MKT 3300 Exam 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
1
New cards
Nondurable goods
–few uses, can be perishable.
•E.g. food products and fuel
•short lives, inexpensive and purchased frequently
•Rely on consumer advertising and wide distribution
2
New cards
Durable Goods
–last over many uses.
•E.g. appliances, cars and smartphones
•cost more and last longer
•Costly durables rely on personal selling
3
New cards
Type of Users
•**Consumer products**
–Purchased by end consumer
•**Business products:**
–B2B products or industrial products
4
New cards
Classifications of consumer goods:
Convenience, shopping, specialty, and unsought goods.
5
New cards
Consumer Products - Convenience
Frequent;
**minimum effort**
\
* toothpaste
* cake mix
**minimum effort**
\
* toothpaste
* cake mix
6
New cards
Consumer products - Shopping
**Compare several alternatives**
* cameras
* TV
* Briefcases
7
New cards
Consumer products - Specialty
**special effort to find and buy**
* Rolls-Royce Cars
* Rolex Watches
* Heart Surgery
8
New cards
Consumer Products - Unsought
**does not know or initially want**
* Burial Insurance
* Thesaurus
9
New cards
Continuous Innovation
Requires no new learning from consumers
* New, improved shaver
* Detergent and toothpaste
\
\
* New, improved shaver
* Detergent and toothpaste
\
\
10
New cards
Dynamically Continuous Innovation
Disrupts consumers normal routine but does not require totally new learning
* Electric toothbrush
* Smartphones
* Electric toothbrush
* Smartphones
11
New cards
Discontinuous Innovation
Requires new learning and consumption patterns by consumers
* Wireless router
* Digital video recorder
* electric car
* Wireless router
* Digital video recorder
* electric car
12
New cards
Continuous Innovation marketing strategy
Gain consumer awareness and wide distribution
13
New cards
Dynamically Continuous Innovation marketing strategy
advertise points of difference and benefits to consumers
14
New cards
Discontinuous Innovation
Educate consumers through product trial and personal selling
15
New cards
**Marketing Reasons for** \n **New Product Failures**
**1. Insignificant “point of difference”: Fingos, Pepsi One**
**2. Incomplete or incorrect market and product definition before product development starts: Target market? Wants and needs? What the product will do? Google glass**
**3. Too little market attractiveness (size and growth of mkt):**
**4. Poor execution of the marketing mix:**
**Minute Maid squeeze-fresh OJ concentrate**
**5. Poor product quality on critical factors: Windows Vista**
**6. Bad timing.**
**7. No economic access to buyers: access shelf-space**
**8. Not fit with the firm’s other products, specialty or image.**
16
New cards
Stages in the new product process
1. New-Product strategy development
2. Idea Generation
3. Screening and evaluation
4. Business Analysis
5. Development
6. Market Testing
7. Commercialization
17
New cards
New-product strategy development
identify new-product niches to reach in light of company objectives
18
New cards
Idea Generation
**consists of developing concepts as candidates for products/services. New product ideas can be generated by:**
**a. customer suggestions**
**b. employee and co-worker suggestions**
**c. R&D breakthroughs**
**d. competitor’s products**
• **Open innovation**
**and customer involvement**
19
New cards
Screening and Evaluation
**Screening and evaluation involve internal and external evaluations of the new product ideas, so as to eliminate those that warrant no further effort.**
**The process can be formal, consisting of criteria developed from internal and external sources. Ideas with the highest scores are considered in the next step of development.**
20
New cards
Business Analysis
* **involves specifying the features of the product and the marketing strategy needed to commercialize it**
* **making necessary financial (forecasts of costs and revenues) projections**
**This is the last checkpoint before significant capital is invested in creating a prototype of the product.**
21
New cards
Development
•**Turning the idea into a prototype.**
•**Results in Demonstrable Product**
•**Lab and Consumer Tests**
22
New cards
Market Testing
The market testing stage involves exposing actual products to prospective consumers under realistic purchase conditions to see if they will buy.
23
New cards
Standard Market Testing
* The ultimate way to test a new consumer product is to put it into full-blown test markets
* The company chooses a few representative cities and puts on a full marketing communications campaign, and the sales force tries to sell the trade on carrying the product and giving it good shelf exposure
* Test marketing also measures the impact of alternative marketing plans by implementing them in different cities
* The company chooses a few representative cities and puts on a full marketing communications campaign, and the sales force tries to sell the trade on carrying the product and giving it good shelf exposure
* Test marketing also measures the impact of alternative marketing plans by implementing them in different cities
24
New cards
Controlled Test Marketing
* It is similar to a field experiment where you can manipulate the marketing mix variables and see which ones are the most effective methods to stimulate sales among consumers
25
New cards
Simulated Test Marketing
It does not involve actual testing in the marketplace. It often use lab results and computer simulation to forecast the sales of a new product
26
New cards
4 Stages of Product Life Cycle
1. Introduction
2. Growth
3. Maturity
4. Decline
27
New cards
Introduction stage
Marketing Objective - Gain awareness
Competition - None
Product - one
Price - skimming or penetration
Promotion - Inform, Educate
Place - Limited
Competition - None
Product - one
Price - skimming or penetration
Promotion - Inform, Educate
Place - Limited
28
New cards
Growth stage
Marketing Objective - Stress Differentiation
Competition - Growing
Product - More versions
Price - Gain Share, deal
Promotion - Stress Competitive differences
Place - More outlets
Competition - Growing
Product - More versions
Price - Gain Share, deal
Promotion - Stress Competitive differences
Place - More outlets
29
New cards
Maturity stage
Marketing Objective - Maintain Brand Loyalty
Competition - Many
Product - Full product line
Price - Defend share, profit
Promotion - Reminder oriented
Place - Maximum outlets
Competition - Many
Product - Full product line
Price - Defend share, profit
Promotion - Reminder oriented
Place - Maximum outlets
30
New cards
Decline stage
Marketing Objective - Harvesting
Competition - Reduced
Product - Best Sellers
Price - Stay profitable
promotion - minimal promotion
Place - Fewer outlets
Competition - Reduced
Product - Best Sellers
Price - Stay profitable
promotion - minimal promotion
Place - Fewer outlets
31
New cards
Dimensions of PLC - Shape
**1. High learning product**
**significant education of consumer– extended introductory period**
**2. Low learning product**
**Benefits easily understood– sales begin immediately**
**3. Fashion product**
**Sales grow, decline, and then return: clothing, movies**
**4. Fad product**
**Typically novelties: rapid growth; rapid decline: car tatoos, vinyl dresses, fleece bikinis.**
32
New cards
Diffusion of innovation
Diffusion of innovation is viewing product life cycle from the consumer adoption perspective.
33
New cards
5 groups of consumer adopters
1. Innovators - venturesome; higher educated
2. Early adopters - leaders in social setting; slightly above average education
3. Early Majority - deliberate; many informed social contacts
4. Late Majority - Skeptical; below average social status
5. Laggards - Fear of debt; neighbors and friends are info source
34
New cards
Three ways to manage the PLC
* Product modification
* Market modification
* Repositioning
* Market modification
* Repositioning
35
New cards
Product modification
**involves altering a product’s characteristic, such as its quality, performance, or appearance, to try to increase and extend the product’s sales, including** ***product bundling.***
36
New cards
Market modification
1\.**Increase a product’s use among existing customers**
2\.**Create new use situations**
3\.**Find new customers.**
37
New cards
Repositioning Strategy
•Reacting to a competitor product
–P&G ivory soap against Lever 2000
•Reaching a new market
–J & J baby oil as make-up remover for women
•Catching a rising trend
–Olive garden’s Gluten Free menu
•Changing the value offered
–Pond’s, Oil of Olay in Asia market
38
New cards
What is a brand
• Branding involves an organization using a name, phrase, design, symbols, or combination of these to identify its products and distinguish them from those of competitors.
\
• Branding is about the consumer’s **perceptions** of the offering – how it performs, how It looks, how it makes one feel, and what message it sends.
•Brand Perceptions are nurtured by:
1\. Market communications
2. Experiences
39
New cards
What is brand equity
**The added value a given brand provides a product beyond the functional benefits provided.**
40
New cards
Multiproduct branding strategy
sunbeam irons, campbell soup
41
New cards
Multibranding strategy
P&G Tide, Cheer, Ivory, Bold
42
New cards
Private (reseller) branding strategy
Sears Kenmore, Craftsmen
43
New cards
Mixed Branding
Michelin tires, Sears Tires
44
New cards
Shifts of demand curve
Change in income, preferences, prices of other goods --> chg. in demand --> shift of the demand curve
45
New cards
Shift along demand curve
Change in price --> change in quantity demanded --> movement along the demand curve
46
New cards
Total Revenue (TR)
Total money received from sales of product
\
Unit Price x quantity sold
\
Unit Price x quantity sold
47
New cards
Average revenue (AR)
The average amount of money received for selling one unit of the product
\
Total Revenue/quantity = unit price
\
Demand curve = average revenue curve
\
Total Revenue/quantity = unit price
\
Demand curve = average revenue curve
48
New cards
Marginal Revenue (MR)
Change in total revenue obtained by selling one additional unit
\
Slope of the total revenue curve
\
Slope of the total revenue curve
49
New cards
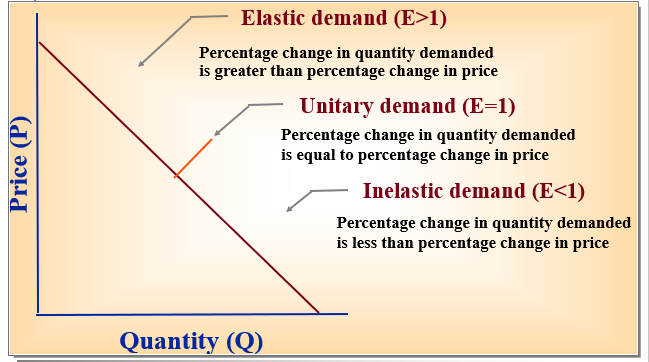
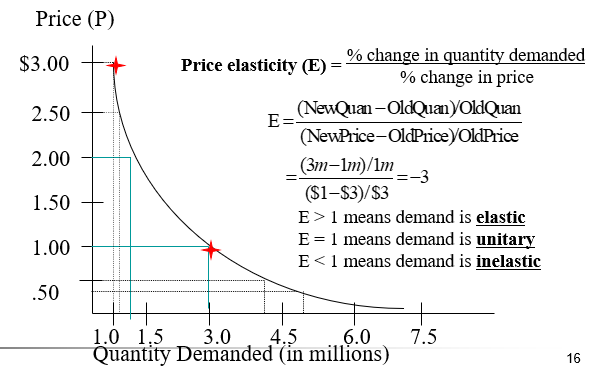
Price Elasticity of Demand
the percentage change in quantity demanded (QD) relative to a percentage change in price (P)
\
E = % change in QD / % change in P
\
E = % change in QD / % change in P
50
New cards
Elastic Demand
% change in QD > % change in P
51
New cards
Inelastic Demand
% change in QD
52
New cards
Unitary Demand
% change in QD = % change in P
53
New cards
Elasticity
•Elastic = flexible = responsive
54
New cards
Factors that lead to more elastic demand
–**More or better quality substitutes**
–**More time to adjust (SR vs. LR)**
–**Larger share of the HH budget**
55
New cards
Price elasticity of demand
* Necessities have lower elasticity
* Close Substitutes have higher elasticity
* Luxuries have higher elasticity
* Close Substitutes have higher elasticity
* Luxuries have higher elasticity
56
New cards
Elasticity Equation
57
New cards
Fixed cost
–Does not change with production
–Examples: Rent, Overhead, Long-term contracts , opportunity cost
58
New cards
Variable Cost
Changes with production
Examples: Cost of materials that go directly into the product, wages
59
New cards
Total Cost (TC)
TC = Fixed Cost (FC) + Unit Variable Cost (UVC)
60
New cards
Marginal Cost (MC)
the change in total cost that results from producing and marketing one additional unit (Q).
61
New cards
Marginal Cost (MC)
MC = Change in TC/1 unit in Q = slope of TC curve
62
New cards
Break-even Analysis
finding out the point at which total cost = total revenue
* TR = TC
* TR = TC
63
New cards
Break Even Volume
BE volume = FC/(P-UVC)
64
New cards
Profit goal
Q = (FC + Profit goal)/(P-UVC)
65
New cards
4 approaches for selecting approximate price level
* Demand Based approach
* Cost based approach
* profit based approach
* competition based approach
* Cost based approach
* profit based approach
* competition based approach
66
New cards
Demand based pricings approaches
•Skimming Vs. Penetration Pricing (New Products)
•Bundle Pricing
•Price Lining
•Odd-Even Pricing
•Prestige Pricing
•Target Pricing
•Yield Management
67
New cards
Prestige pricing
pricing strategy that uses higher prices to suggest quality and exclusivity
68
New cards
Price lining
Set price steps between products in a line
69
New cards
Skimming Pricing vs. Penetration pricing
•(1) Price sensitivity
•(2) Competitive threats
•(3) Price elasticity of demand
•(4) Price signals of quality
•(5) Economies of scale or experience
70
New cards
Skimming Pricing
* Set highest initial price to catch low price sensitive segment
* then lower the price to attract more price-sensitive segments
\
* then lower the price to attract more price-sensitive segments
\
71
New cards
Penetration Pricing:
Set a low initial price to appeal to the mass market immediately
72
New cards
Cost Based approaches
* Standard mark-up
* cost plus
* experience curve pricing
* cost plus
* experience curve pricing
73
New cards
Standard markup pricing
Set price by adding a fixed % to the cost of the product
74
New cards
Cost-Plus Pricing
Set price by adding a fixed $ to the cost of the product
75
New cards
Experience Curve Pricing
Cut the price with the decrease of average cost of the product (learning effect)
76
New cards
Standard markup pricing equation
Markup on cost = (P – C) / C
77
New cards
markup based on price equation
Markup based on Price = (P - C)/ P
78
New cards
Target Profit Pricing
–Target Profit = TR – TC
= (P x Q) – (TFC + (UVC x Q))
– P = (Target Profit + TFC + (UVC x Q))/Q
79
New cards
**Competition-Oriented Approaches**
**include:**
•**customary pricing**
•**above-, at-, or below-market pricing**
•**loss leader pricing**
80
New cards
Below-Market Pricing
steal customers vs. poor quality signaling, price war
81
New cards
At-Market Pricing
highlight other features (differentiate)
82
New cards
Above-Market Pricing
quality signal, added value??
83
New cards
Loss-leader pricing
* Sell below customary price (or below cost)
* Increase store traffic
* Increase store traffic
84
New cards
Customary Pricing
the prices that consumers are used to paying for certain products or services over a long period of time
85
New cards
Power of marginal Analysis in the real world

86
New cards
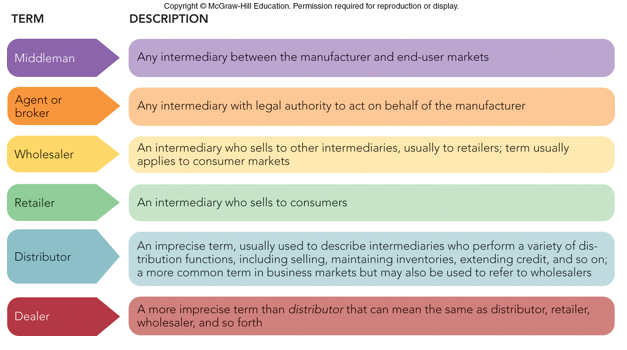
Marketing channels
–Sets of interdependent organizations participating in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption
–Intermediaries: merchants, agents, and facilitators
87
New cards
A marketing channel system
–The particular set of marketing channels a firm employ
–Push vs. pull strategy
88
New cards
•Multichannel marketing
–Using two or more marketing channels to reach customer segments in one market area
–Omnichannel marketing
–Integrated marketing channel system
89
New cards
Channel intermediaries
90
New cards
Functions performed by intermediaries
* transactional
* logistical
* facilitating
* logistical
* facilitating
91
New cards
Transactional function

92
New cards
Logistical function

93
New cards
Facilitating function

94
New cards
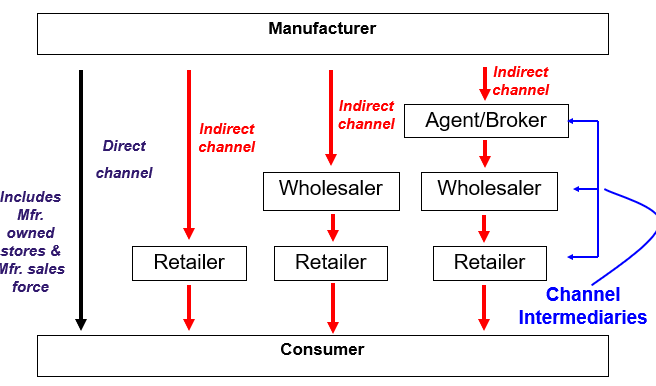
Basic Channel Structures
95
New cards
direct Channel
•**when a producer and ultimate consumer deal directly with each other.**
96
New cards
Indirect Channel
when intermediaries are inserted between the producer and consumers and perform numerous channel functions.
97
New cards
Dual Distribution
•**an arrangement whereby a firm reaches different buyers by employing two or more different types of channels for the same basic product.**
98
New cards
Strategic Channel Alliances
recent innovation in marketing channels, whereby one firm’s channel is used to sell another firm’s products
* –**Starbucks à PepsiCo (used to be Kraft )à Supermarket retailers**
–**McDonalds (McCafe)à Kraft and Coca colaà Supermarkets**
–**General Mills partners with Nestle to distribute its cereals world wide via its joint venture (Cereal Partners Worldwide).**
* –**Starbucks à PepsiCo (used to be Kraft )à Supermarket retailers**
–**McDonalds (McCafe)à Kraft and Coca colaà Supermarkets**
–**General Mills partners with Nestle to distribute its cereals world wide via its joint venture (Cereal Partners Worldwide).**
99
New cards
Why Forming Strategic Alliances in Channels?
•Motives for forming strategic alliances:
–Upstream motives
•Manufacturers can benefit from the distribution network offered by distributors
•Better coverage and lower cost
–Downstream motives
•Distributors can lower inventory costs
•Maintain a steady supply of products
100
New cards
Horizontal Marketing System
• **a retail station within another store**
–**Sephora within JCPenny**
–**Samsung Experience Shop within BestBuy**