Hypersensitivity reactions
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are the types of hypersensitivity reactions?
Type I, II, III, IV
What cell or antibody is involved with Type I hypersensitivity reactions?
IgE
What cell or antibody is involved with Type II hypersensitivity reactions?
IgG
What cell or antibody is involved with Type III hypersensitivity reactions?
Immune-complexes made up of different type of anti-bodies.
What cell or antibody is involved with Type IV hypersensitivity reactions?
T-cells
What are IgE receptors most effective?
When dealing with parasitic infections.
What leads to IgE antibody production?
Repeat exposure to allergens
Describe type 1 hypersensitivity reaction.
- Mast cells contain granules containing histamines in the cytoplasm as well IgE receptors on their surface.
- IgE antibodies bind to the IgE receptors however nothing will take place if the IgE antibodies are not exposed to allergens whilst attached to the mast cell.
- This activates of mast cells which leads to degranulation where histamine is released.
- The immediate hypersensitivity reaction/allergic reaction or a late phase reaction take place.
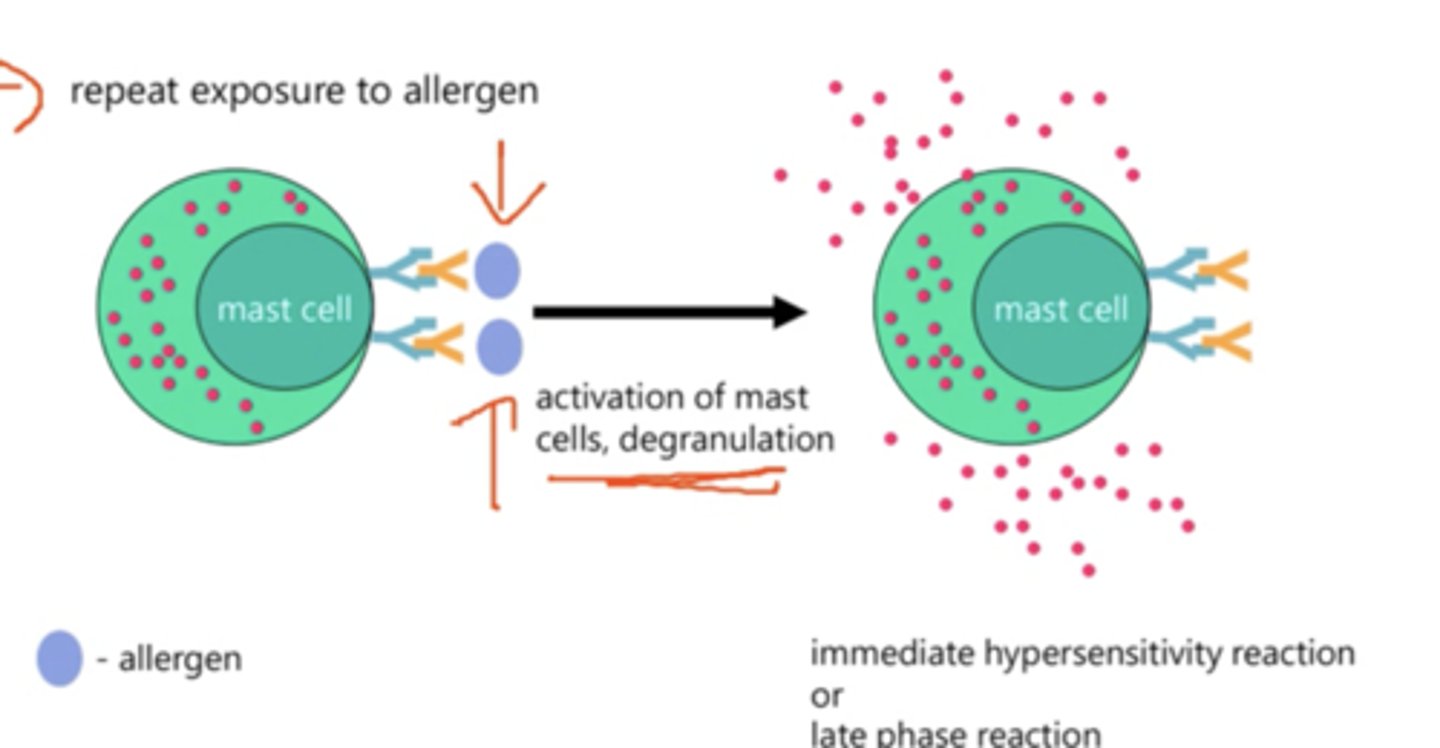
What does the effect of mast cells depend on?
The location of the mast cells
What is the cause of anaphylactic shocks?
Severe allergic reactions
What happens during an anaphylactic shock?
Lots of histamine is released from different parts of the body. Symptoms of anaphylactic shock can develop rapidly.
What are symptoms of anaphylactic shock?
- Respiratory symptoms, constriction of airways
- GI symptoms, abdominal pain
- Fluid can leak into alveoli causing pulmonary oedema
- Can lead to shock.
What are treatments of anaphylactic shock?
- Epinephrine should be injected immediately.
- Intravenous fluids can be provided which support the heart and the circulatory system.
- Antihistamines and corticosteroids can be used to reduce symptoms after epinephrine is used.
What are type IV hypersensitivity reactions?
- Delayed reaction., after 24-48 hours.
- T-cell mediated.
- Required primed antigen-specific T cells e.g., CD4+ and CD8+
Describe Type IV hypersensitivity reactions.
- Toxins from allergic material e.g., poison ivy, make contact with the skin.
- This causes cytokines and chemokines to be released from the skin into the blood.
- Memory T-cells, basophils and monocytes migrate into the tissue.
- APC's present the toxins to the T-cells which causes CD8+ T-cells to activate.
- CD8+ T-cells release IFN-γ which activate basophils and mast cells.
- Activated basophils and mast cells release proteases, TNF, Chemokines and vasodilators to produce the inflammatory response.
What type of receptors does histamine bind to?
H1, H2 and H4 receptors.
What is the effect of H1 receptors in the smooth muscle?
- Bronchoconstriction.
- Contraction of GI system.
What is the effect of H1 receptors in the endothelium?
- Vasodilation
- Increased capillary permeability leading to oedema.
What is the effect of H1 receptors in the sensory nerve endings?
Pain and itch
What is the effect of H2 receptors in the smooth muscle of blood vessels (only in large doses of histamine binding to them)?
Vasodilation
What is the effect of H4 receptors on immune active cells e.g., eosiniphils?
Chemotaxis
What is chemotaxis?
Movement of a cell in response to a chemical stimulus
How can the effect of histamine be reduced?
- Physiologic antagonists.
- Histamine release inhibitors.
- Histamine receptor antagonists (antihistamines).
What are physiologic antagonists for histamine?
Molecules which have opposite smooth muscle actions but act on different receptors are used to counteract histamine's effects. For example epinephrine.
What are histamine release inhibitors?
They reduce immunologic release of histamine from mast cells. For example:
- Mast cell stabilisers e.g., Cromolyn.
- Beta 2 adrenergic agonists
What are the types of histamine receptor antagonists/antihistamines?
First generation and second generation
What are 1st Gen histamine receptor antagonists/antishistamines?
- Can be used on allergic reactions and for motion sickness.
- Very lipofillic so can cross blood brain barrier.
- Short duration of action.
What are 2nd Gen histamine receptor antagonists/antishistamines?
- Can be used on allergic reactions.
- Not lipofillic so cannot cross blood brain barrier.
- Long duration of action.
What effects does being lipofillic have on 1st gen anti-histamines?
- They have lots of effects on the CNS such as causing a sedative effect.
- Also allows them to have an anticholinergic effect which has some side-effects.
- This allows them to effective motion-sickness drugs.
What effects do antihistamines have that are not related to H1 receptors?
- Anticholinergic effects
- Effect the CNS
Describe the anticholinergic effect of antihistamines.
- Many 1st gen antihistamines can inhibit responses to muscarinic receptors e.g., acetylcholine cannot work.
- Can lead to side effects of dry mouth, blurred vision and constipation.
Describe the effects of antihistamines on the CNS.
- Most 1st gen antihistamines have a sedative effect.
- They can have an excitatory effect rather than a sedative effect e.g., convulsions.
- Some 1st gen can prevent motion sickness.