Numerical Weather Prediction
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Two Different General Types of Numerical Weather Prediction Model

Grid-point model: Cover the forecast area with a 3D-grid, solve equations at “grid points”
Spectral model: because atmospheric variables tend to be wavy, build a model using wavy mathematical functions
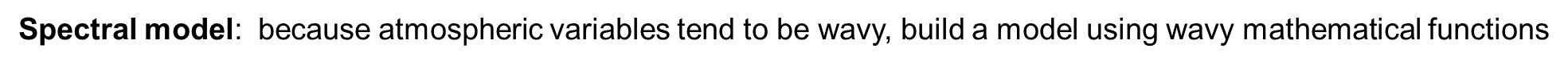

What is a “run”
Spectral model: because atmospheric variables tend to be wavy, build a model using wavy mathematical functions
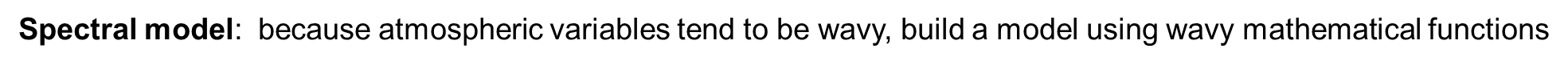
What are “initial conditions”
The values of all the variables that are given to the model at the beginning of a run.

What are some NWP models?
NAM - North American Model
GFS - Global Forecast System
HRRR - High Resolution Rapid Refresh
UKMET - UK Meteorological Office
CANADIAN - Environment Canada
ECMRWF- European Center Medium Range Weather Forecasting
What is NBM?
National Blend of Models
NBM forecasts are typically shown in a…
table
NBM example
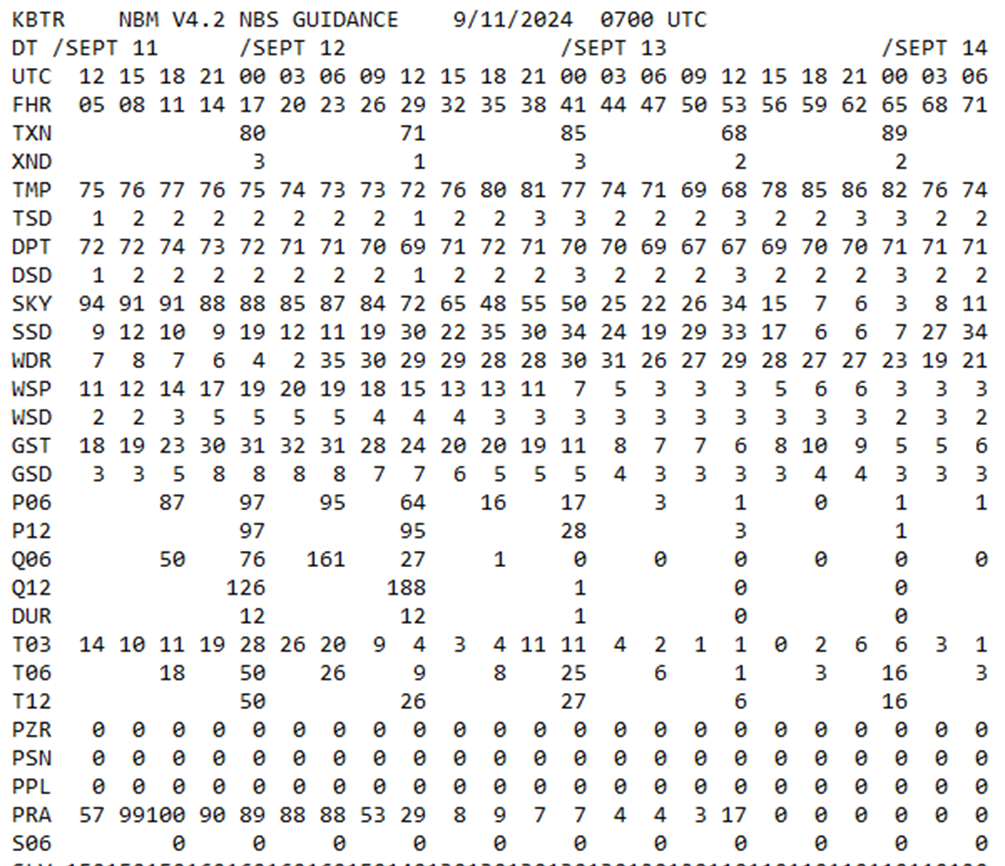
For most variables, forecast given every ______ hours

3 hours, at 00, 03, 06, 09, 12, 15, 18 and 21 UTC
Why do NWP model forecasts “go bad”?

1. Computer models are imperfect
-- Translating the laws of physics into a computer model requires approximations (think of video games … though realistic, they are not perfect representations of reality).
2. Observational limitations
-- We don’t have observations everywhere, so there’s always errors in the initial conditions
-- And measurements are, by nature, imprecise (is the temperature really 70oF?)
3. The atmosphere is a “nonlinear” system
-- The laws of physics are so mathematically complex (“chaotic”) that any errors in initial conditions will, on average, grow bigger with time.

What is “ensemble forecasting”
Consider a set of computer model forecasts (an “ensemble”) rather than just one

What are plume diagrams?
In general, the lines separate as the forecast goes farther out, indicating that the forecast is becoming more uncertain with time
When ensemble members agree, _______ is higher
When ensemble members disagree, _______ is greater
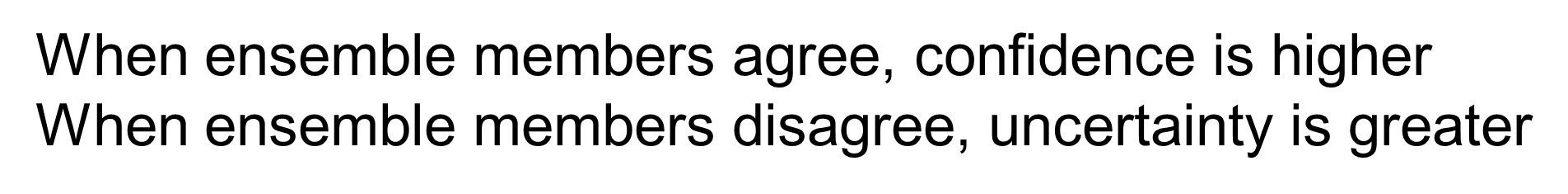
confidence, uncertainty
•What are some characteristics of the best weather forecasters?
•Name and describe three relatively simple forecasting techniques.
•What are some of the fundamental physical equations that are used in numerical weather prediction?
•Name the two primary types of NWP models, and a characteristic of each type.
•What are the “initial conditions”?
•What are the names of the primary U.S. short-range and long-range NWP model?
•Describe how observational limitations impact the accuracy of NWP forecasts.
•Describe how ensemble forecasting works. What are some ways to create an ensemble of forecasts?
