Anat/phys midterm exam
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
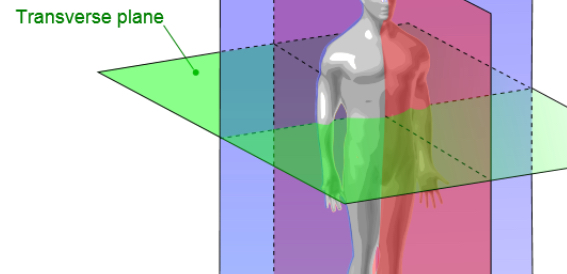
Transverse (axial) plane
Divides into superior and inferior portions
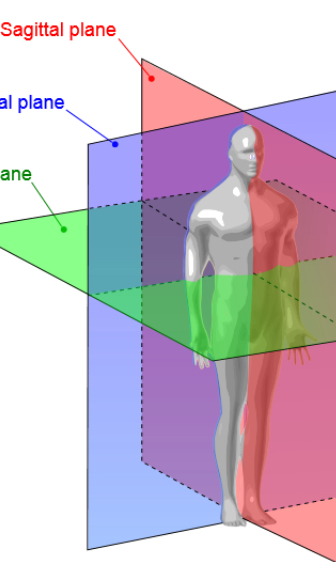
Sagittal plane
Vertical plane that divides into right and left sides
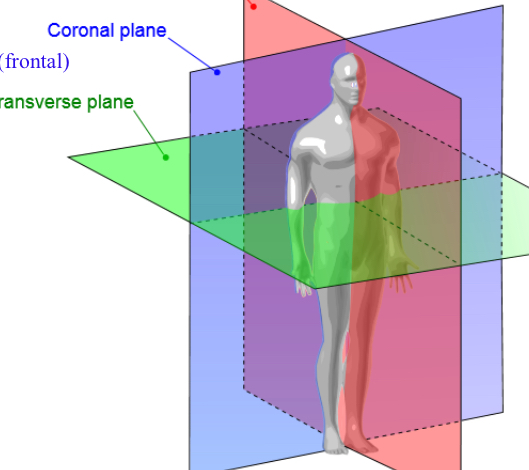
Coronal (frontal) plane
Divides into front and back or ventral and dorsal

Integumentary system
Function: barrier to invading organisms and chemicals; temperature control
Organs: skin, hair, subcutaneous tissue
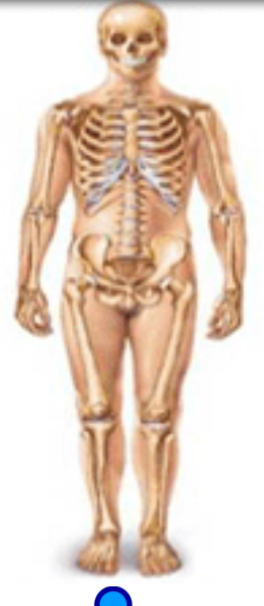
Skeletal system
Function: supports and moves body; protects internal organs; mineral storage; blood formation
Organs: bones, cartilage, ligaments, bone marrow
Muscular system
Function: locomotion; heat production
Organs: muscles, tendons
Nervous system
Function: coordinates activities of other organ systems; responds to sensations
Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves, eyes, ears
Endocrine system
Function: regulates body functions by chemicals (hormones)
Organs: pituitary gland, parathyroid gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, thymus, pancreas gonads
Cardiovascular system
Function: transports oxygen and nutrients to tissues; removes waste products
Organs: heart, blood, blood vessels
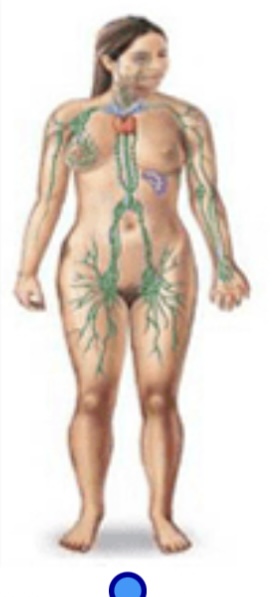
Lymphatic system
Function: returns tissue fluid to blood, defense against foreign organisms
Organs: spleen, lymph nodes, thymus, lymphatic vessels
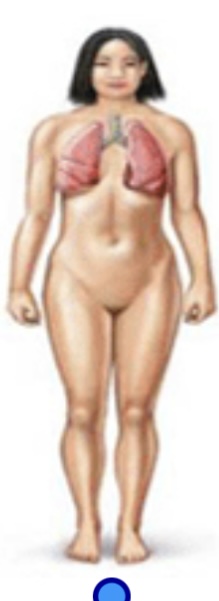
Respiratory system
Function: oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange
Organs: lungs, trachea, larynx, nasal cavities, pharynx
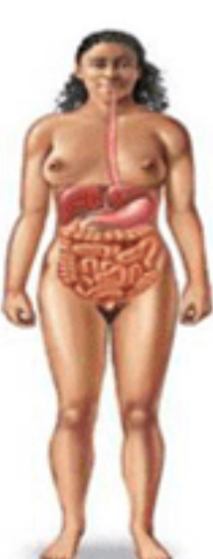
Digestive system
Function: processes foods, absorption of nutrients into body
Organs: stomach, intestinal tract, liver, pancreas, esophagus, salivary glands
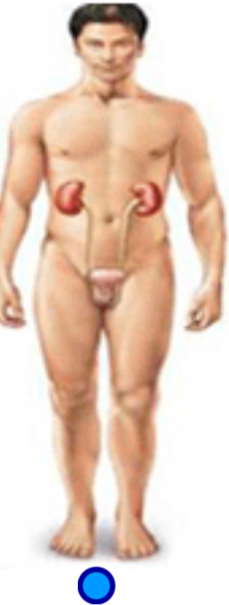
Urinary system
Function: elimination of wastes; regulates pH and volume of blood
Organs: kidneys, urinary bladder, urethra
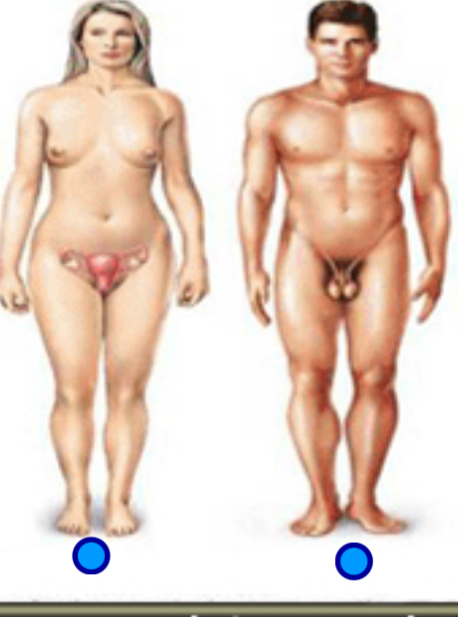
Reproductive system
Function: produces germ cells (eggs and sperm), environment for growth of fetus
Organs: ovaries, uterus, mammary glands, Testes, prostate gland, external genitalia
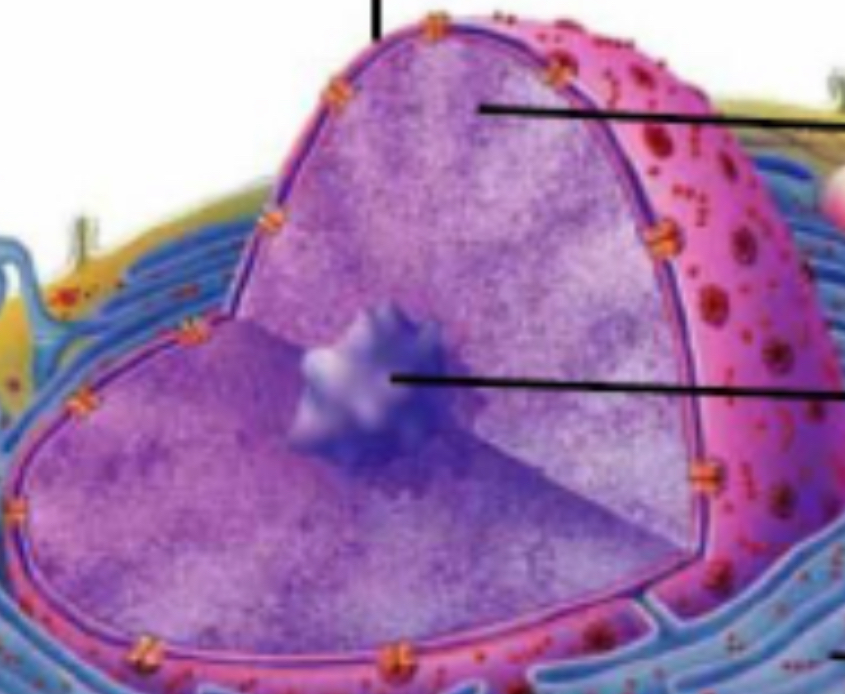
Nucleus
Contains DNA, genetics
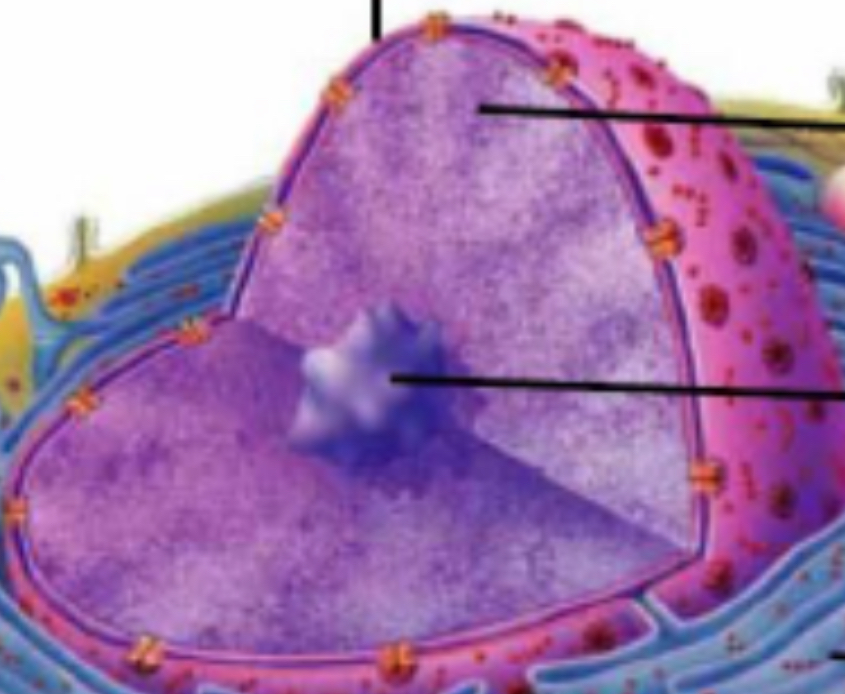
Nuclear membrane (pores)
Protects nucleus
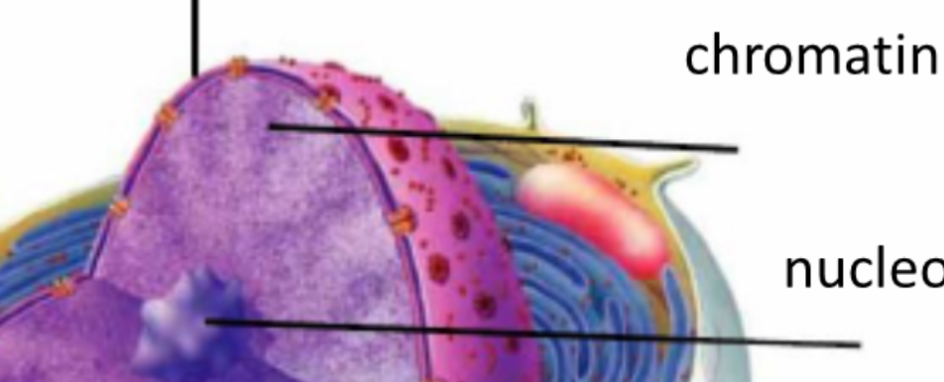
Chromatin and chromosomes
Small genetic material
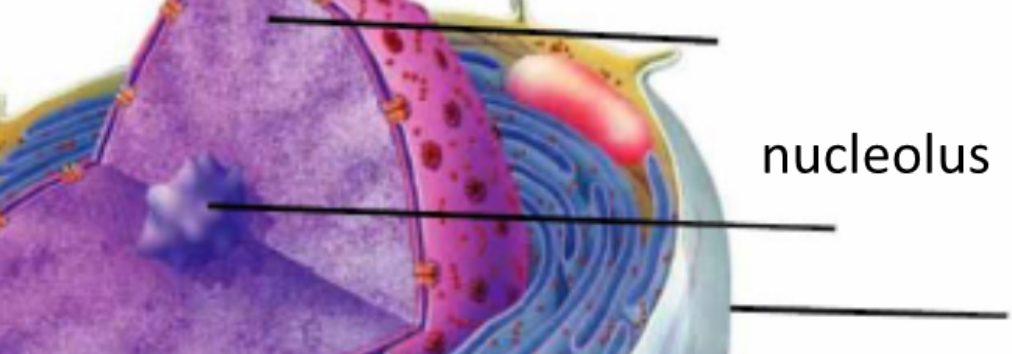
Nucleolus
rRNA produced
Cell membrane
Outer covering, protects, transports
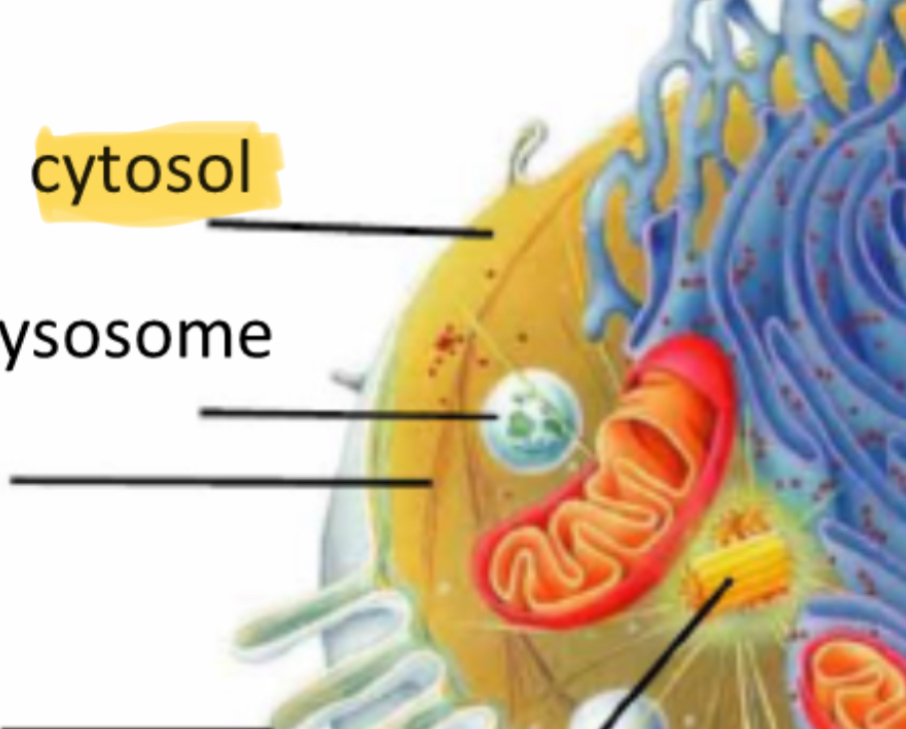
Cytosol
Fluid where the organelles are in

Ribosomes
Protein synthesis

Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Lipids, fats
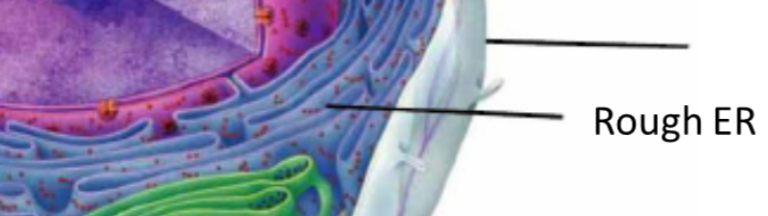
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Transports, protein production
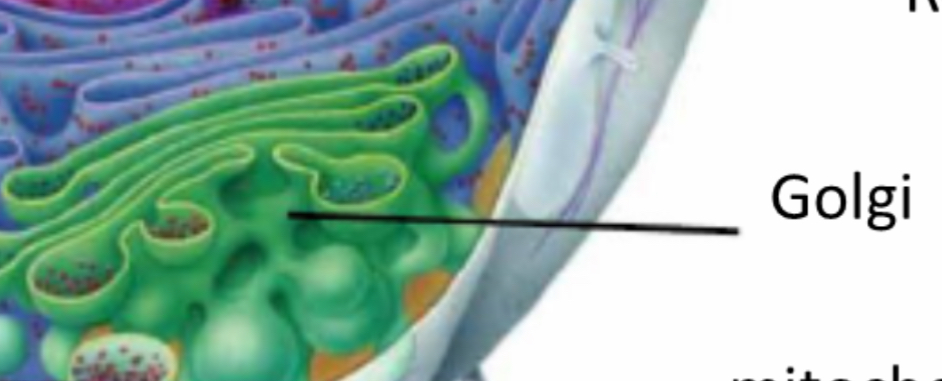
Golgi apparatus
Packaging (proteins don’t always go thru GA, only if they’ll be transferred elsewhere)
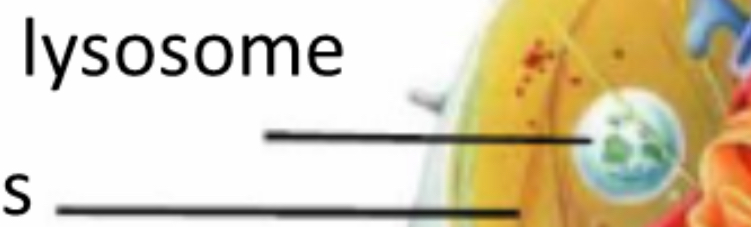
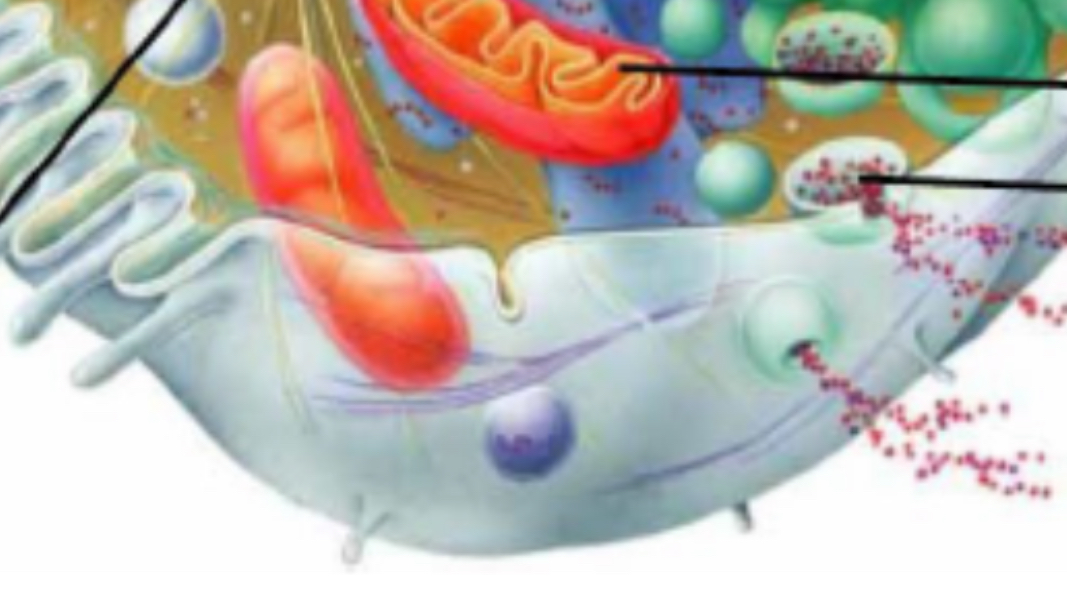
Lysosomes
Breakdown, enzymes
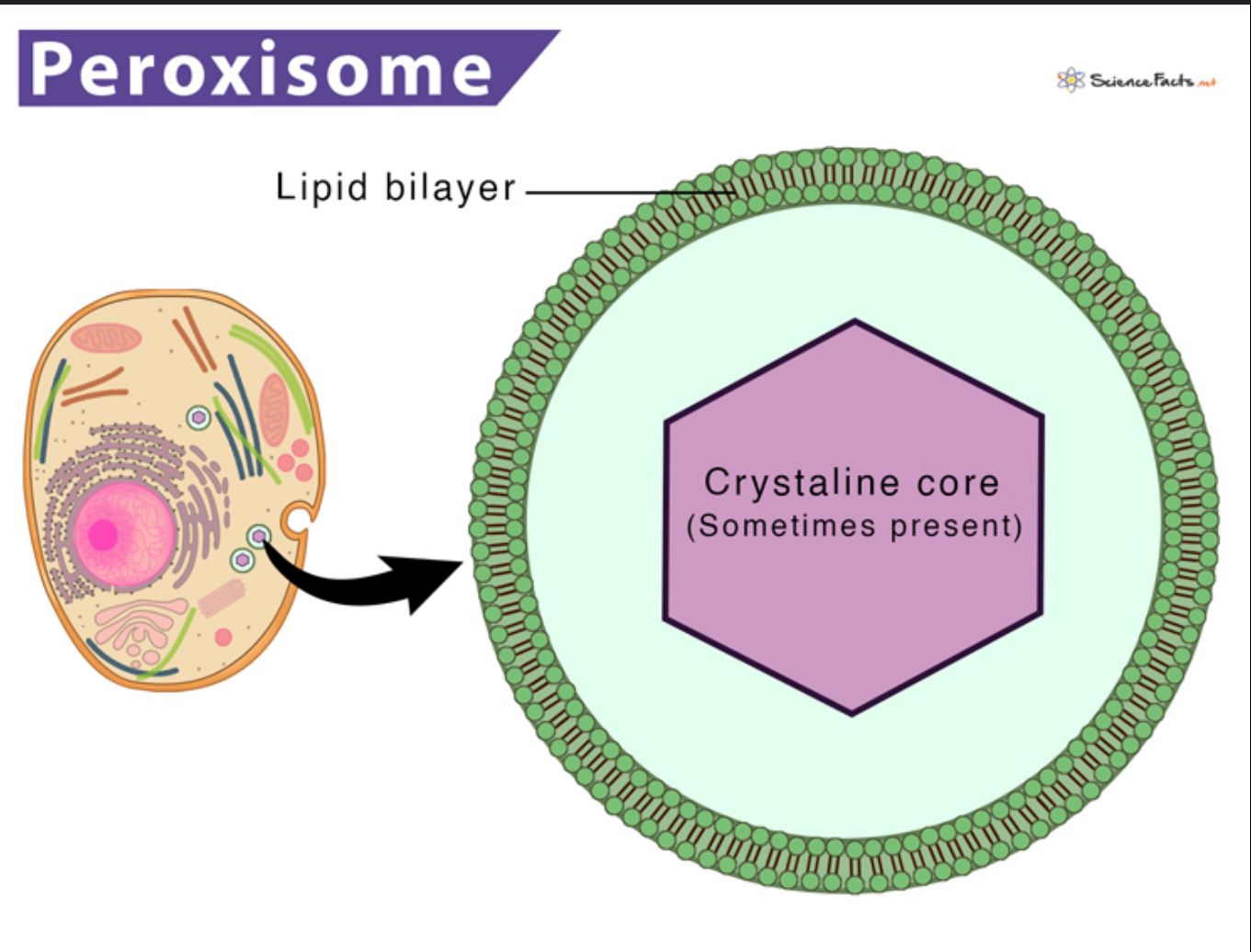
Peroxisomes
Breakdown of fatty acids and produce H2O2
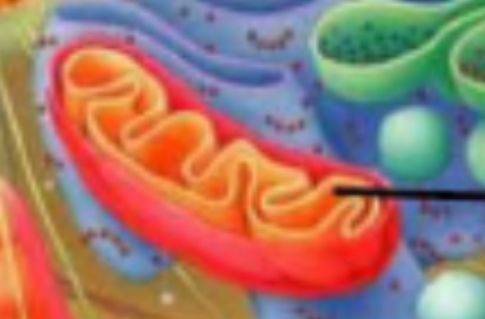
Mitochondria
Energy, ATP, cellular respiration
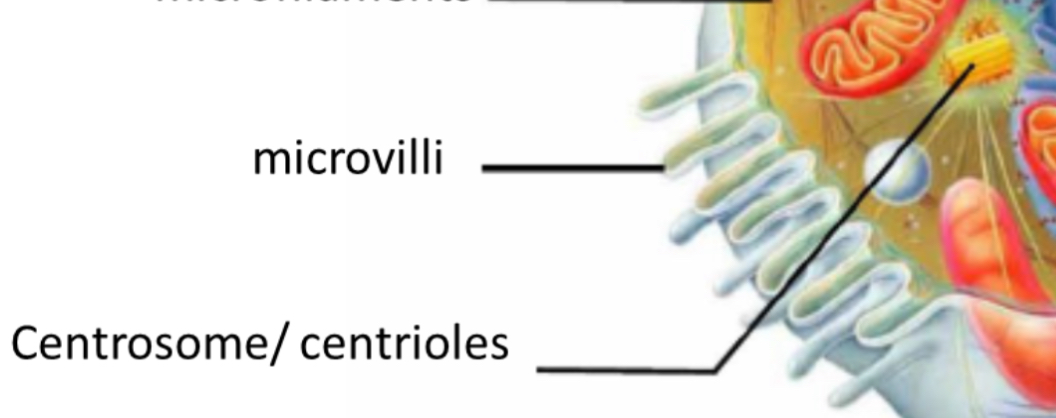
Centrioles
Cell division
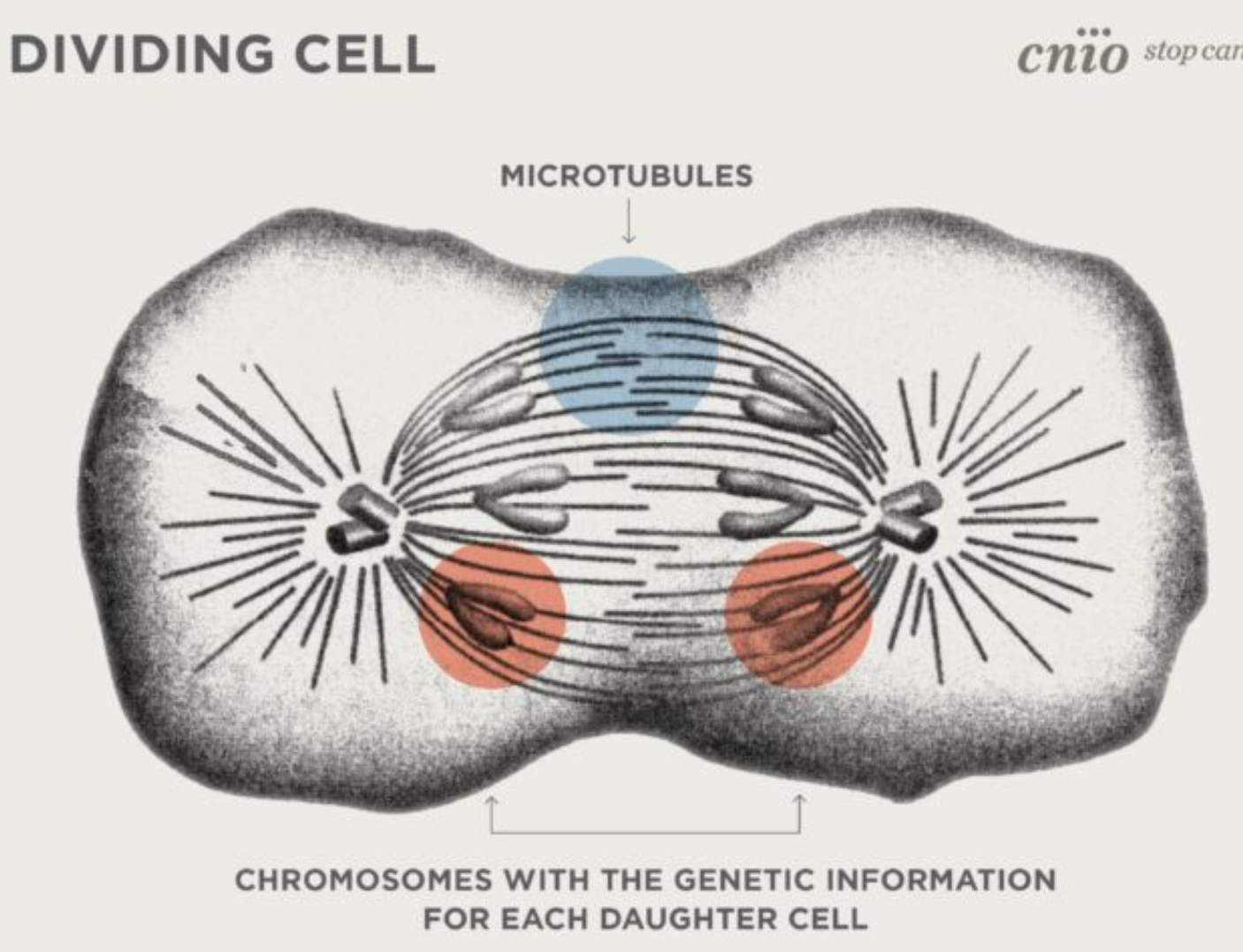
Microtubules
Connect chromosomes during cell division
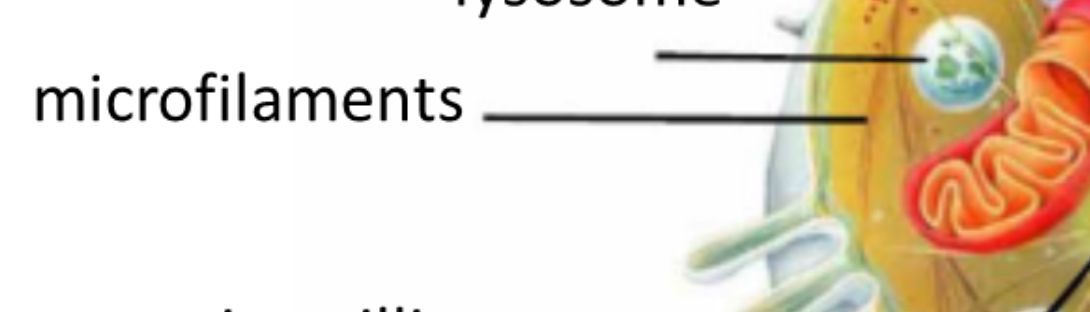
Microfilaments
Structure for cytoskeleton

Vesicle
Secretion
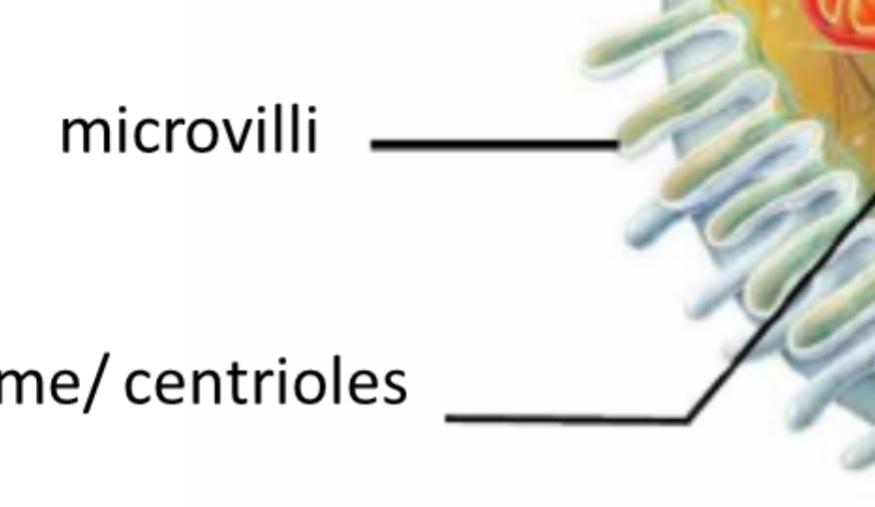
Microvilli
Increases surface area
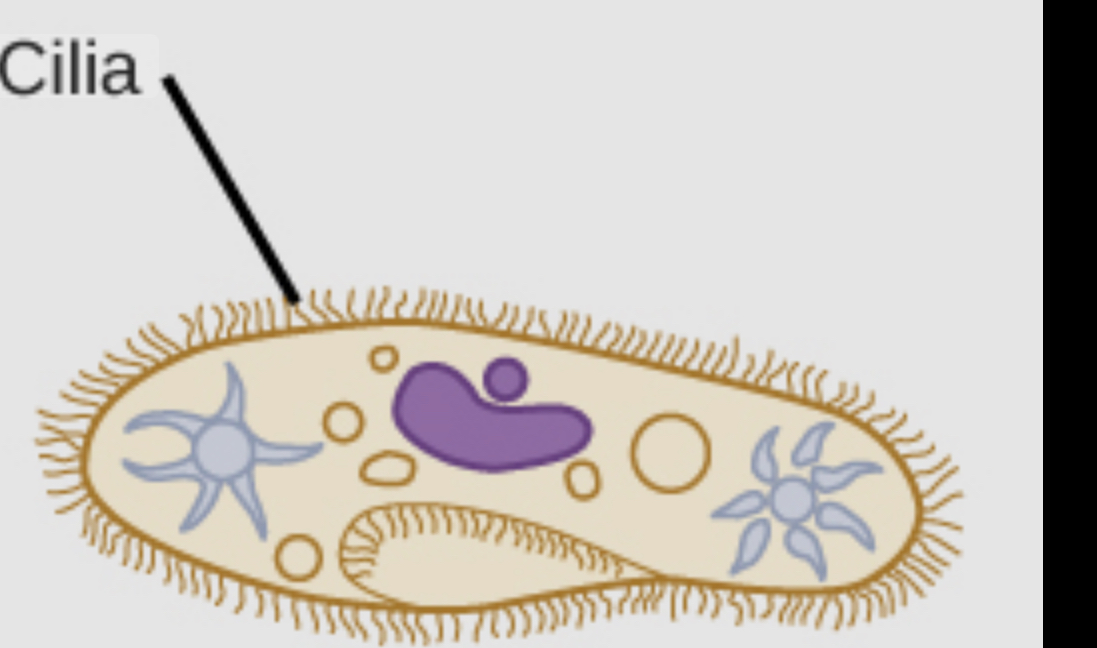
Cilia
Movement
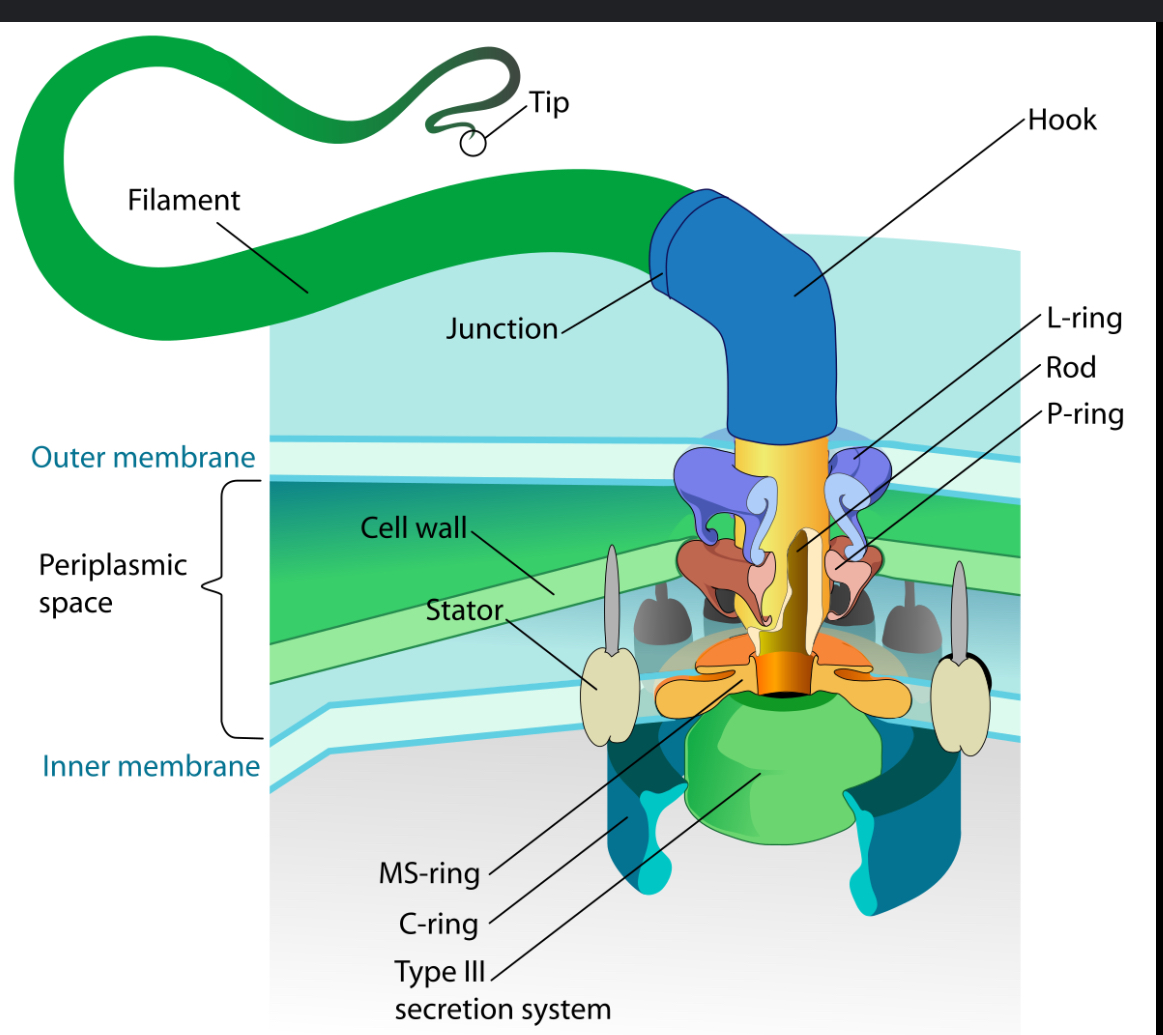
Flagella
Movement
Mitosis or somatic cell division
Consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis
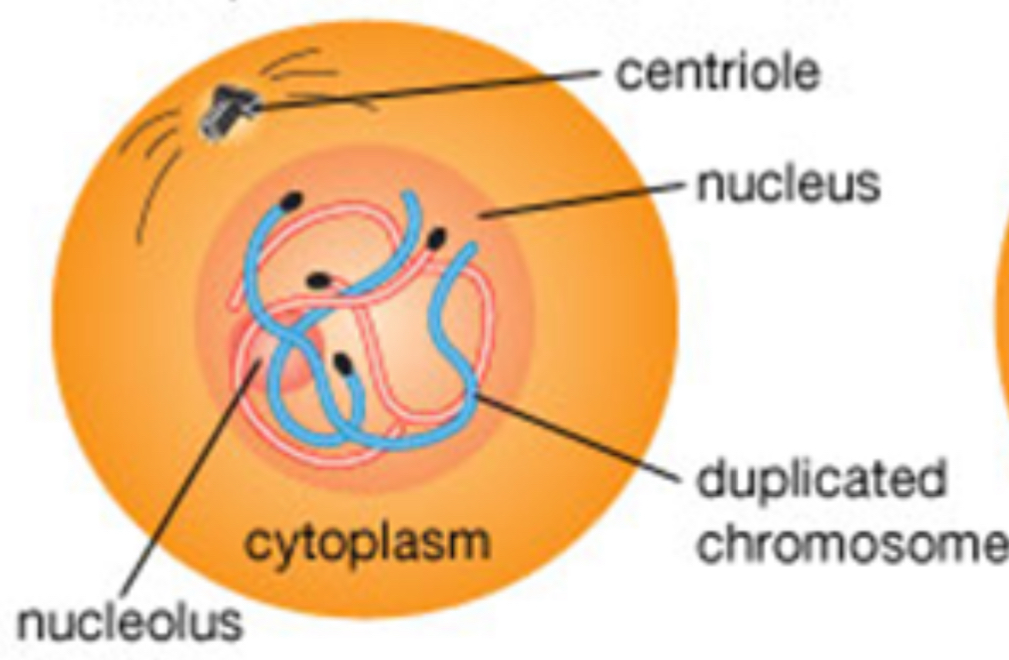
Before mitosis
Prior to mitosis, thin strands of DNA in the cell nucleus thicken into chromosomes, which then duplicate themselves
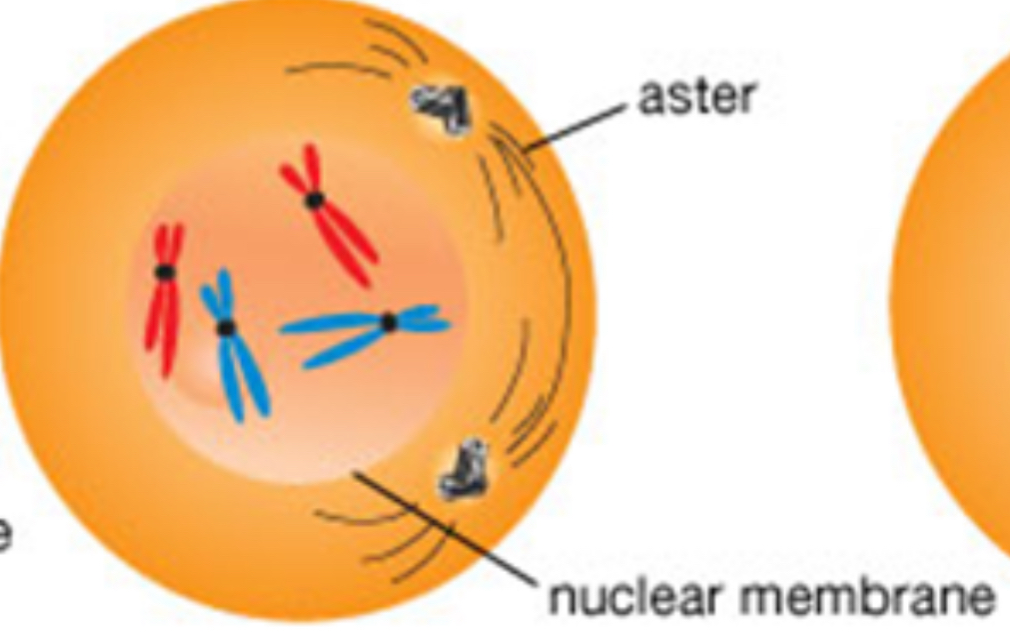
Early prophase
Centrioles divide and w/ asters, move apart
Nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate
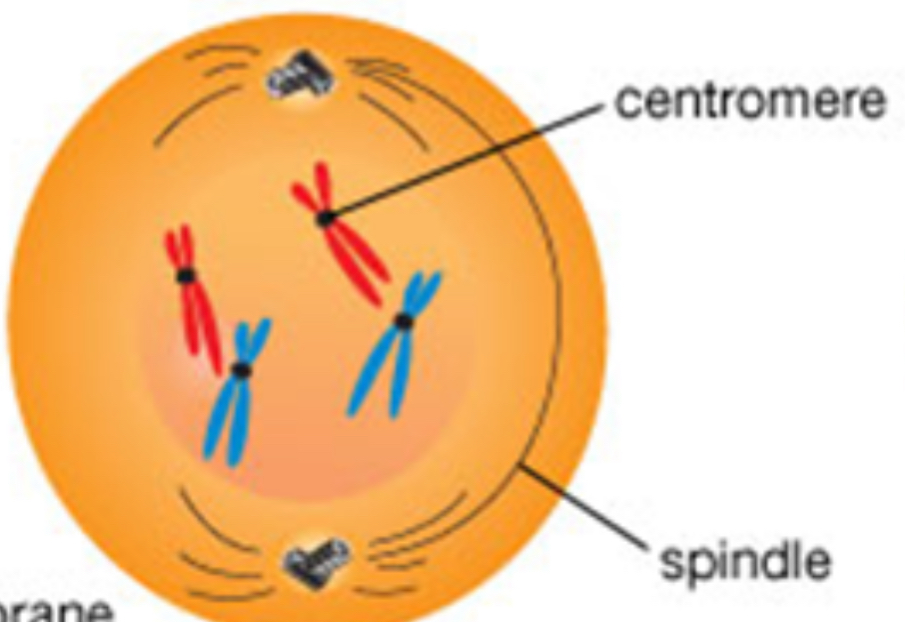
Late prophase
Centrioles and asters are at opposite poles
Nucleolus and nuclear membrane have almost disappeared
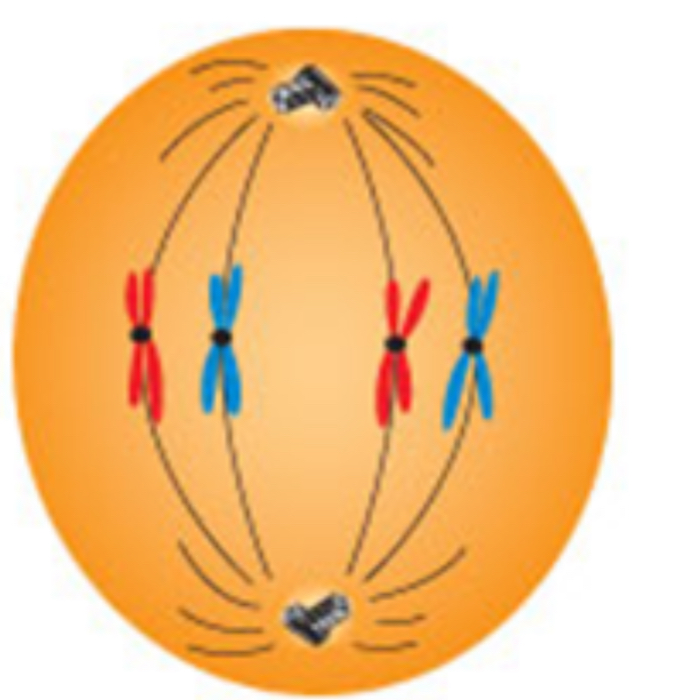
Metaphase
Doubled chromosomes → their centromeres attached to the spindle fibers
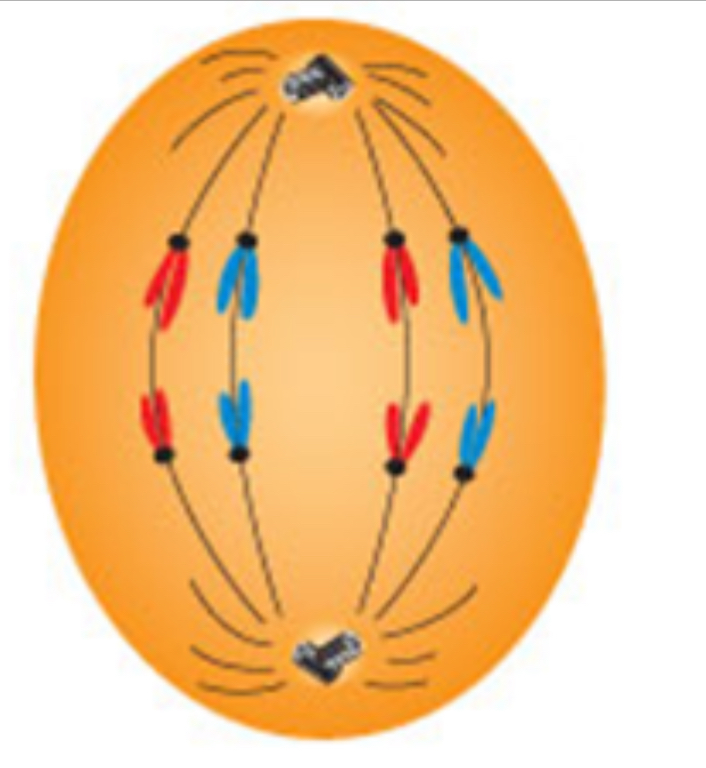
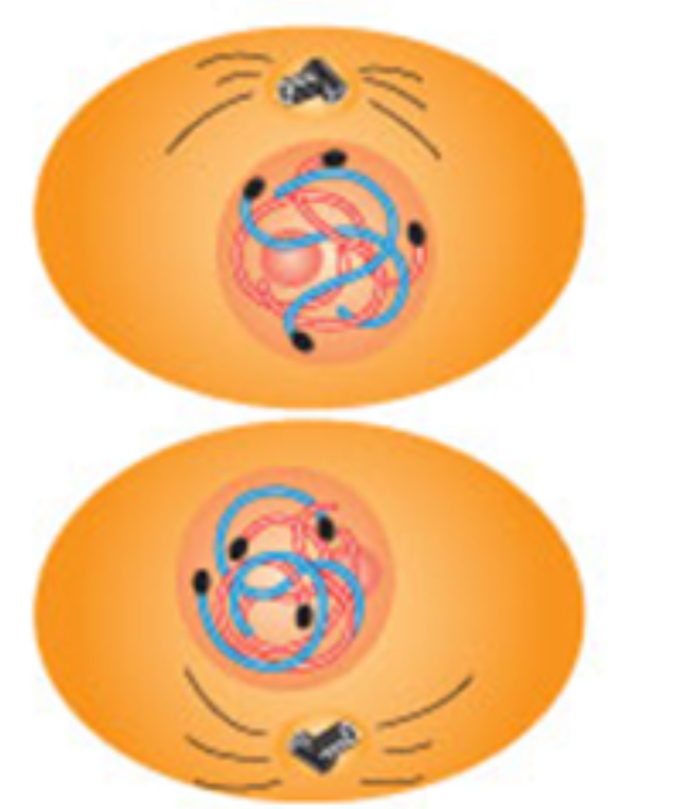
Early anaphase
Centromeres split → half the chromosome move to one pole, half to the other pole
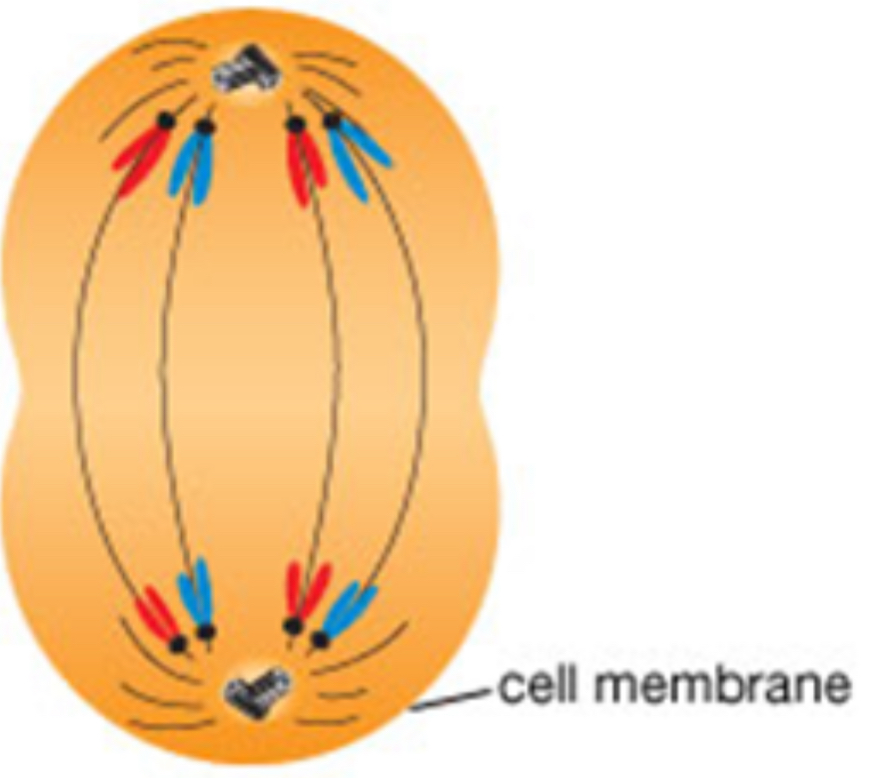
Late anaphase
The chromosomes have almost reaches their respective poles
The cell membrane begins to pinch at center
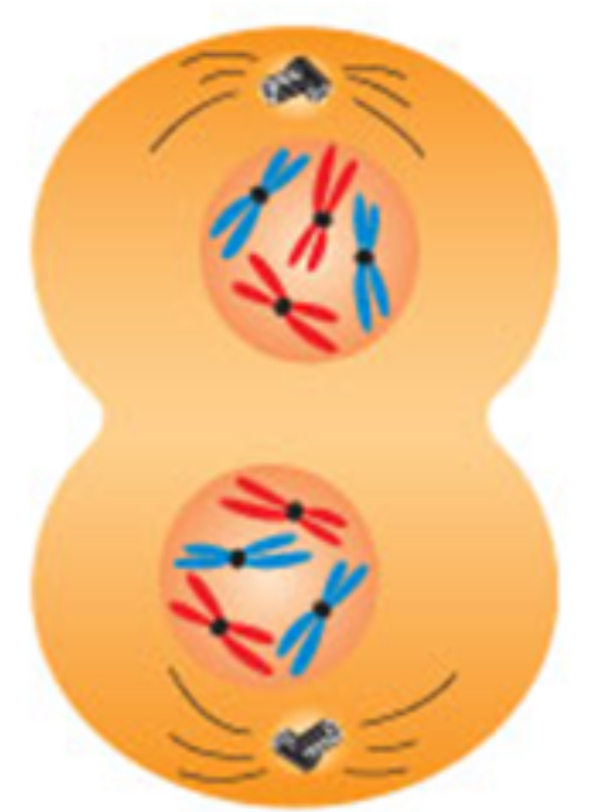
Telophase
Cell membrane completes constriction
Nuclear membranes form around the separated chromosomes
Cytokinesis
Mitosis is completes, there are two daughter cells w/ the same structures and # of chromosomes as the parent cell
Dissociation of electrolytes
Electrolytes dissociate into cations and ions
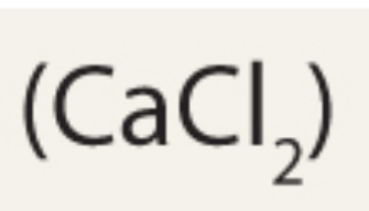
Electrolyte: calcium chloride
Cation: Ca²+
Anion: 2 Cl-

Electrolyte: Disodium phosphate →
Cation: 2 Na+
Anion: HPO4²-
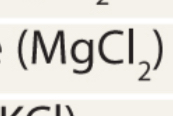
Electrolyte: Magnesium chloride →
Cation: Mg²+
Anion: 2 Cl-
Electrolyte: Potassium chloride (KCl) →
Cation: K+
Anion: Cl-

Electrolyte: sodium bicarbonate →
Cation: Na+
Anion: HCO3-
Electrolyte: sodium chloride (NaCl)
Cation: Na+
Anion: Cl-
Solvency
The ability to dissolve other chemicals
Water is called the _________ ________
Universal solvent
Hydrophilic (polar)
Substances that dissolve in water
molecules must be polarized or charged (ex: sugar)
Hydrophobic
Substances that don’t dissolve in water
molecules are nonpolar or neutral (ex: fats)
Metabolic reaction depend on ______ of water
Solvency
Glucose (carbohydrate → monosaccharide)
Blood sugar → energy source for most cells
Galactose (carbohydrate → monosaccharide)
Converted to glucose and metabolized
Fructose (carbohydrate→ monosaccharide)
Fruit sugar → converted to glucose and metabolized
Sucrose (carbohydrate → disaccharide)
Cane sugar → digested to glucose and fructose
Lactose (carbohydrate → disaccharide)
Milk sugar → digested to glucose and galactose; important in infant nutrition
Maltose (carbohydrate→ disaccharide)
Malt sugar → product of starch digestion, further digested to glucose
Cellulose (carbohydrate → polysaccharide)
Structural polysaccharide of plants, dietary fiber
Starch (carbohydrate → polysaccharide)
Energy storage in plant cells
Glycogen (carbohydrate → polysaccharide)
Energy storage in animal cells (liver, muscle, brain, uterus, vagina)
Glycoprotein (carbohydrate → conjugated carbohydrates)
Component of the cell surface coat and mucus, among other roles
Glycolipid (carbohydrate → conjugated carbohydrate)
Component of the cell surface coat
Proteoglycan (Carbohydrate → conjugated carbohydrate)
Cell adhesions; lubrication; supportive filler of some tissues and organs
2 types of nucleic acid
DNA and RNA
How DNA differs from RNA
Usually double-stranded
Thymine as a base
Deoxyribose as the sugar
Maintains protein-encoding info
Cannot function as an enzyme
How RNA differs from DNA
Usually single-stranded
Uracil as a base
Ribose as the sugar
Carries protein-encoding info and controls how info is used
Can function as an enzyme
Protein function : structure
keratin - tough structural protein of hair, nails, skin surface
Collagen - contained in deeper layers of skin, bones, cartilage, and teeth
Protein function : communication
some hormones and other cell-to-cell signals are proteins
Ex: ligand: a molecule that reversibly binds to a protein
Receptors to which signal molecules bind are proteins
Protein function - membrane transport
channel proteins in cell membranes govern what passes
Carriers - transport solutes to other side of membrane
Protein function - catalysis
Most proteins are globular proteins
Protein function - cell adhesion
Protein adhere and help with cell adhesion
Hierarchy of complexity (largest to smallest)
Organism → organ systems → organs → tissues → cells → organelles → molecules → atoms
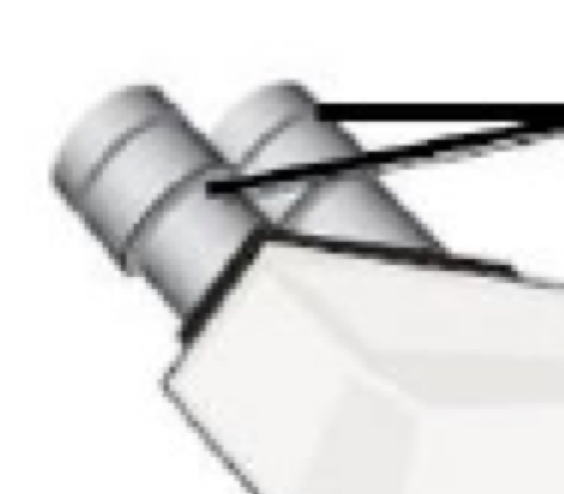

Part of microscope
Ocular lens

Part of microscope
Objective lens

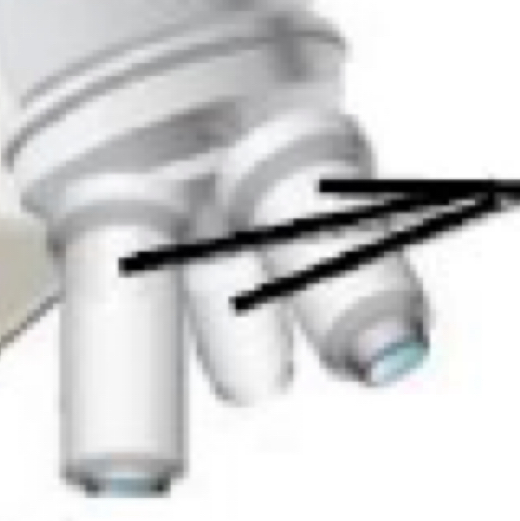
Part of microscope
Stage
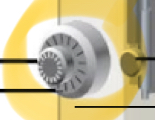
Part of microscope
Coarse focus knob
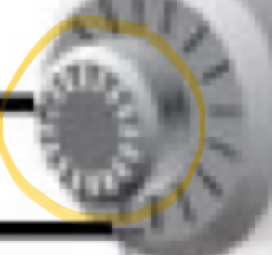
Part of microscope
Fine focus knob
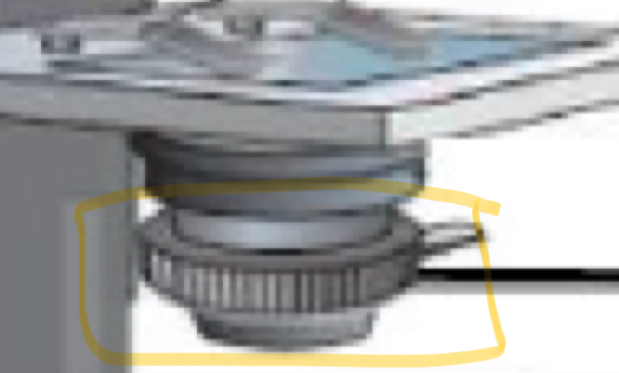
Part of microscope
Iris diaphragm
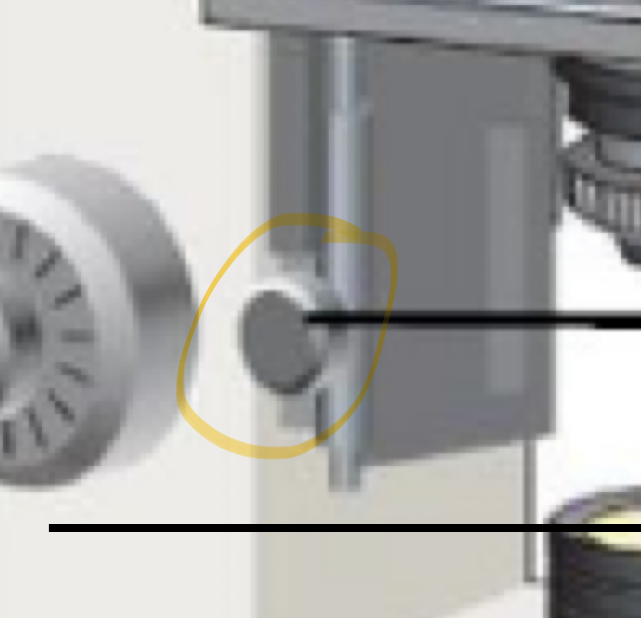
Part of microscope
Mechanical stage adjustment knob
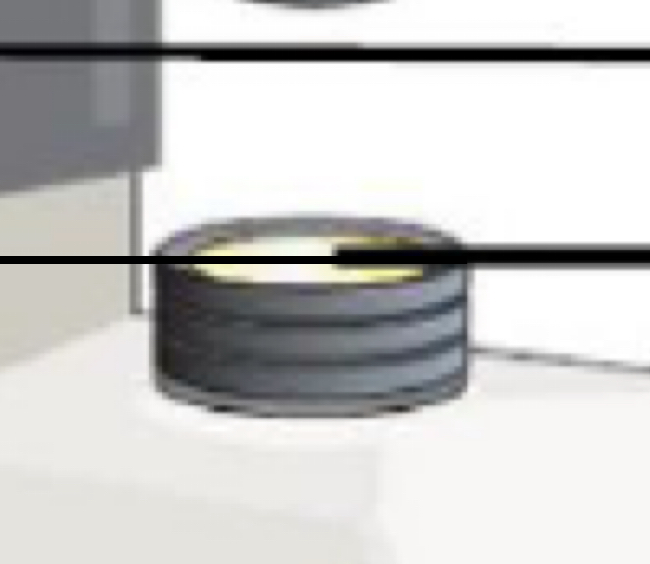

Part of microscope
Lamp
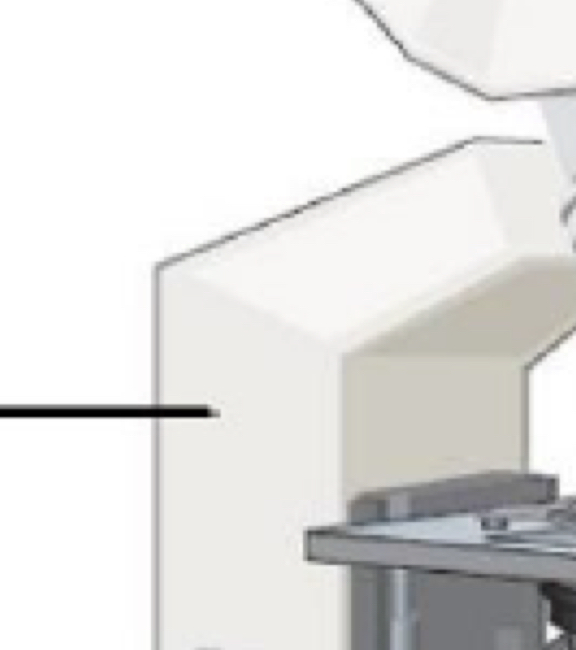
Part of microscope
Arm
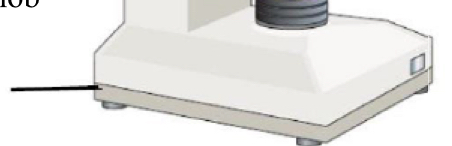
Part of microscope
Base
Calculate total magnification
Objective lens magnification x ocular lens magnigucation
Lowest power lens (red) → calculate total magnification
4 (ob) × 10 (oc) = 40
Intermediate power lens (yellow) → calculate total magnification
10 (ob) x 10 (oc) = 100
Highest power lens (blue) → calculate total magnification
40 (ob) x 10 (oc) = 400
Epithelial tissue (2 types)
Simple and cuboidal
Simple epithelial tissue (4 types)
squamous
Cubiodal
Columnar
Pseudo-stratified
Stratified epithelial tissue (4 types)
squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Transitional
Connective tissue (4 types)
cartilage
Bone
Blood
Connective tissue tissue
Cartilage connective tissue (3 types)
hyaline
Elastic
Fibrous
Connective tissue proper (6 types)
areolar
Adipose
Reticular
Elastic
Dense regular
Dense irregular
Muscle tissue (3 types)
smooth
Skeletal
Cardiac
Nervous tissue (2 types)
Neurons and neuroglia
Simple epithelia (description)
contain one layer of cells
Named by shape of cells
All cells touch basement membrane
Stratified epithelia (description)
contain more than one layer
Named by shape of apical cells
Some cells rest on top of others and do not touch basement membrane