3.2 Sources of Finance (copy)
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
4 key reasons why businesses need finance
Start-up capital
Working capital
Renewal
Expansion
Internal Sources of Finance
Finance from within the business
Usually involve no cost
However, are finite and will not always be sufficient
External Sources of Finance
Finance from organisations outside of the business
Usually involves increasing debt and paying interest OR selling part of the business (equity)
Can be short-term or long-tem
Sources of Finance table
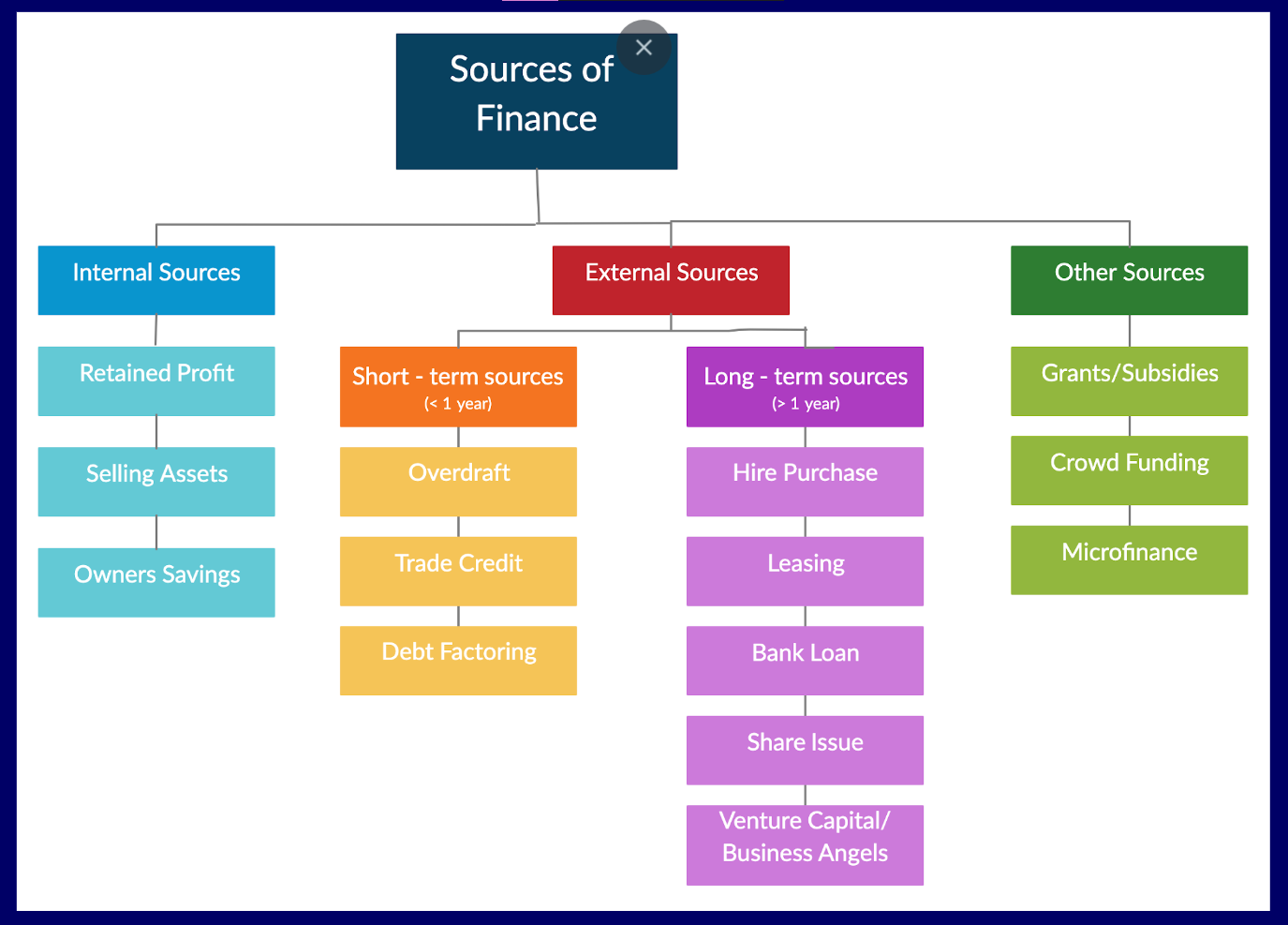
Internal Sources include
Personal Funds/Owners Savings
Retained Profit
The sale of assets
External Sources include:
Trade Credit
Overdraft
Debt Factoring
Leasing
Bank loan
Hire purchase
Business Angel
Share Capital/Share Issue
Mortgage
Grants
Subsidies
Microfinance
Crowdsourcing
Sale of Assets
Internal Source - The business sells assets, usually those that it no longer needs.
Advantages:
You make some sort of revenue selling the things you don't need
If it's a production line, it frees more space for new machinery for example
Disadvantages:
Business could not make a lot of profit from assets
Assets will not sell
Personal Funds/Owners Capital
Internal Source - The owners of the business invest their own personal money into the business. This is often used as a means of funding a start-up
Advantages:
Quick way to get cash
No pressure to repay because its personal funds
Disadvantages:
Finite amount of money depending on the owner
The major disadvantage is that not all owners have additional capital to call on. This method would be used if the money were required long-term and if the amount was not large.
Retained Profits
Internal Source - Rather than paying the business profits out as dividends to shareholders, part or all of the profits are kept in the business to be used as a source of finance.
Advantages:
Advantages include the ability to boost value and set aside funding for emergencies.
Disadvantages:
Yet on the other hand, disadvantages of retained profit include potentially turning off shareholders by retaining money that could be used for dividends.
May take a long time to get enough profit for a big investment
Trade Credit
External Source - Short term - A business does not always have to pay for goods/services received as soon as they receive them, instead they can be given a period of credit by their supplier, normally of around 30-60 days
Advantages:
No interest
Instant access to supplies without having to pay immediately
Disadvantages
usually small amounts
it’s short term so it must be paid off quickly
Overdraft
External Source - Short term - A flexible borrowing facility on a bank current account which is repayable on demand. The bank account of the business is permitted to be negative – i.e. in the red, up to a maximum agreed amount.
Advantages:
Flexible
Only pay for what you use
There are no monthly costs
Disadvantages:
If you have to extend your overdraft, you usually have to pay an arrangement fee.
Your bank could charge you if you exceed your overdraft limit without authorisation.
Debt Factoring
External Source - Short term - A business sells its outstanding customer accounts (those debtors who have not paid their debts to the business) to a factoring company.
The factoring company pays the business 80-90% of the face value of the debts - and then collects the full amount from the customer. If the debt is paid by the customer, the factoring company will pay the remaining amount to the business minus their fee.
Advantages:
Improves cash flow
Saves time and resources
ACCELERATES GROWTH
Disadvantages:
Reduces profits
PUTS BUSINESSES IN TEMPORARY DEBT
Leasing
External Source - Long term - The business rents an asset (equipment/machinery/furniture/vehicle/property) rather than buying it. The business pays a regular amount for an agreed period of time, but ownership of the asset stays with the leasing company.
Advantages:
cheaper to lease assets like equipment, buildings, and machinery
suitable for business customers who do not have the initial capital to buy such assets
repairs and maintenance are the responsibility of the lessor
Disadvantages
Potential early termination liability.
No equity/ownership in the vehicle
Potential end-of-lease costs like excess wear and tear and additional.
Mileage charge (vehicles)
In the long term, leasing will eventually become more expensive than buying the asset
Bank Loan
External Source - Long term - A fixed amount is borrowed from the bank. Repayments are made monthly over an agreed period of time. The interest rate charged is often determined by the amount borrowed, the repayment period and the level of perceived risk
Advantages:
low interest rates
easy and quick access
Disadvantages:
banks may require you to provide collateral
Assets may be taken if the business fails to repay the loan
Increases the gearing of the business
Difficult for a new business to access
Hire Purchase
External Source - Long term - The business makes a downpayment (usually 20-30%) on an asset (usually equipment or vehicles) the remaining balance plus interest is then paid in monthly installments over an agreed period of time (2-5 years)
Advantages:
assets that are expensive can be paid back over time
much easier to get than a bank loan
Disadvantages:
There is interest charged
equipment is not officially owned by the business until the entire fee is paid
Business Angel
External Source - Long term - Wealthy, entrepreneurial individuals provide capital in return for a proportion of the company equity. They take a high personal risk in the expectation of owning part of a growing and successful business. This type of finance tends to be used for high risk, high potential reward investments.
Advantages:
All locations and industries are eligible
Paperwork is minimal
Monthly payments aren't required
Disadvantages:
owner loses some control to the business angel since the business angel takes a proactive role when setting up the business
the organization may eventually have to buy out the stake wonder by the business angels
Share Capital/Share Issue
External Source - Long term - Selling new shares to new investors. For Plcs this will be to the general public and investing institutions through the stock exchange. For Ltds new shareholders must be found privately and agreed between existing shareholders.
Advantages:
can provide a huge amount of finance
Disadvantages:
It dilutes control for the founders – The more shares that are issued, the more shareholders there are who own part of the business.
The business is vulnerable to takeover – As a business grows and sells more shares, it becomes vulnerable to the threat of a takeover.
Other sources of Finance
Grants and/or Subsidies
Crowd Funding
Microfinance
Grants
Other sources of finance - The government or charities provide assistance to qualifying businesses. This can be in the form of cash gifts or sometimes low interest loans. In order to qualify, businesses must apply and prove that they meet certain criteria, often linked to:
Protecting jobs in failing/declining industries
Creating jobs in areas of high unemployment.
Research and development
Providing ‘merit’ goods and/or services
Advantages:
Technically free money (for a very very specific reason)
Domino effect (Once you’ve been awarded one grant, you’re more likely to receive others.)
Disadvantages
Time consuming
Difficult to Receive
Strings Attached (Although grants are free money, they still come with plenty of restrictions and conditions.)
Subsidies
Other sources of finance - Money given to businesses by the government in order to reduce their costs of production. This is often done in order to:
Protect domestic industries from foreign competition
Reduce the price of essential goods and services in order to make them affordable to customers
Advantages:
Inflation control and moderation of supply and demand
Disadvantages
Potential increase in taxes on citizens in subsidizing countries.
Microfinance
Other sources of finance - This refers to the financial services provided to low-income individuals or groups who are typically excluded from traditional banking. It often involves offering credit in the form of small loans, sometimes called microloans or microcredit
Advantages:
helps smallest businesses raise funds to start
collateral free loans
Disadvantages
small loan amount
high interest rate
Crowdsourcing
Other sources of finance - This is when businesses fund a venure without using traditional means, but instead launch a campaign via an internet platform to solicit for small donations from many people.
These usually have set time frames for when money can be raised and disclose specific monetary goals.
Investors may make a donation or a loan, or in some cases will receive rewards or equity in return for their money
Advantages:
creates hype/buzz around the product/business
build customer contacts
saves costs and time
Disadvantages
risk of manipulation
other business’ may copy the idea