Bio 120 A&P Body Orientation
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Right Upper Quadrant
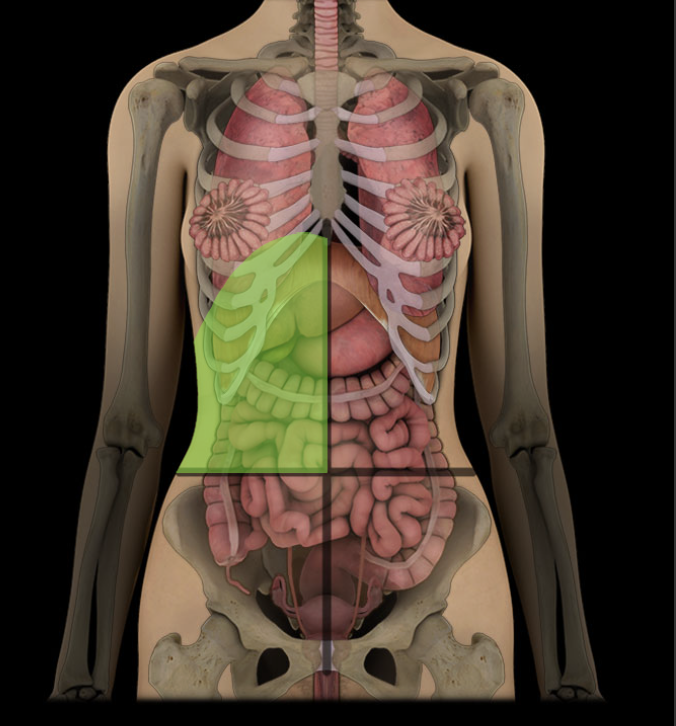
Contents include right kidney and suprarenal gland, gallbladder, and parts of liver, stomach, pancreas, and small and large intestines
Upper right lateral area of the abdominopelvic cavity
Sacral Region

Subdivision of the back
Includes sacrum and attached muscles
Sagittal Plane
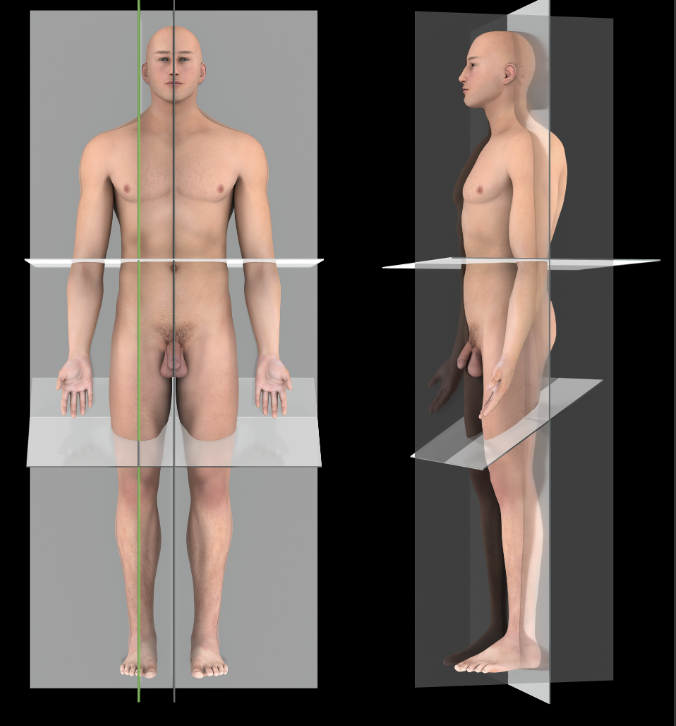
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body, dividing it into right and left portions
Skeletal System
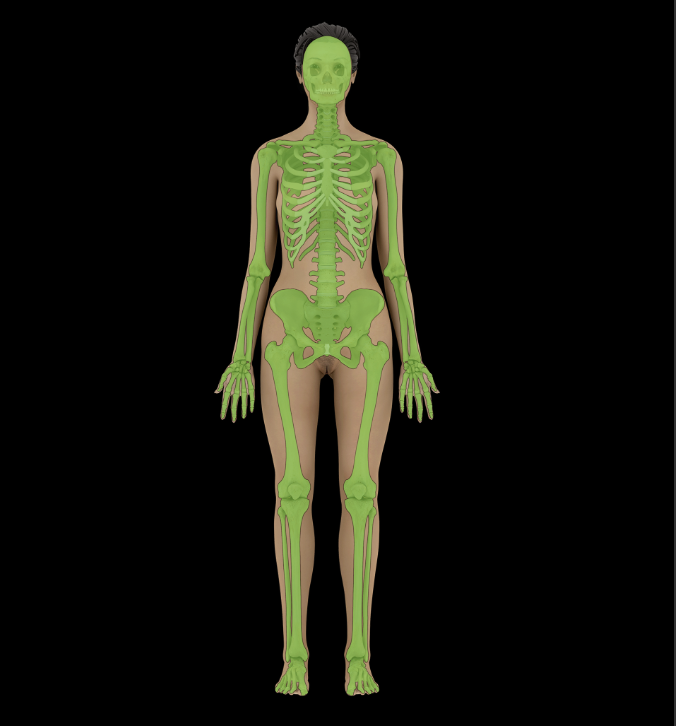
Provides site of attachment for muscles
Support for, and protection of body
Movement of body via joints
Hemopoiesis
Storage of calcium and phosphorusSupport for, and protection of body
Provides site of attachment for muscles
Movement of body via joints
Hemopoiesis
Storage of calcium and phosphorus
Abdominal region
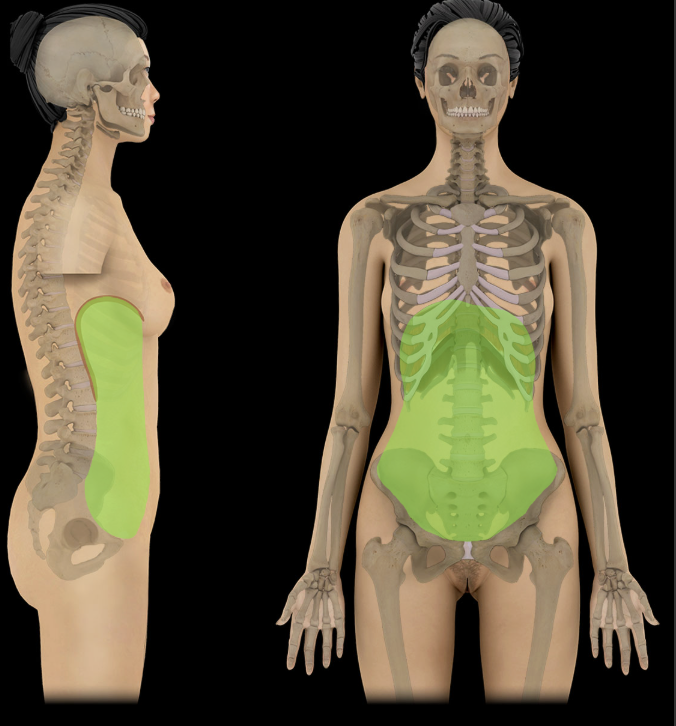
Bounded by abdominal walls, thoracic diaphragm (superior), and pelvic brim (inferior)
Major organs include: stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and ureters, suprarenal glands, aorta, inferior vena cava, and lumbar nerve plexus
Abdominopelvic cavity
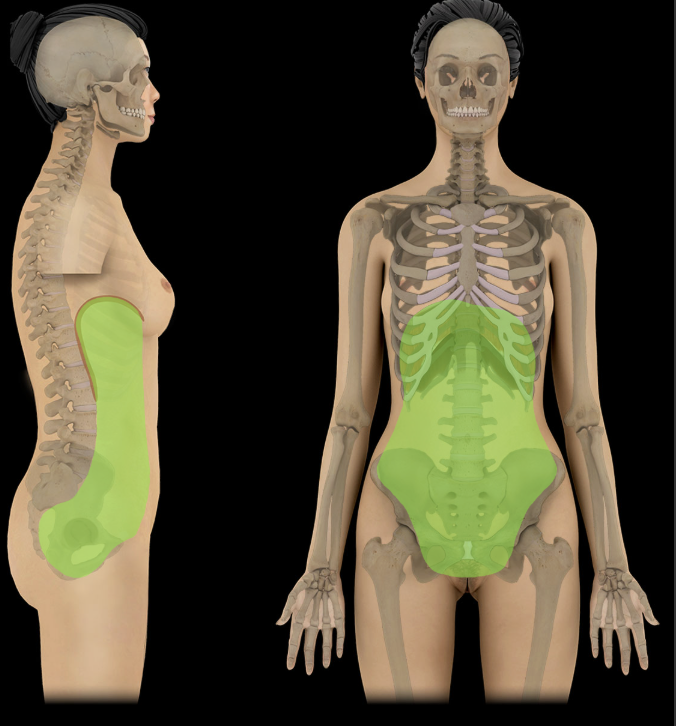
Continuous cavity formed by the abdominal and pelvic cavities
Major abdominal organs include: stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and ureters, suprarenal glands, aorta, inferior vena cava, and lumbar nerve plexus
Major pelvic organs include: urinary bladder, loops of small intestine, inferior part of sigmoid colon, rectum, and reproductive organs (ovaries, uterus, vagina in female; prostate and seminal glands in male)
Anatomical Position
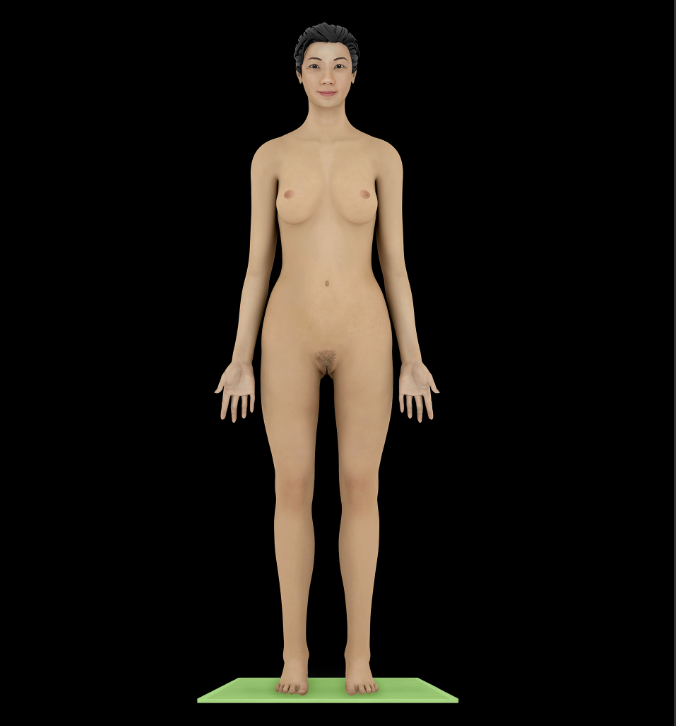

Reference position for anatomical description
An individual in anatomical position is standing erect with arms at sides, palms facing forward with fingers pointing downward, feet parallel to each other and flat on the floor, and eyes directed forward
Anterior
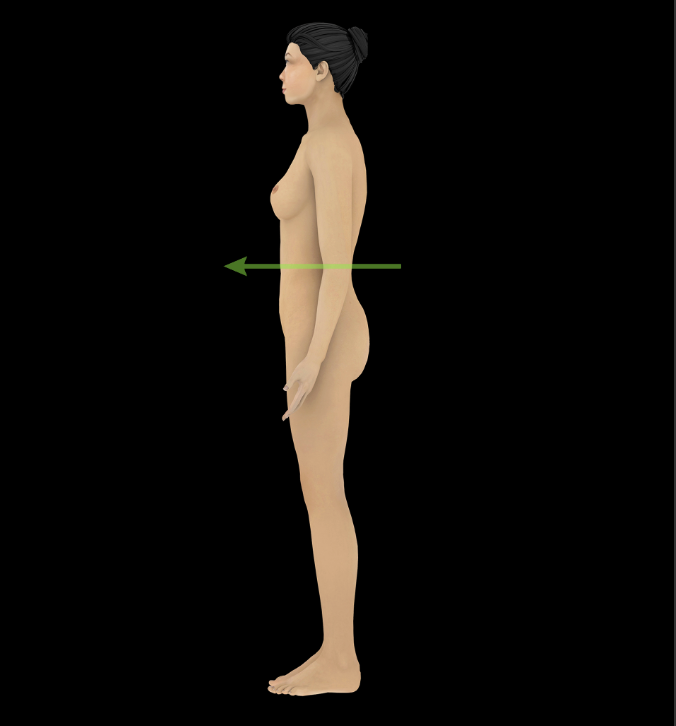
Toward the front of the body (e.g., the sternum is anterior to the heart)
Opposite of posterior
Cardiovascular system
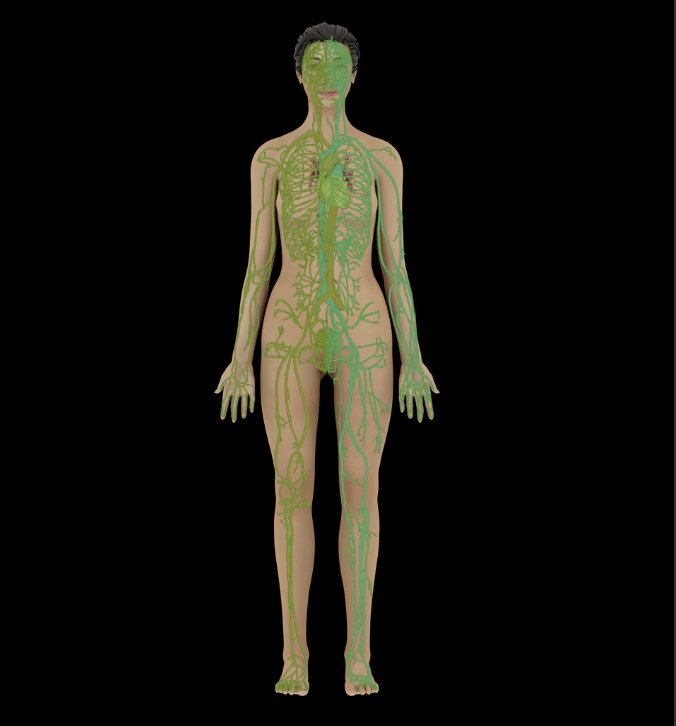
Two circulatory divisions: pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation
Heart moves blood through blood vessels
Blood and blood vessels distribute hormones, nutrients, and gases, and transport waste products
Pulmonary circulation: movement of blood between heart and lungs
Systemic circulation: movement of blood between heart and peripheral tissues
Coronal Plane
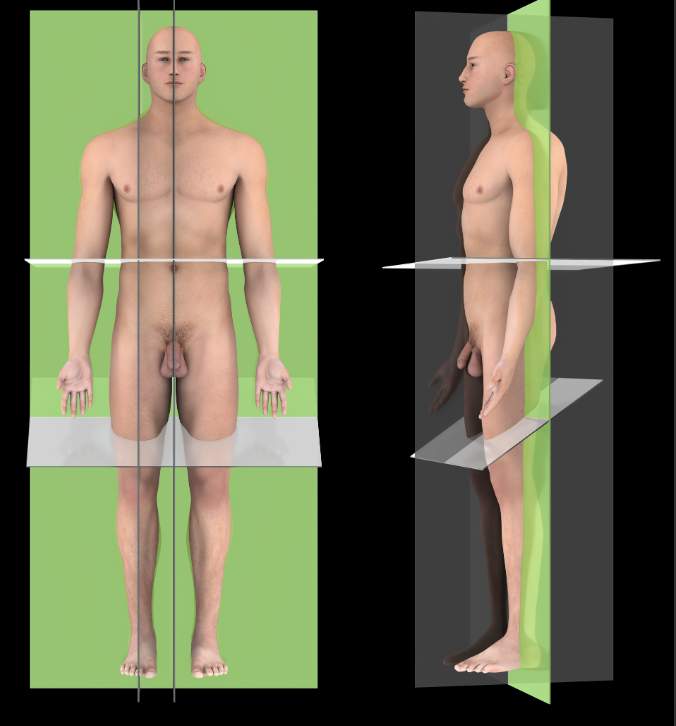
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior portions
Cranial Cavity
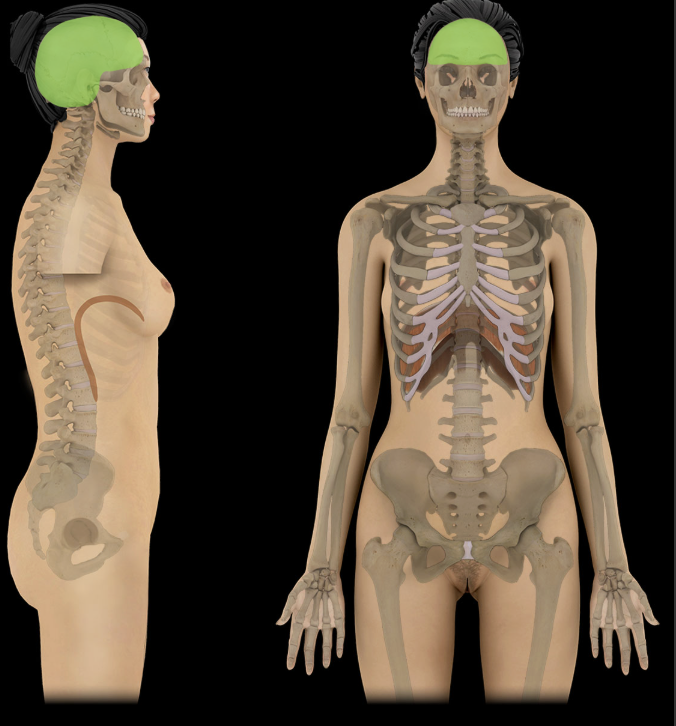
Space in skull that contains brain, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Formed by frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid bones, parietal, and temporal bones
Cubital Region
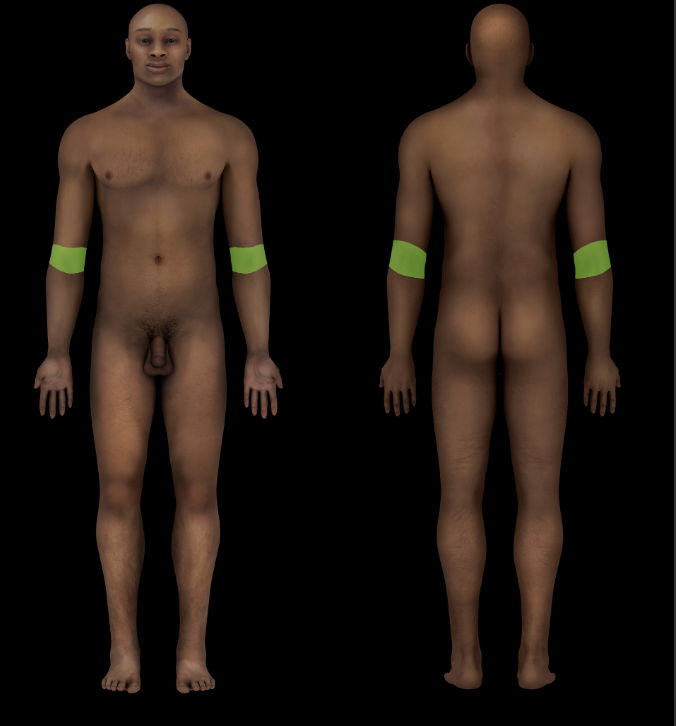
Subdivion of upper limb
Deep
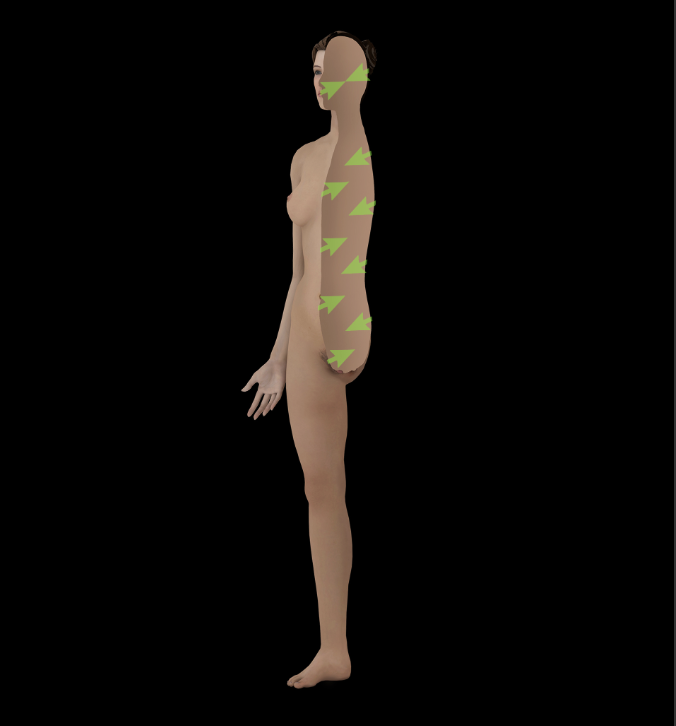
Away from the surface of the body or organ
Diaphragm
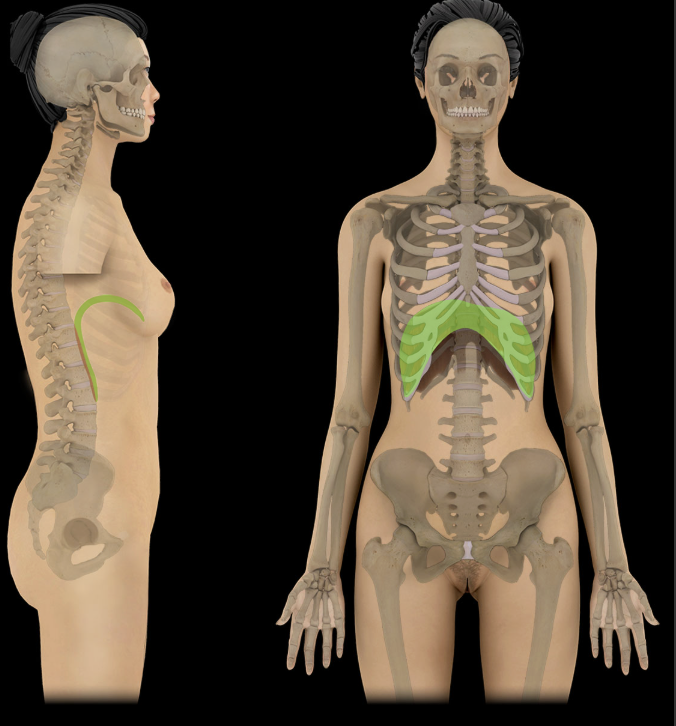
Dome of diaphragm flattens during inspiration
Contraction increases vertical dimension of thoracic cavity
Digestive system
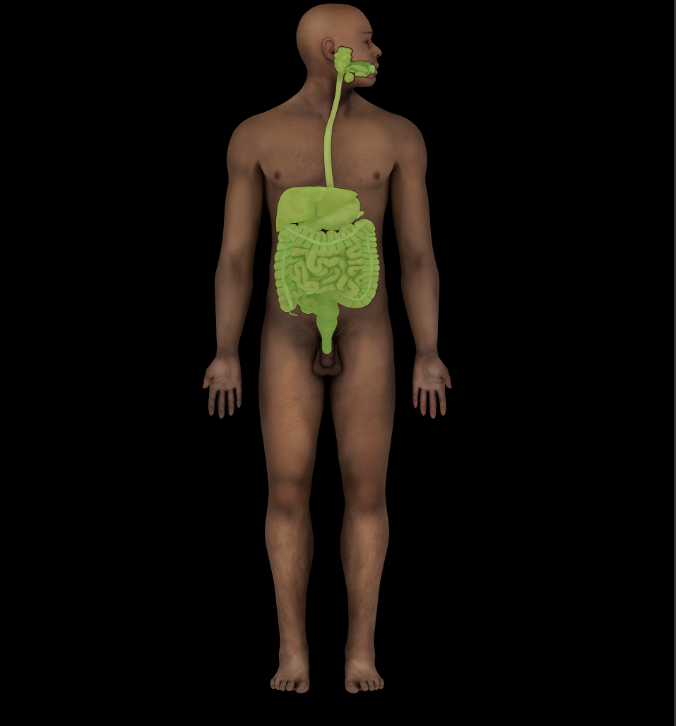
Muscular tube lined by epithelium
Gastrointestal (GI) tract: oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus. stomach, small intestine, and large intestine
Accessory digestive organs: teeth, tongue, salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
Distal
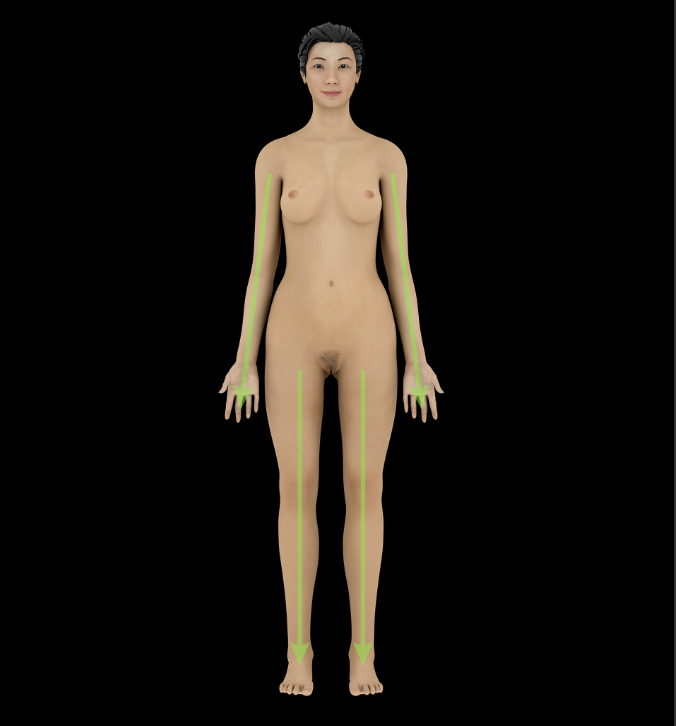

Farther from trunk or origin of a structure (e.g., the wrist is distal to the elbow)
Opposite of proximal
Endocrine System
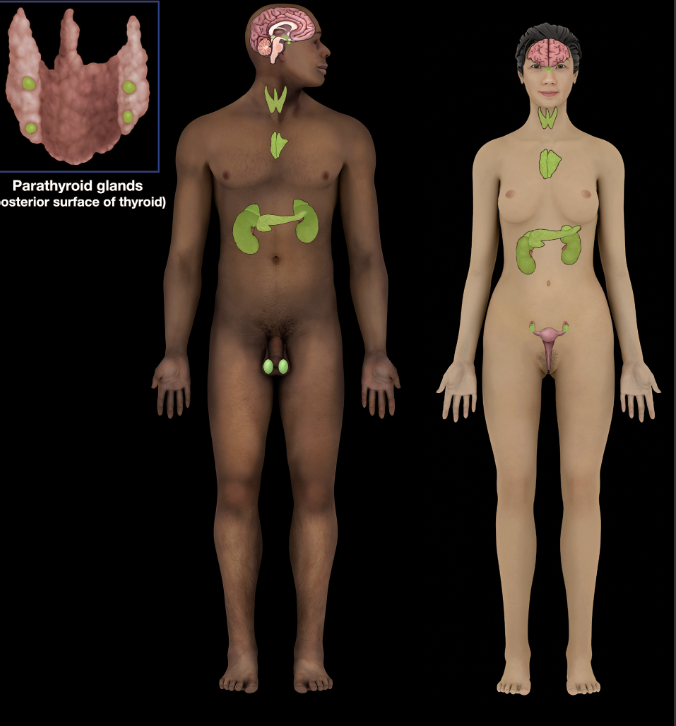
Head: hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and pineal gland
Neck: thyroid and parathyroid glands
Thorax: thymus and heart
Abdomen: pancreas, suprarenal glands, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and kidneys
Pelvis: ovaries
Scrotum: testes
Epigastric Region
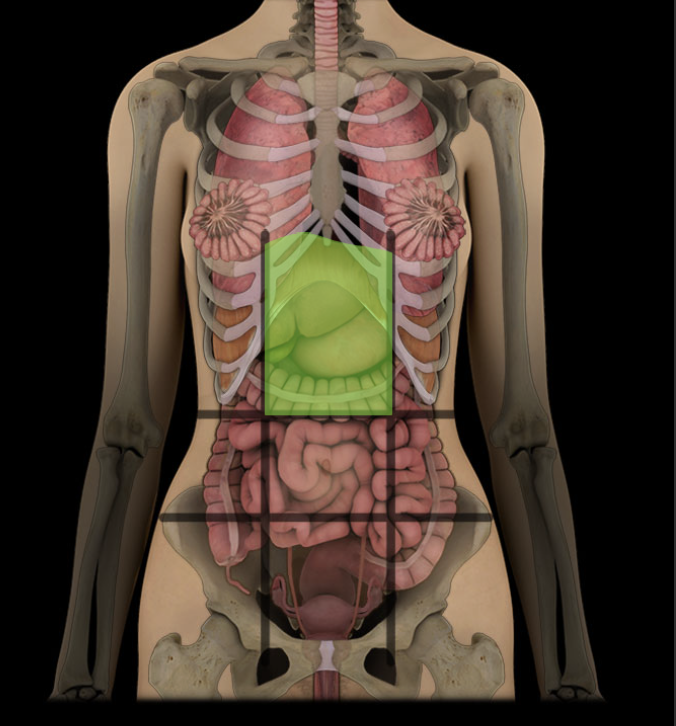
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Upper median region (flanked by right and left hypochondriac regions)
Contents include suprarenal glands and parts of stomach, large intestine, liver and gallbladder, and pancreas
Female reproductive system
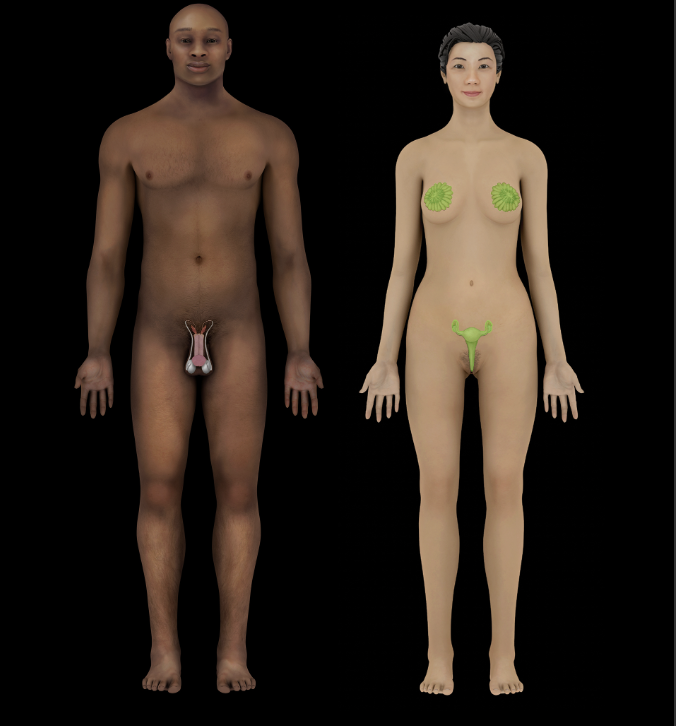
Gonads (ovaries)
Accessory glands (greater vestibular glands)
Uterus
External genitalia (mons pubis, labia majora and minora, vestibule (between labia minora), bulb of vestibule, greater vestibular glands, vaginal and external urethral orifices, hymen, and clitoris)
Mammary glands (in breast on anterior thoracic wall)
Frontal Region
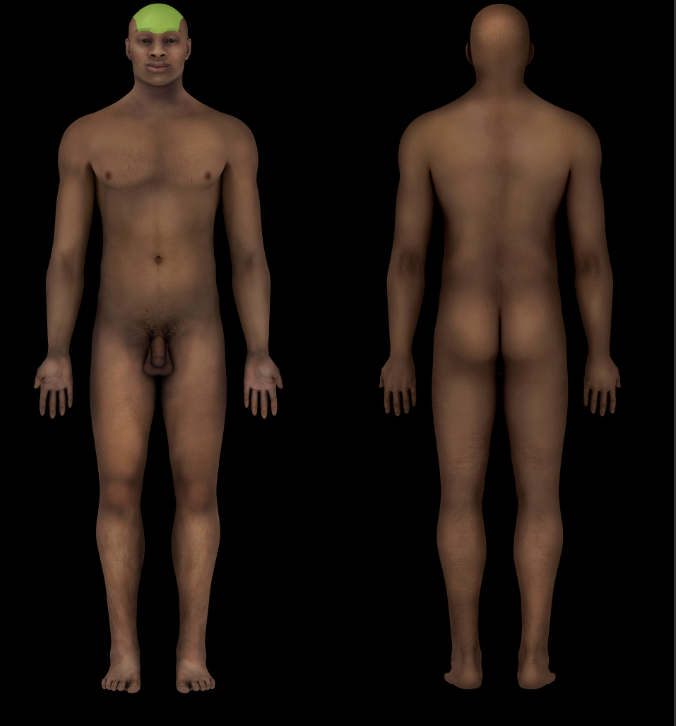
Head (anterior superior part of cranial region)
Greater omentum
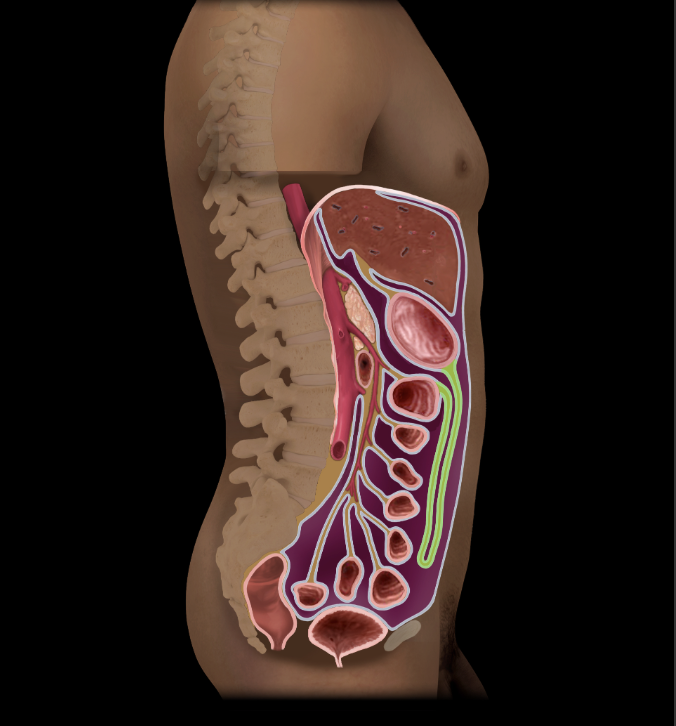
Double-layered peritoneum folded on itself so it has 4 layers
Suspended ("apron-like") from greater curvature of stomach
Attached to anterior surface of transverse colo
Hypogastric region
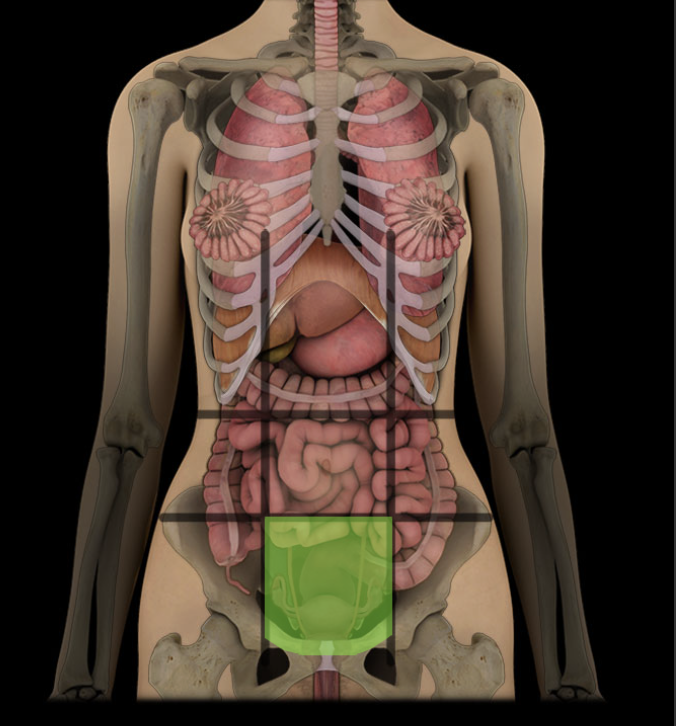
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Lower median region (flanked by right and left inguinal regions)
Contents include urinary bladder (when distended), and parts of small and large intestines
Inferior
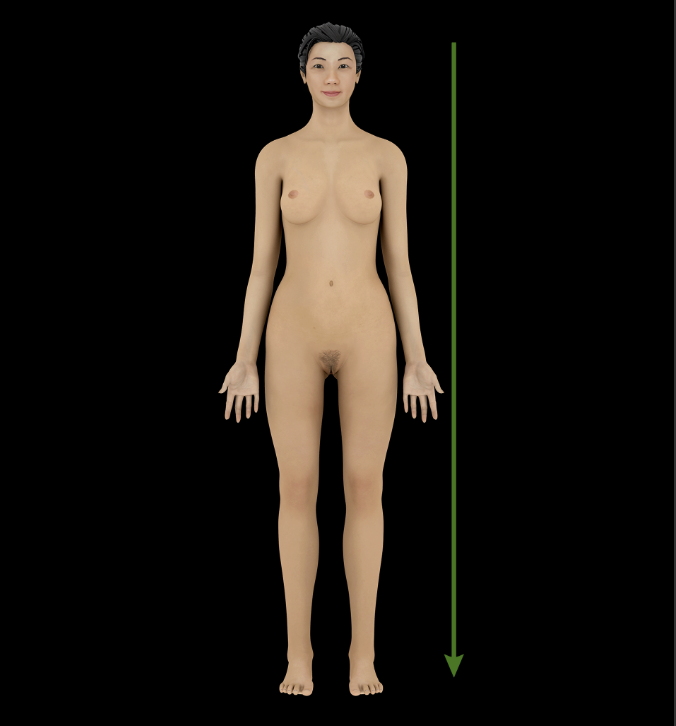
Downward or below (e.g., the diaphragm is inferior to the heart)
Opposite of superior
Integumentary system
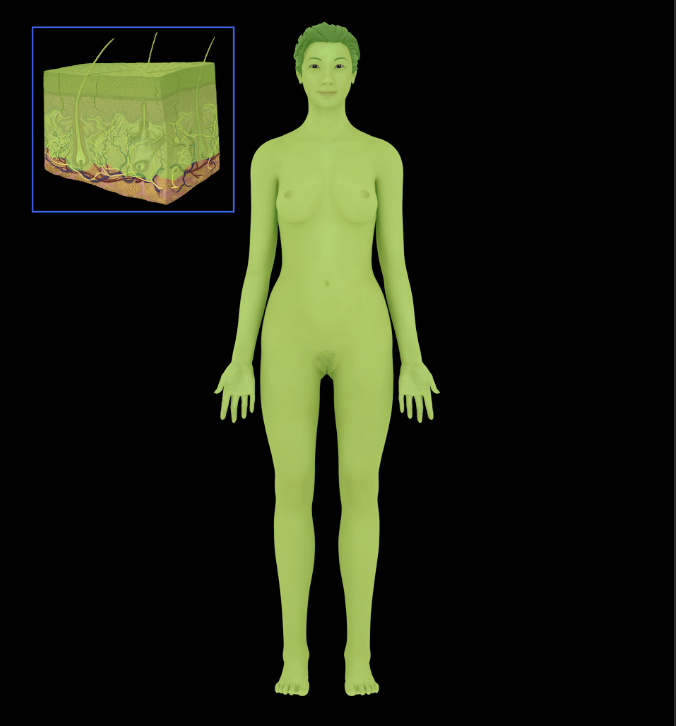
External surface of body
Lateral
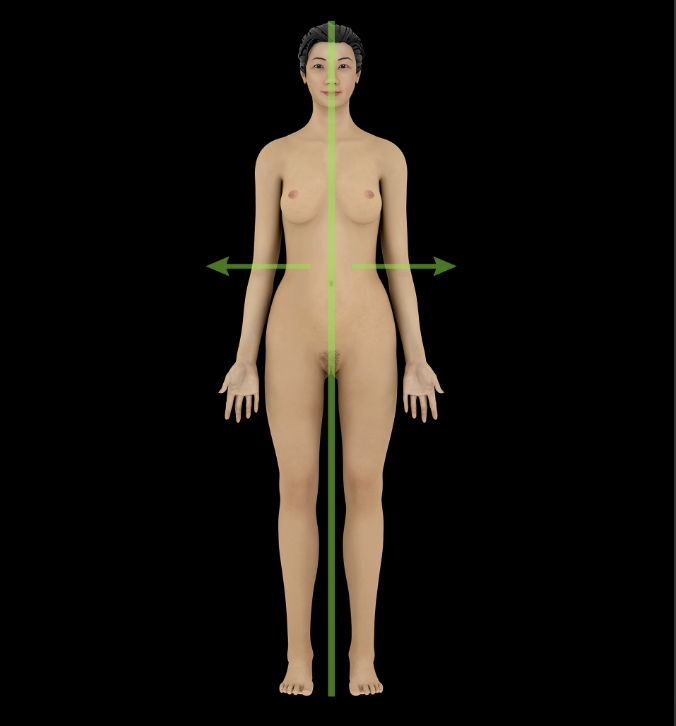
Away from the midline of the body (e.g., the lungs are lateral to the heart)
Opposite of medial
Left hypochondriac region
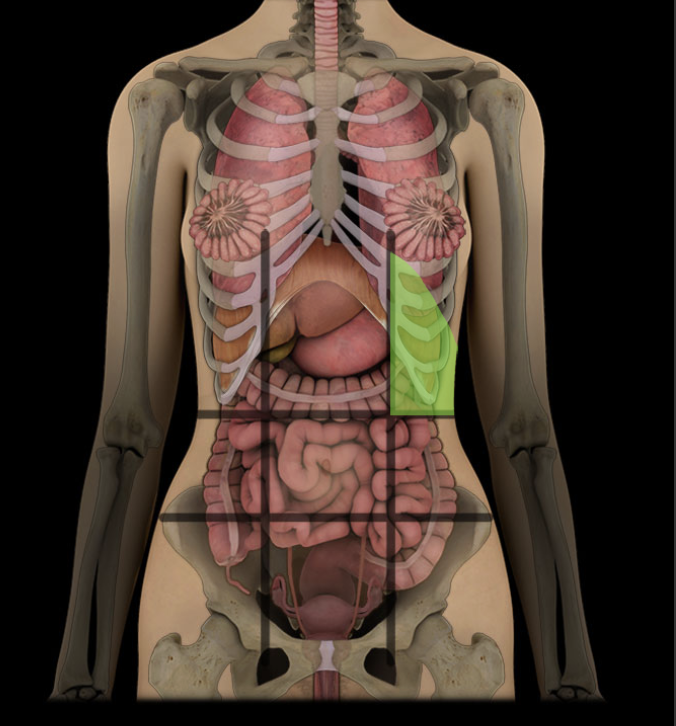
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Left upper lateral region
Contents include spleen and parts of stomach, large intestine, pancreas (tail), and left kidney
Left inguinal region
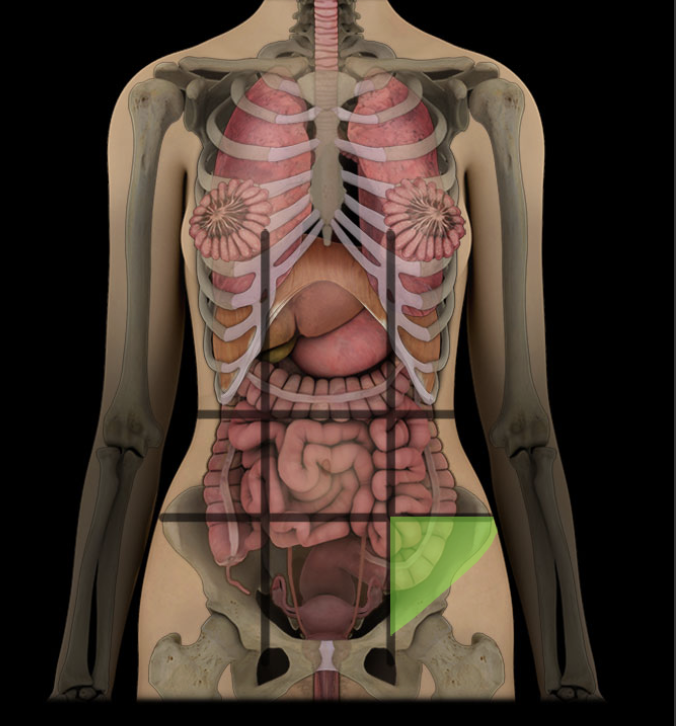
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Left lower lateral region
Contents include parts of small and large intestines
Left lateral region of abdomen
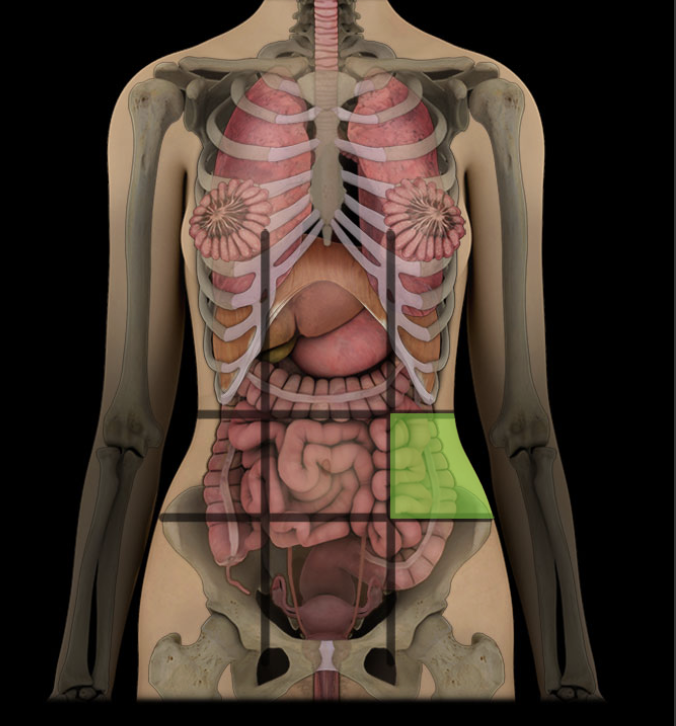
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Left lateral region
Contents include parts of small and large intestines, and left kidney
Left lower quadrant
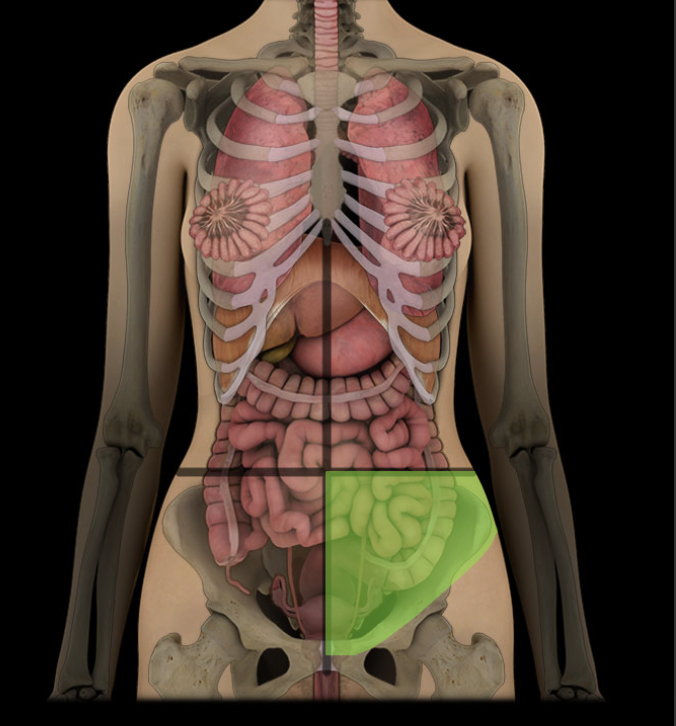
Lower left lateral area of abdominopelvic cavity
Contents include parts of small intestine, large intestine, urinary bladder (when distended), and left uterine tube and ovary
Left upper quadrant
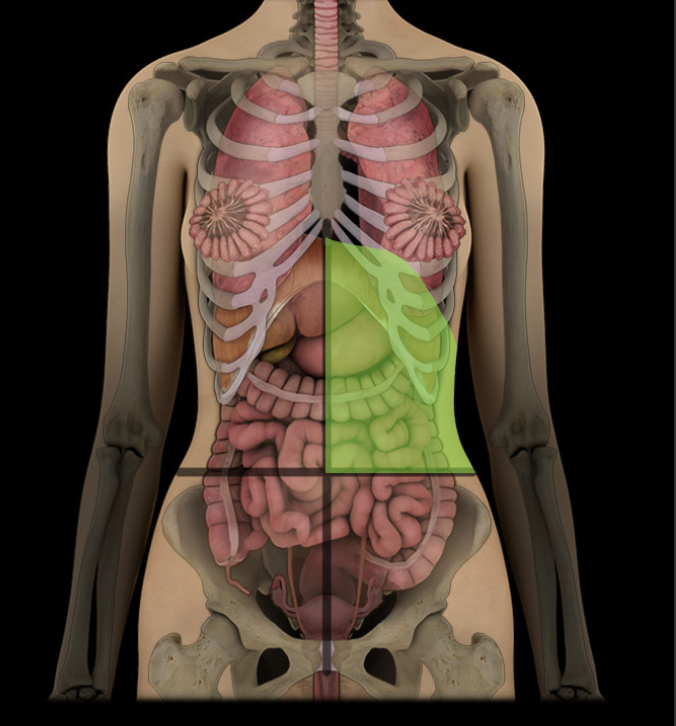
Upper left lateral area of abdominopelvic cavity
Contents include spleen, left kidney and suprarenal gland, and parts of liver, stomach, pancreas, and small and large intestines
Lesser omentum
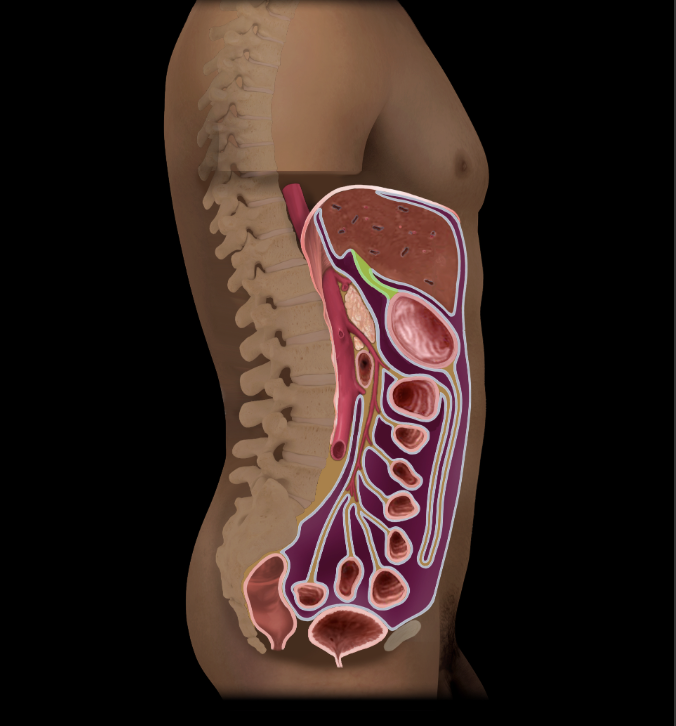
Double layer of peritoneum
Two parts: hepatogastric and hepatoduodenal ligament
Lumbar region
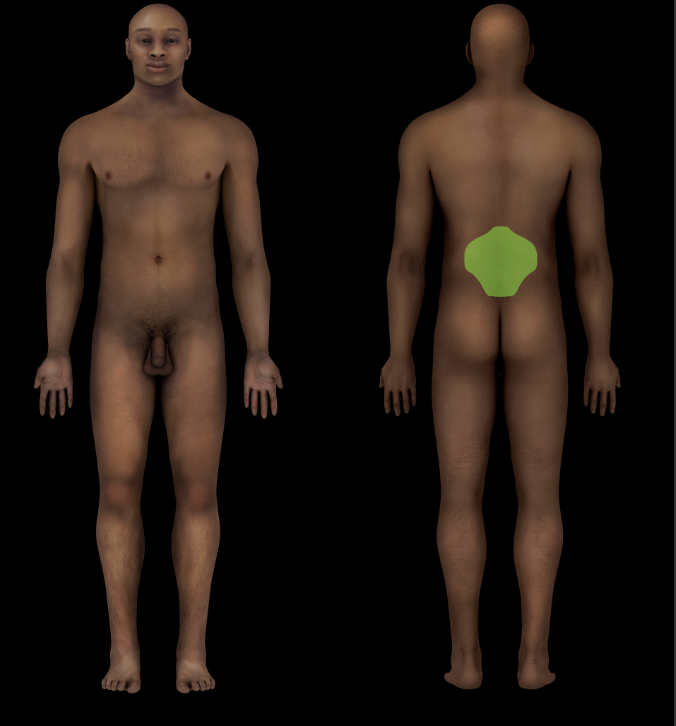
Subdivision of back
Includes lumbar vertebrae and attached muscles
Lymphatic system
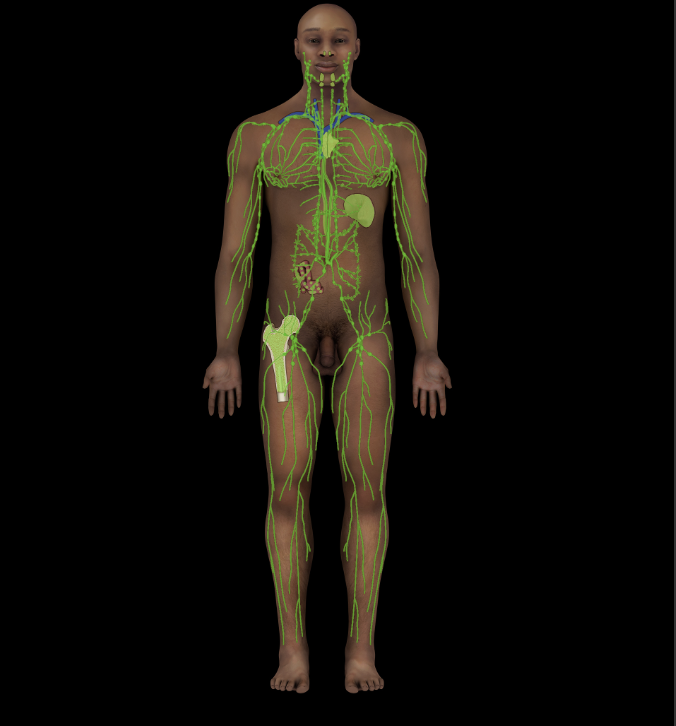
Produces lymphocytes
Transports and filters lymph (lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes)
Filters blood (spleen)
Male reproductive system
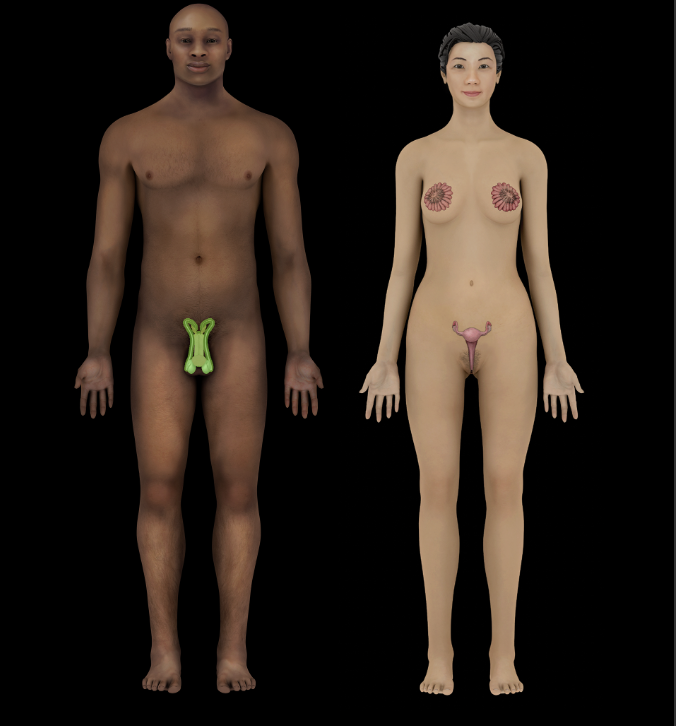
Gonads (testes)
Accessory glands (e.g., prostate, seminal vesicles, and bulbourethral glands)
External genitalia (penis and scrotum)
Medial
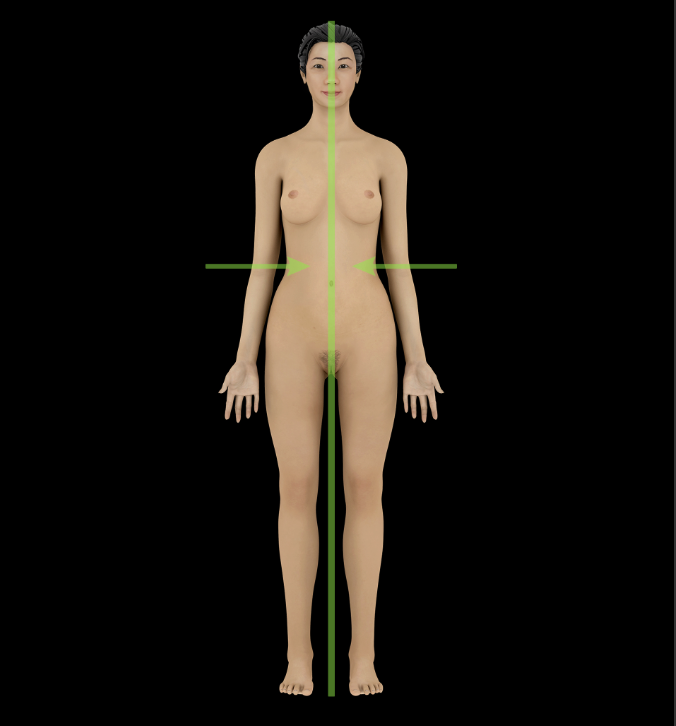
Towards the mindline of the body
Medial plane
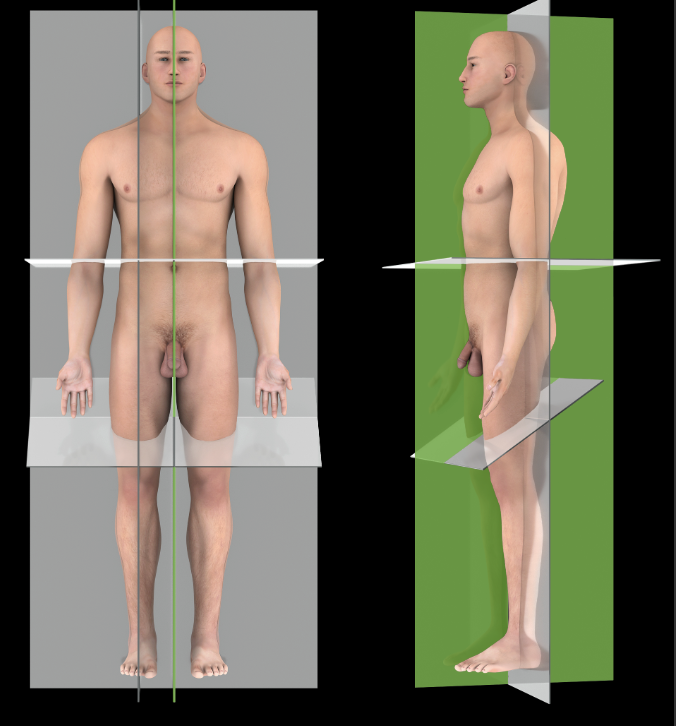
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body through the midline of the body, dividing it into equal right and left halves
Mediastinum
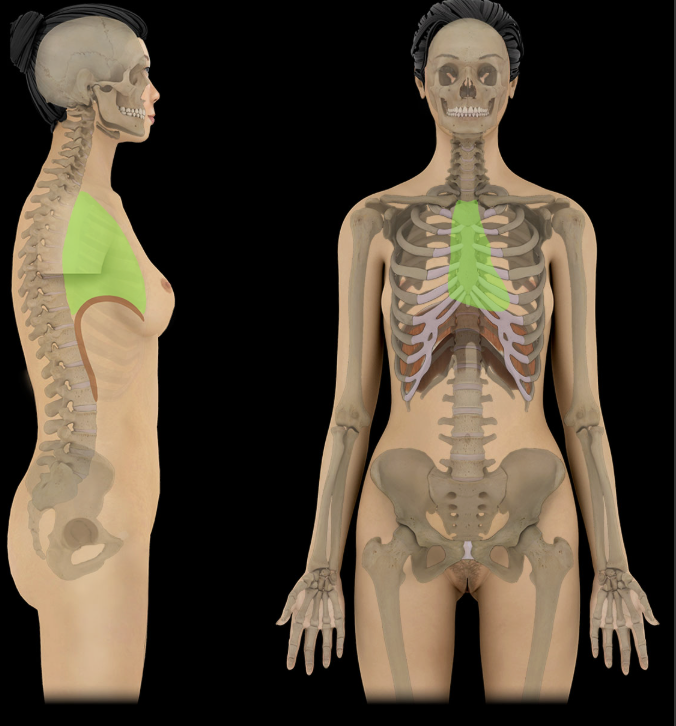
Middle region of thorax
Lies between sternum and thoracic vertebral bodies
Separates right and left pulmonary cavities
Divided into superior and inferior parts
Inferior mediastinum subdivided into middle, posterior, and anterior parts
Mental region
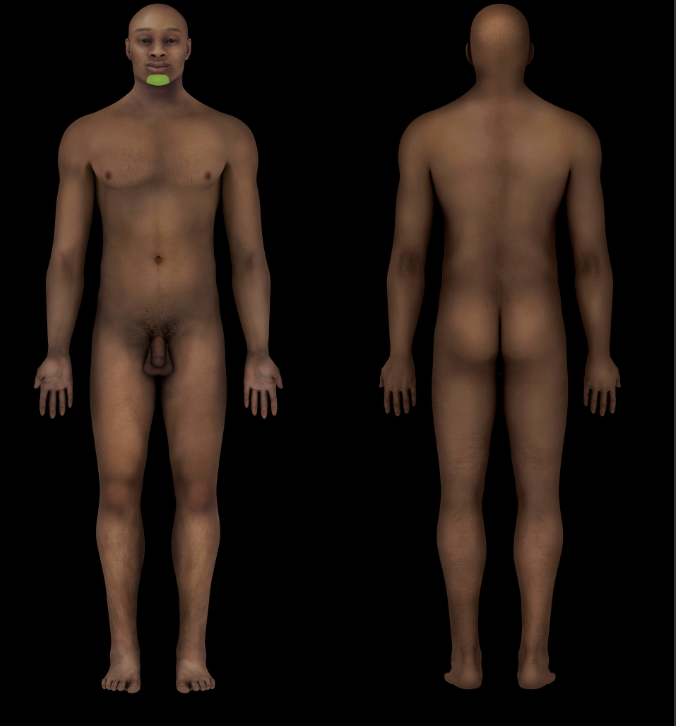
Head (anterior inferior part of facial region)
Mesentery of the small intestine
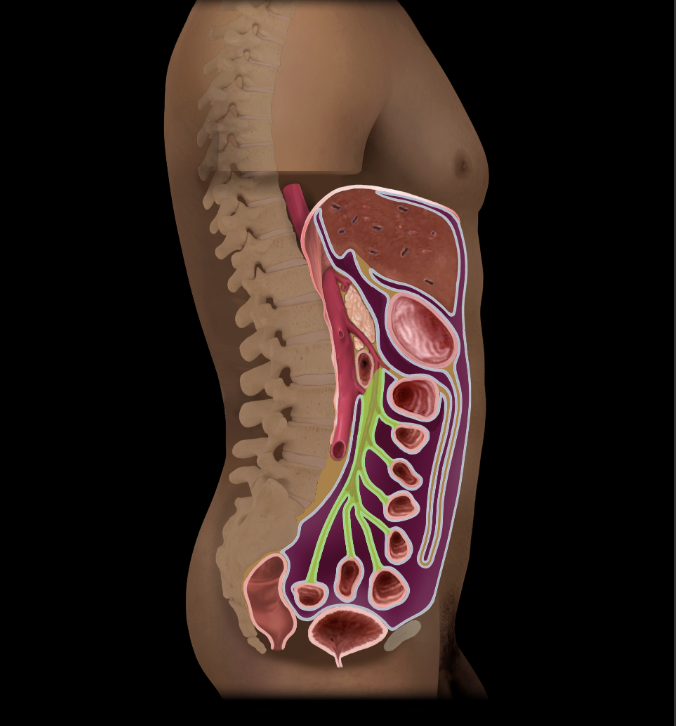
Double layer of peritoneum
Muscular system
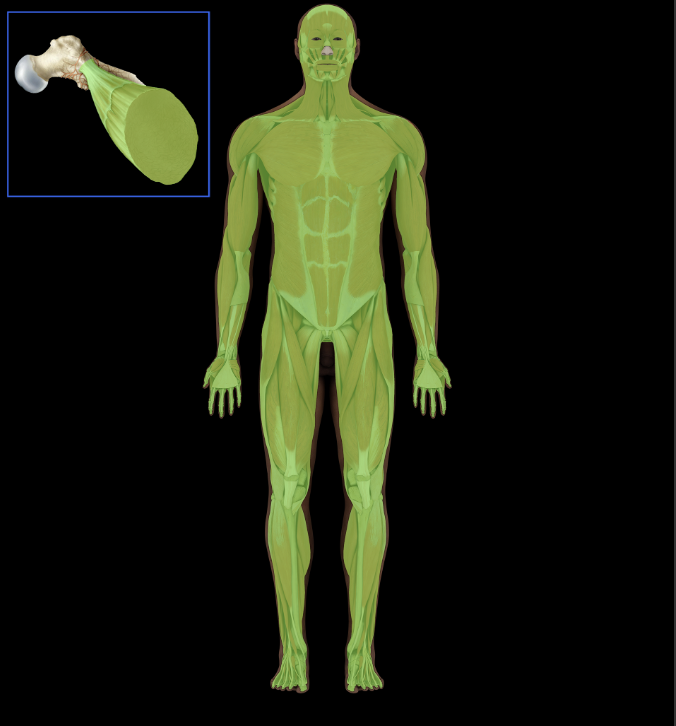
Three types of muscle tissue: skeletal (striated), cardiac, and smooth
Skeletal muscles divided into axial and appendicular
Cardiac muscle found in walls of heart
Smooth muscle found in walls of hollow organs (e.g., gastroinestinal tract, blood vessels); in iris and ciliary body of eye
Nervous system
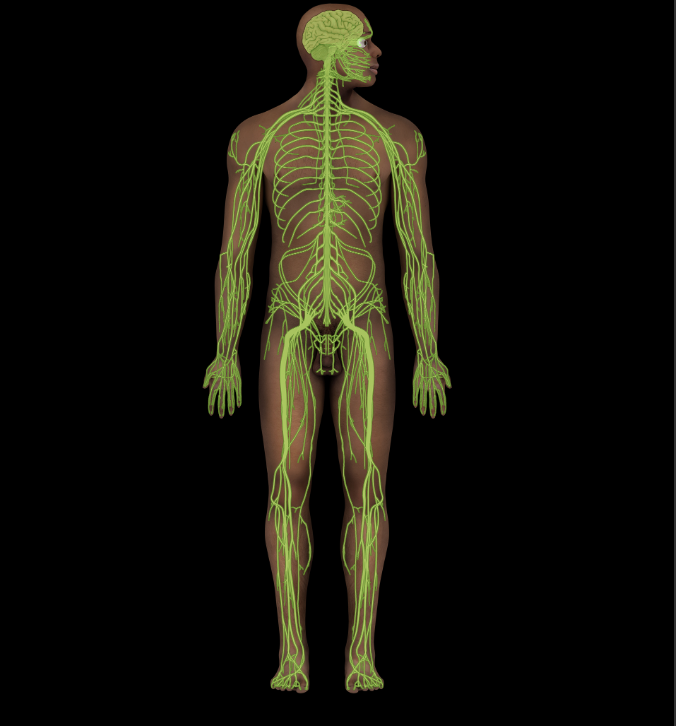
Structural divisions: CNS and PNS
CNS includes brain and spinal cord
PNS includes nerves that extend from brain and spinal cord, and ganglia
Functional divisions: afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor)
Oblique plane
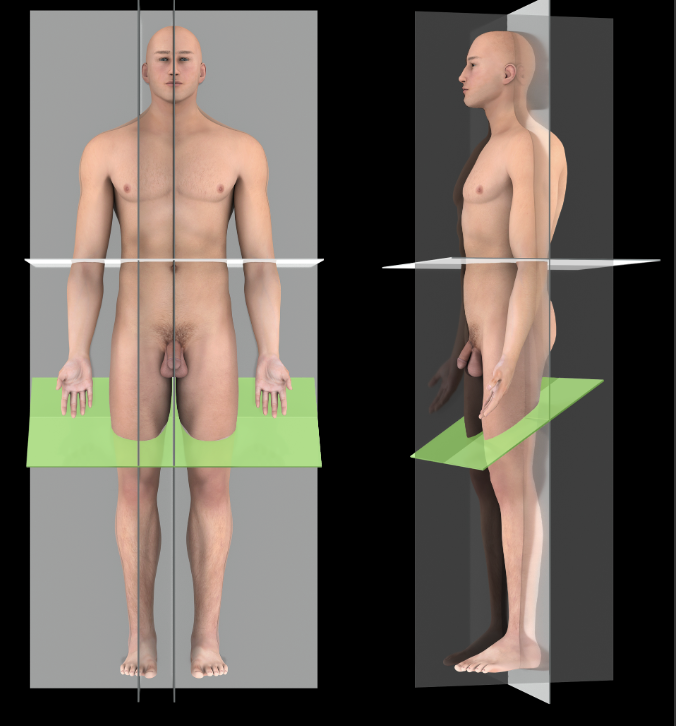
A plane that passes through the body on an angle, and is not one of the standard anatomical planes
Occipital region
P
art of cranial cavity related to occipital bone
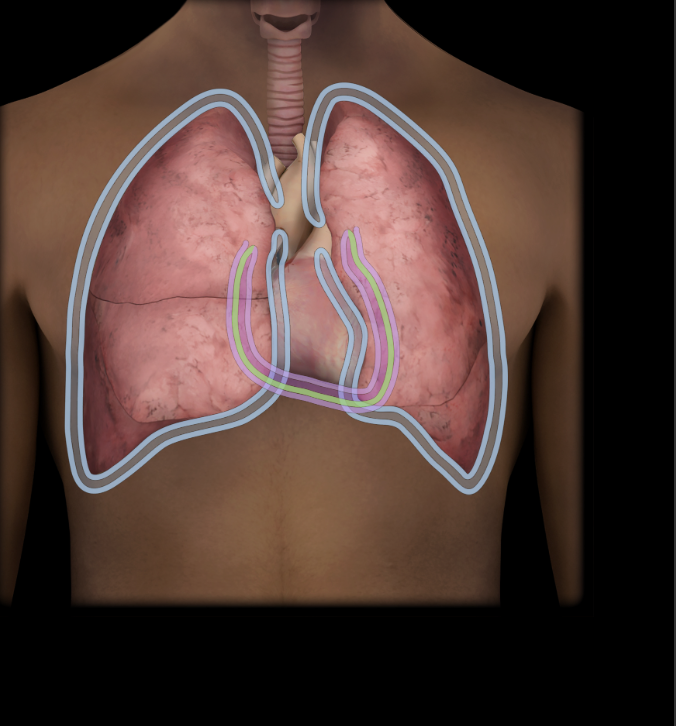
Parietal layer of serous pericardum
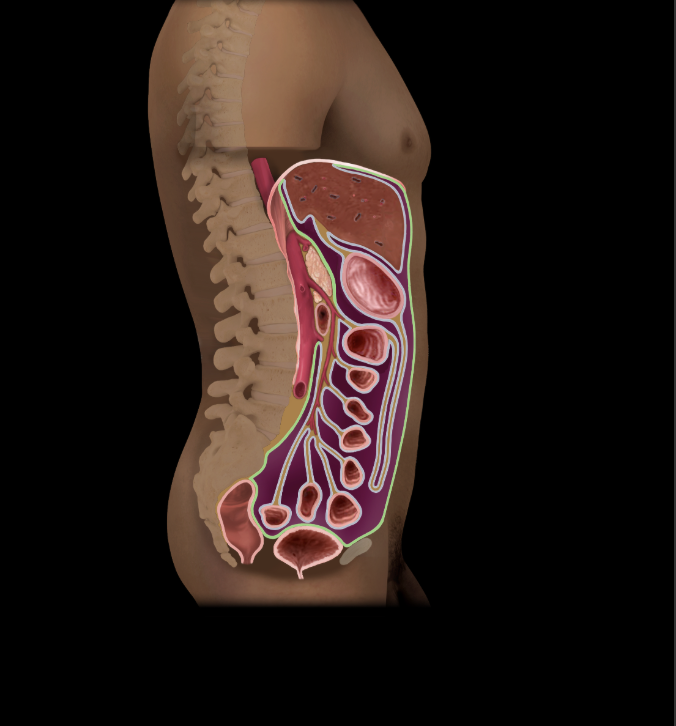
Parietal peritoneum
Lines wall of abdomen
Single layer of serous membrane with surface epithelium (mesothelium)
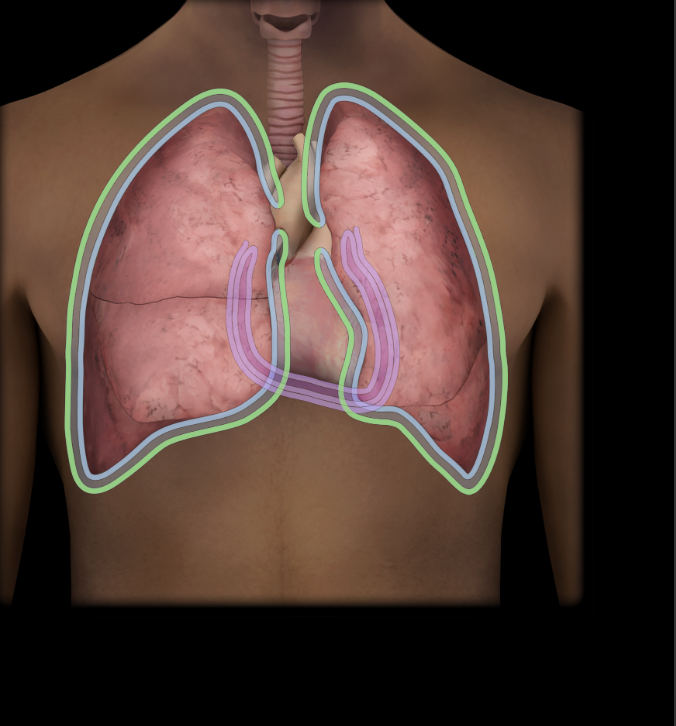
Perietal pleura
Thin, serous membrane
Lines pulmonary cavity
Fused to internal walls of thoracic cavity and lateral surface of mediastinum
Continuous with visceral pleura at root of lung
Regions include mediastinal, cervical, diaphragmatic, and costal
Parietal region
Part of cranial cavity related to parietal bone
Partoid region
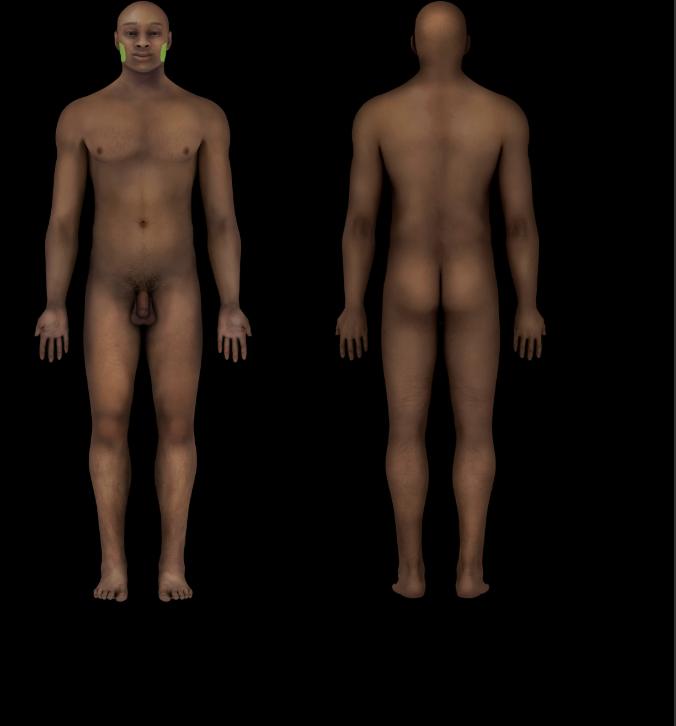
Part of facial region related to parotid salivary gland and ramus of mandible
Pelvic Cavity
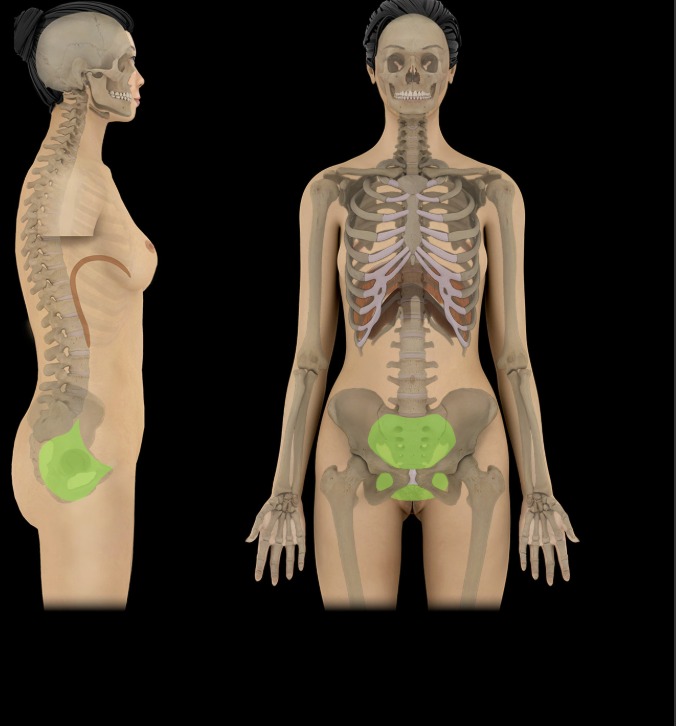
Bounded by pelvic inlet (superiorly) and pelvic outlet (inferiorly)
Major organs include: urinary bladder, loops of small intestine, inferior part of sigmoid colon, rectum, and reproductive organs (ovaries, uterus, vagina in female; prostate and seminal glands in male)
Continuous superiorly with abdominal cavity
Pericardial cavity
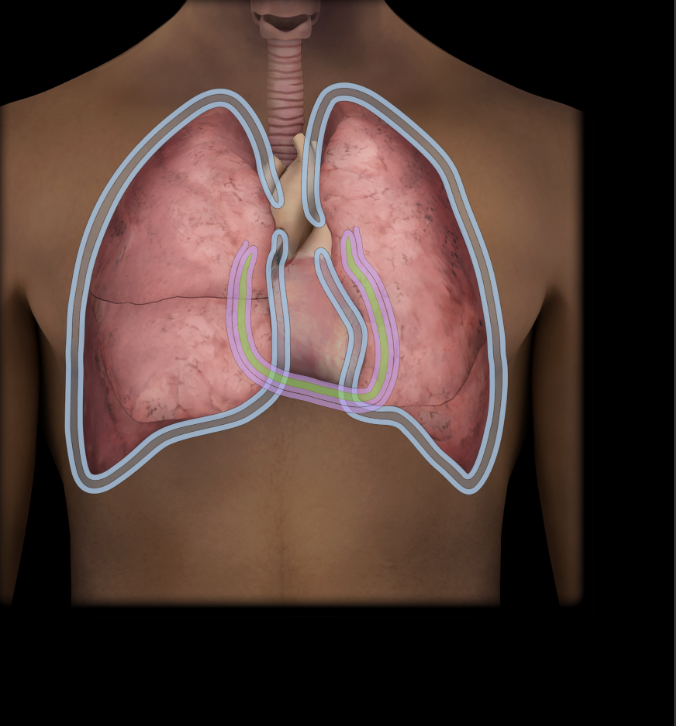
Potential space between parietal and visceral layers of serous pericardium
Peritoneal cavity
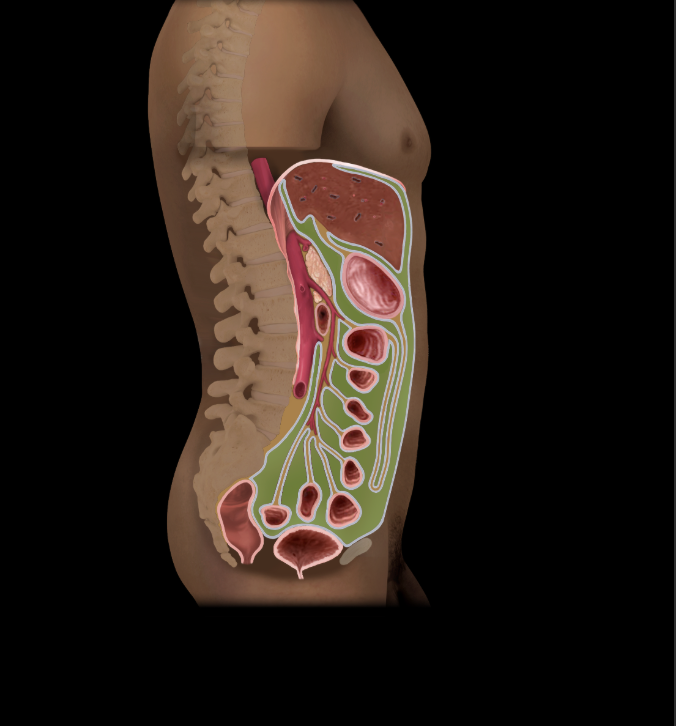
Potential space between parietal and visceral layers of peritoneum
Pleural cavity
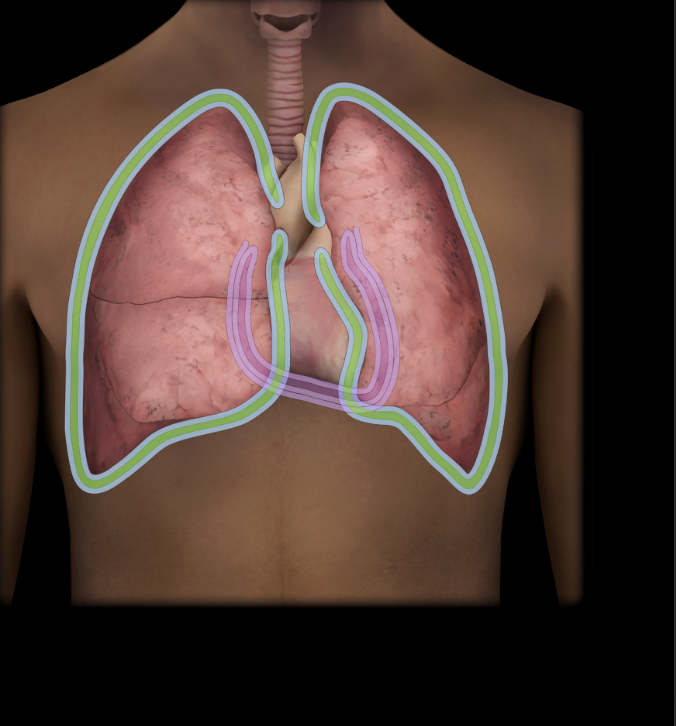
Bilateral potential spaces between parietal and visceral layers of pleura
Popliteal fossa
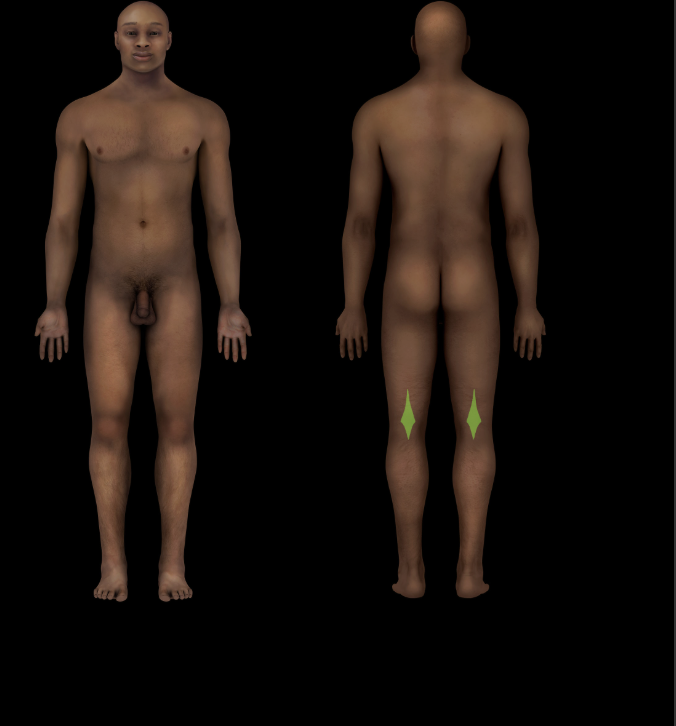
Subdivision of posterior knee region
Skin, muscles, nerves, and vessels associated with diamond-shaped region on posterior aspect of knee region
Bounded by biceps femoris, semimembranosus and semitendinosus, gastrocnemius, skin and popliteal fascia (roof), and posterior capsule of knee joint (floor)
Important structures include: small saphenous vein, popliteal artery and vein, tibial and common fibular nerves, posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh, and popliteal lymph nodes
Posterior
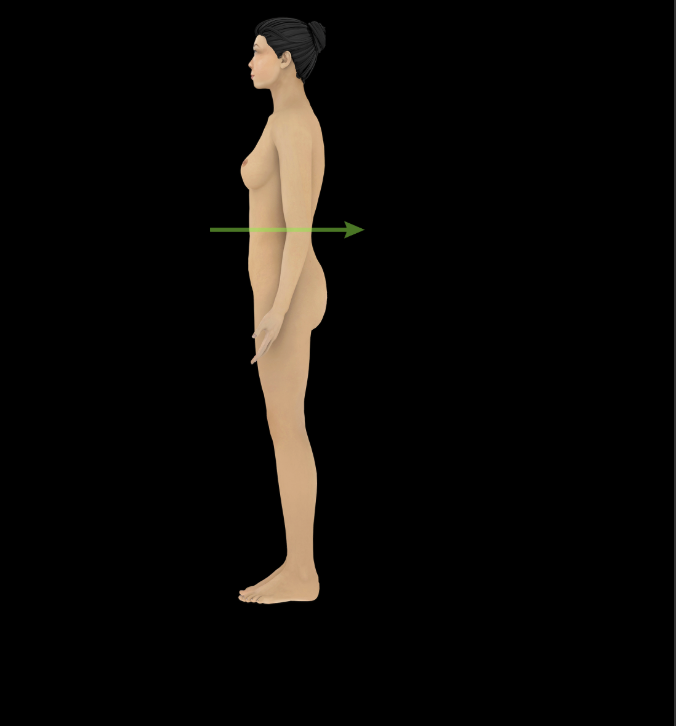
Toward the back of the body or relating to the back (e.g., the heart is posterior to the sternum)
Prone
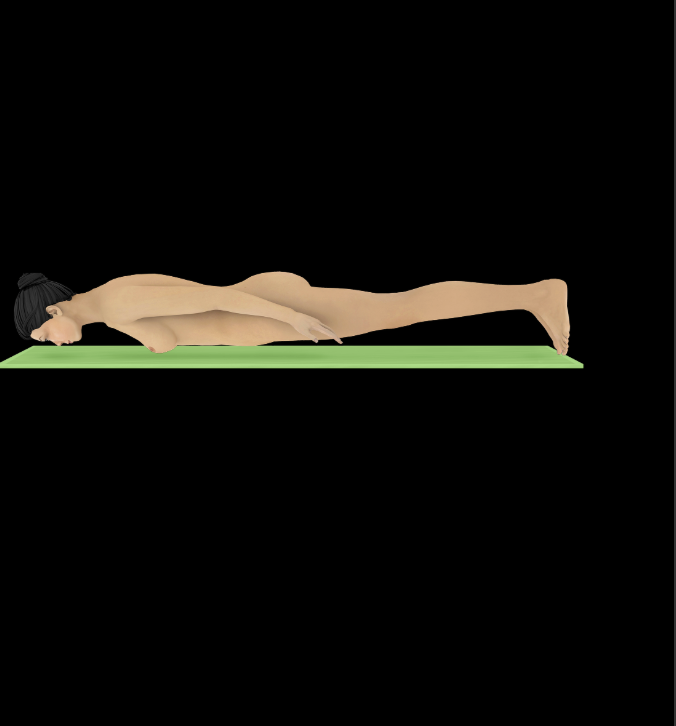
Position of the body when lying face down
Proximal
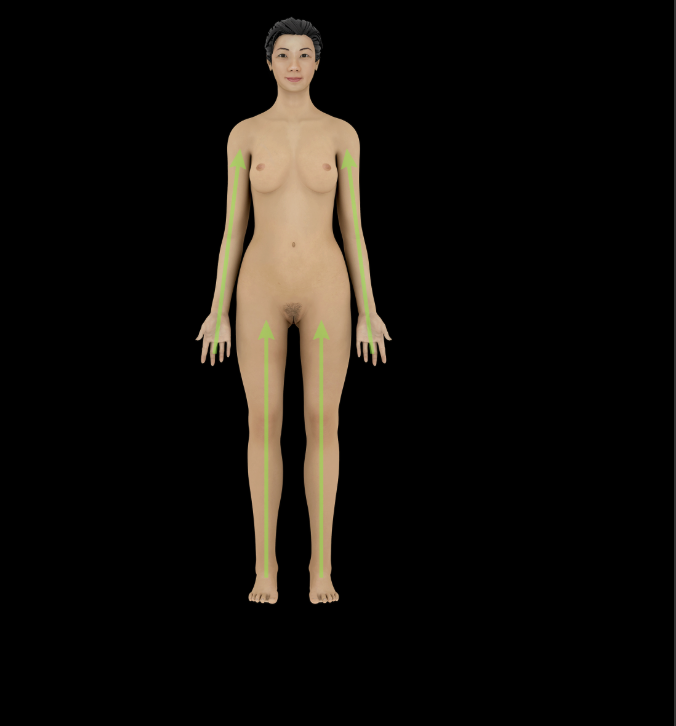
Closer to trunk or origin of a structure (e.g., the elbow is proximal to the wrist)Opposite of distal
Pulmonary cavity
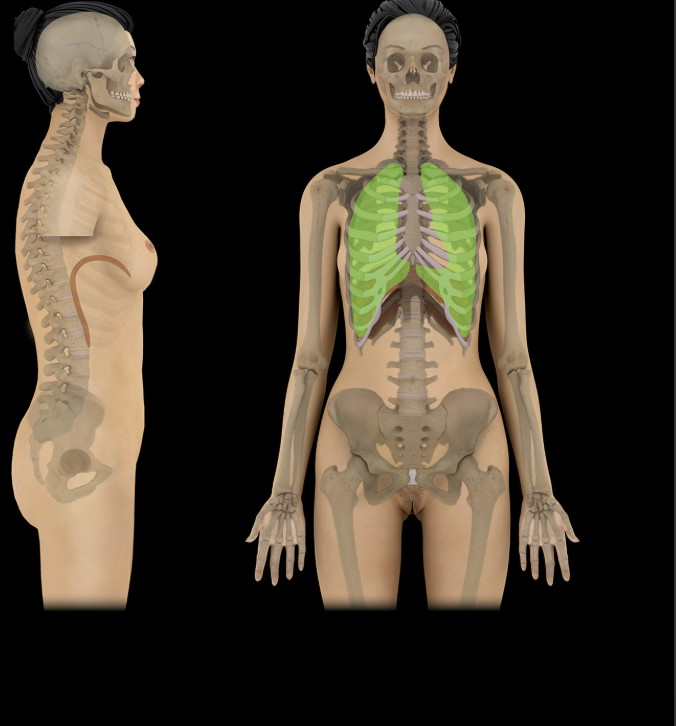
Bilateral subdivision of thoracic cavity (separated by mediastinum)
Contain lungs and pleurae
Lined by parietal pleura
Respiratory System
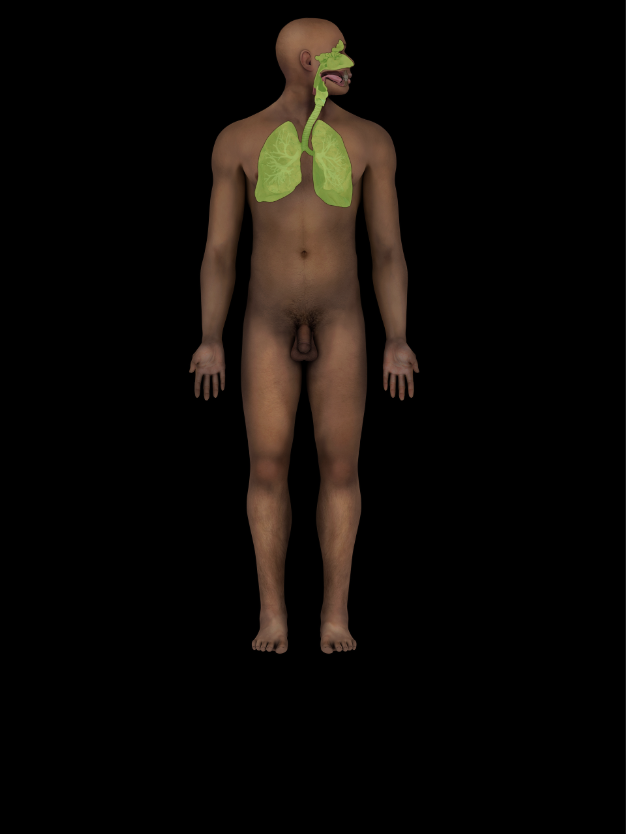
Air passes through nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs
Air is cleaned, warmed, and humidified
Phonation
Lungs are primary organs of respiration (gas exchange)
Acid-base balance
Right hypochondriac region
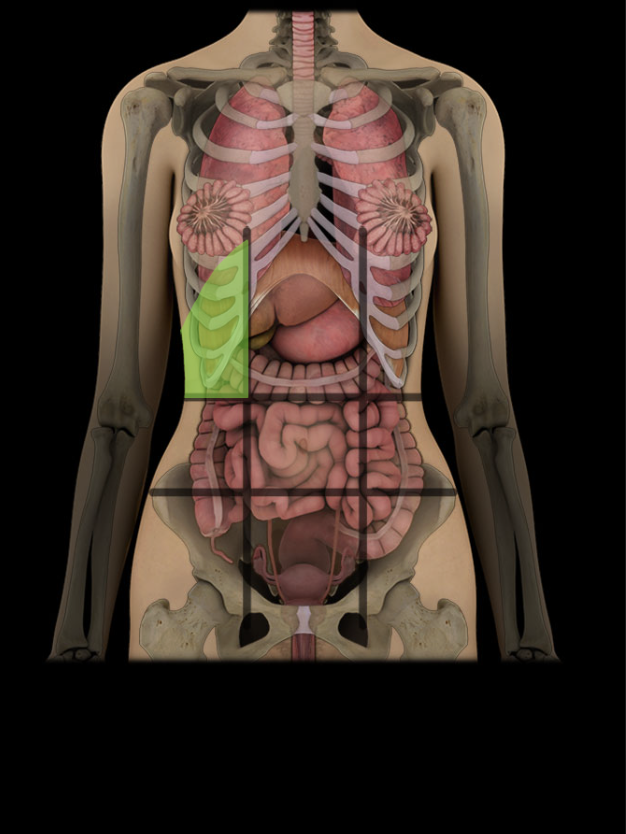
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Right upper lateral region
Contents include parts of large intestine, liver and gallbladder, and right kidney
Right inguinal region
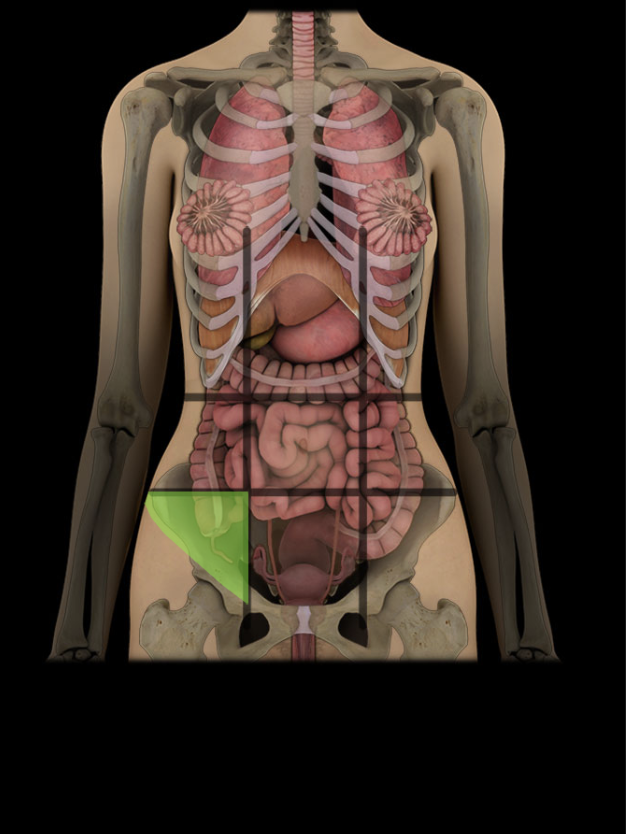
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Right lower lateral region
Contents include parts of small and large intestine (including cecum and vermiform appendix)
Right lateral region of abdomen
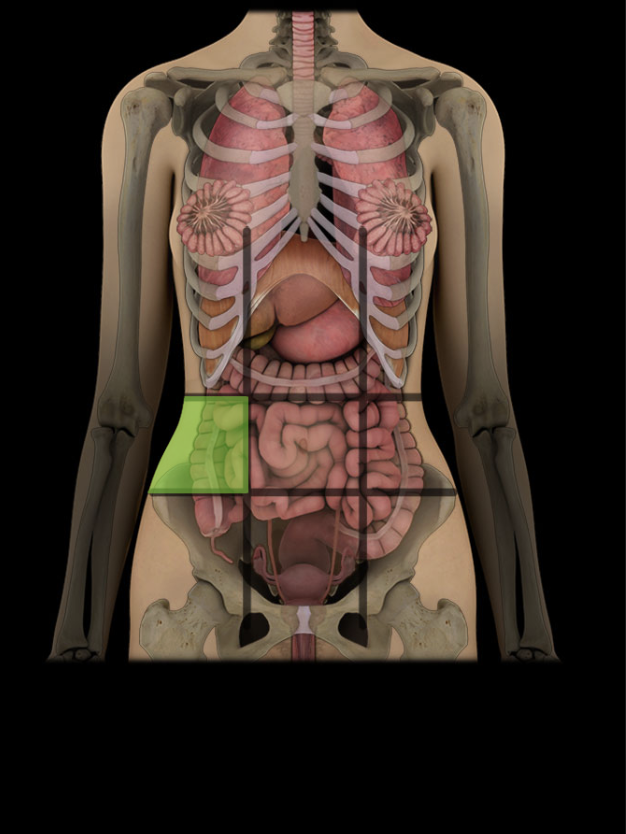
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Right lateral region
Contents include parts of small and large intestine, and right kidney
Right lower quadrant
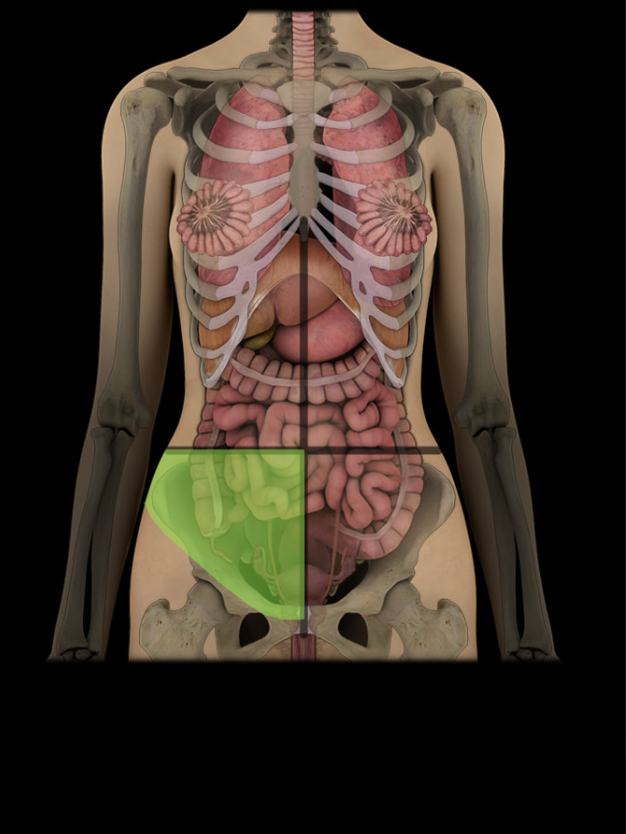
Lower right lateral area of abdominopelvic cavity
Contents include parts of small intestine, large intestine (including cecum and vermiform appendix), urinary bladder (when distended), and right uterine tube and ovary
Right upper quadrant
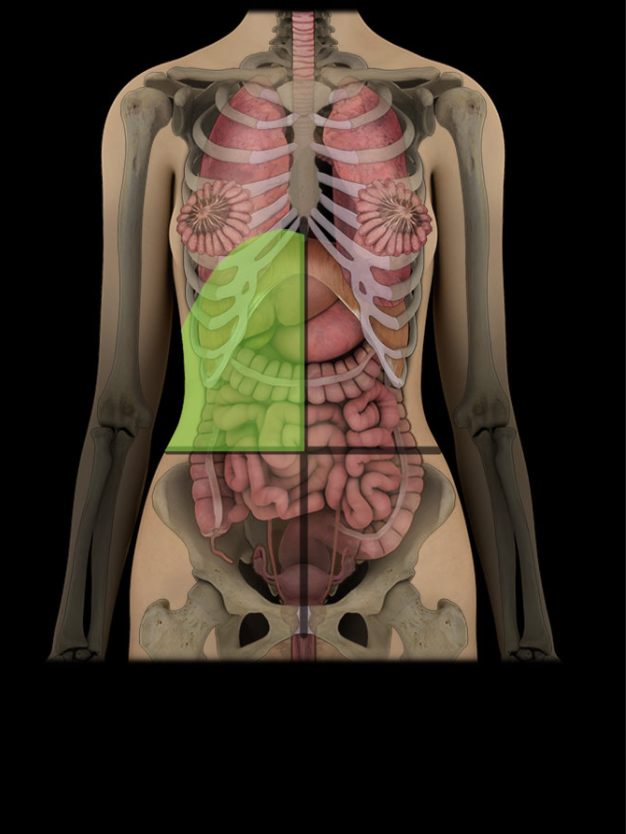
Upper right lateral area of abdominopelvic cavity
Contents include right kidney and suprarenal gland, gallbladder, and parts of liver, stomach, pancreas, and small and large intestines
Sacral region
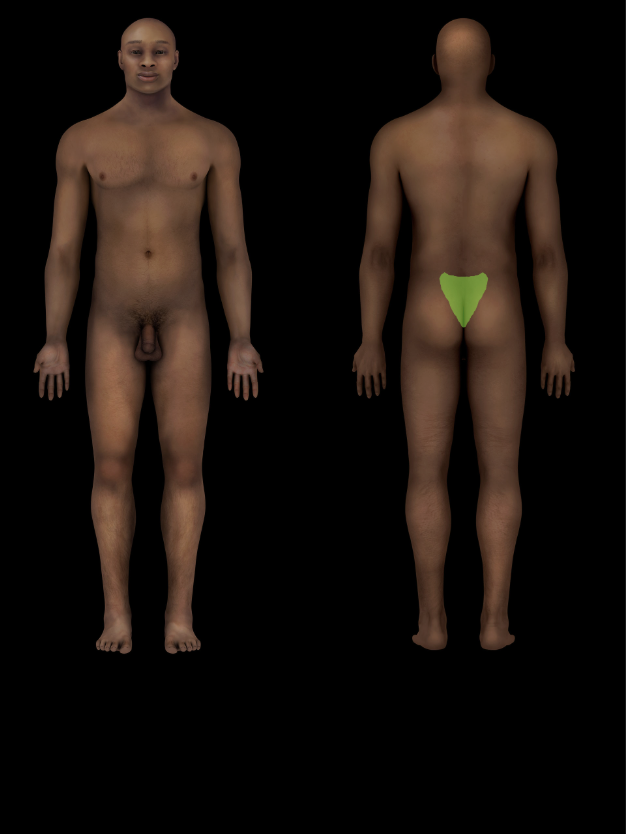
Subdivision of back
Includes sacrum and attached muscles
Sagittal Plane
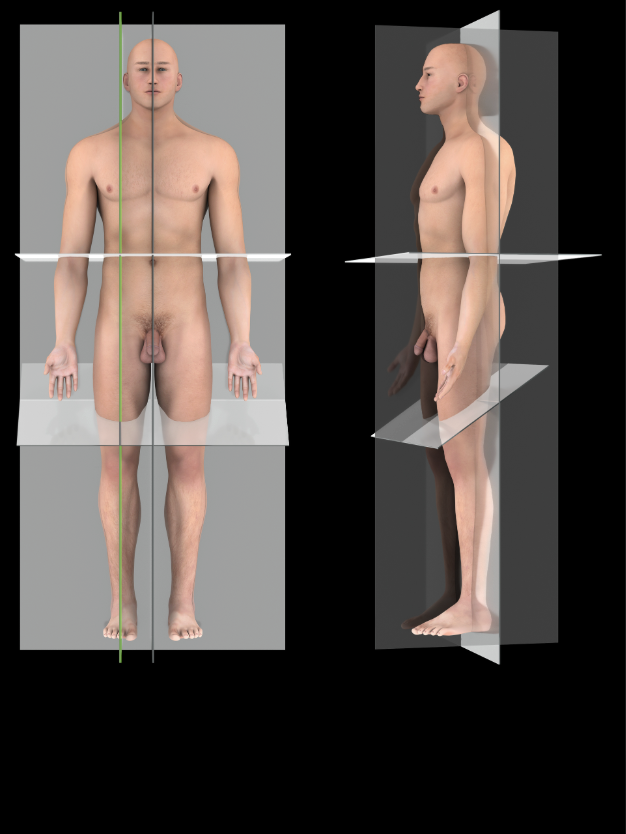
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body, dividing it into right and left portions
Skeletal system
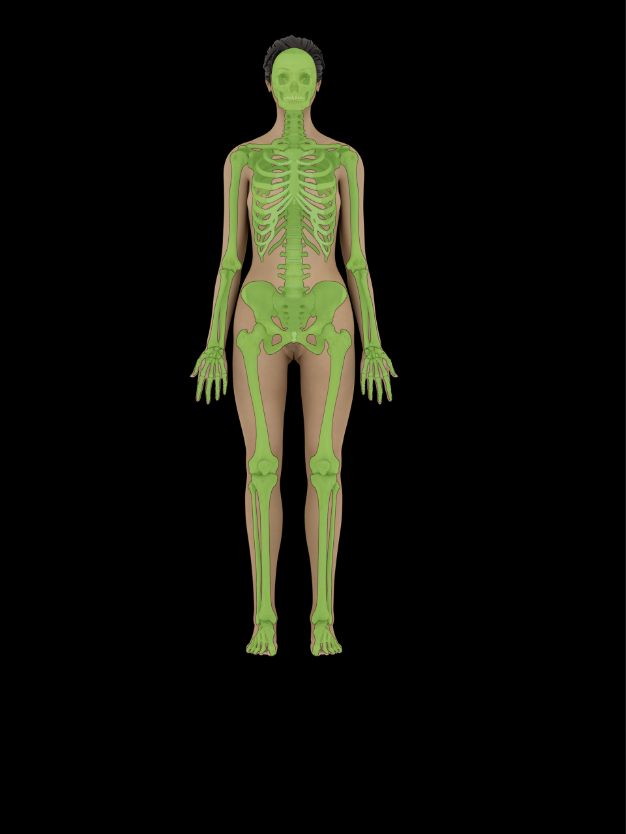
Support for, and protection of body
Provides site of attachment for muscles
Movement of body via joints
Hemopoiesis
Storage of calcium and phosphorus
Superficial
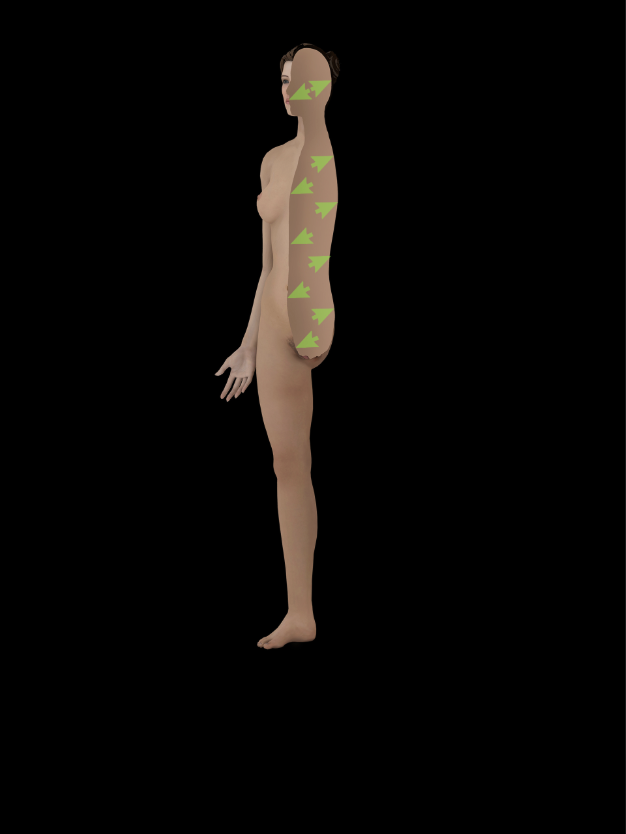
Toward the surface of the body or organ (e.g., Skin is superficial to muscles)
Opposite of deep
Supine
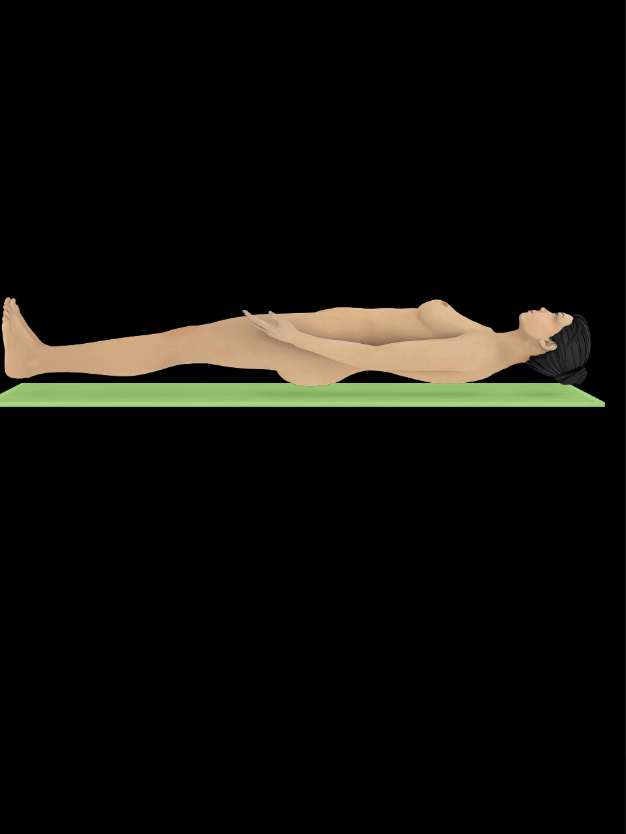
For forearm movement (in anatomical position), supination directs palm anteriorly
Opposite of prone
Temporal region
Part of cranial region related to temporal bone
Thoracic cavity
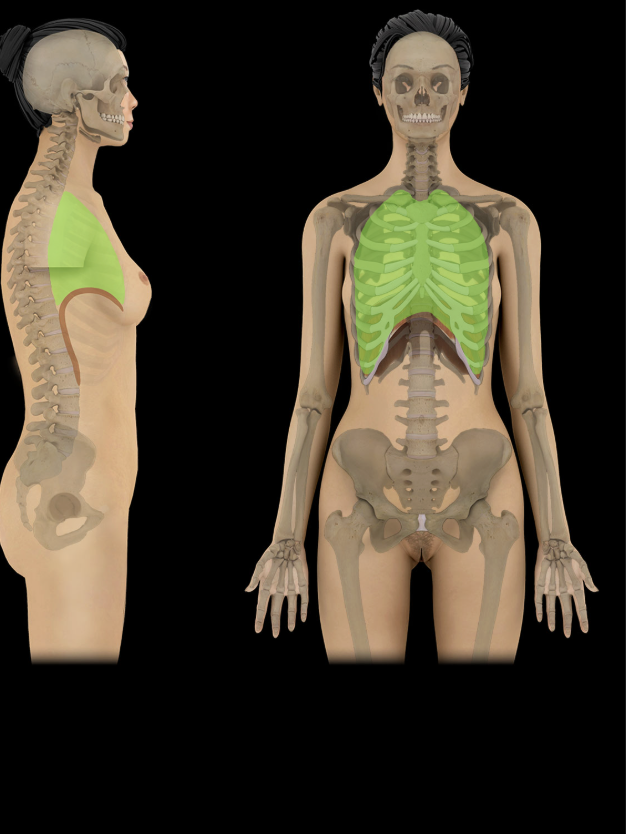
Cavity of the chest
Bounded by sternum, ribs and costal cartilages, intercostal muscles, thoracic vertebrae, and diaphragm
Three subdivisions: a central mediastinum (contains heart and thoracic parts of great vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus) and bilateral pulmonary cavities (contains lungs and plurae)
Transverse plane
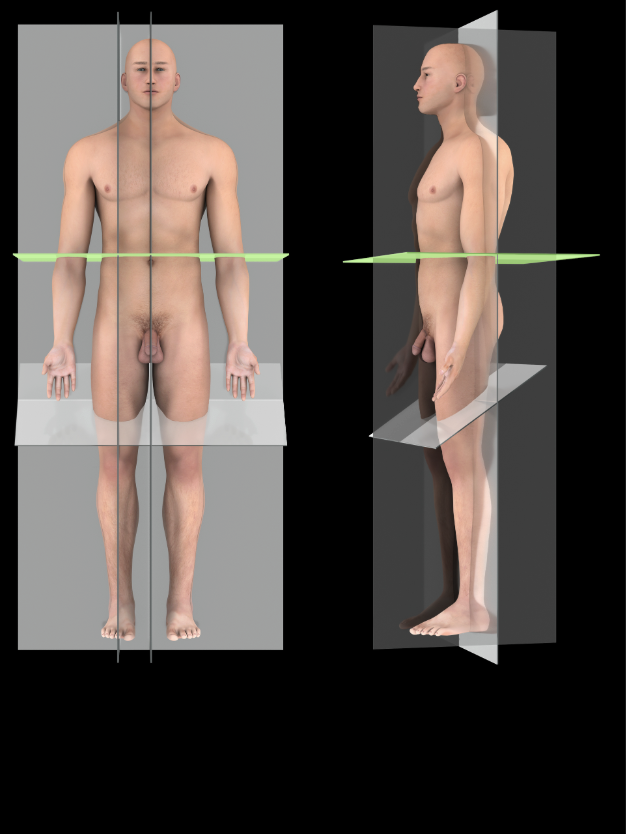
A horizontal plane that passes perpendicular to the long axis of the body, dividing it into superior and inferior portions
Triangle of auscultation
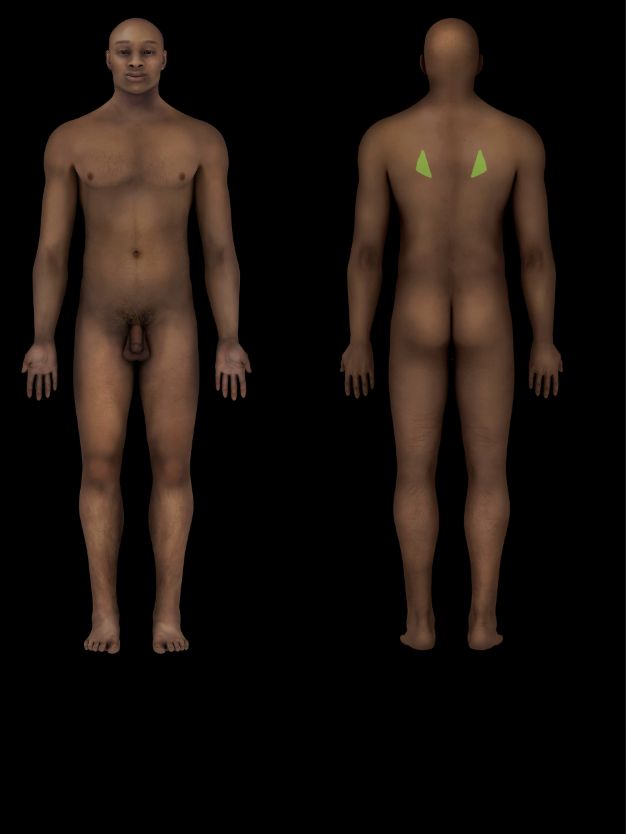
Small, triangular gap between trapezius and latissimus dorsi muscles and inferior part of medial scapular border
Floor of triangle formed by rhomboid major muscle and thoracolumbar fascia
Umbilical region
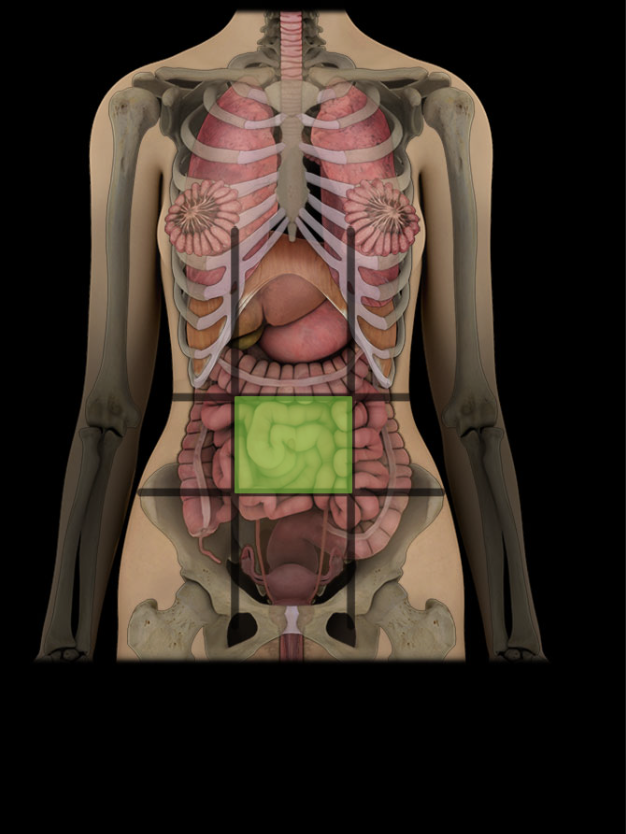
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Median region (flanked by right and left flank regions)
Contents include parts of small and large intestines
Urinary System
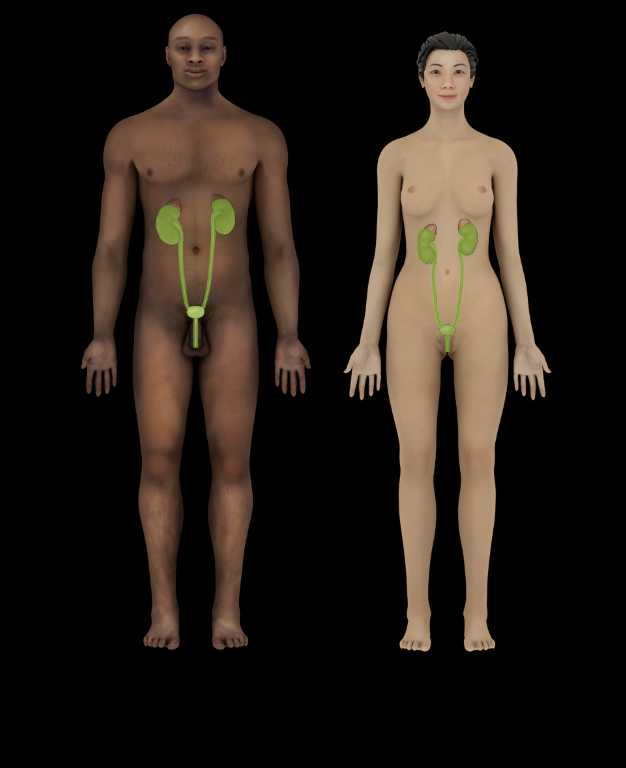
Kidneys filter blood to remove waste products and concentrate waste products in urine
Ureters transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder
Urinary bladder stores and, with urethra, expels urine from body
Visceral layer of serous pericardium
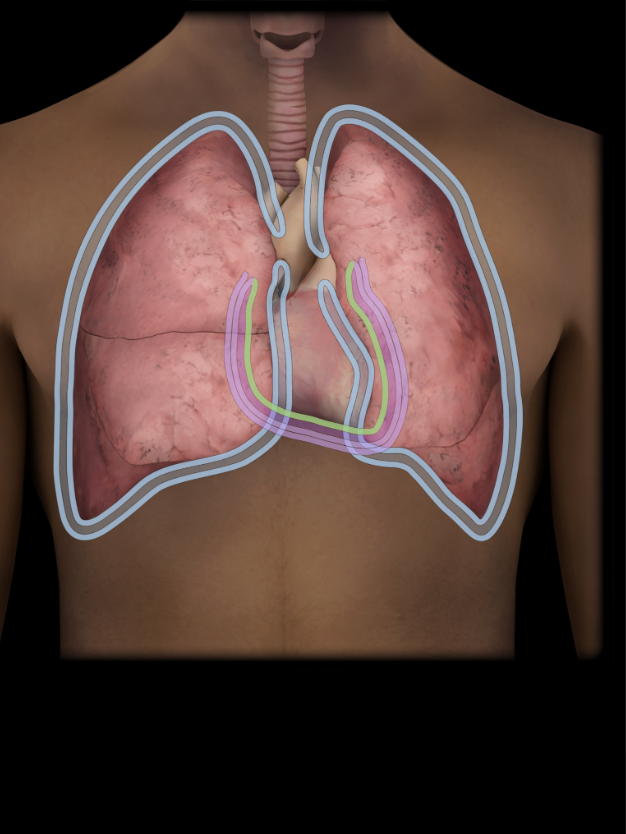
Thin, serous membrane fused to surface of heart (myocardium)
Inner limit of pericardial cavity
Continuous with parietal layer of serous pericardium
Visceral peritoneum
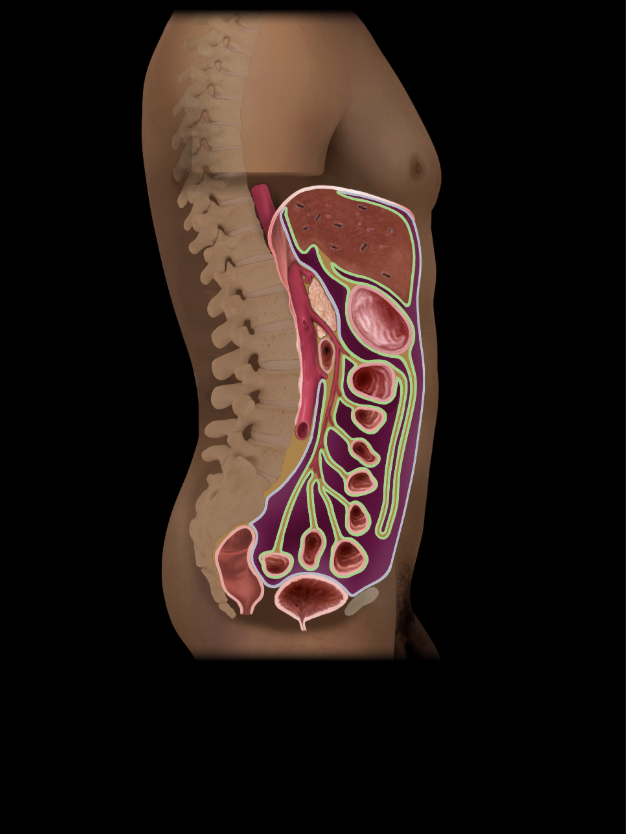
Coats outer surface of many abdominal organs
Single layer of serous membrane with surface epithelium (mesothelium)
Visceral pleura
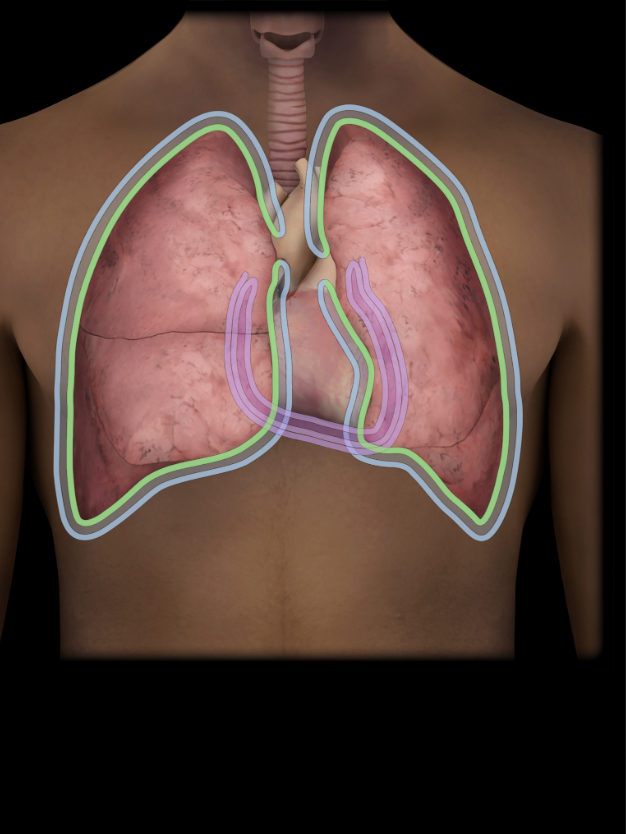
Thin, serous membrane
Fused to surface of lung
Continuous with parietal pleura at root of lung
Separated from parietal pleura by pleural cavity
Zygomatic region
Part of cranial region related to zygomatic bone