Principles of Reuse
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
How to Write Scalable Code
Integrate high-quality third-party classes into your code
Write reusable code. Assume that others will integrate your classes into their applications
Libraries
collections of prewritten, precompiled code
Procedural languages provide a sets of functions
Object Oriented languages provide sets of classes
C++ is half and half
Anyone can create one
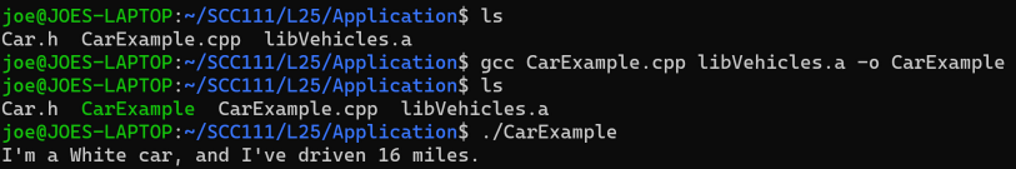
Creating a Library
creating is simple
designing a good one is quite hard
create your classes, and C functions as normal
separate out your function and class declarations into header files
separate your function/method implementation into .cpp files
do NOT include a main function
compile your code with the -c flag
this means "compile only", and does not attempt to create a final, executable program… instead you will get one or more object files. (.o files)
Using a Custom Library
add the precompiled .a file when we compile the application (the thing with a main method in it)
you can add as many libraries as you like on the command line
this provides strong decoupling of library code from application code…
different programmers can develop the different parts at different times
C++ Standard Libraries
<iostream> library that deals with basic input and output
Imported using #include <iostream>
It serves as a modern alternative to the stdio.h library (printf and scanf)
<string> library provides the string type
<regex> <queue> <stack> <list> <map> <strstream> <utility>
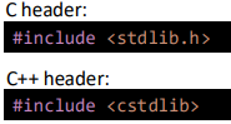
From C:
<cstring> provides string related functions (string.h)
<cmath> provides cos(), sin(), round(), sqrt(), pow() and more
<cstdlib> provides conversion, memory handling, sorting, search ..
iostream - What’s New
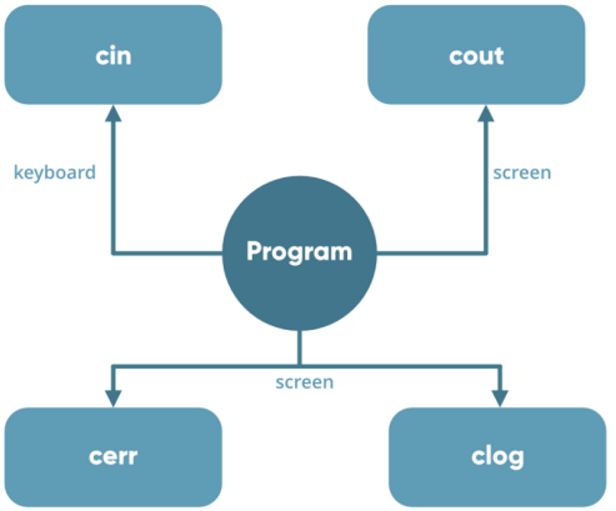
cin: Equivalent to scanf for input
cout: Equivalent to printf for output
cerr: Used for printing errors
clog: Employed for logging purposes
Namespaces
The C++ standard library uses a namespace call std
Namespaces provide space where we can define or declare identifiers. i.e. variables, methods and classes
A namespace is designed to differentiate functions, classes, variables with the same name available in different libraries
In essence, a namespace also defines a scope
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << "Enter your full name: ";
char name[50];
std::cin >> name;
std::cout << "Hello, " << name << "!" << std::end1;
}The string Class
In C, we represent strings as a null terminated sequence of chars in memory and use a pointer to the start of that memory to refer to it (char *)…
This can be a bit limiting however…
We either used fixed length arrays
Or need to deal with dynamic memory allocation (malloc/free)
C++ wraps this functionality in the string class
The string class definition can be imported using #include
string provides access to a wide range of methods useful for string manipulation