Organic Chemistry Exam 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
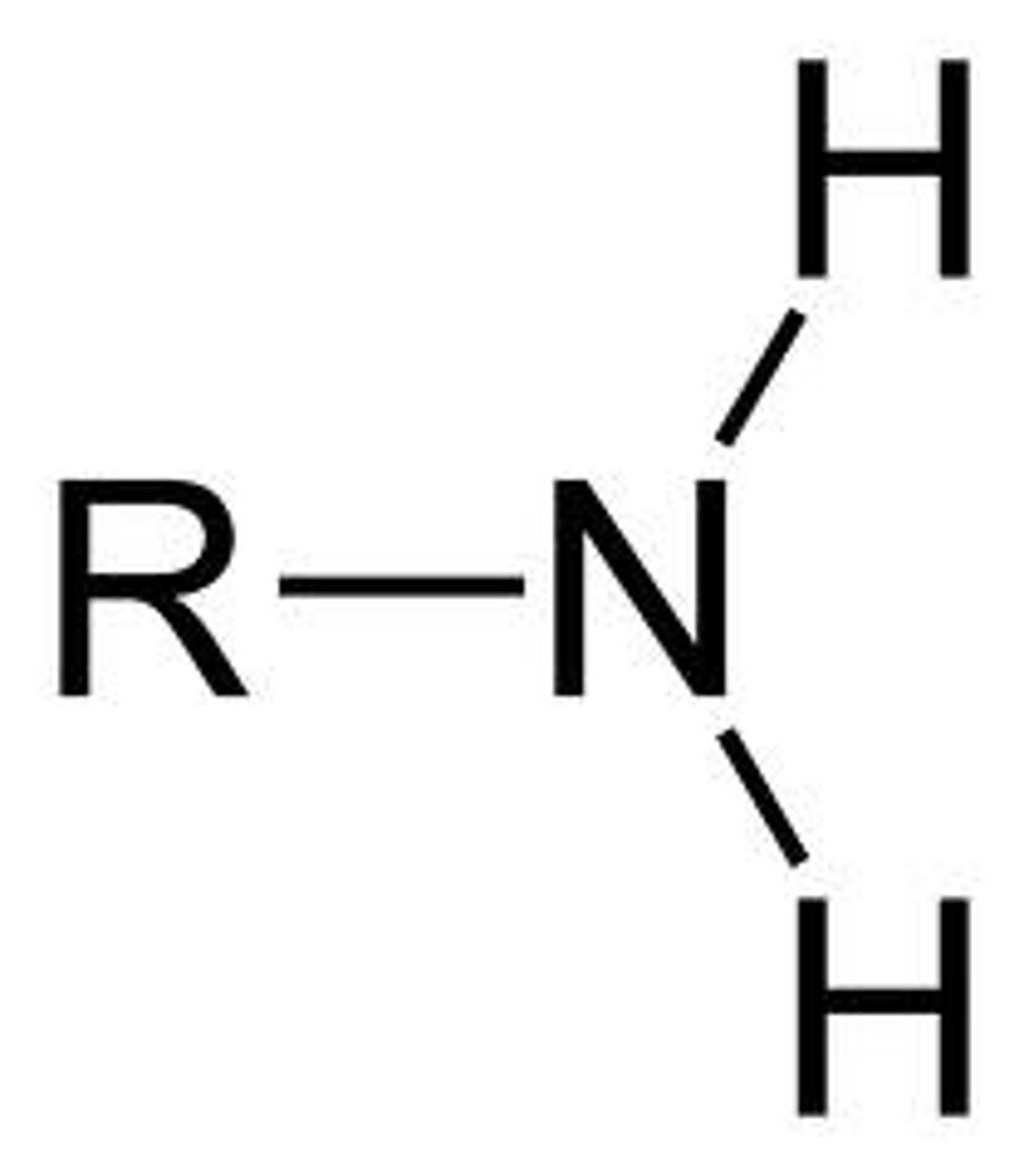
Amine
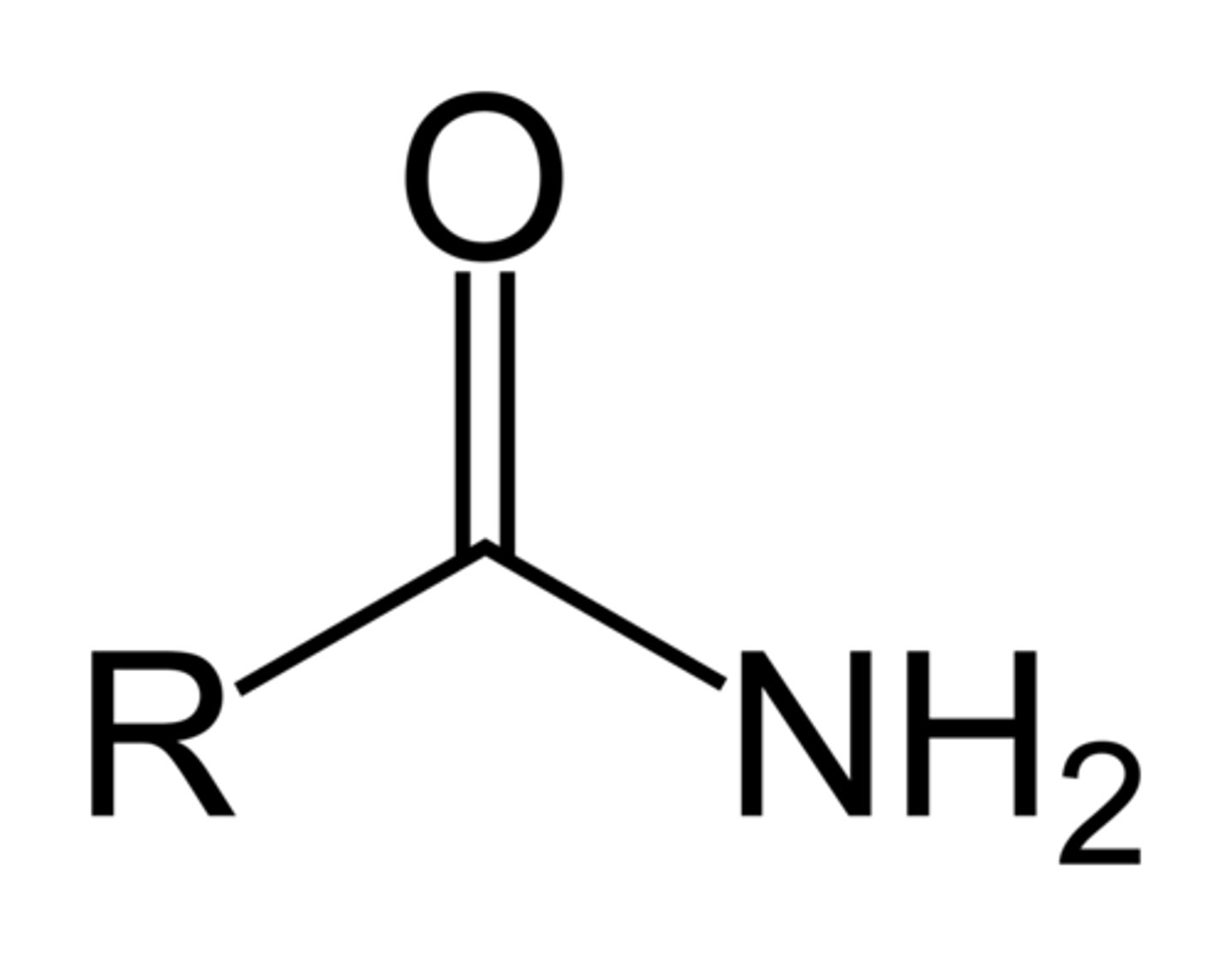
Amide
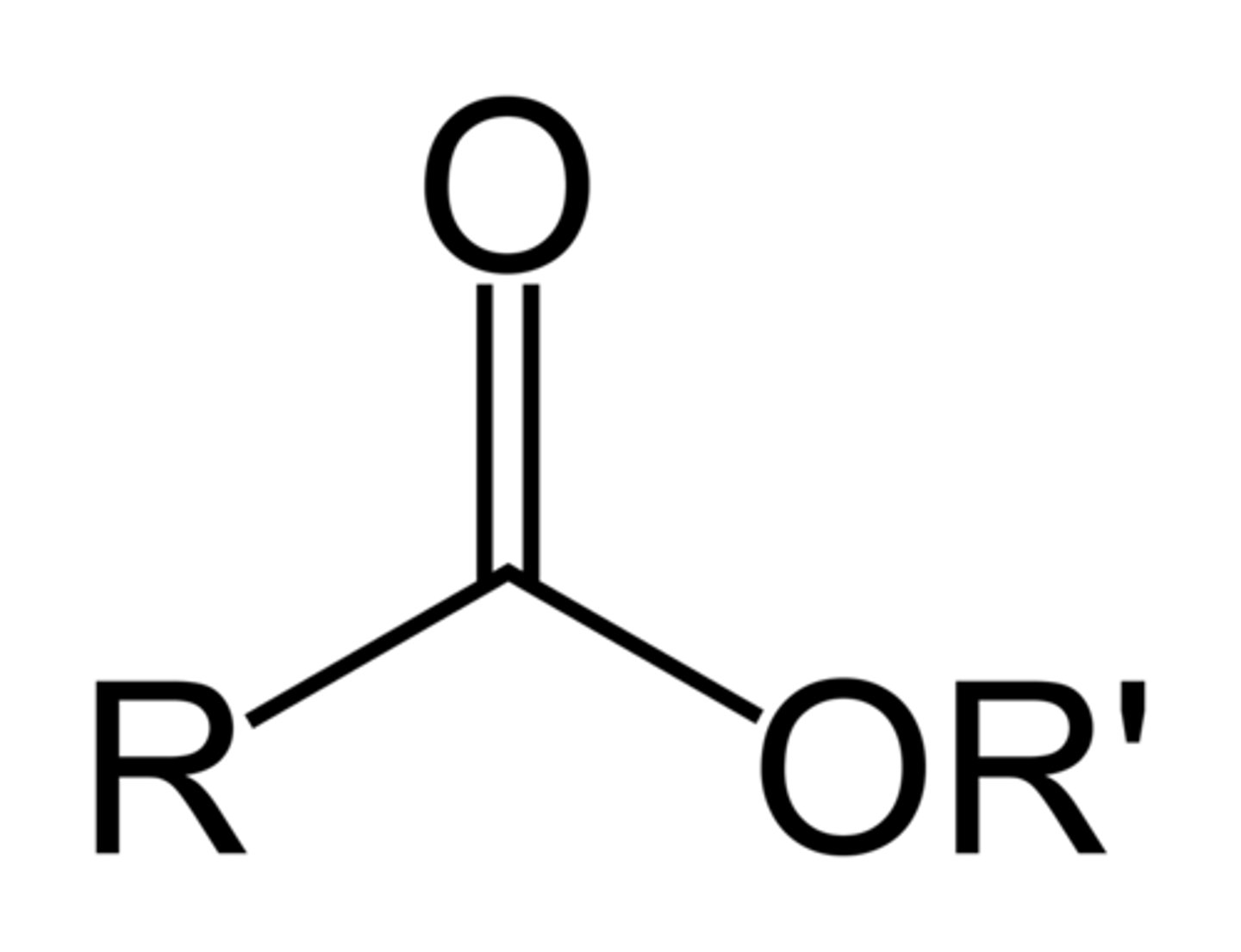
Ester
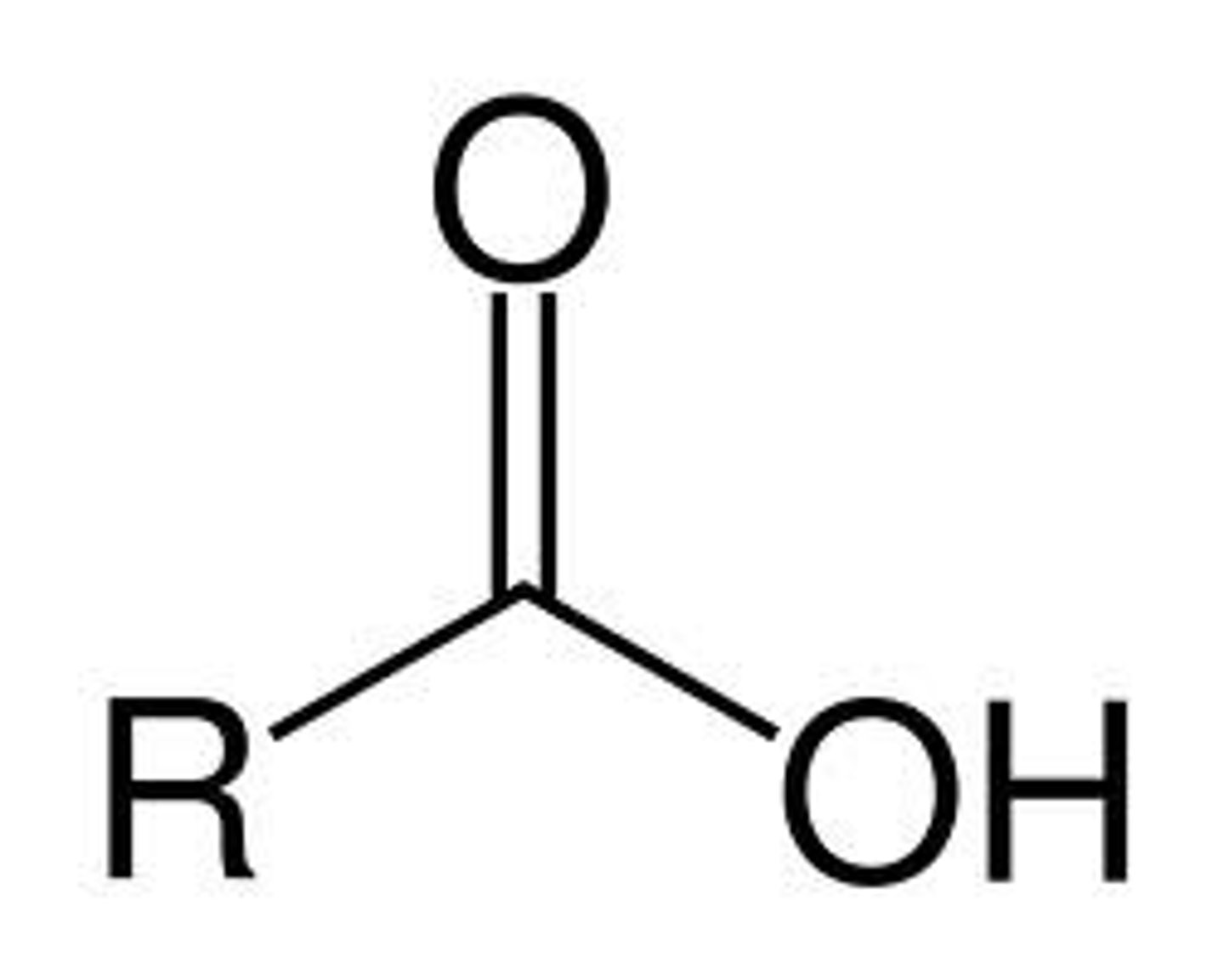
Carboxylic Acid
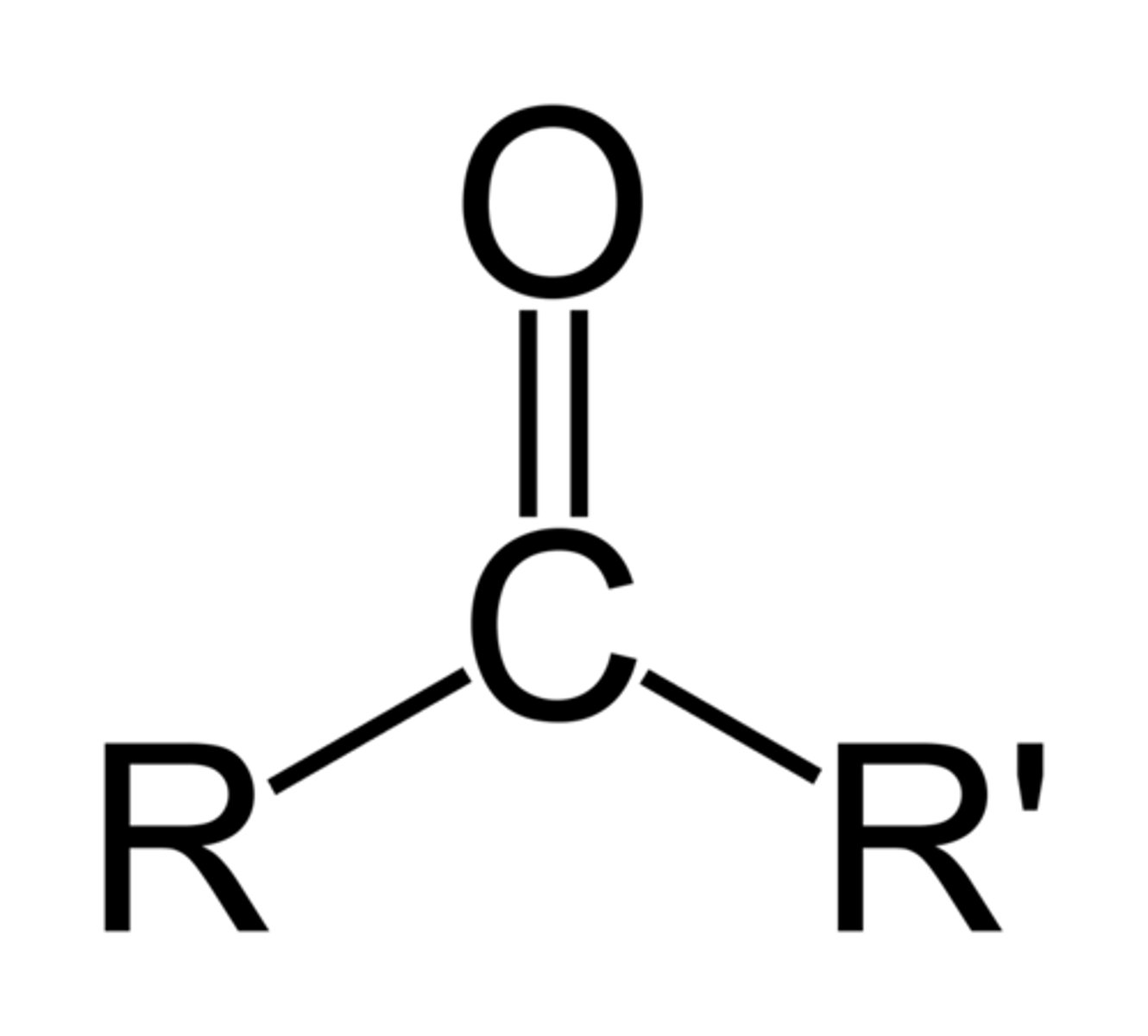
Ketone
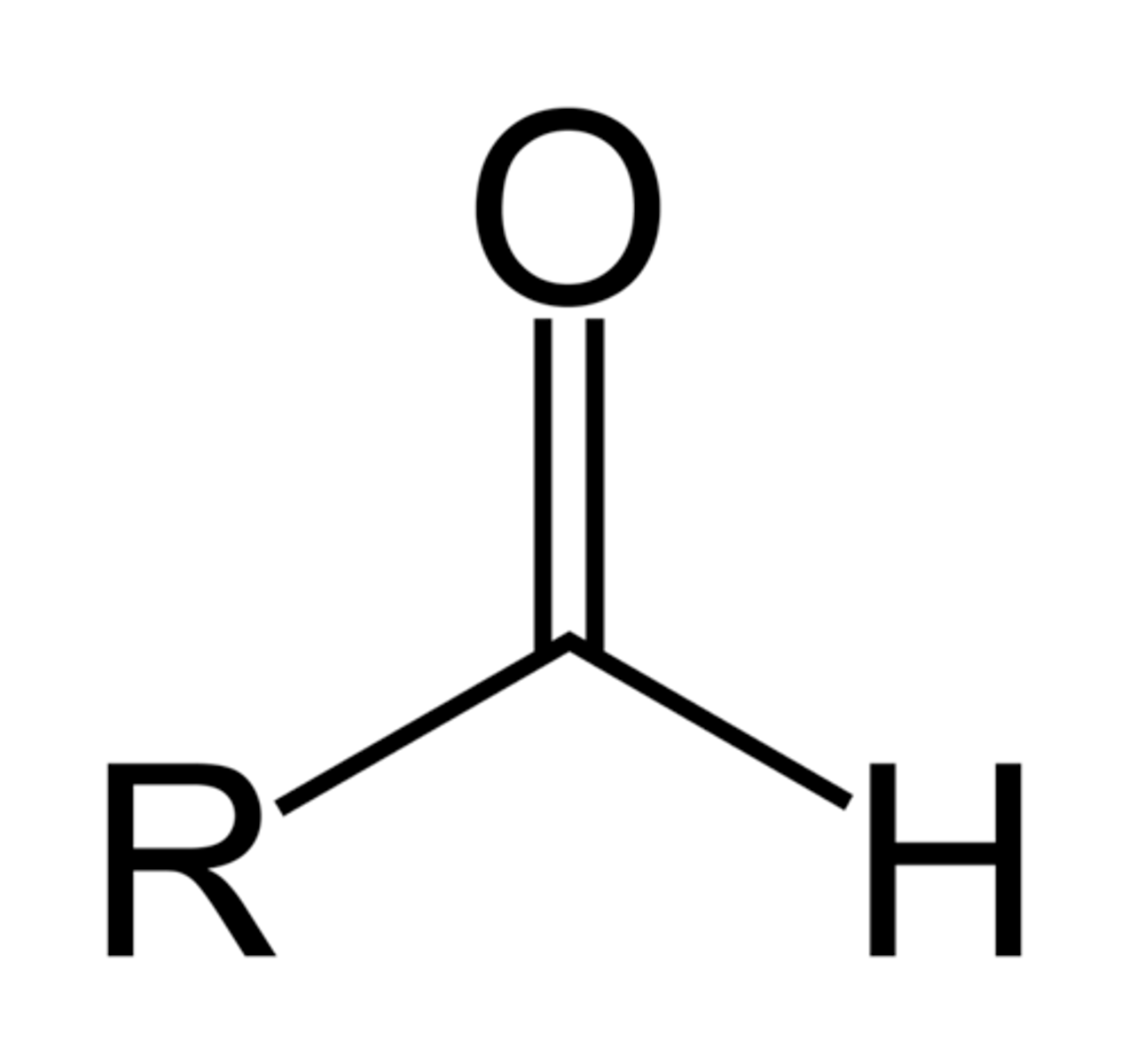
Aldehyde
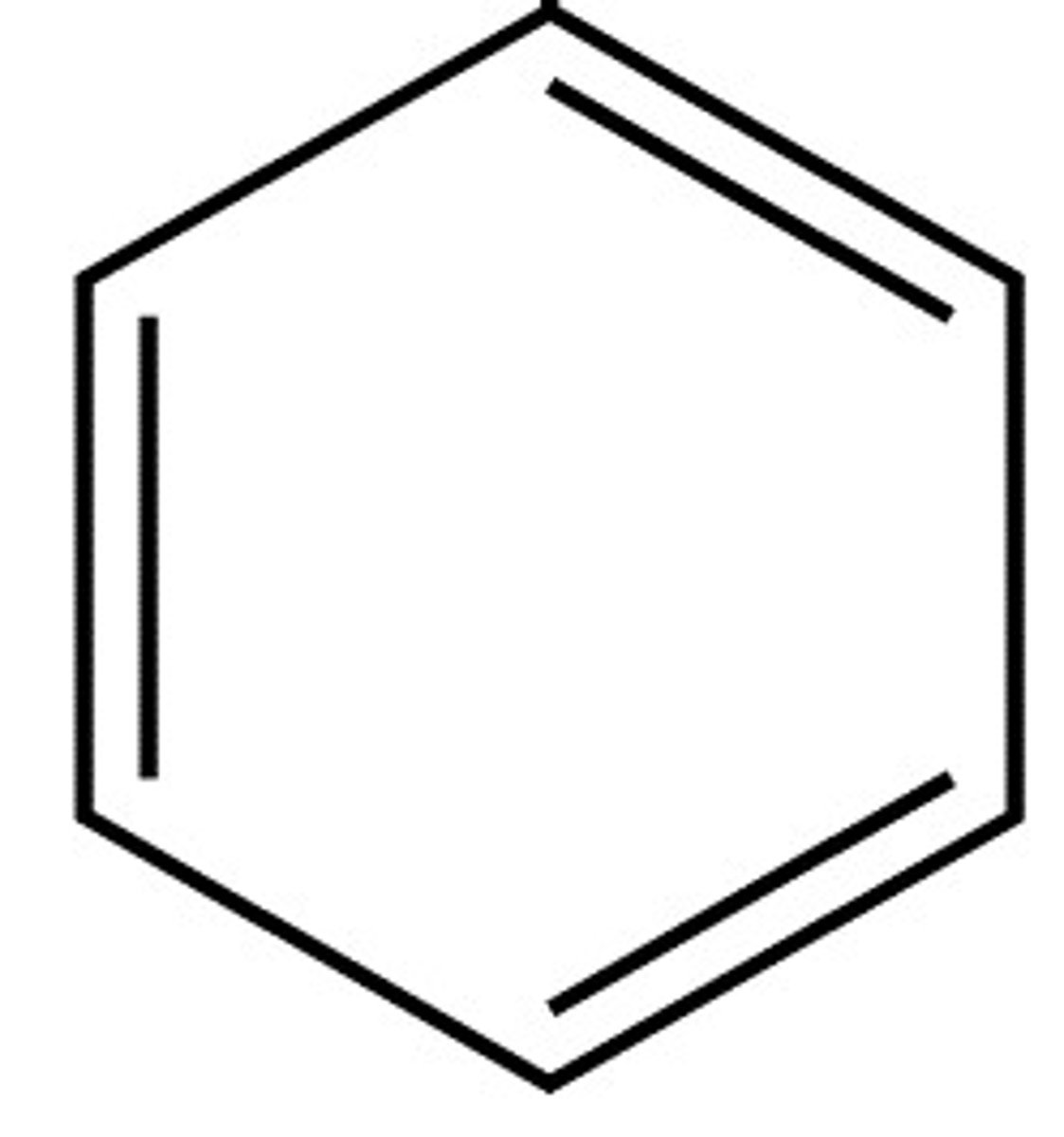
Benzene
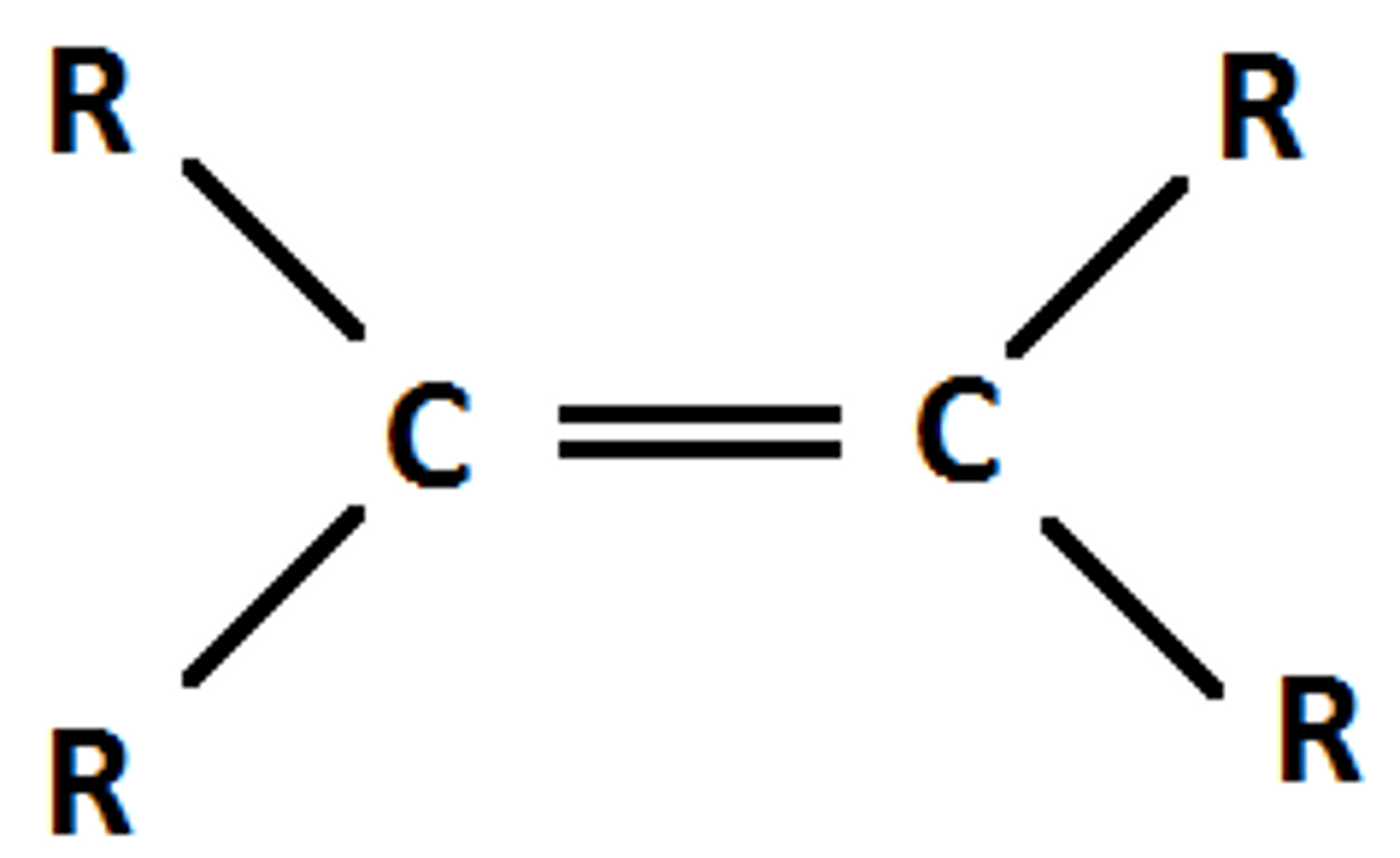
Alkene
Alkyne
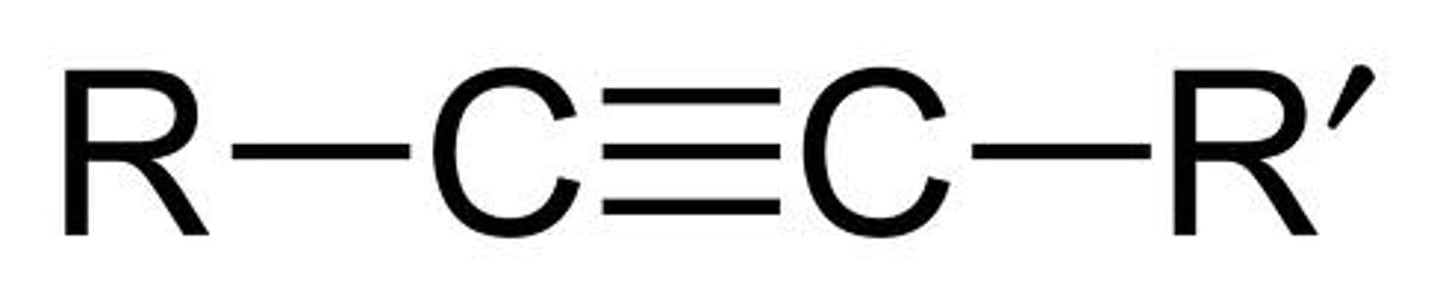
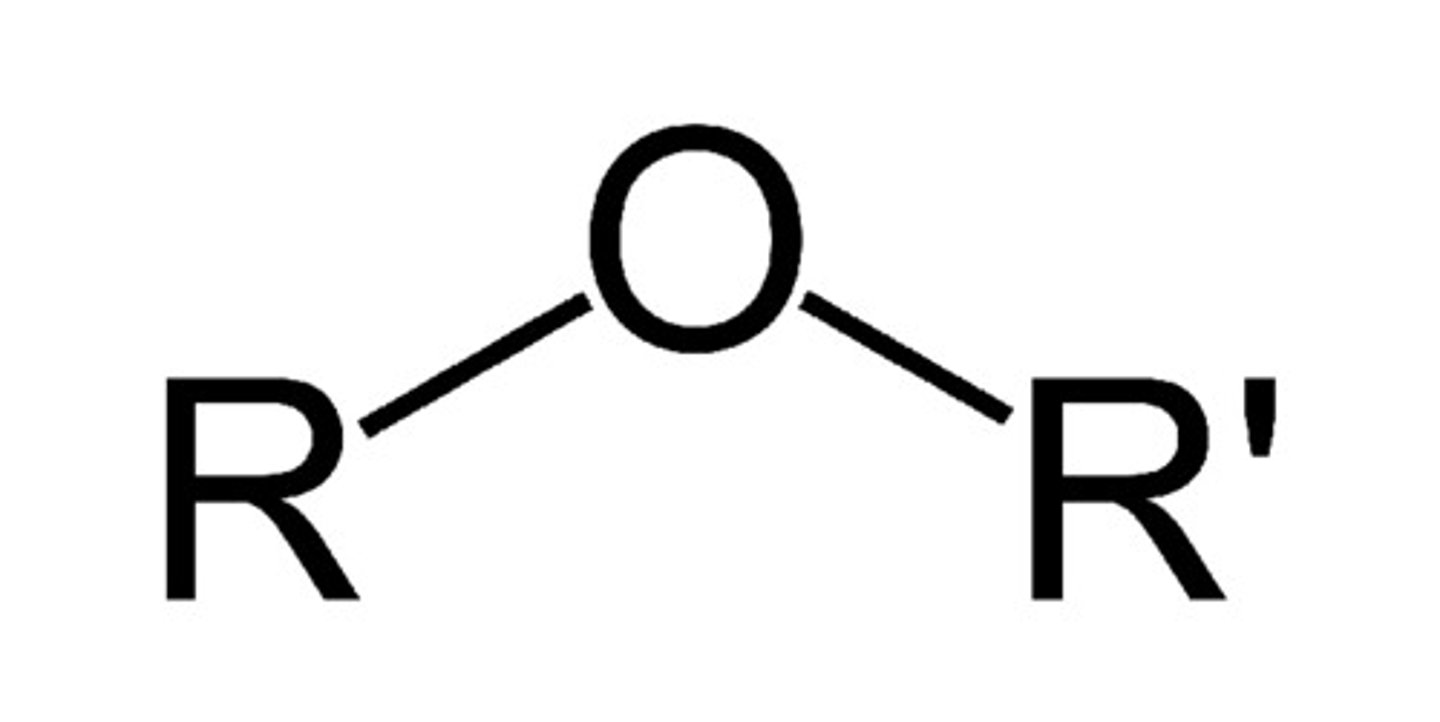
Ether
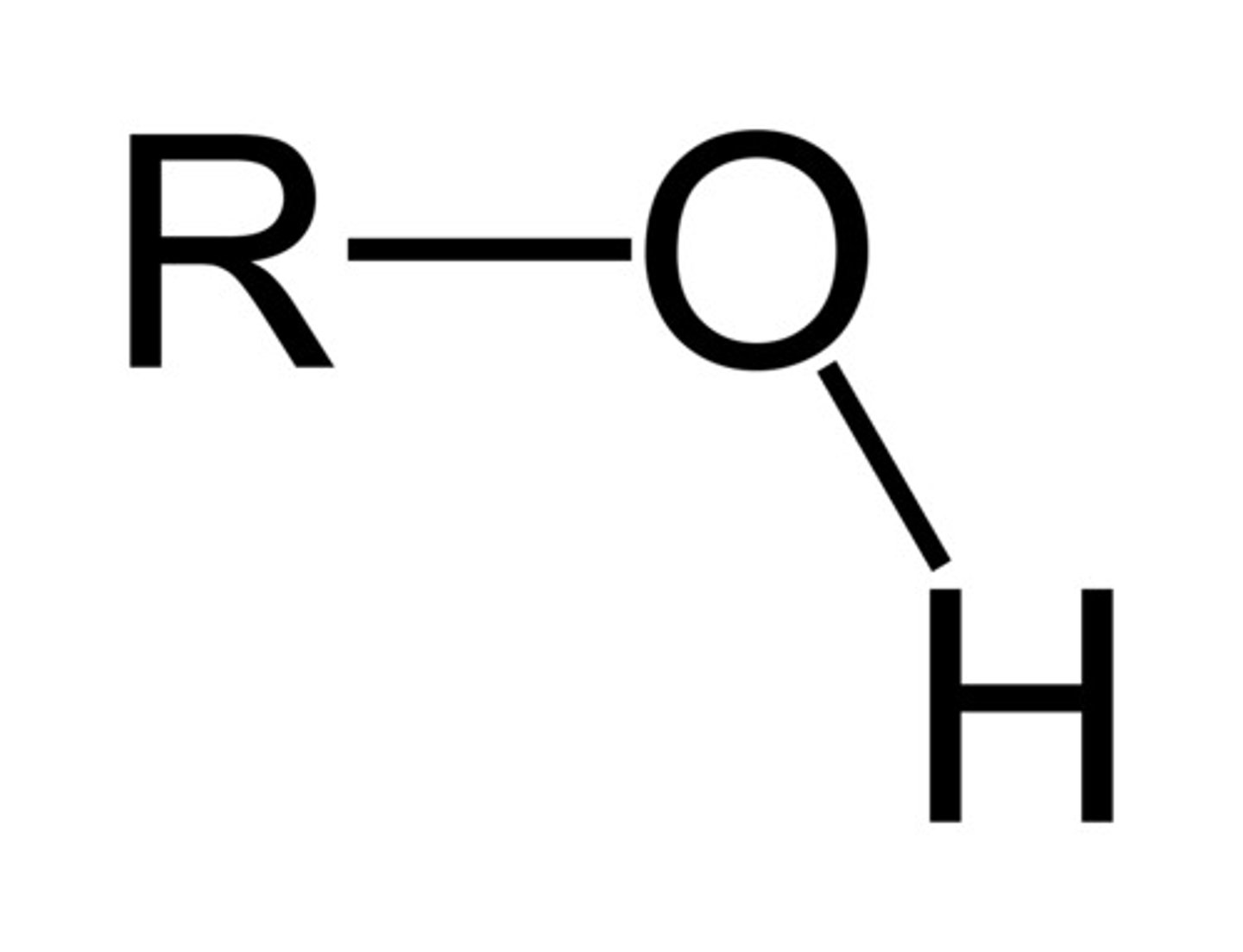
Alcohol
4 atoms/lone pairs hybridization
sp^3
3 atoms/lone pairs hybridization
sp^2
2 atoms/lone pairs hybridization
sp
2 bonds, 0 lone pairs
linear
3 bonds, 0 lone pairs
trigonal planar
3 bonds, 1 lone pair
angular/bent
4 bonds, 0 lone pairs
tetrahedral
4 bonds, 1 lone pair
trigonal pyramidal
4 bonds, 2 lone pairs
angular/bent
5 bonds, 0 lone pairs
trigonal bipyramidal
carbon negative charge
3 bonds, 1 lone pair
carbon neutral charge
4 bonds
carbon positive charge
3 bonds, no lone pairs
nitrogen negative charge
2 bonds, 2 lone pairs
nitrogen neutral charge
3 bonds, 1 lone pair
nitrogen positive charge
4 bonds
oxygen negative charge
1 bond, 3 lone pairs
oxygen neutral charge
2 bonds, 2 lone pairs
oxygen positive charge
3 bonds, 1 lone pair
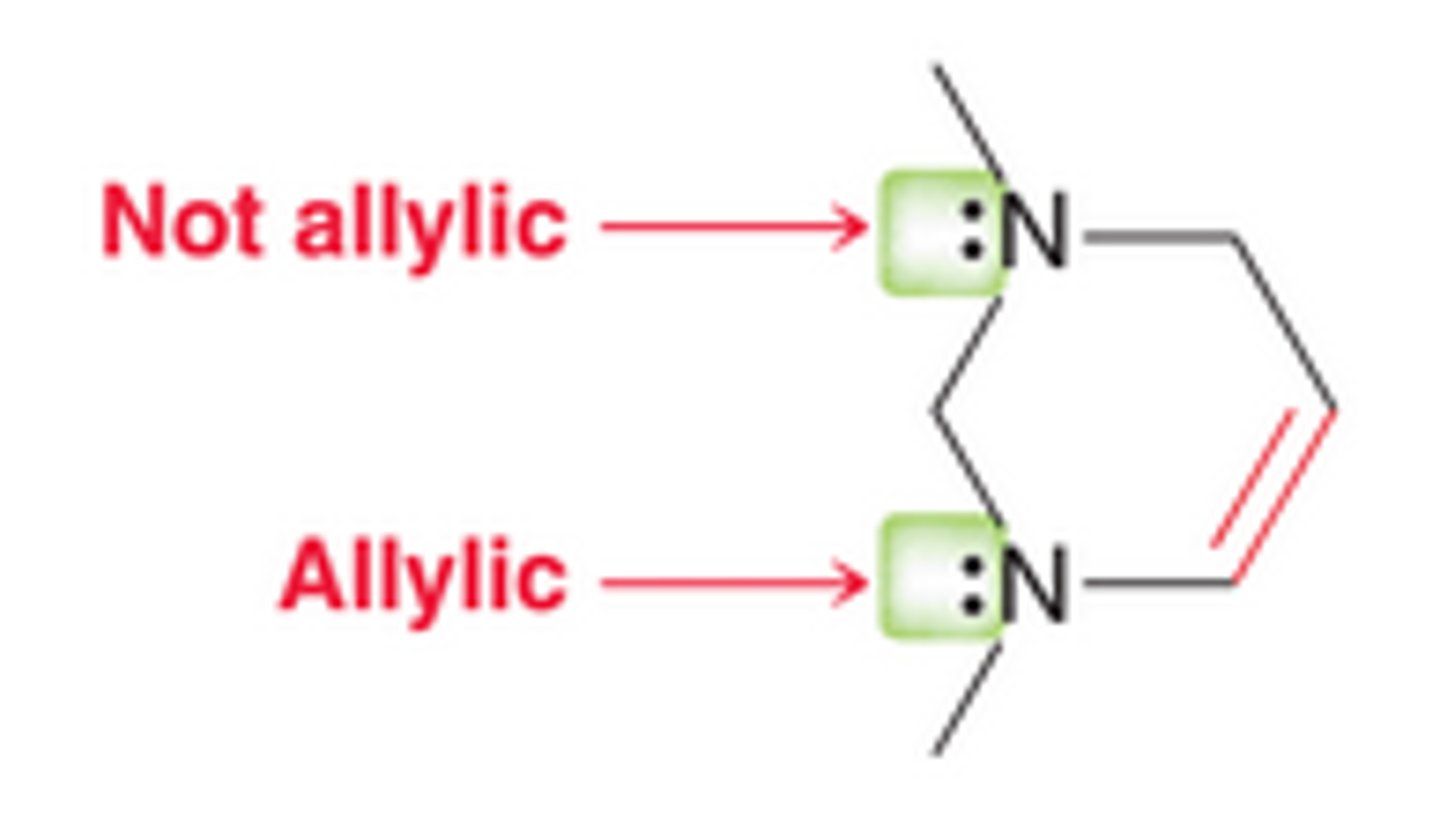
allylic lone pair
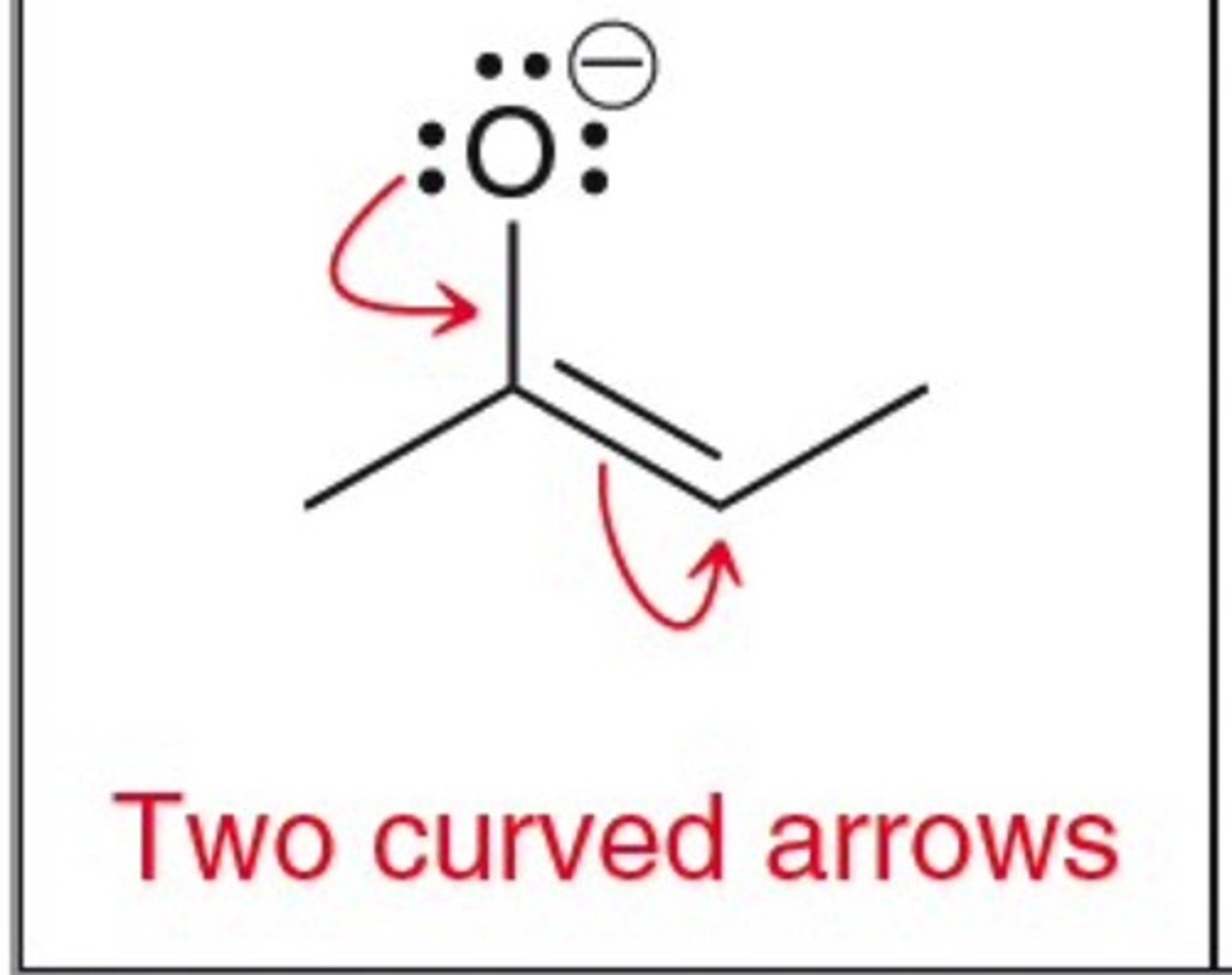
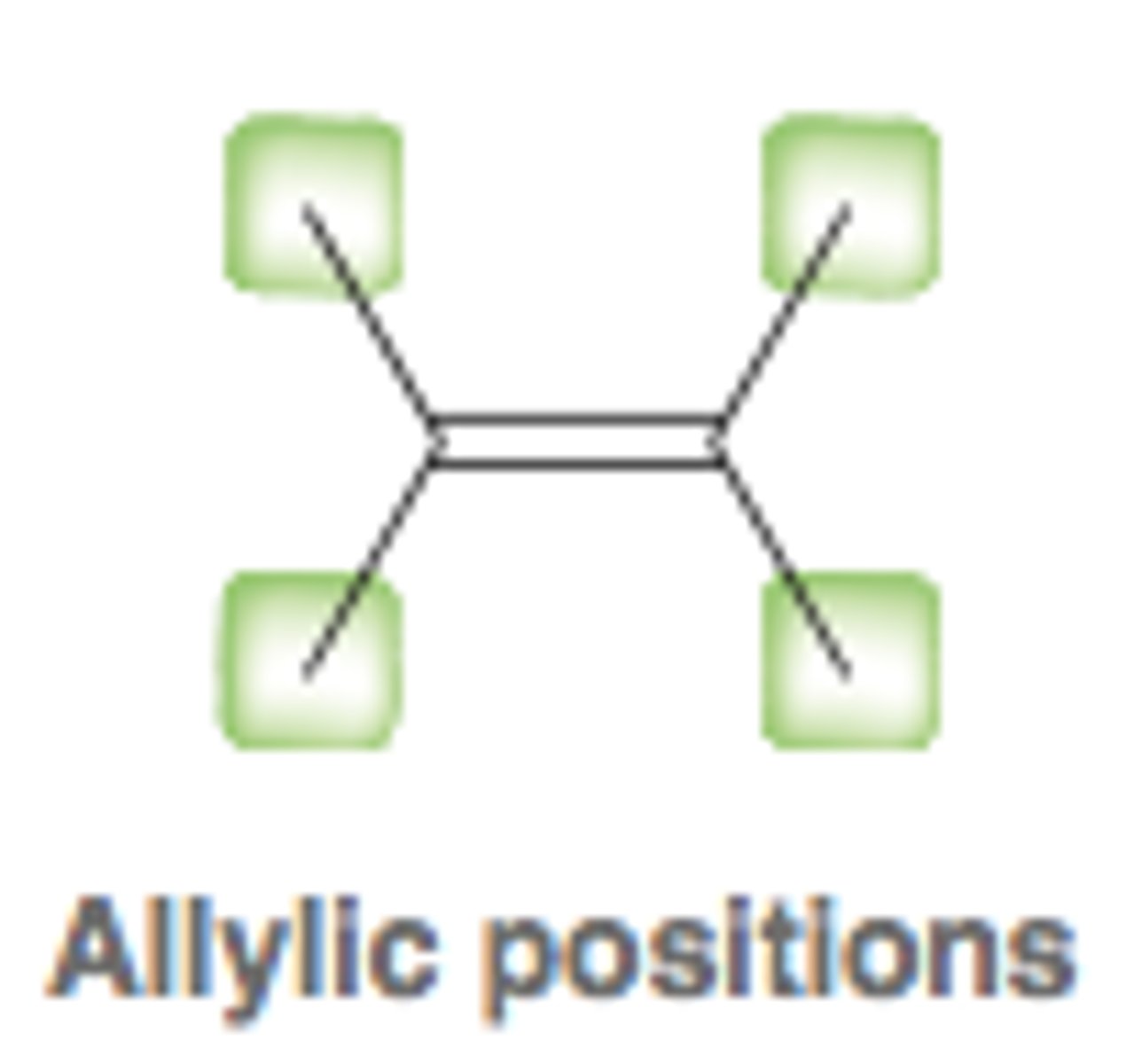
allylic position
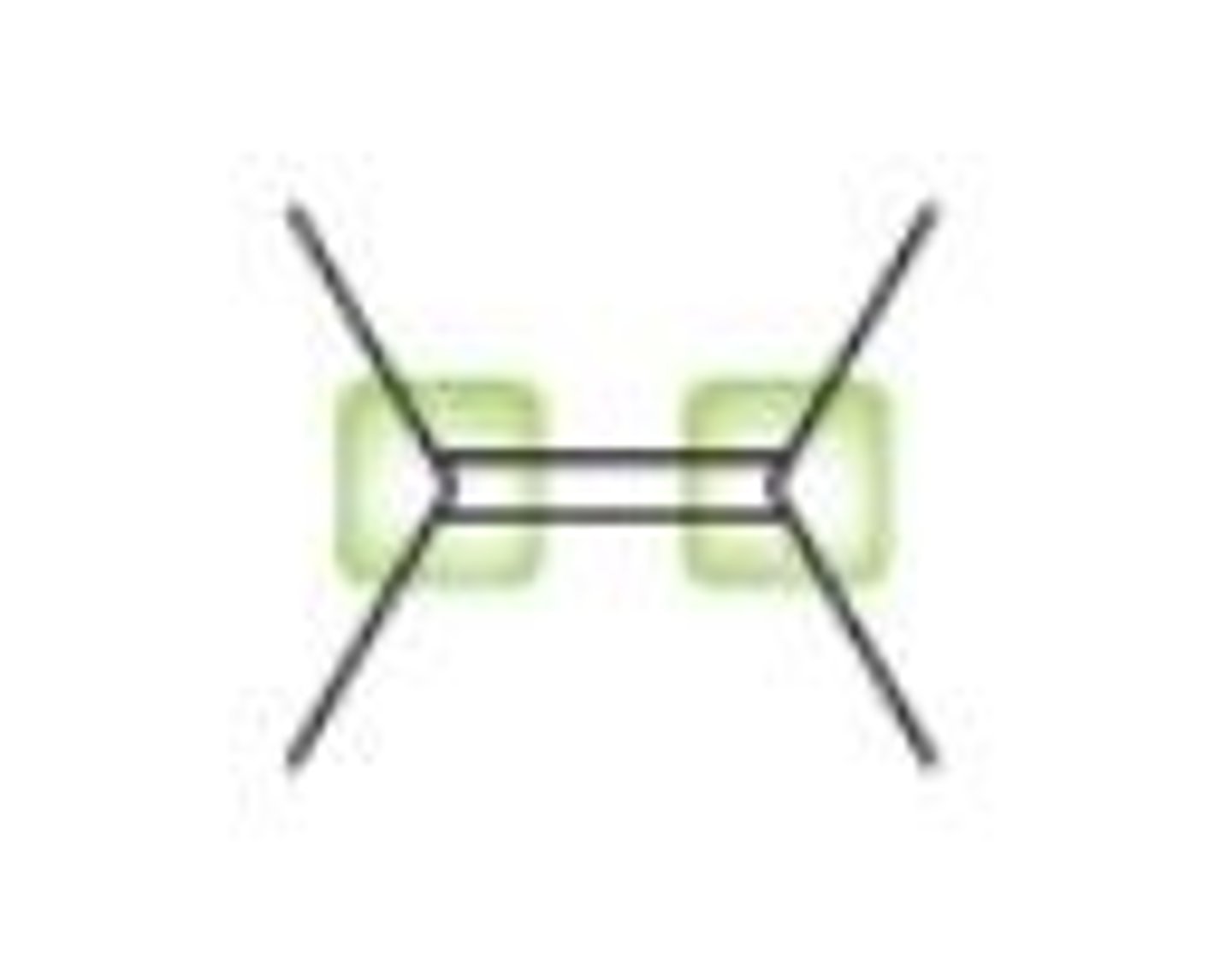
vinylic position
allylic vs not allylic
allylic carbocation
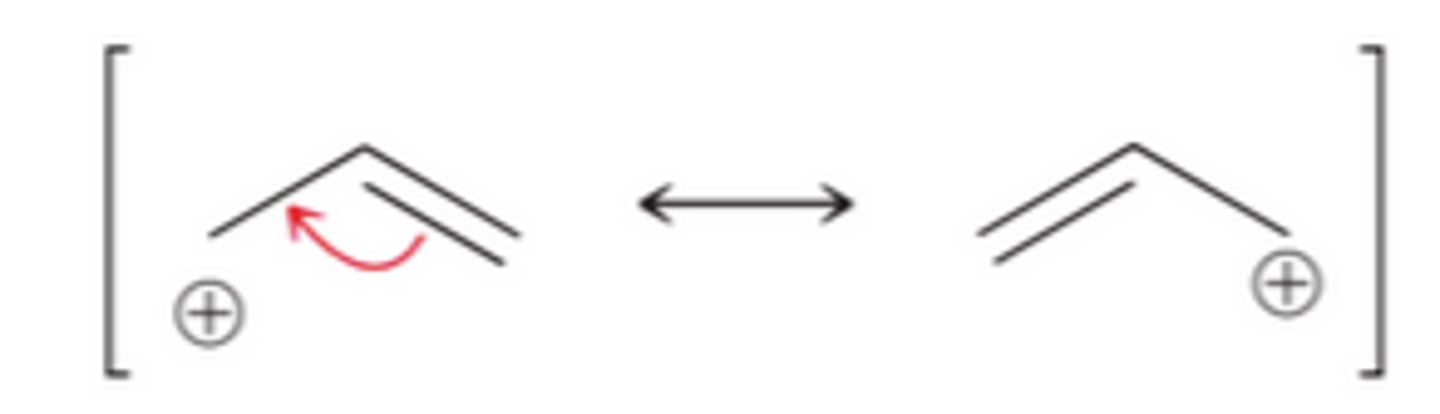
a lone pair adjacent to C+
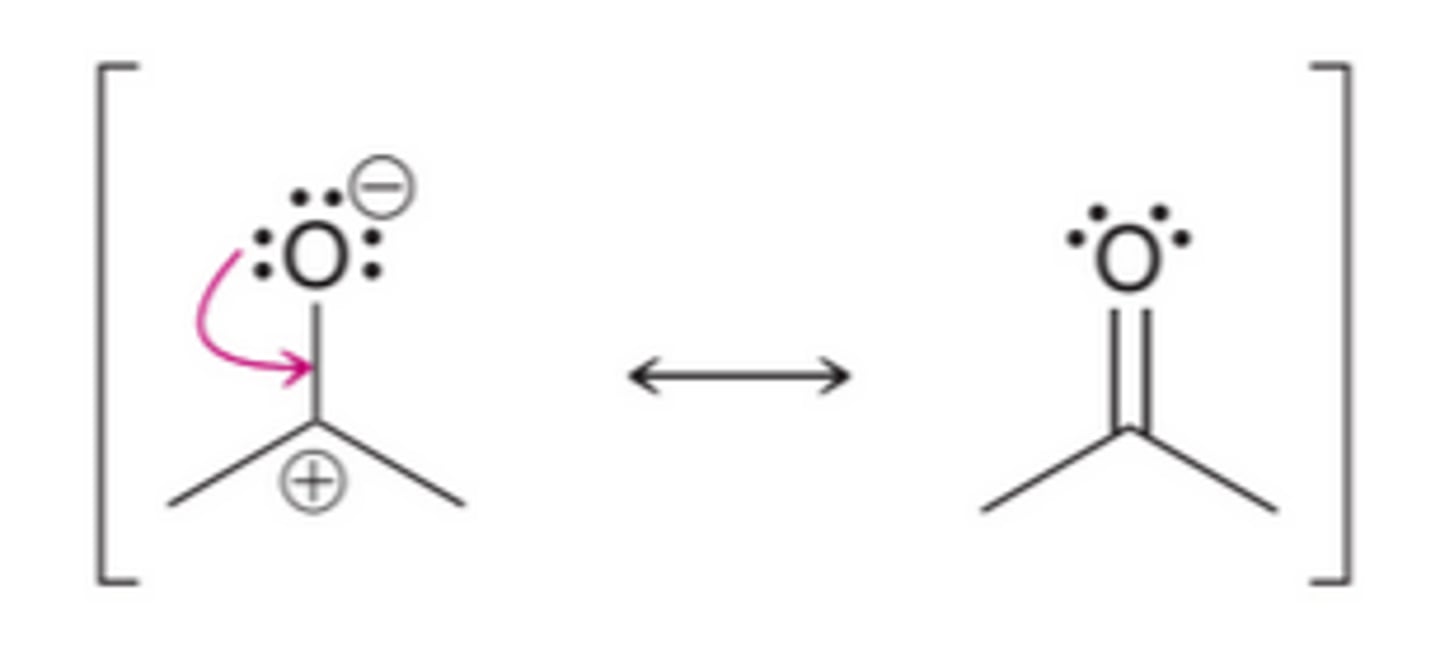
A π−bond between atoms of different electronegativity
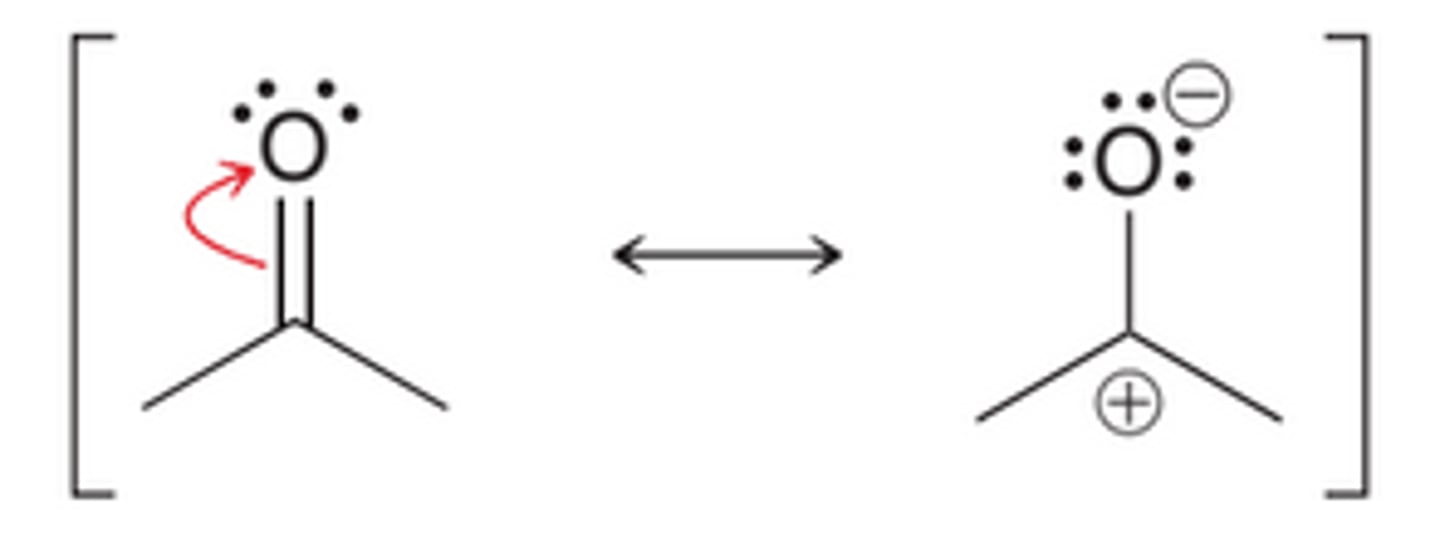
Conjugated π−bonds in a ring
localized electrons
are not in resonance
delocalized electrons
are in resonance
is a pi bond or a sigma bond strong
sigma
rank the sigma bond overlap from shortest to longest
sp-sp < sp²-sp² < sp³-sp³
what intermolecular force do all molecules have
london dispersion forces
ionic bond
chemical bond where electrons are shared between metals and nonmetals
polar covalent bond
bond formed when two atoms share electrons, but those electrons are shared unevenly.
non-polar covalent bond
Chemical bond in which electrons are shared equally between two bonded atoms
how do electronegativity increase
up and to the right
more branching in a molecule = lower surface area =
weaker london dispersion forces
hydrogen bonding
- special dipole-dipole attraction between two polar molecules when the H atom is attracted to F, O, or N of another molecule
dipole-dipole
Present in polar molecules.
Attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule
which molecular geometry are nonpolar
linear, trigonal planar, and tetrahedral
stronger intermolecular forces =
higher boiling point
higher pKa
weaker acid
equilibrium favors the _______ acid
weaker
A in ARIO
atom the carries the charge
R in ARIO
resonance
delocalized = ______ stable
more
localized = ______ stable
less
less stable = ________ acid
less
I in ARIO
inductive effect
O in ARIO
more electronegative = _______ stable
more
Alkyl halide

thiol

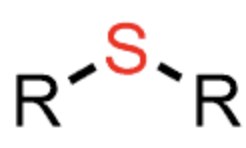
sulfide
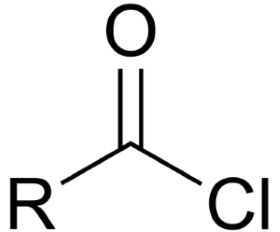
acyl halide
anhydride

what are the two molecular geoemtries that are delocalized
trigonal planer and bent (bent can sometimes be localized)