marine biology exam 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Plankton
organisms that live in the water column and are too small to swim counter to the current
Nematocysts
The stinging cells in cnidarians
Holoplankton
Spend their entire life as plankton
Phytoplankton
plant plankton, rely on light to produce food,
Meroplankton
Part of their life is spent as plankton
Zooplankton
animal plankton
Cyanobacteria
blue-green algae, most abundant photosynthetic organism
Briefly describe diatom reproduction
Reproduce asexually by binary fission, diatoms shrink through each division, eventually once the diatom gets small enough they reproduce sexually
Briefly describe nitrogen fixation
N2 is captured through nitrogen-fixing bacteria, blue-green algae, creating ammonia (NH3), which gets converted to nitrite NO2, to nitrate NO3, n03 can then get converted by denitrifying bacteria
Compare and contrast diatoms and dinoflagellates
They both use asexual and sexual reproduction, dinoflagellates can swim, diatoms cannot, diatoms are mostly autotrophic, dinoflagellates are can be heterotrophic or mixotrophic. Diatoms suffer a size reduction when asexually reproducing, dinoflagella do not.
Briefly explain how algal blooms occur and why we care.
Algal blooms occur when there is an excess of nutrients in an ecosystem, we care because some of these can be harmful to humans, or can cause eutrophication, anoxia, and subsequently mass killings of fish
Compare and contrast cnidarians and ctenophores
- Cnidarians - include true jellies and siphonophores like the Portuguese man of war, use nematocysts (stinging cells) to capture prey
Compare and contrast cnidarians and ctenophores
Ctenophores - comb jellies, do not use nematocysts, feed on smaller zooplankton, invertebrate larvae (microcarnivores), bioluminescent
Briefly describe the importance of crustacean zooplankton
Crustacean zooplankton serve as a crucial food source for much larger organisms such as baleen whales, higher trophic level animals consuming such a low trophic levels allows for high energy transfer and for organism to grow very large
Nekton
Organisms that live in the water column and can swim against the water currents
Pinniped
Animals including, seals, sea lions, walruses that lack the thick blubber of cetaceans but have hair
Otolith
Part of the fish ear that allows it to hear and sense vibrations, know where it is (inner ear, saccule, and utricle), and what it is made out of (calcium carbonate and water)
Mustelidae
Sea otters
Lateral line
External mechanoreception, can sense changes in pressure and vibrations
Sirenian
Sea cows, dugongs, manatees, sluggish and herbivorous, lack blubber making then susceptible to cold snaps
Describe the Functional-Morphology Plane for Locomotion in fishes (distinguish between acceleration, cruising, and maneuvering specialists)
- Acceleration specialist - minimal resistance - fins towards the back, lots of fast-twitch white muscle, lie and wait predator (pike, barracuda)
Describe the Functional-Morphology Plane for Locomotion in fishes (distinguish between acceleration, cruising, and maneuvering specialists)
Cruising - fast swimming, minimize drag and friction (move through the water as quickly as possibly) (tuna)
Describe the Functional-Morphology Plane for Locomotion in fishes (distinguish between acceleration, cruising, and maneuvering specialists)
Maneuvering - fish with a balance of fins around the center of the body, think reef fish made for short quick turns (butterfly fish)
What is the difference in swim bladder rete mirable lengths between shallow and deep sea fish?
Deep sea fish have much longer rete mirable
What are the 3 different feeding mechanisms fish use?
Ram feeding - fish overtakes prey by ramming water through its open mouth
Suction feeding - creates suction through rapid expansion of the buccal pouch creating a negative pressure that sucks the food back in
Manipulation - behaviors like biting, scraping, grasping
Biting - think sharks (catastrophic), cookie-cutter sharks
Why do fish need to hear?
To avoid predators (cetaceans use sound to find fish, if they can hear they can avoid)\
To communicate - ex. haddock use sound to communicate during mating
Water is effective at transmitting sound - sound is useful as it is not obscured by darkness or murkiness of water
What is the biggest difference between Odontoceti and Mysticeti?
Odontoceti have teeth, and Mysticeti use baleen
Describe some key features of seabirds (i.e migration is common)
Often colonial breeders - crowded breeding sites
Often monogamous
Courtship involves elaborate displays
Long distance migration between feeding and breeding sites are common
What are the 2 problems with diving in marine mammals? How do marine mammals achieve such long dives (Name at least 2-3 reasons why). (Long Answer)
Must breathe at the surfacer
Need enough oxygen for long dives
Solutions:
bradycardia (slowing down their heart beat rate)
increased blood cell concentration
increased volume of arteries and veins
Describe some key features of the sea turtle life cycle (LA)
hatch on the same beach their mother hatched on, they then race towards the ocean using light and magnetic field to guide them towards the ocean, but many don't make it.
Fertilization happens at sea (females can store and reject sperm)
Adults use the magnetic field to find their way back (their migration)
Only females return to shore
Diurnal vertical migration
zooplankton rise to shallow water during night and sink to deeper water during the day
Counterillumination
use of bioluminescence on an organism's ventral side to match their background
Predation hypothesis
Food is more energy plentiful at the surface, and there are fewer predators at night, meaning they can maximize their energy usage
Bioluminescence
organisms use either a luciferin-luciferase system or a photoprotein calcium system to produce light often as a defense mechanism against predators
What are some of the defenses plankton utilize?
Large, elaborate spines, transparent bodies, toxic substances, bioluminescence
What are some of the benefits of schooling?
Protection against predators (lots of eyes, hard time attacking individual fish, reduction of drag
Describe what happens during the diurnal vertical migration. (LA)
Zooplankton ascend during the night and descend during the day back to darkness
Describe one of the hypotheses used to describe the process (LA)
The predation hypothesis states that during the night visual predators are unable to see the zooplankton, they sink when the sun rises and predators become more active. They rise to the surface during the night as there is more prey there for them. This means they can maximize food intake and minimize risk of getting caught
Limiting nutrients
Often phosphorous or nitrogen, these functionally control the amount of primary producer growth can occur in an ecosystem
Briefly describe the nitrogen cycle
Ammonia is excreted by fish in the form of NH4, this is either taken up by plants or converted to no2 and then no3 and can then be taken up by plants again or can be turned back into N2 by denitrifying bacteria
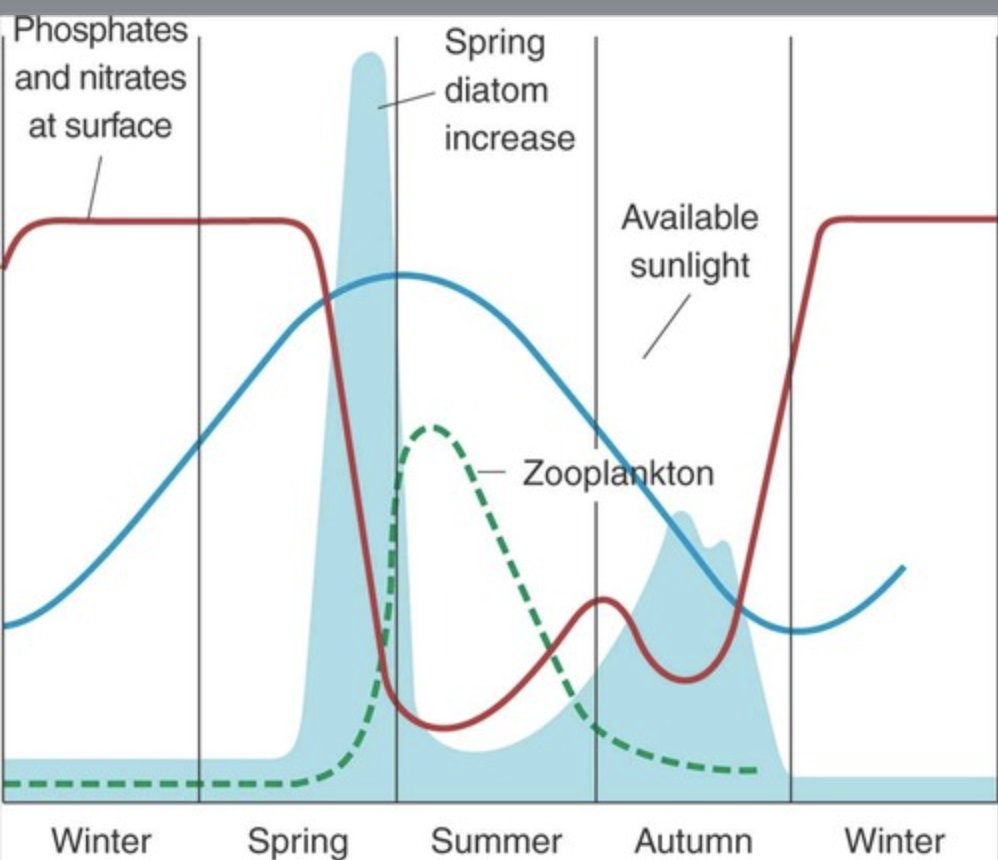
Be able to describe what is happening in Figure 11.1 (LA)
During the winter, there is little biological activity, which allows for phosphates and nitrates to accumulate, as sunlight heats up the water and nutrient availability is at a high, the diatoms feast and cause a drastic increase in their concentration. Diatoms act as the food source for zooplankton; these zooplankton act as food for other organisms. As diatoms consume the nutrients, nutrient levels go down, as zooplankton consume diatoms and diatoms' food sources go down, the diatom population decreases. The water column is also stable which means diatoms sink as they are more dense than water.
Which nutrient is generally thought to be the most limiting, and what are some sources of it? (LA)
Nitrogen fixation occurs when N2 is captured by nitrogen-fixing bacteria like blue-green algae; this gets converted by NH3, which is converted to No2, and then NO#, which gets converted by denitrifying bacteria or is uptaken by plants. Another way nitrogen is introduced is through ammonia excretion.
What would happen if more of this nutrient were added to the ecosystem? What type of ecological regulation would this be an example of? (LA)
Algal blooms would likley result (ie increase in primary production), this is an example of bottom up regulation.
Biomass
The mass of living material present at any time
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
Total carbon fixed during photosynthesis
Productivity (Primary & Secondary)
Primary - productivity due to photosynthesis, Secondary - productivity due to consumers of primary producers
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
Total primary fixated during photosynthesis minus (-) what is respired
Food chain
Linear sequence showing which organism consumes which other organisms, making a series of trophic levels
Food web
more complex diagram showing feeding relationships between organisms, not restricted by linear hierarchy (a composition of food chains)
Why is energy lost from one trophic level to the next (3 reasons)
Some material is not eaten
Not all food eaten is converted with 100% efficiency
Metabolic costs are a loss
Describe 3 reasons for the differences in geographic variation of productivity (LA)
One reason is primary productivity for example is the area a upwelling or gyre, another is the efficiency of the food chain, and a third is the number of trophic levels
Prokaryotes
Those that do not have a nucleus, lack membrane-bound organelles, and a nuclear membrane
Eukaryotes
Have a nucleus, have membrane bound organelles, are often multicellular, and are found in plants and animals
Archaea
Extremophiles, have a distinct lipid-cell membrance, unique ribosomal RNA
Stipe
The stem of seaweed
Bacteria
prokaryotes, most numerous organisms in the ocean, reproduce through fission, some are heterotrophic, others are autotrophic
Holdfast
the roots of seaweed
Cyanobacteria
photosynthetic bacteria, the most abundant photosynthetic organism
Pneumatocysts
the air-filled bulbs in seaweed that bring fronds closer to the surface so it caan come in the most possible contact with sunlight -stay near the surface for photosynthesis
Rhizomes
roots that act as offshoots for new plants to grow off of
What are the primary characteristics of seaweeds? How do they differ from true plants? Be able to identify the key parts.
Sea weeds have a holdfast, a stipe, and blades. While these traits are analogous to roots, a stem and leaves they are not the same. Sea weeds also have pnuematocysts, these are air bubbles used to help keep the leaves towards the surface to maximize photosynthesis.
How do seagrasses differ from seaweeds?
Seagrasses have the typical characteristics of land plants, such as flowers, roots, stems, where as sea weeds don't flower and only reproduce through.
Be able to distinguish the different types of bacterial metabolism (LA)
Autotrophic- Need light and inorganic nutrients (phosphate, nitrate)
Photosynthetic- light energy, typically from sunlight, is converted into chemical energy, primarily in the form of sugars, by organisms like plants, algae, and cyanobacteria
Chemoautotrophic- Oxidize or reduce substances to obtain energy
Heterotrophic- organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon
Aerobic- use oxygen to break down organic matter
Anaerobic- use fermentation to obtain energy in the absence of oxygen.
Match seaweeds with examples (i.e. brown seaweed = kelp; coralline algae = red) (LA)
Brown (Phaeophyta) - dominate low intertidal, shallow subtidal areas, include the largest seaweeds (kelp- the fastest growing seaweeds), usually more morphologically differentiated than green seaweeds (ex. Laminaria, fucus)
Red (Rhodophyta) - appear red because of phycoerythrin, this is the most diverse group ex corallina, carragenan
Green (Chlorophyta) - Use Photosynthetic pigments similar to higher plants that store starch ex. Ulva, Codium
Brown Seaweed
Phaeophyta, dominate low intertidal, shallow subtidal areas, include the largest seaweeds (kelp- the fastest growing seaweeds), usually more morphologically differentiated than green seaweeds (ex. Laminaria, fucus)

Red Seaweed
Rhodophyta, appear red because of phycoerythrin, this is the most diverse group ex corallina, carragenan

Green Seaweed
Chlorophyta, Photosynthetic pigments similar to higher plants that store starch ex. Ulva, Codium
