OPT 317 Trauma, HA, Retinal Breaks
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are some S/S of corneal abrasions?
pain
photophobia
tearing
corneal staining
(-) infiltration
injection
AC rxn
(-) Seidel sign
How do we tx a corneal abrasion?
debride loose epithelium
abx gtts or ung for prophylaxis
cycloplegia for pain
DPP
bandage CL
pain meds = topical NSAIDs, oral opioids, gabapentin, pregabalin
Which types of corneal abrasion should we NOT patch?
dirty wound = vegetative, fingernails, CL wearer
What are some S/S of foreign bodies?
FB sensation
pain
history of FB in eye
staining around FB
(-) Seidel sign
What is the tx for foreign bodies?
check for intraocular FB if high velocity object
DLE
remove FB with speed, needle, magnet, forceps
Alger brush to remove rust ring
tx as corneal abrasion
What are some S/S of conj lacerations?
redness
subconj heme
"eye is bleeding"
NaFl pooling in area
(-) Seidel test
What is the tx for conj lacerations?
push edges together with applicators
patch
suture larger lacerations
What are some S/S of intraorbital FB?
Hx of trauma
+/- pupil involvement
+/- VA affected
(+) Seidel test
What is the tx for intraorbital FB?
CT to determine depth of FB
DON'T remove FB at slit lamp
refer for OR consult for irrigation of wound, suturing
What 3 things do we specify in our ICD-10 codes for any trauma?
the injury and eye = corneal FB, eyelid laceration, contusion
how it happened = pecked by turkey, struck by a ball
where it happened = athletic court, courtyard of prison

What are the 3 options for the 7th digit in the ICD-10 injury code?
A = initial
D = subsequent
S = sequelae

What is the difference between primary vs secondary HA?
primary = cannot be attributed to known structural, toxic, metabolic abnormalities
secondary = definable abnormalities that causes the HA
What S/S may indicate a HA is secondary?
HA after age 55
jaw/scalp/chewing pain
ONH swelling
fever
altered behaviour
stiff neck
decreased vision
neuro signs
pre-retinal hemes
What warrants a migraine being considered chronic?
15+ days per month
Migraines make up what % of all HA?
54%
Migraines affect what % of the US population?
13%
Migraines are 3x more common in which gender?
females >>> males
What is the pathophysiology of migraine?
brain has reduced threshold to stimuli (triggers, menstrual cycle, sleep cycle) = cortical excition, starting in visual cortex (aura) = followed by spreading wave of depression that moves anteriorly = BV dilation in meninges = pain
What 3 components contribute to trigeminal afferent activation in migraine pathophysiology?
neuropeptide release = CGRP, VIP
pain signal pathway = trigeminocervical nociceptors around eyes send signal to thalamus
BV dilation/contraction = only causes HA in migraneurs!
What are some features of aura?
scintillation patterns build in intensity = marching aura moves across VF
What is the difference between classic vs common migraine?
classic = with aura = 20%
common = without aura = 80%
What are some symptoms of migraine?
HA typically in periorbital or retro-orbital areas, onset in 20-60min
nausea/vomiting
photophobia
phonophobia
What are some tx for migraine?
R/O accom and BV issues
avoid triggers
pain relievers = NSAIDs, aspirin, opioids
botox
refer to PCP/neuro for triptans, ergots, CGRP blockers, anti-nausea meds, TCAs, glucocorticoids, anti-seizure meds
What is the pathophysiology of an ocular migraine?
vasopasm in retinal/post ciliary circulation = ischemia to retina, choroid, ONH = artery attenuation and occlusion DURING attack only = monocular visual changes
Accoridng to the IHS, what are the 5 main criteria to classify something as an ocular migraine?
2+ attacks minimum
reversible, monocular visual changes
HA during or within 60min of visual changes
normal eye exam between attacks
no other disorder causing it like CRAO, focal ischemia, optic actrophy, NAION/AAION, CRVO
What is the tx for ocular migraine?
R/O TIA from embolus, vascular disease
What do we call aura WITHOUT headache?
acephalgic migraines AKA typical aura without headache
What is the most common type (90%) of HA?
tension type HA = unilateral or bilateral tightness/aching in frontal, temporal, occipital regions
+/- neck symptoms
+/- sleep abnormalities
When are tension type HA most likely to happen during the day?
4-8am
OR
4-8pm
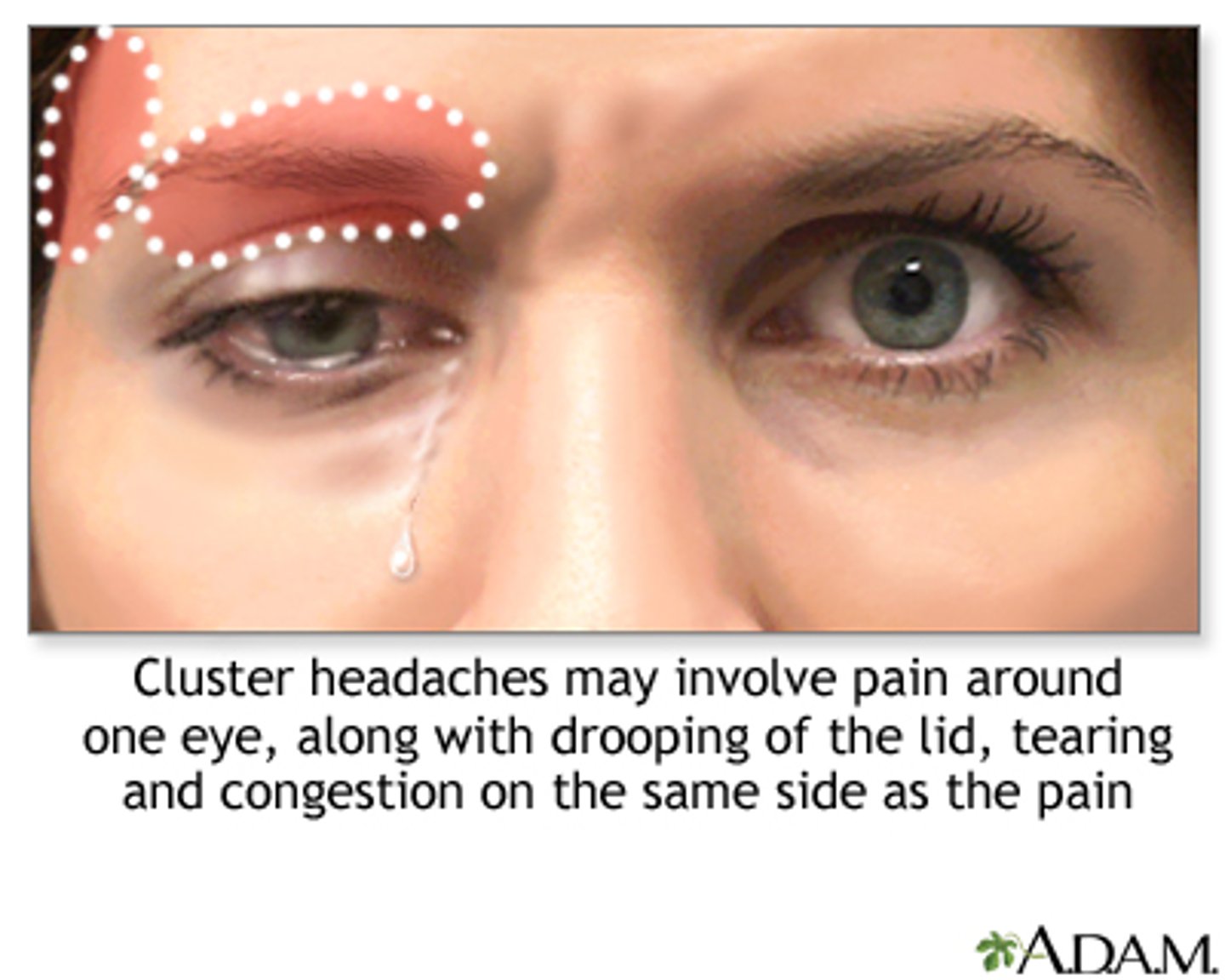
What is a cluster HA?
severe, boring/burning unilateral pain for 45-60mins that often onset at sleep (peak in spring and fall) = clusters of HA for 8-12 weeks = remission for 12-18 mos
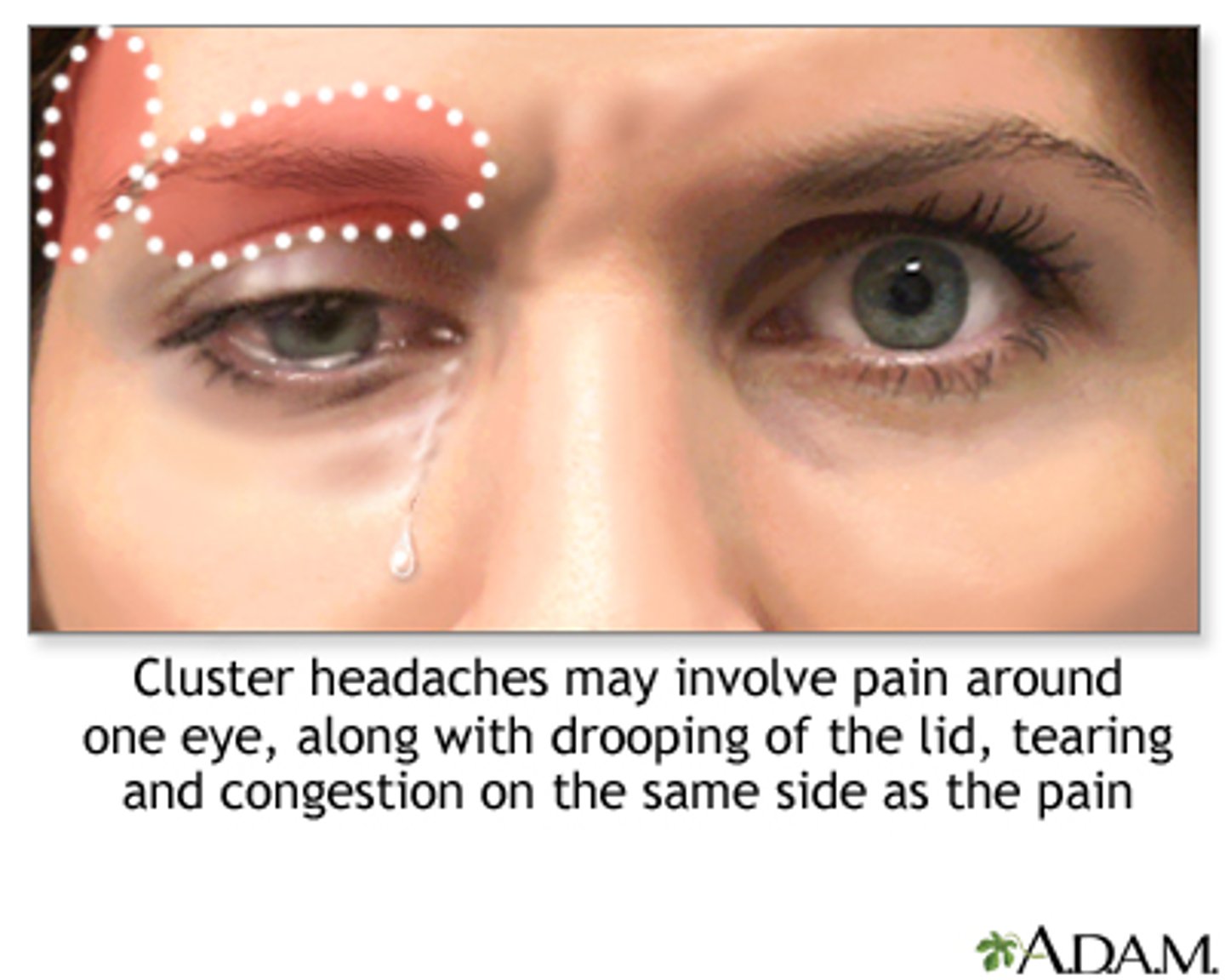
Aside from the severe retro-orbital or temporal pain, what are some other symptoms in cluster HA?
trigeminal ANS symptoms:
lacrimation
rhinorrhea
ptosis
pupil constriction
facial flushing
conj injection

What demographics are most often affected by cluster HA?
males almost exclusively
age 20-30
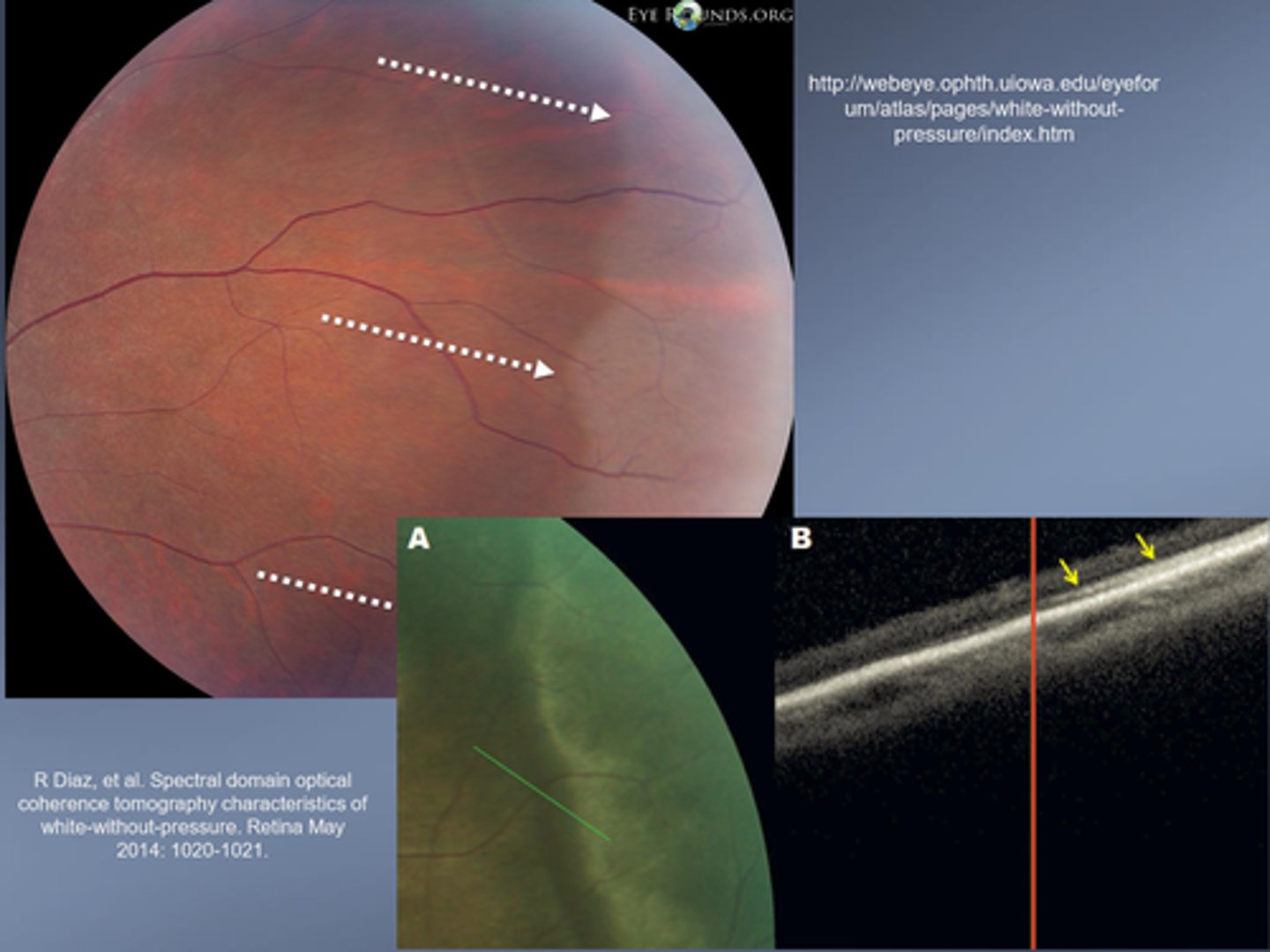
What typically causes WWOP?
hyper-reflectance of ellipsoid portion of PR inner segments
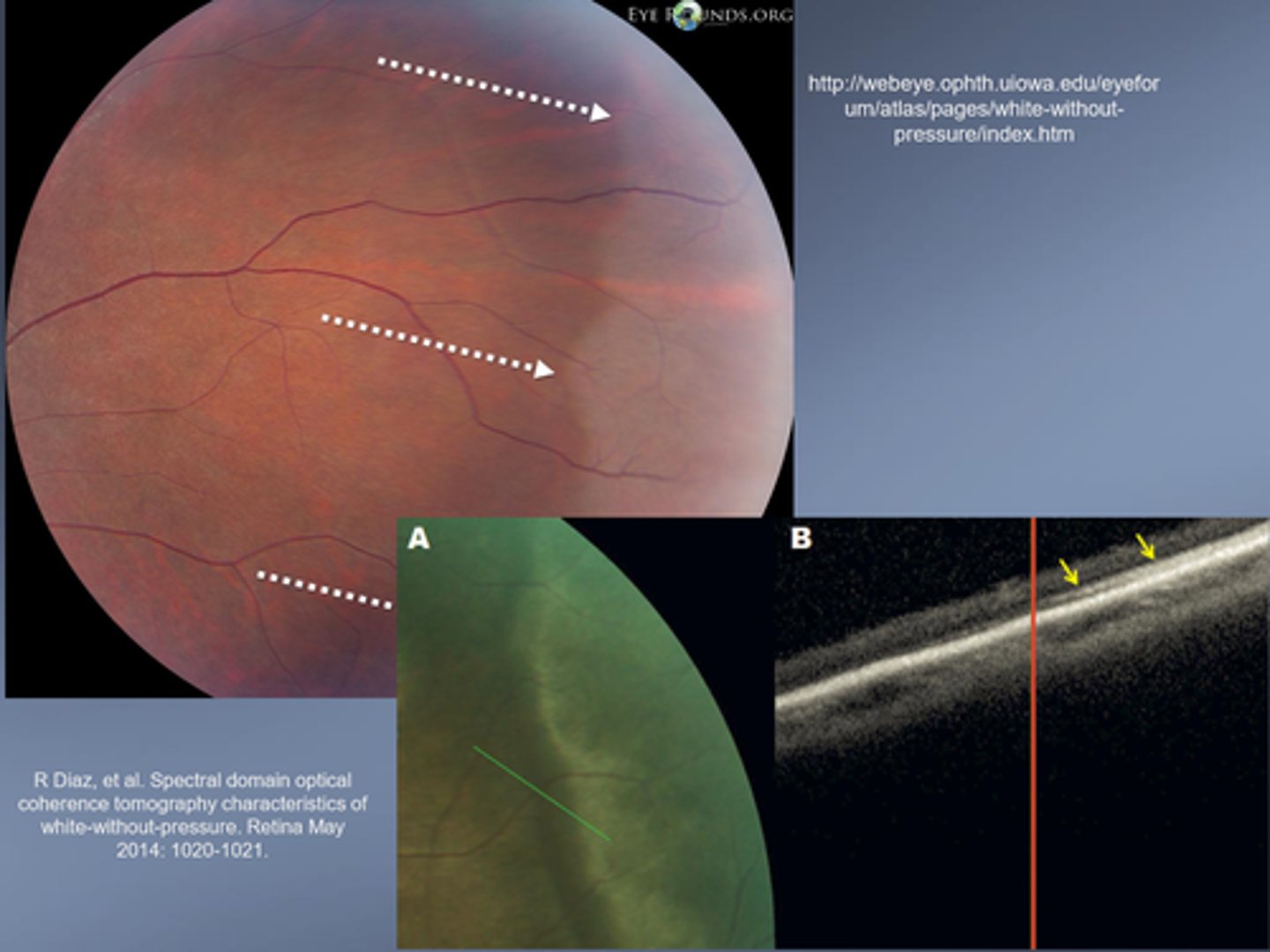
What is the tx for WWOP?
prophylactic photocoagulation possible d/t small association with retinal tear
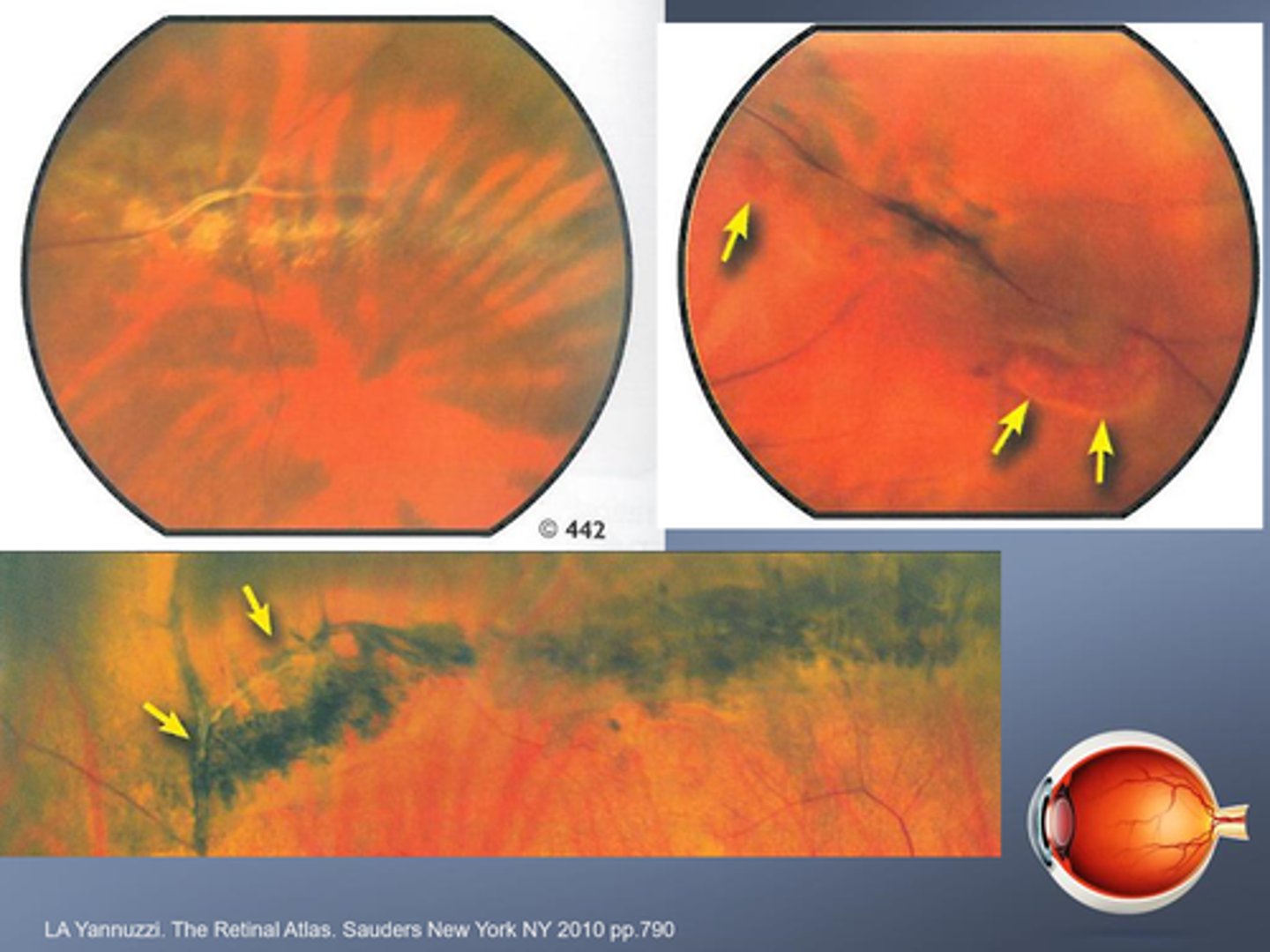
What is lattice degeneration?
inner retinal layer thinning with...
abnormal pigmentation
RPE hyperplasia
attenuated/sheathed BV
strong vitreal adhesion at edge = increased risk of tears/holes
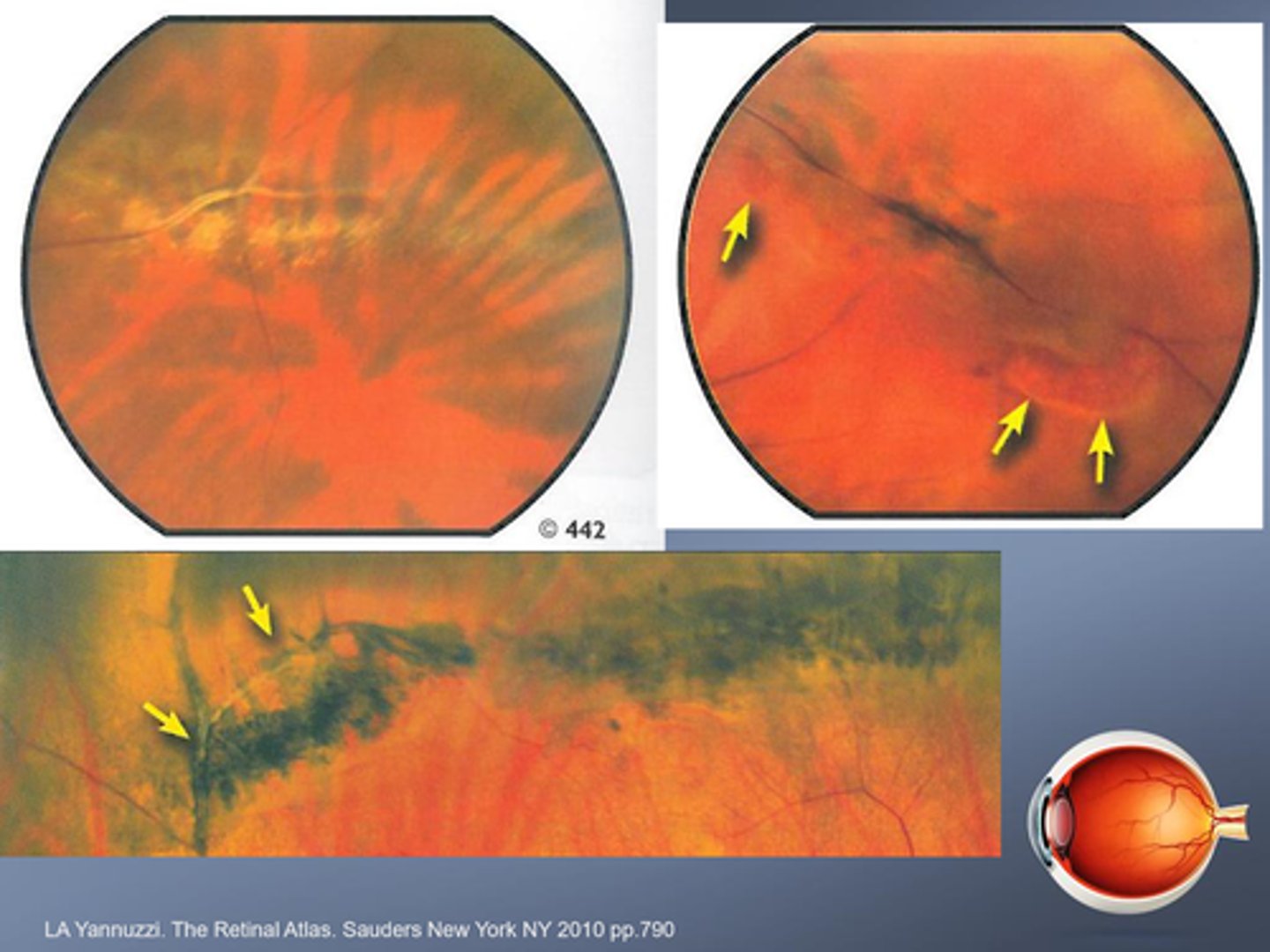
Present in 8% of the population, who is more likely to get lattice degeneration?
myopes esp moderate to high myopia
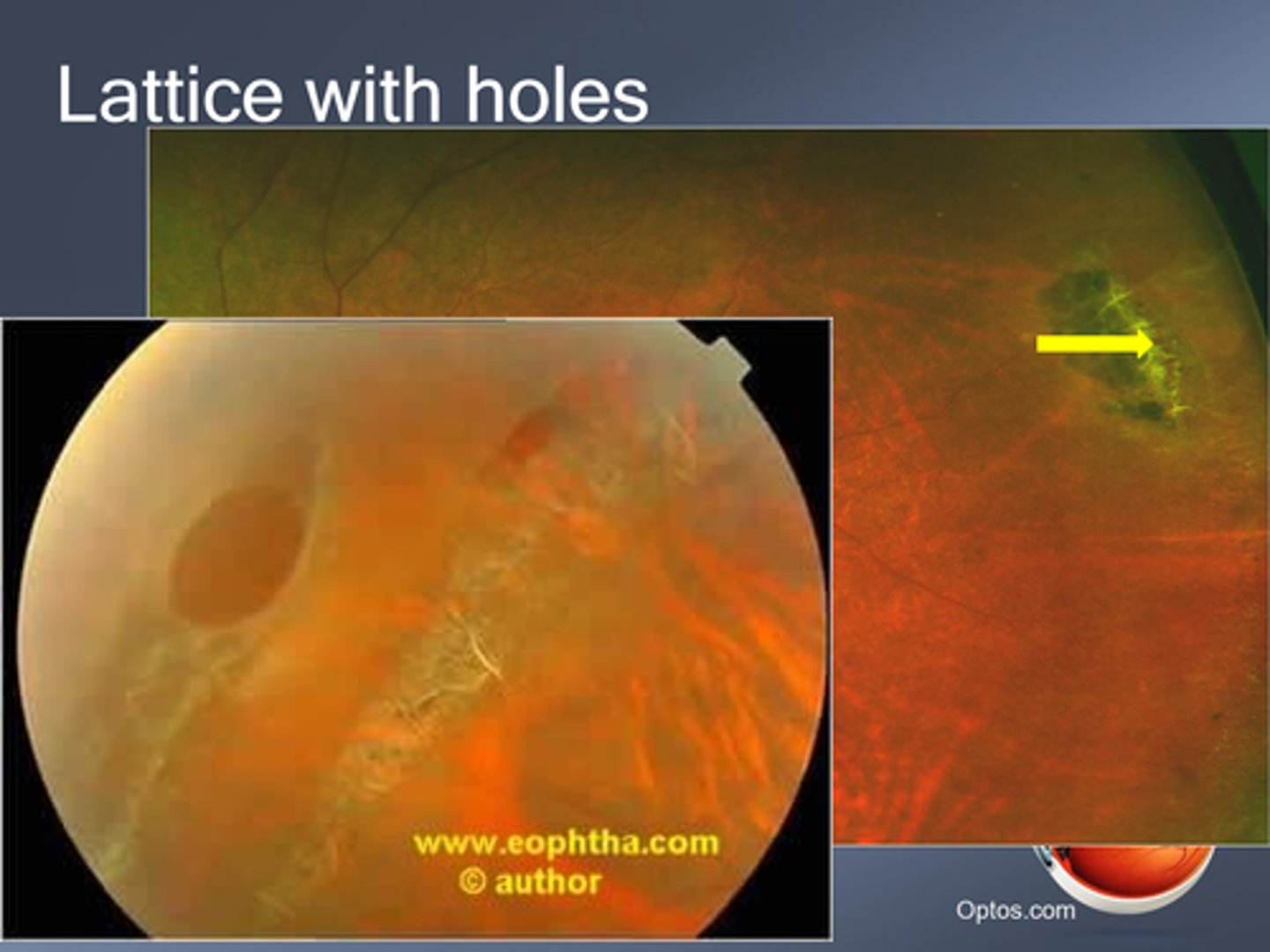
What is the tx for lattice degeneration?
monitor for retinal tears, RD
prophylactic laser
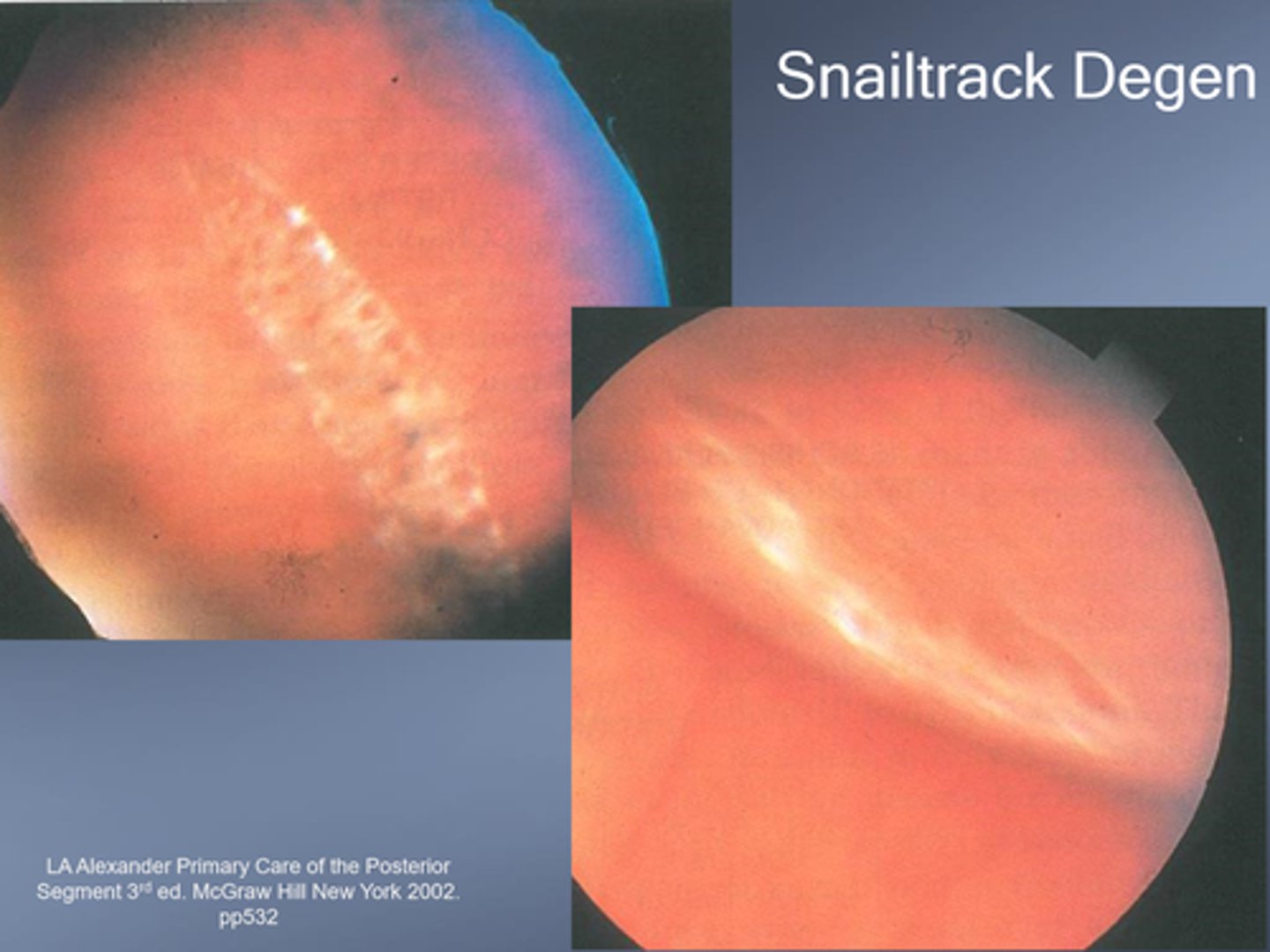
What is snailtrack degeneration?
similar to lattice, but different appearance d/t microglial cells containing lipoprotein
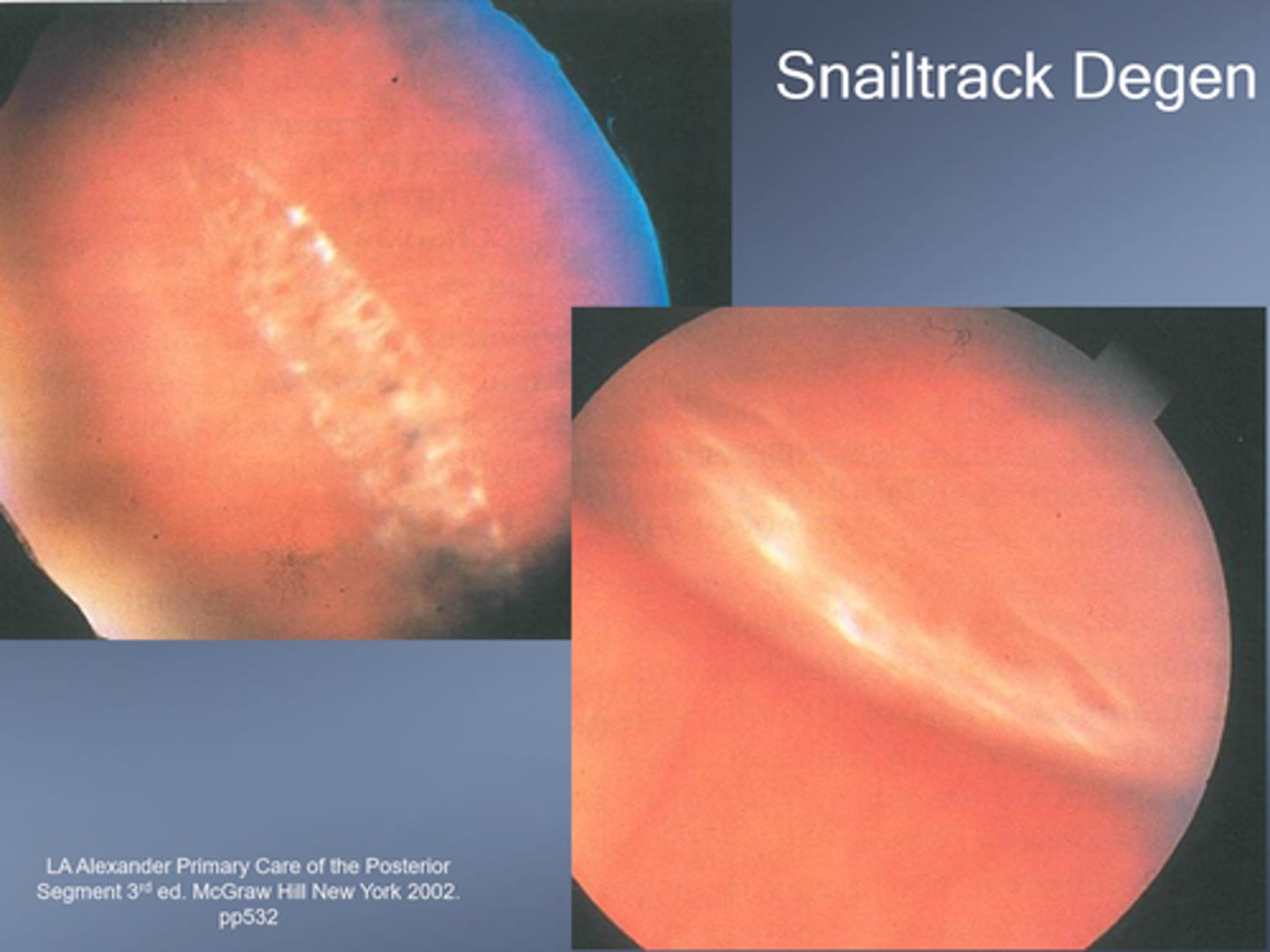
Is snailtrack degeneration more or less likely to have strong vitreous traction at the edge (compared to lattice)?
less likely
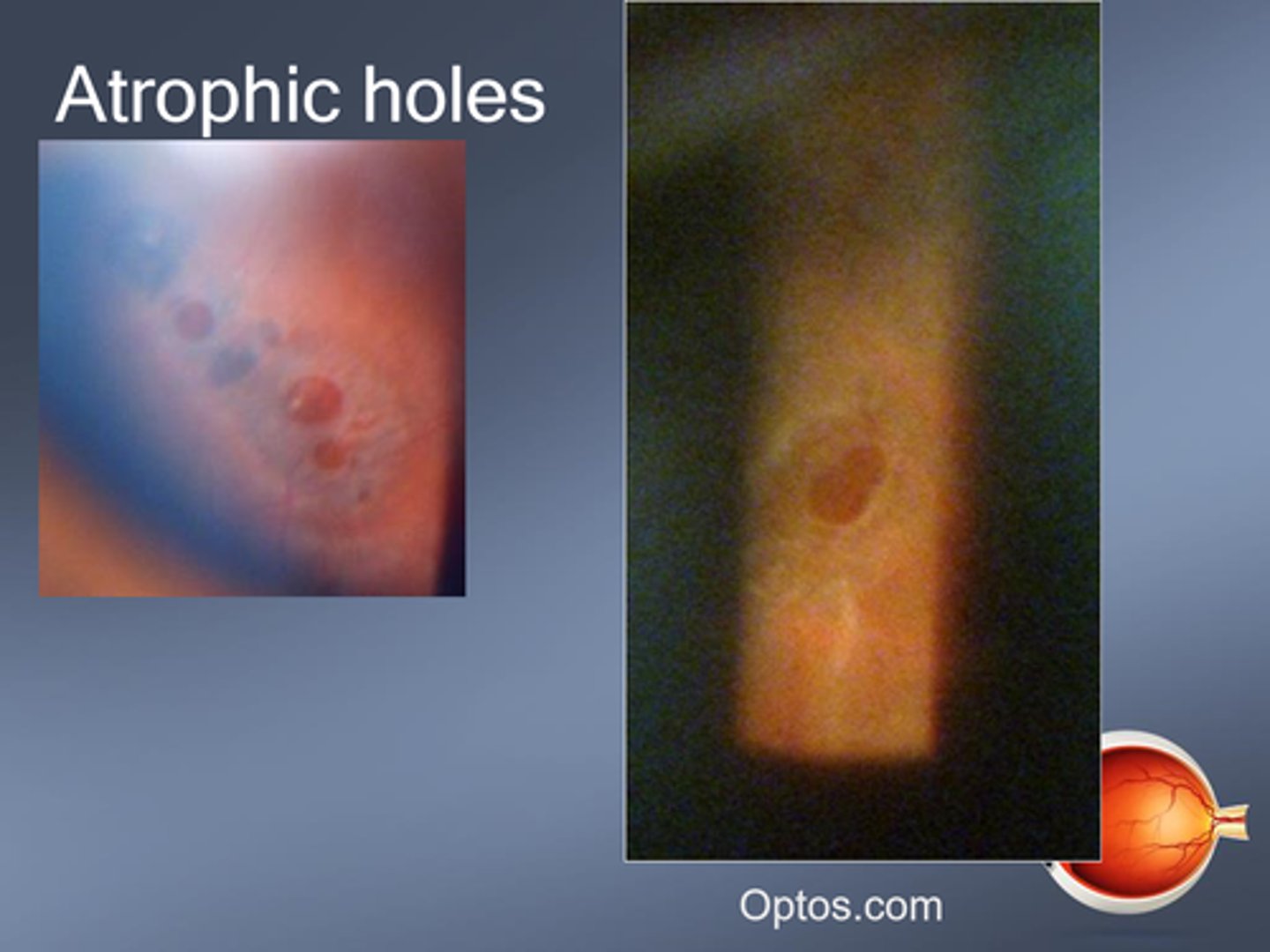
What are atrophic retinal holes?
progressive retinal thinning causing a break in the retina = liquified vitreous may enter = surrounding fluid cuff = RD
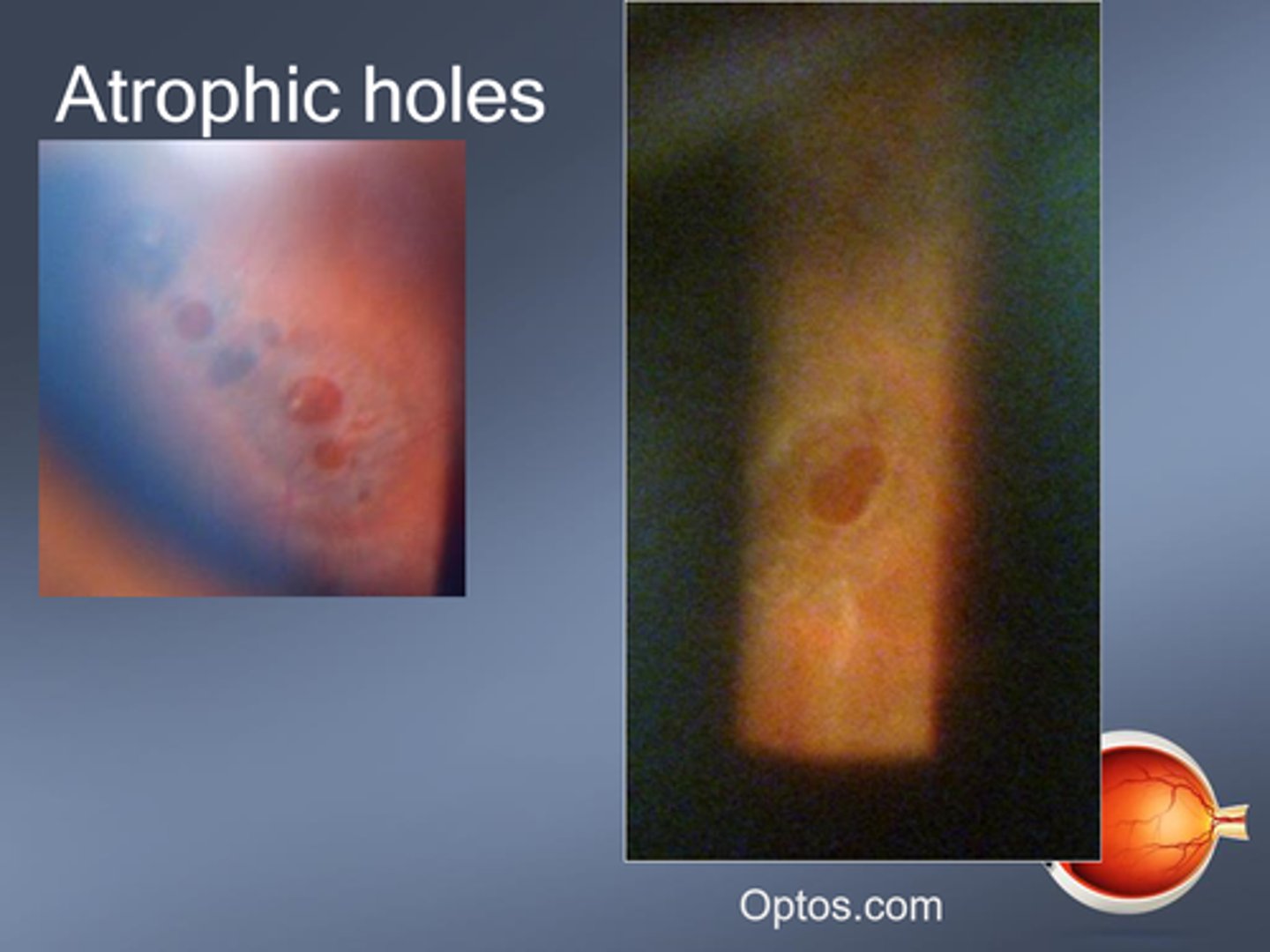
What indicates that an atrophic retinal hole has been present for 3+ months and is stable?
pigment around hole = reactive RPE hyperplasia
What is an operculated retinal hole?
vitreoretinal traction pulls an operculum of retina that will overly the retinal hole
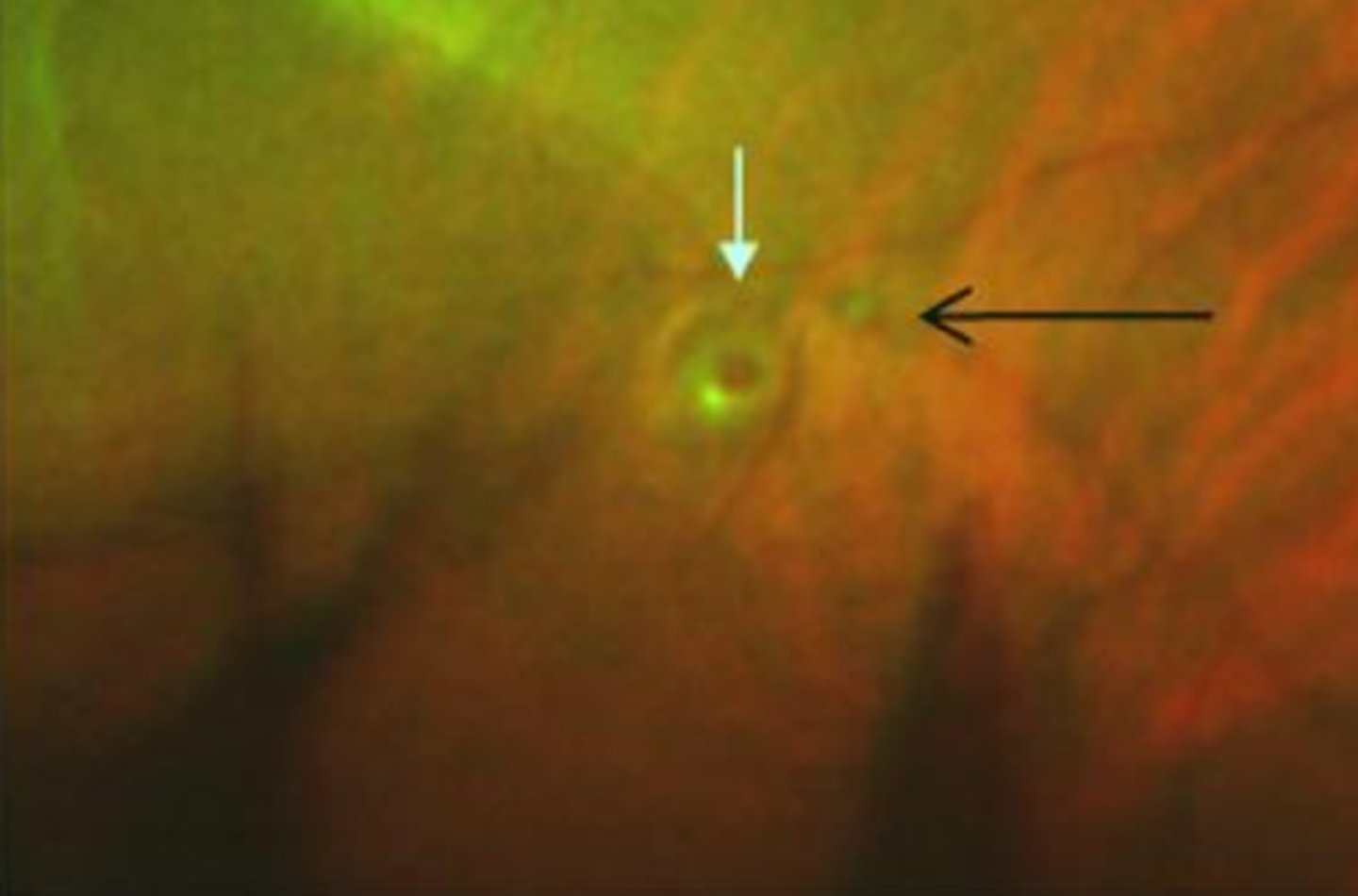
What is the difference between intrabasal vs juxtabasal operculated retinla holes?
intrabasal = within vit base = held down better
juxtabasal = next to vit base = greater risk of RD
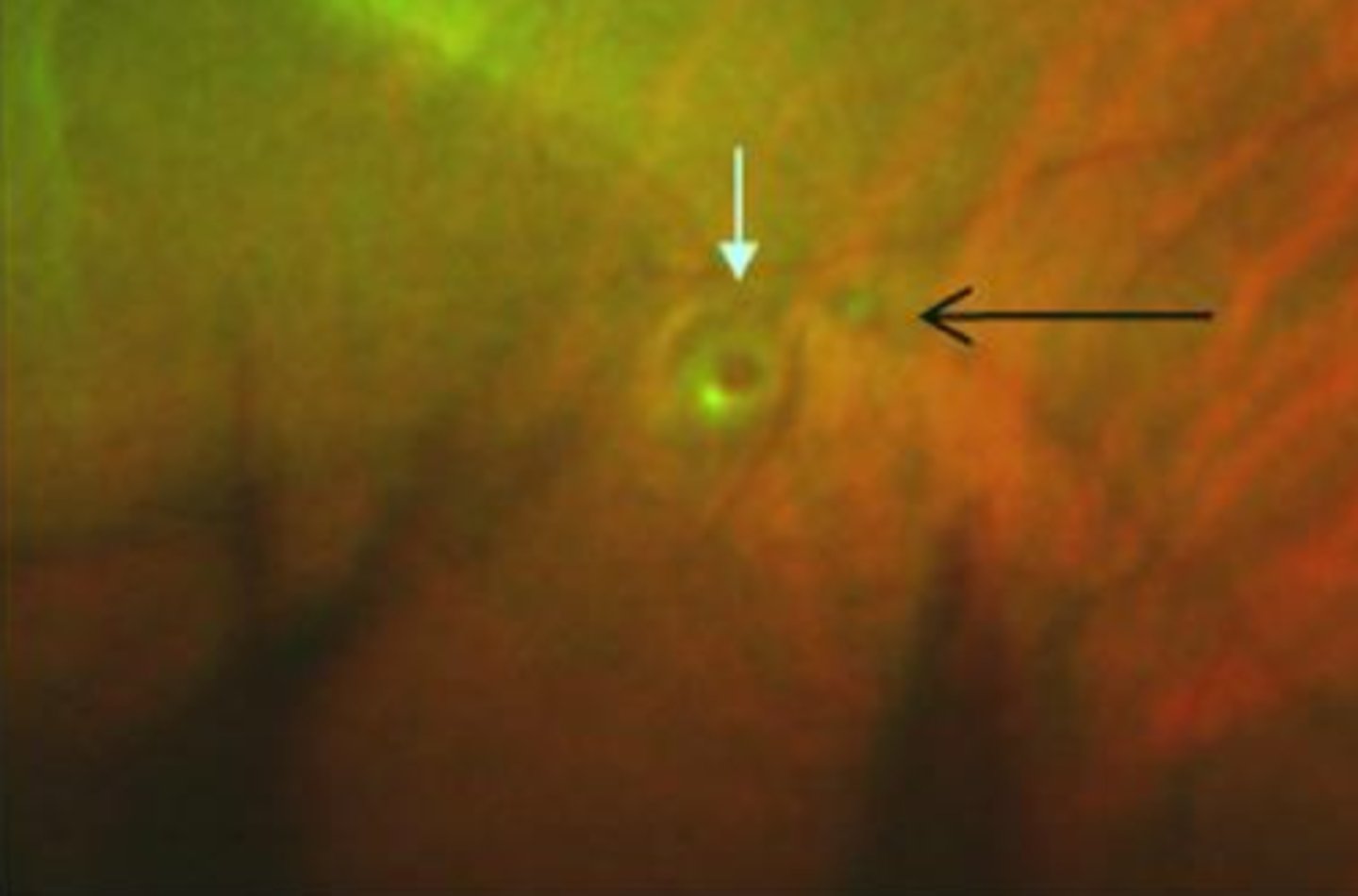
What is the tx for operculated retinal holes?
monitor if <1DD fluid cuff
refer for photocoagulation if >2DD fluid cuff, symptomatic, aphakic, Hx of RD
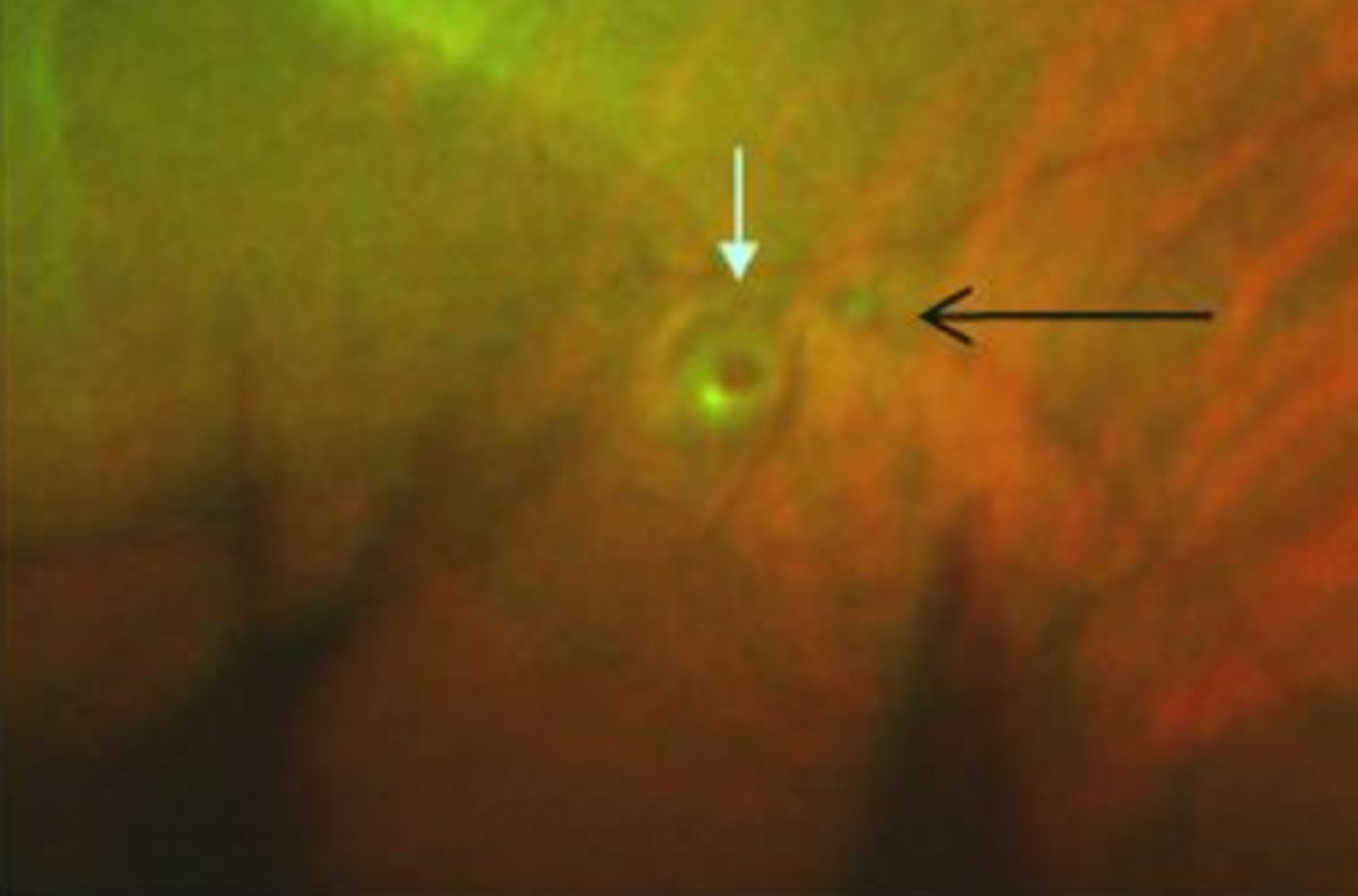
What is retinoschisis?
splitting of internal layers of sensory retina, often bilateral and IT
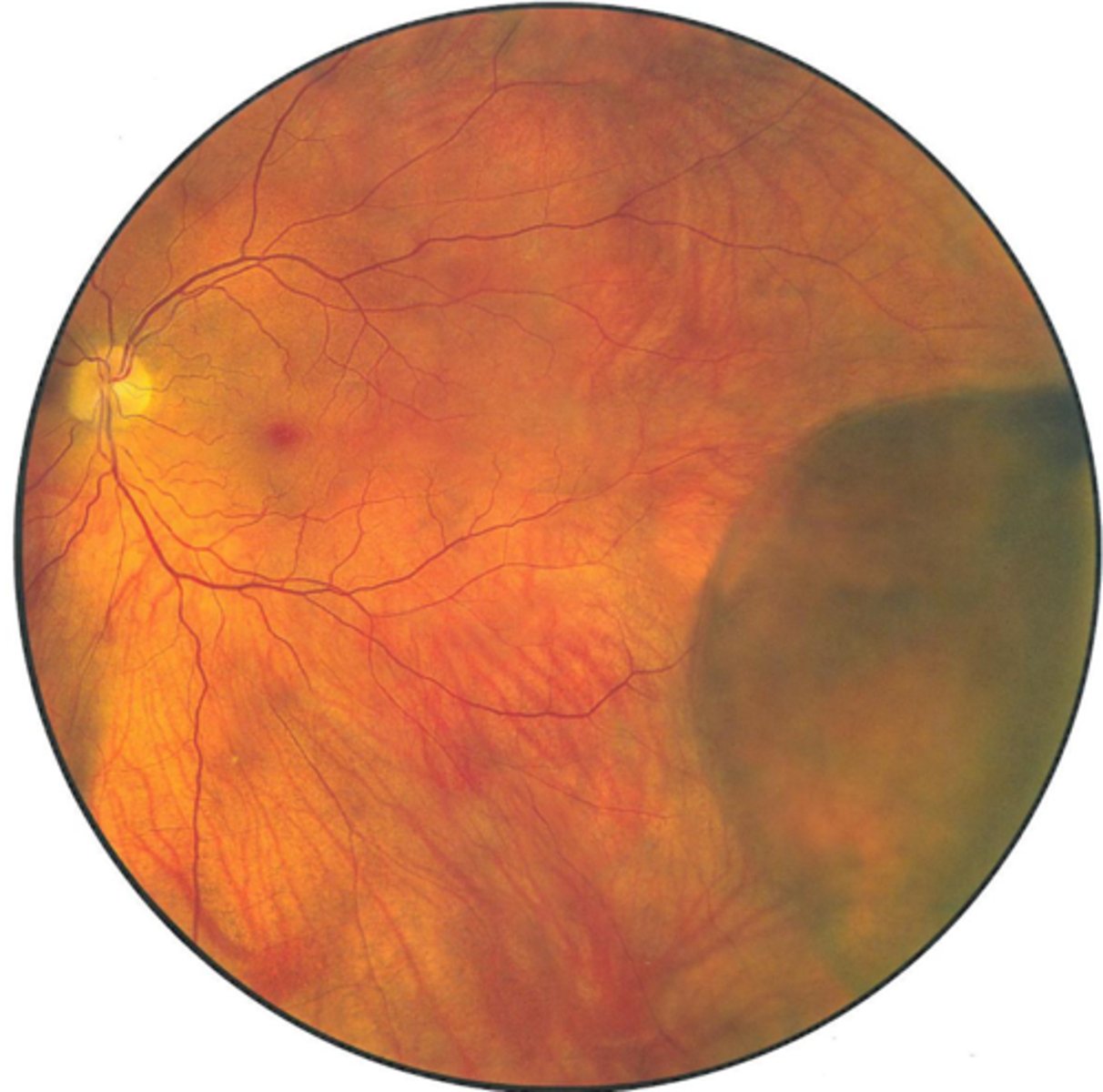
What is the difference between flat vs bullous retinoschisis?
flat = split occurs at OPL
bullous = split occurs anterior to OPL (thin inner wall)
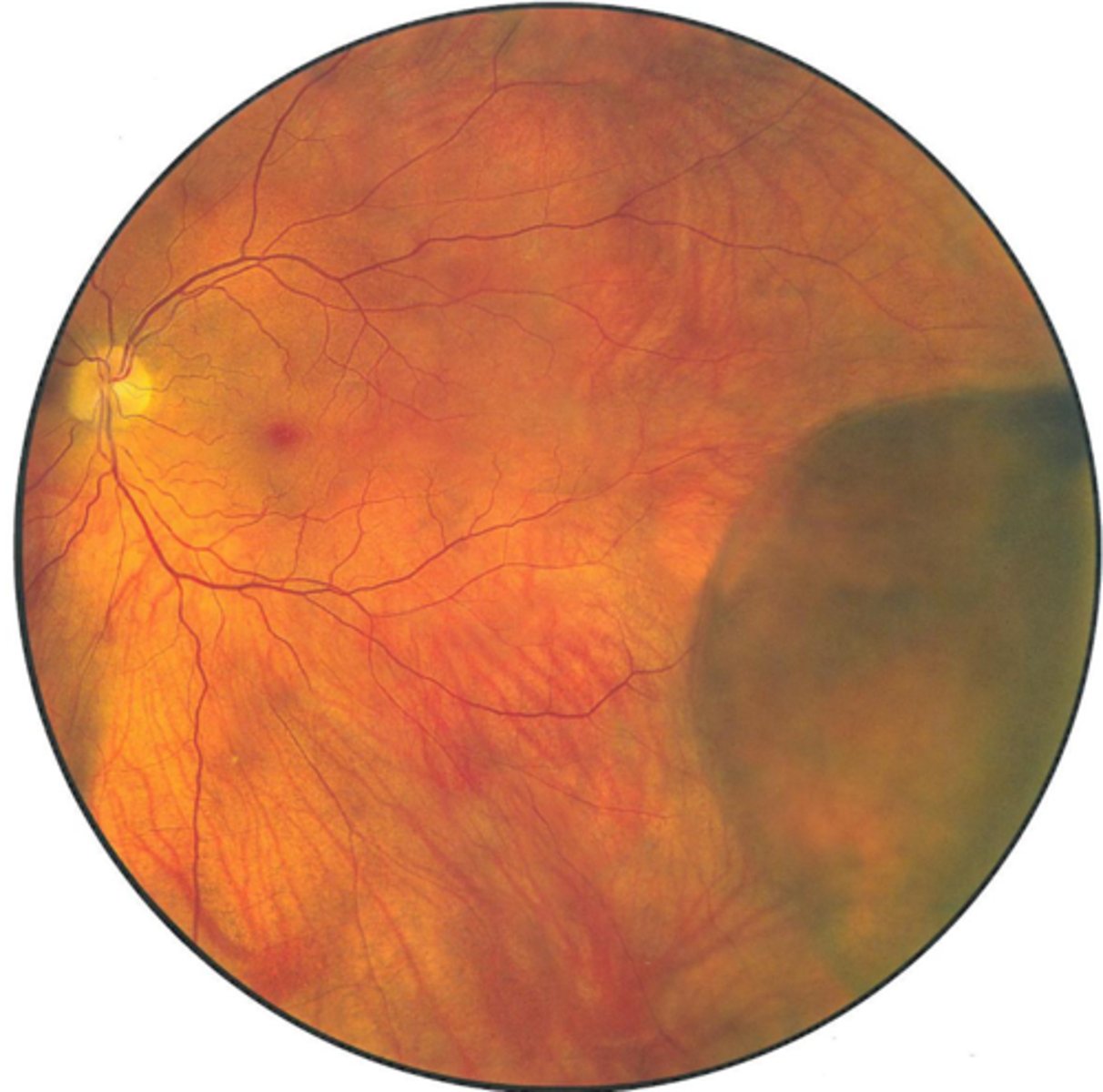
How can we differentiate retinoschisis from RD? 3 ways.
schisis does NOT move with eye movements
schisis has true retina colouration (not white)
schisis CAN see choroid details beneath
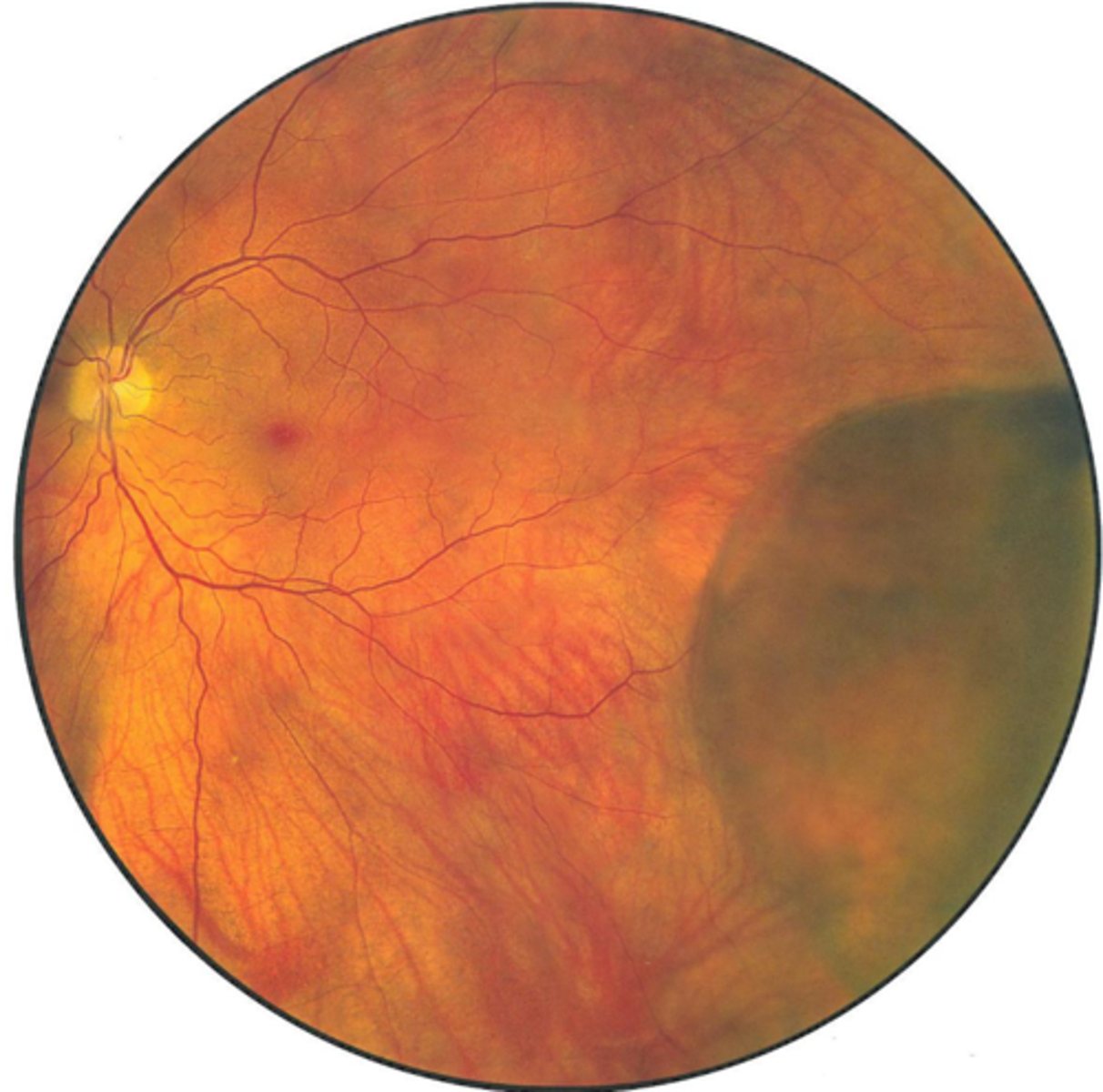
What is the tx for retinoschisis?
monitor
refer for photocoagulation if holes
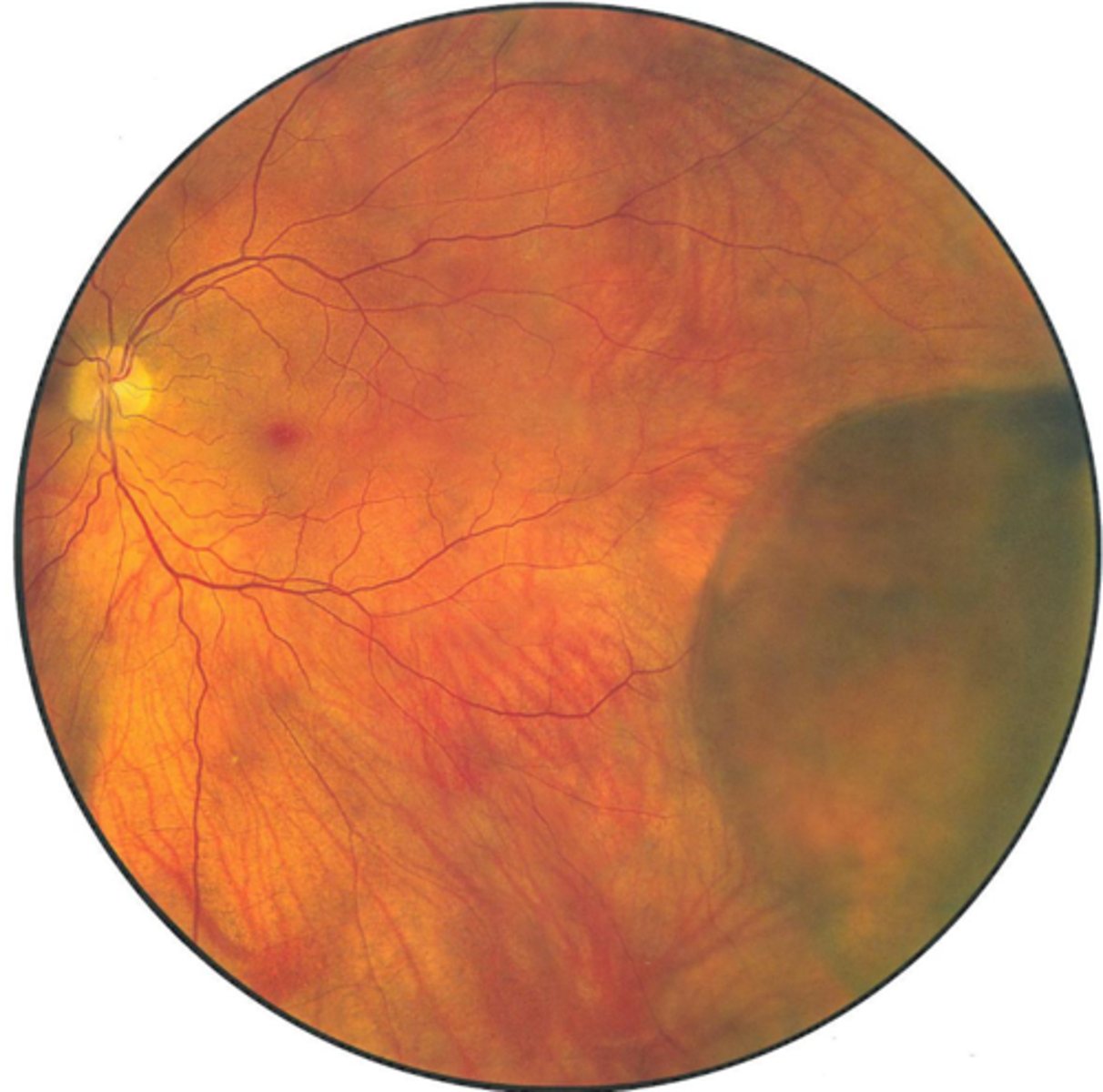
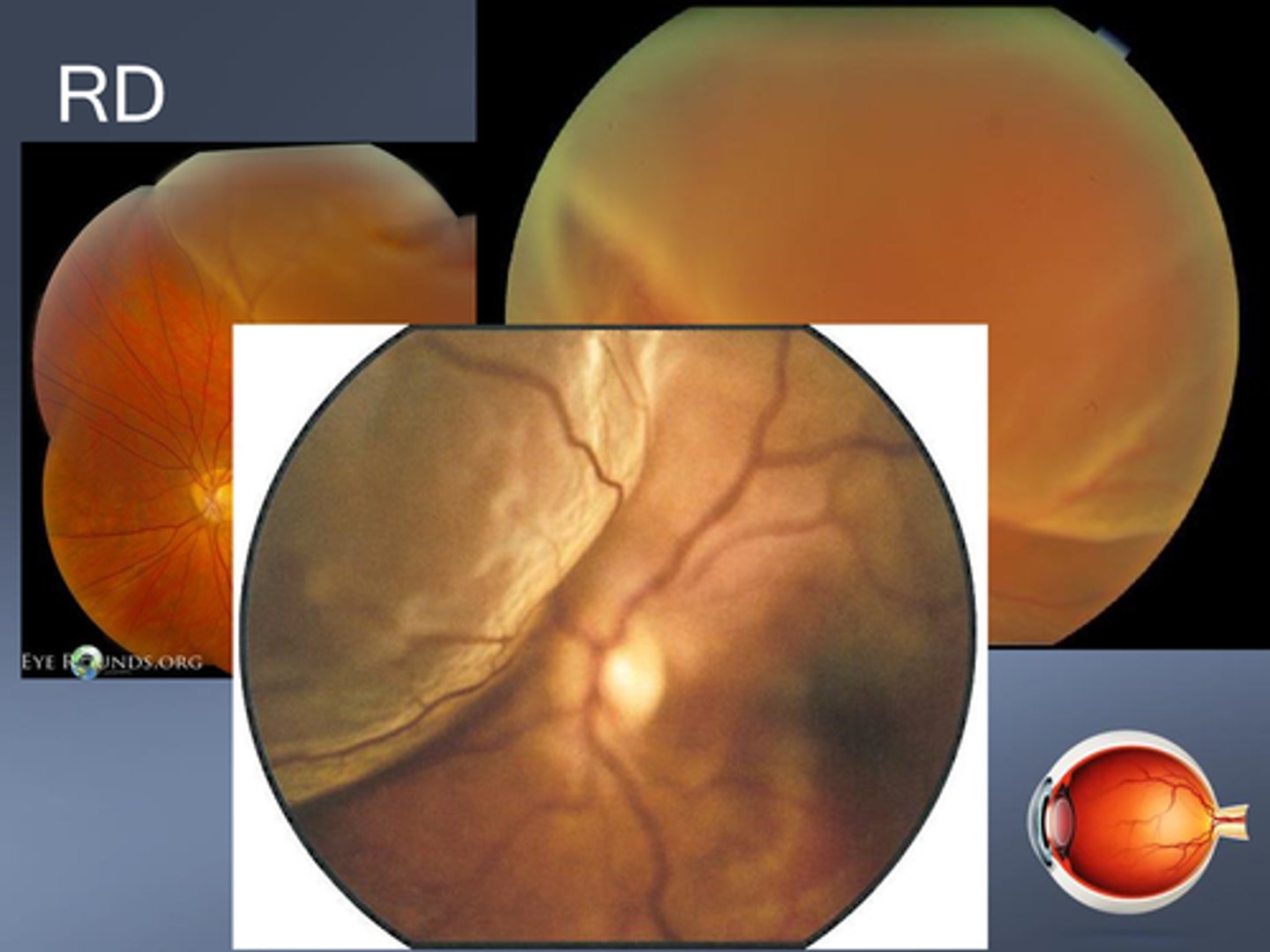
What are some signs of RD?
F/F
(+) tobacco dust sign
APD if significant
reduced IOP
iritis
retina looks opaque, folded/corrugated
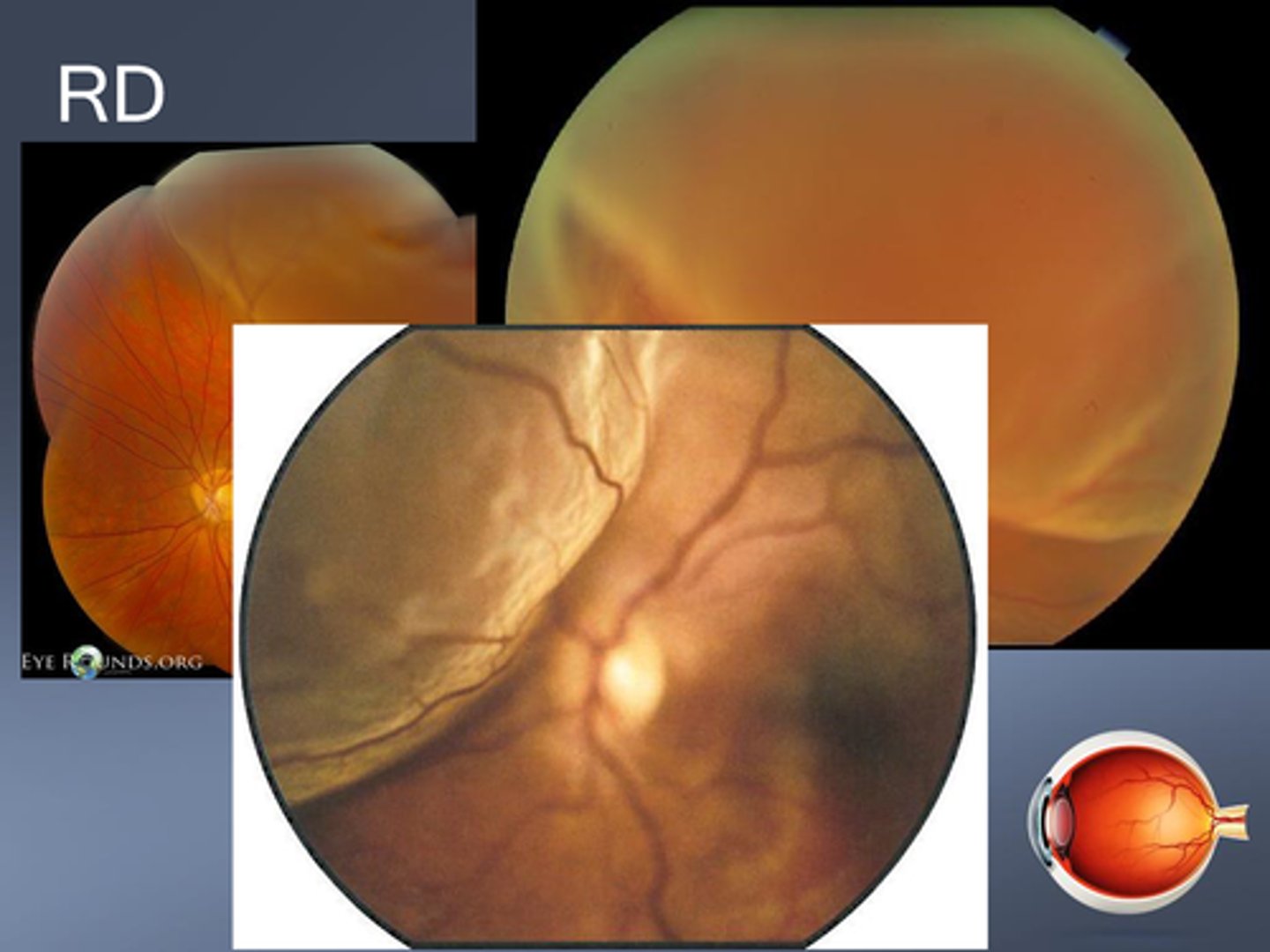
Is mac on or mac off RD a greater emergency?
mac on bc still can save macula, whereas mac off has worse prognosis
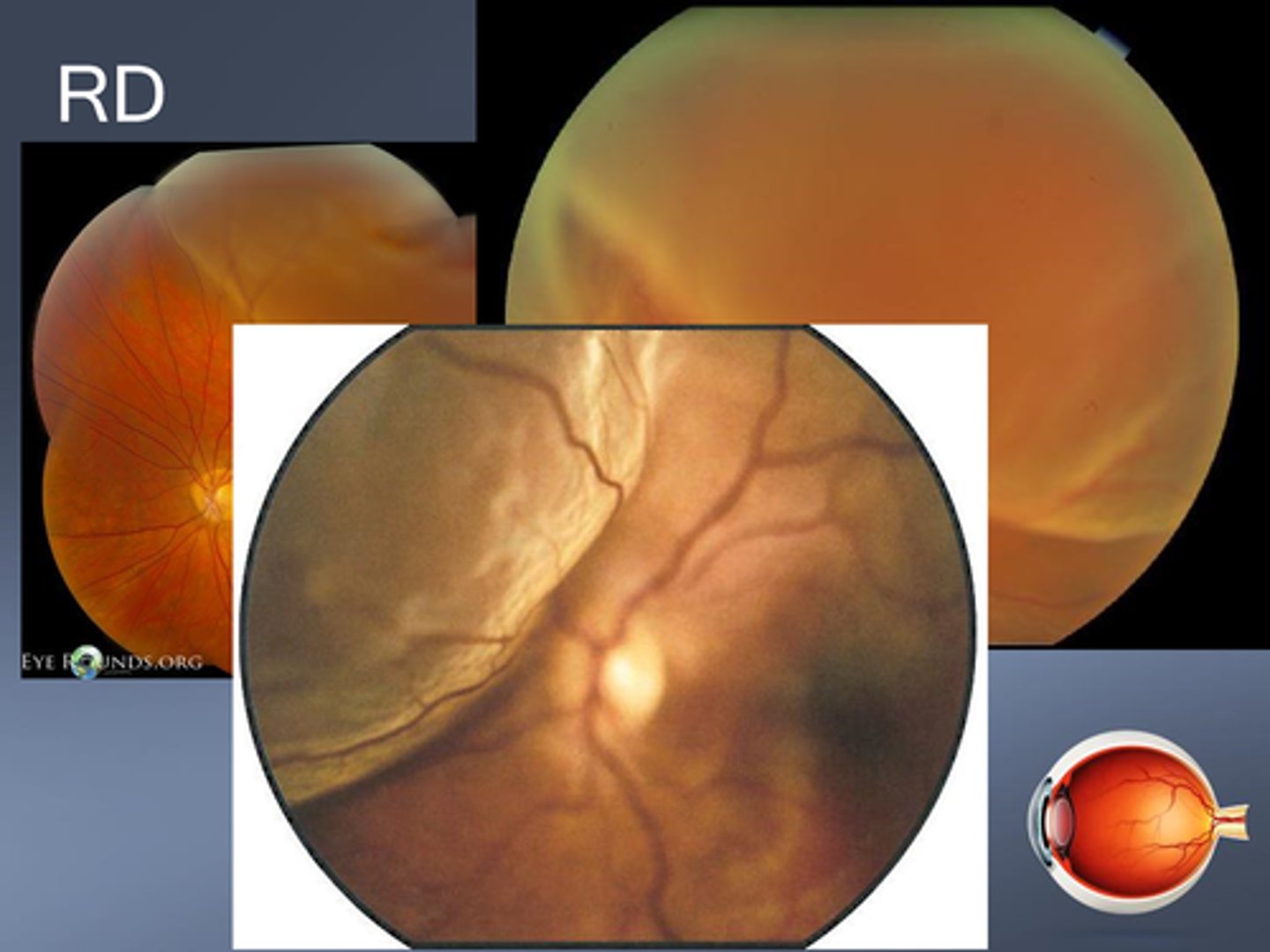
What are some signs that a RD has been present for a while?
pigment demarcation line
taut surface of RD
thinned retina
intraretinal cysts
intraretinal exudates