Module 1 - Overview of Dentitions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is dental anatomy?
The area of dental science dealing with the morphology (or shape/form) of the teeth
Why is this important?
Patient education
Fluoride therapy
Sealants
Periodontal and tooth assessment
Instrumentation
Primary Dentition
Starts with eruption of mandibular incisors at 6 months
All primary teeth erupted at about 2 ½ years of age
20 teeth
8 incisors
4 canines
8 molars
Mixed Dentition
“Ugly Duckling”
Occurs between 6 to 12 years of age
Larger in size
Darker in color
Jaw growth
Crowding
Permanent Dentition
Begins around age 12
32 teeth
8 incisors
4 canines
8 premolars
12 molars
Maxillary Arch
Immovable
Mandibular Arch
Movable
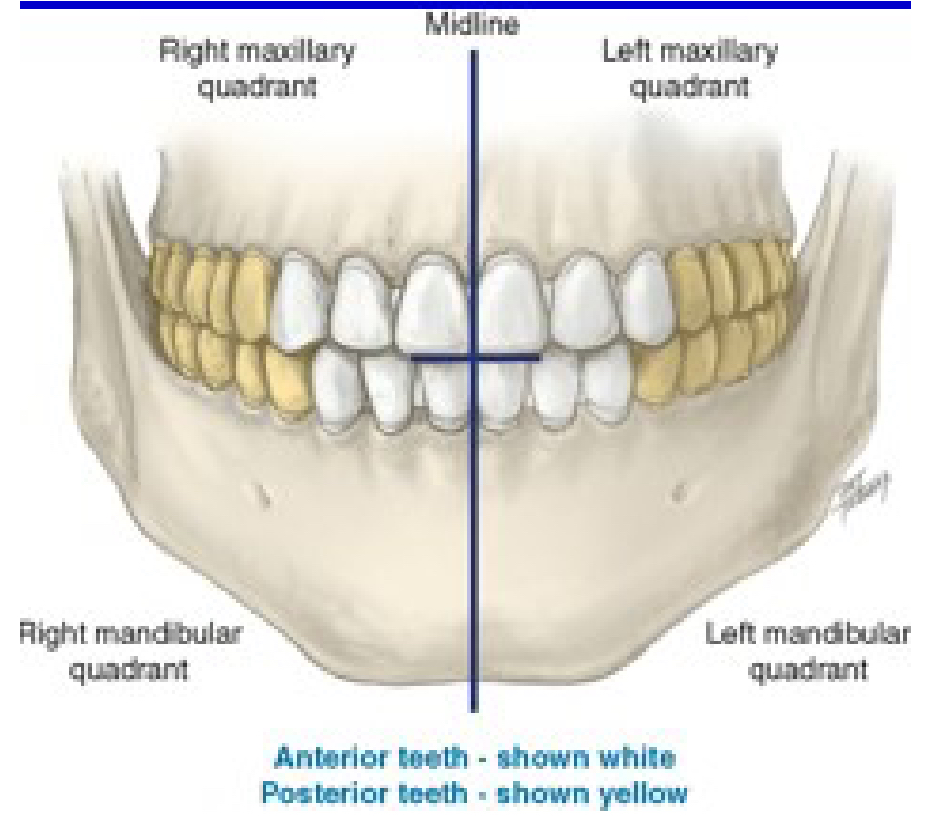
How many quadrants are in the entire oral cavity?
4
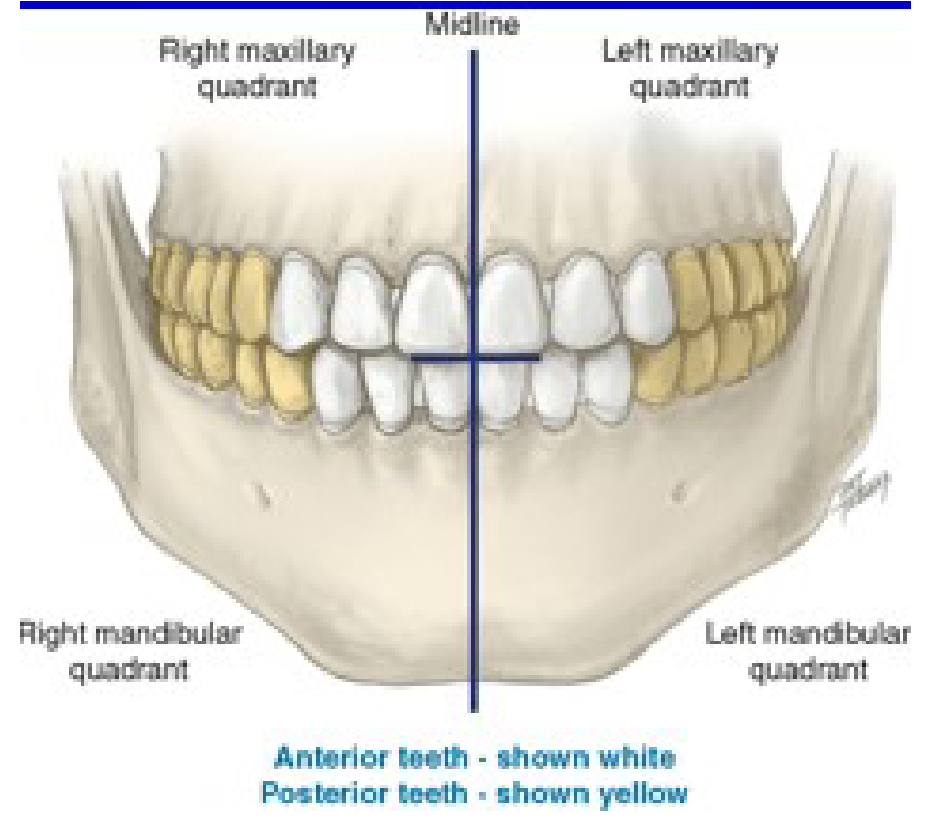
Right maxillary
Quad 1
Upper Right (UR)
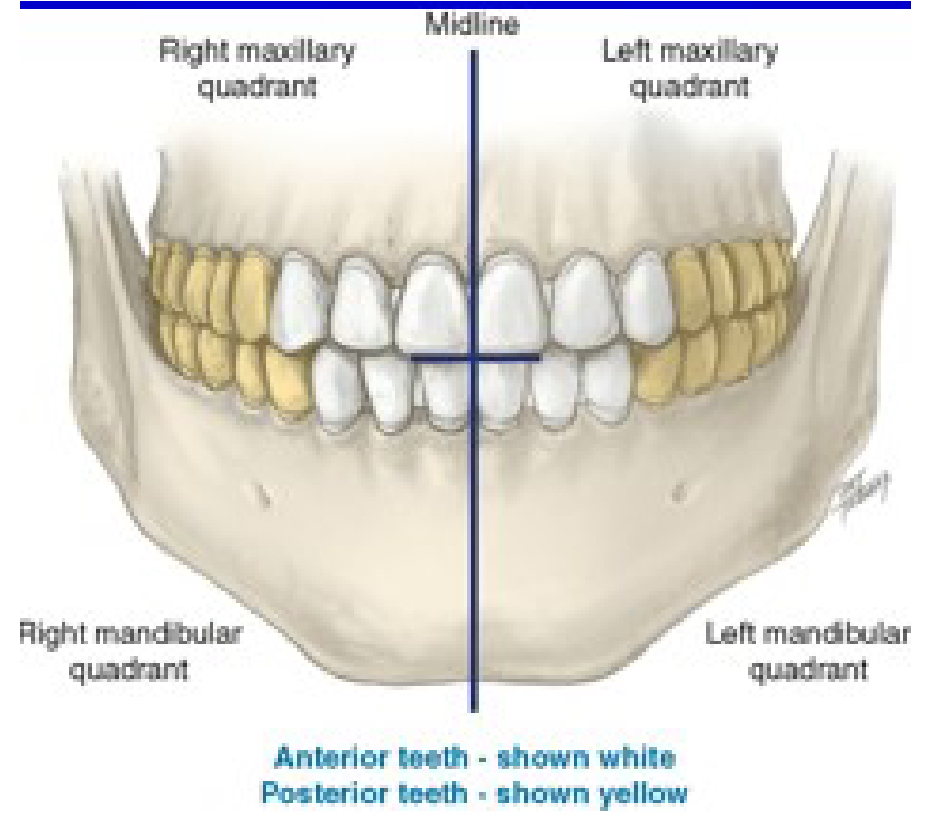
Left maxillary
Quad 2
Upper Left (UL)
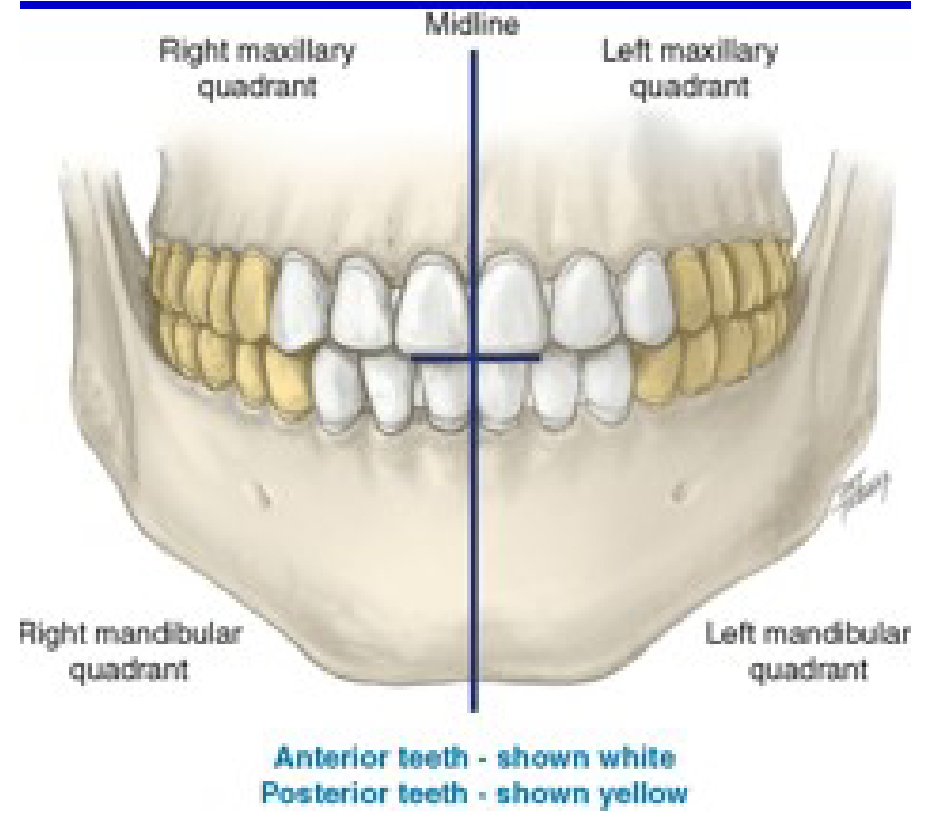
Left mandibular
Quad 3
Lower Left (LL)

Right mandibular
Quad 4
Lower Right (LR)
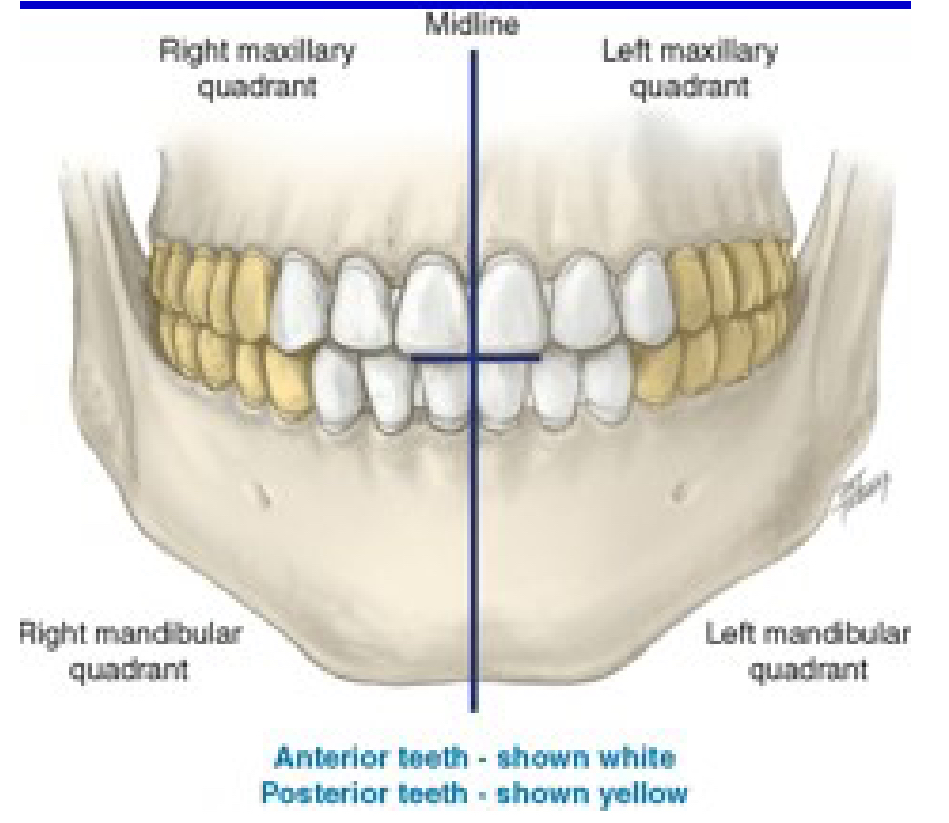
Which one is the anterior teeth?
White

Which one is the posterior teeth?
Yellow
What does the D-A-Q-T System stand for?
D
Dentition
Permanent or Primary Tooth?
A
Arch
Maxillary or mandibular?
Q
Quadrant
Left or right?
T
Tooth type
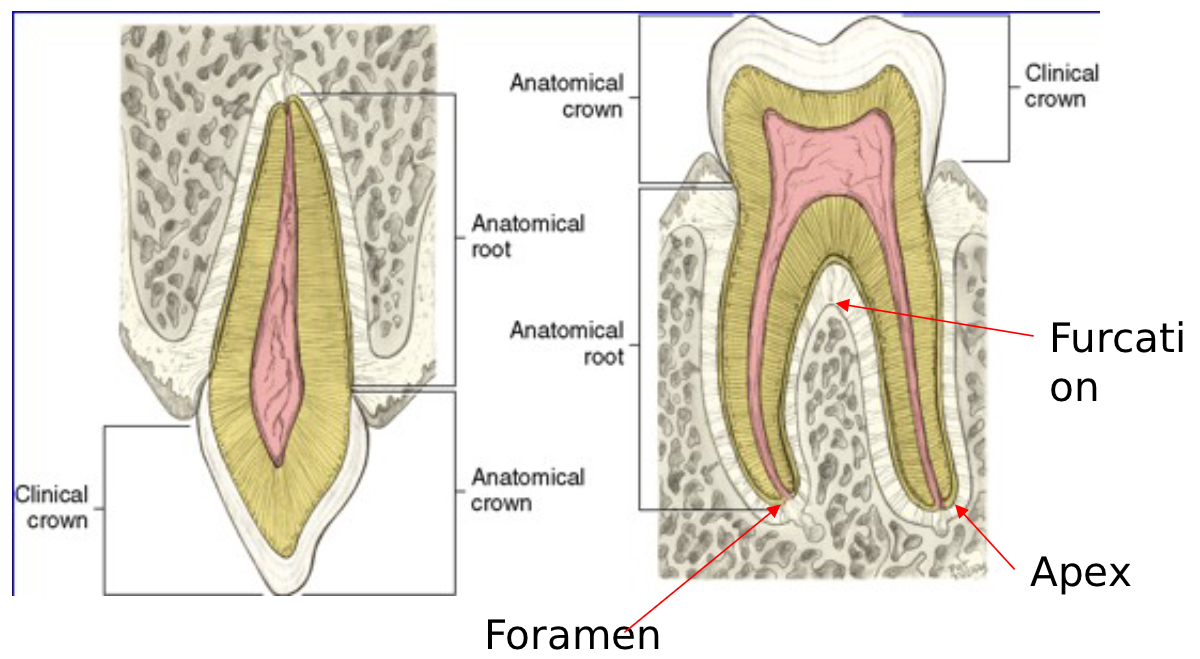
Parts of the Tooth: Crown - Anatomic
Part of the tooth covered by enamel
96% mineralized
Dentin underneath
70% mineralized
Remains constant even if patient undergoes gingival recession (shrinking)
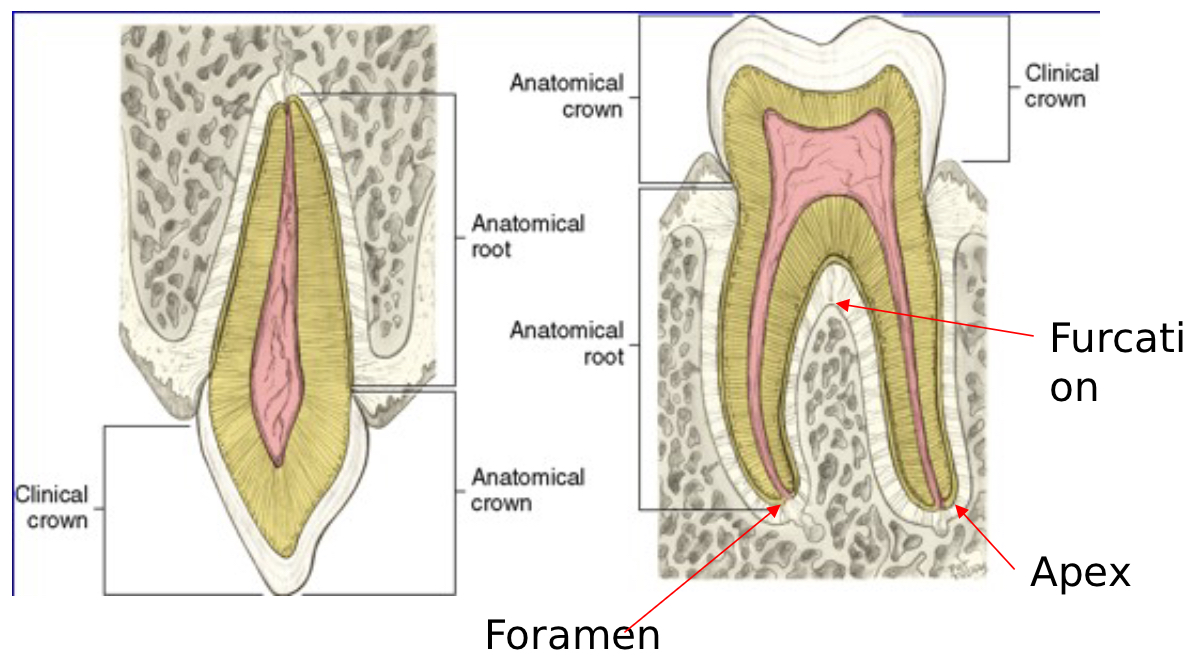
Clinical
Portion of tooth that is visible in the oral cavity
Parts of the Tooth: Root
Covered with cementum
50-65% mineralized
Dentin underneath
Apex
Rounded end of the root
Foramen
Opening at the apex in which blood vessels and nerves enter
Furcation
Area in where the root divides
Root axis line (long axis)
Imaginary line that bisect the root and crown into equal halves

Tissues of the Tooth: Pulp
Innermost noncalcified tissue containing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves
Pulp canal
Pulp chamber
Pulp horns
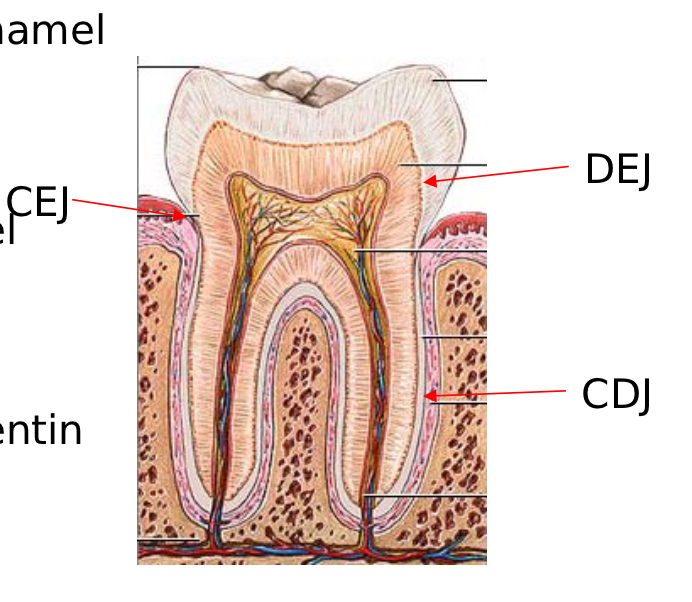
CEJ
Cementoenamel Junction
Junction of cementum and enamel
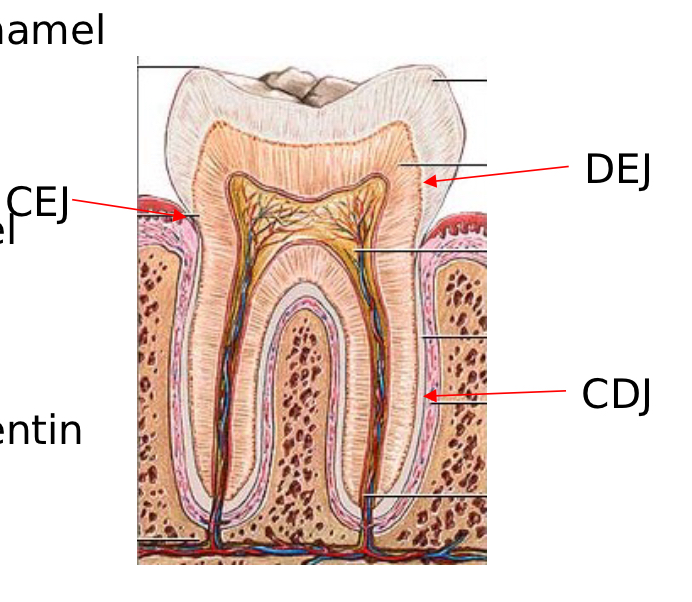
DEJ
Dentoenamel Junction
Junction of dentin and enamel
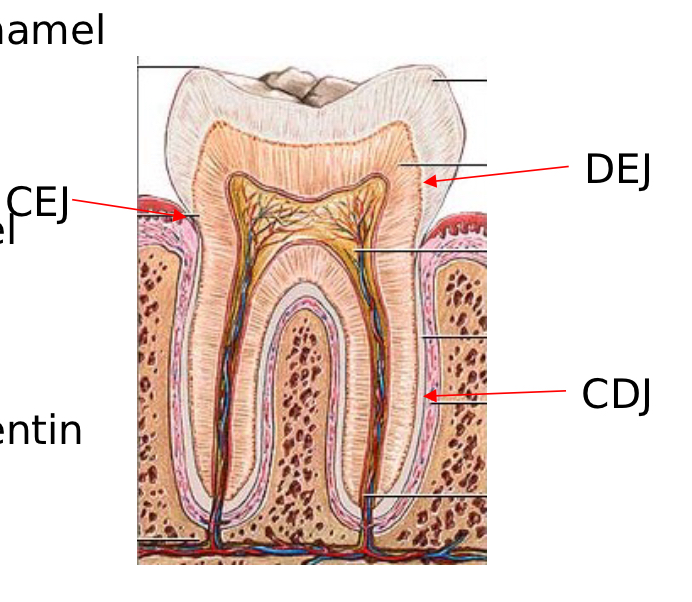
CDJ
Cementodentin Junction
Junction of cementum and dentin
Occlusal
Chewing surface of posterior teeth
Incisal
Biting surface of anterior teeth
Cusp
Large, rounded elevated area of enamel
Ridge
Rounded, linear elevation of enamel
Groove
Narrow linear depression
Fossa
Shallow, broad depression
Pit
Sharp, pointed depression generally located at the junction of developmental grooves
Facial
Toward the face
Labial
Toward the lips (facial surfaces of anterior teeth)
Buccal
Toward the cheeks (facial surfaces of posterior teeth)
Lingual/Palatal
Surface toward the tongue/palate
Proximal
Toward adjacent teeth
Mesial
Toward the midline
Distal
Proximal surface farthest from the midline
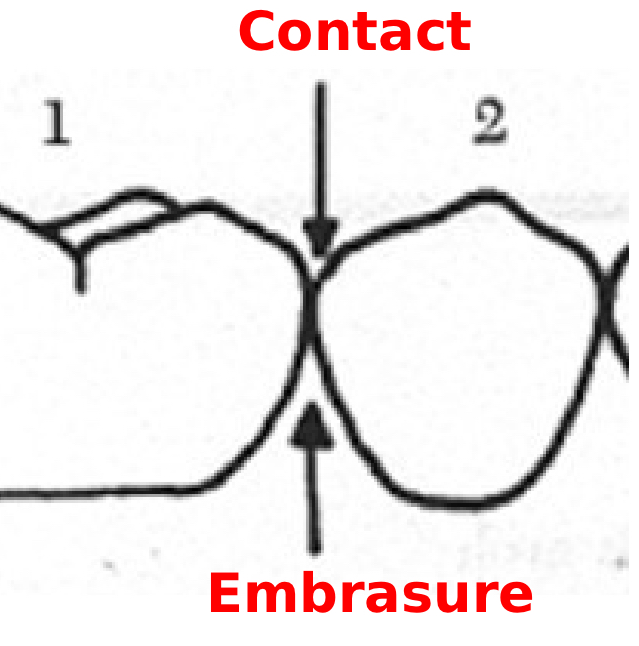
Contact Area
Area that touches the adjacent tooth in the same arch
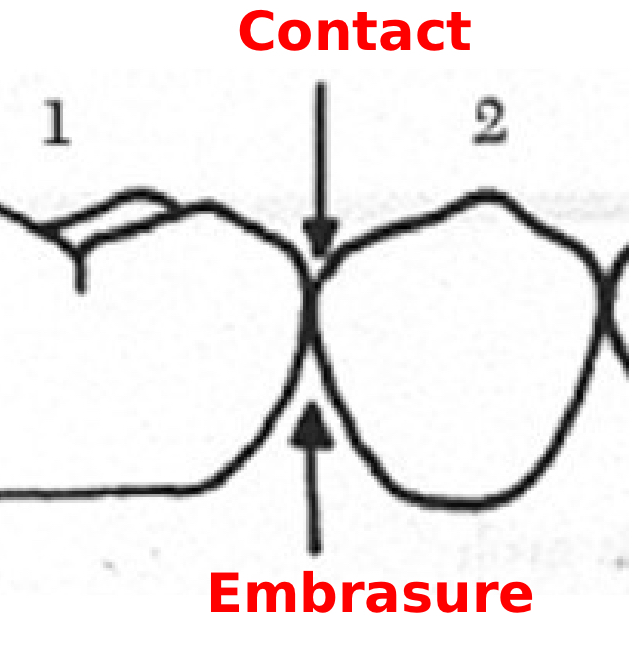
Embrasure
The interproximal space between teeth that consist of triangular spaces