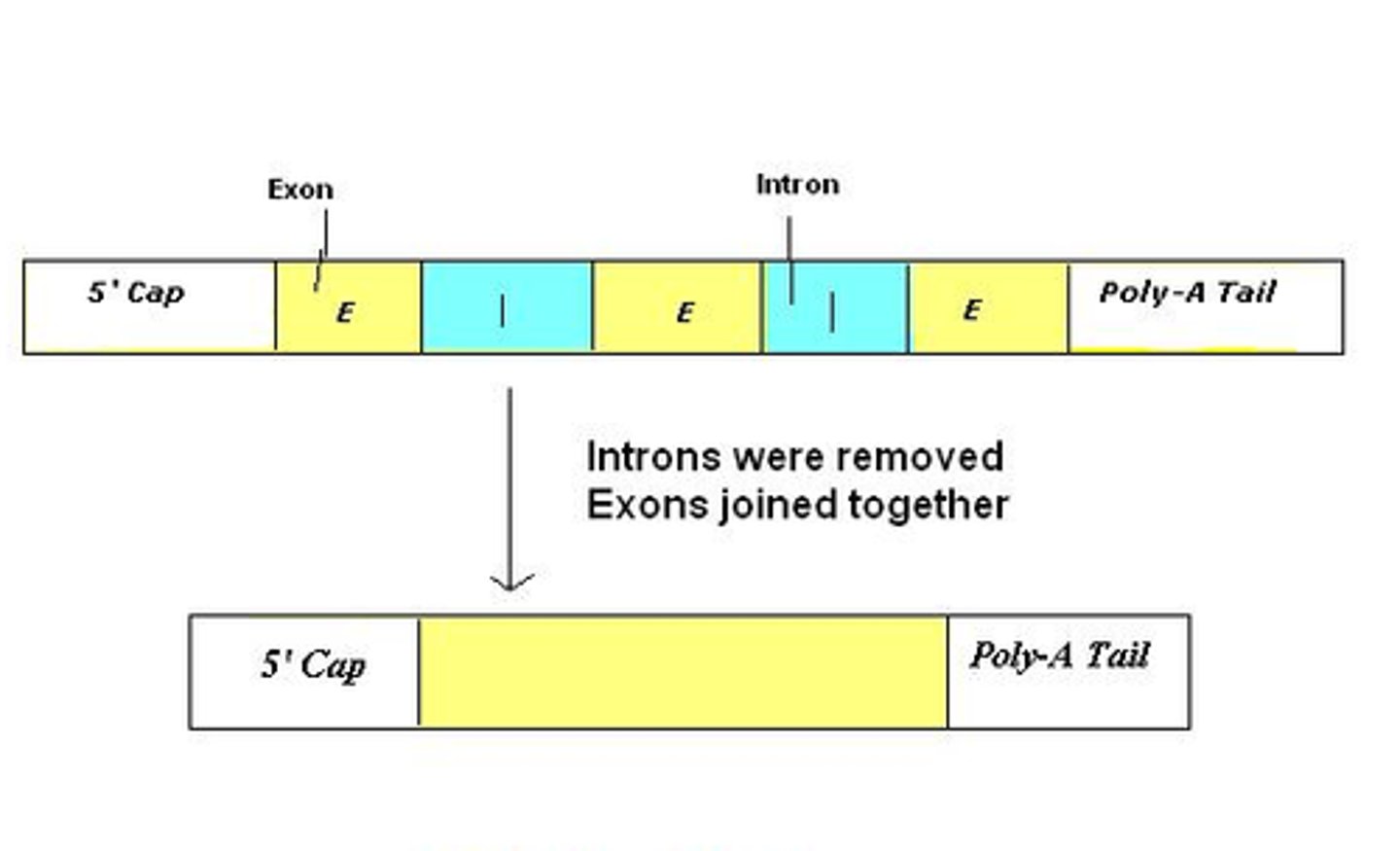
Exon
sequence present in protein-coding mRNA after completion of splicing
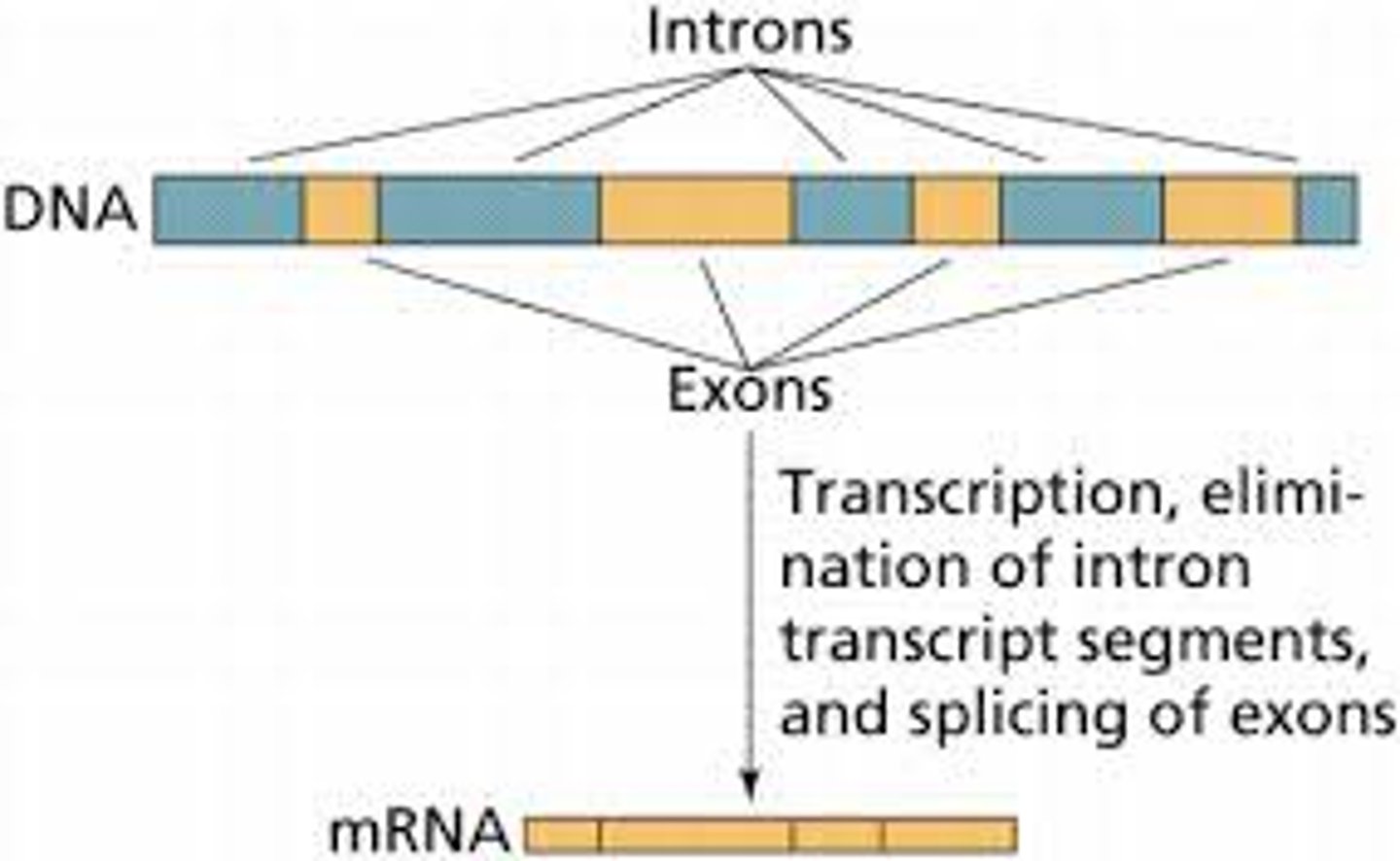
Intron
non-protein-coding intervening sequences that are spliced from mRNA during RNA processing
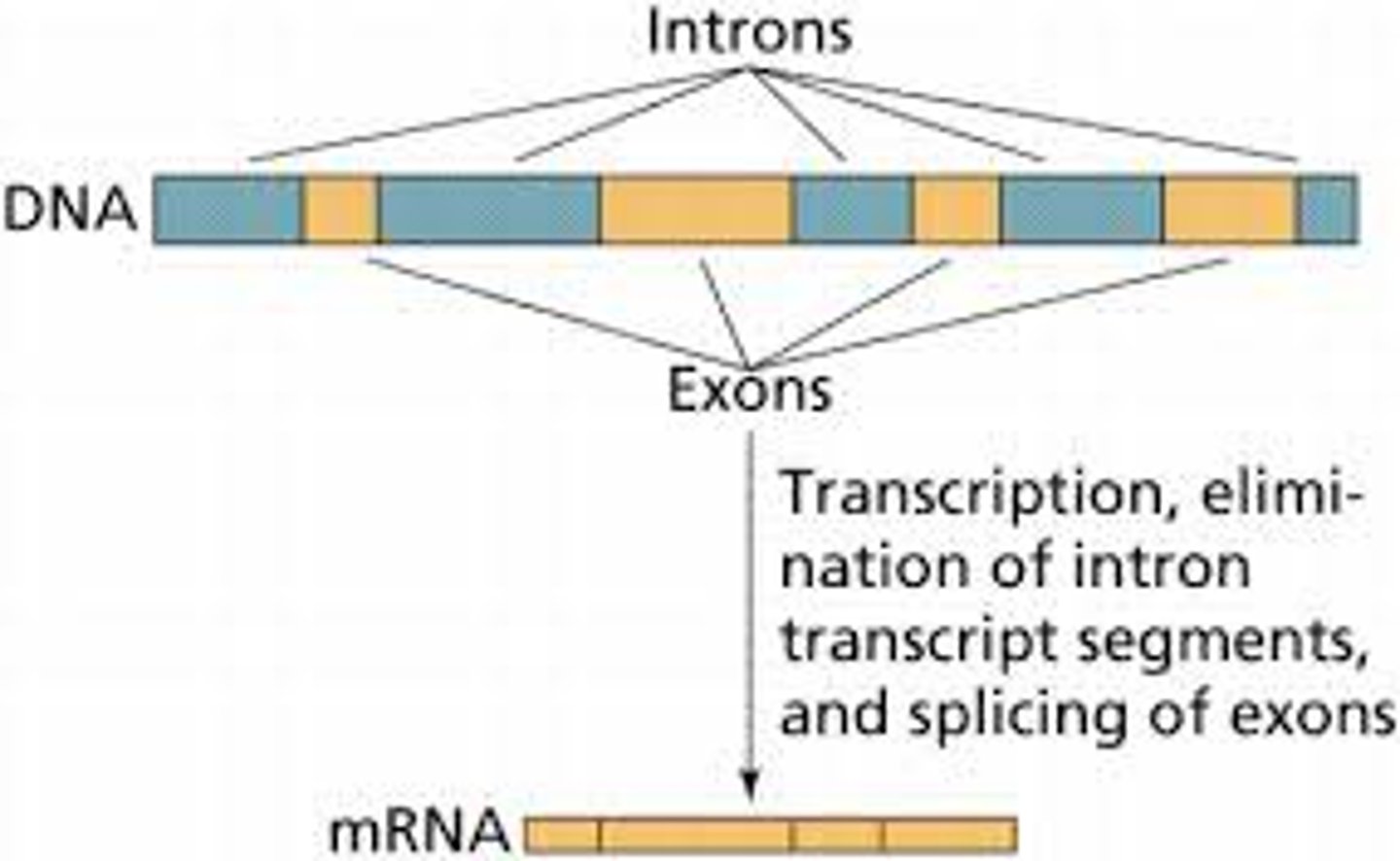
Splicing
the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons in a pre-mRNA
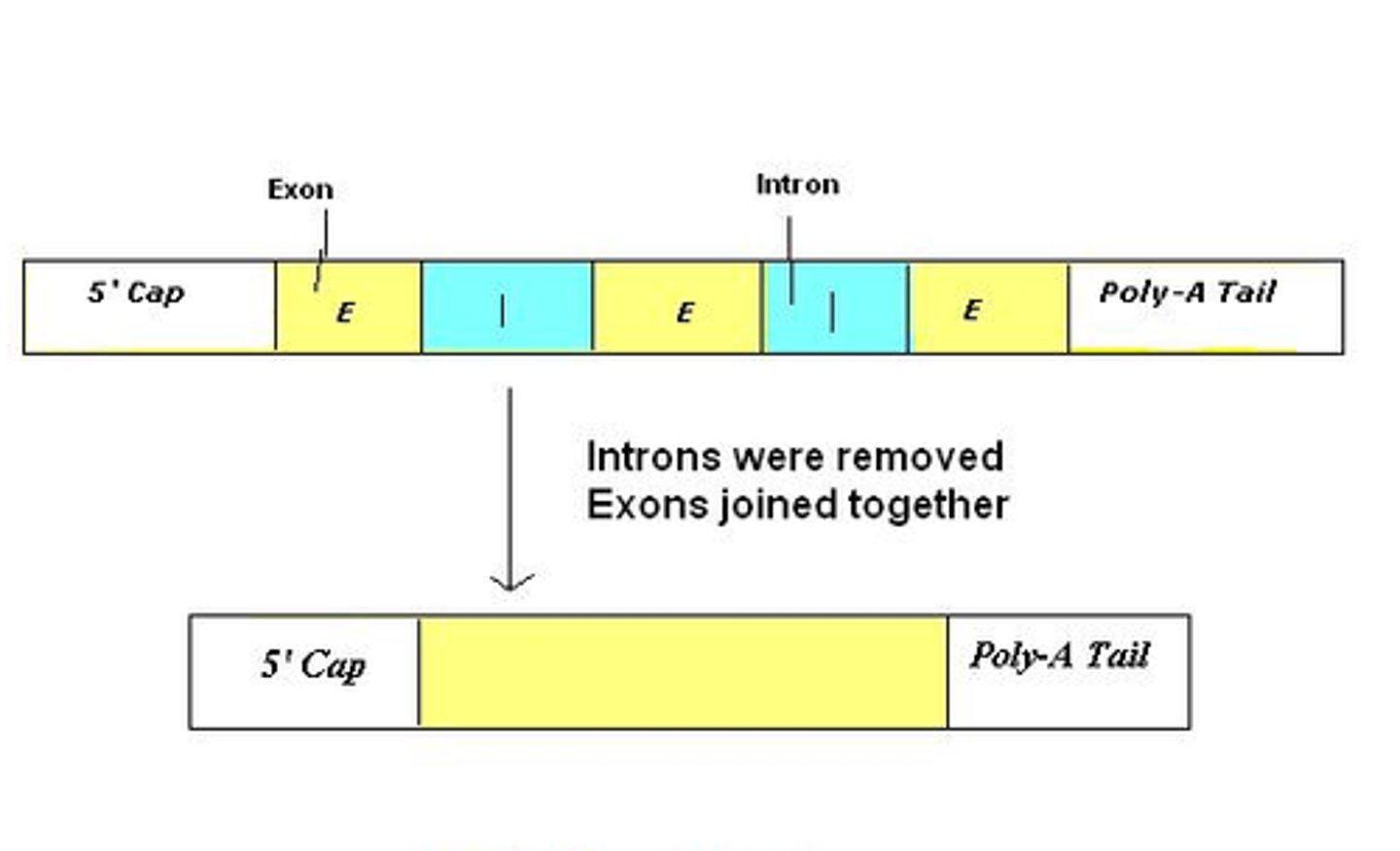
What 2 things are added to form mature mRNA?
5' guanine cap and 3' poly-A tail
What is a 5' guanine cap?
A modified guanine nucleotide that attaches to the 5' end of the pre-mRNA
What is a 3' poly-A tail?
A long chain of adenine nucleotides that is attached to the 3' end of the pre-mRNA
What is translation?
process through which RNA directs the protein's formation
Proteins are made of _________________
polypeptide chains
Polypeptide chains are made of _________
amino acids
A ______________ is a covalent bond that connects adjacent amino acids in a polypeptide
peptide bond
In their structure, each amino acid has...
An amino group, carboxyl group, and central carbon
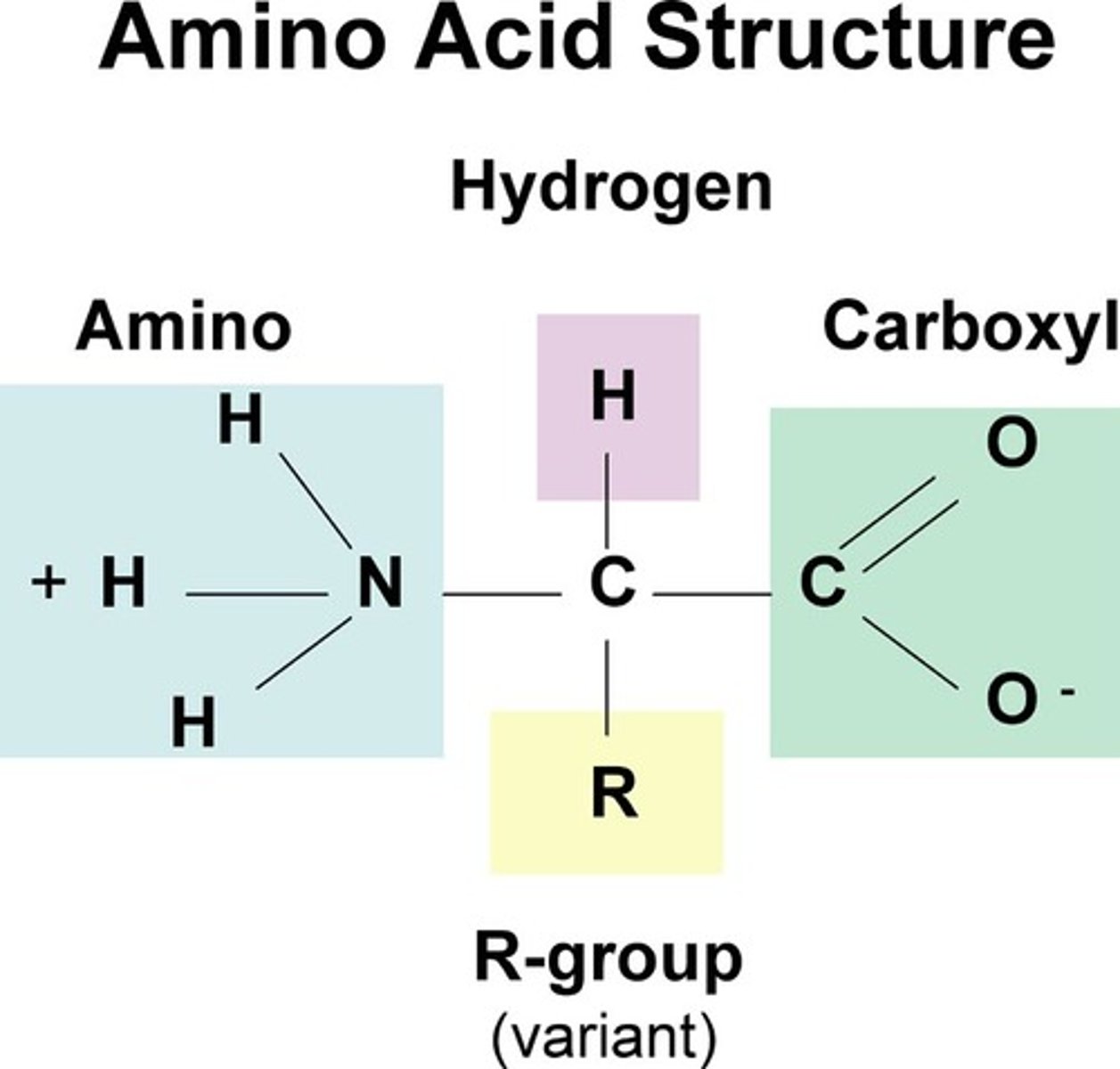
peptide bonds form between two ______________
amino acids
how are peptide bonds formed? (what type of rxn)
dehydration reaction
what specific groups between amino acids are peptide bonds formed by?
carboxyl group and amino group
polypeptide
many peptide bonds
what end of the amino acid is N-terminus?
amino end
what end of the amino acid is C-terminus?
carboxyl end
Where is N-terminus positioned?
front
Where is C-terminus positioned?
end
Each _______ of an mRNA molecule "codes" for an amino acid or Stop
codon
what are three consecutive nucleotides in mRNA that specify the insertion of an amino acid or the release of a polypeptide chain during translation?
codons
steps of translation (in order)
initiation, elongation, termination
what happens during initiation
initiation complex forms
what happens during elongation
polypeptide is translated from mRNA
what happens during termination
ribosome finds stop codon and polypeptide is released
during which step is polypeptide synthesized?
elongation
__________ synthesizes polypeptides
ribosomes
what are the subunits during elongation, composed of?
proteins and ribosomal RNA
1. Charged tRNA enters the A-site of the ribosome, matching its anticodon to the mRNA codon.
2. peptide bond forms between the amino acid in the A-site and the growing polypeptide in the P-site.
3. The polypeptide chain transfers to the tRNA in the A-site.
4. The ribosome shifts 3 nucleotides (1 codon) along the mRNA in the 3' direction.
5. The now uncharged tRNA moves from the P-site to the E-site and exits the ribosome.
6. The tRNA carrying the polypeptide moves from the A-site to the P-site.
7. A new charged tRNA w/ the correct anticodon enters the A-site, and the cycle repeats.
steps of elongation
______________ charged w/ an amino acid migrates to ribosome
transfer RNA (tRNA)
tRNA enters the _______
A-site
_________ of tRNA is complementary to the codon of mRNA
anticodon
uncharged tRNA moves from _______ to ______ and exits ribosome
P-site, E-site
tRNA attached to polypeptide moves from _______ to _______
A-site, P-site
next tRNA w/ correct anticodon binds to codon in ______.
A-site
a variant of a protein that differs slightly from another version
isoform
isoforms can arise from _______ __________
alternative splicing
different exons are combined to create distinct proteins from the same gene
alternative splicing
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
membranous cell organelle outside nucleus
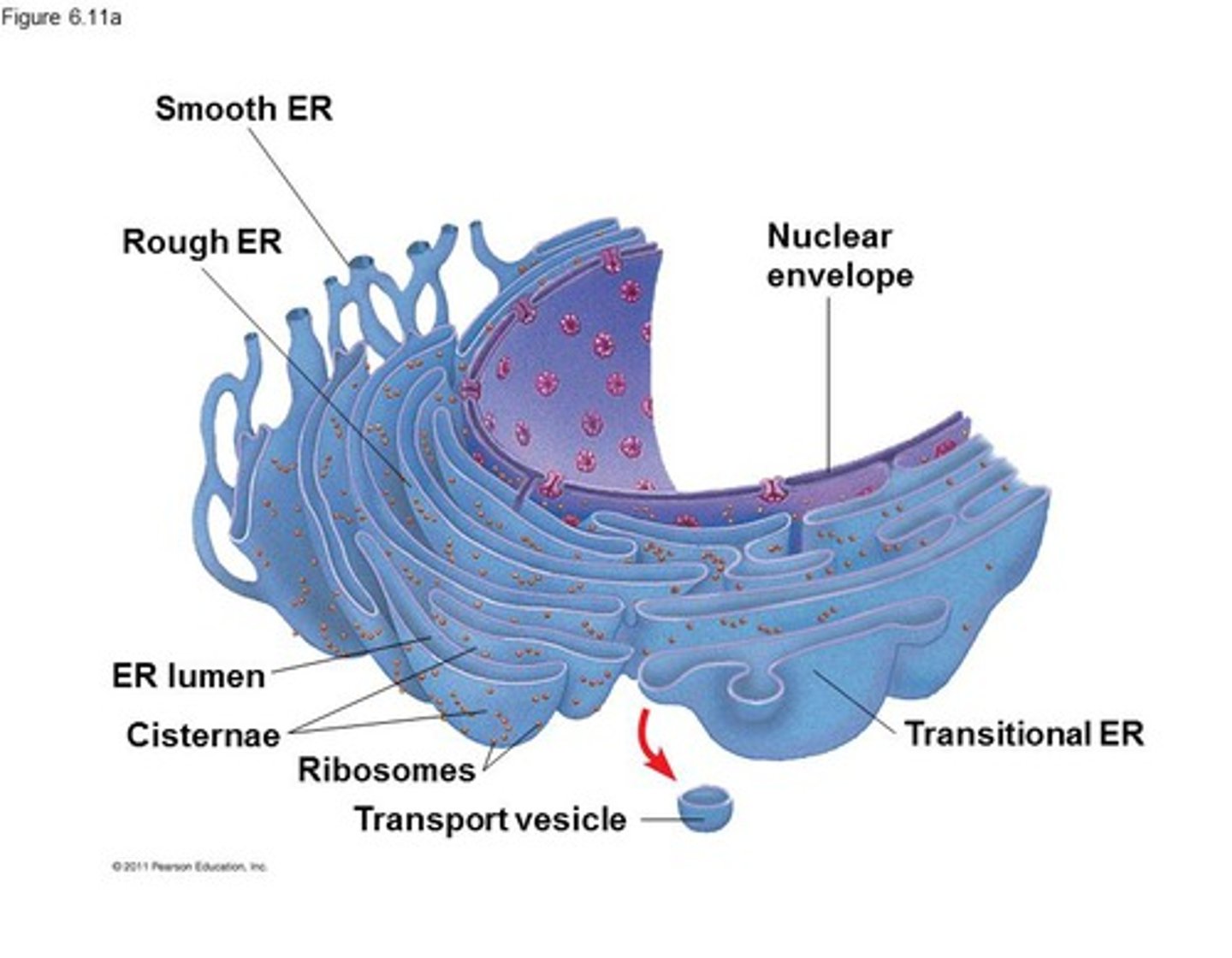
rough ER
ribosome embedded in ER membrane
secretory and membrane bound proteins synthesized at _________
Rough ER
Other proteins (not secretary and membrane bound proteins) are synthesized by freely floating __________ in the cytoplasm.
ribosomes
vesicles carrying proteins bud from the _______________________________
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
proteins are sorted, tagged with/ carbohydrates (____________), and packaged into ____________ at the _______________
glycosylation, transport vesicles, Golgi apparatus
a transport vesicle from the Golgi apparatus delivers a protein to ______________________________
the plasma membrane
a phospholipid bilayer w/ embedded proteins
plasma membrane
embedded proteins that extend from the inner to the outer surfaces of the plasma membrane
transmembrane proteins (or integral proteins)
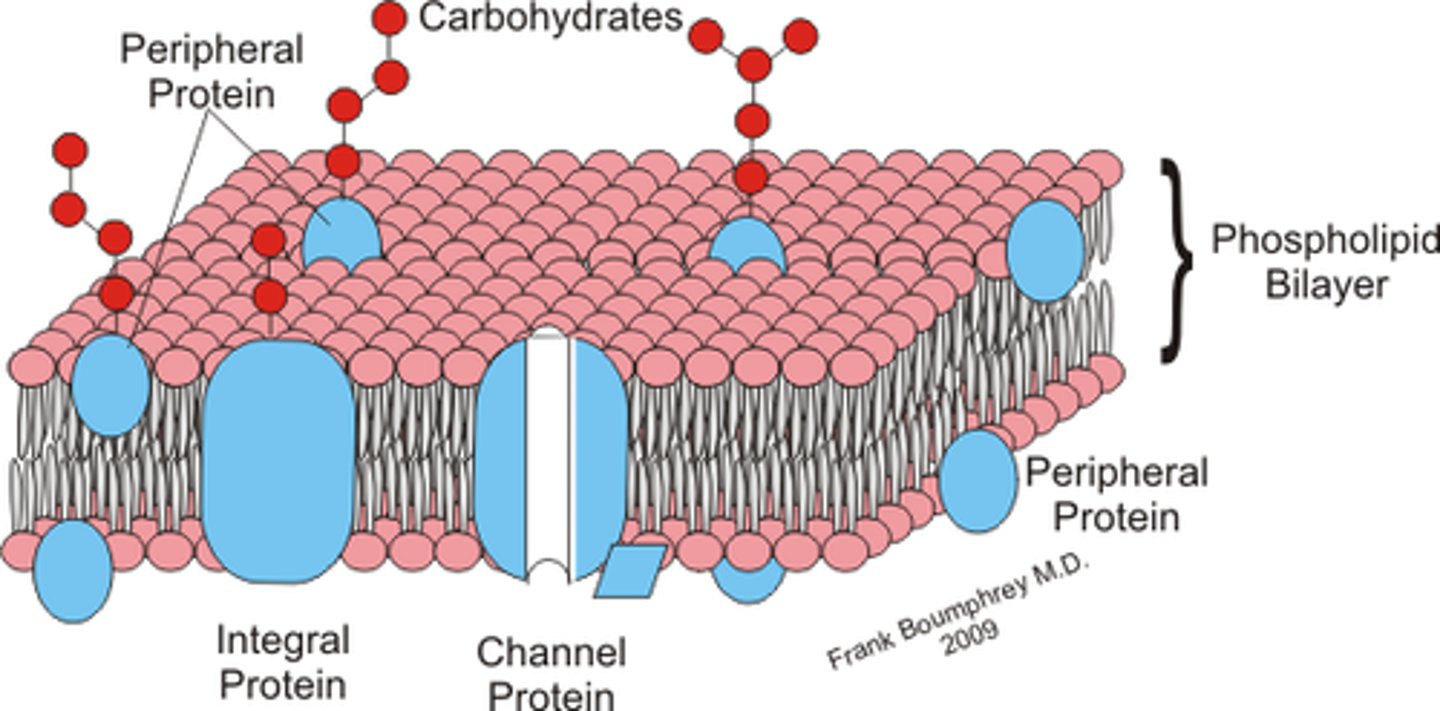
glycoprotein
a protein that is attached to a carbohydrate
cell adhesion molecule
proteins that help cells stick to each other and to the surrounding extracellular matrix
cell adhesion molecules are embedded in the __________________
plasma membrane
homotypic binding
between two of the same molecule
heterotypic binding
between two different molecules
the basigin gene ______ for ______ (how many) ________.
codes, 2, isoforms
both isoforms are ______________________
transmembrane glycoproteins
both isoforms function as ________________
cell-adhesion molecules