UNIT 4 GUIDE: CENTRAL DOGMA AND THE CELL CYCLE
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
3’ end
Enzymes that replicate or transcribe DNA and RNA always add new nucleotides to this end
5’ end
It is the start of the strand in the context of how nucleic acids are synthesized and read.
Adenine (A)
A purine nucleotide that always pairs with thymine (T).
Thymine (T)
A pyrimidine nucleotide that always pairs with adenine (A).
Cytosine (C)
A pyrimidine nucleotide that always pairs with guanine (G).
Guanine (G)
A purine nucleotide that always pairs with cytosine (C).
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
a molecule that helps DNA turn genetic instructions into proteins. It acts as the "messenger" between DNA and the protein-building parts of your cells.
Uracil (U)
A pyrimidine nucleotide that is unique to RNA and replaces Thymine (T) found in DNA.
Transcription
Occurs in the cell’s nucleus. DNA stays safely in the nucleus, acting like an original blueprint that cannot leave the building. RNA acts as a messenger that copies the instructions from DNA. The result is a single-stranded RNA copy of DNA instructions, called mRNA. (DNA → RNA).
Translation
Occurs in the cell’s ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes read the mRNA instructions in groups of three letters called codons. Each codon matches one specific amino acid. Amino acids link together like beads on a string, forming a protein. Proteins carry out functions in your body. (RNA → Protein).
Semiconservative Model
The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each function as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand. Each new molecule has one original strand and one new strand.
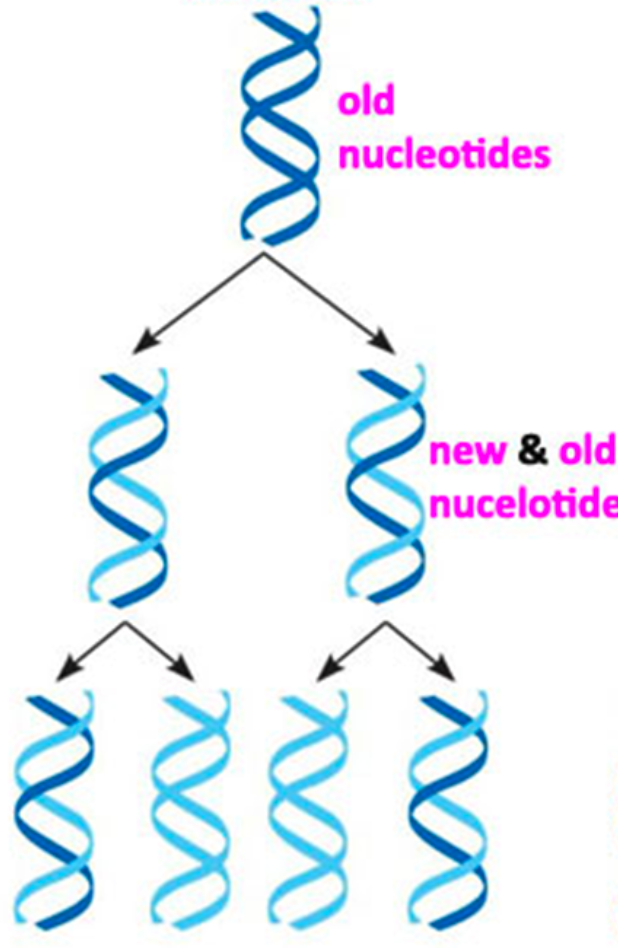
semiconservative model
Purine
2 Ring Structure; Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
1 Ring Structure; Cytosine and Thymine