Chapter 14: Skin, Hair, and Nails Assessment
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
function of skin
protection, prevents penetration, perception, temperature regulation, identification, communication, wound repair, absorption and excretion, production of vitamin D
older adult considerations
perspiration, flexibility, and mobility decreases
increased risk for pressure injury
paler skin
skin lesions
drier, coarser, and slower hair growth
drier and less turgor
objective assessment key points
◦ Inspect skin color, temperature, moisture, texture.
◦ Check skin integrity.
◦Be alert for skin lesions.
◦ Evaluate hair condition for loss or unusual growth.
◦Note nail bed condition and capillary refill.
inspection of skin
coloration
odors
any color variations
skin integrity
lesions
pallor
Extreme or unnatural paleness
cyanosis
bluish discoloration of the skin
Acanthosis nigricans
thickening and darkening of skin near axillary region, A/w Diabetes Type II and gastric carcinoma
erythema
redness of the skin
palpation of skin
texture: smooth and even
thickness
moisture
temperature
mobility and turgor
edema
assessment of scalp and hair
◦ General color and condition
◦ Cleanliness, dryness or oiliness, parasites, lesions
◦ Amount and distribution of scalp, body, axillae, pubic hair
assessment of nails
Inspect for color, shape, contour, thickness
assess nail angle
Note grooming, use of polish, false nails, and nail biting
Palpate texture, consistency, and cap refill
seborrheic keratosis
a benign skin growth that has a waxy or "pasted on" look
cutaneous tag
raised papule with a depressed center
cutaneous horn
hard epidermal projection often seen on senior citizens
cherry angiomas
ruby red papules
risk for pressure injuries
◦ Prolonged pressure to body (bony prominences)
◦Decreased/absent perception or sensation
◦Decreased/absent mobility
◦ Increased moisture
◦Increased/decreased nutrition
◦ Friction or shearing forces
◦ Fragile tissues and skin due to age, vascular incompetence, diabetes, mellitus, body weight
stage 1 pressure injury
non-blanchable erythema of intact skin
stage 2 pressure injury
partial thickness skin loss with exposed dermis
stage 3 pressure injury
full thickness tissue loss with visible fat
stage 4 pressure injury
Full-thickness skin and tissue loss with exposed or directly palpable fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage or bone in the ulcer. Slough and/or eschar may be visible.
unstageable pressure injury
obscured full-thickness skin and tissue loss
reducing risk for pressure injuries
inspect skin daily
bathe with mild soap or other agent with warm water
use moisturizers
avoid vigorous massage
careful positioning
incontinence care
macule vs patch
both:
•Small, flat, nonpalpable skin color change
•Skin color may be brown, white, tan, purple, red
macule:
>1cm and circumscribed border
patch: greater than 1cm and irregular border
papule vs plaque
both are raised, defined, any color, solid mass
papule is < 0.5 cm, circumscribed border
plaque is > 0.5 cm
ex of papules
elevated nevi, warts, lichen planus
ex of plaques
psoriasis, eczema, actinic keratoses
nodule vs tumor
both: elevated, solid palpable mass that extends deeper into dermis than papule
nodule: 0.5 to 2 cm and circumscribed
tumors: greater than 1 to 2 cm and do not always have sharp borders
vesicle vs bulla
both: Circumscribed elevated, palpable mass containing serous fluid
vesicle: less than 0.5 cm
bulla: greater than 0.5 cm
ex of vesicle
Herpes simplex/zoster, Varicella (chicken pox), poison ivy and second-degree burn
ex of bulla
Pemphigus, contact dermatitis, large burn blisters, poison ivy, and bullous impetigo
wheal
Elevated Mass with transient borders
Often irregular
Size and color vary
Caused by movement of serous fluid into the dermis
Does not contain free fluid in a cavity (like a vesicle)
Ex. Urticaria (hives) and insect bites
pustule
Pus-filled vesicle or bulla
Ex. Acne, impetigo, furuncles and carbuncles
cyst
Encapsulated fluid-filled or semisolid mass Located in the subcutaneous tissue or dermis Ex. sebaceous cyst and epidermoid cyst
erosion
Loss of superficial epidermis that does not extend to the dermis. Depressed, moist area.
ulcer
Skin loss extending past epidermis, with necrotic tissue loss. Bleeding and scarring possible.
fissure
Linear crack in the skin that may extend to the dermis and may be painful. Ex. chapped lips or hands and athlete's foot. Interdigital tinea pedis with fissures and maceration is pictured below.
petechia
Round red or purple macule that is 1 to 2 mm in size. Secondary to blood extravasation and associated with bleeding tendencies or emboli to skin
ecchymosis
Round or irregular macular lesion Larger than petechial lesion Color varies and changes: black, yellow, and green hues. Secondary to blood extravasation Associated with trauma and bleeding tendencies.
hematoma
A localized collection of blood creating an elevated ecchymosis Associated with trauma.
spider angioma
Red arteriole lesion with a central body with radiating branches Usually noted on the face, neck, arms, and trunk Rare below the waist Compression of the center of the arteriole completely blanches the lesion. Associated with liver disease, pregnancy, and vitamin B deficiency.
Telangiectasia
Bluish or red lesion with varying shape (spider-like or linear) found on the legs and anterior chest. Does not blanch when pressure is applied.
linear configuration
straight line as in a scratch or streak
ex dermatographism
angular configuration
Circular lesions. An example is tinea corporis.
clustered configuration
Lesions grouped together Ex. is herpes simplex
discrete configuration
Individual and distinct lesions. Ex. multiple nevi.
nummular configuration
Coin-shaped lesions Ex. nummular eczema
confluent configuration
Smaller lesions run together to form larger lesion Ex. tinea versicolor
longitudinal ridging
Parallel ridges running lengthwise. May be seen in the elderly and some young people with no known etiology.
half and half nails
Nails that are half white on the upper proximal half and pink on the distal half. May be seen in chronic renal disease.
pitting nails
seen with psoriasis
Koilonychia
Soft spoon nails with a concave shape that appear scooped out.
From iron deficiency anemia, endocrine or cardiac disease
yellow nail syndrome
Yellow nails grow slow and are curved may be seen in aids and respiratory syndromes
paronychia
infection around the nail
types of skin cancer
Melanoma: African Americans, Asians, and Hispanics are susceptible.
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): more common in Whites
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): more common in darker skin
skin cancer risk factors
sun exposure
moles
fair skin
age
family history
male
HPV
alcohol intake
smoking
inadequate niacin
skin cancer ABCDE
A-asymmetry
B-borders
C-color
D-diameter
E-elevated
MRSA
Type of infection resist to many antibiotics May be hospital-acquired infection (HAI) or community-acquired infection
risk factors for MRSA
• Recent or prolonged hospitalization
• Residence in a long term care facility
• Recent antibiotic therapy
• HIV infection
• Men who have sex with men
• Injection drug use
• Hemodialysis
• Living with many people: jail
• Sharing needles, razors, or sports equipment
• Diabetes
• Swine farming
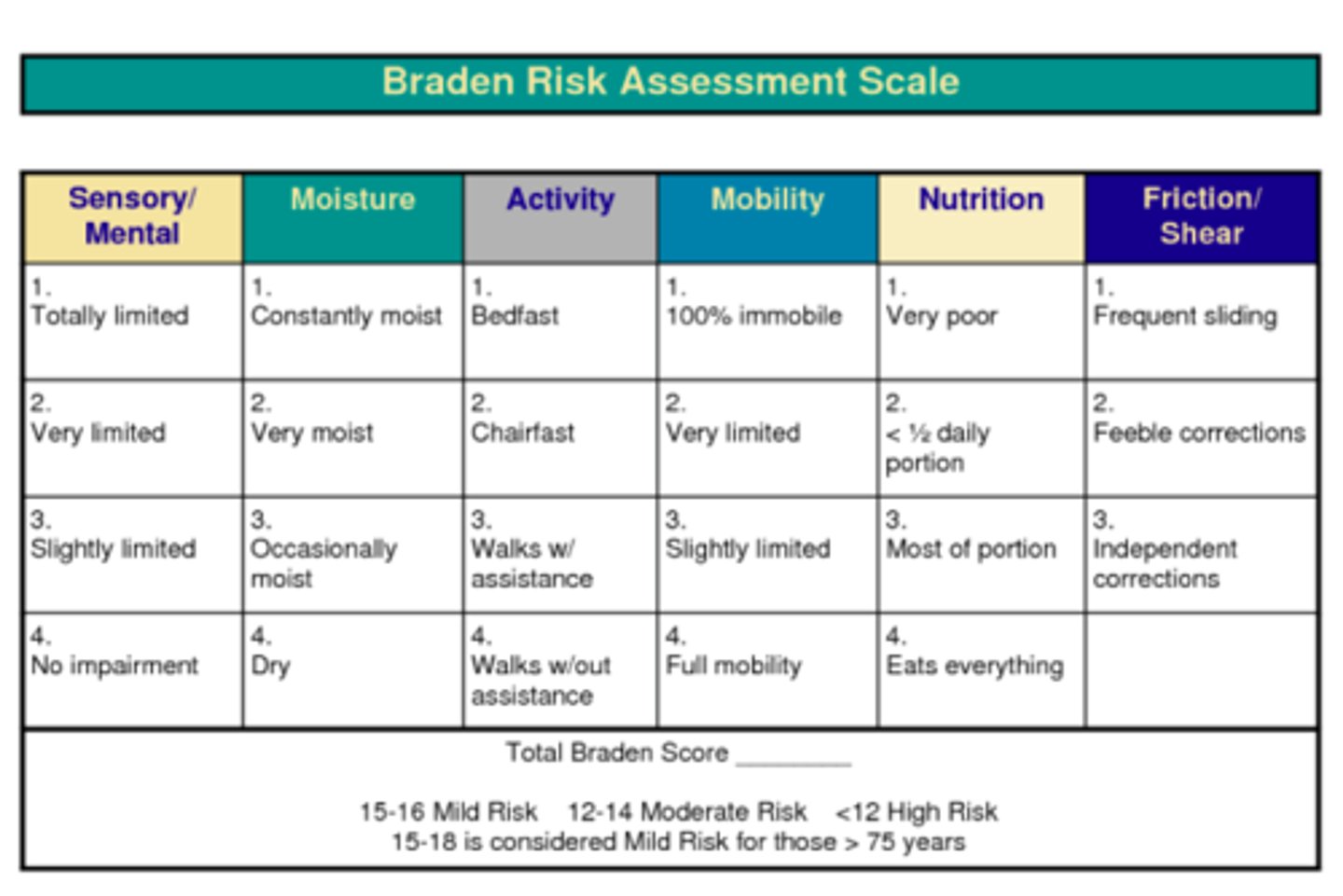
Braden scale
sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, friction and shear