nat 5 economics- unit 1
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
the basic economic problem
also known as scarcity, arises because human wants for goods and services are unlimited due to greed, but we have limited resources. all countries are affected by scarcity, and it is not the same as a shortage
factors of production
resources which are used to produce goods/services
land- naturally occuring resources eg oil and fish
labour - the human workforce that produces goods and services. eg factory workers
capital- man made resources eg machines
enterprise- when an entrepeuner combines these to produce a good/service.
returns to the factors of production
land - rent
labour - wages
capital - interest
enterprise - profit
opportunity cost
the sacrifice of the next best alternative
mobility
the speed and ease with which a resource can change its location or use
effective demand
a want backed up by the money to buy the good/service you want
why does the demand curve slope downwards
law of diminishing marginal utility - consumers are willing to pay less for each additional unit
income effect - as price falls, consumers are able to buy more with the same amount of income
substitution effect - as a goods price decreases, substitutes appear more expensive, so demand for the cheaper good increases
willingness and ability to pay - as price falls, consumers are more willing and able to buy it
marginal utility
the extra satisfaction gained from consuming one more of a good or service
the law of diminishing marginal utility
the more of something you consume, the less marginal utility you gain from it
determinants of demand
income
price of substitute or complementary goods
tastes and fashion
advertising and publicity
population
weather and seasons
state of the economy
supply vs output
supply is the amount of good or service a firm is willing and able to send to the market at a certain price, in a certain time
output refers to the entire production of a good or service
why does the supply curve slope upwards
firms are only willing and able t increase their production as price increases, as they need to cover additional csts of production
when price therefore profit is high, new firms will start to produce the same product so overall supply increases
(assuming firms are profit maximisers)
higher costs
determinants of supply
costs of production
technology
weather and natural disasters
taxes and subsidies
competetive and joint supply
market
when buyers and sellers of a good or service come into effective contact, agree a price and then exchange the product for money
different types of market
goods eg cars
services eg transport
factors (cell) eg labour
money eg forex
fixed and variable costs
fixed costs are payments that dont change as output changes. eg rent and rates
variable costs are payments which directly changes with output. eg raw materials and wages
profit
the amount of money a firm has left over after they have paid all their costs.
TSR - TC
total sales revenue
the total amount of money/ income a firm recieves from selling their products
TSR = price x quantity sold
ASR = income per unit sold
short run cost diagram
ATC - summation of AVC and AFC
AVC - law of diminishing marginal returns
AFC - spreading fixed cost over more output
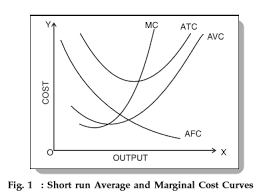
short run
long run
period of time where at least one factor of producition is fixed
when al the factors of production are variable, therefore costs are variable
the law of diminishing returns
in the short run, marginal cost will decrease initially, but will always start to increase at some level of input
how to lower costs in supply
reduce wages
invest in technology
find cheaper supplies
improve training
greater specialisation
productivity
the relationship between output and input ( how much is being produced with a certain amount of resources )
methods of improving productivity
pay workers bonuses
use more division of labour
improve training of workers
invest in more efficient machinery