W2L1: Dopamine and Desire
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
dopamine: pathways
projects locally at basal forebrain: Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) and Substantial Nigra (SN)
dopamine: function
reward system, influences motivation, learning, movement, mood, satisfaction
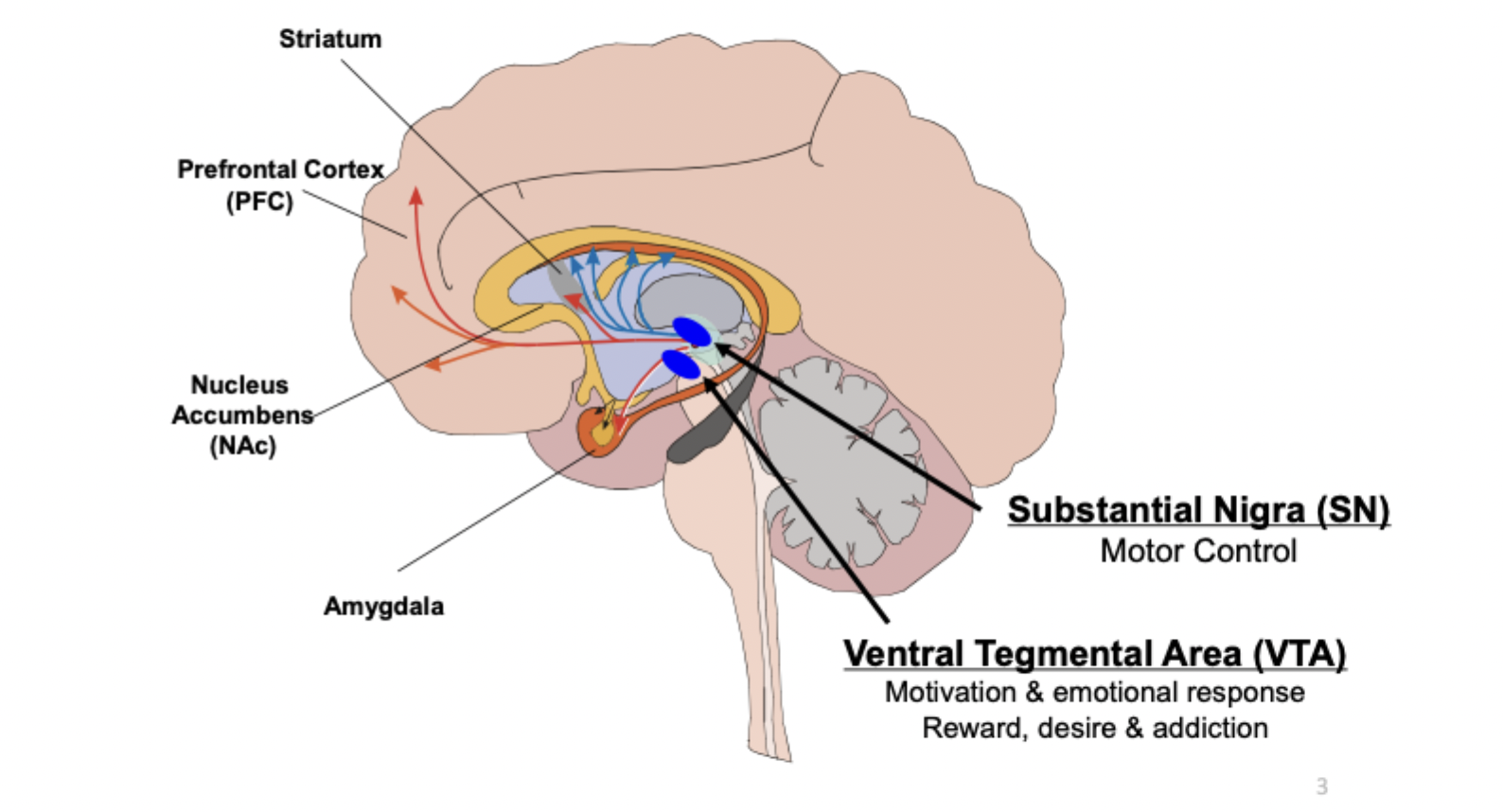
dopamine: pathways: VTA
Ventral Tegmental Area responsible for motivation, emotional response, reward, desire, addiction
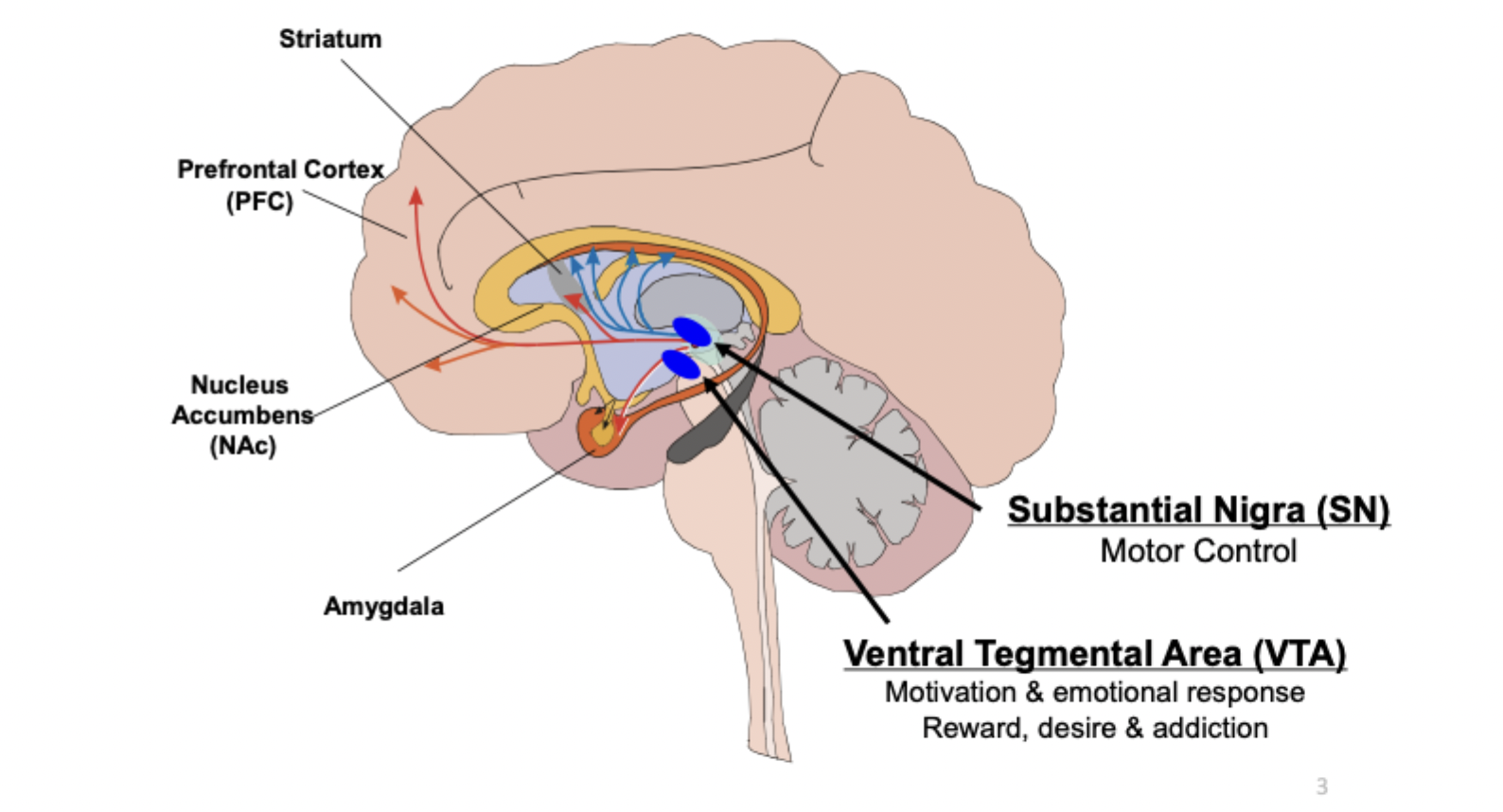
dopamine: pathways: substantial nigra
responsible for motor control
dopamine: synthesis
get dopamine from tyrosine, amino acid converted into L-DOPA and then converted to dopamine in brains (one step away from noradrenaline)
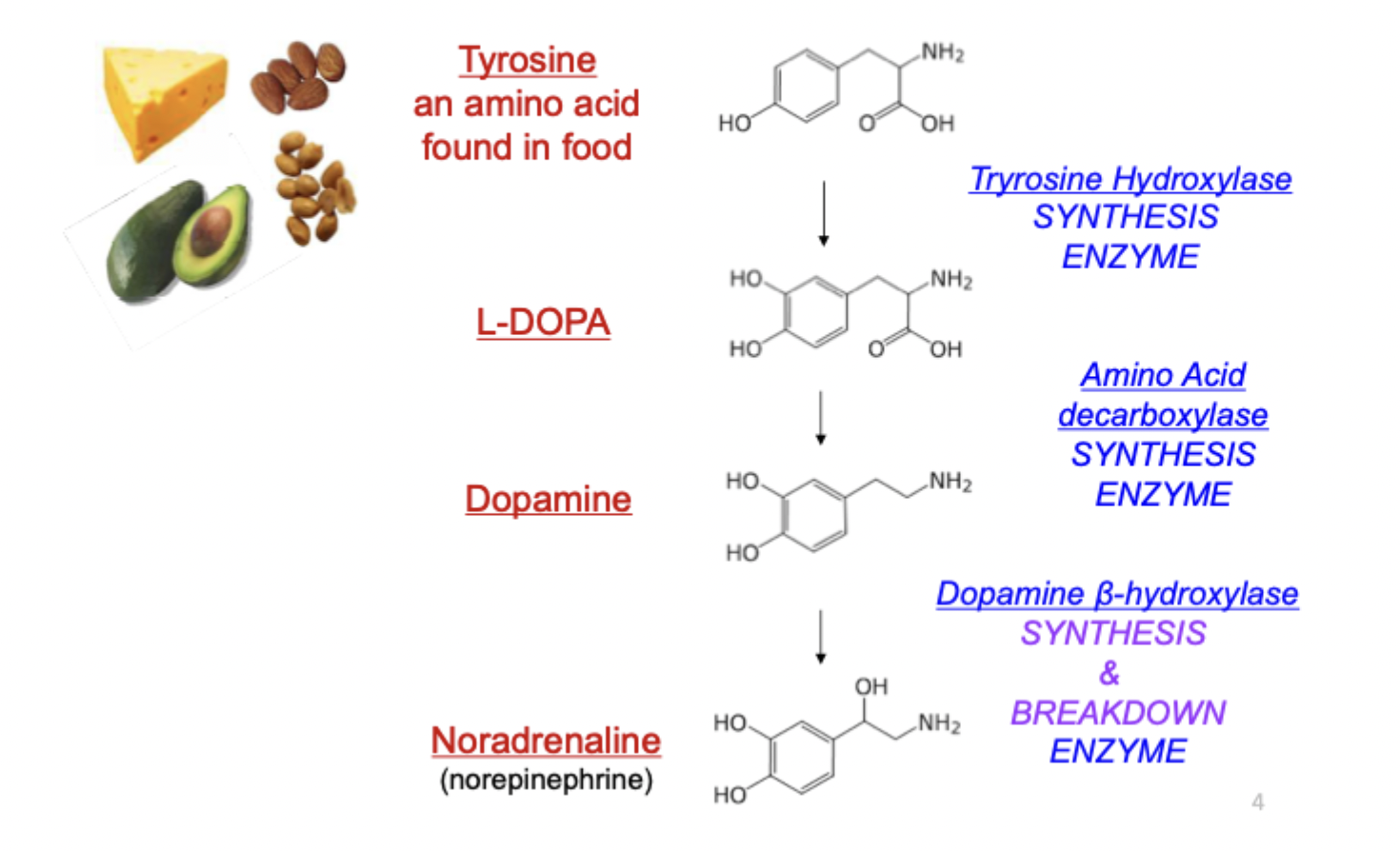
dopamine: tyrosine
amino acid found in food (cheese, nuts, avocados)
dopamine: synthesis: L-DOPA
can boost dopamine by giving people this drug (often given to people with Parkinson’s disease)
dopamine: L-DOPA presctiprion: Parkinson’s
Upregulates natural L-DOPA so that in conjunction with enzymes end up producing more dopamine to compensate for cell loss occurring in substantia niagra that happens during Parkinson's
Parkinson’s
caused by death of dopamine cells in substantia nigra
Parkinson’s: L-DOPA: don’t use
not recommended for people with psychosis because it can lead to neuroleptic sensitivity because of role dopamine plays in underpinning and driving psychotic symptoms
dopamine: reward prediction error: unexpected reward
dopamine neurone become more active and release burst of dopamine
dopamine: reward prediction error: repeatedly given reward after stimulus
reward will be expected and no dopamine will be released with reward but will now be released at time of stimulus presentation
dopamine: reward prediction error: if reward is expected but not provided
dopamine neurons will be suppressed
dopamine: value-modulated attentional capture task (VMAC)
designed to measure propensity to learned reward-related cues at expense of adaptive functioning/goals
dopamine: value-modulated attentional capture task (VMAC): findings
the more points given to a task the worse the performance because attention is captured by high value reward cue rather than the task itself
dopamine: cognitive control and reward
dopamine codes both goal reward and effortful costs and aversive feeling of cognitive effort reflects opportunity cost
dopamine: cognitive effort and reward
task persistence is justifiable only while progress outpaces accruing costs
gambling
brains are bad at encoding real value of things - easier to encode positive unexpected high wins (not able to balance cost-benefit ration of what is capitalised)
drug addiction
chronic relapsing disorder which consists of a compulsive pattern of drug-seeking and drug-taking behaviour
drug addiction: crux
about reward-anticipation - huge rush when anticipating/ craving drugs (even when performing act of taking becomes less rewarding over time feeling of anticipation have power)
dopamine: drugs: cocaine
blocks reuptake of presynaptic neurotransmitter transmitter (excess dopamine in synaptic cleft which continues stimulating post-synaptic neuron)
dopamine: drugs: amphetamines (ice and speed)
reverses uptake transporter actively expelling dopamine and noradrenaline out of neuron which prevents dopamine uptake
dopamine: drugs: amphetamines: cell death
because neurotransmitters are being flushed out and prevented from reuptake (over excitation and toxic processes)
drugs: addictive nature
how quickly you receive a reward after any reward cues (when reward is much later than cues it isn’t as addictive)
dopamine: drugs: levels released
more dopamine released greater the high produced by drugs like cocaine and ice
drugs: addiction and free will: cognitive control
“top down” control is reduced by impaired function of prefrontal cortex (PFC) caused by excessive dopamine (can’t provide homeostatic control and are overwhelmed - bottom up excitation)