Respiratory System
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
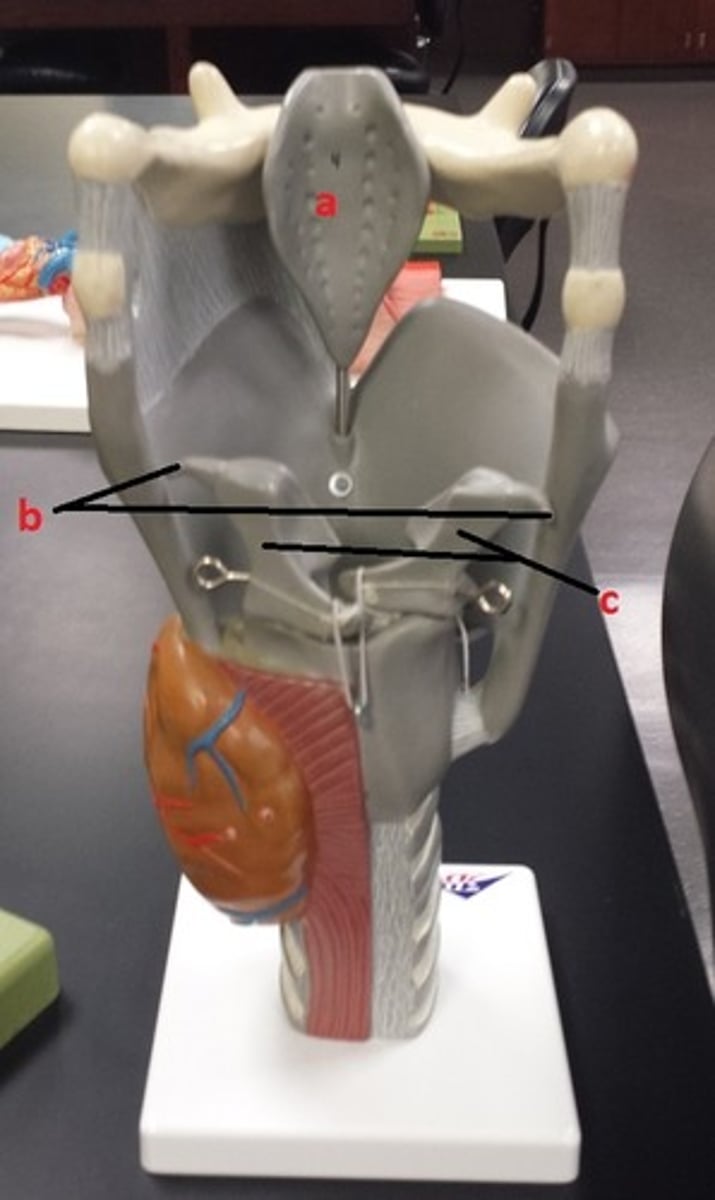
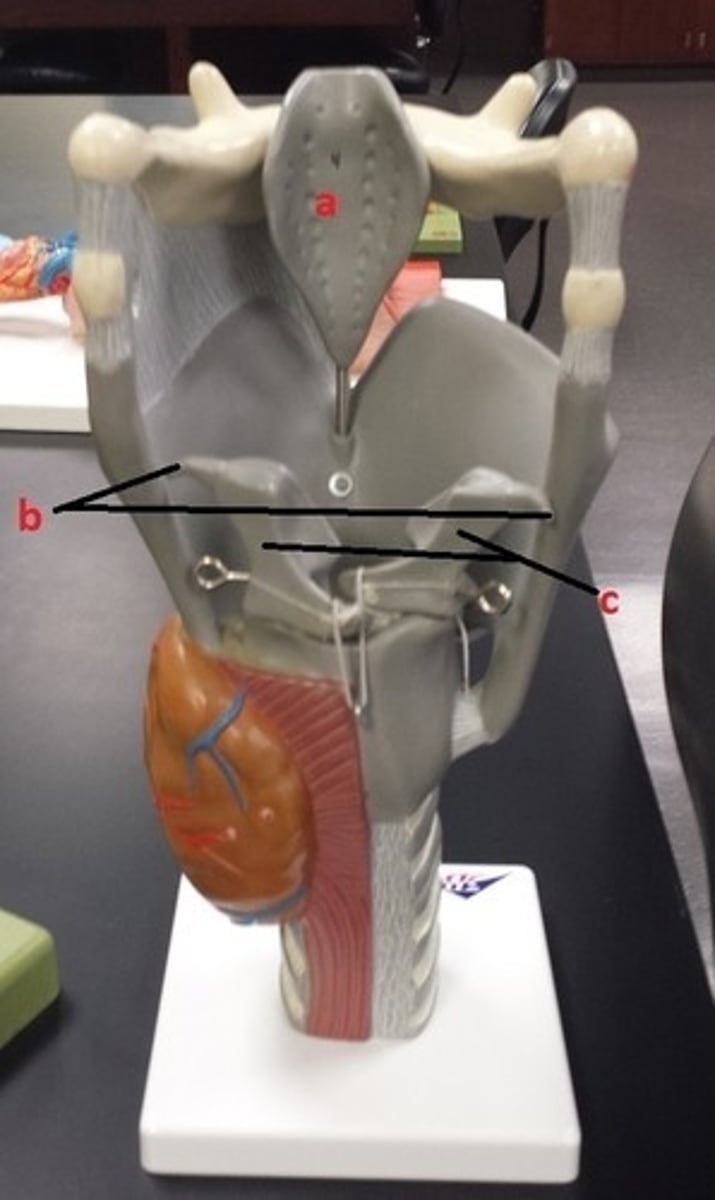
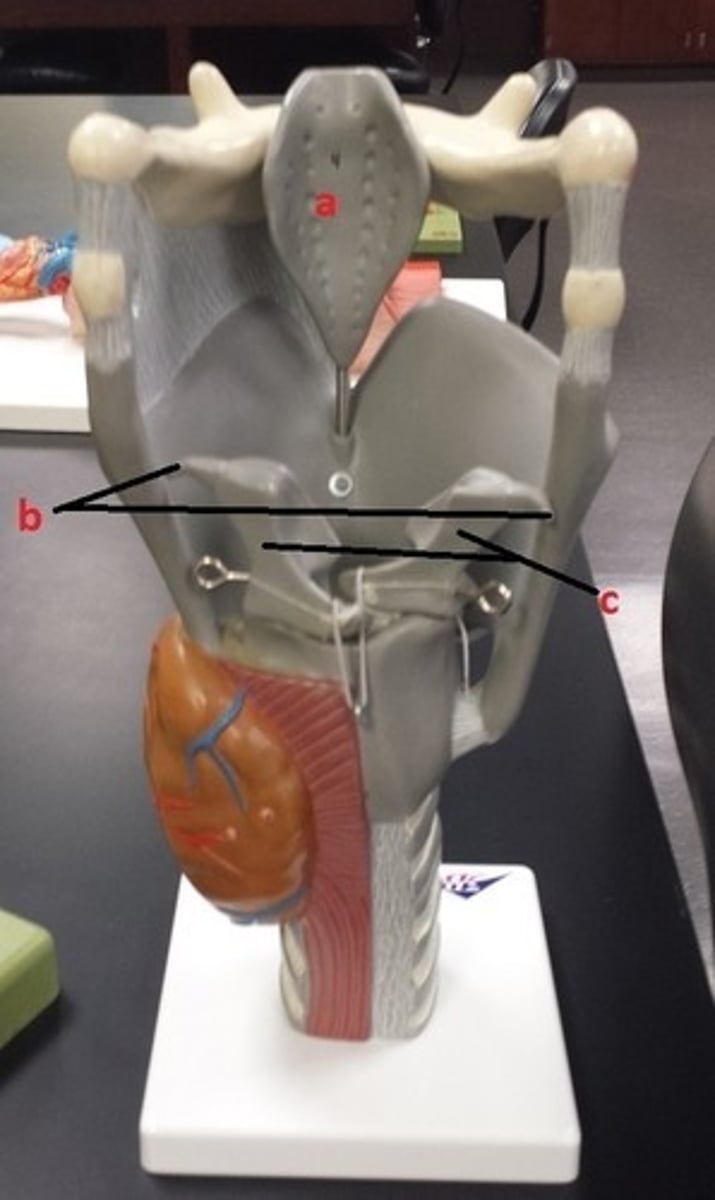
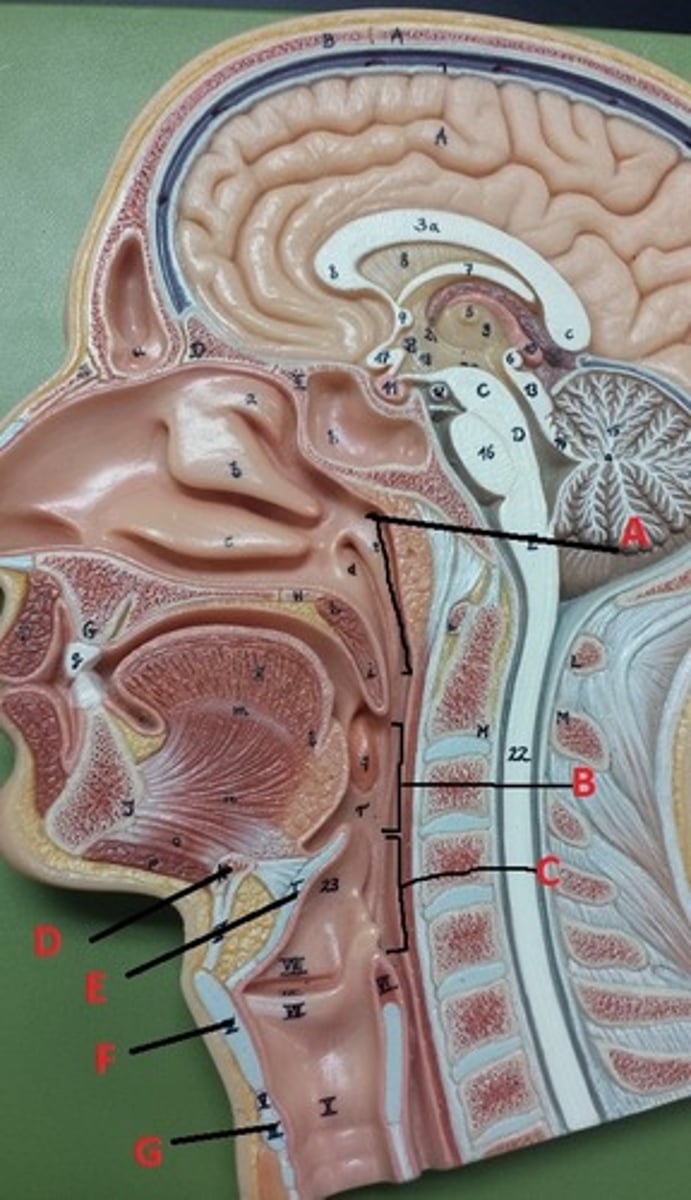
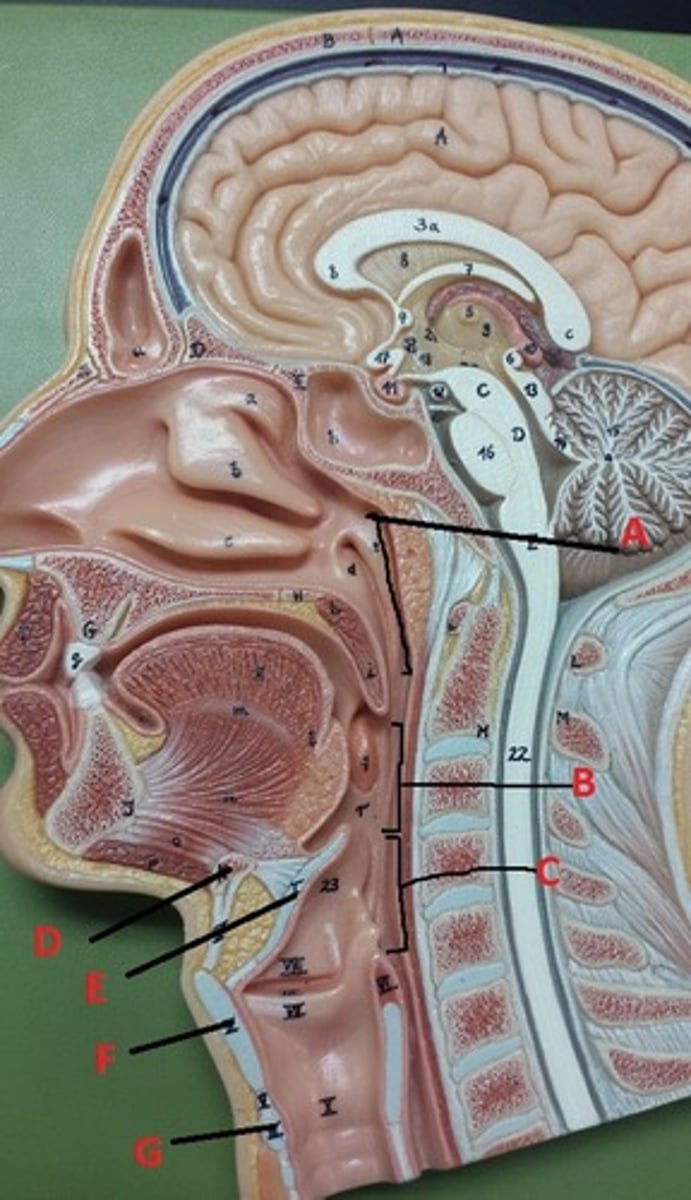
hyoid bone
A
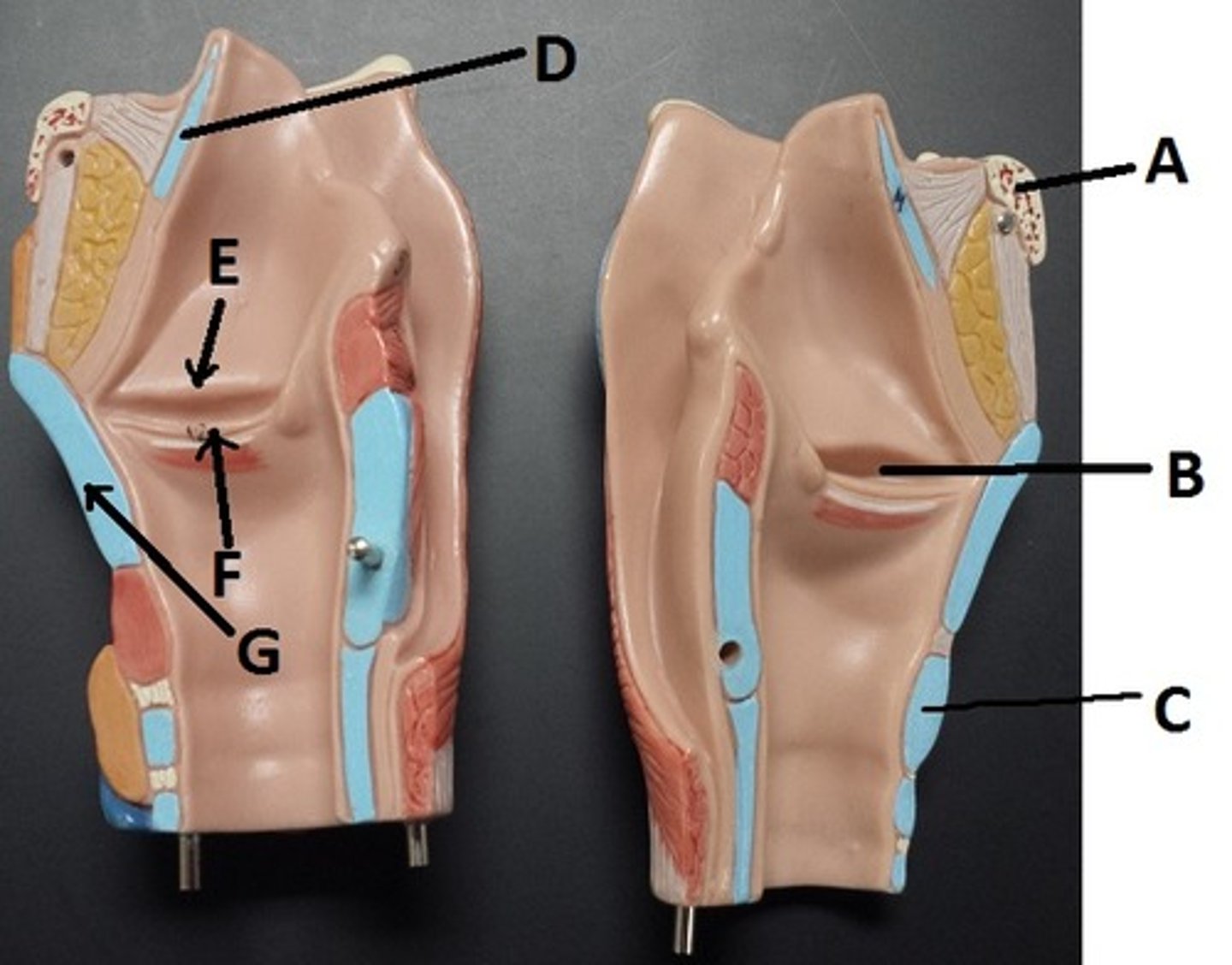
glottis
B
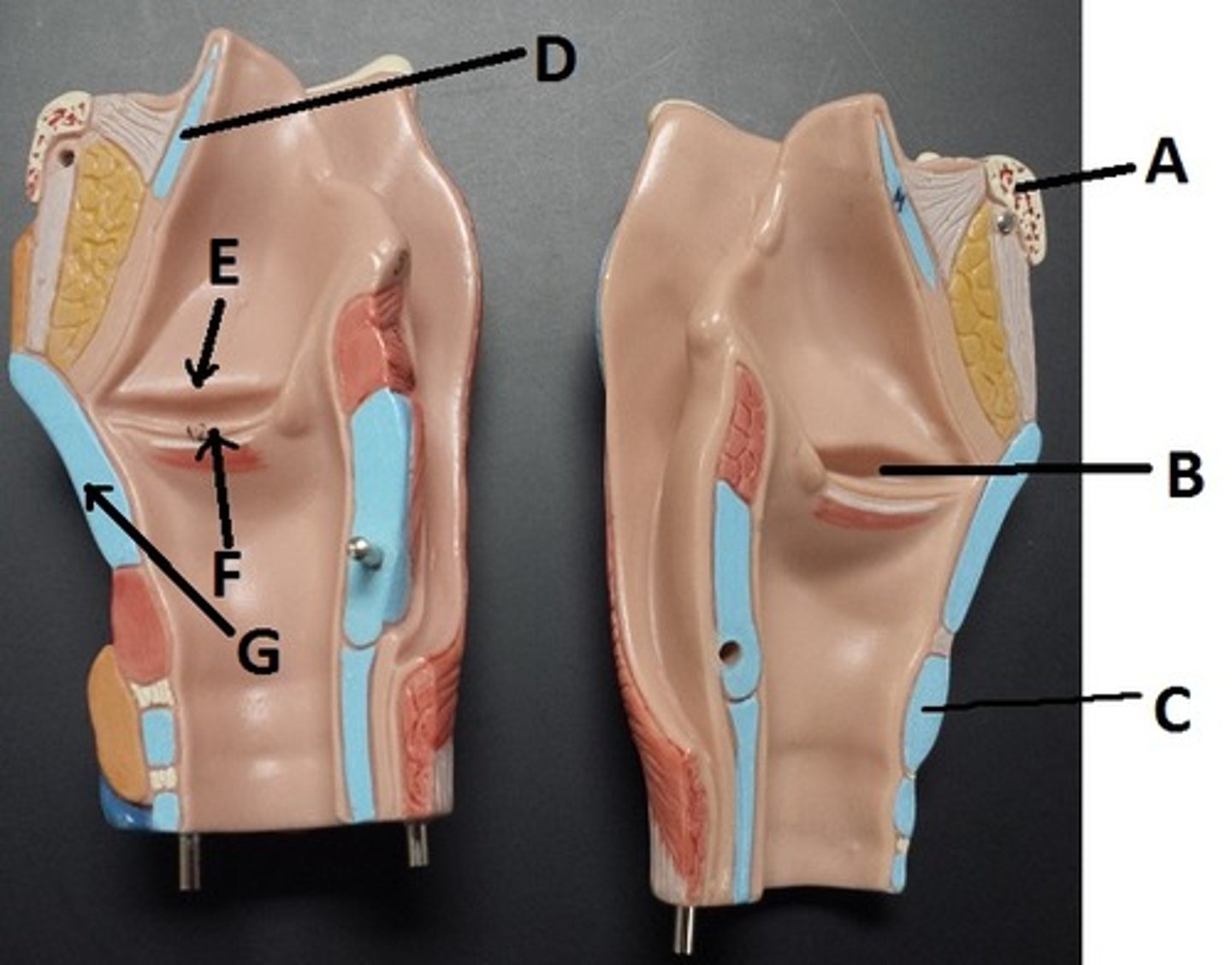
cricoid cartilage
C
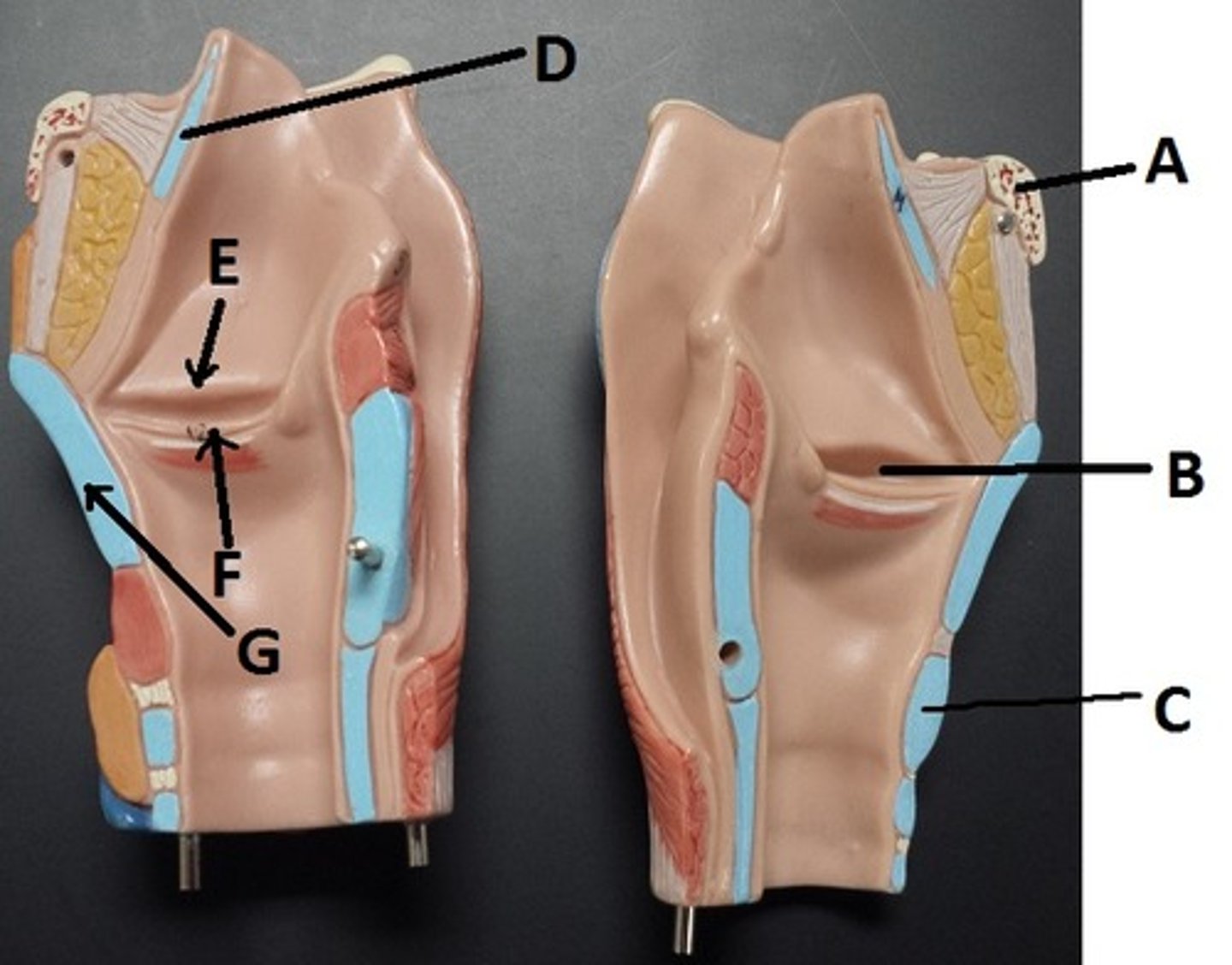
epiglottis
D
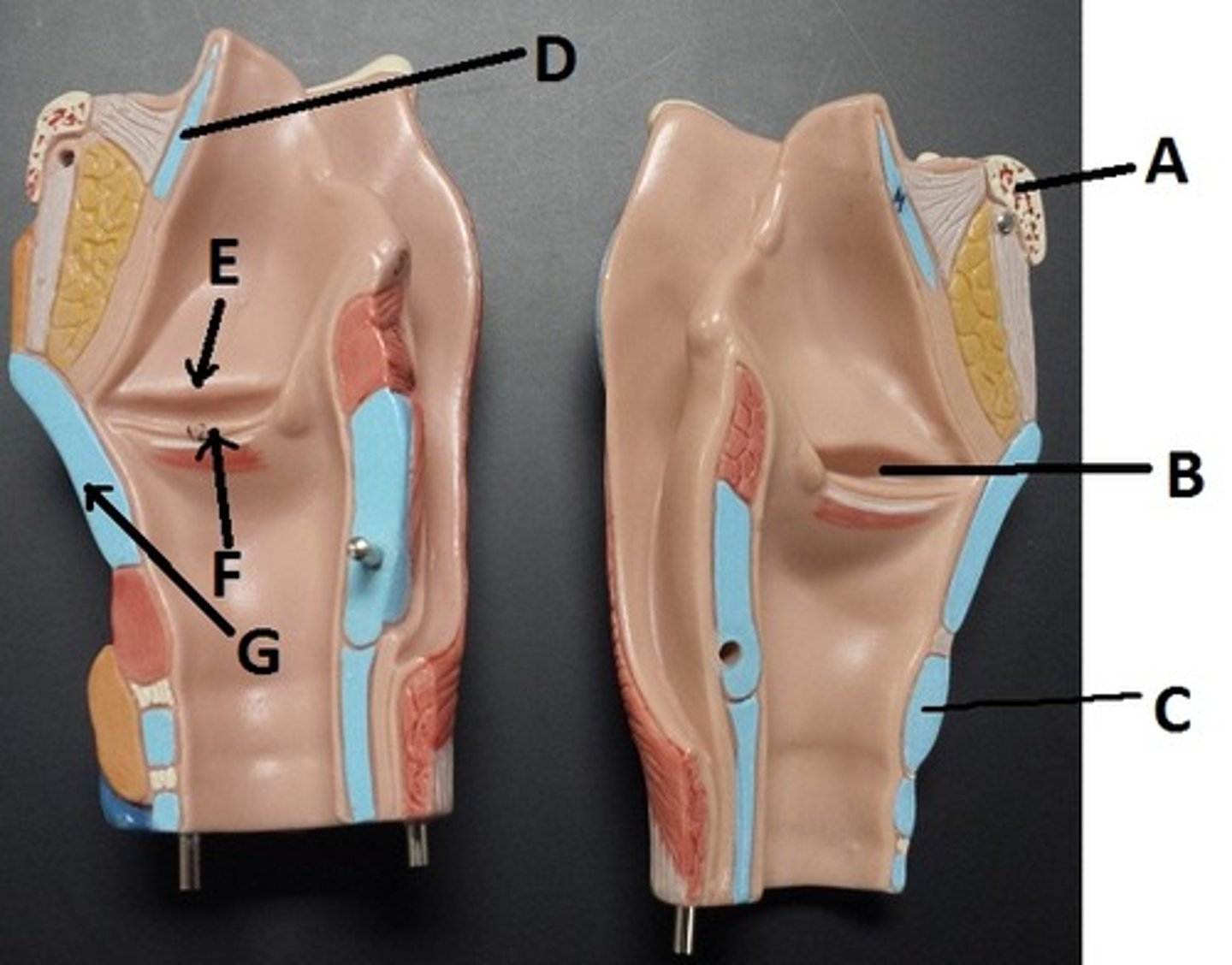
vestibular folds
E
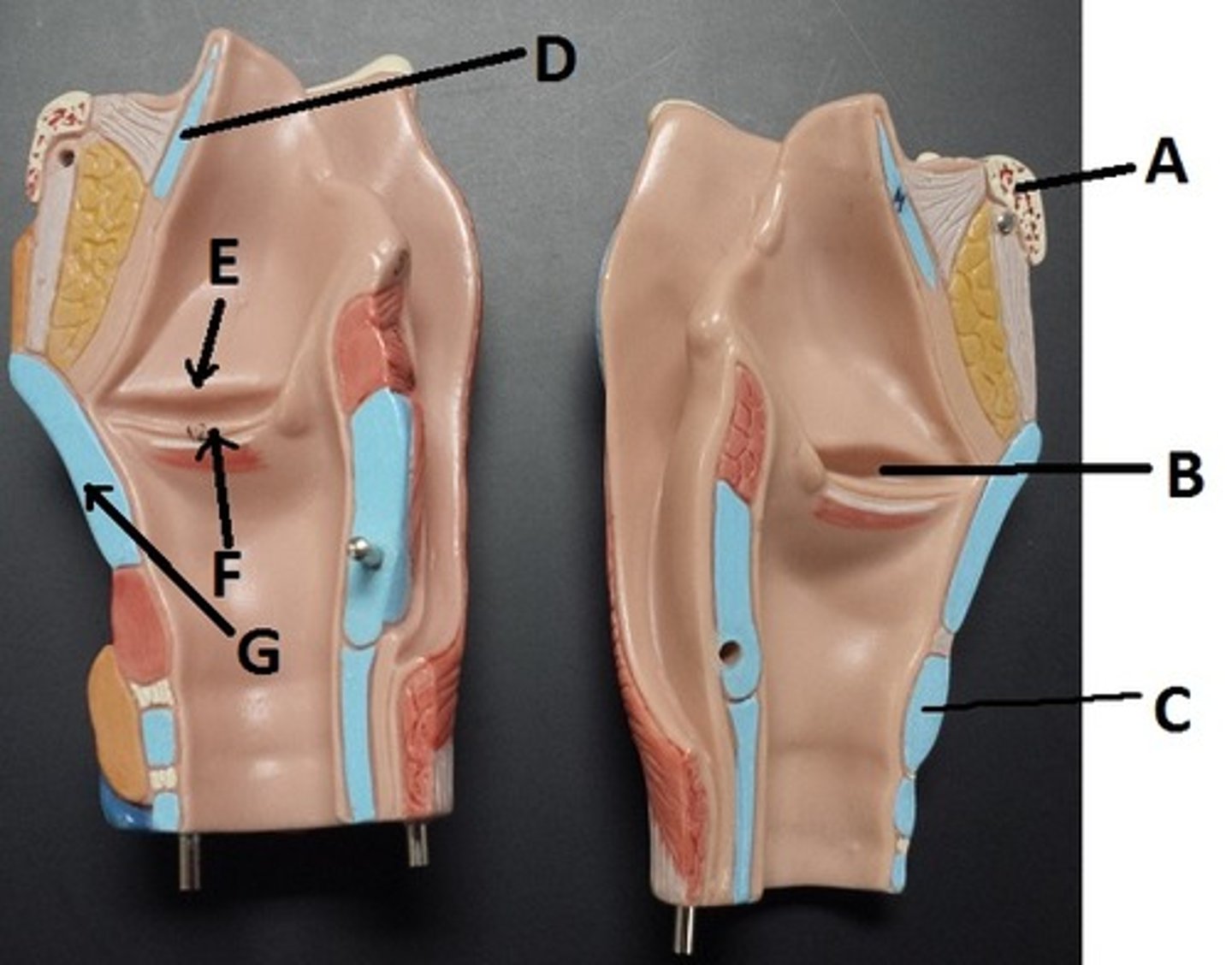
true vocal cords
F
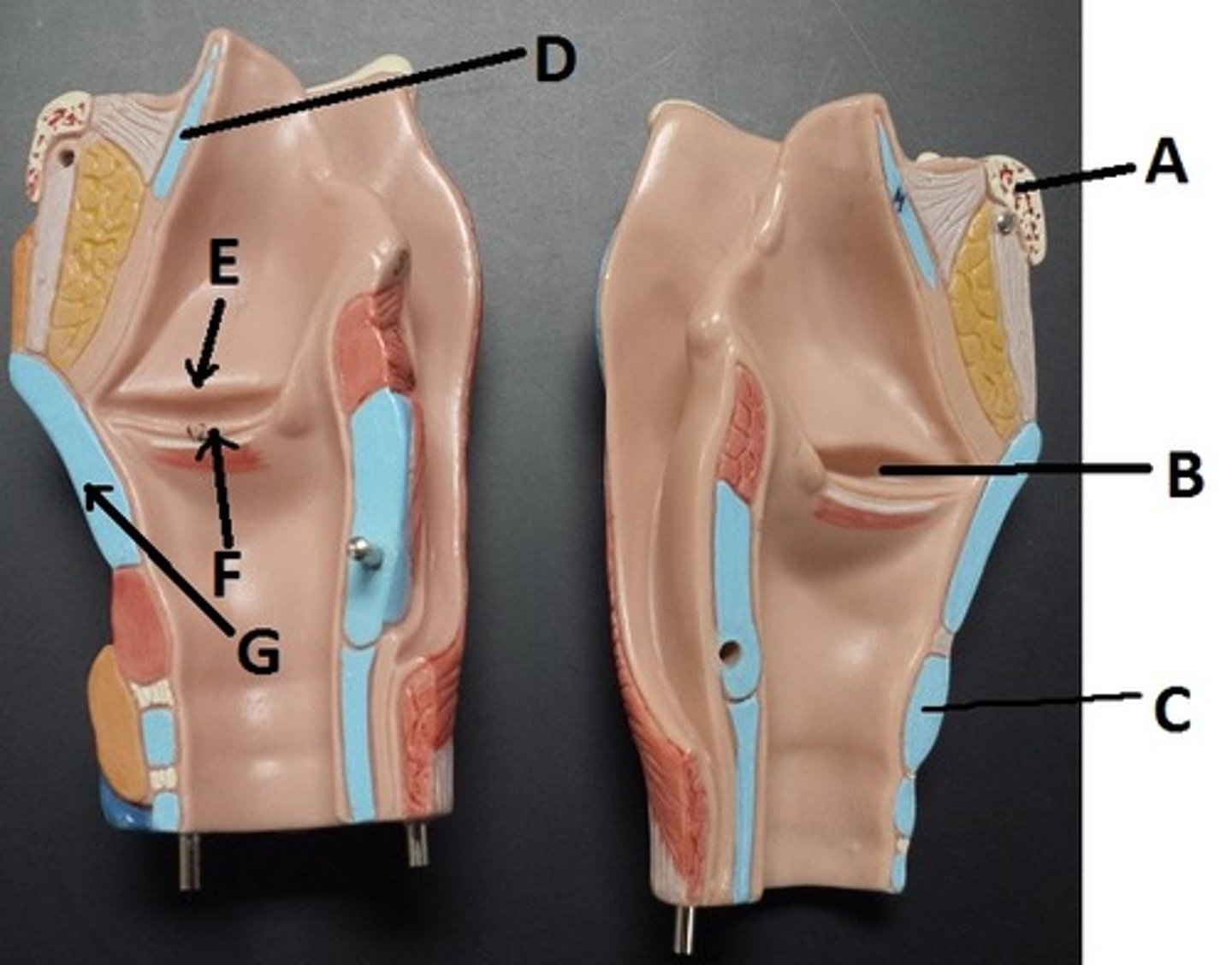
thyroid cartilage
G
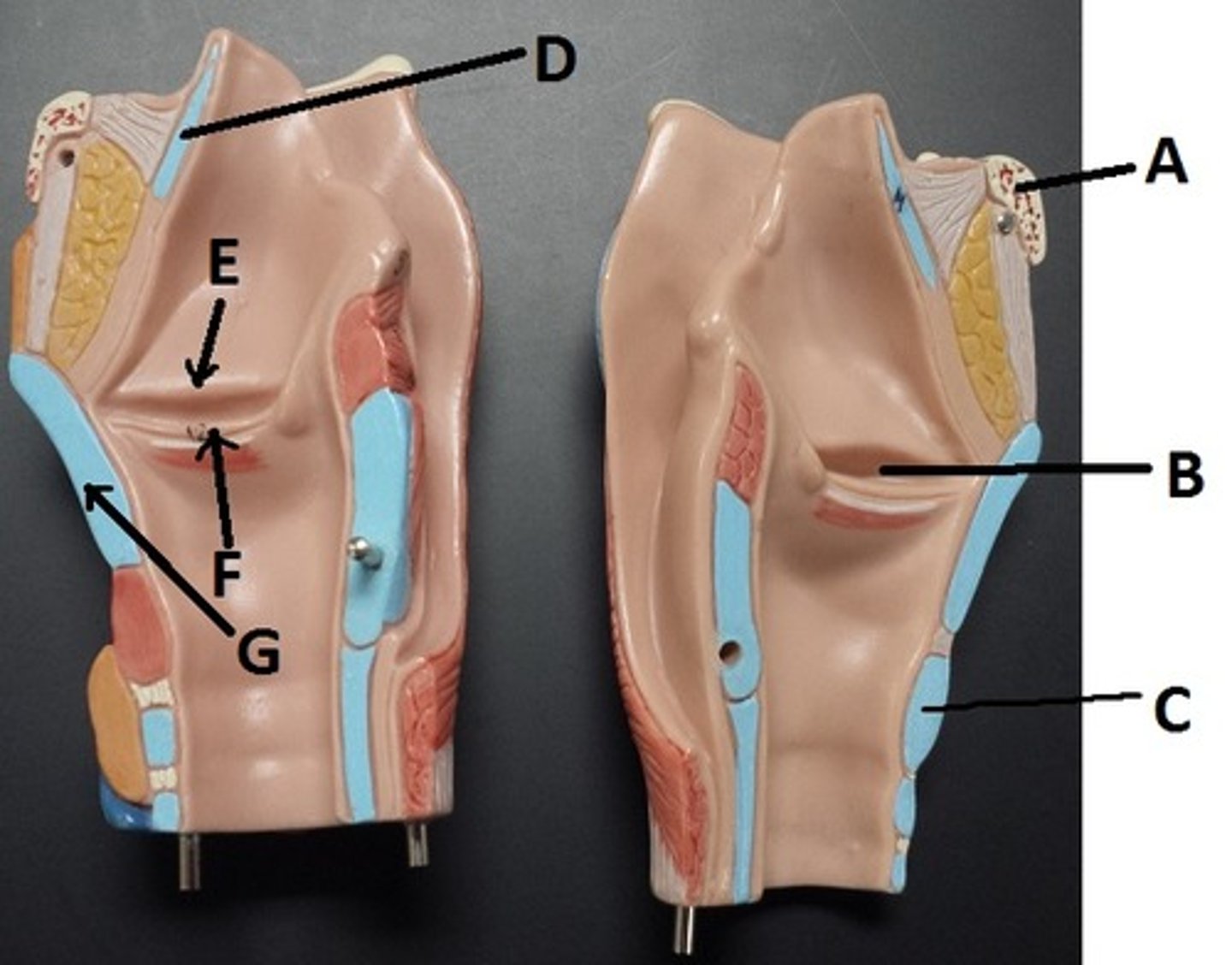
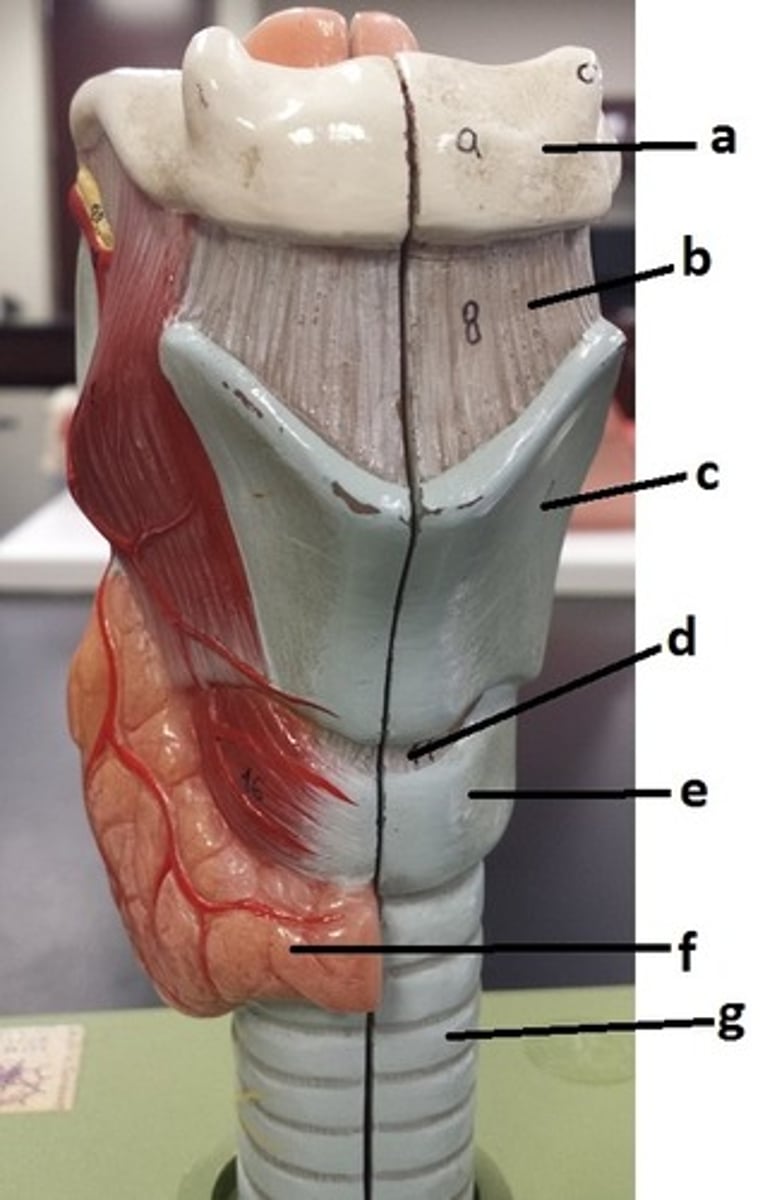
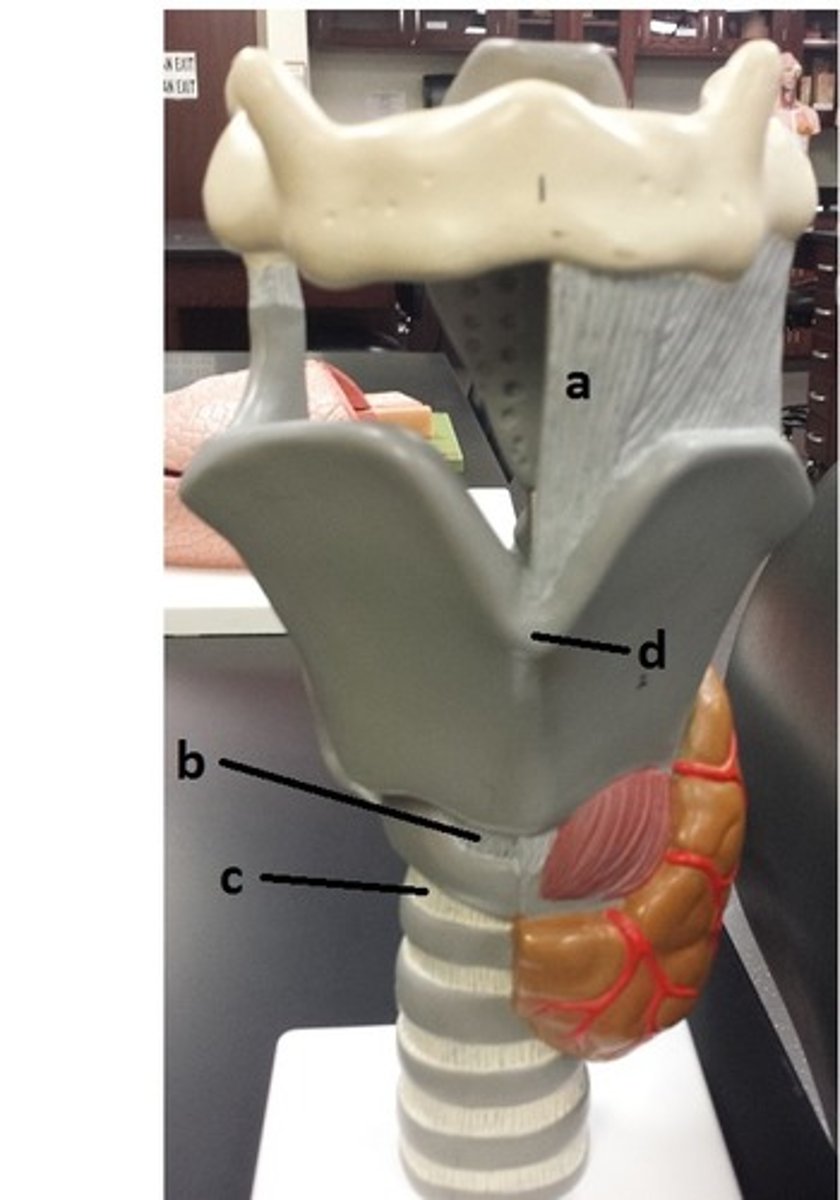
hyoid bone
a
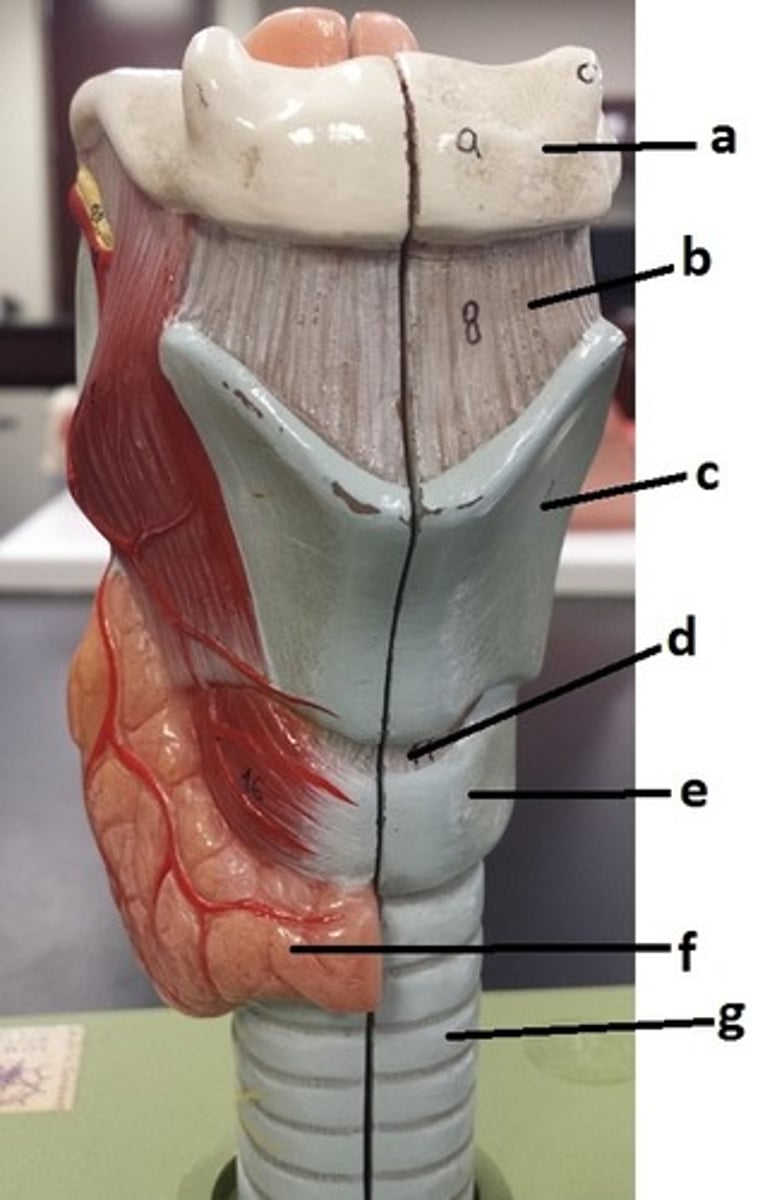
thyrohyoid ligament
b
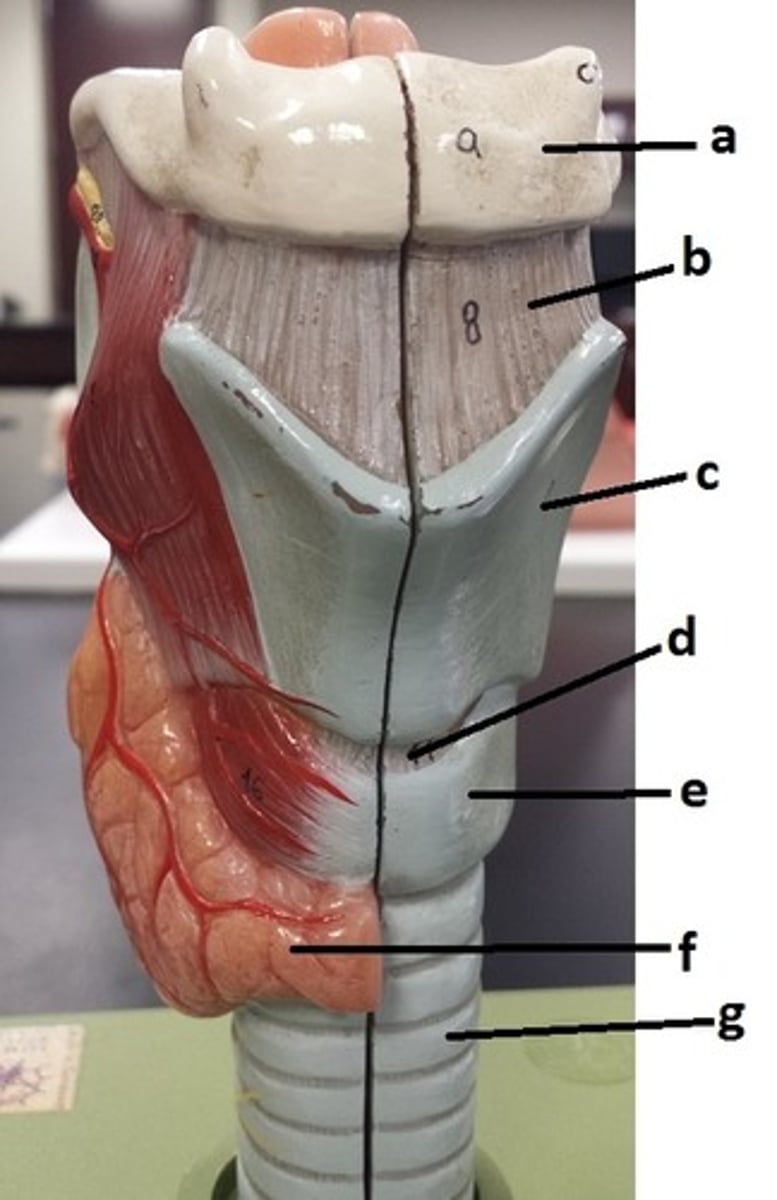
thyroid cartilage
c
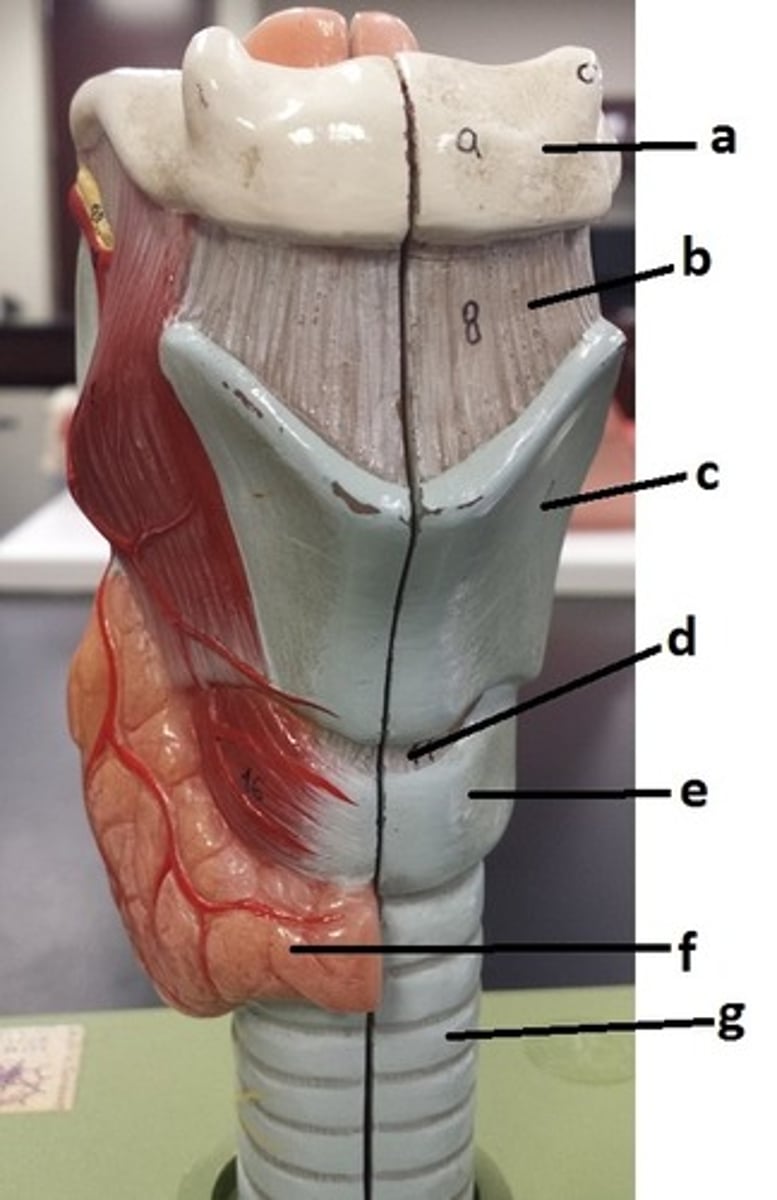
cricothyroid ligament
d
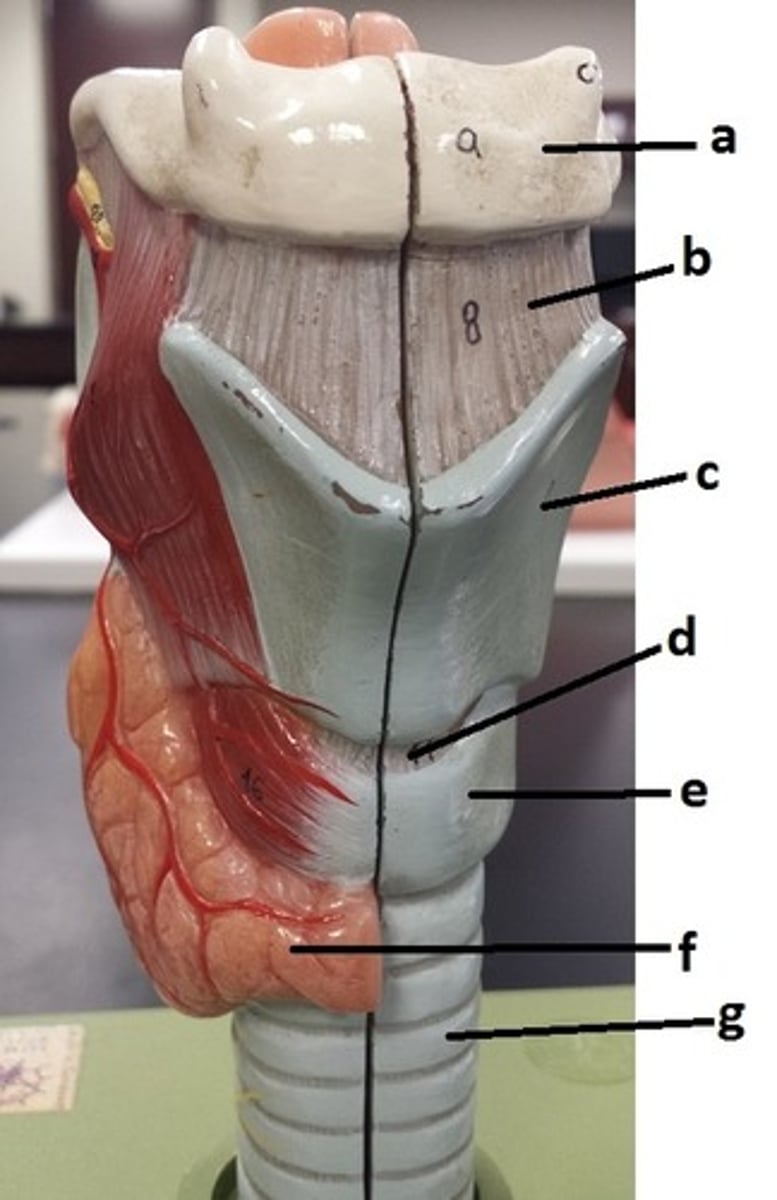
cricoid cartilage
e
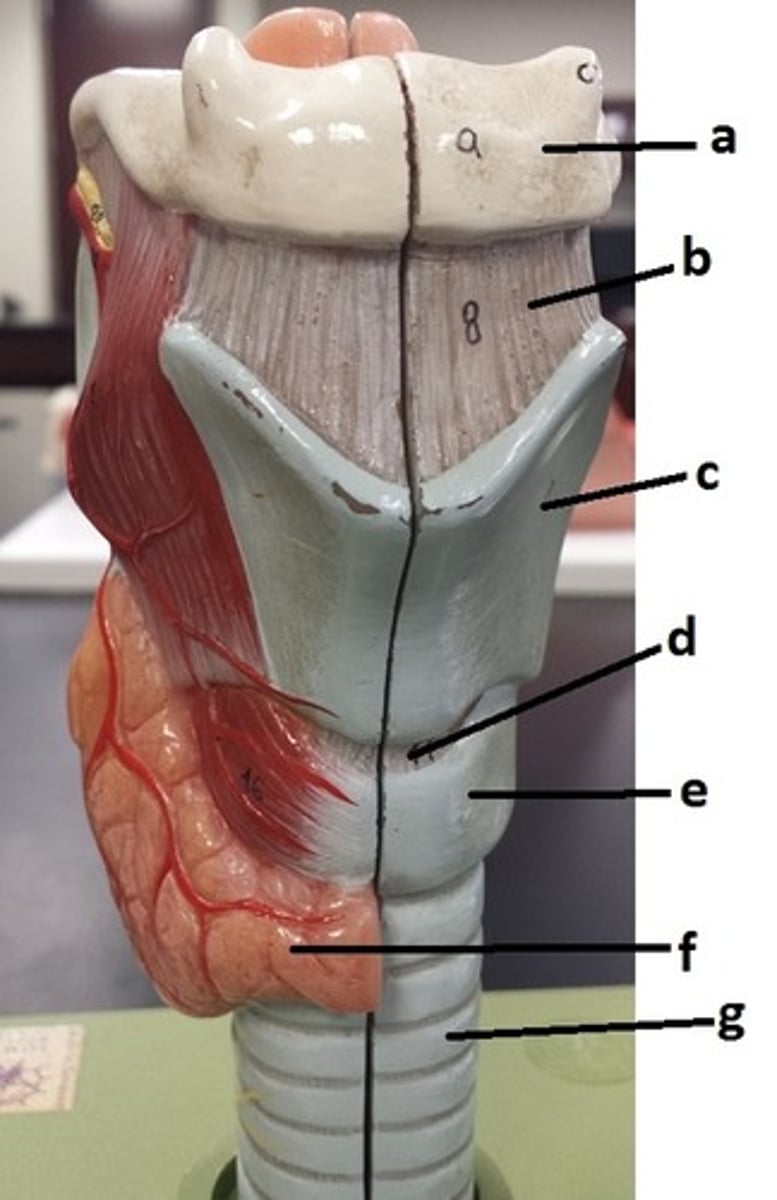
thyroid gland
f
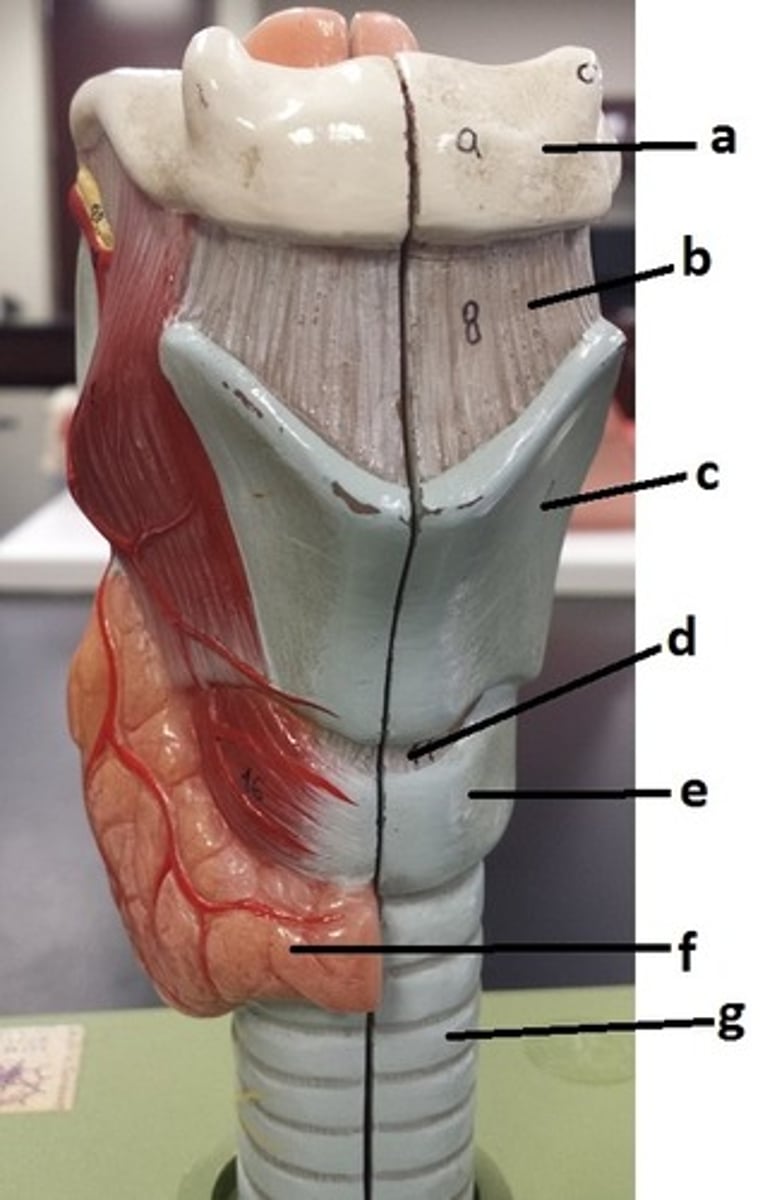
tracheal cartilage (C-ring of trachea)
g
epiglottis
a
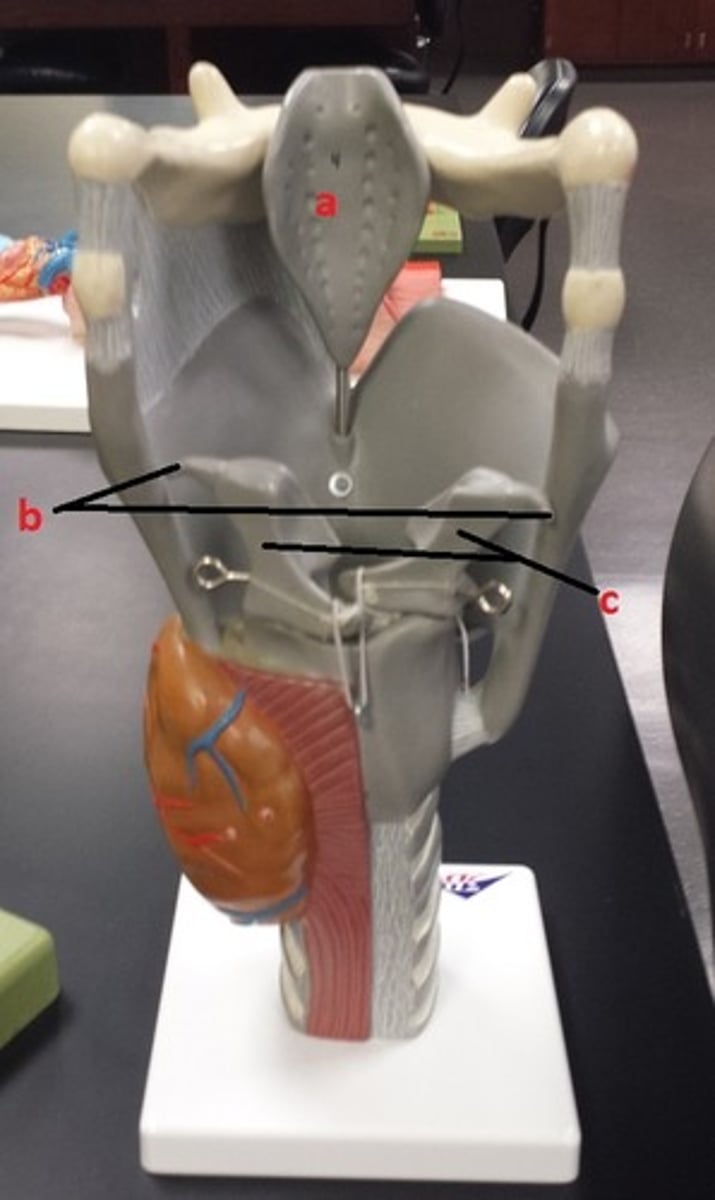
corniculate cartilages
b
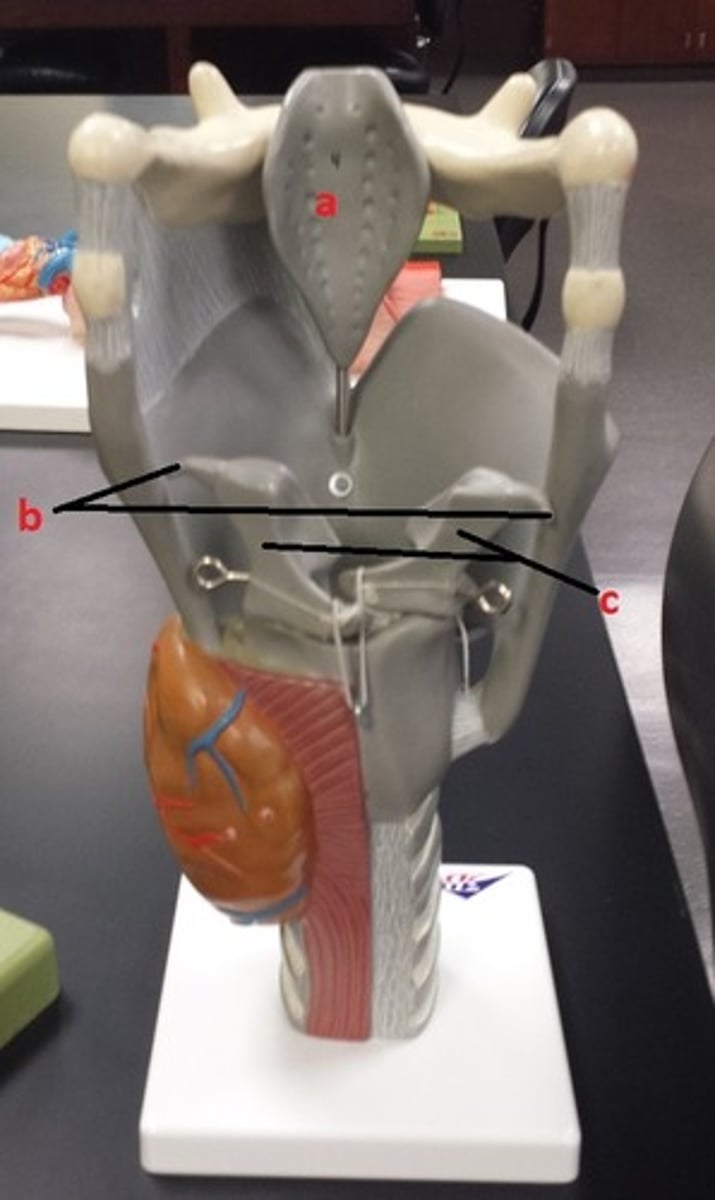
arytenoid cartilages
c
most of c except tips
Which letter(s) represent structure(s) composed up of hyaline cartilage?
a and b; tips of c
Which letter(s) represent structure(s) composed up of elastic cartilage?
thyrohyoid ligament
a
cricothyroid ligament
b
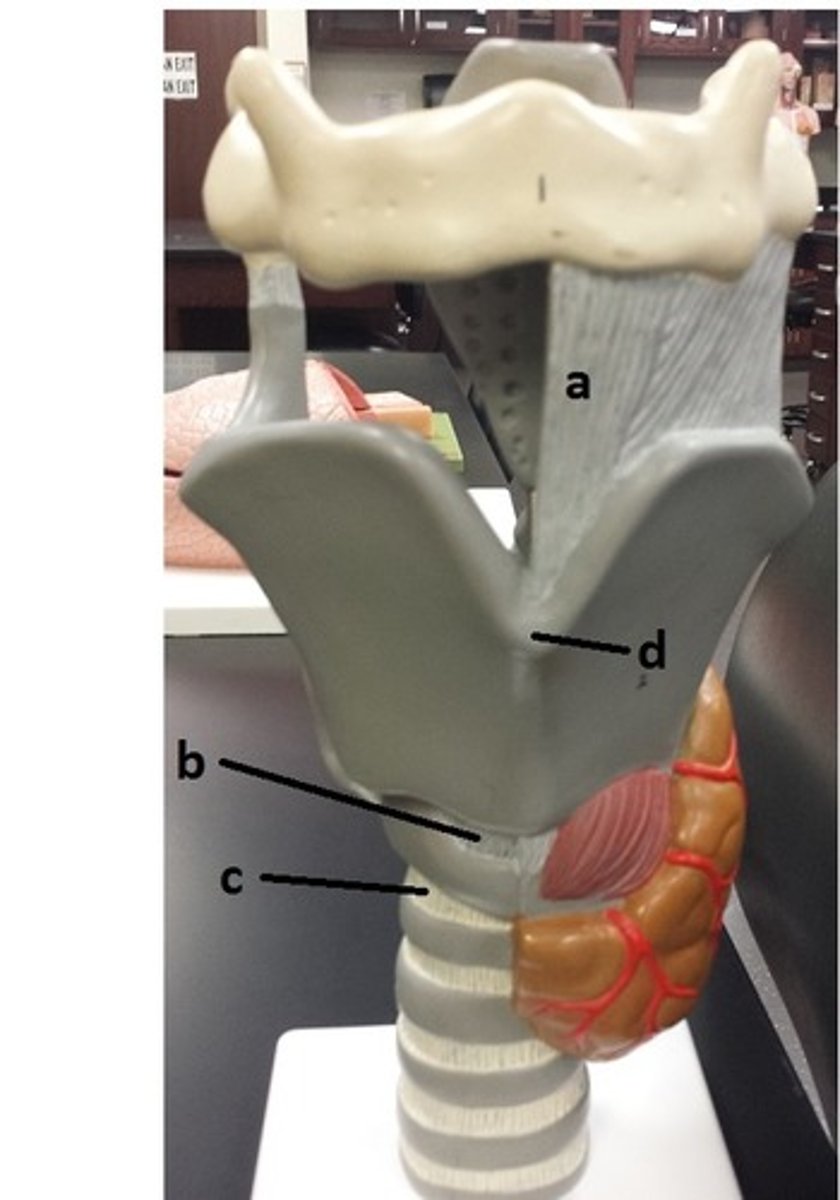
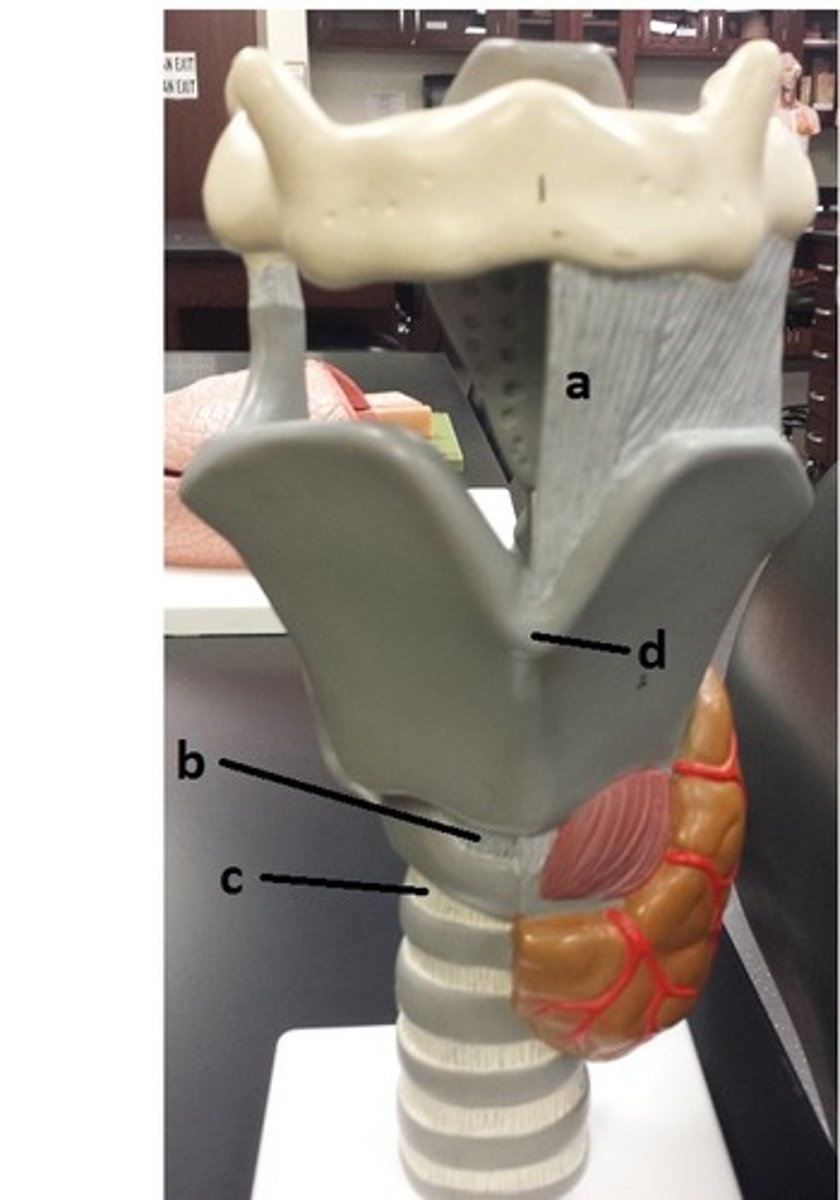
laryngeal prominence
d
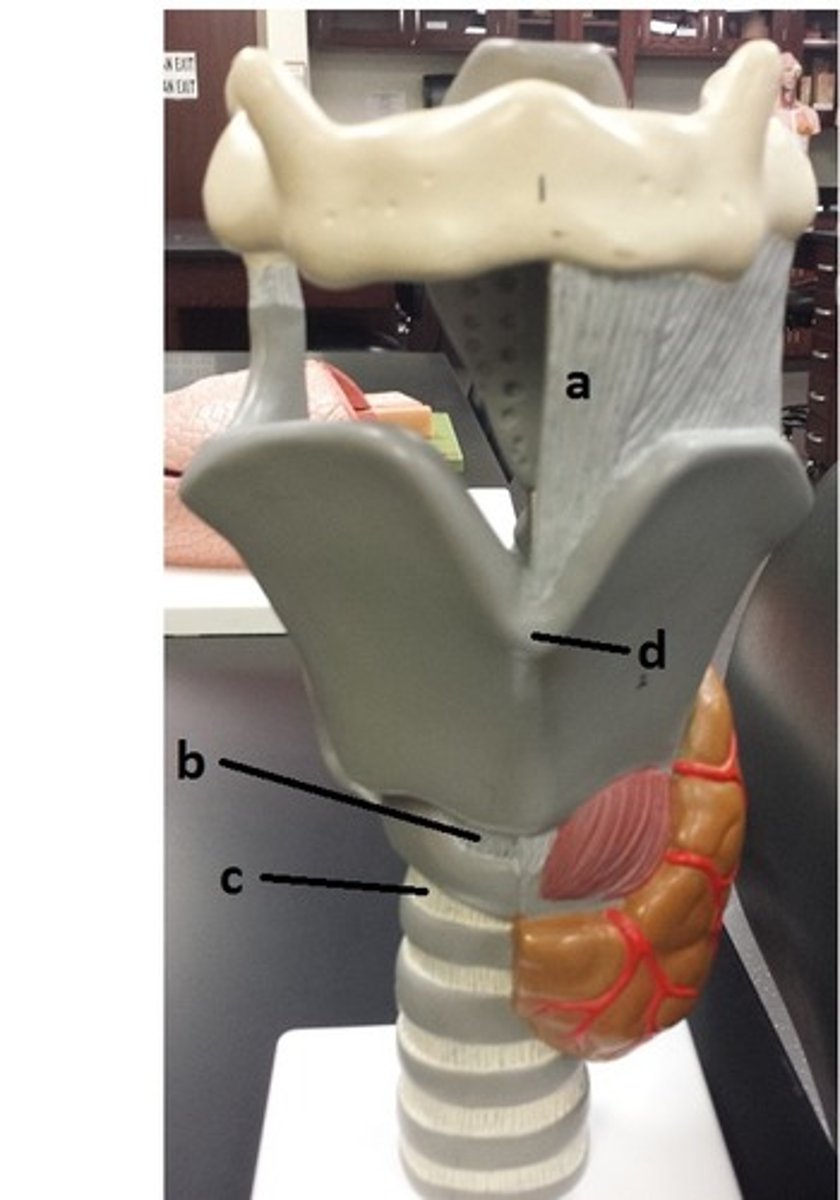
cricotracheal ligament
c
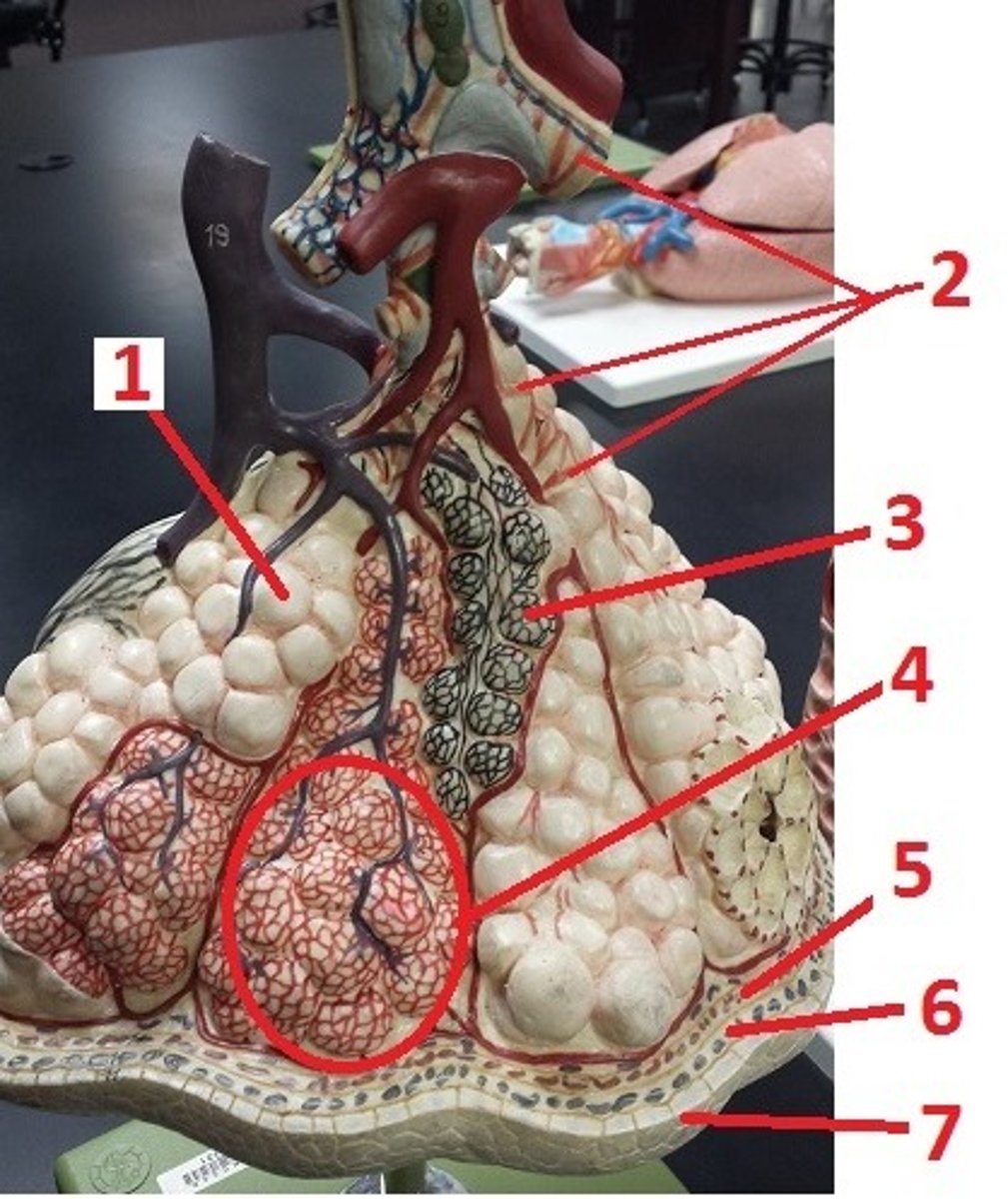
alveolus
1
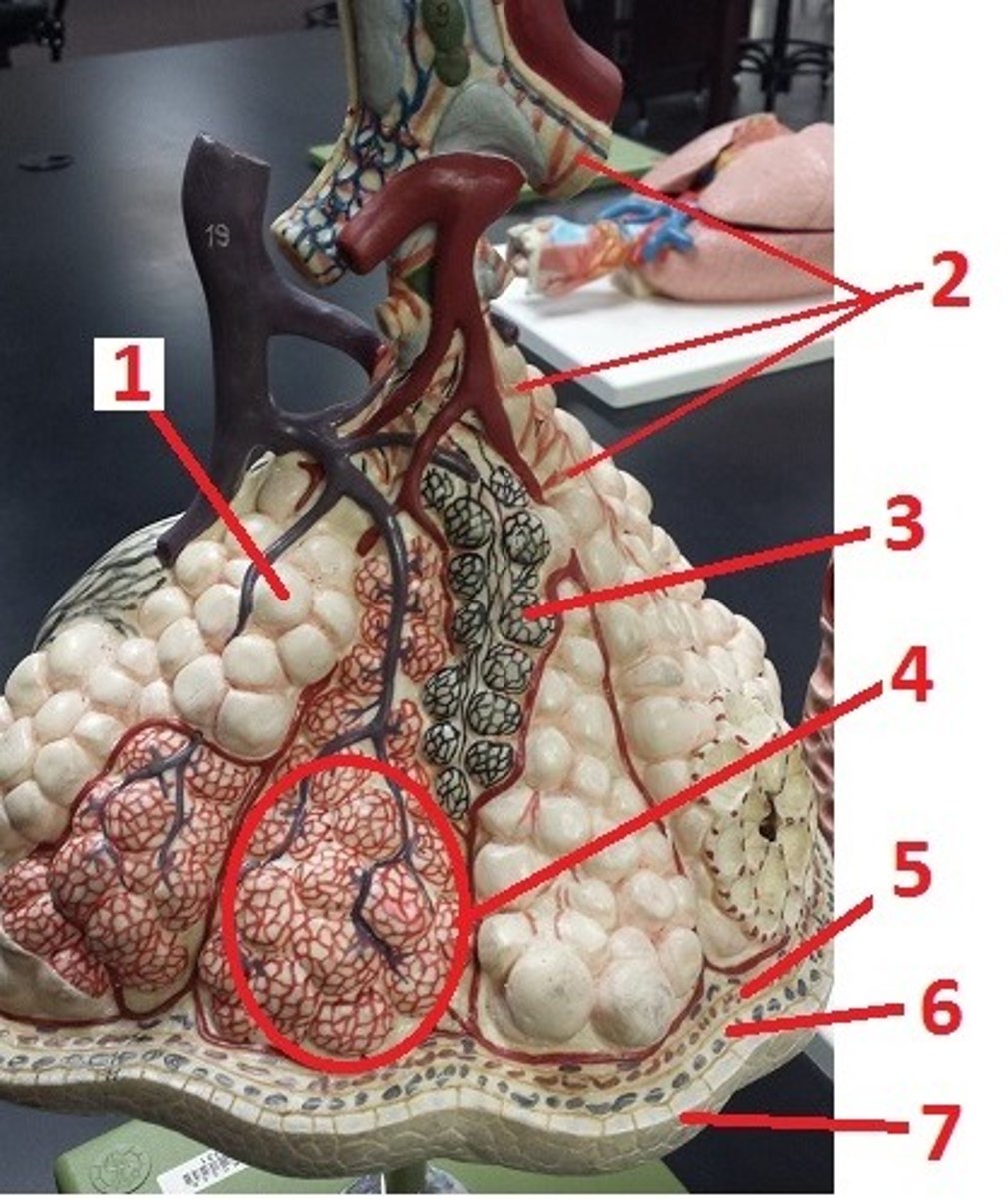
alveolar sac
4
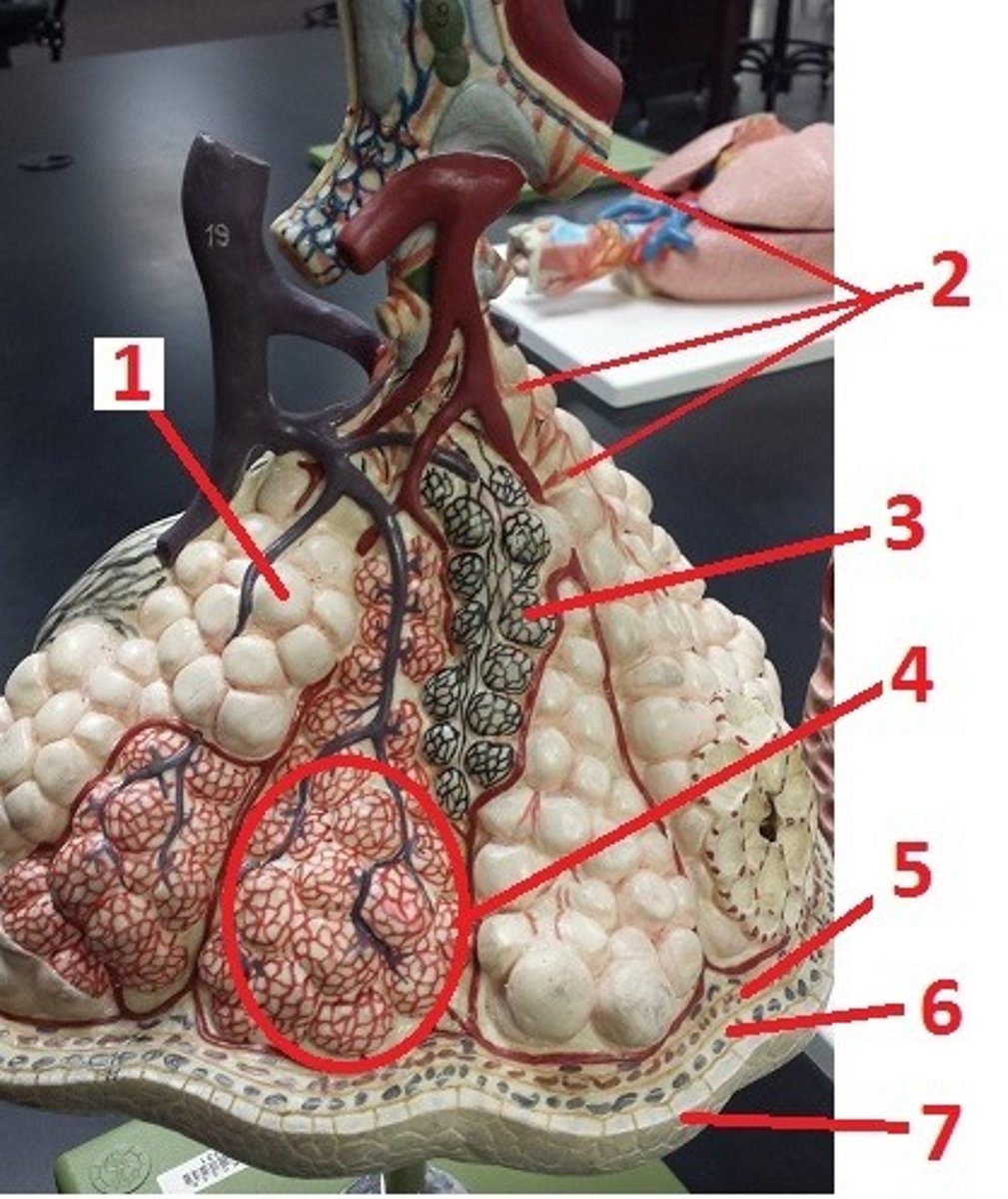
visceral pleura
5
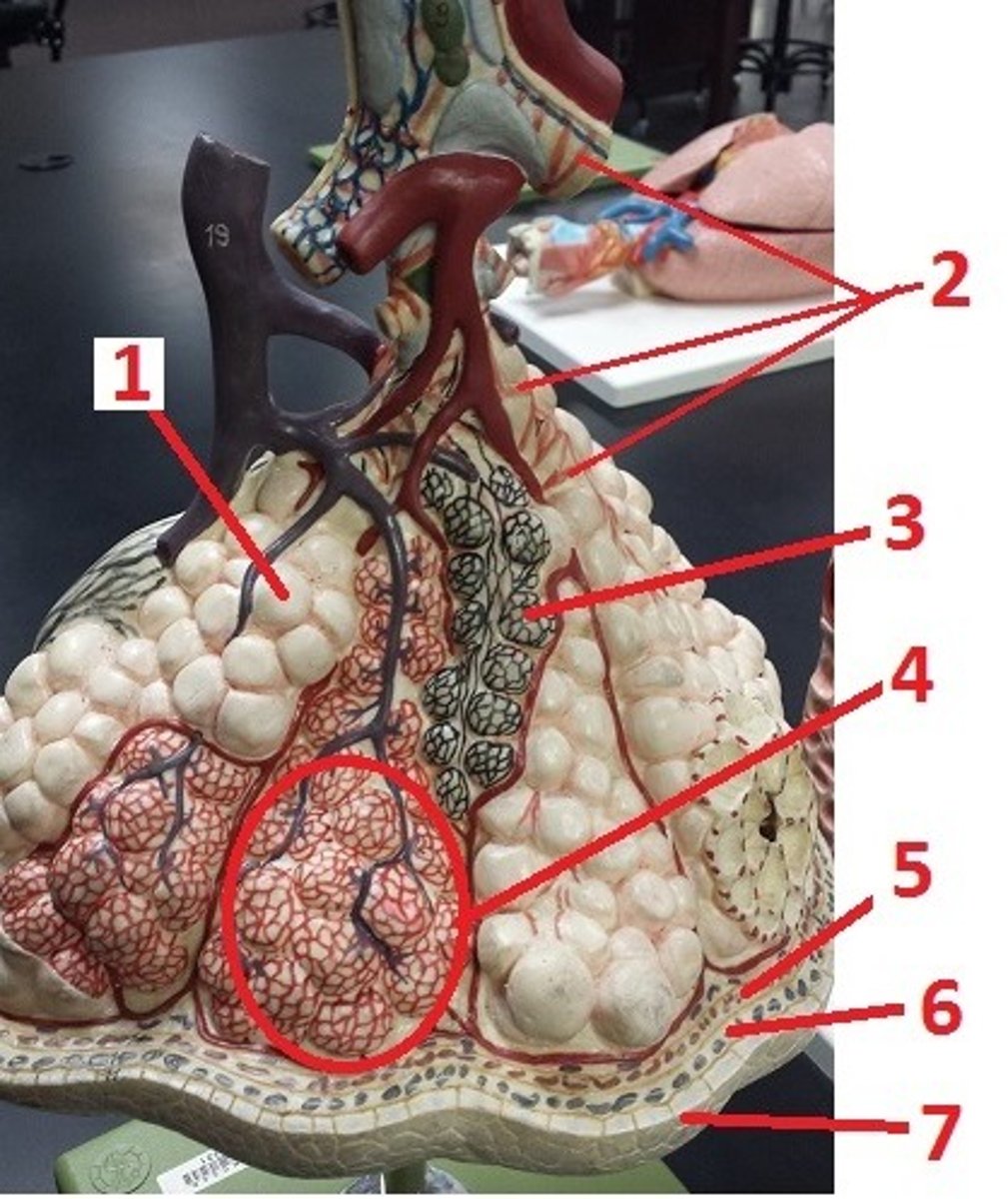
pleural space
6
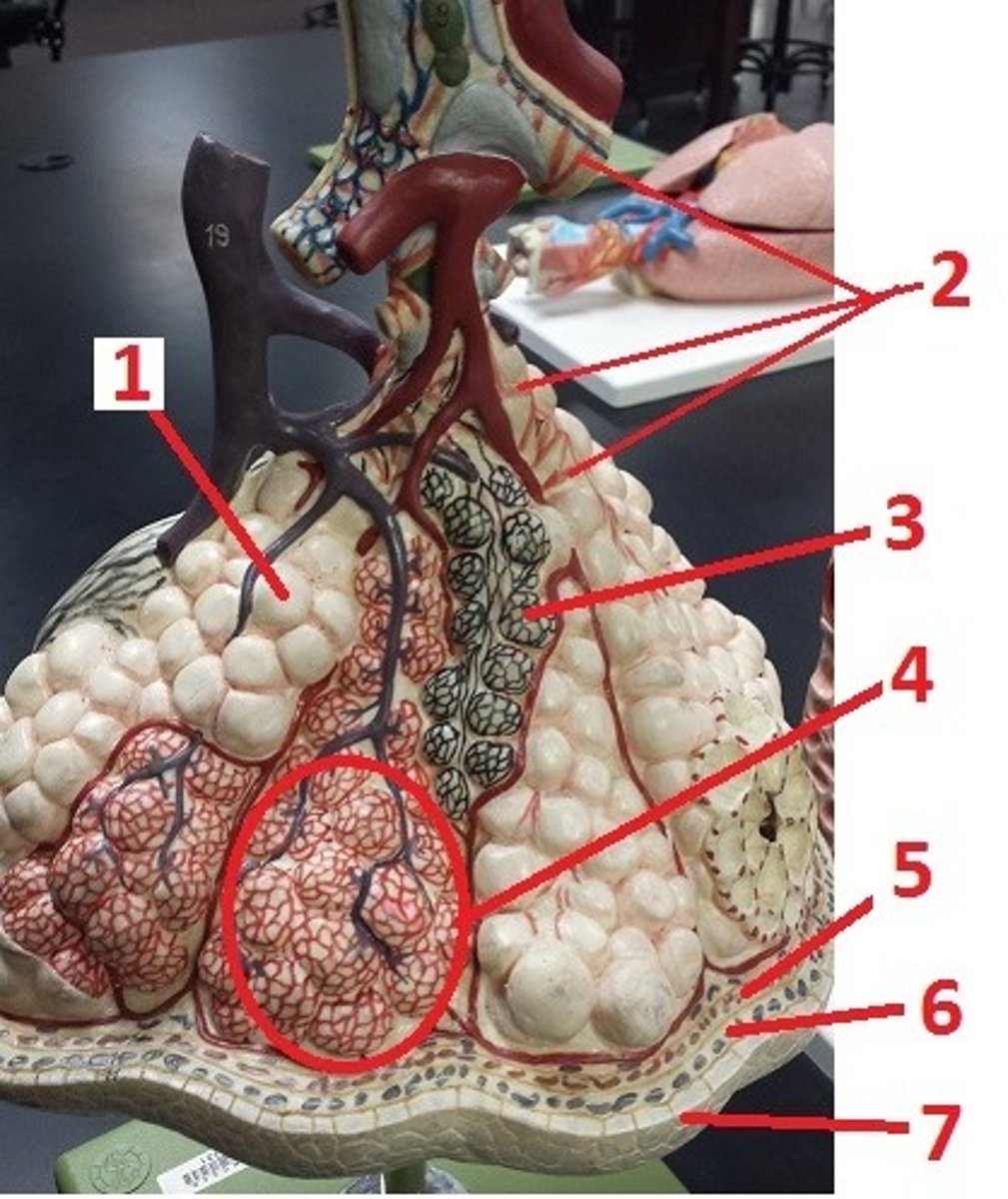
parietal pleura
7
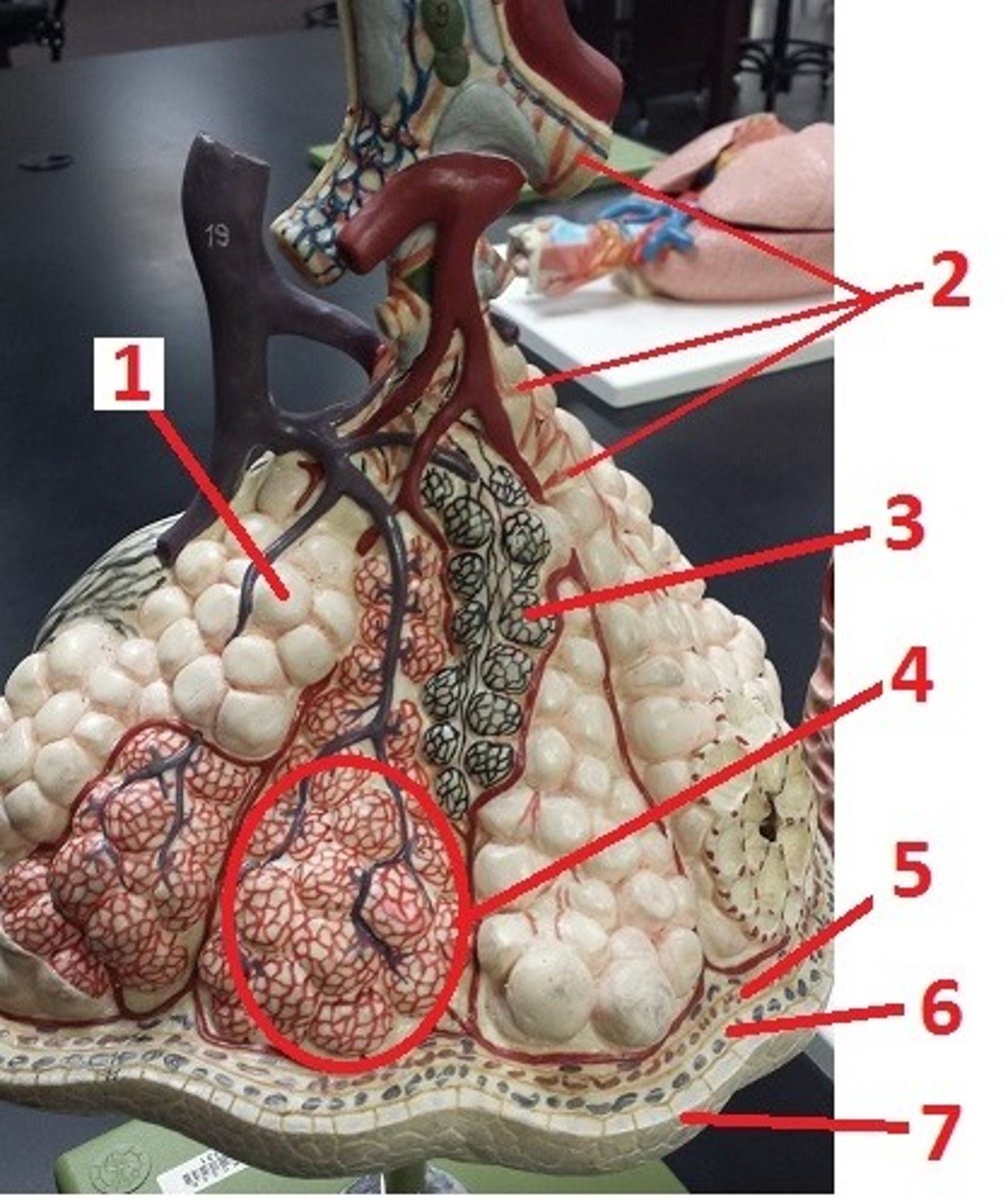
contraction of smooth muscle and decreases airflow
What is the effect of histamine on 2 and airflow?
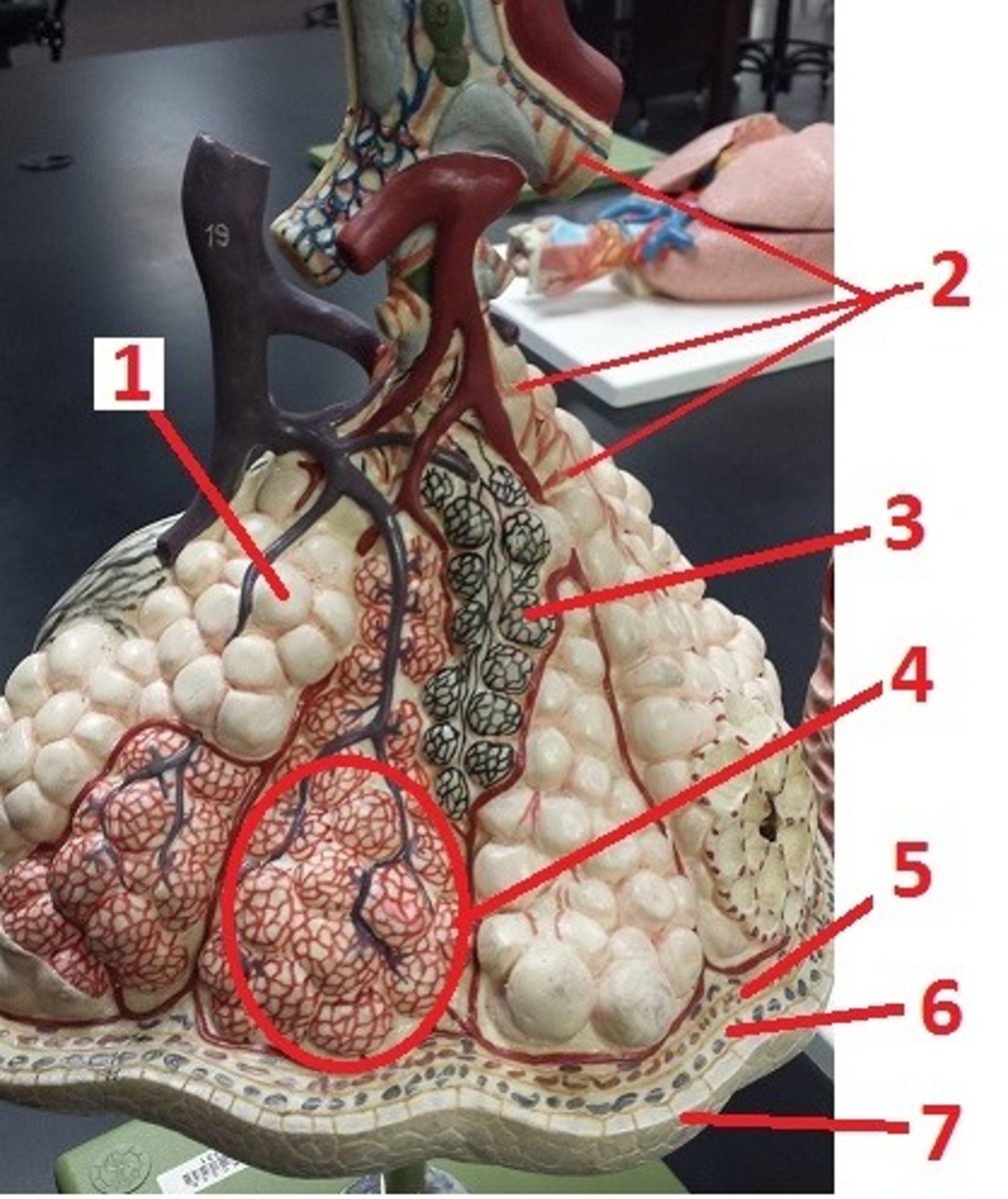
recoil of these fibers permits the alveoli to go back to their original size and aids in expiration
What is the function of 3?
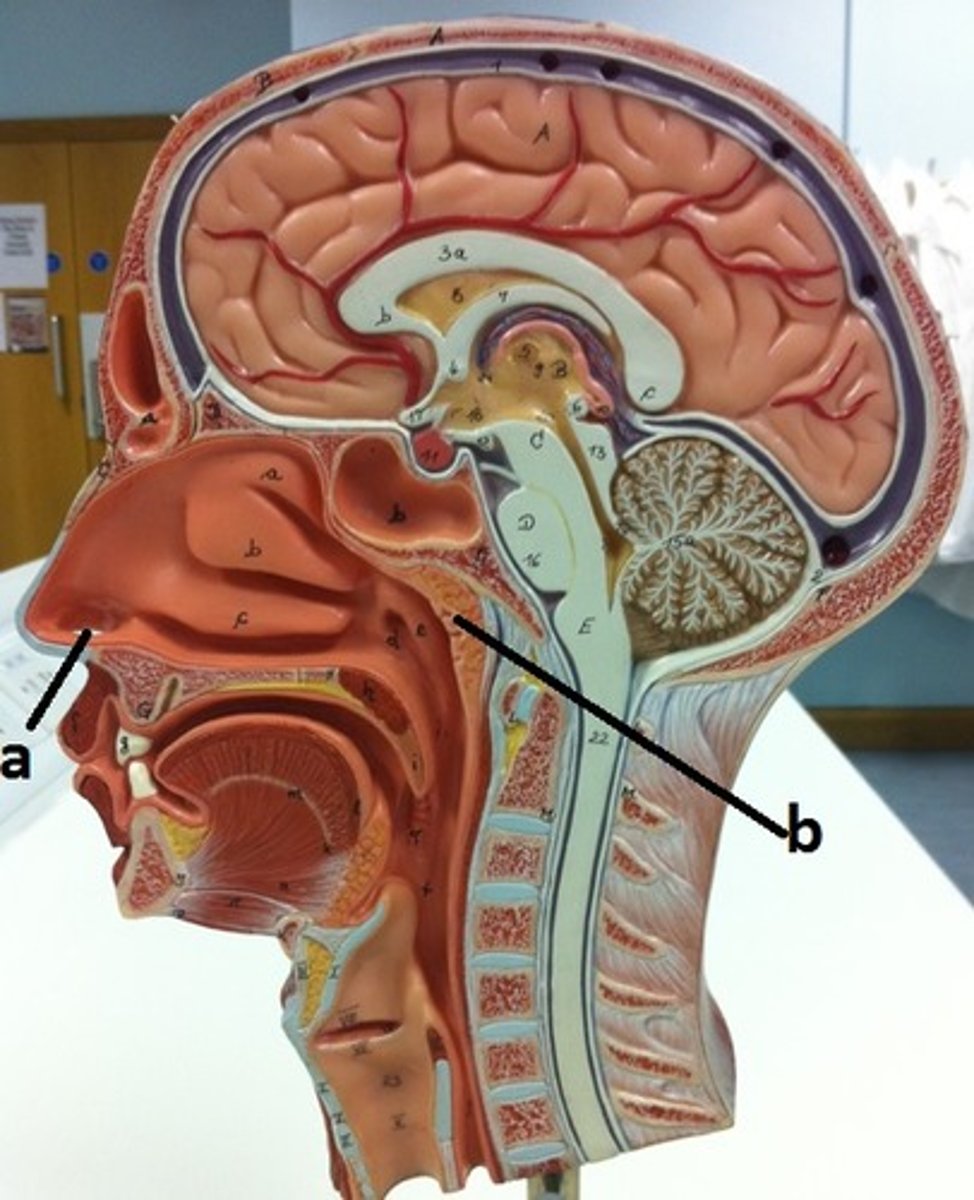
external nares
a
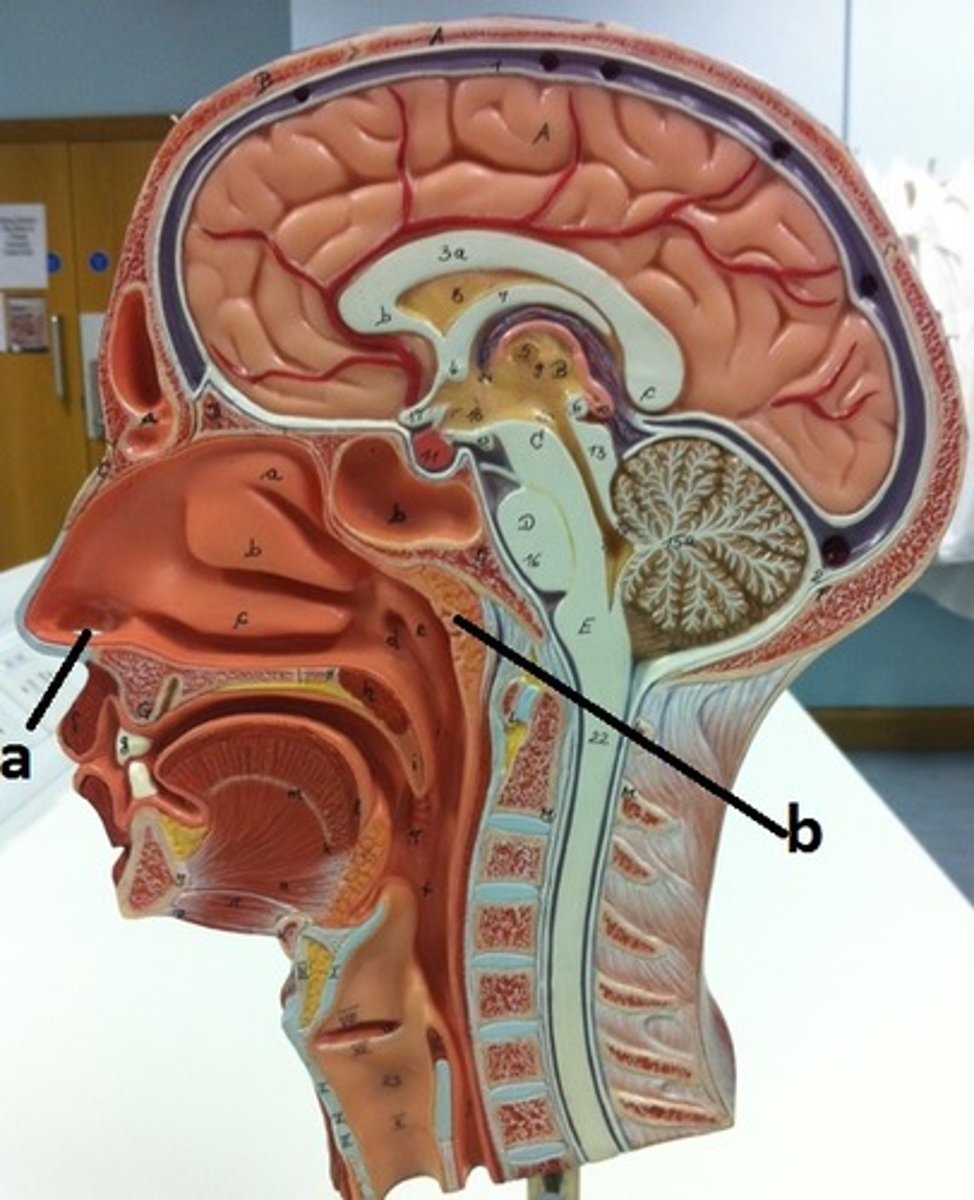
pharyngeal tonsil
b
hyaline cartilage
What is 1 made of?
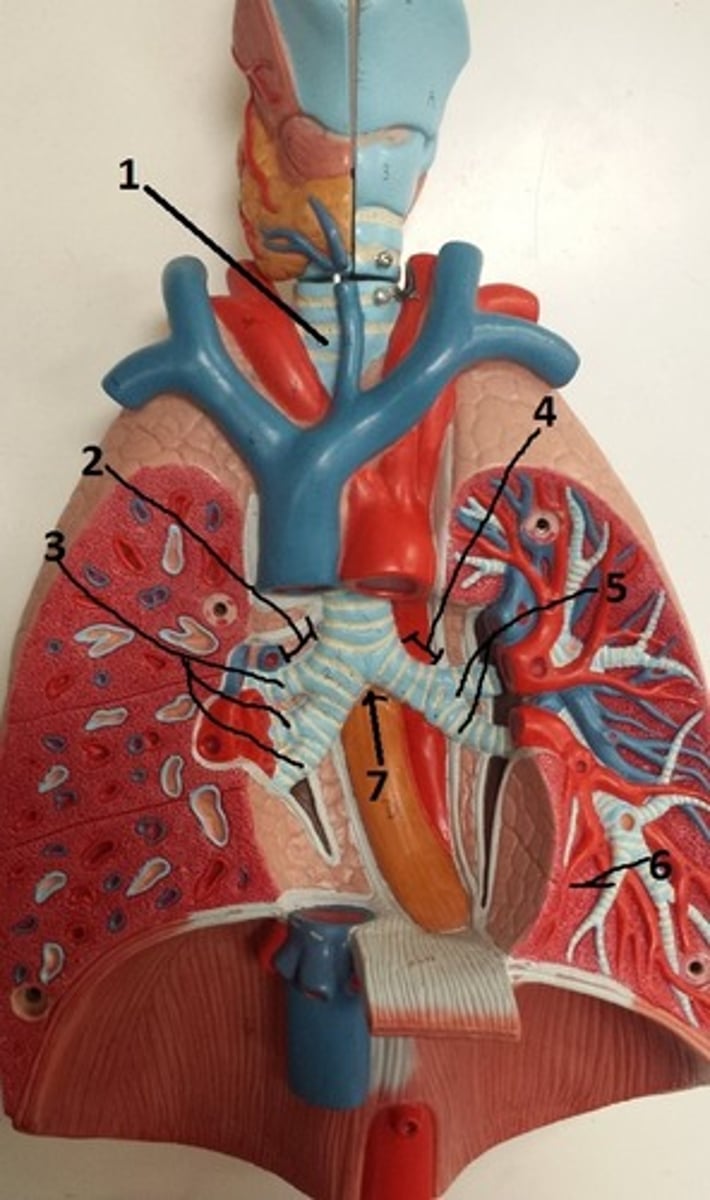
primary bronchus of right lung
2
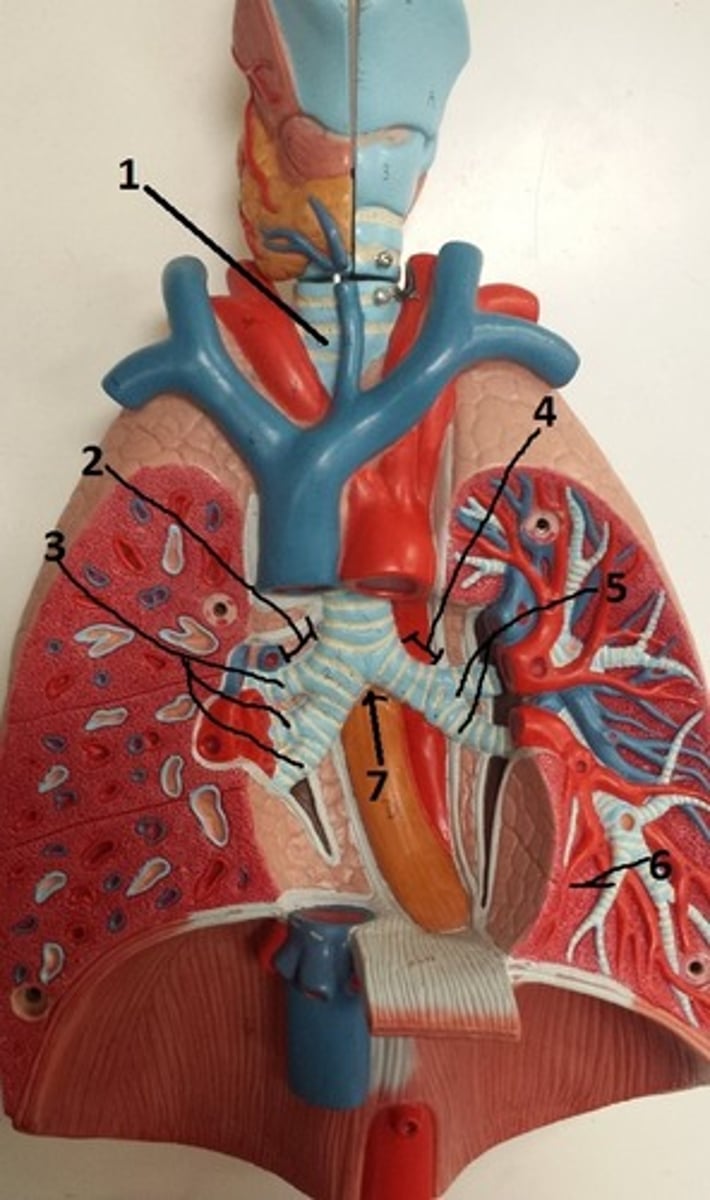
secondary bronchi of the right lung
3
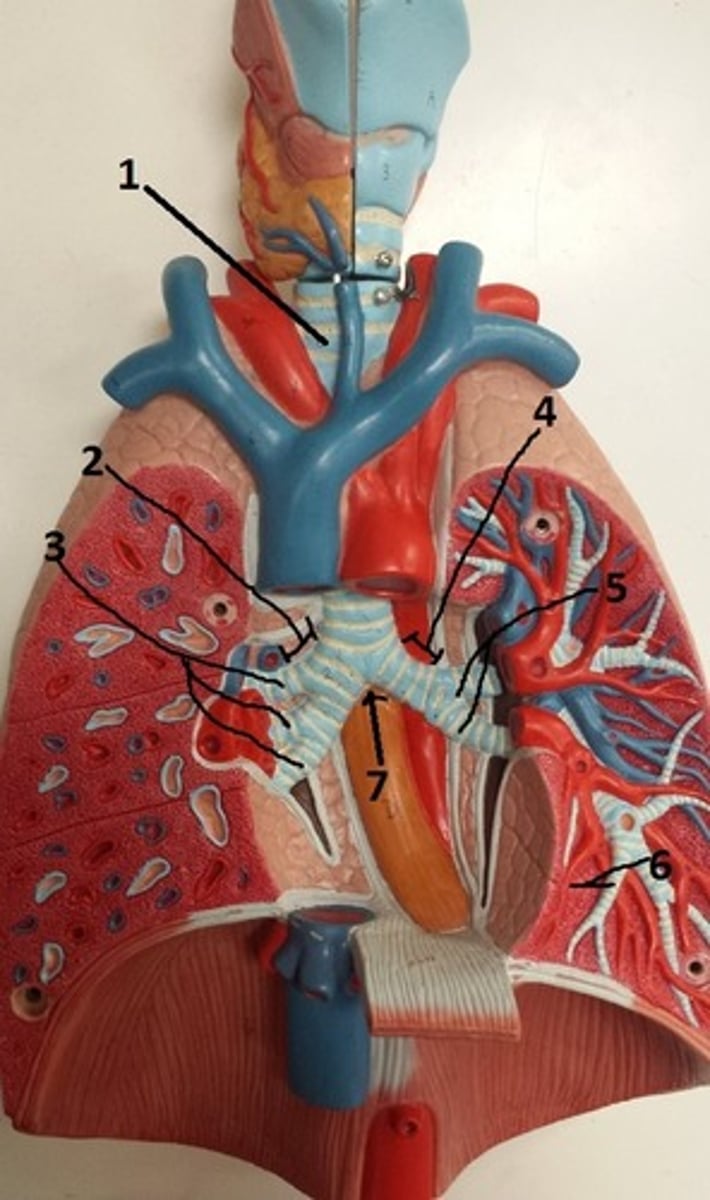
primary bronchus of left lung
4
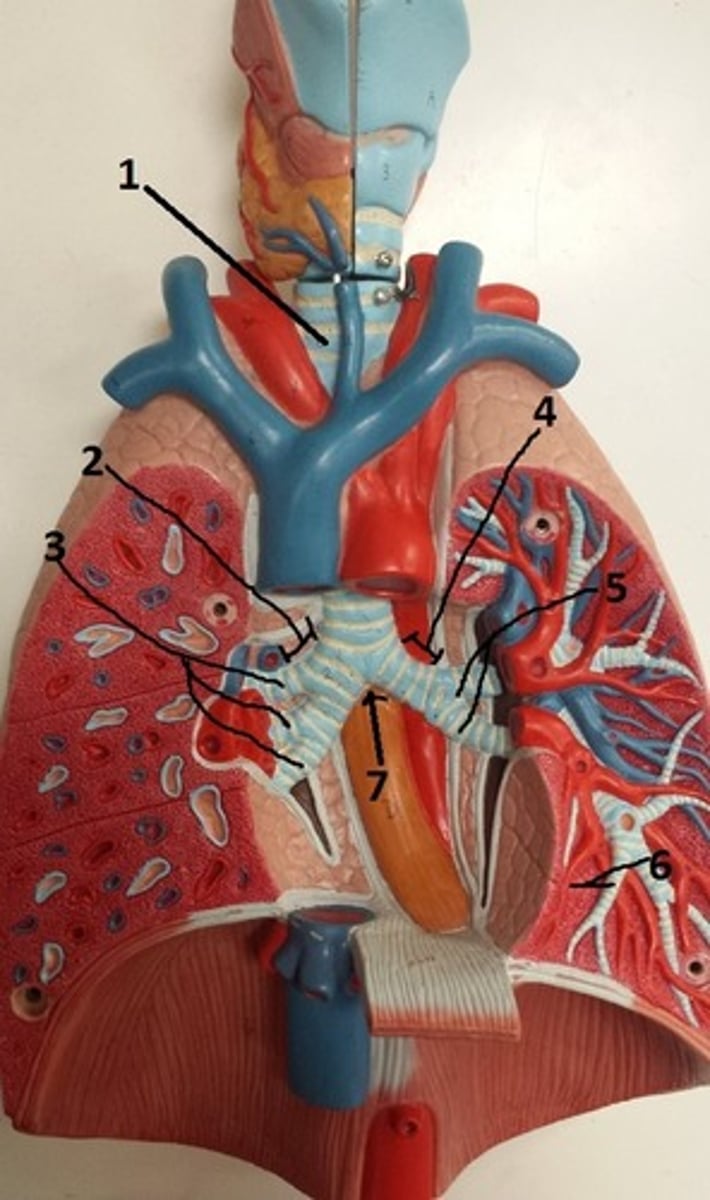
secondary bronchi of the left lung
5
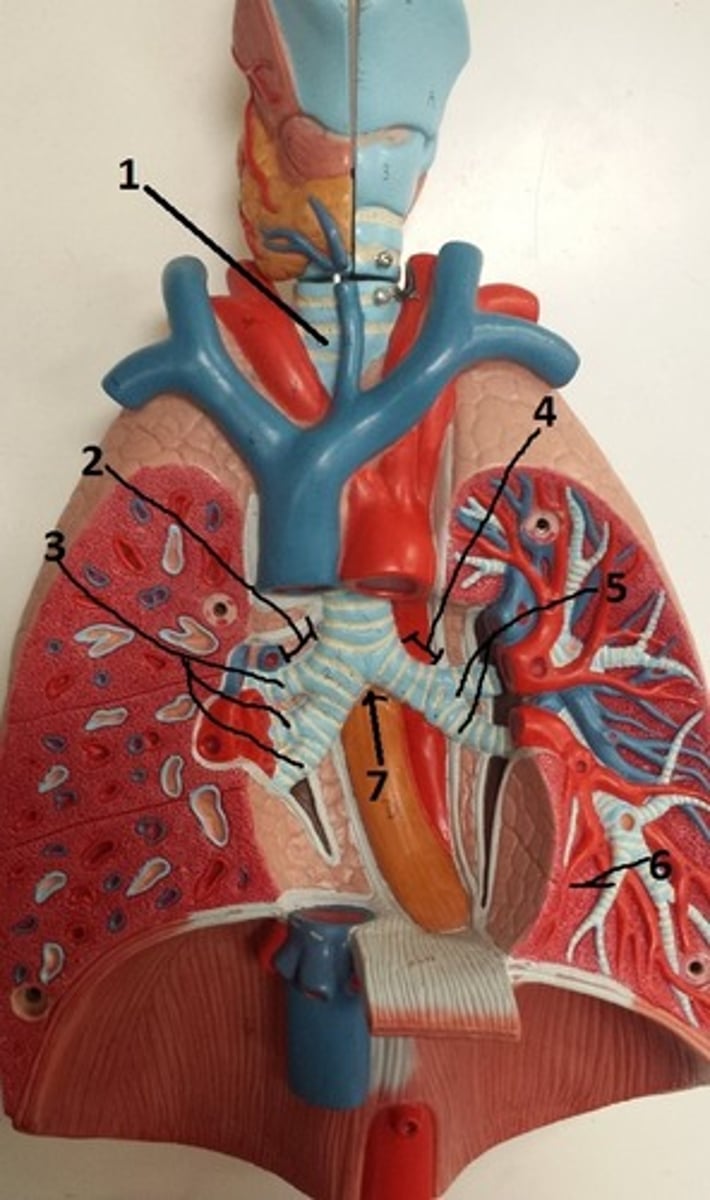
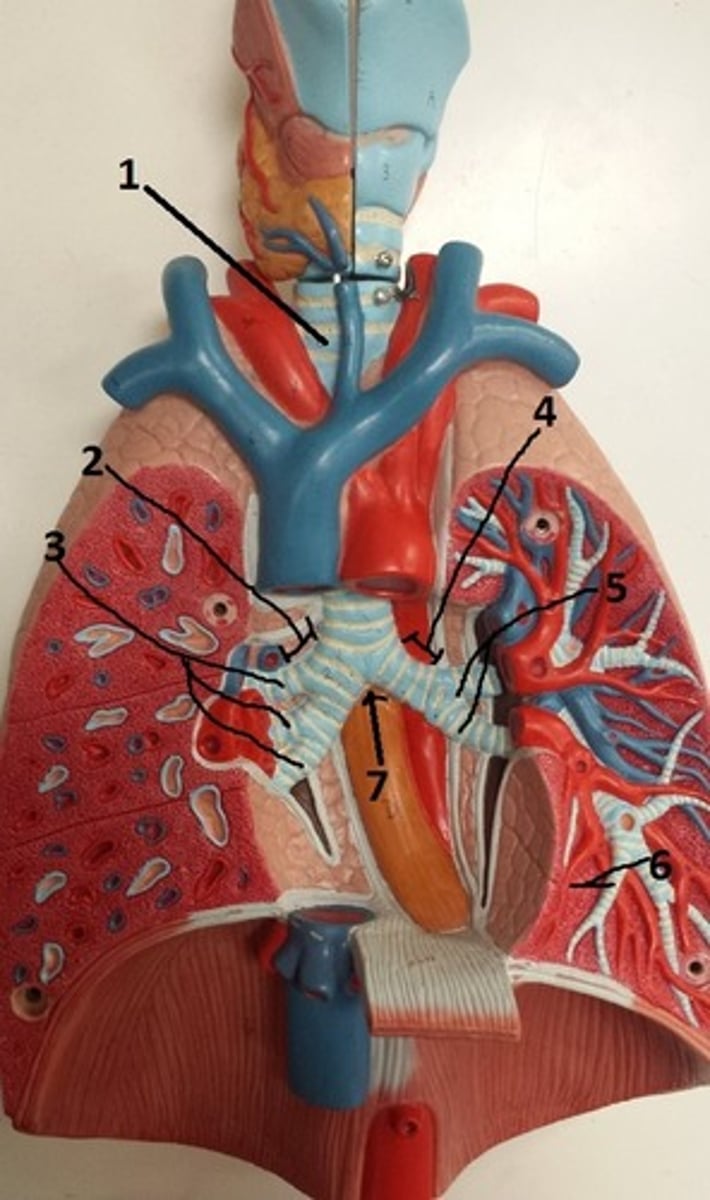
tertiary bronchus of the left lung
6
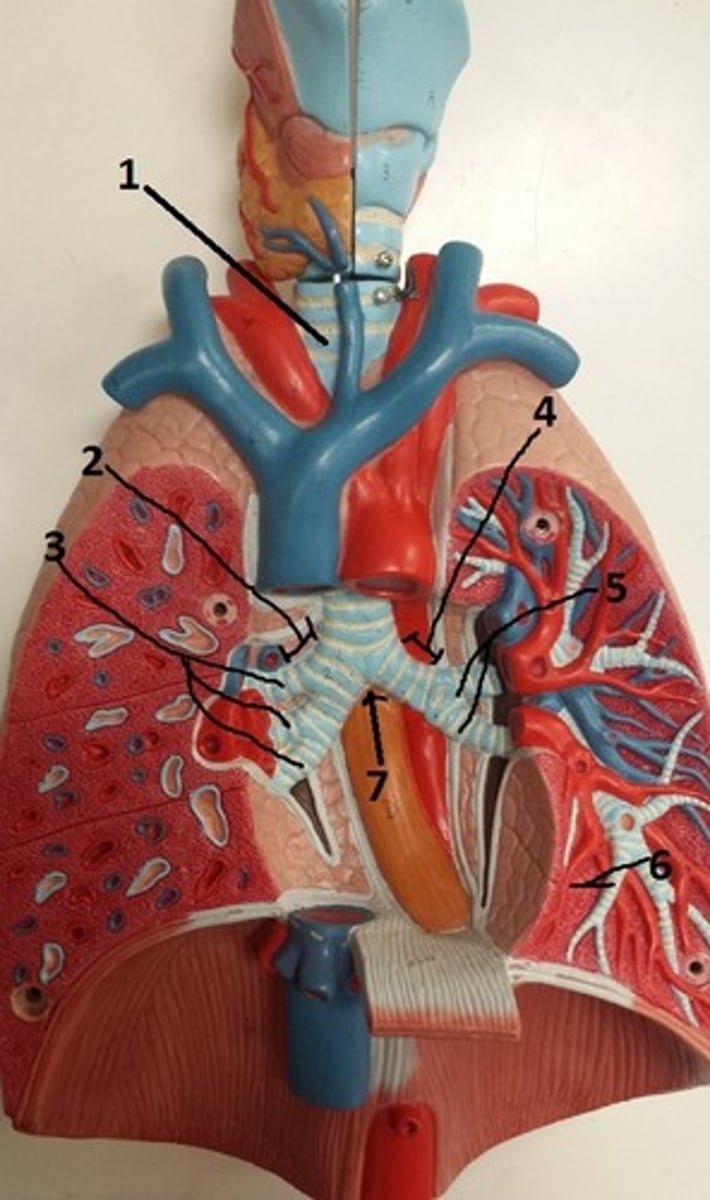
carina of the trachea
7
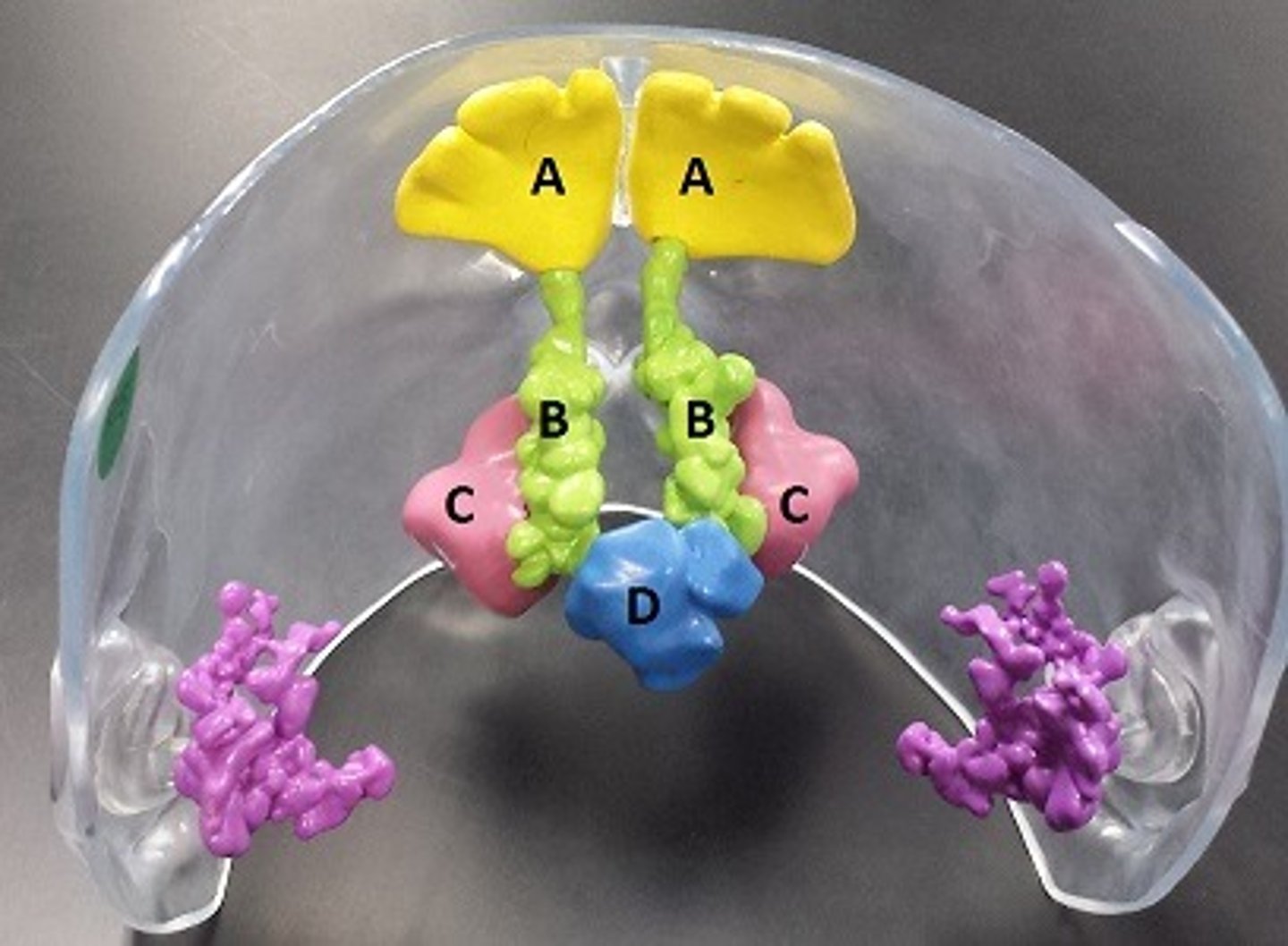
frontal sinuses
A
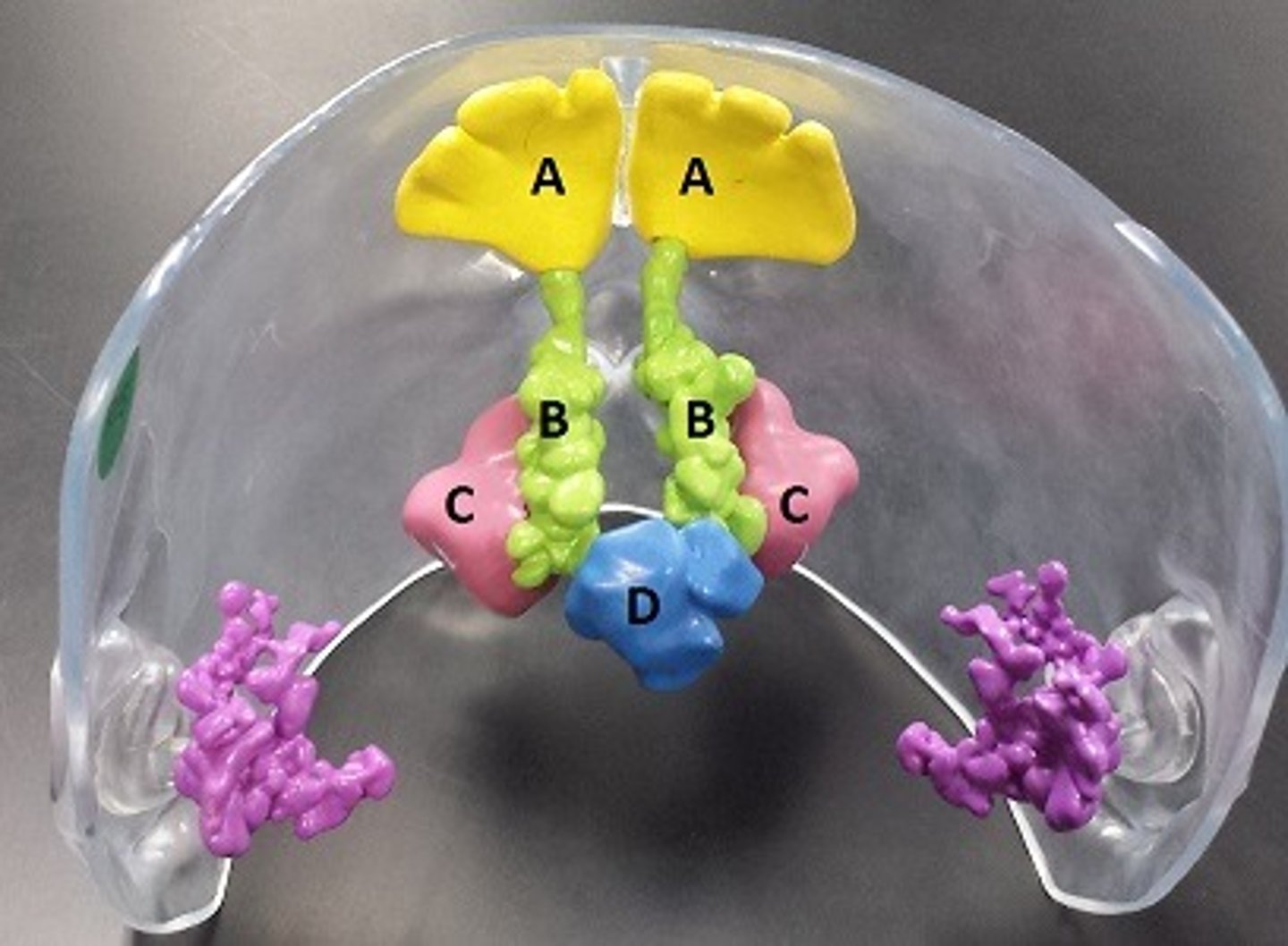
ethmoidal sinuses
B
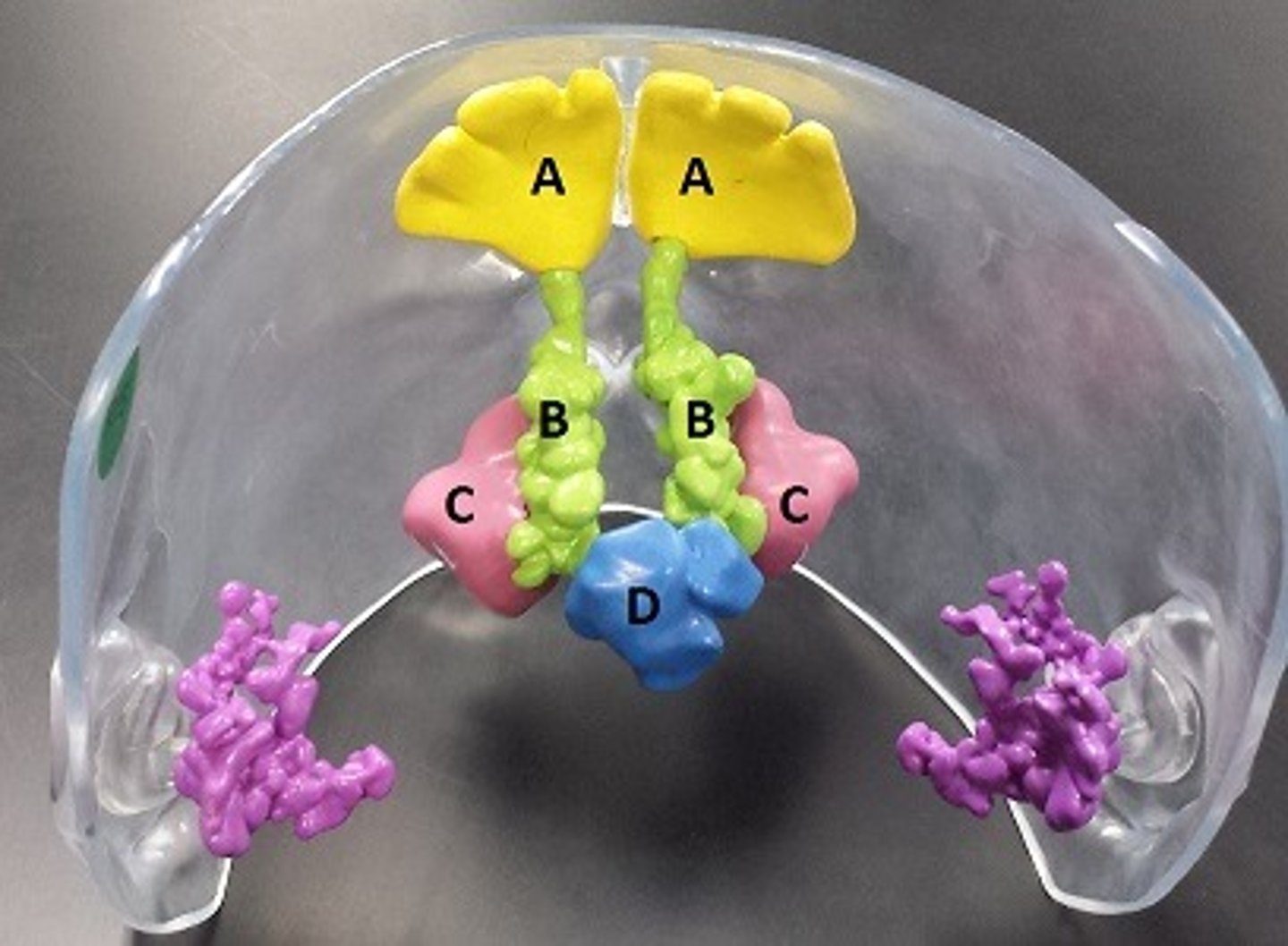
maxillary sinuses
C
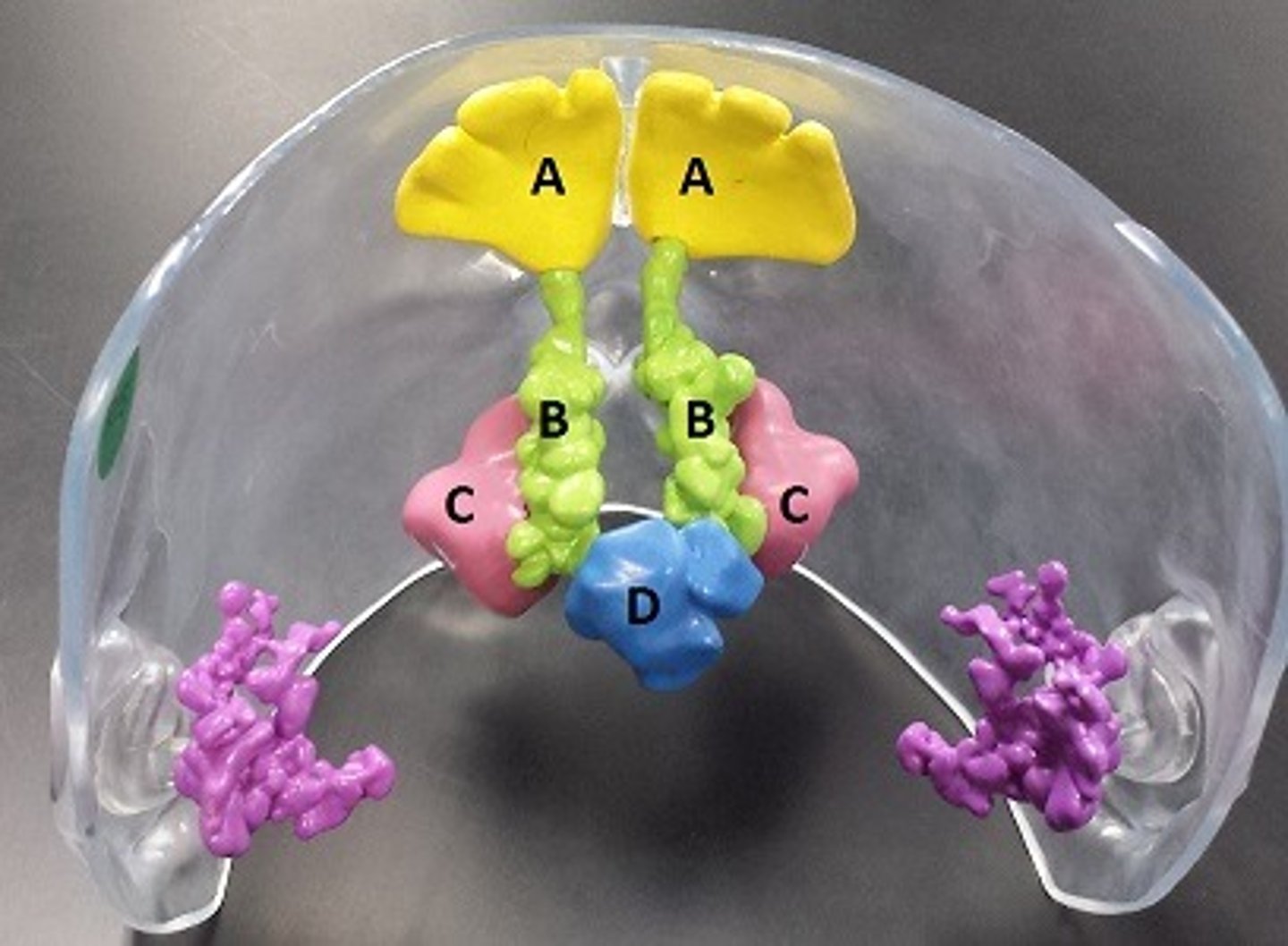
sphenoidal sinuses
D
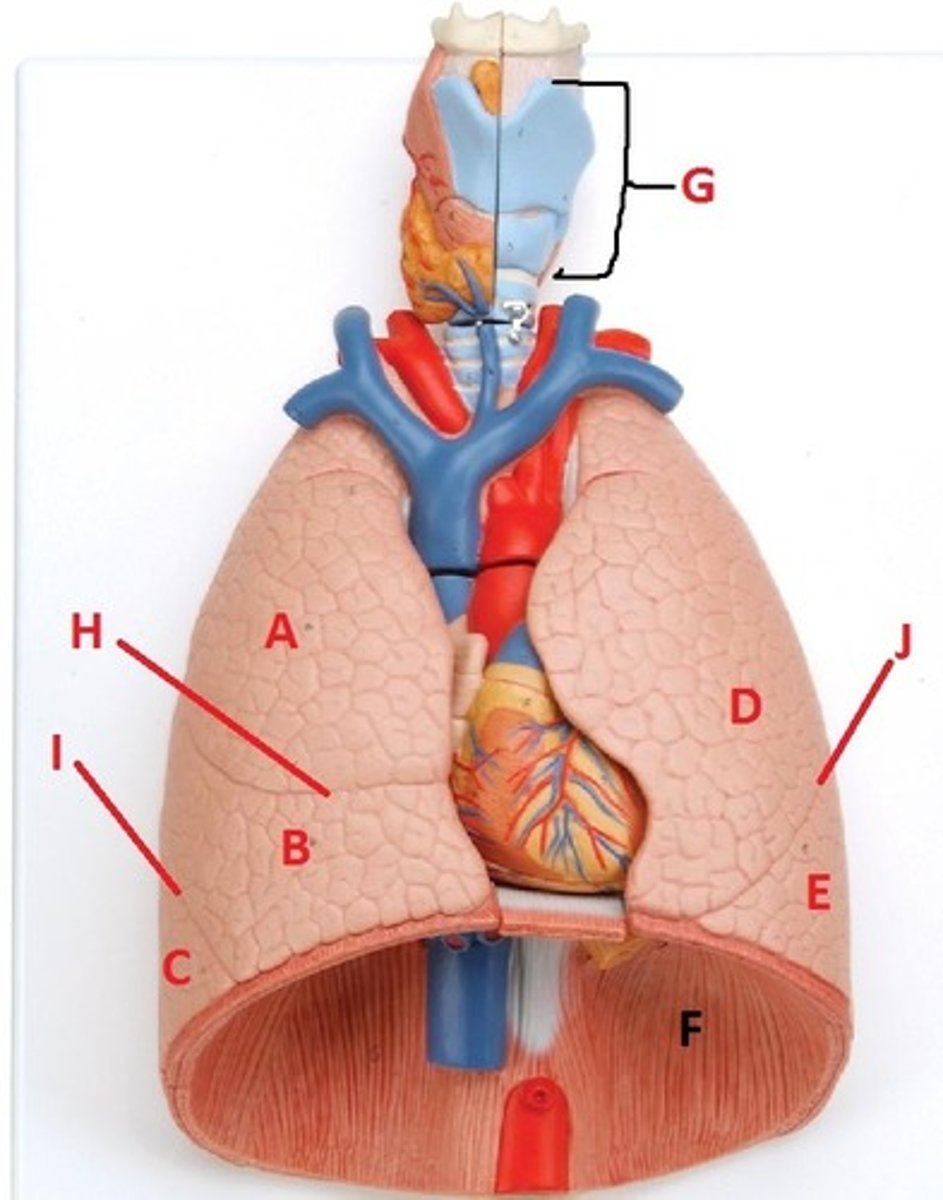
superior lobe of the right lung
A
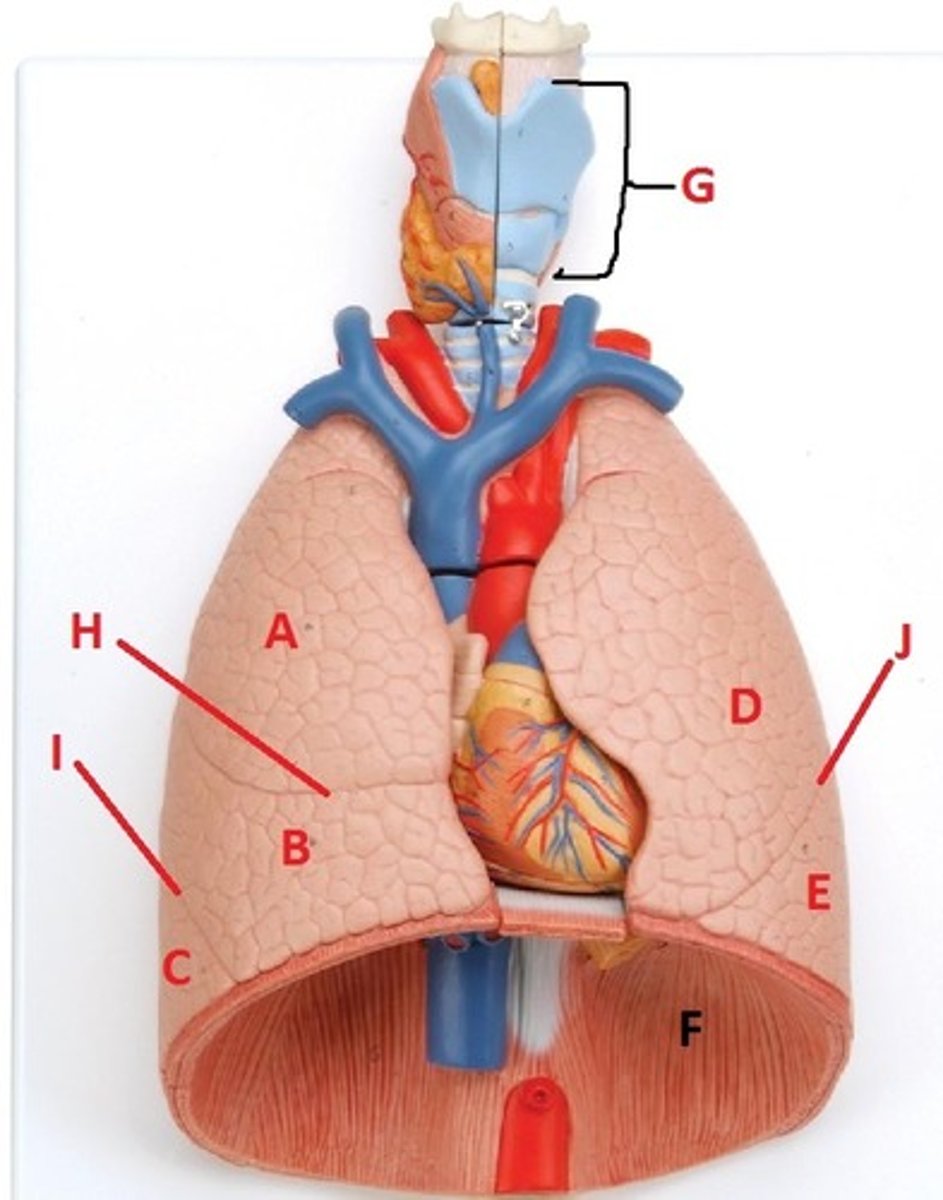
middle lobe of the right lung
B
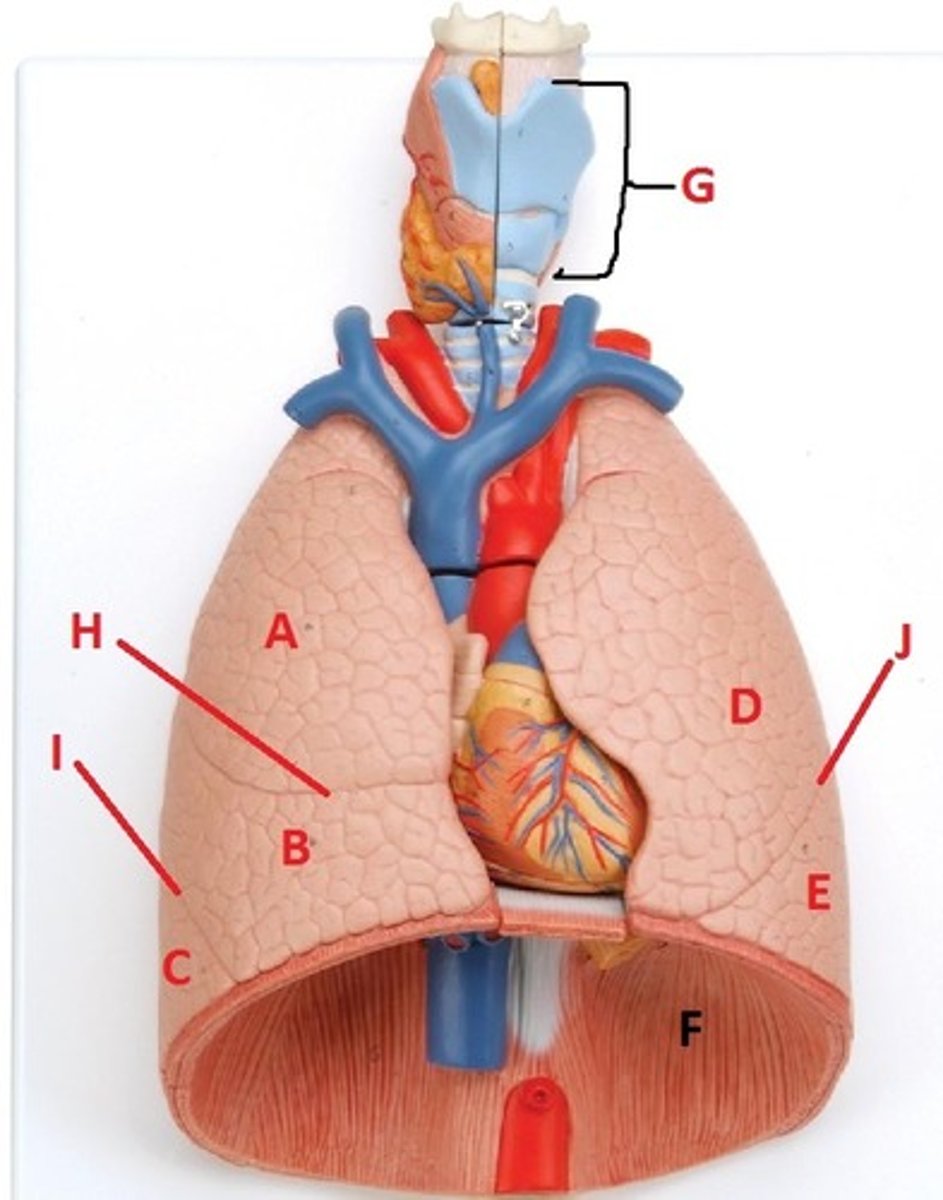
inferior lobe of the right lung
C
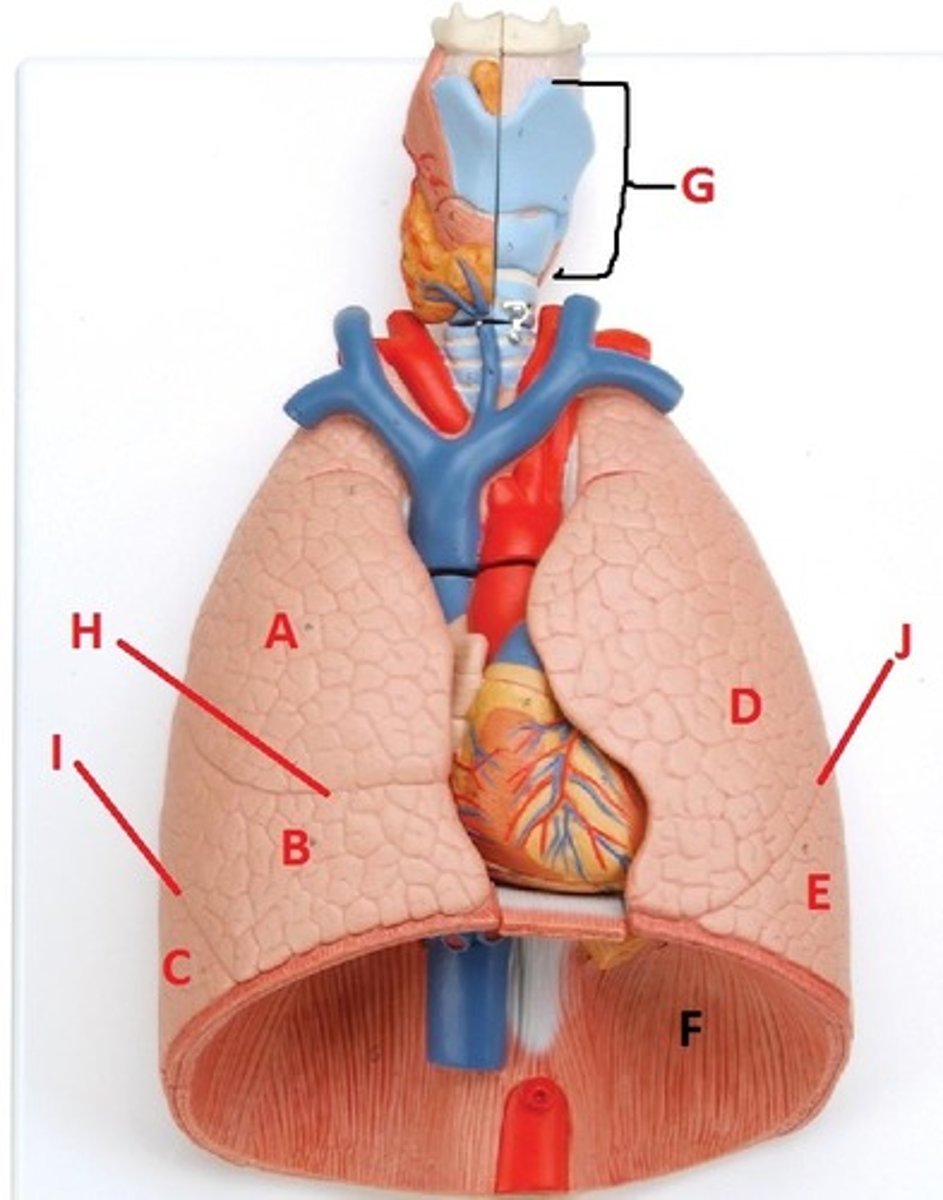
superior lobe of the left lung
D
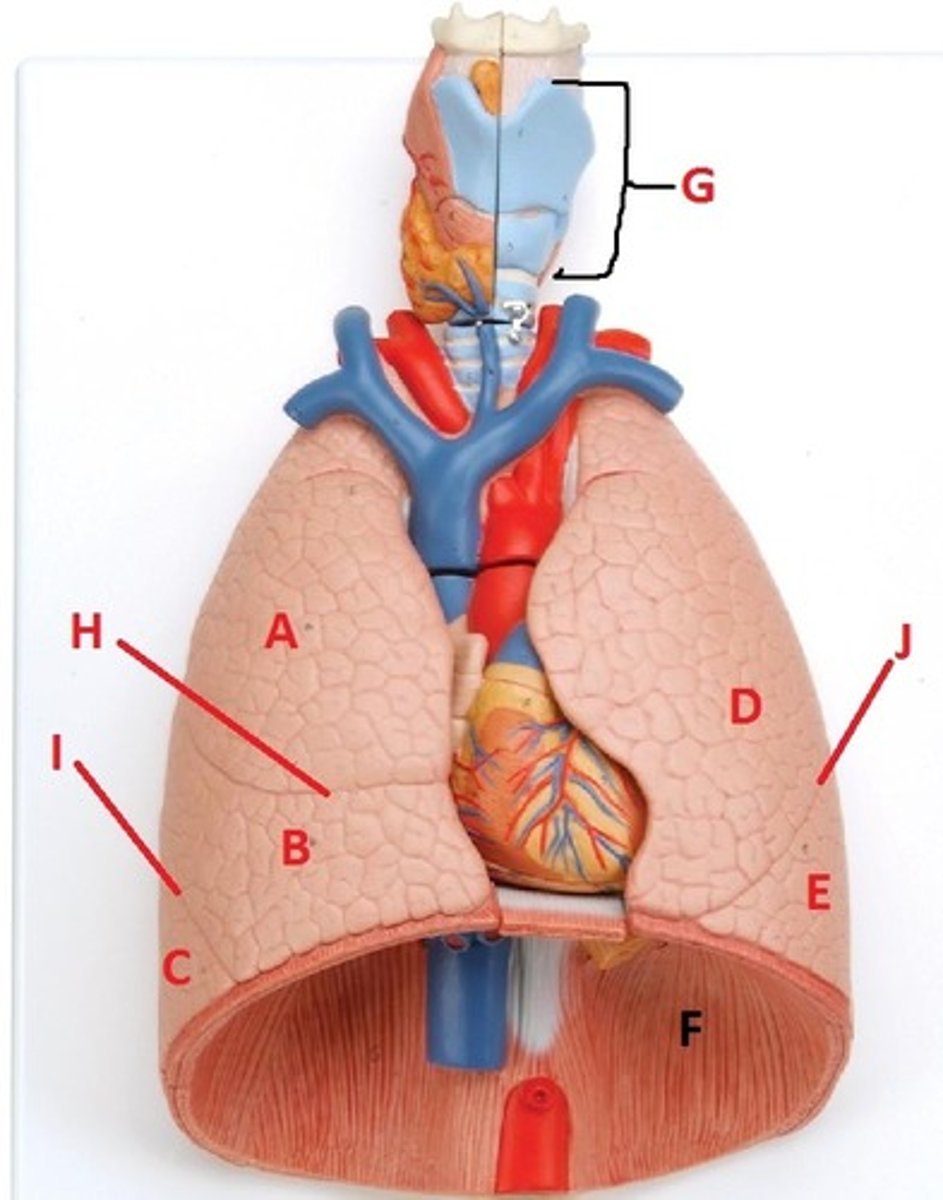
inferior lobe of the left lung
E
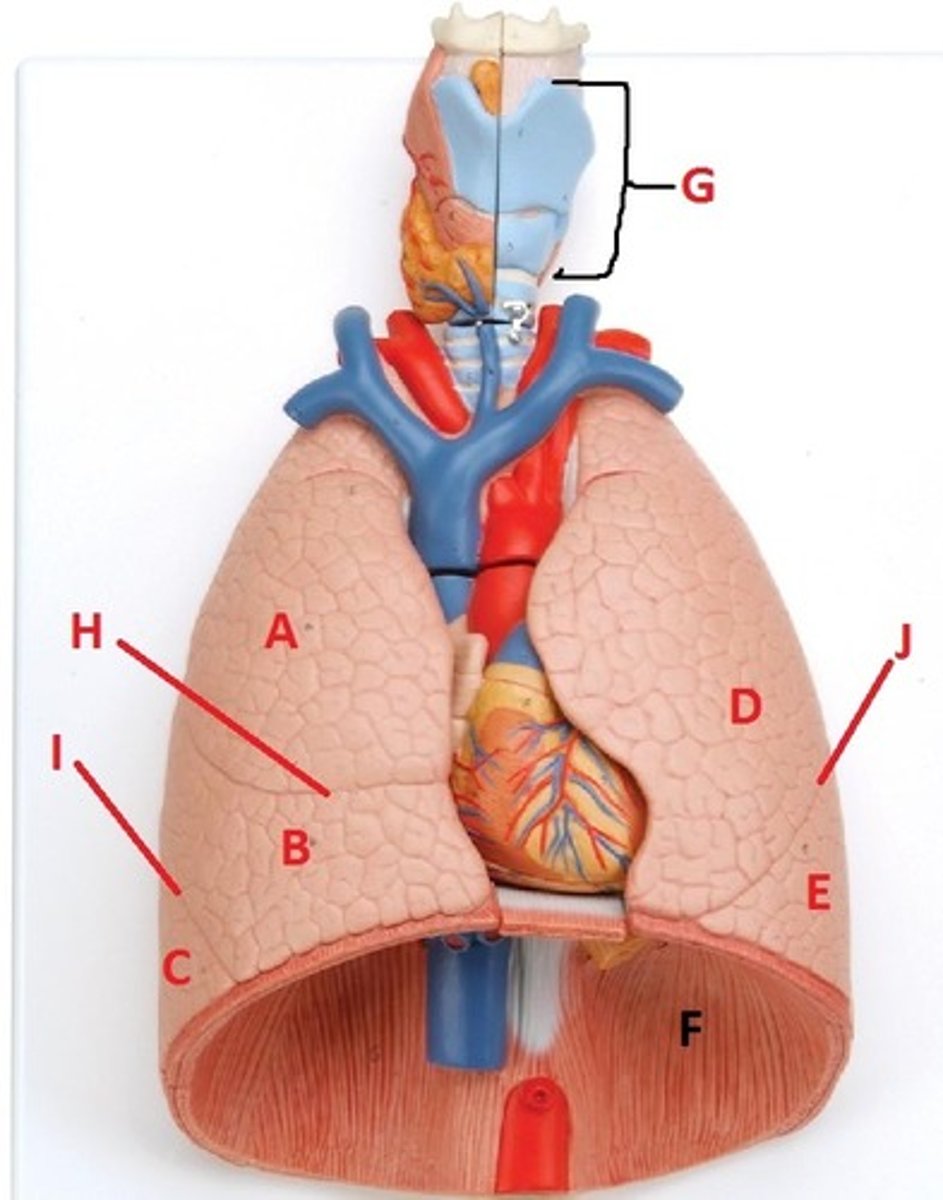
diaphragm
F
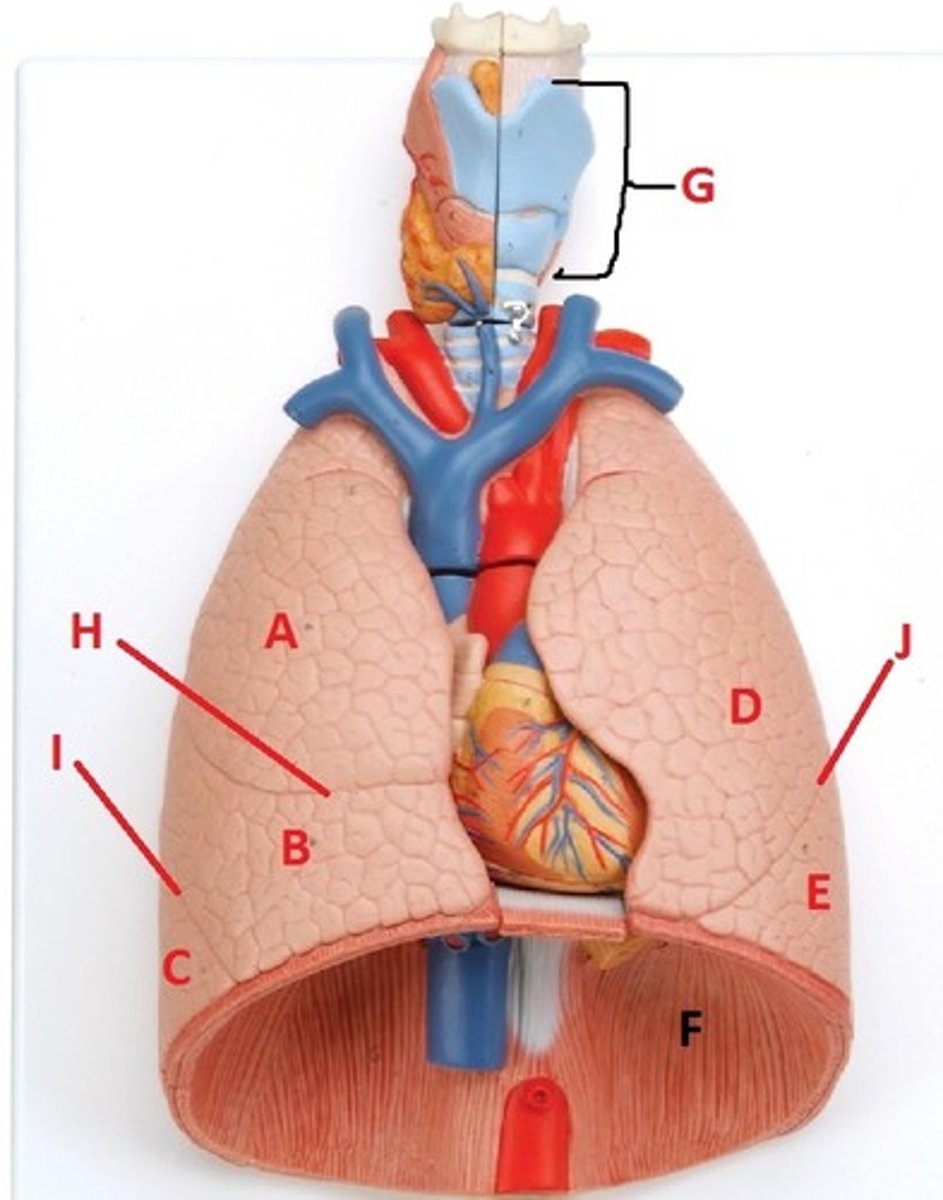
larynx
G
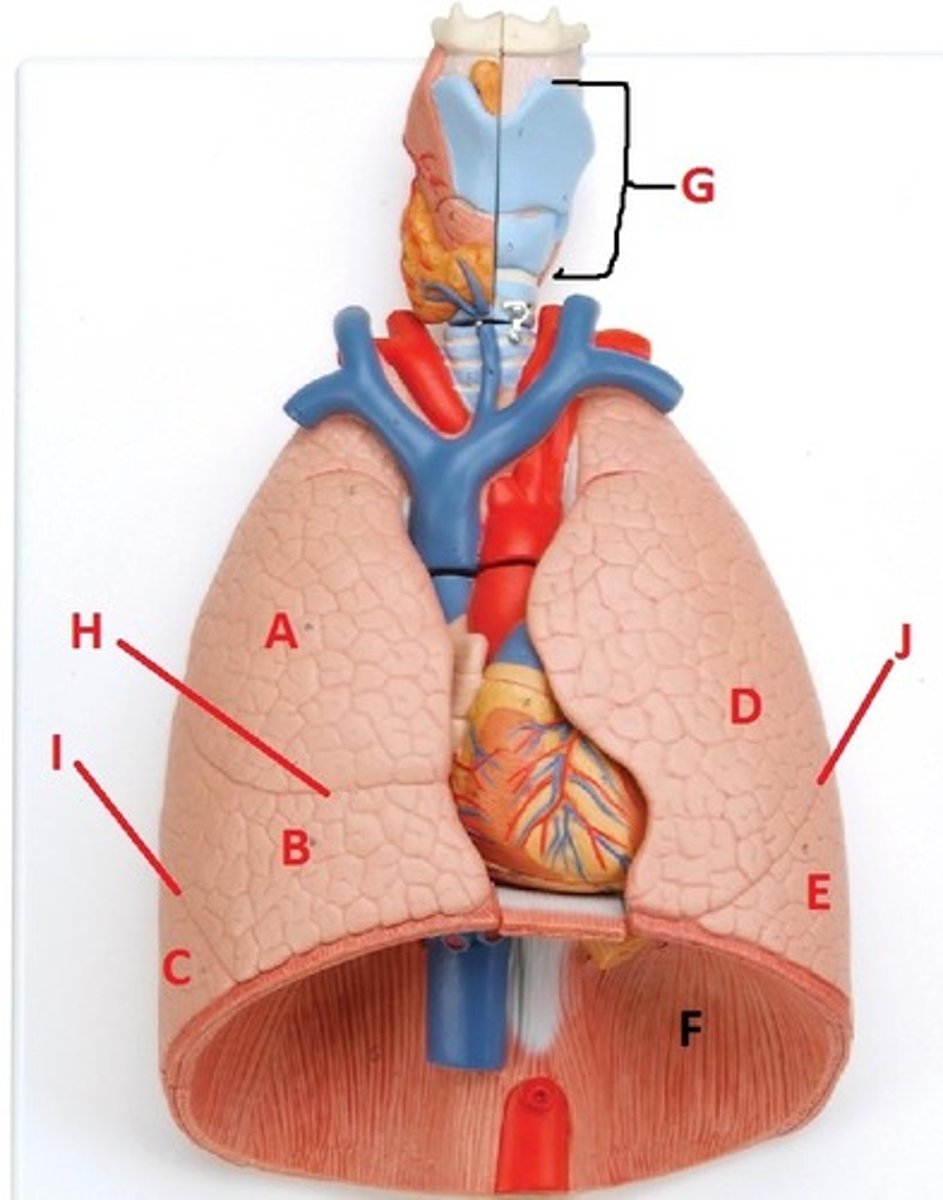
horizontal fissure of the right lung
H
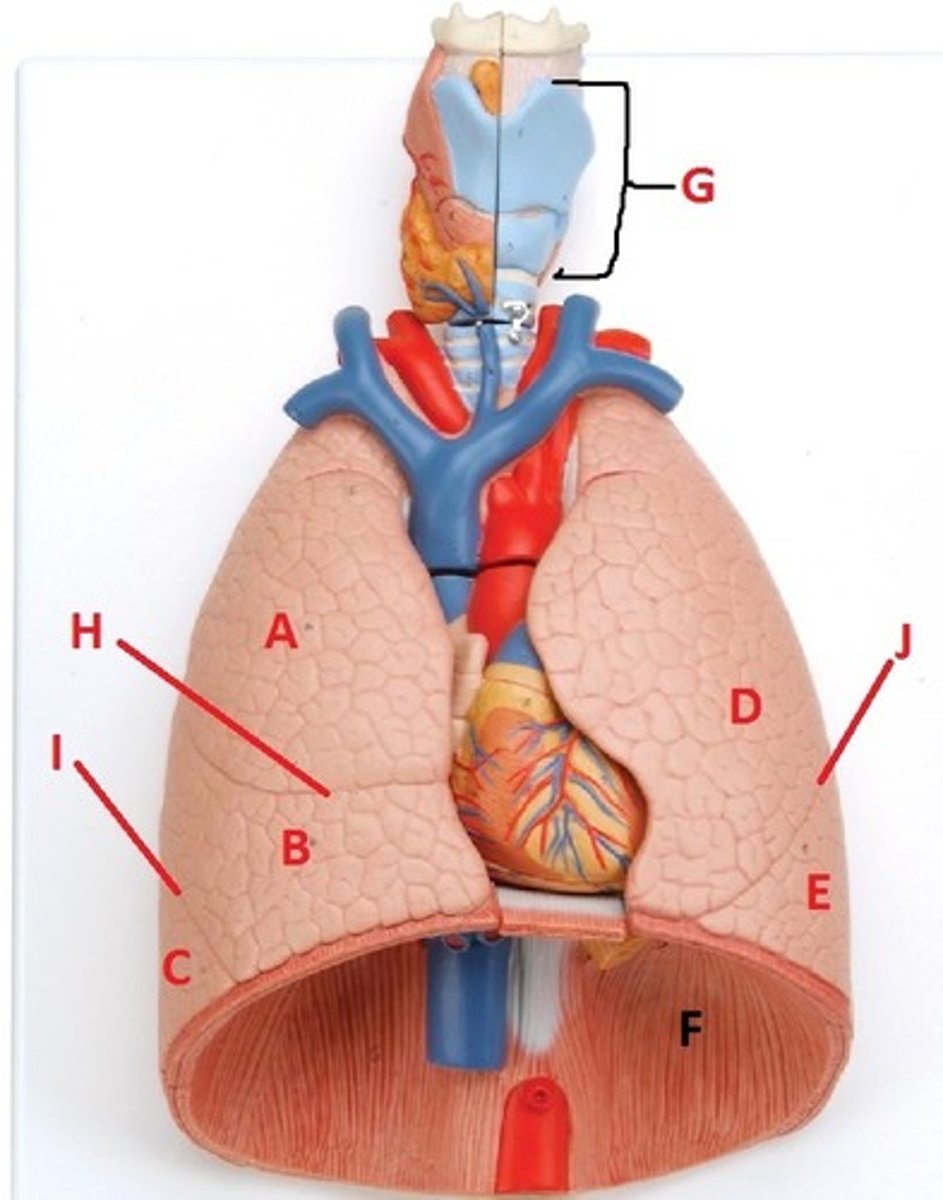
oblique fissure of the right lung
I
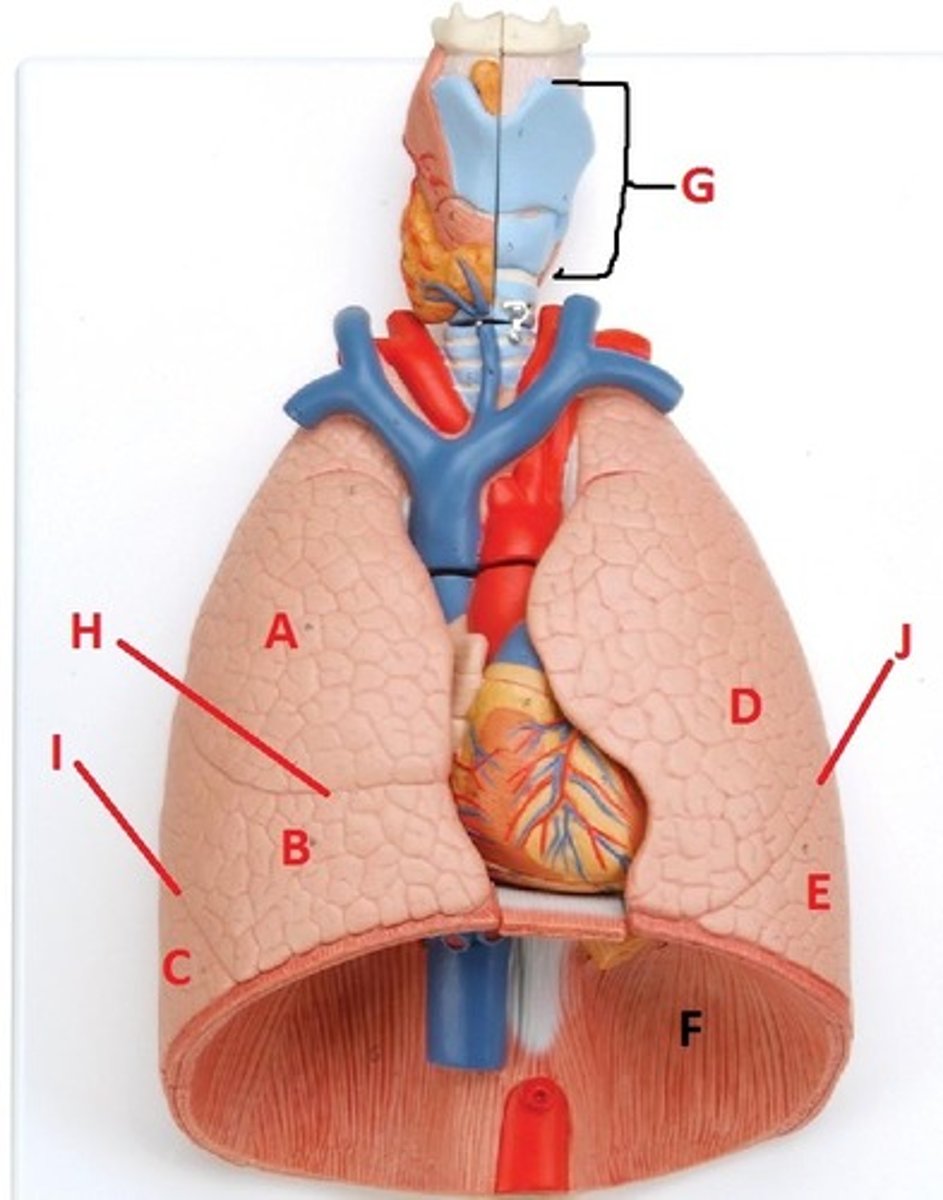
oblique fissure of the left lung
J
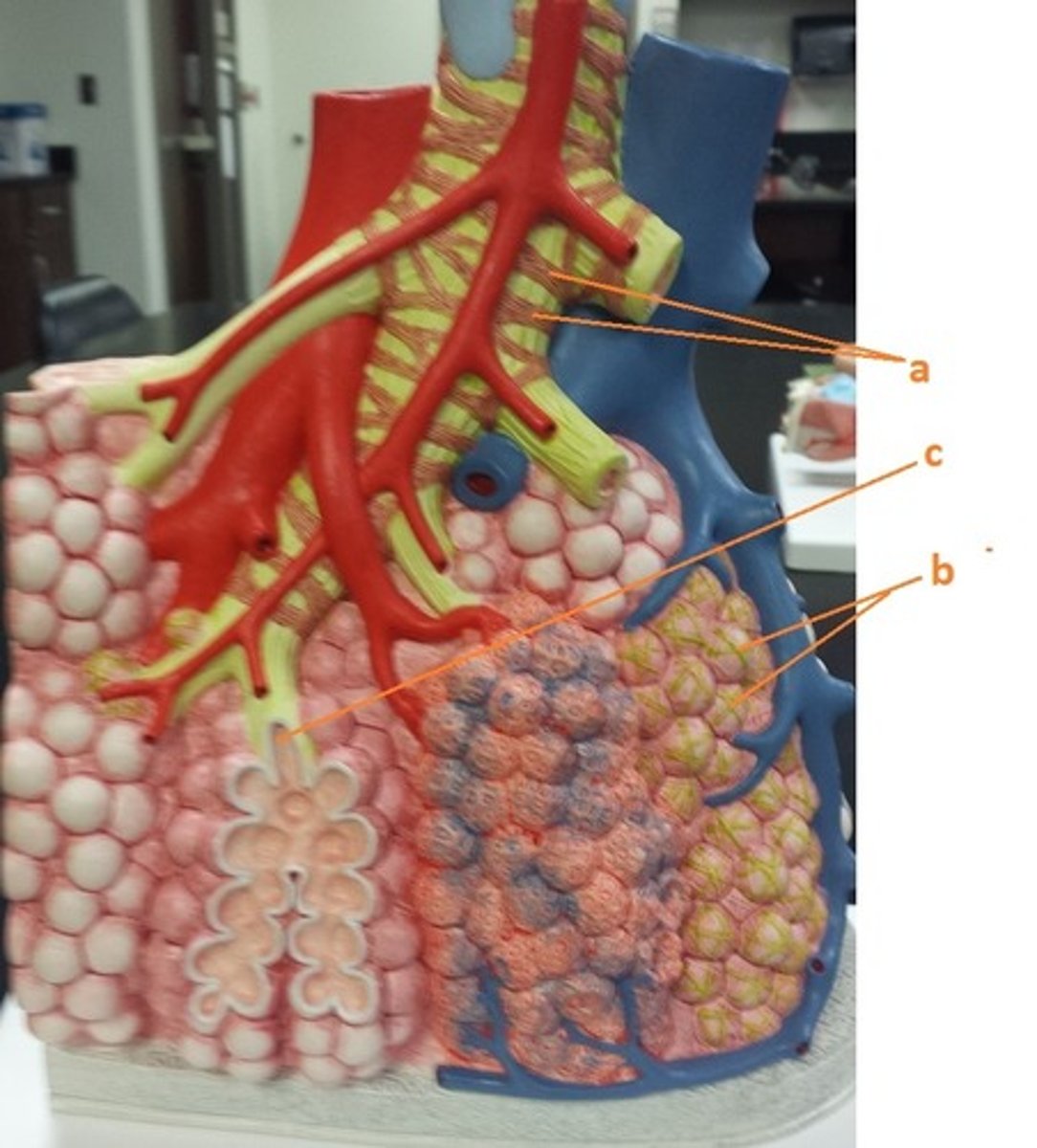
smooth muscle
a
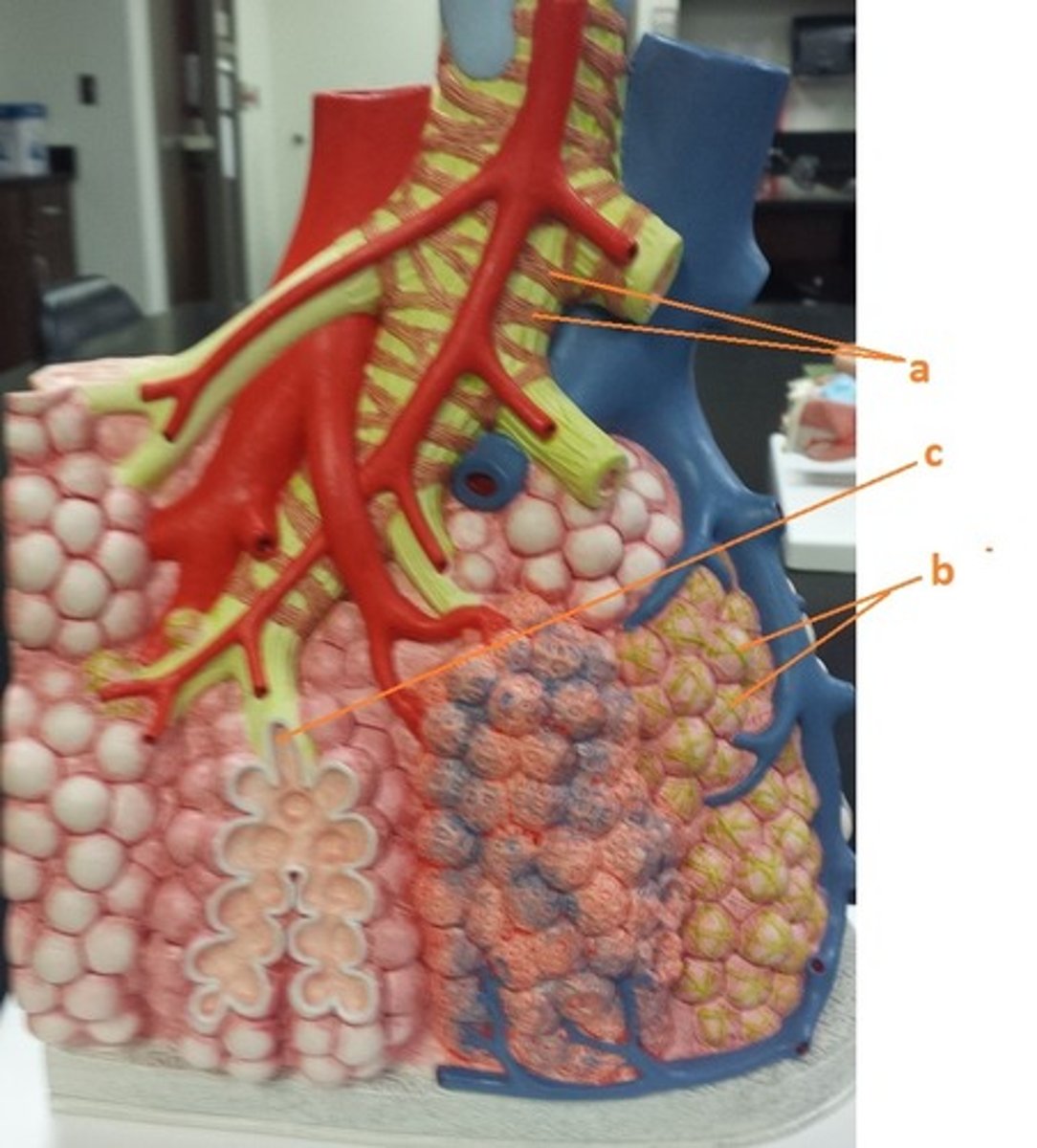
elastin fibers
b
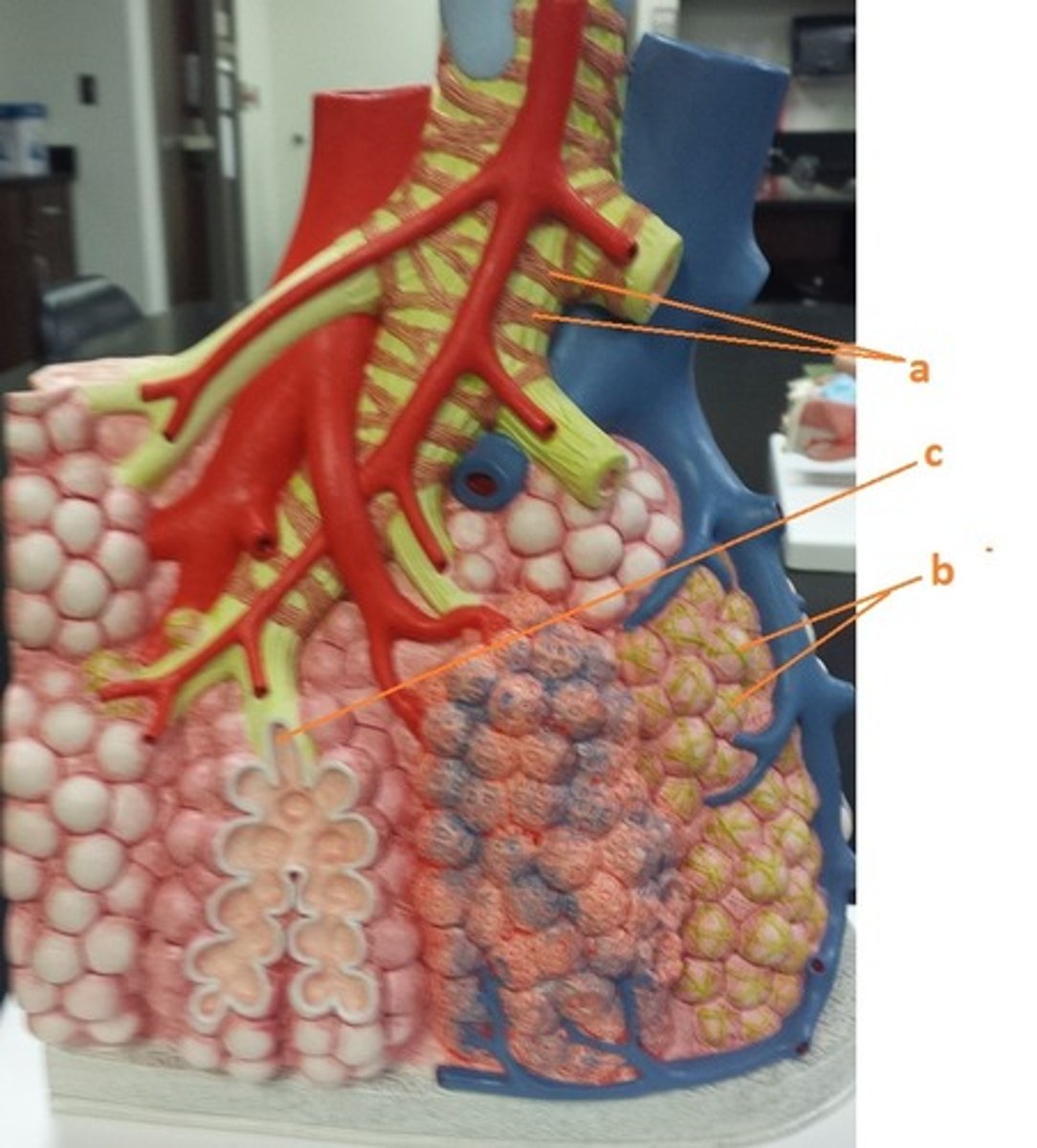
alveolar duct
c
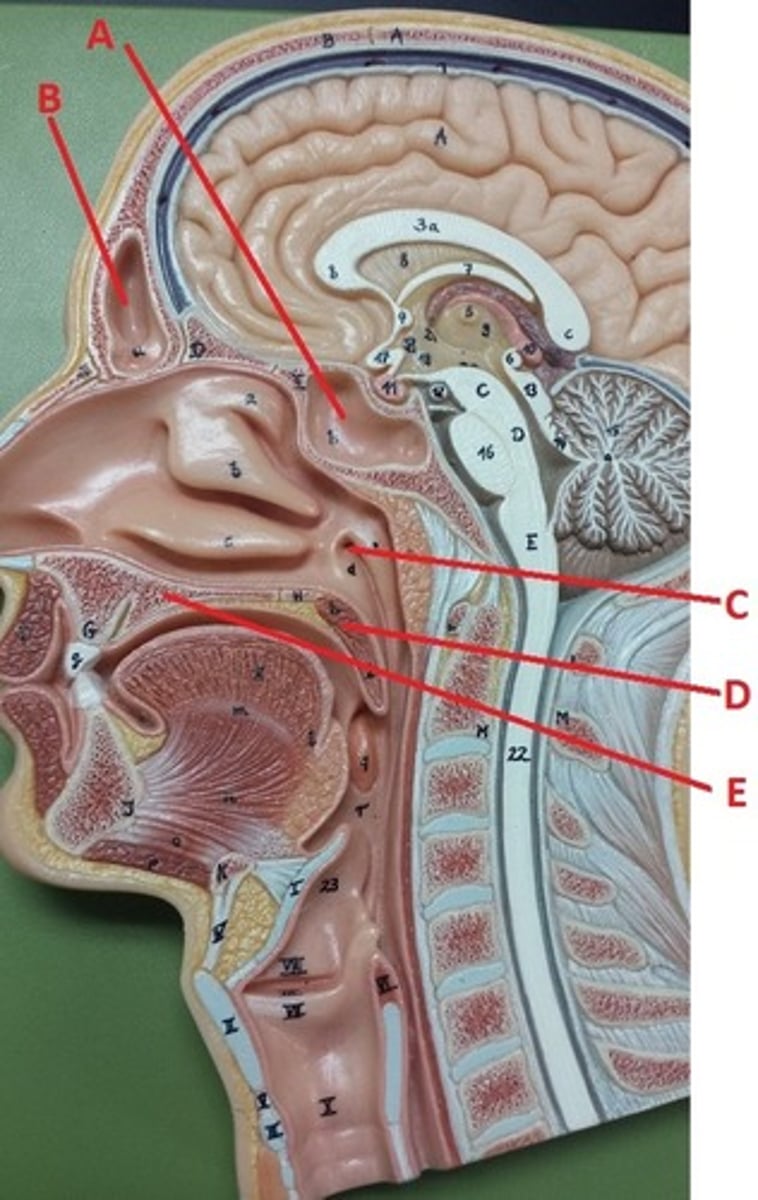
sphenoidal sinus
A
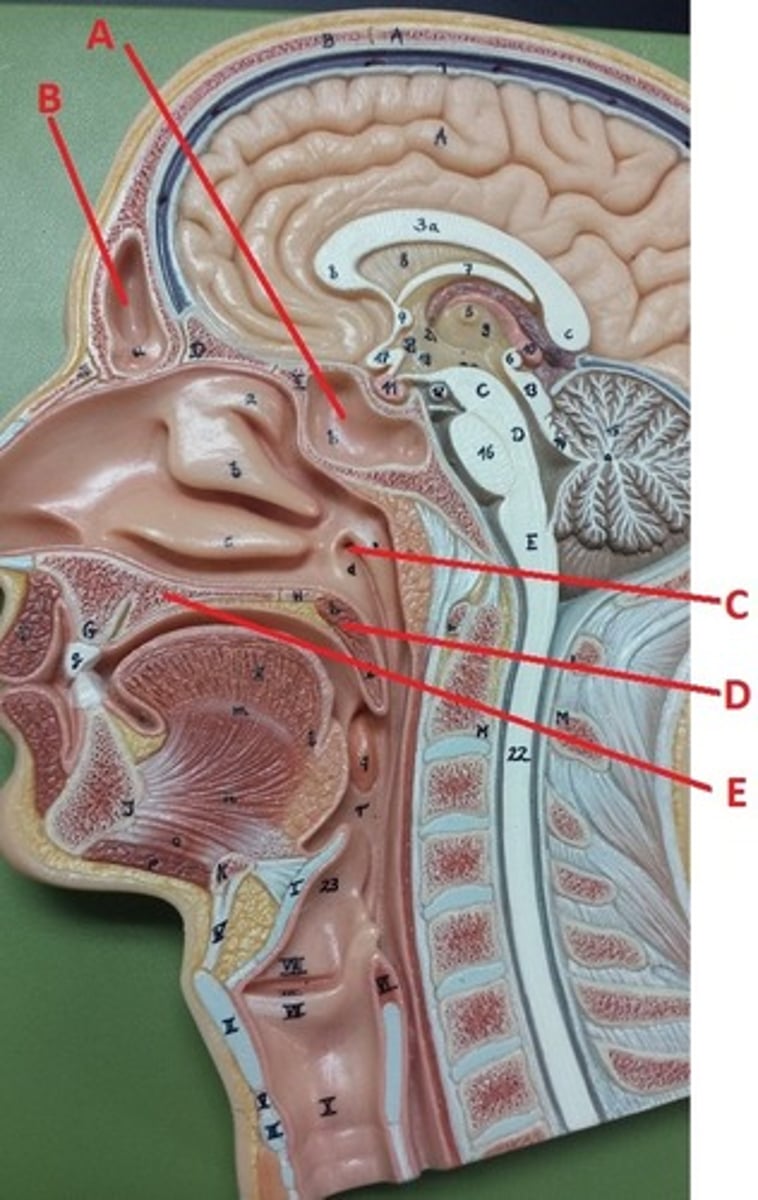
frontal sinus
B
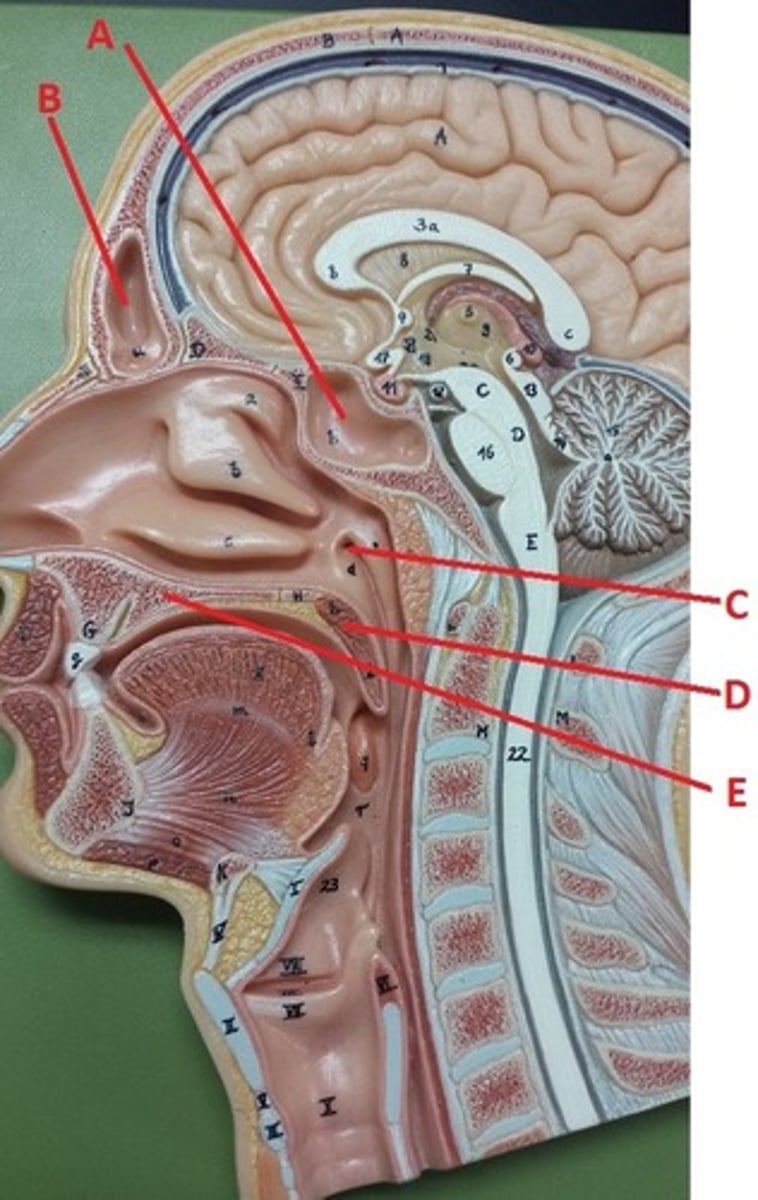
opening to auditory tube
C
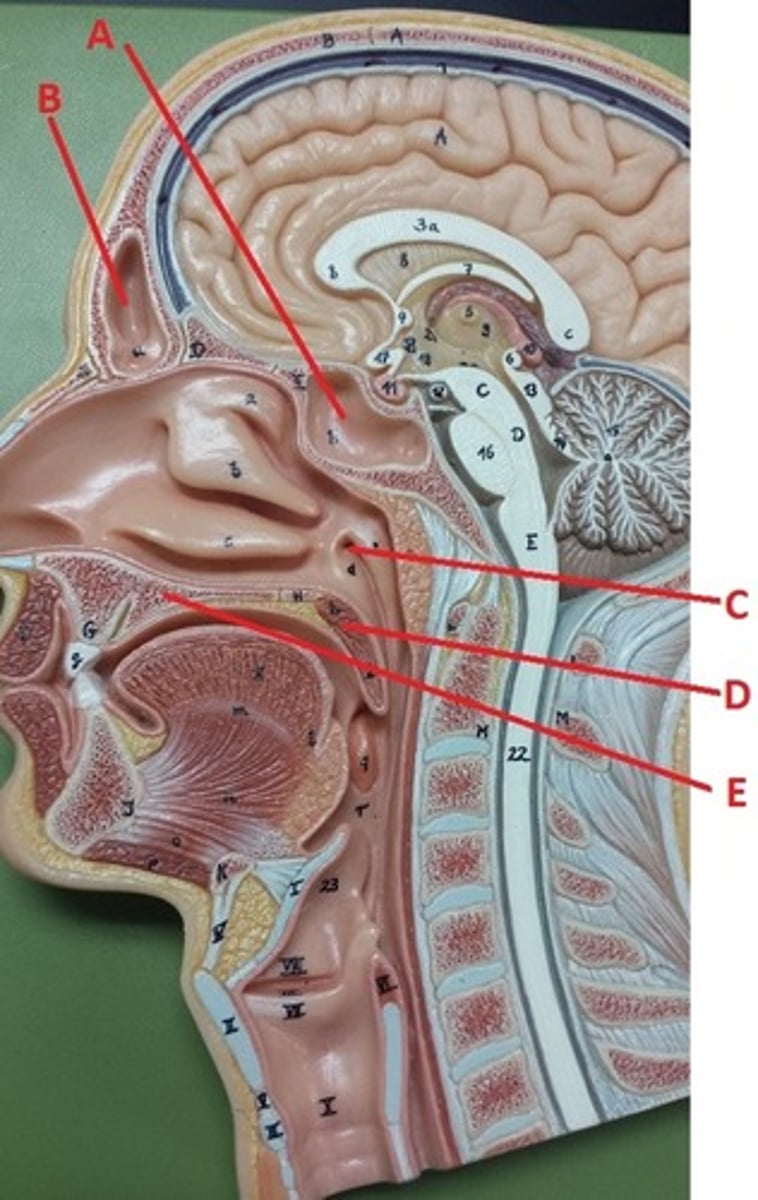
soft palate
D
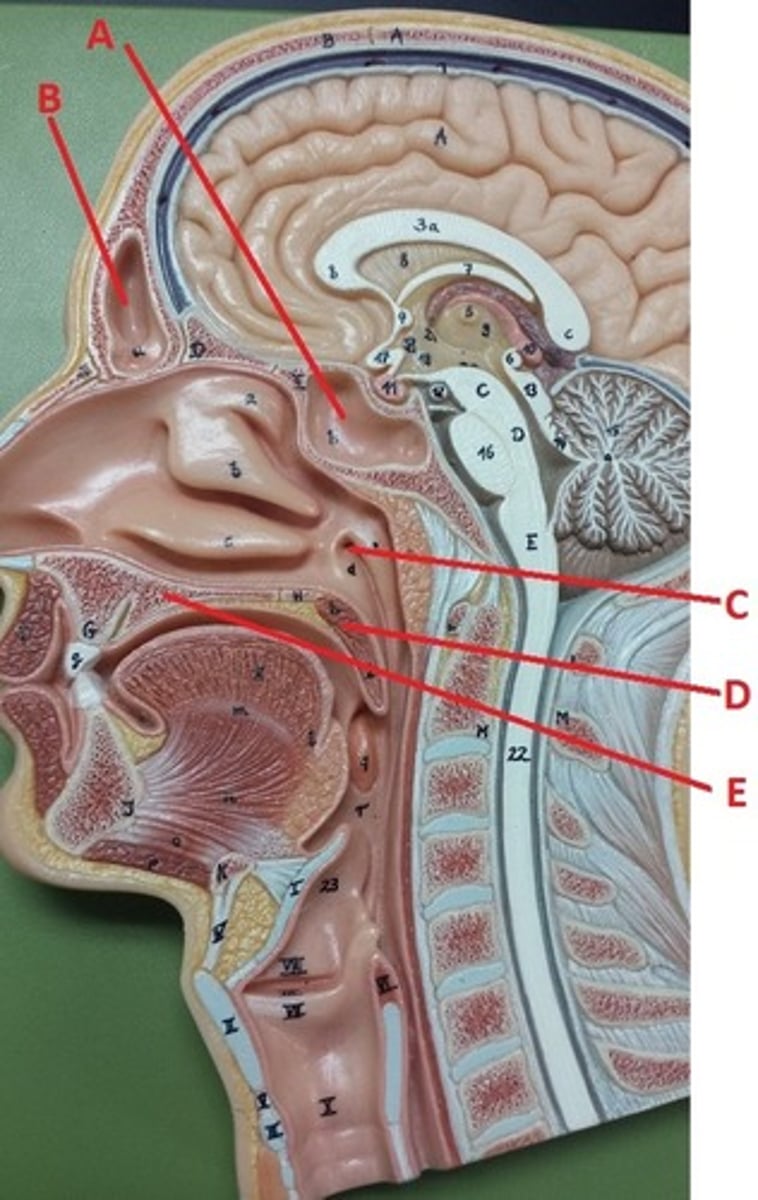
hard palate
E
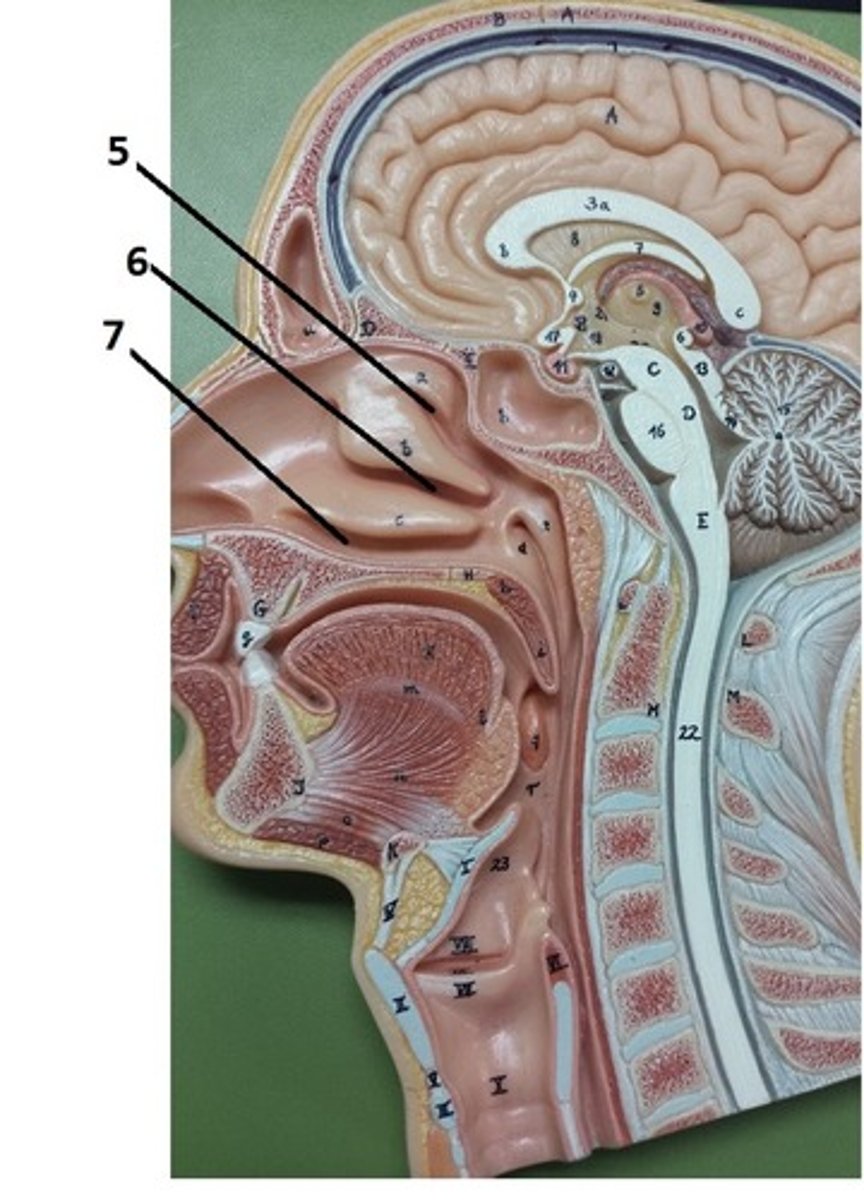
superior nasal meatus
5
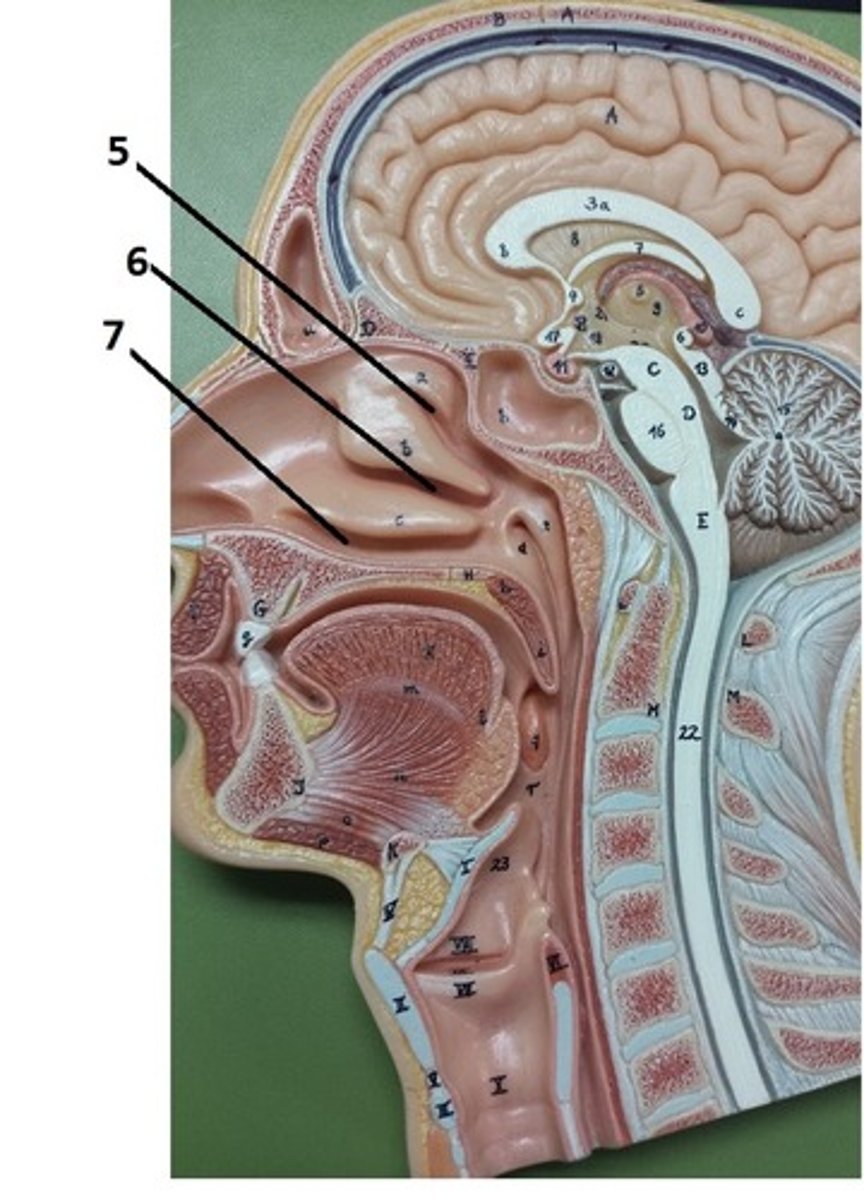
middle nasal meatus
6
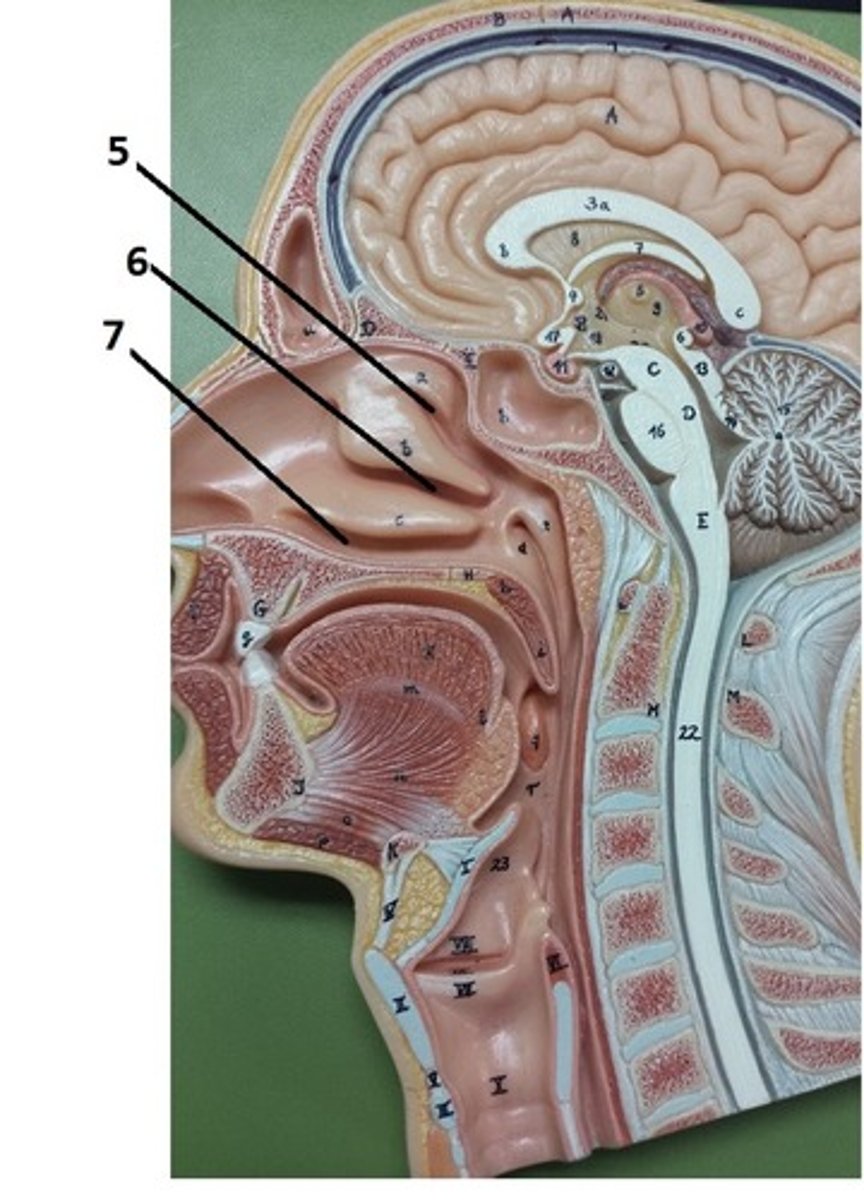
inferior nasal meatus
7
superior nasal concha
1
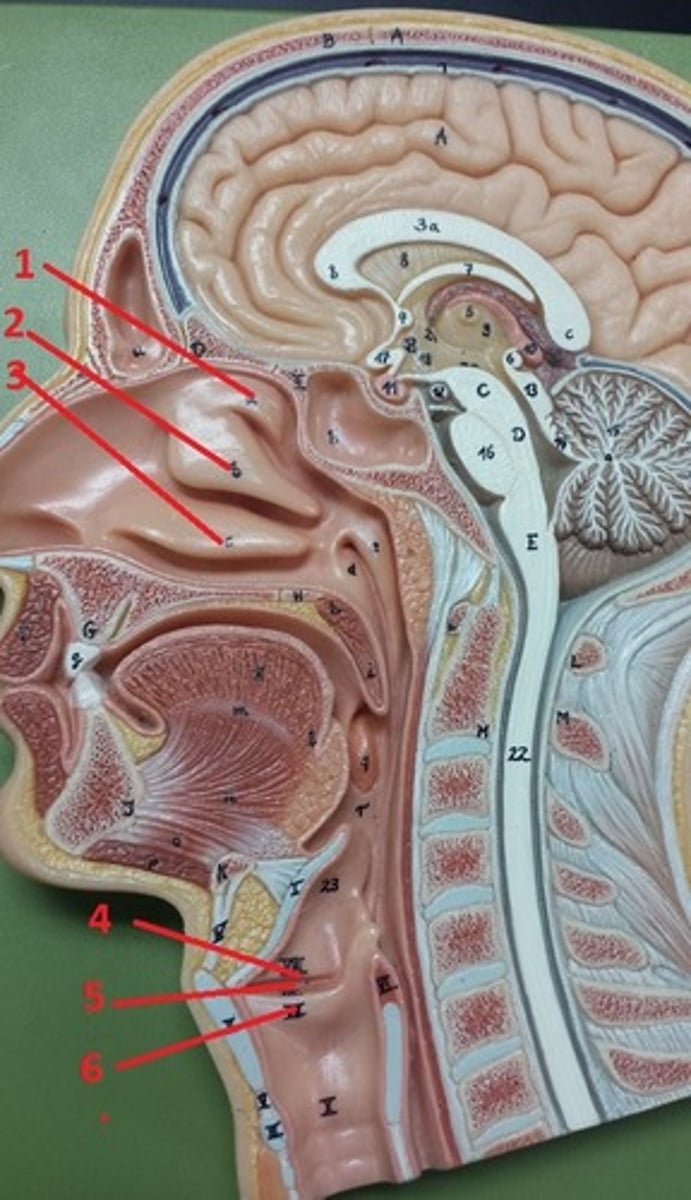
middle nasal concha
2
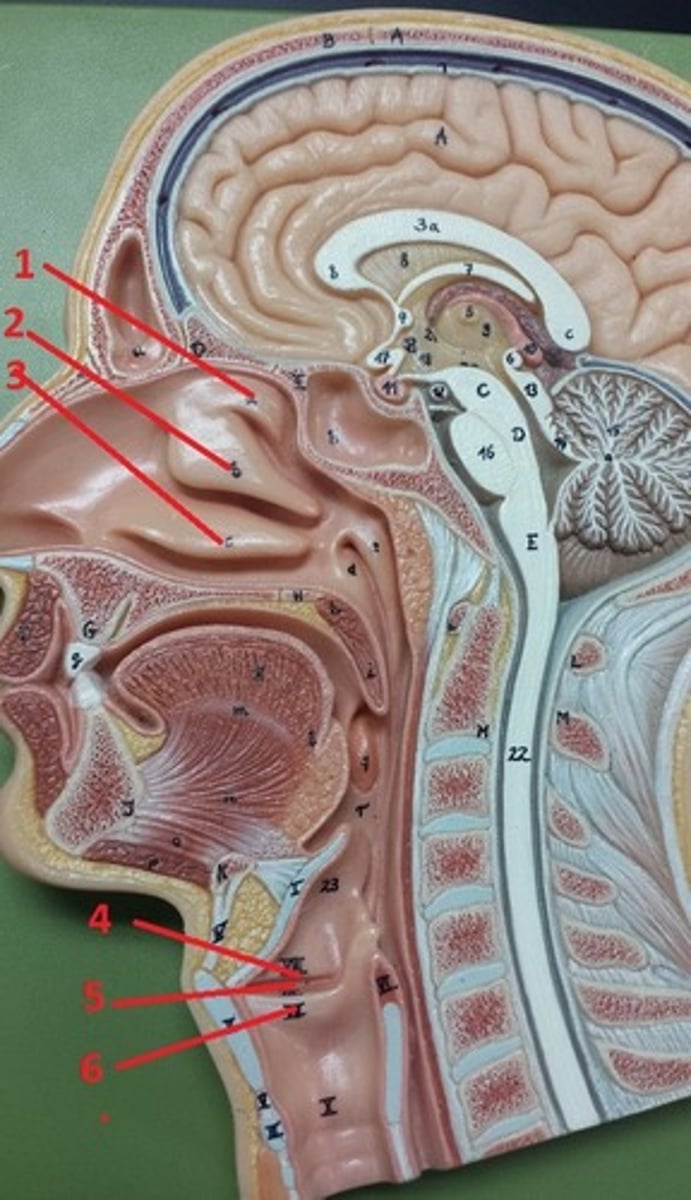
inferior nasal concha
3
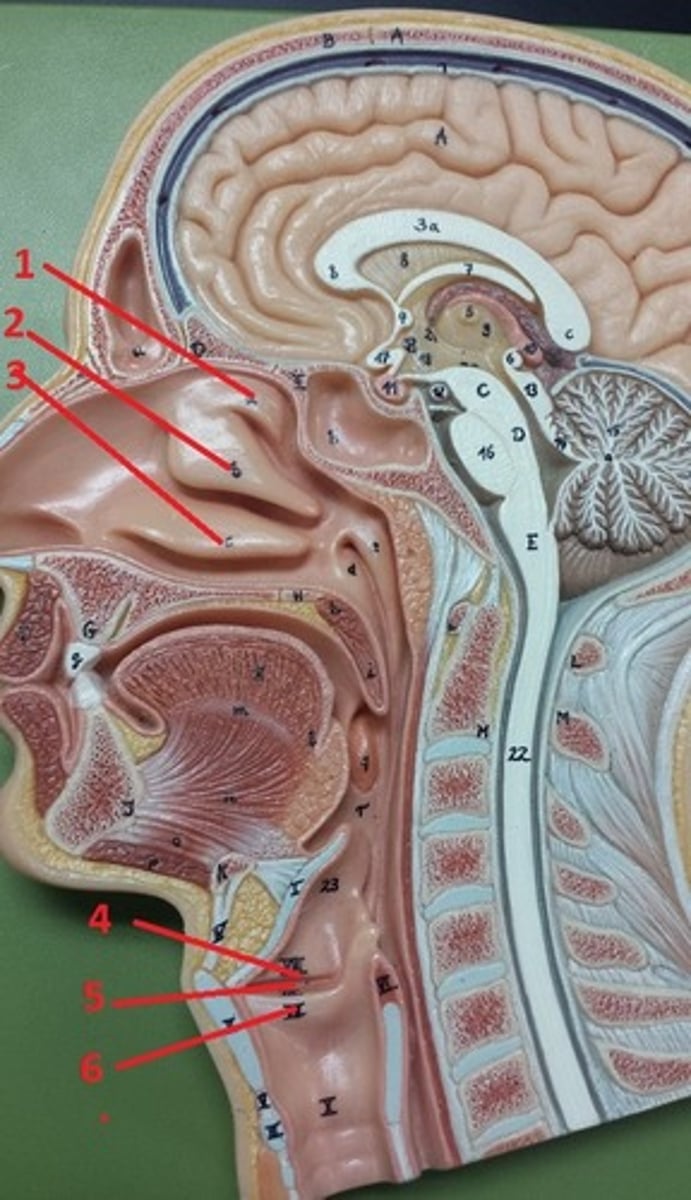
vestibular folds
4
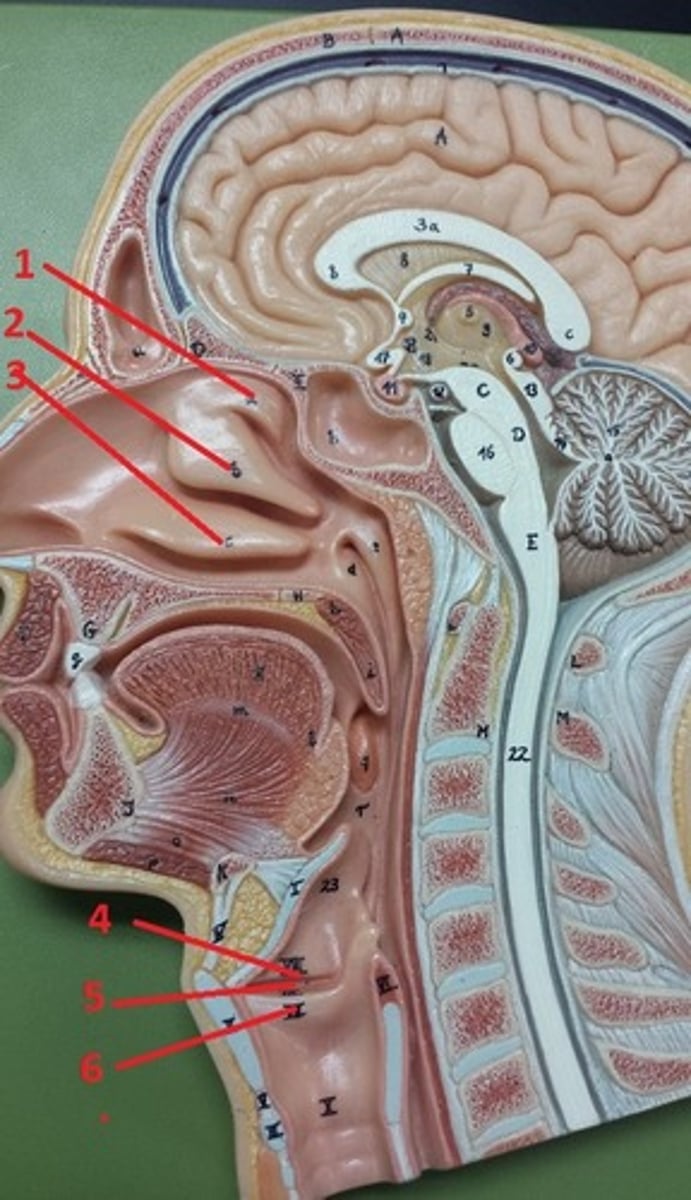
glottis
5
true vocal cords
6
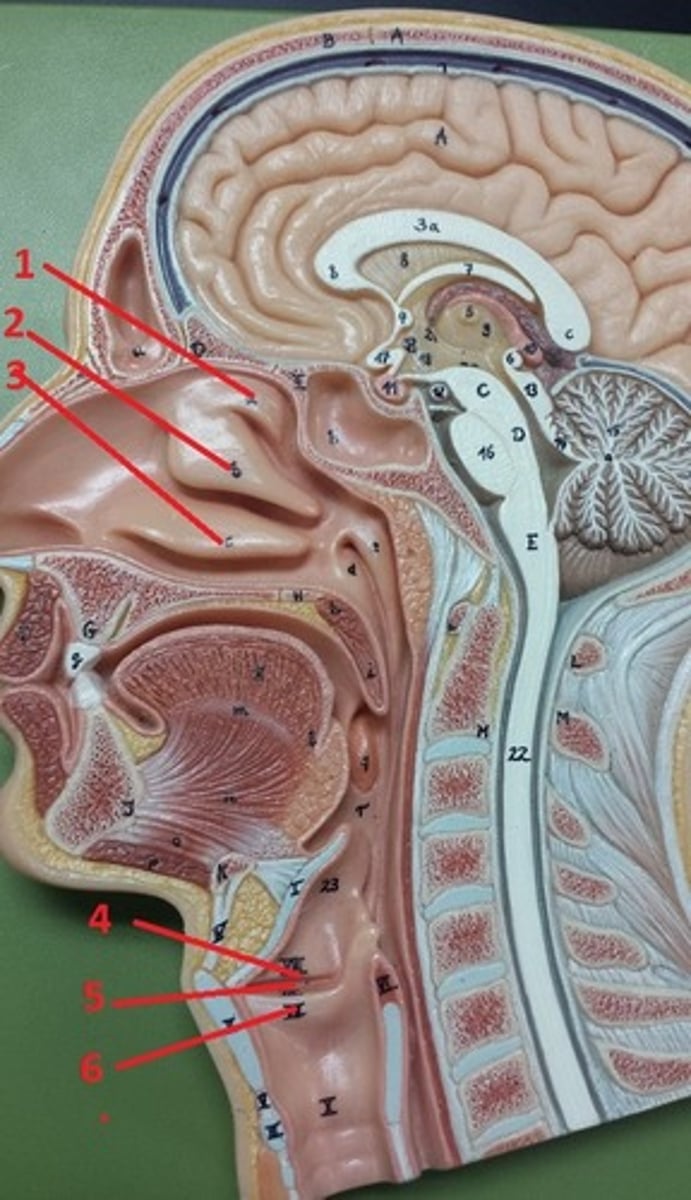
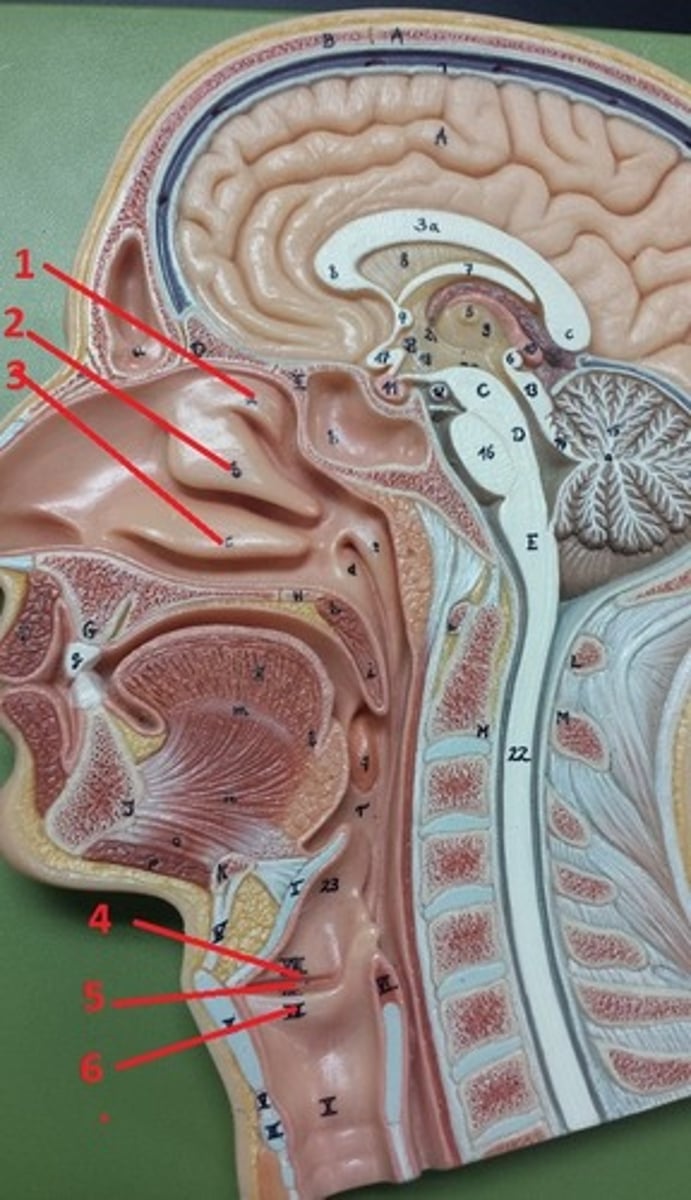
nasopharynx
A
oropharynx
B
laryngopharynx
C
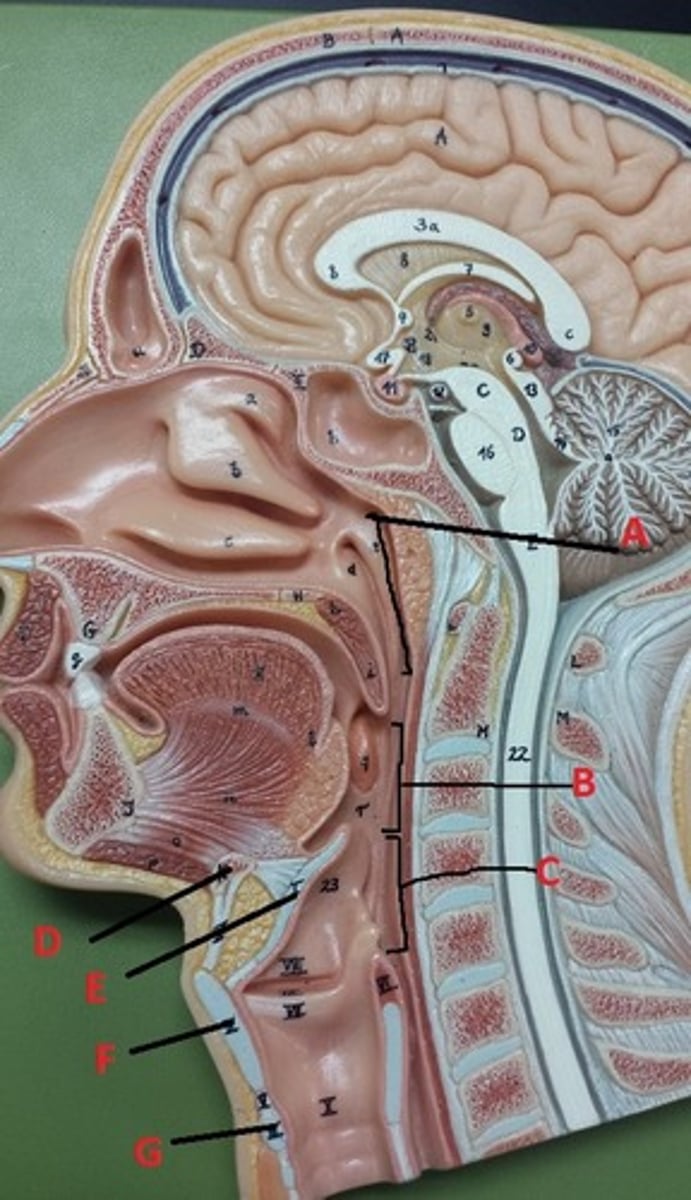
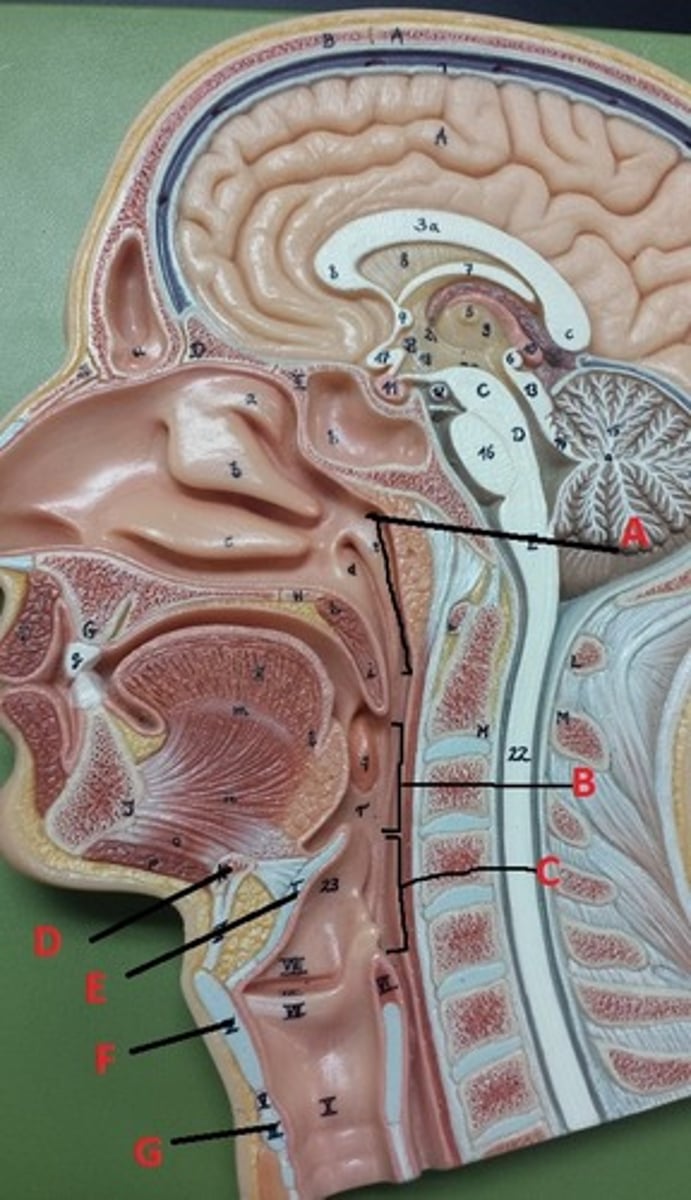
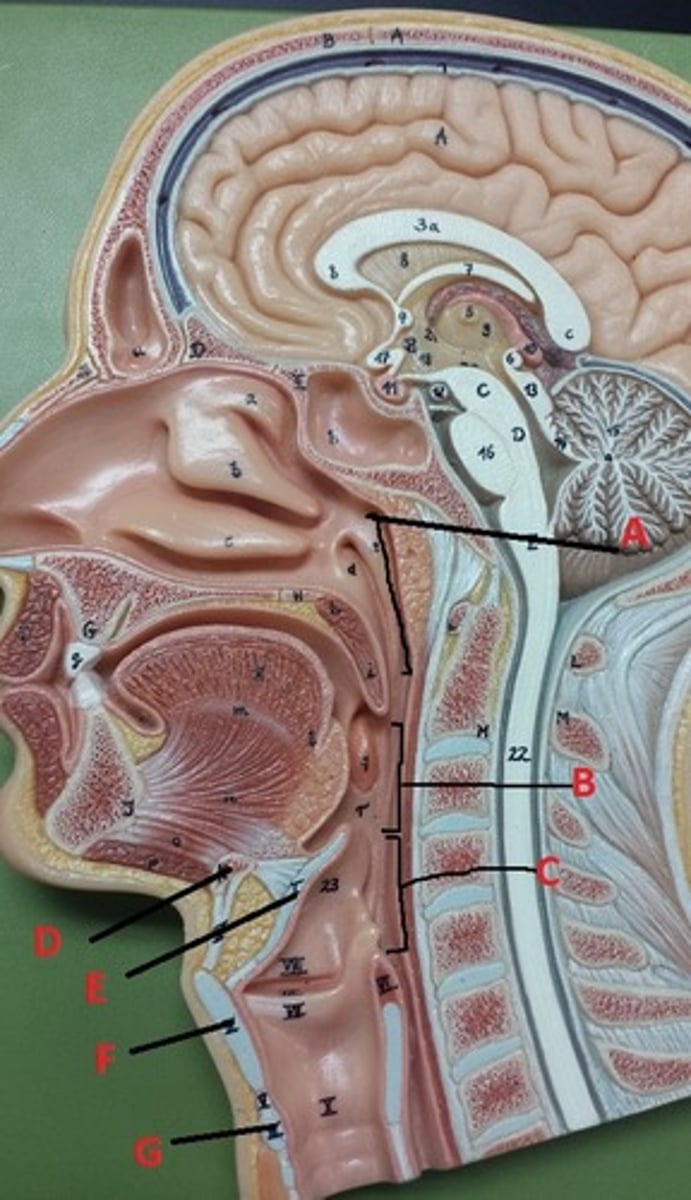
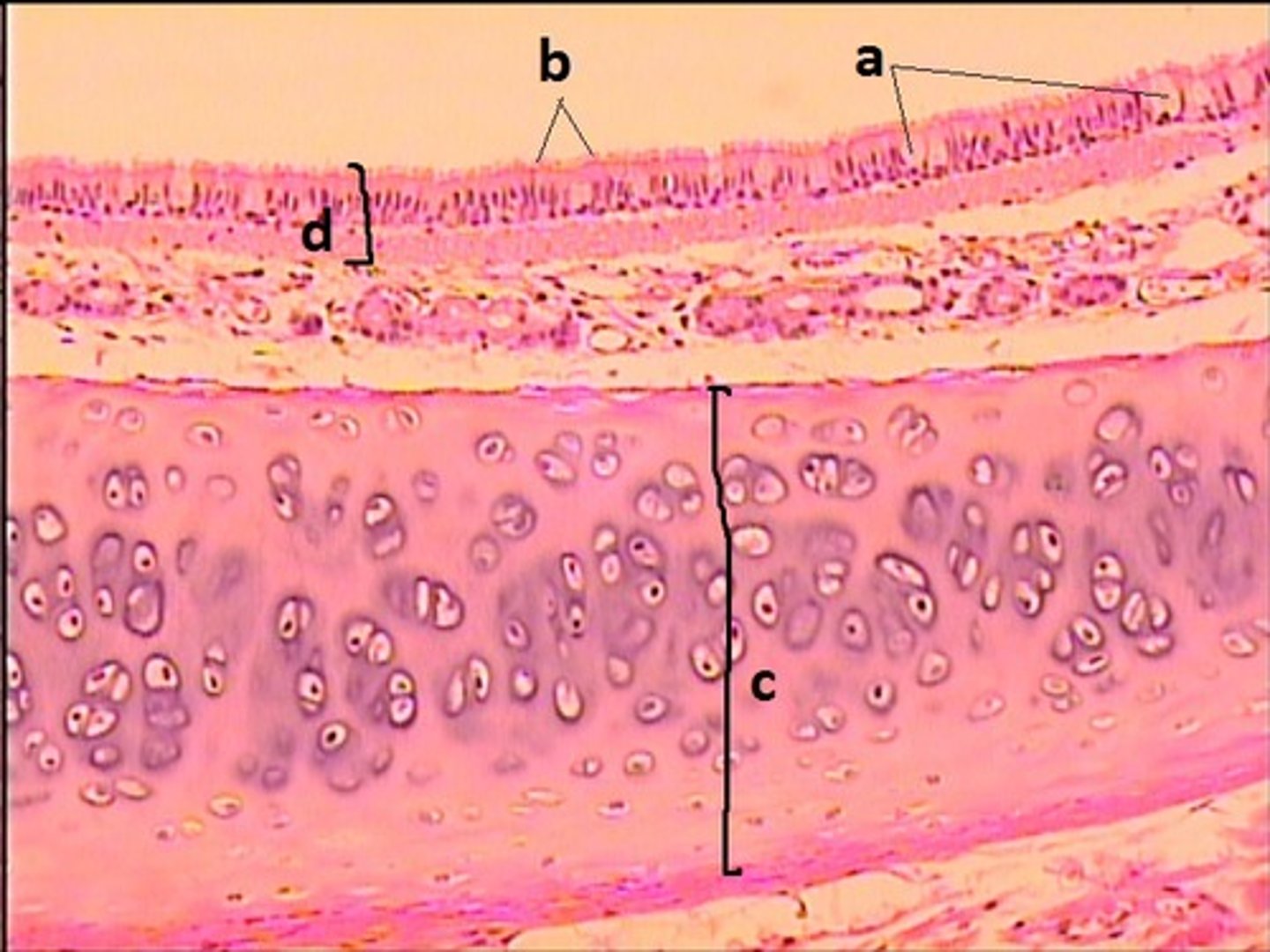
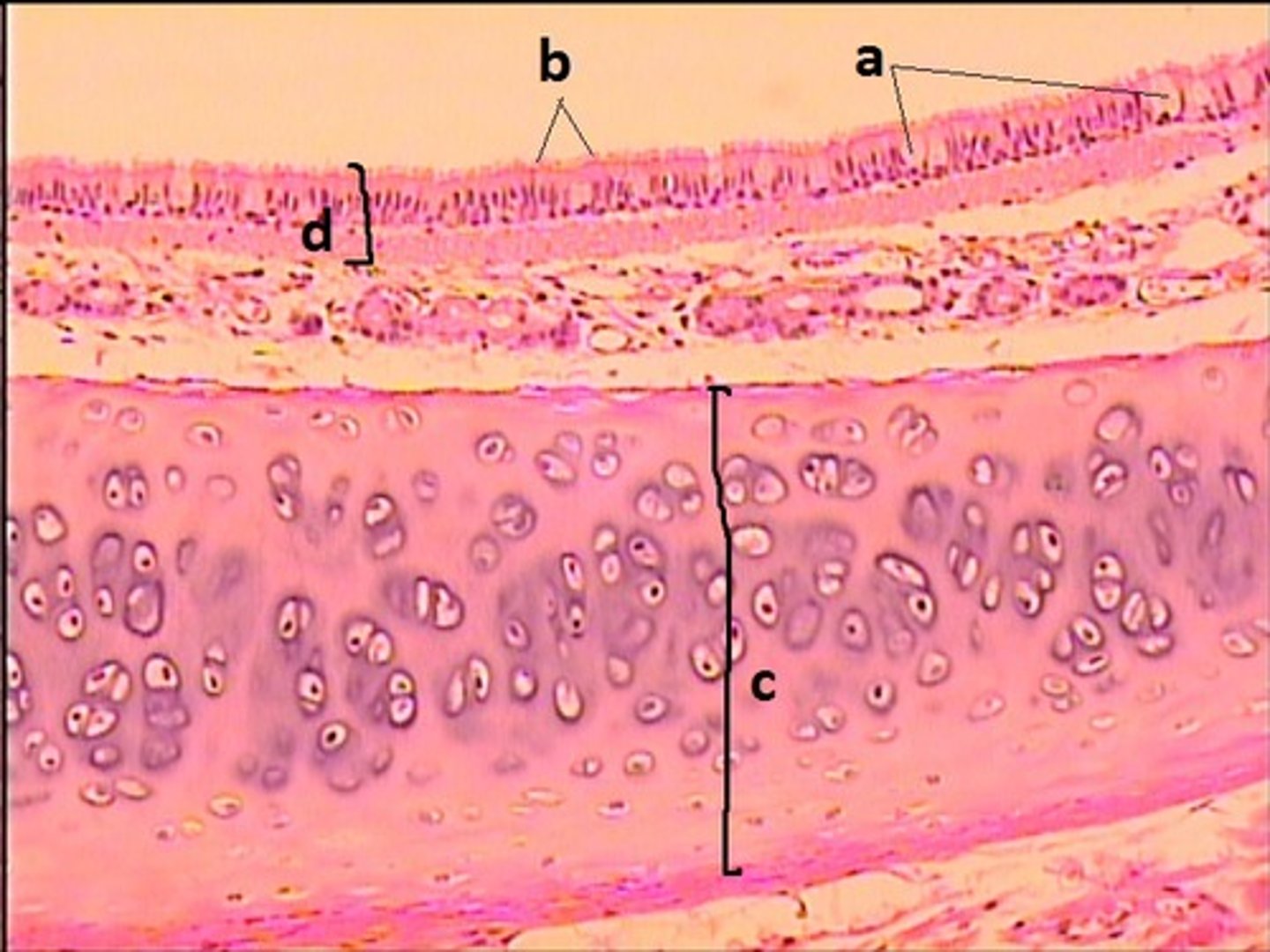
bone
What connective tissue is D?
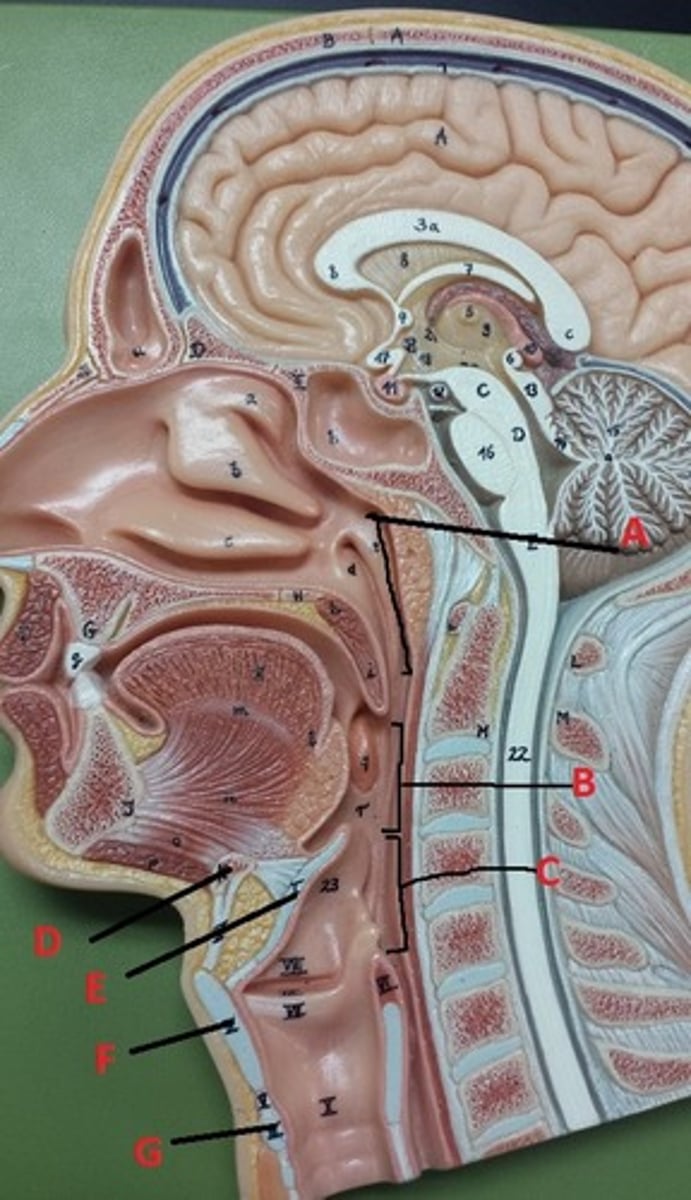
elastic cartilage
What is the major connective tissue found in E?
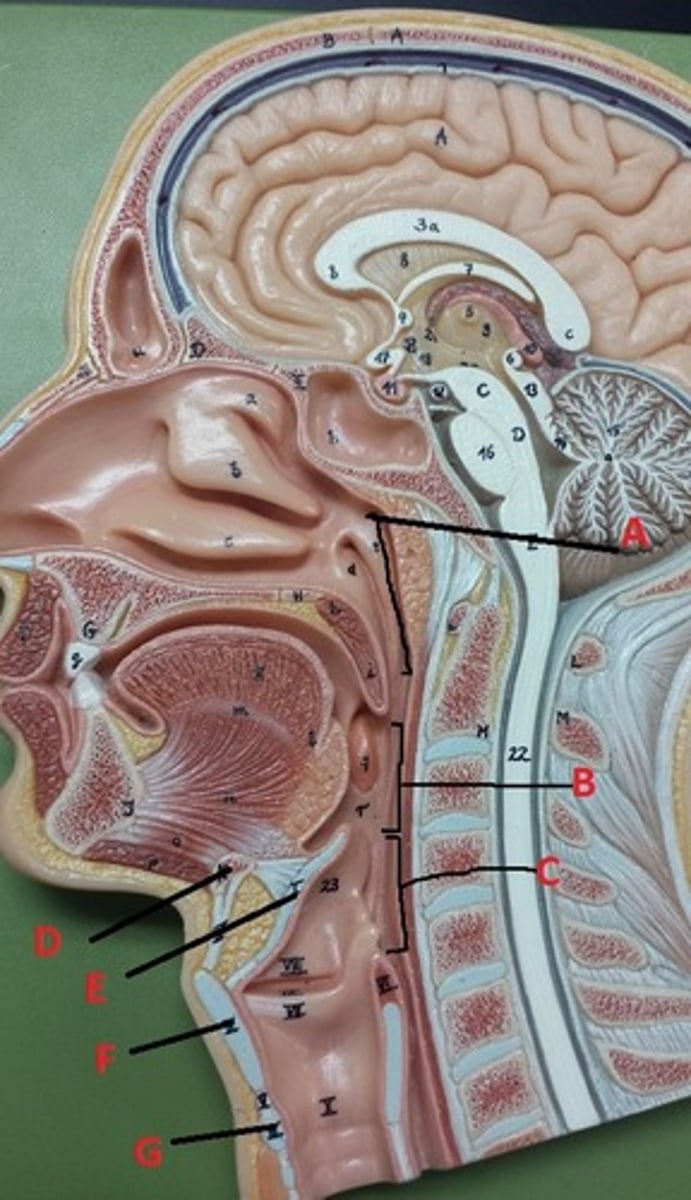
hyaline cartilage
What is the major connective tissue found in F and G?
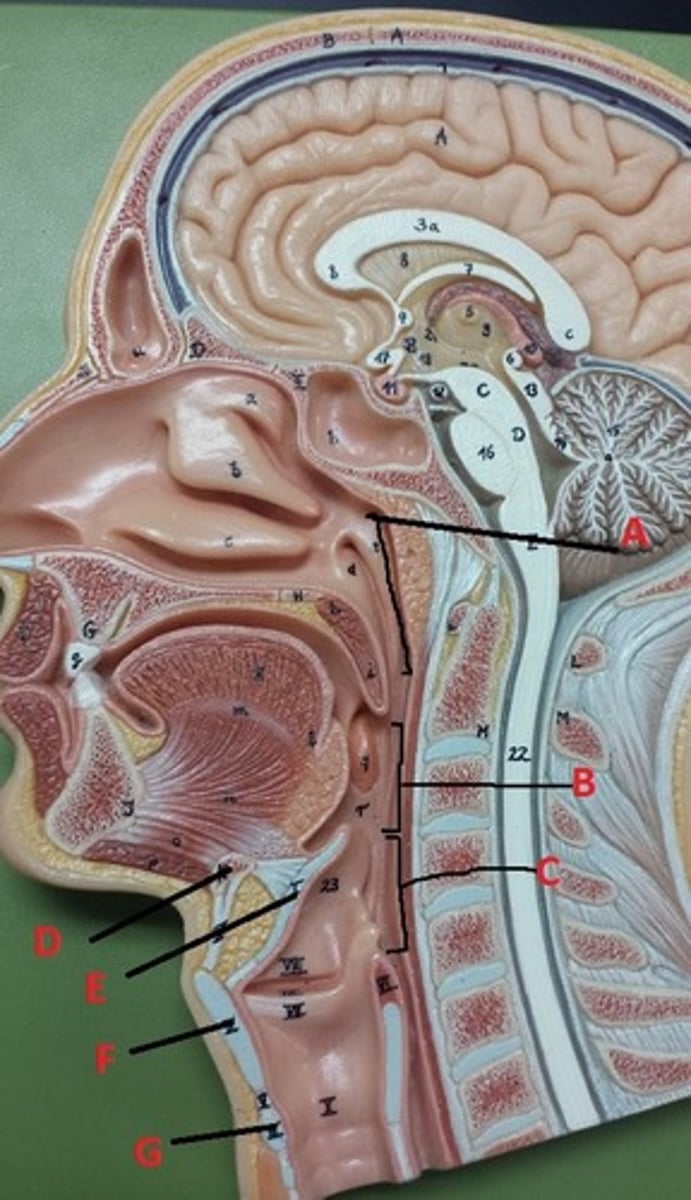
stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
What epithelial tissue lines B and C?
PCCE
What epithelial tissue lines A?
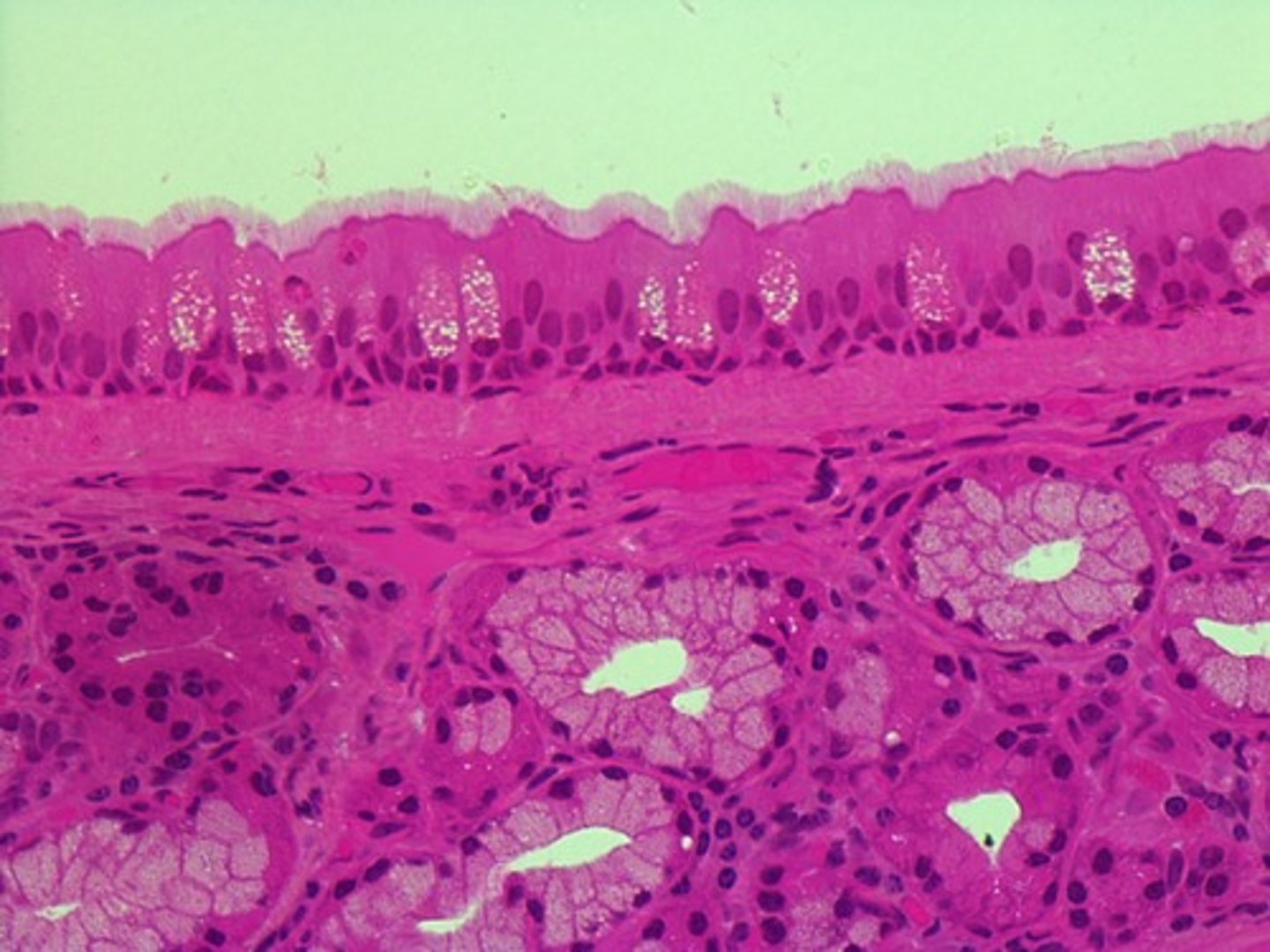
goblet cells
a
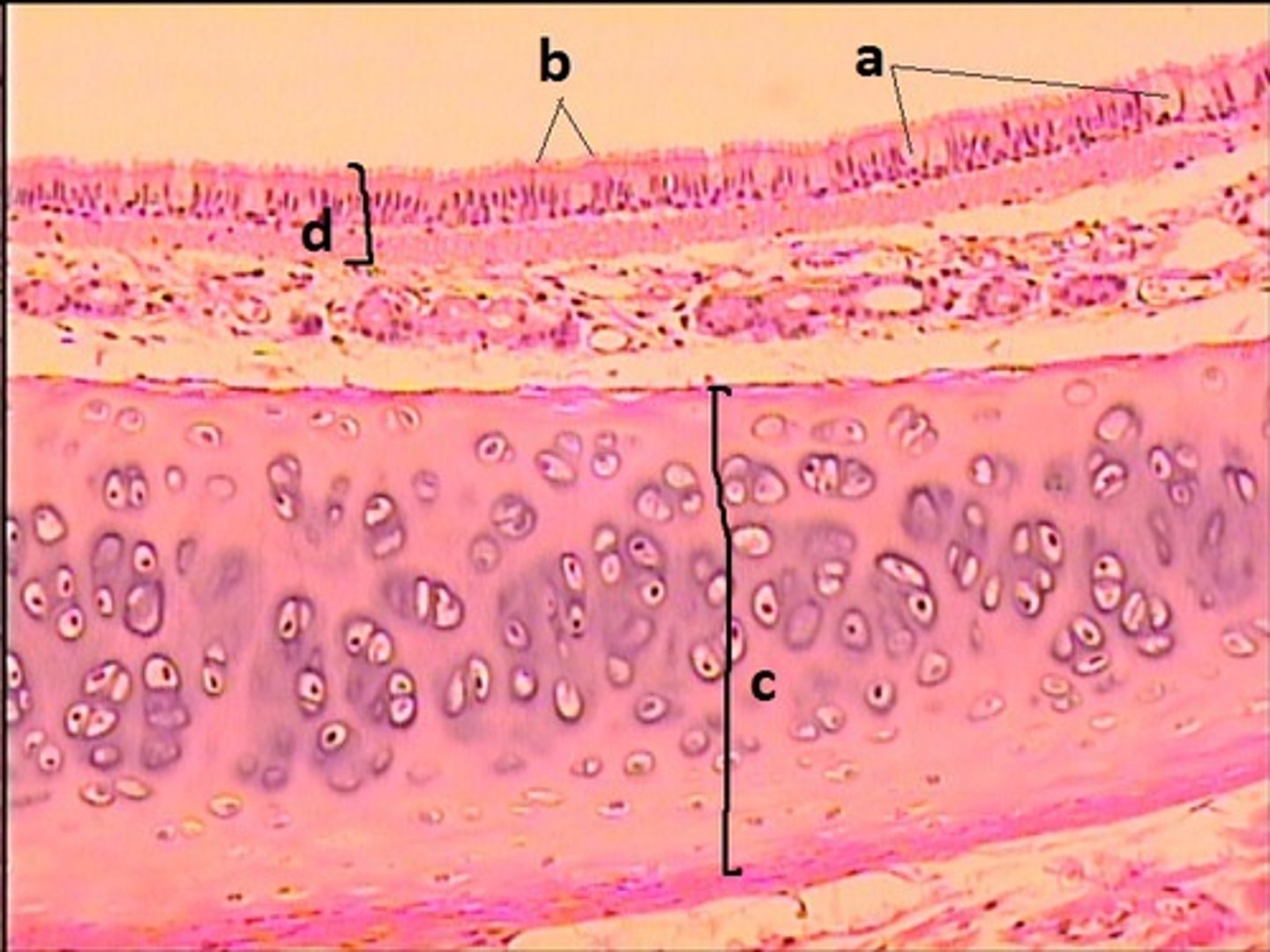
cilia
b
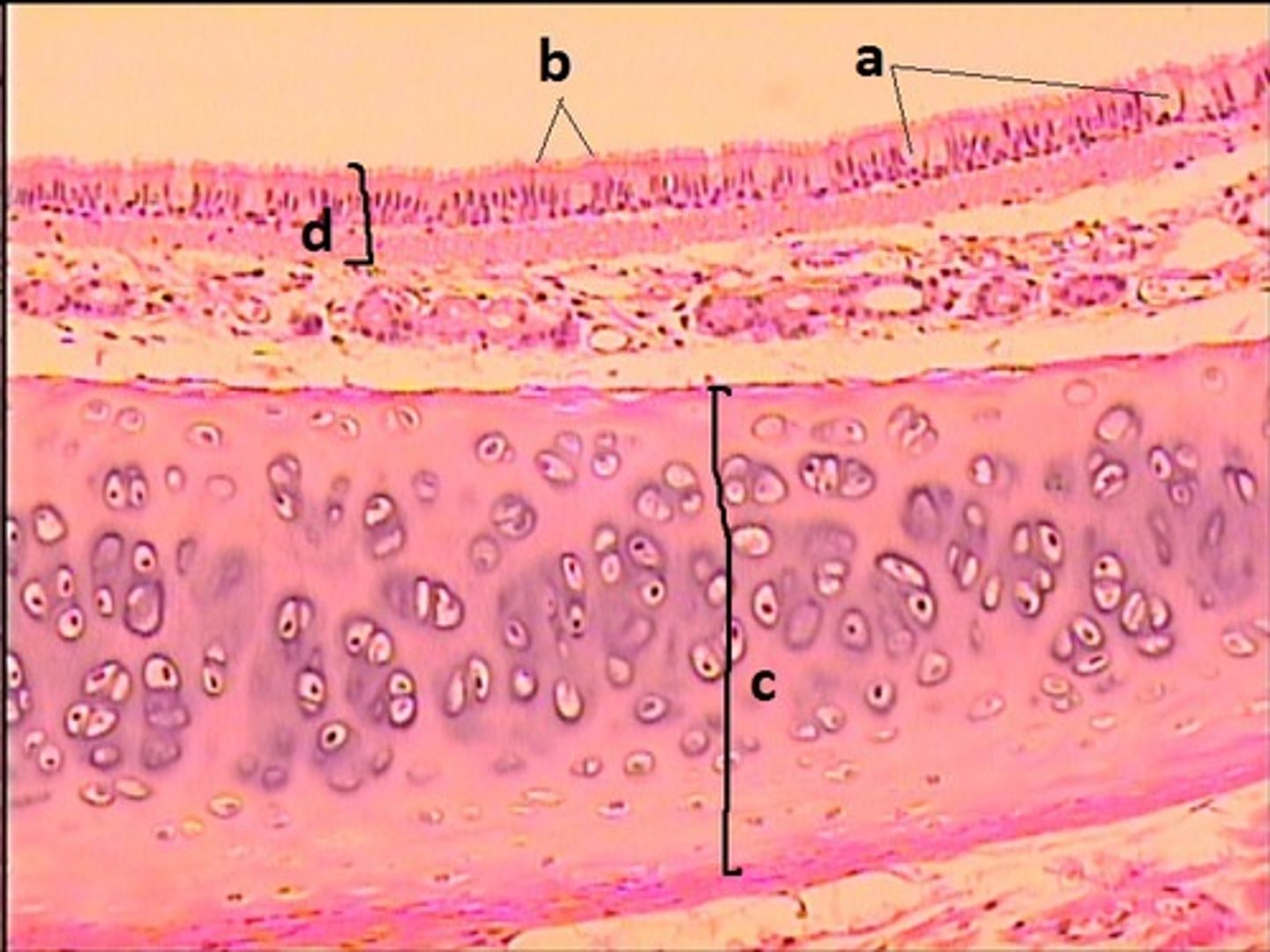
hyaline cartilage
c
PCCE
d
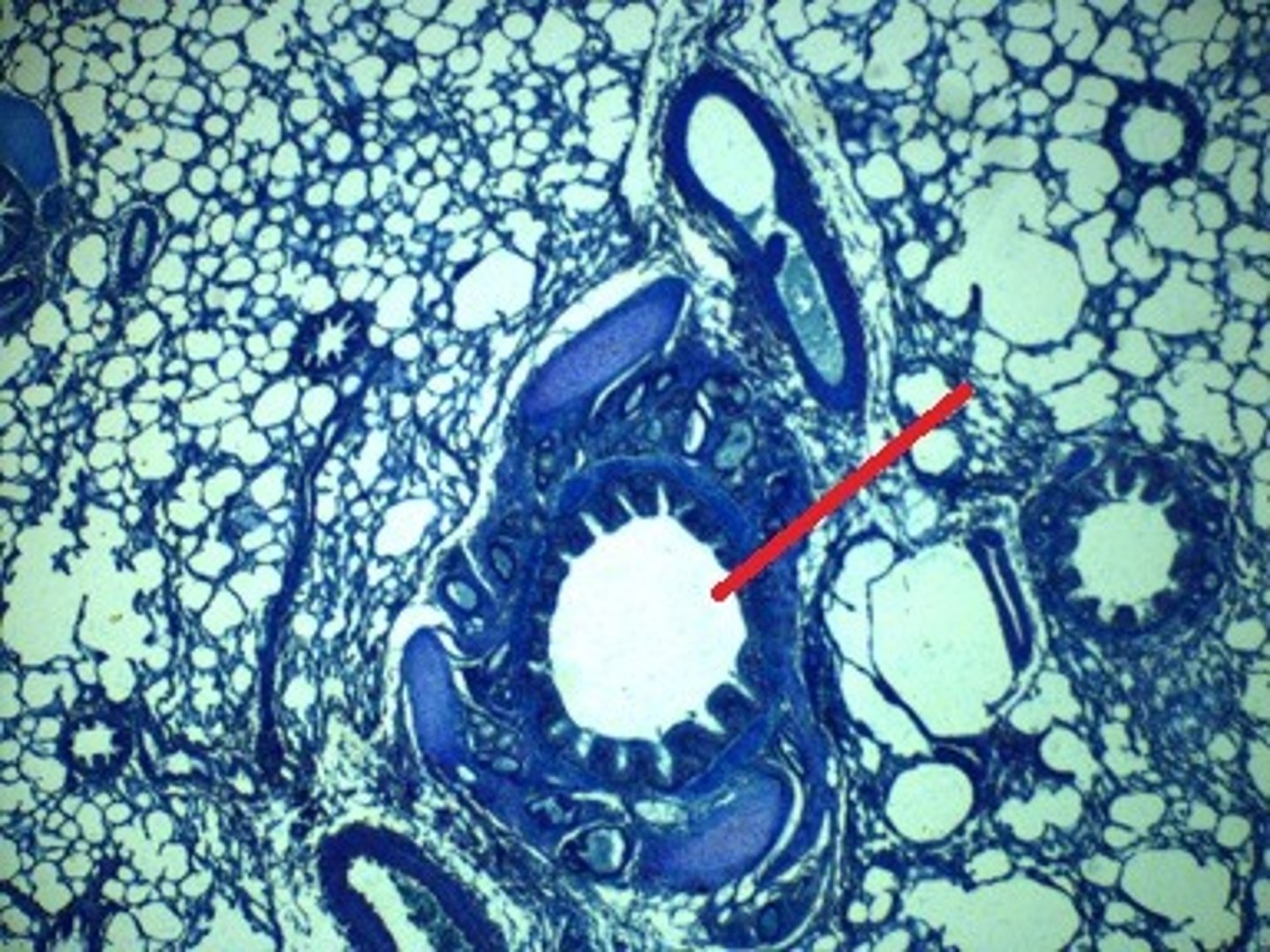
trachea
structure?
bronchus
structure?
alveolus
structure?
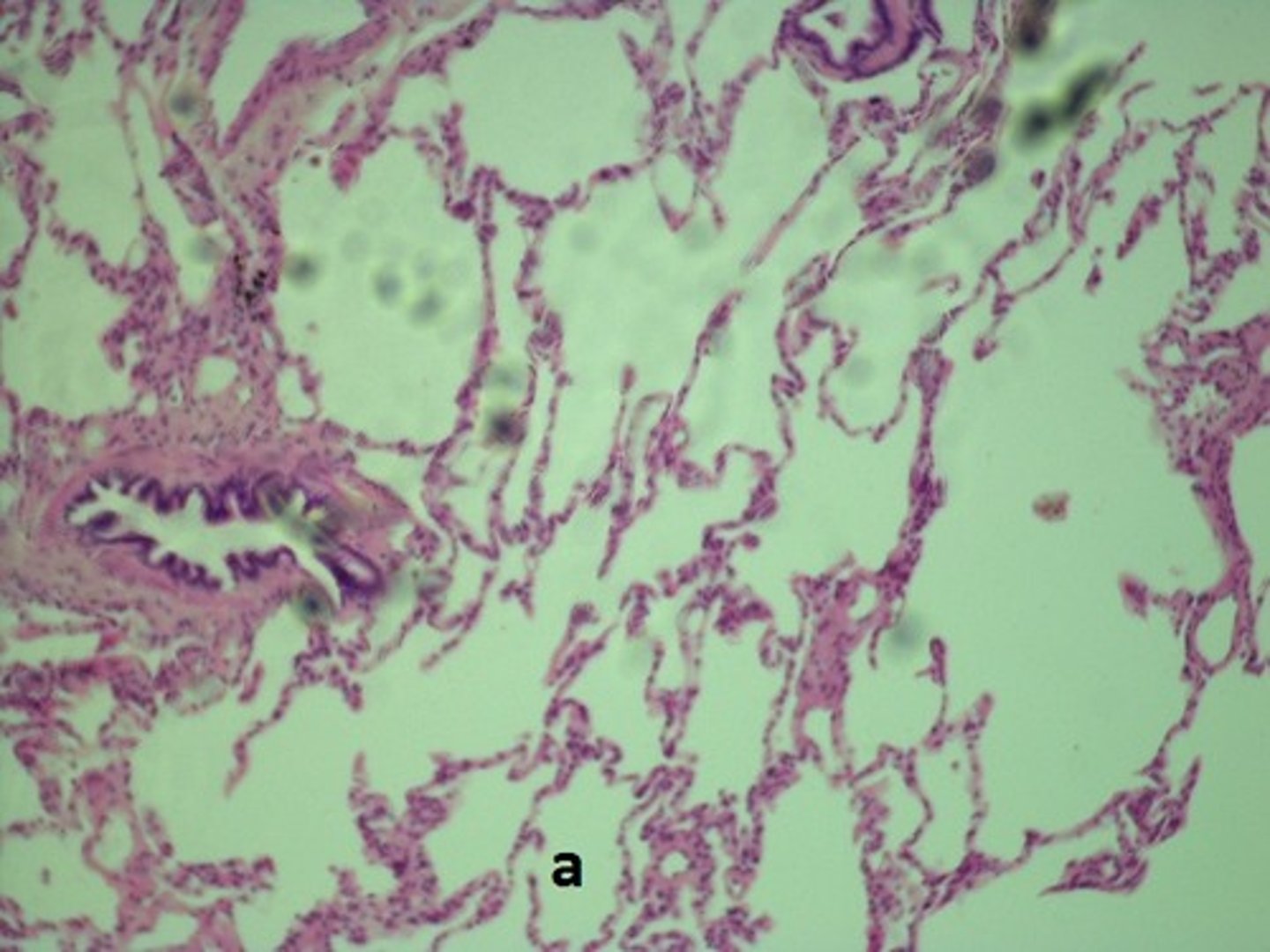
bronchiole
structure?
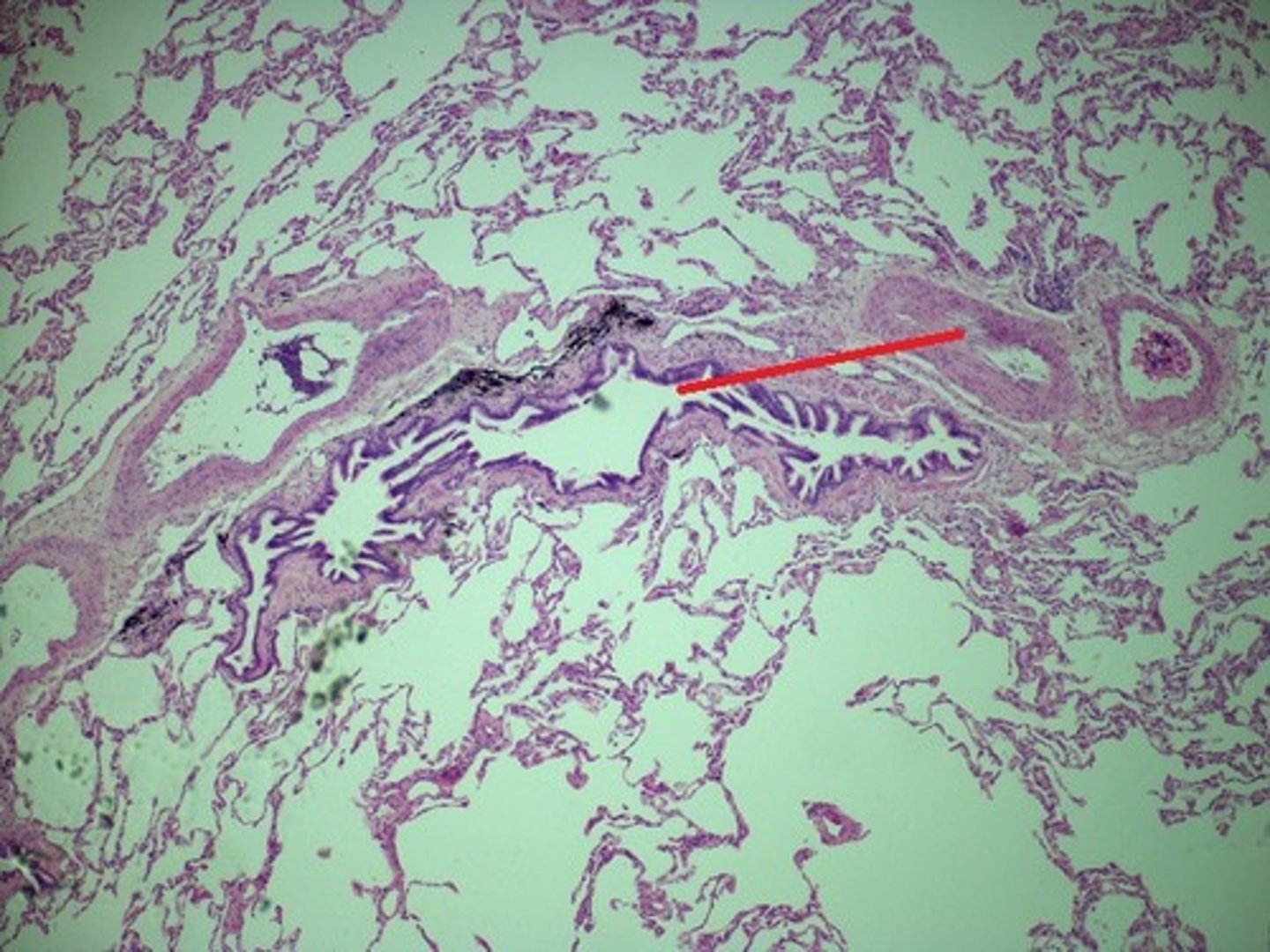
emphysema
Is this lung biopsy from a person with pneumonia, emphysema, or pulmonary edema?
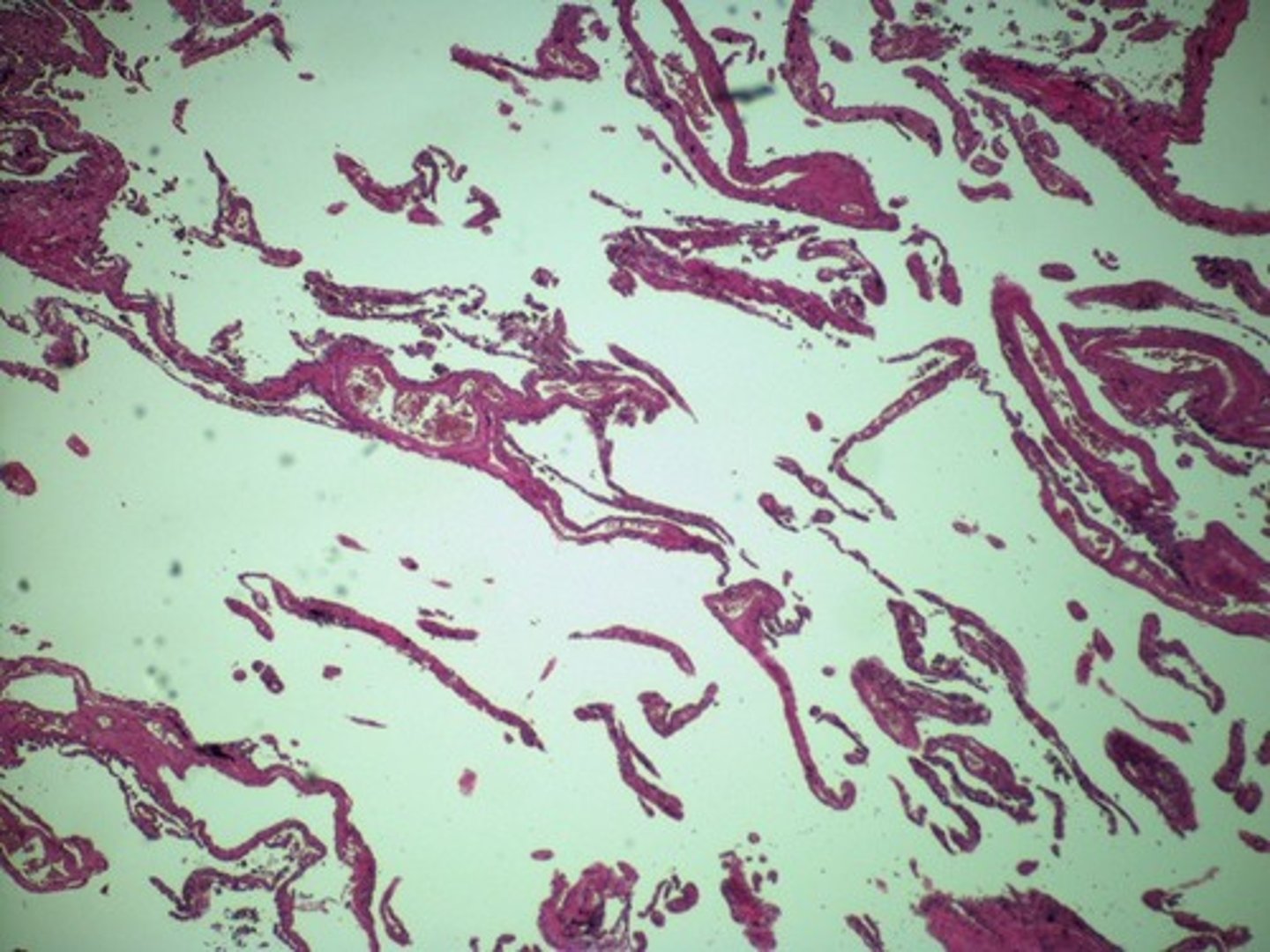
pulmonary edema
Is this lung biopsy from a person with pneumonia, emphysema, or pulmonary edema?
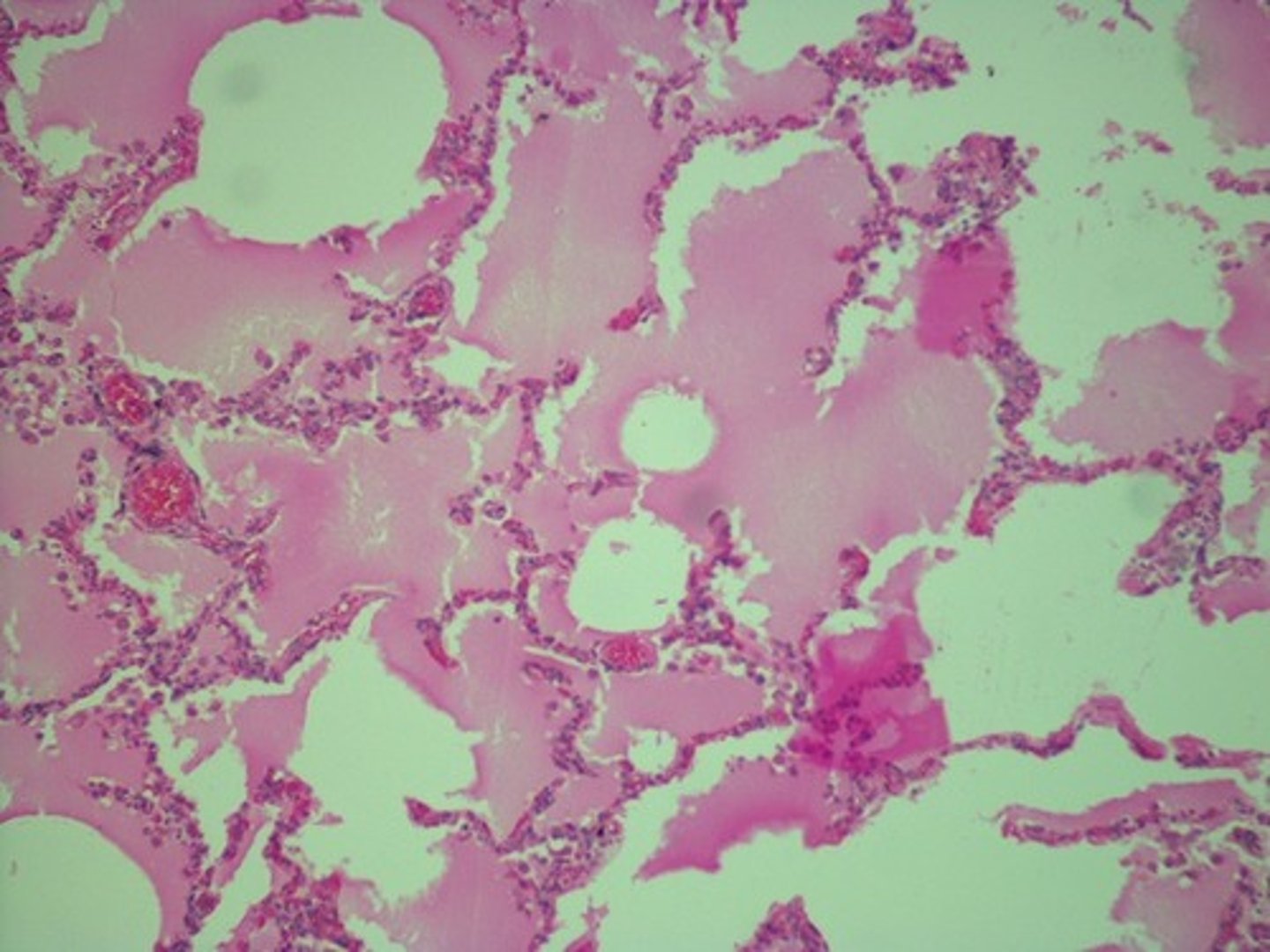
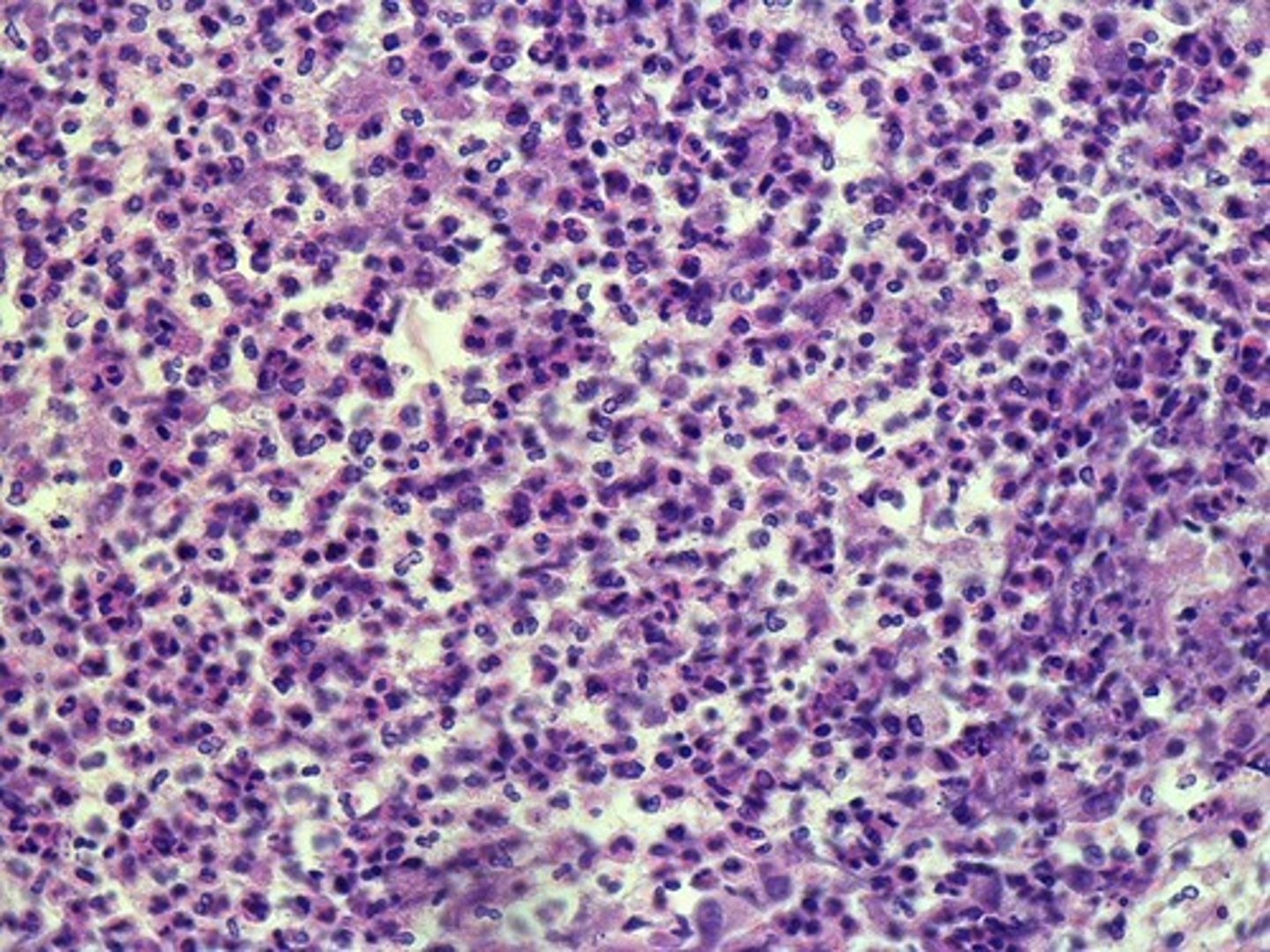
pneumonia
Is this lung biopsy from a person with pneumonia, emphysema, or pulmonary edema?
upper respiratory tract
The airway from the nose to the larynx forms the _____ and functions in filtration, warming, and humidification of entering air.
simple squamous epithelium
type of epithelium in alveoli
1 epiglottis, 1 thyroid cartilage, 1 cricoid cartilage, 2 arytenoid cartilages, 2 corniculate cartilages, and 2 cuneiform cartilages
Names of cartilages and number of cartilages of the larynx
lower respiratory tract
The larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli all make up the _________ and function in
phonation, further filtration of air, and gas exchange.
(1) its rigidness ensures that the trachea is held open (provides an open airway). (2) the epiglottis folds down to seal the trachea during swallowing, thus directing food the espohagus, and (3) this is where the vocal cords are found (phonation).
the 3 main functions of the larynx
glottis
opening between the vocal cords in the larynx
functions to cause turbulent air flow (heat) and increases mucosal surface area
nasal conchae
type II pneumocytes
What type of cells of the respiratory system secrete surfactant?
vestibular folds
structure lined by PCCE help to close the larynx during swallowing; if food contacts this structure, it will trigger a cough reflex; also referred to as false vocal cords
Lowers alveolar surface tension by interspersing between water molecules lining alveoli, prevents smaller alveoli from collapsing and allow alveoli to deflate evenly
function of pulmonary surfactant
seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering during swallowing
function of epiglottis