OPERATING SYSTEMS QUIZ 2
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
process
a _______ is a program in execution; execution must progress in a sequential fashion. no parallel execution of instructions of a single ______.
text section
program counter
stack
data section
heap
multiple parts of a process
text section
the program code part of the process
program counter
part of the process; current activity including _____, processor registers
stack
part of the process; contains temporary data; function parameters, return addresses, local variables
data section
part of the process; contains global variables
heap
part of the process; containing memory dynamically allocated during run time
passive, active
prorgam is ______ entitty stored on disk (executable file); process is _______
loaded into memory
program becomes process when an executable file is ___________
GUI mouse clicks, command line entry of name
execution of program can start with _____________________, _____________, etc.
one, several
______ can be ________ processes
stack, heap, data, text
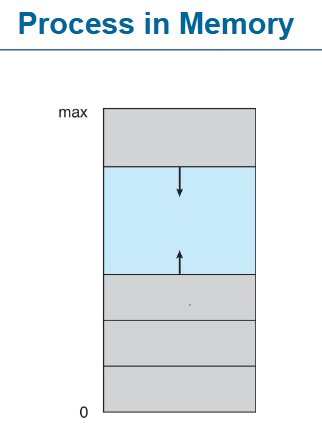
argc, argv
stack
heap
uninitialized data
initialized data
text
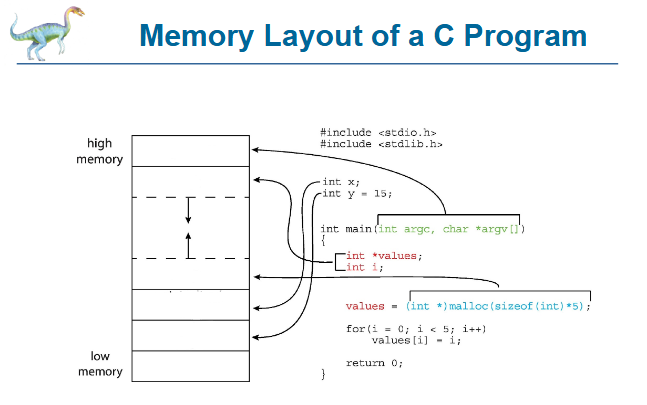
new, running, waiting, ready, terminated
as a process executes, it changes states:
new
process state; the process is being created
running
process state; instructions are being executed
waiting
process state; the process is waiting for some event to occur
ready
process state; the process is waiting to be assigned to a processor
terminated
process state; the process has finished execution
new, ready, waiting, running, terminated
diagram of process state
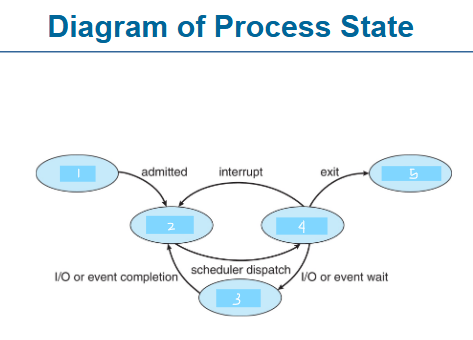
task control block
information associated with each process
process state
program counter
CPU registers
CPU scheduling information
memory-management information
accounting information
I/O status information
process control blocks
process state
process control block
running, waiting, etc.
program counter
process control block
location of instruction to next execute
CPU registers
process control block
contents of all process-centric registers
CPU scheduling information
process control block
priorities, scheduling, queue pointers
memory-management information
process control block
memory allocated to the process
accounting information
process control block
CPU used, clock time elapsed since start, time limits
I/O status information
process control block
I/O devices allocated to process, list of open file
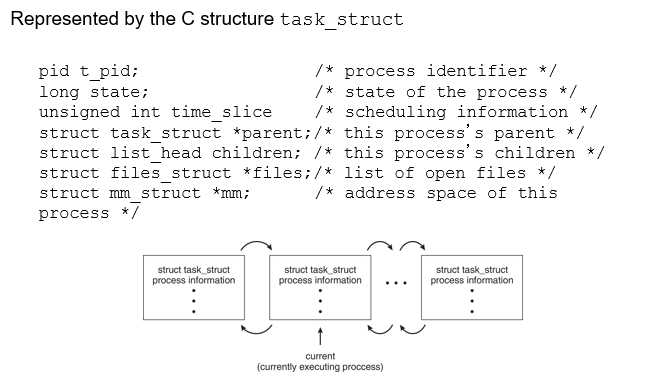
single thread
so far, process has a _____ of execution
process representation in linux
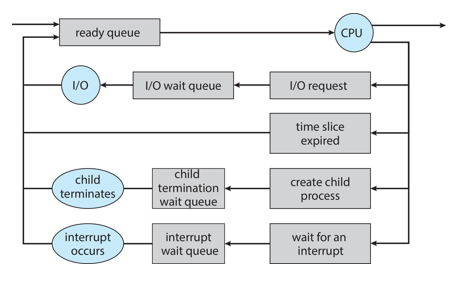
process scheduler
selects among available processes for next execution on CPU core
maximize CPU use and quickly switch processes onto CPU core
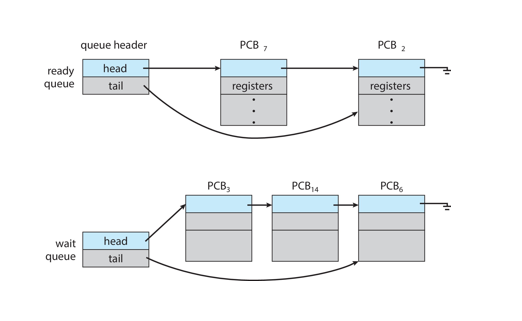
ready queue
wait queue
role of process scheduling;
maintains the scheduling queues of processes
ready queue
set of all processes residing in main memory, ready, and waiting to execute
wait queue
set of processes waiting for an event (i.e. I/O)
ready and wait queues
representation of process scheduling
CPU switch from process to process
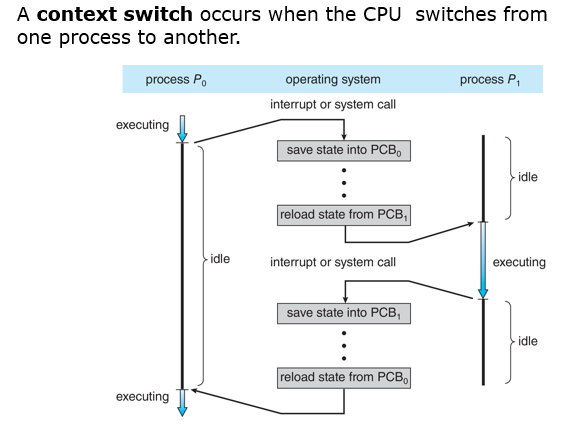
save the state
save state
context switch
when the CPU switches to another process, the sustem must _________ of the old process and load the _______ for the new process via a __________.
foreground process
controlled via user interface
background processes
in memory, running but not on the display, and with limits
process creation
process termination
systems must provide mechanisms for
parent
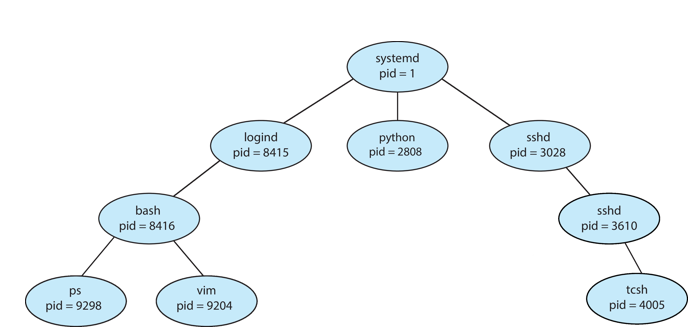
children
tree
_____ process create _______ process which, in turn, create other processes, forming a ______ of processes
process identifier (PID)
process is identified and managed via ________
UNIX process creation
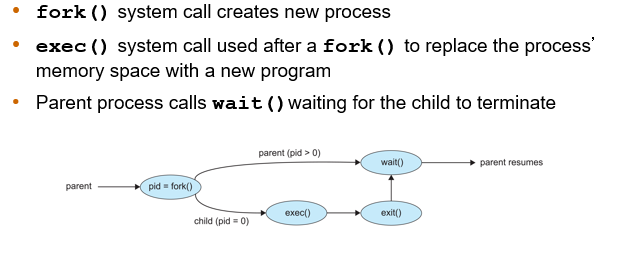
linux tree processes
cascading termination
if a process terminates, then all of its children must also be terminated
all children, grandchildren, etc are terminated initiated by the OS
foreground
visiible
service
background
empty
most to least important android process importance hierarchy
independent or cooperating
processes within a system
information sharing
computation speedup
modularity
convenience
reasons for cooperating processes
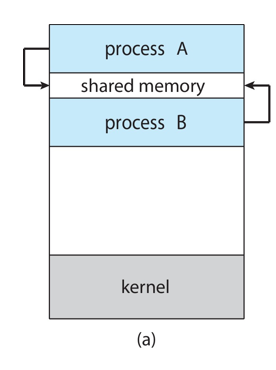
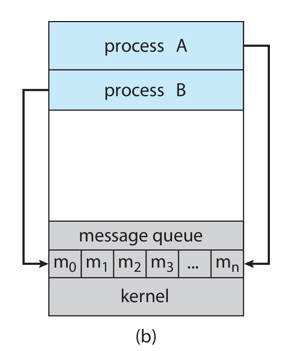
interprocess communication (IPC)
cooperating processes need
shared memory
message passing
two models of interprocess communication (IPC)
shared memory
message passing
unbounded buffer
places no practical limit on the size of the buffer:
producer never waits
consumer waits if there is no buffer to consume
bounded-buffer
assumes that there is a fixed buffer size:
producers must wait if all buffers are full
consumer waits if there is no buffer to consume