Unit 1: Intro to Anatomy
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
a
not, without
ation
condition, process
cyte
cell
dynia, algia, alge (si)
pain
hydro
water
itis
inflammation of
ism
condition
macro
large
meta
beyond
micro
small, tiny
ology
the study of
osis
abnormal condition
phys
to grow, nature, natural order
scopy
viewing of
therm
heat, tempature
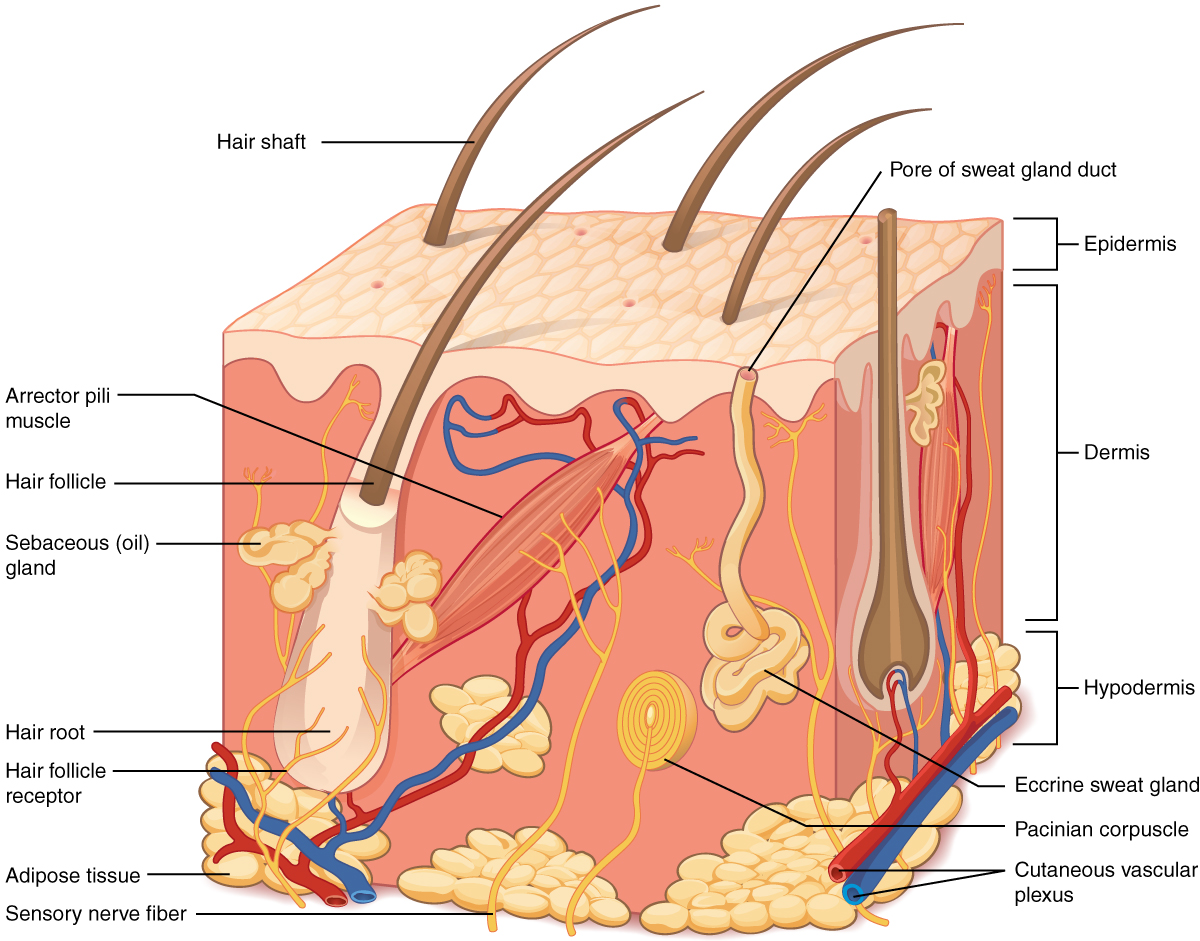
integumentary System
physical barrier that protects the body, senses stimuli, regulates body temperature, and produces vitamin D
skeletal System
body support and structure; allows movement; makes blood cells; protects organs; stores minerals such as calcium
muscular system
causes movements by contracting and relaxing
nervous system
carries electrical signals throughout the body to control thoughts and responses
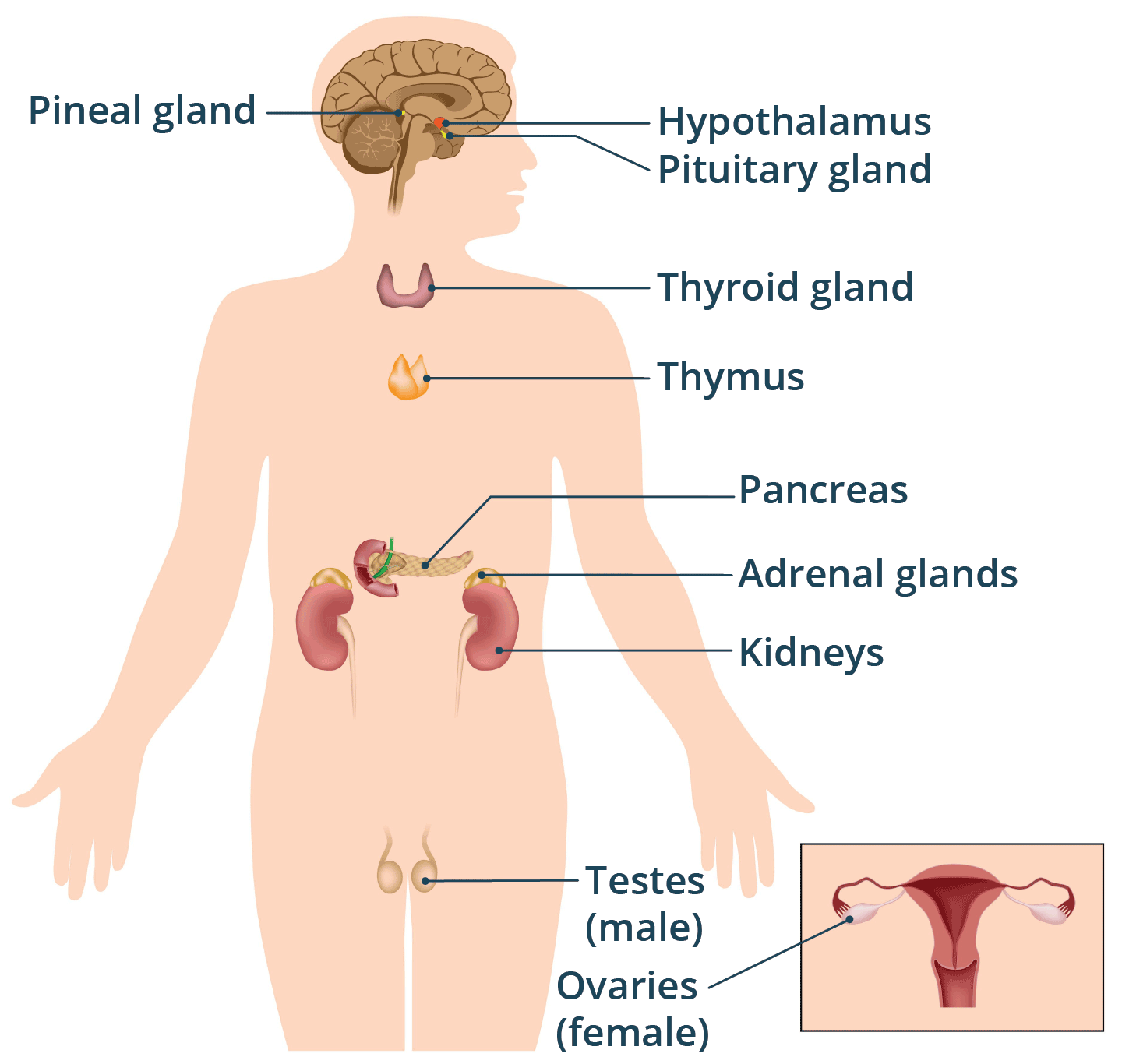
endocrine system
makes hormones to regulate a wide variety of bodily functions
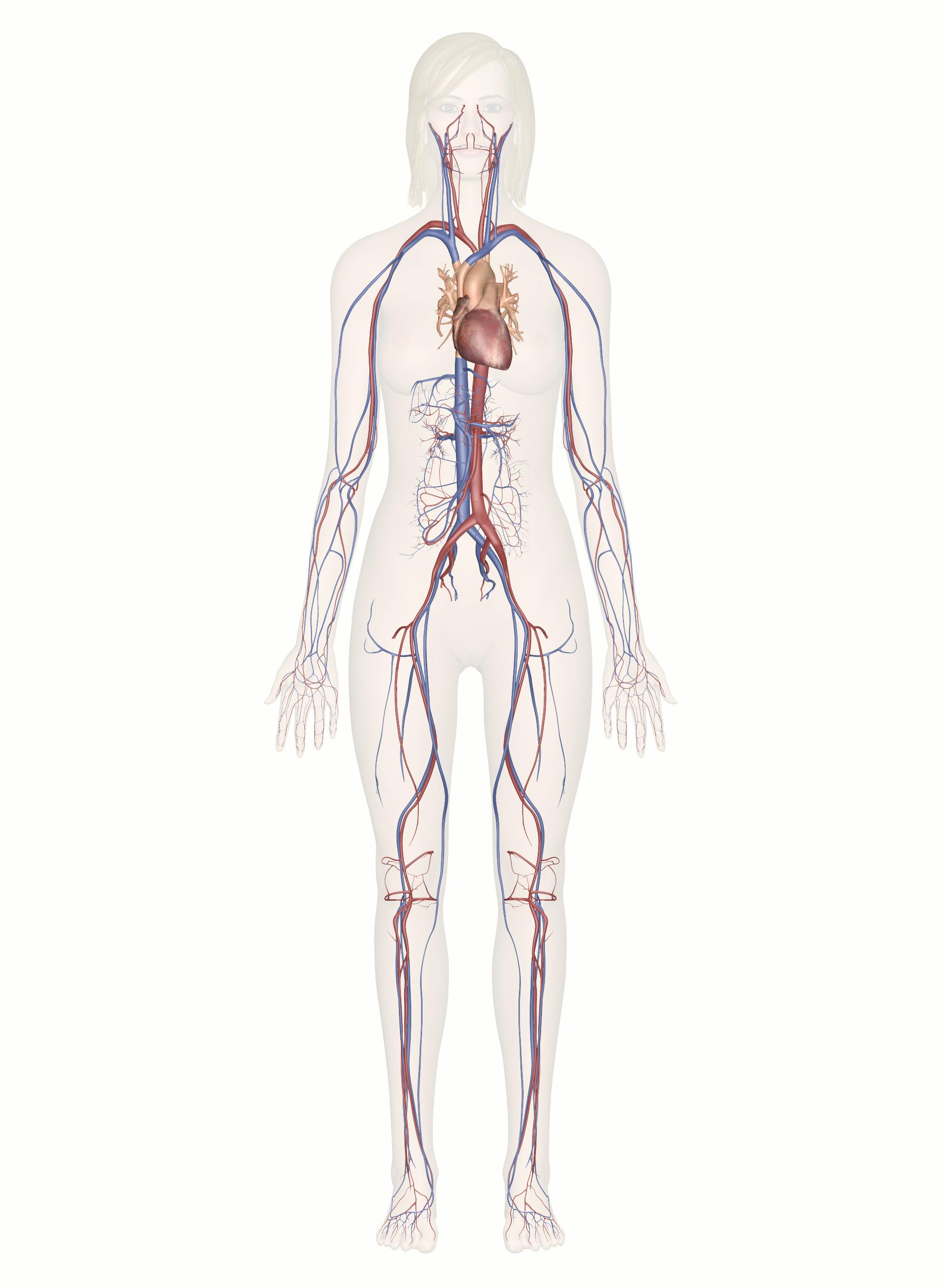
cardiovascular system
transportation of oxygen, nutrients, hormones and waste products throughout the body
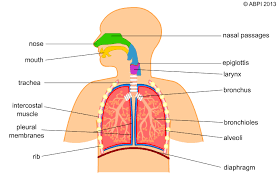
respiratory system
exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the atmosphere
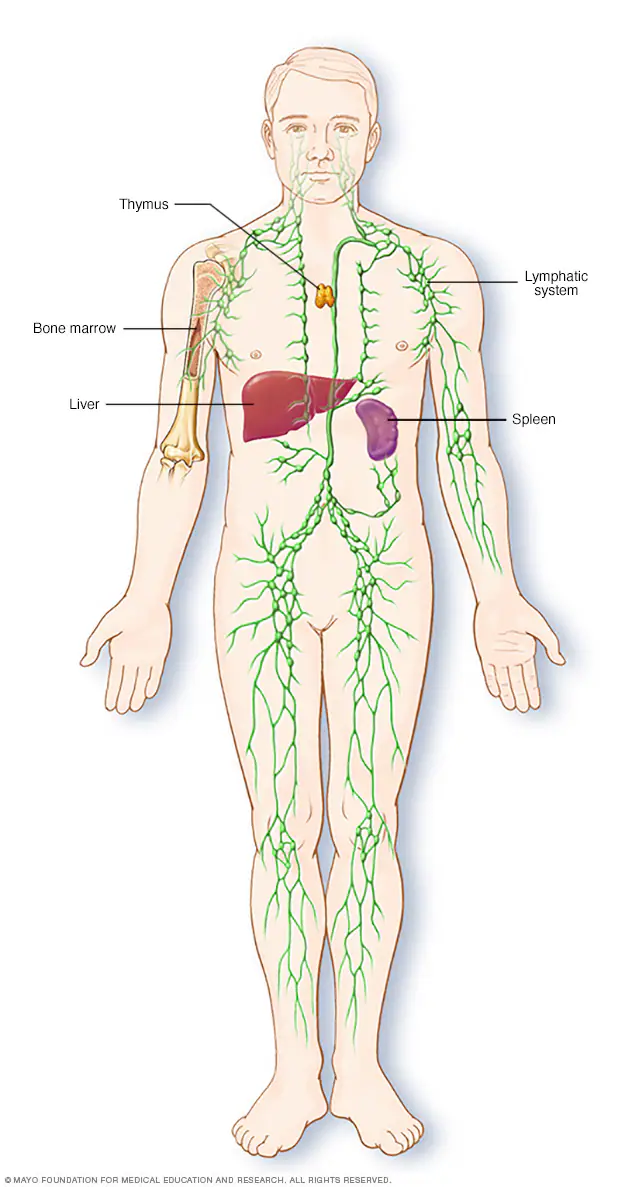
immune/ Lymphatic system
prevents and minimizes infection of the body. returns excess fluid in the tissues back into the bloodstream.
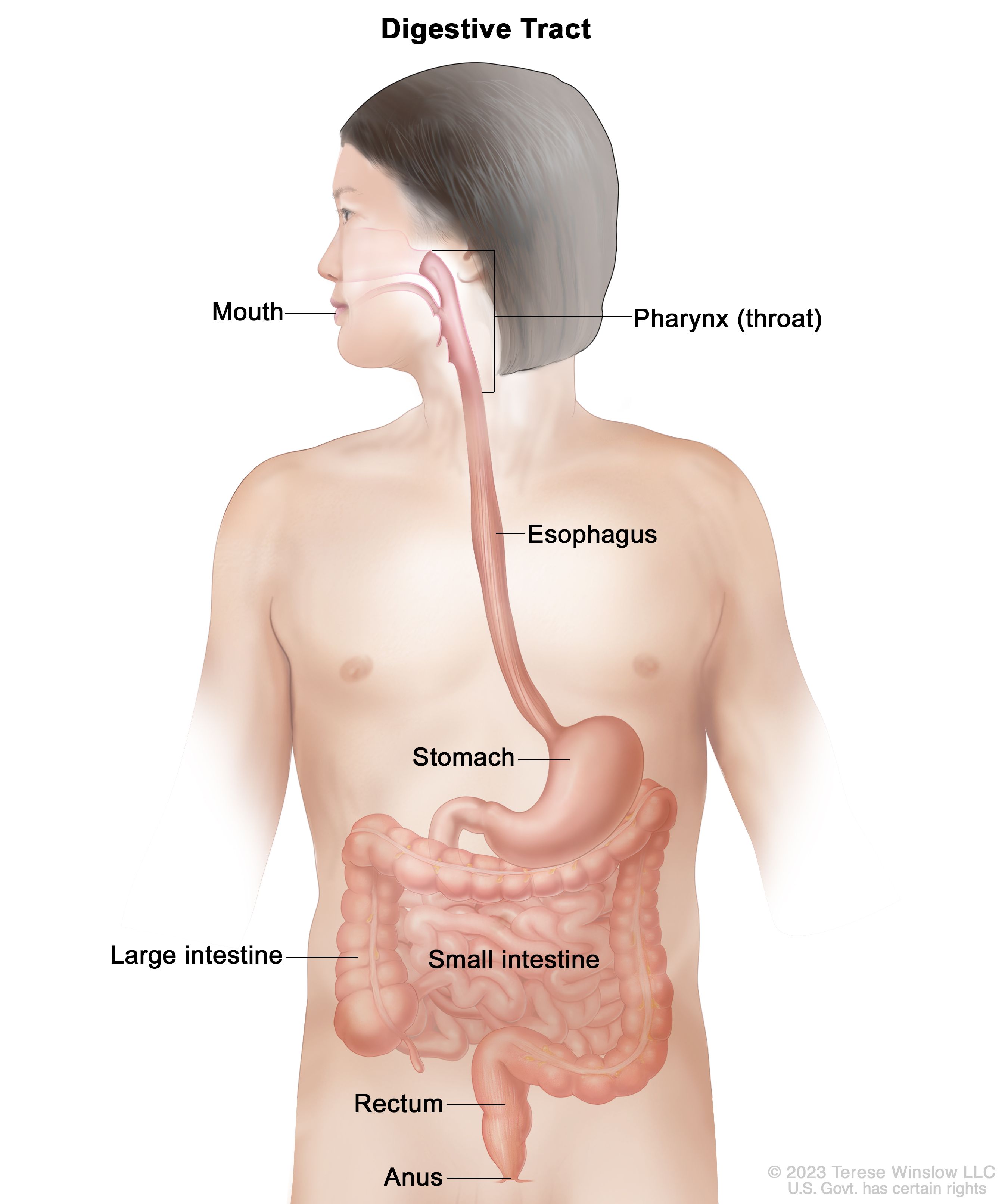
digestive system
breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste
urinary system
filters blood and removes excess waste by producing and excreting urine.
reproductive system
produces and sustains sperm and egg cells, enables fertilization, and supports developing offspring
anatomy is the study of _
the structure of an organism
physiology is the study of _
how that organism’s body functions
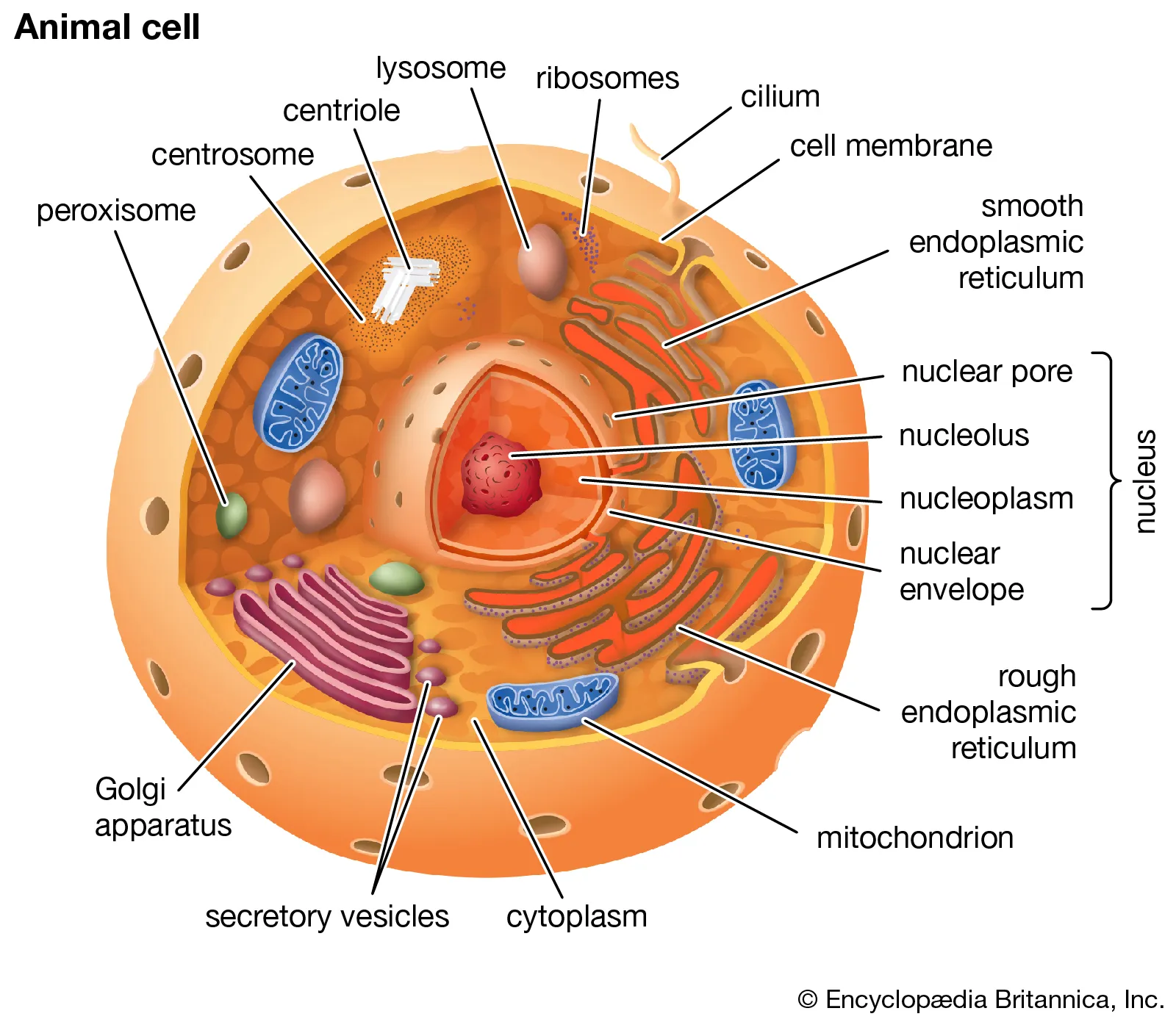
cell
smallest unit of all living things
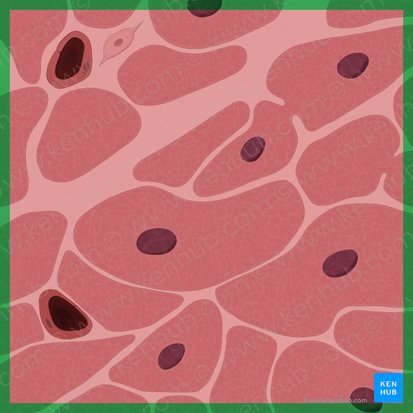
tissue
similar cells with a common function
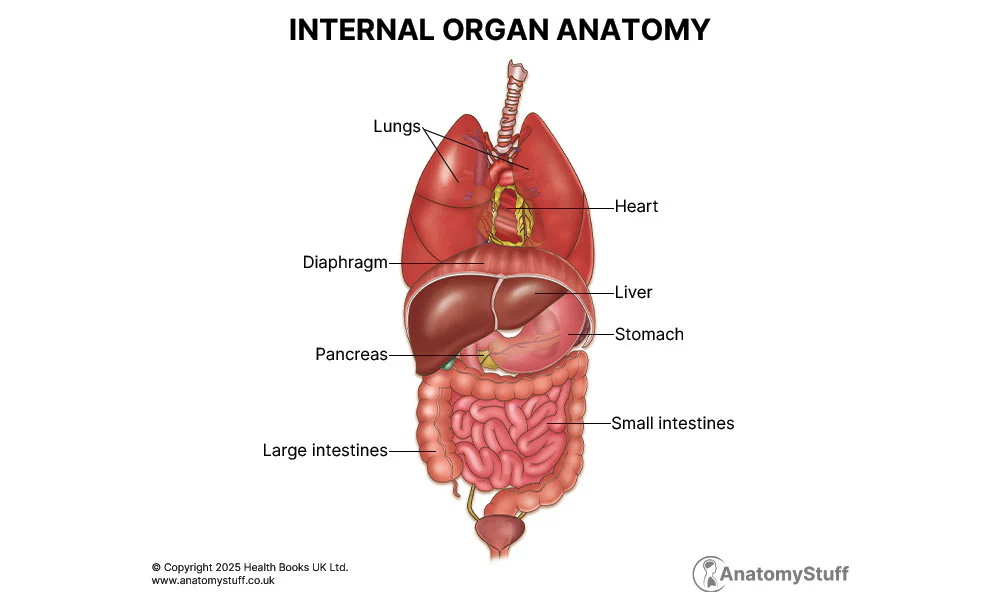
organ
made of 2 or more types of tissues
system
group of organs working toward a common goal
organism
highest level of structural organization for an individual
skeletal system function
provides support and protection, gives body shape.
skeletal system major organs
bones, ligaments, cartilage, joints
nervous system function
detects impulses from the senses; control center.
nervous system major organs
brain,spinal cord, senses, nerves
circulatory systems function
transports nutrients and gases around the body.
circulatory systems major organs
heart,blood vessels, blood
respiratory systems function
exchanges gases (oxygen & CO2)
respiratory systems major organs
lungs,sinuses, diaphragm
digestive systems function
breaks down and absorbs food
digestive system major organs
mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder
muscular systems function
provides movement for all parts of the body.
muscular systems major organs
skeletal and smooth muscles
integumentary systems function
protect the body, regulate temperature, and prevent water loss.
integumentary systems major organs
skin, hair, nails
lymphatic systems function
fights infection and provides fluid for cells.
lymphatic systems major organs
spleen,thymus gland, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes
excretory systems function
removes waste from the blood
excretory systems major organs
kidneys, bladders, ureters, urethra
endocrine systems function
secretes hormones
endocrine systems major organs
glands (Hypothalamus, pineal, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries or testes)
reproductive systems function
produces cells used in sexual reproduction.
reproductive systems major organs
-female: ovaries, vagina, uterus, mammary glands
-male: testes, penis, prostate gland
the anatomy of the human body describes _
structures found within it
these structures are organized into _
different levels of complexity
the __ systems made of __ work together in a __
The 11 systems made of cells, tissues, and organs work together in a individual organism.
maintaining boundaries necessary for life
some substances in and keeps others out (ex: skin protects absorbs and keeps in water, which preventing entry of pathogens)
movement necessary for life
internal movement (ex: digestive contractions) and ability to move through surroundings
responsiveness necessary for life
sensing and reacting to changes in environment (ex: pain felt when finger is cut with a knife)
digestion necessary for life
breaking down and absorbing nutrients
metabolism necessary for life
building larger molecules from small ones (anabolism) and breaking down of larger molecules into smaller ones (catabolism)
excretion necessary for life
removal of wastes (ex: urine, sweat)
reproduction necessary for life
production of offspring
growth necessary for life
increase in cell size or overall body size
nutrients aid in survival
(through digestion & metabolism)
oxygen’s aid in survival
heart and lungs
normal body temperature’s aid in survival
(skin, blood, and muscles)
water aid’s in survival
(allows molecules to move through the body)
normal atmospheric pressure’s aid in survival
(provides appropriate gas exchange between lungs and environment)