week 7 ~ glacial
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards

what is this?
glacial trough/U-shaped valley
2
New cards

what is this?
hanging valley
3
New cards

what is this?
fjord → U-shaped valley with sea level high enough to fill
4
New cards

what are these?
grooves
5
New cards

what are these?
plastically moulded forms (p-forms)
diff lithology causing diff levels of abrasion
diff lithology causing diff levels of abrasion
6
New cards

what are these?
striations
7
New cards

what is this?
glacial polish
8
New cards
how are partly streamlined landforms produced?
combination of abrasion and rock fracturing
9
New cards

what is this?
roche moutonnee
10
New cards
how are roche moutonnees formed?
stoss - striated surface due to abrasion from moraine at glacier base
lee - materials plucked from lee side
lee - materials plucked from lee side
11
New cards

what is this?
crag and tail
12
New cards
how is crag and tail formed?
stoss - plucking and abrasion erode side
lee - less resistant moraines deposited giving it a tail
lee - less resistant moraines deposited giving it a tail
13
New cards

what is this?
cirque and tarn
14
New cards

what is this?
horn → pyramidal peak
15
New cards

what are these?
arete → saw tooth like ridges
16
New cards

what is this?
nunatak (glacial islands) → high elevated bed rock that has not been glaciated
17
New cards
what is the low lying area between horns and aretes?
col

18
New cards

what is this?
erratics → pieces of material transported from glacier, vary in size
19
New cards
what is a moraine?
mound of till
20
New cards
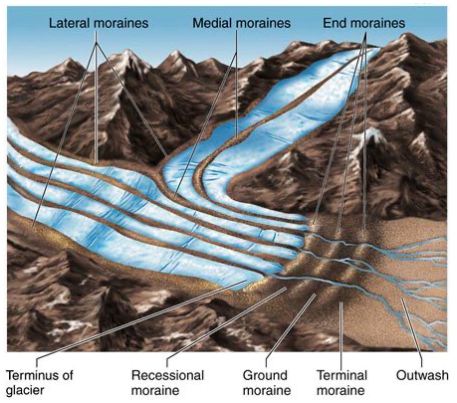
what are the types of moraines?
lateral → formed along edge of valley
medial → joining of 2 lateral moraines
end → formed at end of glacier
terminal → type of end glacier, furthest one formed
recessional → end moraine marking times of temp pauses
medial → joining of 2 lateral moraines
end → formed at end of glacier
terminal → type of end glacier, furthest one formed
recessional → end moraine marking times of temp pauses
21
New cards
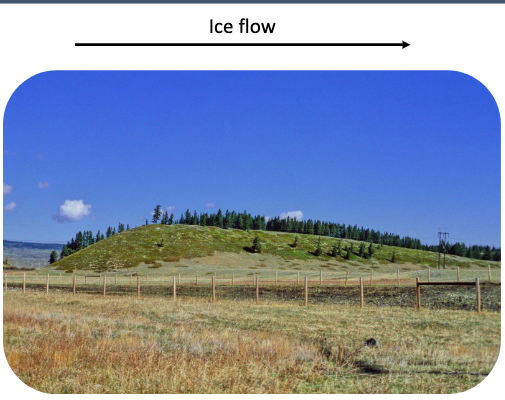

what is this?
drumlin → stream lined, formed through subglacial deposition
22
New cards
what are the types of glacial sediment?
glacial till → from ice directly
glaciofluvial → from melted glacial water rivers
glaciolacustrine → from melted glacial water lakes
glaciofluvial → from melted glacial water rivers
glaciolacustrine → from melted glacial water lakes
23
New cards

what are these?
eskers
24
New cards
how are eskers formed?
when rivers/lakes are formed under or right at the edge of a glacier and leave behind a pile of material when the ice melts
25
New cards

what are these?
kames
26
New cards

what are these?
kettle lakes
27
New cards
how are kames formed?
formed when supraglacial sediment is deposited on top and the ice melts leaving a mound of debris
28
New cards
how are kettle lakes formed?
formed when you have a block of ice that eventually melts surrounded by outwash material or tills
29
New cards
what is permafrost?
zones of permanently frozen ground (more than 2 years)
30
New cards
what is continuous vs discontinuous ground ice?
cont → entire thing frozen
discont → pockets of frozen/unfrozen
discont → pockets of frozen/unfrozen
31
New cards
what is an active layer?
seasonally thaws/freezes
32
New cards
what is a permafrost table?
line where permanent ice begins
33
New cards

what is this?
frost cracking
34
New cards
what is frost heave?
when ice lens layers thickens and the frozen zone experiences volume expansion/shrinkage due to frost heaving/thawing
35
New cards

what are these?
frost wedges

36
New cards

what are these?
melted ice wedges
formed when series of ice wedges are formed in the same area
formed when series of ice wedges are formed in the same area
37
New cards

what are these?
frost mounds. → pockets of soil filled with icea
38
New cards

what are these?
pingos
39
New cards
how are pingos formed?
giant ice mounds
formed when there is a pocket of water underneath which pushes the ground upwards as it freezes
formed when there is a pocket of water underneath which pushes the ground upwards as it freezes
40
New cards

what is this?
thermokarst → irregular terrain with depressions and hummocks between them
41
New cards
how is thermokarst formed?
thawing of ground ice and material collapsing
42
New cards

what are these?
stone circles
43
New cards

what are these?
polygons
44
New cards

what are these?
stone stripes
45
New cards

what are these
hummocks