Health Literacy and Occupational Therapy
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What do patients have the right to understand?
Patients have the right to understand health care information that is necessary for them to safely care for themselves
What do patients have the right to choose?
Patients have the right to choose among available alternatives
What do health care providers have a duty to provide?
Information in simple, clear, and plain language
What do health care providers have a duty to check before ending the conversation?
That patients have understood the information
As allied health professionals, what do occupational therapist's have the responsibility to ensure?
Highest quality of care for all patients
True or False: Each practice area is unique and each physical facility presents its own distinct barriers and limitations to health literacy.
True
What term can be defined as the ability to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions and follow instructions for treatment?
Health literacy
Health Literacy
Ability to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions and follow instructions for treatment
2 Types of Health Literacy
1. Personal
2. Organizational
What type of health literacy can be defined as the degree to which individuals have the ability to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others; personal and organizational?
Personal health literacy
Personal Health Literacy
The degree to which individuals have the ability to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others
What type of health literacy can be defined as the degree to which organizations equitably enable individuals to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others; personal and organizational?
Organizational health literacy
Organizational Health Literacy
The degree to which organizations equitably enable individuals to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others
Where does the disconnect in health literacy lie?
Patient ability and health care communication
What is the average reading level?
8th grade
What does poor health literacy lead to?
Confusion and a feeling of helplessness
What impact does poor health literacy have on healthcare?
Use services more
Increase healthcare costs
How can clinicians create a shame-free environment?
Adopt an attitude of helpfulness
Convey a safe, nonjudgement environment
Be alert to clues (e.g. incomplete forms)
Develop forms that screen for health literacy
Review patient medications with them (e.g. brown bag test)
Engage entire staff
How can clinicians mitigate the barriers and limitations of poor health literacy?
Create a shame-free environment
Improving communication skills
How can clinicians improve their communication skills?
Slow down
Convey most important concepts
Use living room/plain language that anyone can understand
Explain through examples and visual aids
Involve family members
Do not ask them if they understand
Employ the teach-back method
According to the 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy, what percent of Americans can not read or understand complicated and complex information including health and medication information?
14%
What 3 types of health literacy were surveyed in the 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy?
1. Prose (e.g. editorials, news stories, brochures)
2. Document (e.g. job applications, maps)
3. Quantitative (e.g. measurement, percentages, graphs)
Results of the 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy
Proficient - 13% (e.g. read, and understand all text)
Intermediate - 44% (e.g. reading/understanding is challenging)
Basic - 29% (e.g. everyday reading, basic pamphlets)
Below Basic - 14% (e.g. read short set of instructions)
Program for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies (PIAAC)
A program designed to assess and compare adults' skills in participating countries over a broad range of abilities, from reading simple passages to complex problem-solving skills, and to collect information on an individual's skill use and background
National Healthcare Initiatives for Health Literacy
Institute of Medicine ("A Prescription to End Confusion")
Healthy People 2010, 2020, 2030
National Action Plan to Improve Health Literacy 2010
Affordable Care Act, 2010
What 4 skills are included in health literacy?
1. Reading
2. Verbal comprehension
3. Numeracy
4. Analyzing information
Are health literacy skills static or dynamic?
Dynamic
Health literacy skills change depending on what 5 factors?
1. Age
2. Health
3. Education
4. Previous experiences
5. Culture
What is an important part of an occupational therapist's job?
To ensure the patient has understood their role in the rehabilitation process
How can occupational therapist's ensure the patient has understood their role in the rehabilitation process?
By matching written materials and verbal communication to the patient's level of comprehension
When is the self-management of healthcare possible?
Once the patient is offered information that is clear and appropriate for their level of understanding
What do therapists routinely issue to their patient? Why?
Written information to support their home programs
What does the patient's ability to benefit from the written information provided to them from their therapist depend on?
Their level of understanding
What does the degree of basic literacy skills affect?
The extent of their comprehension
How can occupational therapists promote health and contribute to efforts to create a more health-literate society?
Through the development and use of health education approaches and materials that are understandable, accessible, and usable by the full spectrum of consumers
What does health literacy affect?
Individuals' ability to make health decisions and actively participate in health-related activities
What does the definition of health literacy include?
Gather, interpret, and use information to make health decisions
Individual ability and professional communication skills
Context/environment in which information is being presented
What does health literacy promote when all aspects are considered?
Participation
Empowerment
Control over daily life
What is low health literacy a strong predictor of?
Health status
Specific Issues Related to Low Health Literacy
Less awareness of preventative health measures
Less knowledge of medical condition and self-care
Less healthy behaviors
Poorer health status, worse health outcomes
Increased costs for health care system
What populations are most commonly affected by low health literacy?
Older adults
Low income
Did not finish high school
Those whose first language is not English
Individuals living in poverty
Can a therapist tell if a person has low health literacy by looking at them; yes or no?
No
What are 3 quick screening tools used to inform a therapist about a patient who may have low health literacy?
1. Word recognition
2. Reading
3. Numeracy
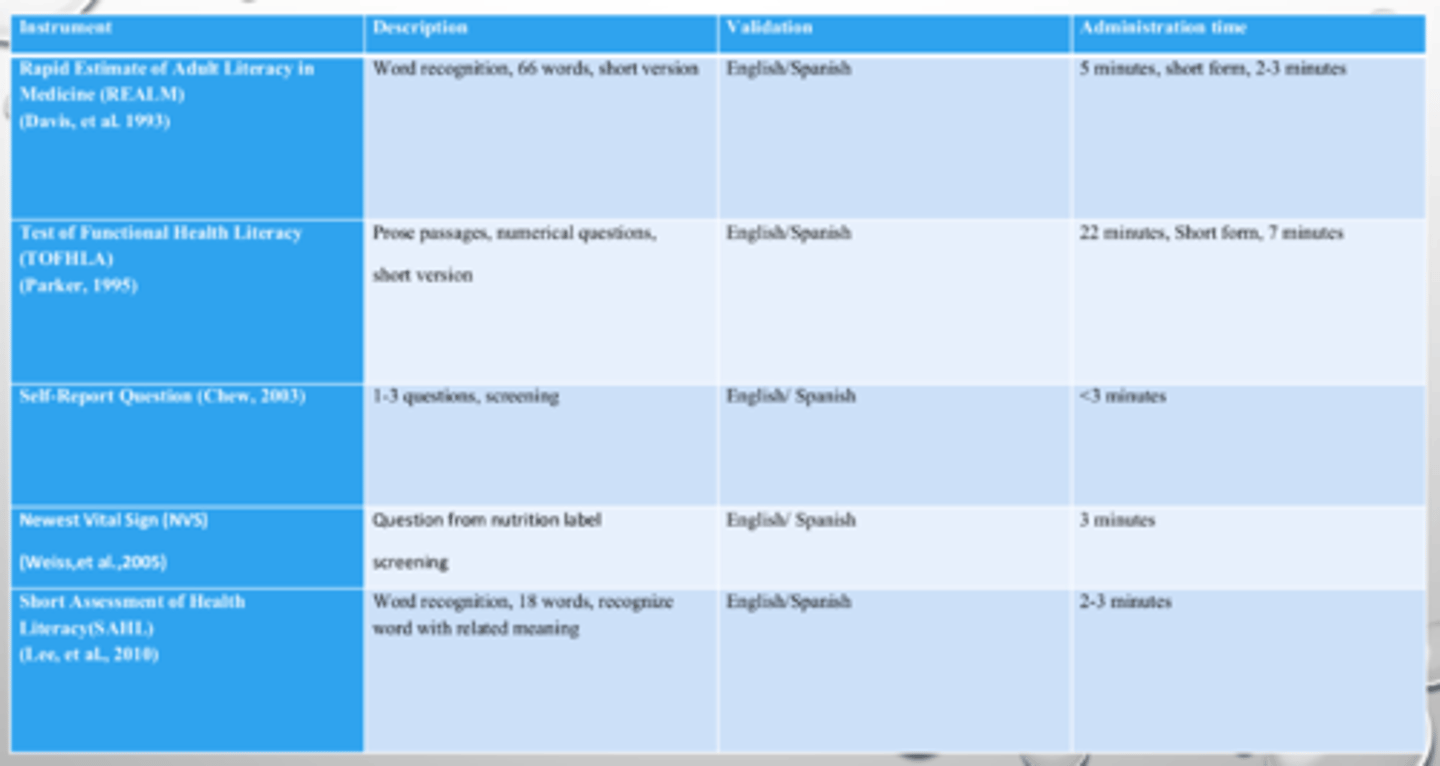
Health Literacy Assessments
Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine (REALM)
Test of Functional Health Literacy (TOFHLA)
Self-Report Question
Newest Vital Signs (NVS)
Short Assessment of Health Literacy (SAHL)
CHEW Self-Report Questionnaire
BRIEF Health Literacy Screening Tool
Short-Form Health Literacy
Organization Health Literacy Assessments
Health Literacy Environment of Hospitals and Health Centers
Building Health Literate Organizations
Health Literacy Environment Activity Packet
Health Literacy Environment of Hospitals and Health Centers
An assessment tool for identifying facilitating factors and barriers to information, care, and services
Building Health Literate Organizations
An assessment tool that evaluates a patients capacity for achieving change
Health Literacy Environment Activity Packet
An assessment tool based on first impressions from when patients first walk-in the clinic
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) Health Literacy Universal Precautions Toolkit
A toolkit used to help primary care practices reduce complex health care, increase patient understanding of health information, and enhance support for patients of all health literacy levels
What does the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) Health Literacy Universal Precautions Toolkit address?
Path to improvement
Spoken communication
Written communication
Self-management and empowerment
Supportive systems
Why do patients find it hard to communicate in healthcare?
Fear and intimidation
Embarrassment out of not understanding diagnosis
Not feeling well
What should the therapist do if the patient is not feeling well enough to participate in therapy?
Continue treatment at another time
Provide them with contact if questions arise
How many aspects of their diagnosis should a therapist discuss with the patient if time permits during the treatment session?
1-3 main aspects (and how they will manage the diagnosis)
What should the therapist discuss with friends or family members of the patient with their permission?
Health information (using the patient's native language)
Red Flags Indicating Low Health Literacy
Reports that they don't have their glasses to read the handout
Can only identify pills by color/shape, not label information
Not compliant with medication directions (e.g. crushing pills)
Can not complete registration forms
Miss numerous appointments or may come on the wrong day
Can not explain diagnosis, prognosis, or reason for surgery
Can not demonstrate their exercises as instructed
Trouble accurately reporting medical history
What should therapists encourage their patients to do?
Ask questions
How can therapists encourage their patients to ask questions?
Provide pen and paper to write questions down
Note patient responses during appointments (e.g. confusion)
Inform them that there are not any bad or stupid questions
Follow methods for better communication (e.g. pictures)
Do not use medical jargon (e.g. plain language is better)
Explain terminology if using medical jargon
Limit talking points (keep discussion brief)
Discuss the 3 most important things first
How can a therapist be sure that their patient understands what they are trying to teach them?
By using the teach-back technique
Teach-Back Technique
An approach to determine what the patient understands and what questions or concerns they may have about the information shared
What does the teach-back technique allow?
Interactive communication loop
Interactive Communication Loop
A process in which participants alternate positions as sender and receiver in order to ensure the message has been received
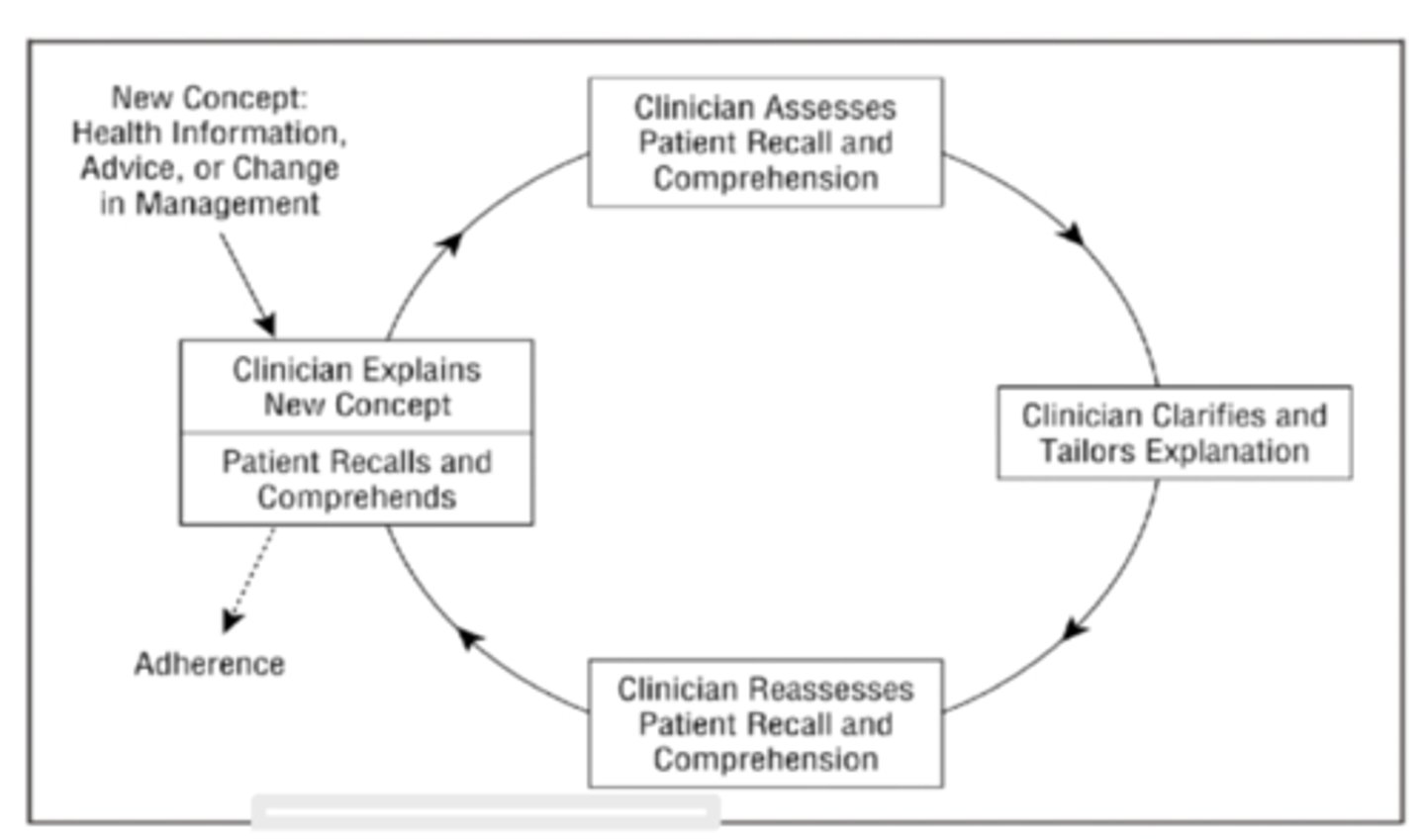
10 Teach-Back Techniques
1. Have a caring tone (no shame)
2. Always make eye contact
3. Use plain language
4. Ask the patient to explain or repeat back
5. Confirm comprehension (use open-ended questions)
6. Do not use questions that can be answered with "yes" or "no"
7. Assure the responsibility to explain clearly is on the therapist
8. Explain AGAIN if the patient can not teach-back correctly
9. Printed materials should be easy to read and understand
10. Include patient response to teach-back in notes
What has research shown a discrepancy between?
Written patient education and their health literacy level
Are informational materials, including internet information, written above or below the reading level of most patients?
Above
How can therapist's be sure that their informational material is appropriate for their patient?
By checking the reading level of their informational material using a formula for reading levels (e.g. Flesch-Kincaid Readability Tool)
Should therapists write at a higher or lower grade level to improve written communication for patients?
Lower
Should written material being shared with the patient be published in small or large font?
Large font
At what grade level should written text be prepared at or below?
6th grade level
Resources for Communication Information
CDC Clear Communication Index
Federal Plain Language Guidelines
Simply Put (e.g. guide for creating easy-to-read materials)
Suggestions to Prepare Clear Language Text
Use plain language
Prepare text at or below 6th-grade reading level
Use large serif/times roman font, at least a 14 point
Incorporate white space in document
Use pictures or drawings to demonstrate information
Always prepare content in the spoken language of the patient
Consider patient’s culture and social norms
Include reputable resources for additional information
Include chunks of material, do not exceed 3 key points
Use short sentences and short paragraphs
Use headings to divide material
Simple charts or bulleted lists are easier to read than lines
In addition to pamphlets and handouts, patients use of what for medical information has increased?
Internet
What are the majority of internet searches for?
Medical conditions
What is our responsibility as therapist's in the use of the internet?
To guide patients to reputable, trusted websites for valid information
Digital Health Literacy
The ability to seek, find, understand, and appraise health information from electronic sources and apply the knowledge gained to addressing or solving a health problem
National Institute of Health (NIH) Recommendations for Evaluating Health Information
Content:
Is the content serious?
Who is the author?
Is the site connected to an organization?
Updated:
Is this internet site updated regularly?
When was it created?
Does it offer links to other current webpages?
Accuracy:
Is the page edited?
Does the site reference other resources?
Is a bibliography included?
Fact-Based:
Is the information factual?
Is it straightforward and without advertising?
What is the purpose of the site?
Is it population, clinical, or scholarly?
10 Attributes/Building Blocks of a Health Literate Organization
1. Leadership/management must make health literacy a priority
2. Conduct assessments to best meet patient needs
3. Train the staff in techniques to address health literacy
4. Seek input from patients and consumers to identify barriers
5. Practice universal precautions (e.g. allocate resources)
6. Use specific strategies for verbal and written communication
7. Design systems to be accessible to all patients (e.g. website)
8. Create all informational material in an easy to read style
9. Address medications and patient self-management
10. Clearly explain costs and charges for services