Micro 265 - Antibiotics (7)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
antibiotic
naturally occurring compound produced by microorgs to inhibit growth of other microorgs.
In soil and aquatic habitats
what produces antibiotics?
bacteria, fungi
why produce antibiotics?
eliminate competition for limited resources
do antibiotics affect viruses?
no
antibiotic targets
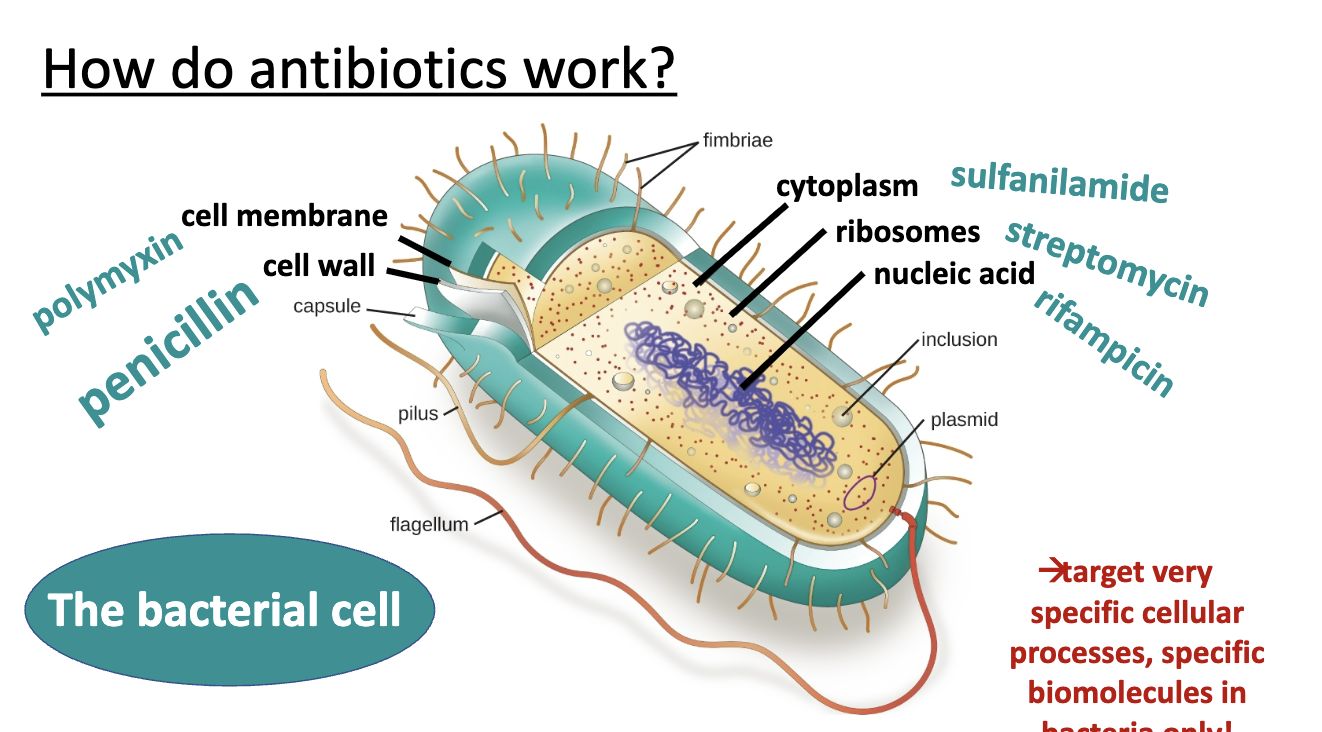
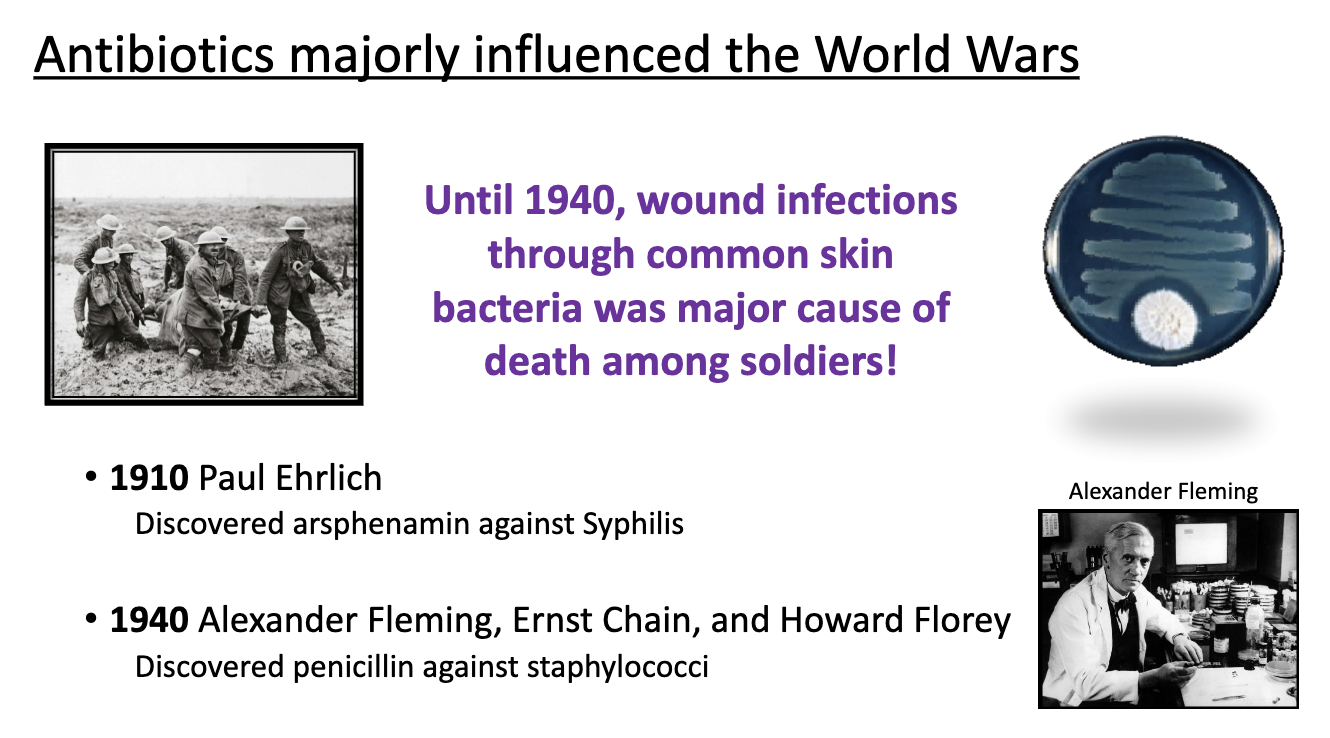
antibiotics + world wars
cell wall synthesis inhibitors
INHIBIT cross-linking of peptidoglycan cell wall
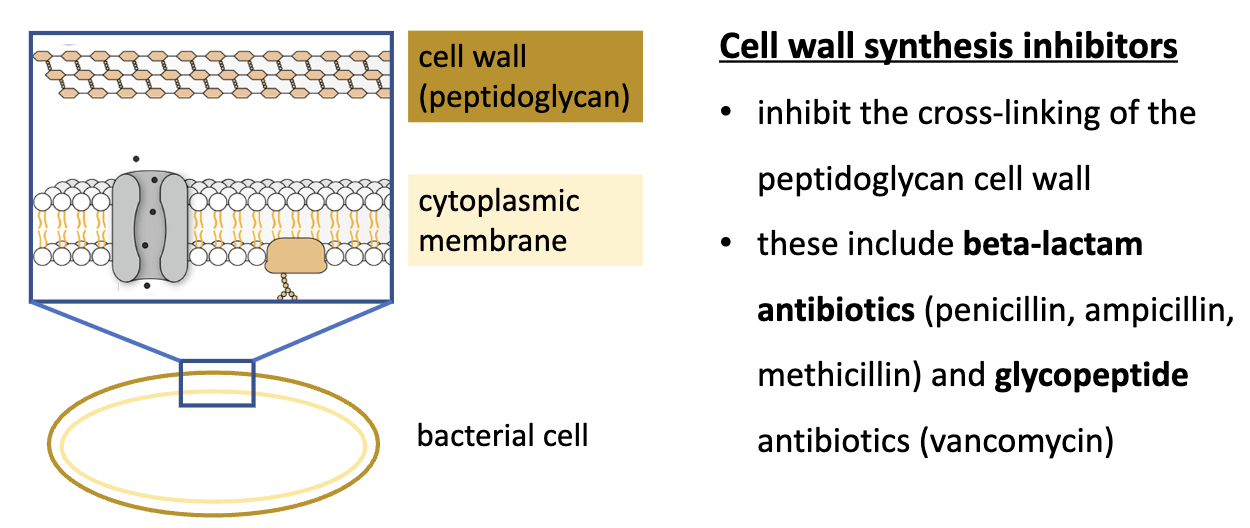
cell wall synthesis inhibitors - examples
1.) beta-lactam antibiotics
penicillin, ampicillin, methicillin
2.) glycopeptide antibiotics
vancomycin
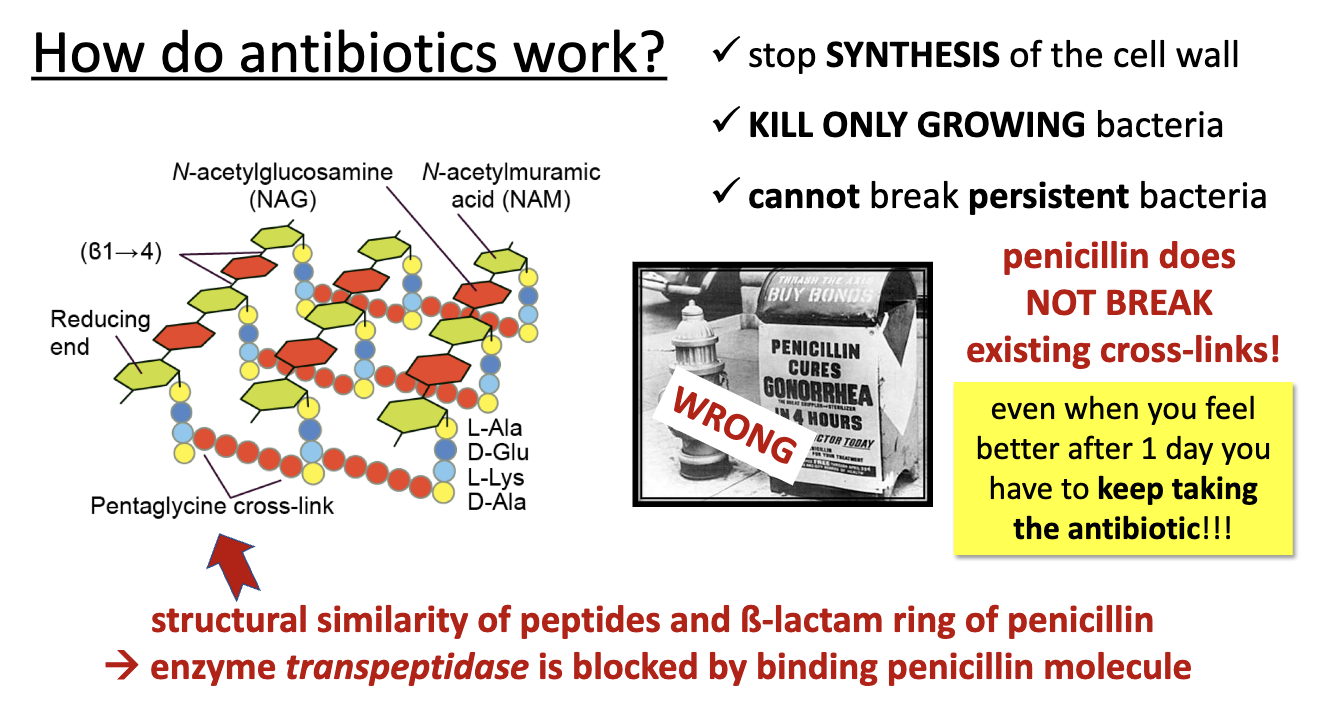
** KILL ONLY GROWING BACTERIA, not persistent ones, doesn’t break existing cross-links
do cell wall synth inhibitors kill growing bacteria?
yes, only growing ones. Doesn’t break existing crosslinks and doesn’t kill persistent bacteria
beta-lactam antibiotics
cell wall synthesis inhibitors
Ex: penicillin, ampicillin, methicillin
how do beta-lactams work?
structural similarity of peptides and ß-lactam ring of penicillin
(transpeptidase is blocked by penicillin binding)
penicillin
cell wall synthesis inhibitor
ampicillin
cell wall synthesis inhibitor
methicillin
cell wall synthesis inhibitor
glycopeptide antibiotics
effective against Gram-positive bacteria, particularly methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Ex: vancomycin
vancomycin limit
cell wall synthesis inhibitor - doesn’t penetrate membrane of Gram neg
protein synth inhibitors
bind to 30S or 50S ribosomal subunit, interfere with translation
Ex: aminoglycosides — streptomycin, gentamicin, erythromycin, tetracycline
protein synth inhibitors - examples
aminoglycosides:
streptomycin, gentamicin, erythromycin, tetracycline
erythromycin limit
doesn’t penetrate membrane of Gram neg
streptomycin
protein synth inhibitor
gentamicin
protein synth inhibitor
erythromycin
protein synth inhibitor
tetracycline
protein synth inhibitor
inhibitors of cell membrane fxn
disrupt plasma mem of cells, causing ion and macromolecule leakage
Ex: polymyxins like colistin
colistin
a polymyxin that inhibits cell membrane function
colistin limit
doesn’t penetrate cell walls of Gram positive
nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors
RNA synth inhibitors target RNA pol —> rifampicin
DNA synth inhibitors target DNA gyrase —> ciprofloxacin
rifampicin
RNA synth inhibitor that inhibts RNA pol
ciprofloxacin
DNA synth inhibitor that inhibts DNA gyrase
folic acid synthesis inhibitors
inhibit diff enz in the folic acid synthesis pathway. Typically used together
Sulfanilamide, trimethoprim
folic acid synthesis inhibitors - examples
Sulfanilamide, trimethoprim
sulfanilamide
folic acid synthesis inhibitor
trimethoprim
folic acid synthesis inhibitor
antibiotics limits
not all effective against each bacterium
toxic or have harsh side effects
1% of all known antibiotics usable in humans
allergies
persistent bacteria start growing again if not taken long enough
broad vs narrow spectrum
vancomycin limit
Gram neg outer membrane prevents vancomycin from entering cell
ciprofloxacin limit
nerve and tendon damage
tetracycline limit
hepatitis
antibiotic resistance
to inactivate antibiotics or prevent their damage —> naturally, to keep fighting for limited resources
antibiotic resistance mechanisms
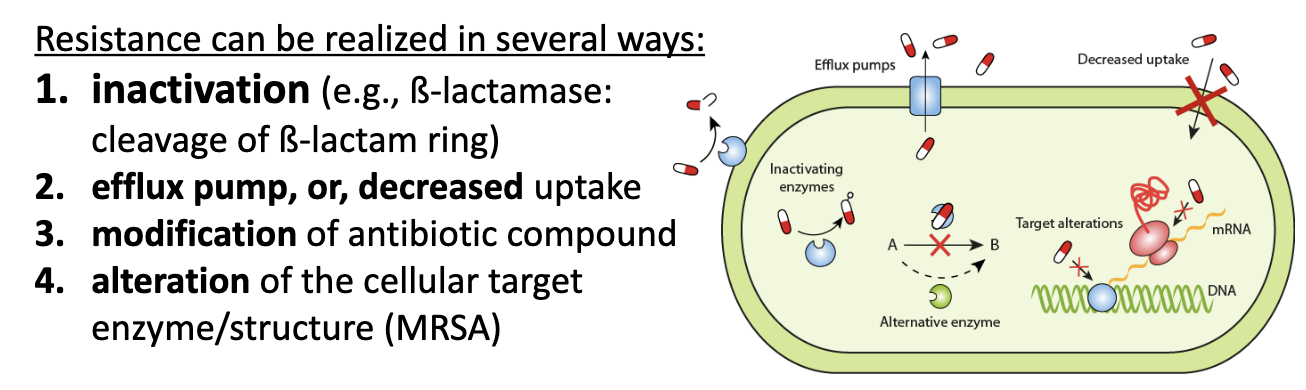
overuse of antibiotics
can cause antibiotic resistance
horiz gene transfer
many antibiotic resistance genes are encoded on mobile genetic elements (plasmids, transposons), move easily btw bacteria via horizontal gene transfer
antibiotic resistant strains
MRSA
VRSA
VRE
CRE
MRSA
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
common
resist B-lactams
VRSA
vancomycin-resistant S. aureus
rare
resist vancomycin
VRE
vancomycin-resistant enterococci
getting common
resist vancomycin
CRE
carbapenem-resistant enterics
rare
resist B-lactams
preventing antibiotic resistance
1.) decide with professional if antibiotic treatment is actually useful
2.) prevent infections via hygiene - reduce the need for antibiotics
Kirby-Bauer test
to test susceptibility/resistance of bacteria against antibiotics.
spread dilute bacteria culture over Mueller-Hinton plate = lawn
small paper discs w known [antibiotic]
plate culture is incubated
if bacteria are affected, zone of growth inhibition around disc. Resistant bact grow closer to the disc
![<p>to test susceptibility/resistance of bacteria against antibiotics.</p><ul><li><p>spread dilute bacteria culture over Mueller-Hinton plate = lawn</p></li><li><p>small paper discs w known [antibiotic]</p></li><li><p>plate culture is incubated</p></li><li><p>if bacteria are affected, <strong>zone of growth inhibition</strong> around disc. Resistant bact grow closer to the disc</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4eee4061-3197-4089-8b23-e92c7492ee76.png)
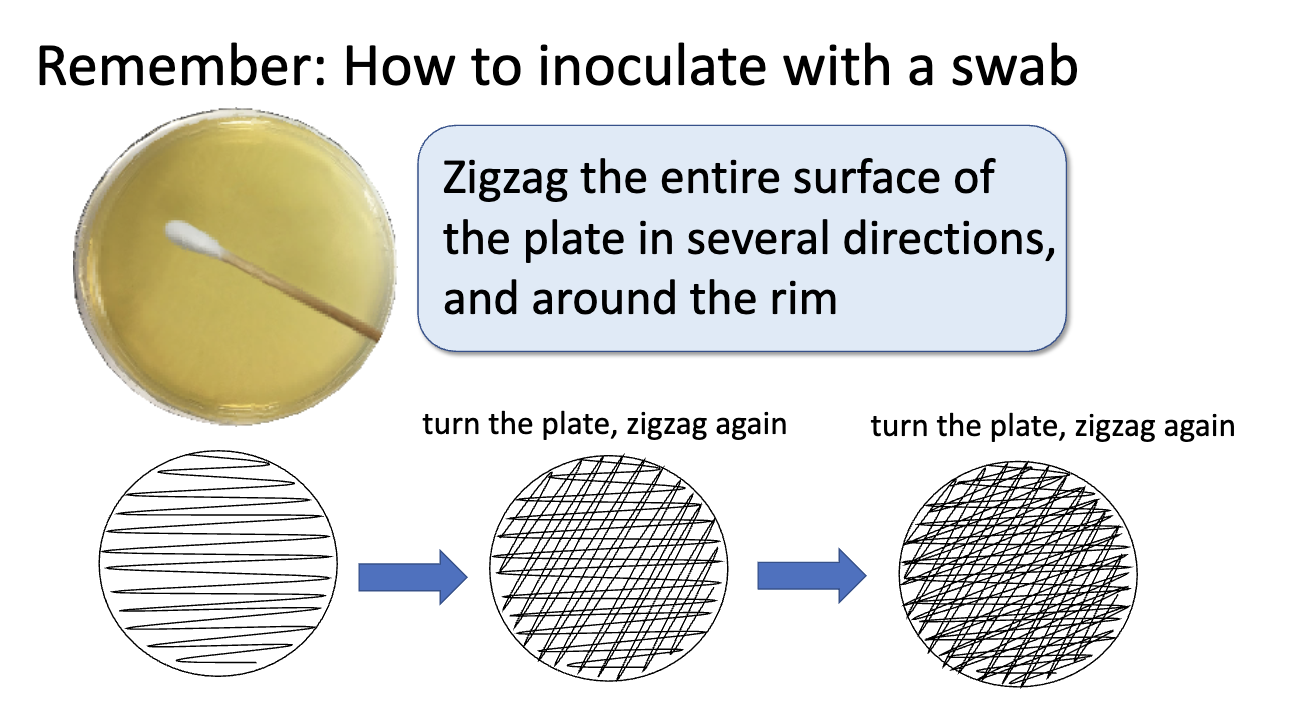
how to inoculate with swab
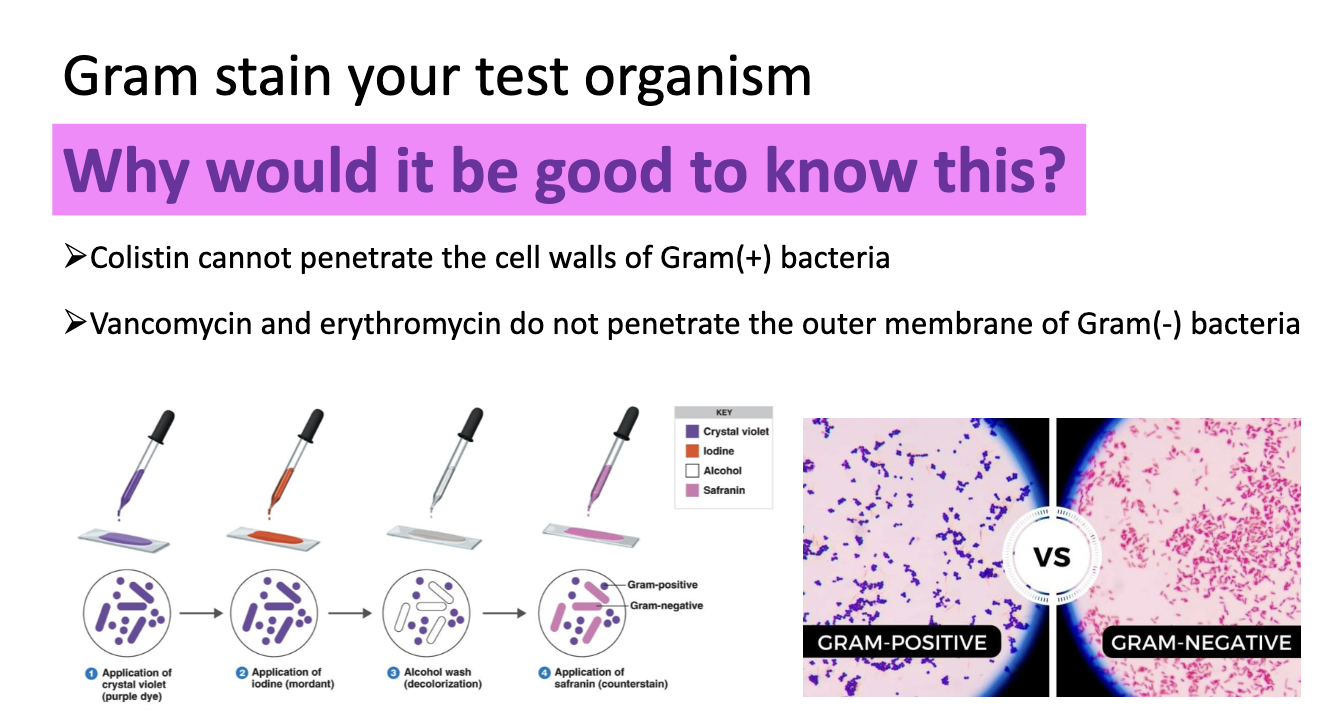
why gram stain for KB test?
minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
best effective, yet lowest dose conc. of an antibiotic
avoids creating resistance opportunities in patients
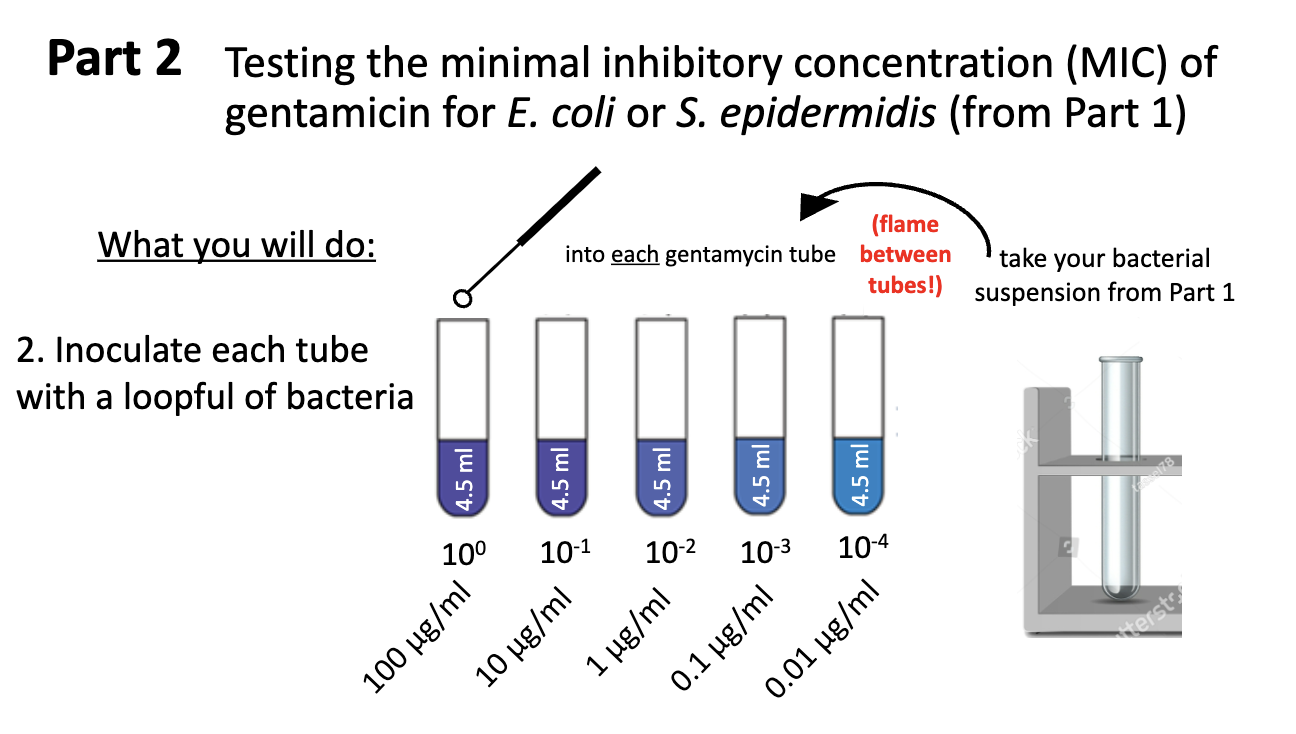
how to determine MIC?
inoculate same bact culture into medium with different defined concs of an antibiotic
McFarland standard
to measure turbidity of diluted bacteria in saline. Hold against index card with black lines

MIC lab - serial dilution?
1:10
make serial dilution of antibiotic containing medium (TSB + 100 ug/mL gentamicin) into regular TSB.
Will later incolulate all 5 tubes with same amount of bacteria.
what do you need to do mix serial dilutions of gentamicin?
vortex
swirl all tubes well
remember this when comparing against McFarland standard
bacterial growth makes the liquid medium ________
turbic
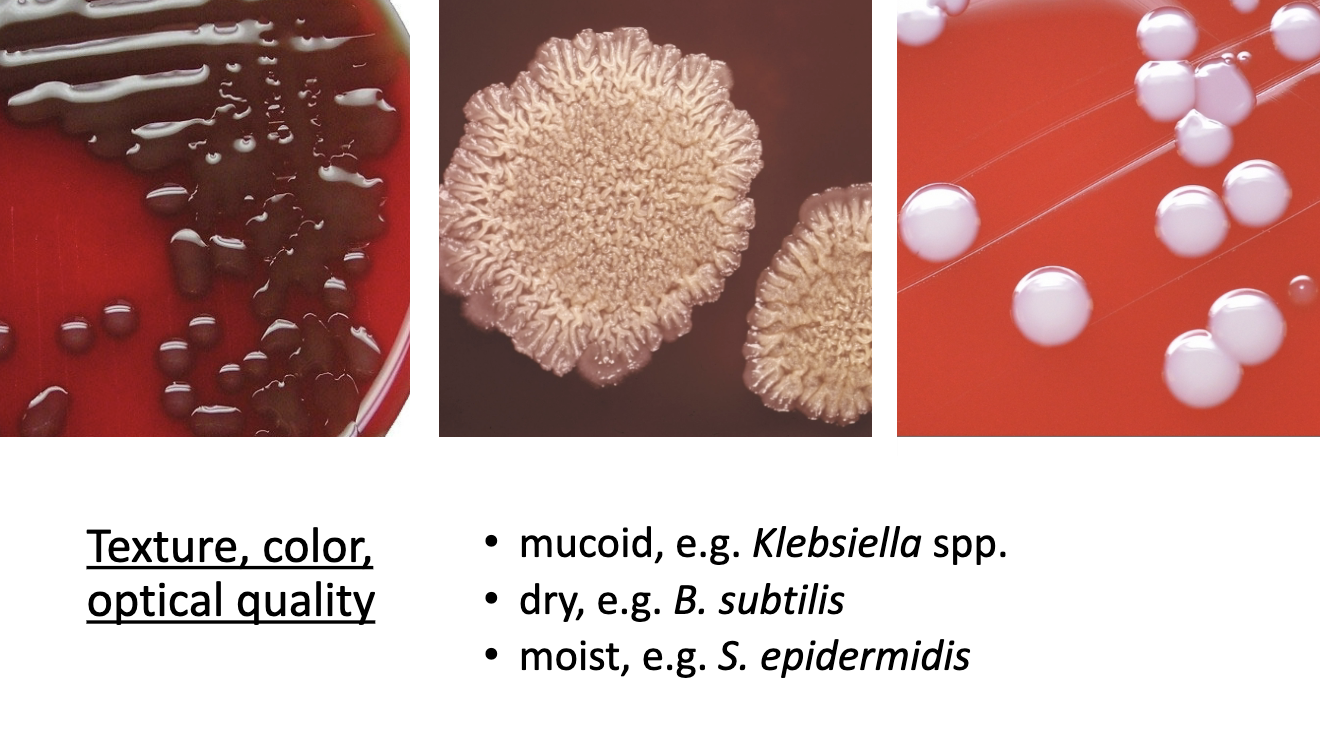
biomass description

colony description
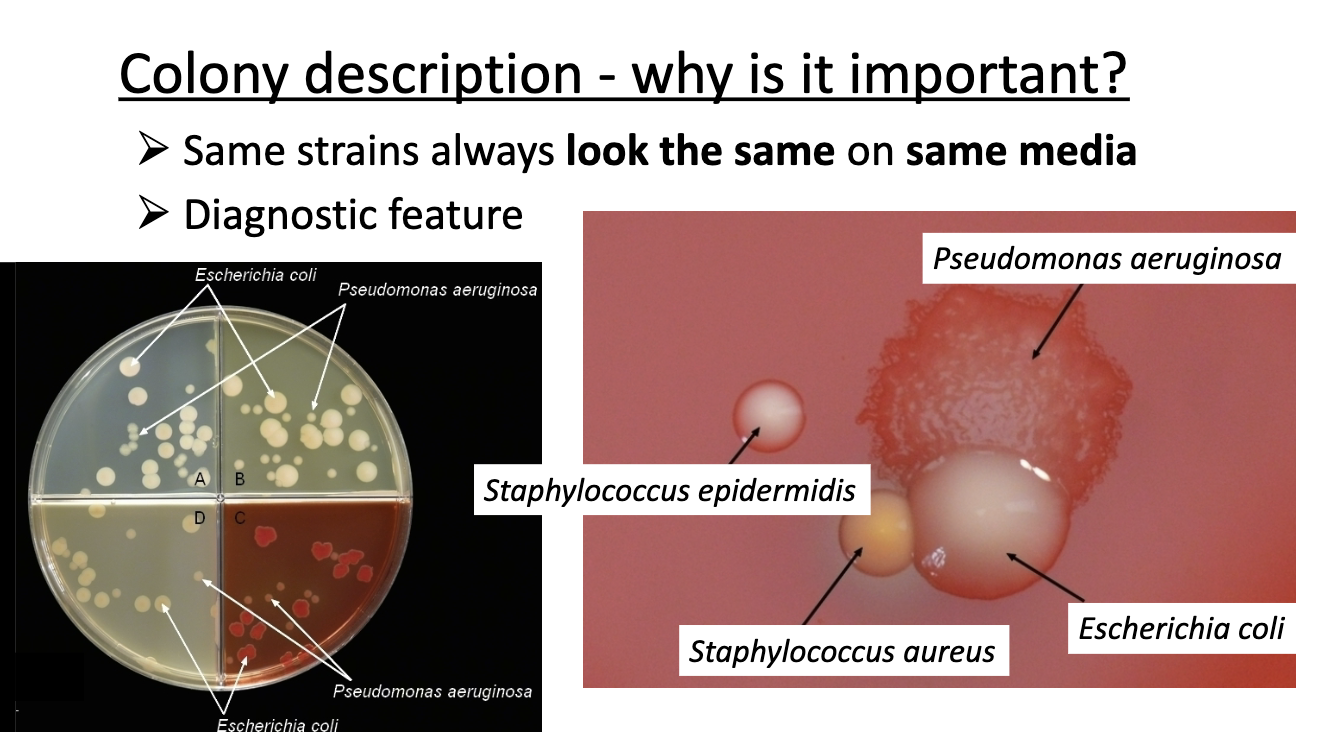
colony description words
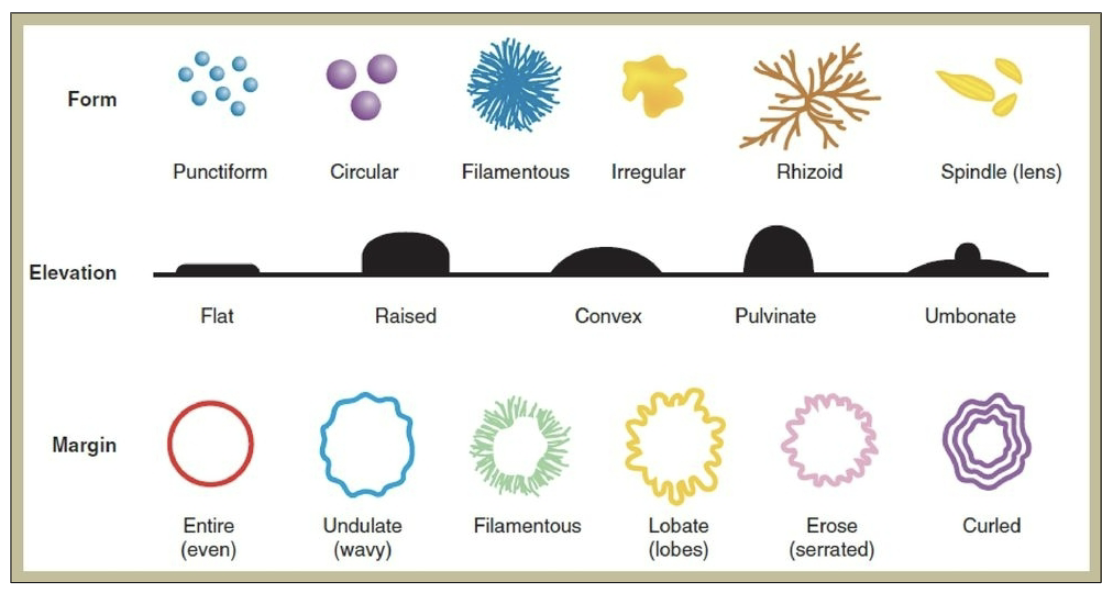
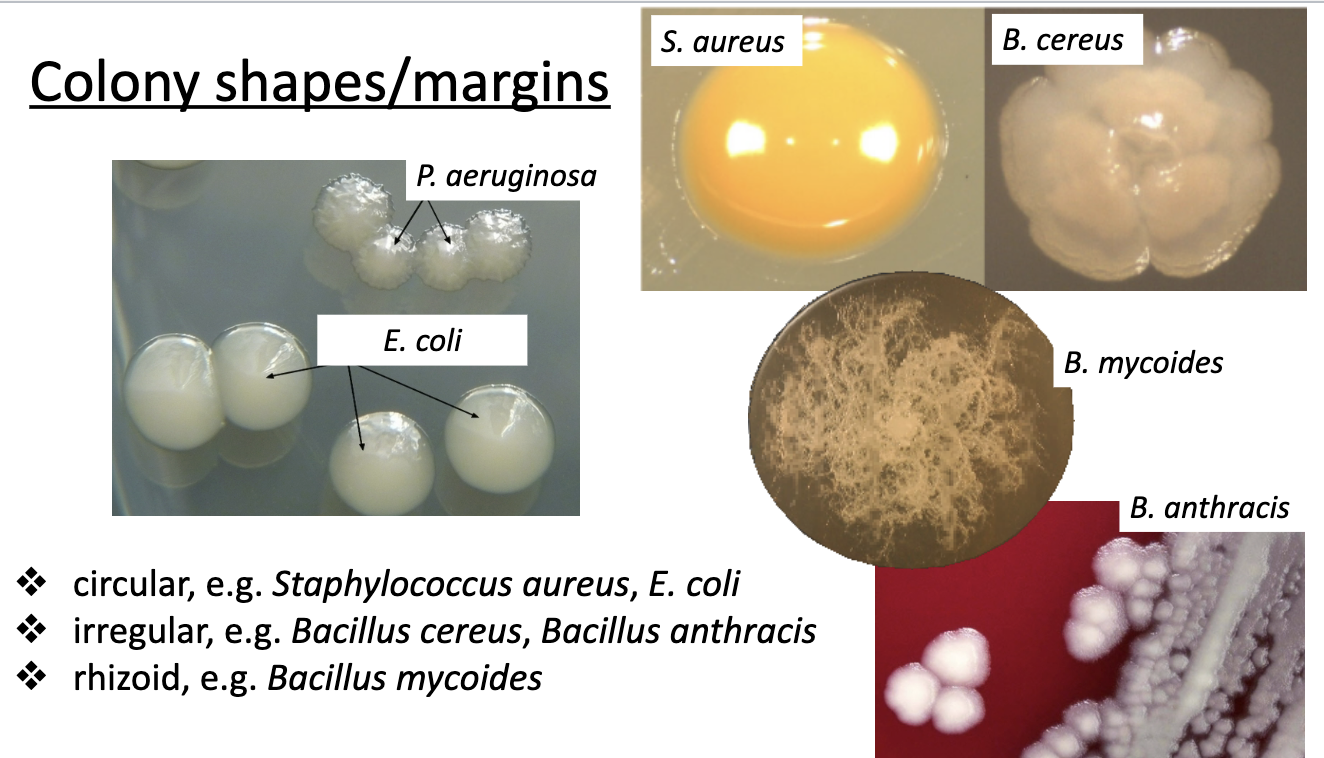
colony shape
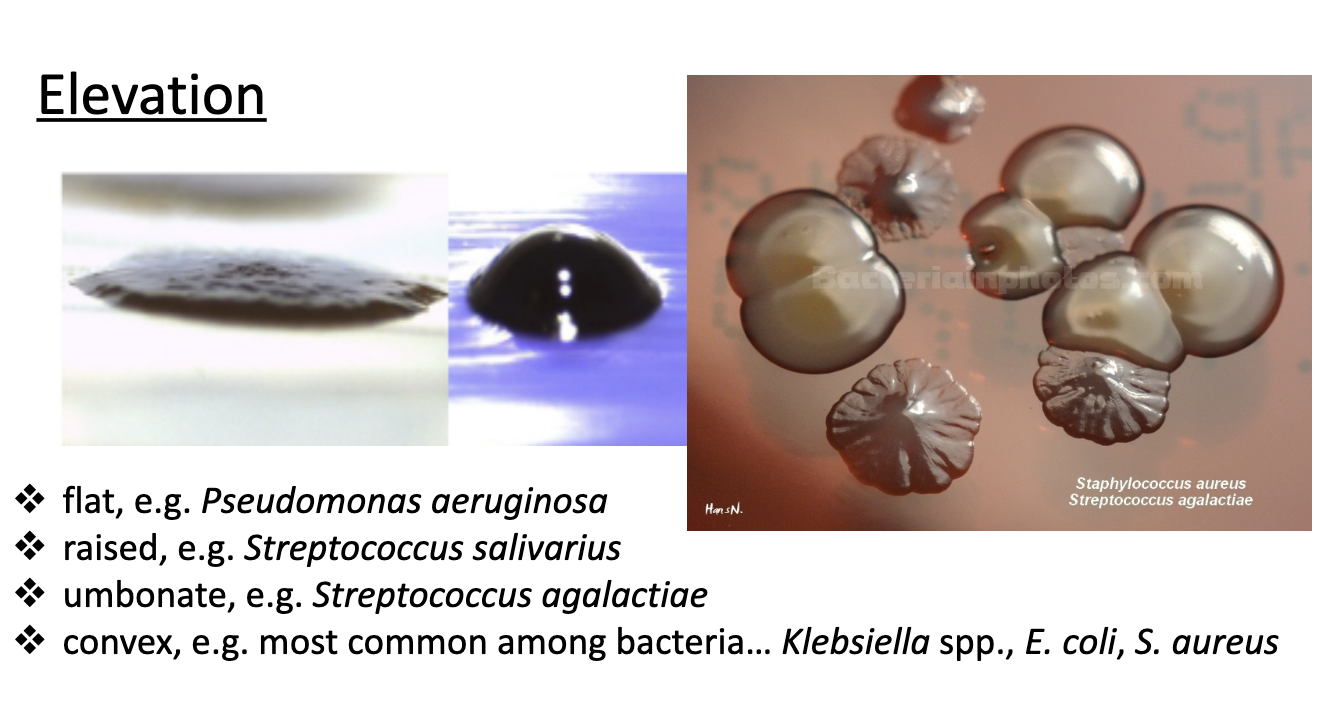
colony elevation
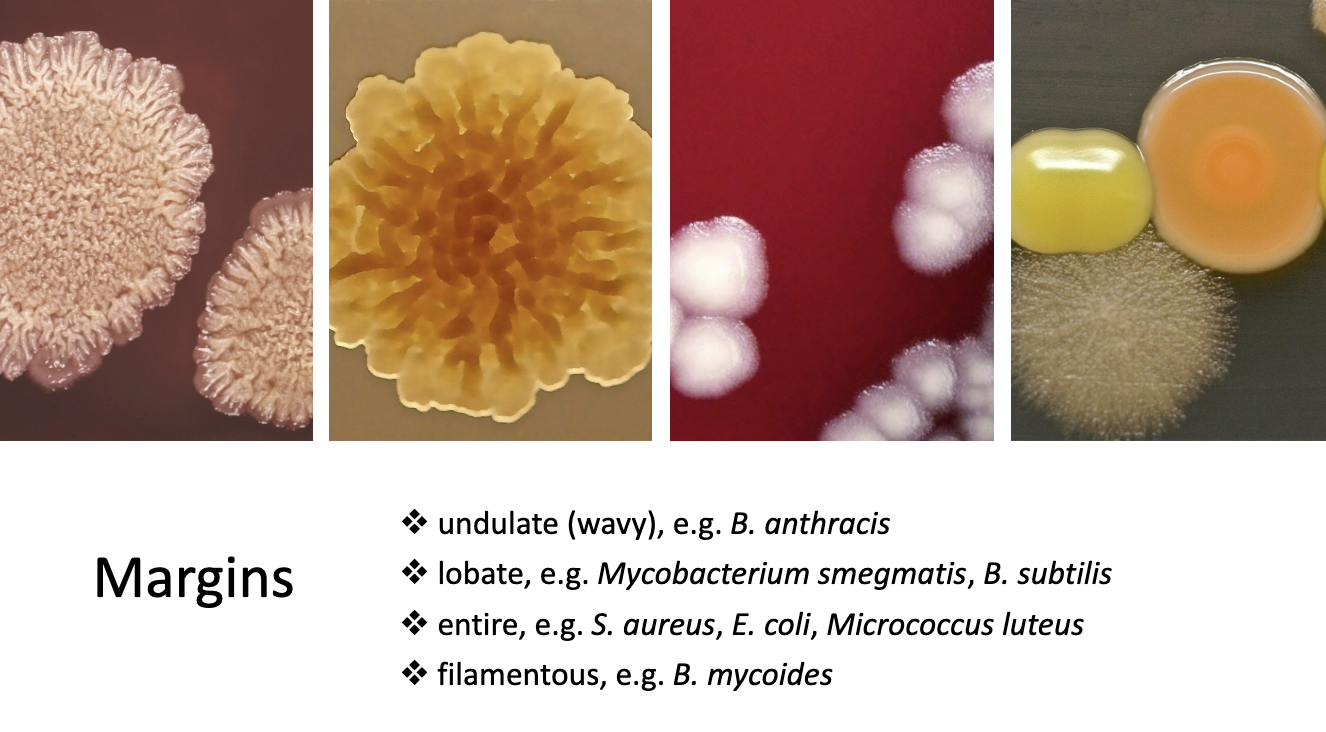
colony margins
colony optical quality