RADT W5L2 Ch 11, 22 - Film Mounting, Exposure and Technique Errors
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What does Anatomic Order refer to?
How teeth are arranged within the dental arches
Who is responsible for mounting radiograph films?
Any trained dental professional who possesses knowledge of the normal anatomic landmarks
Usually mounting film is the responsibility of the office dental radiographer
When and where are films mounted?
When: immediately after processing
Where: clean, dry, light coloured work surface in front of an illuminator or view box
Why are film mounts useful?
quick and easy for viewing and interpreting
decreases changes of error in determining the patients right and left side
What information must be on a film mount?
Pt full name
Date of exposure
Dentist name
Radiographers name
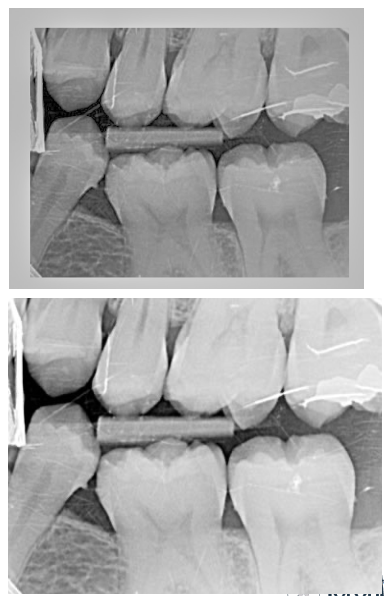
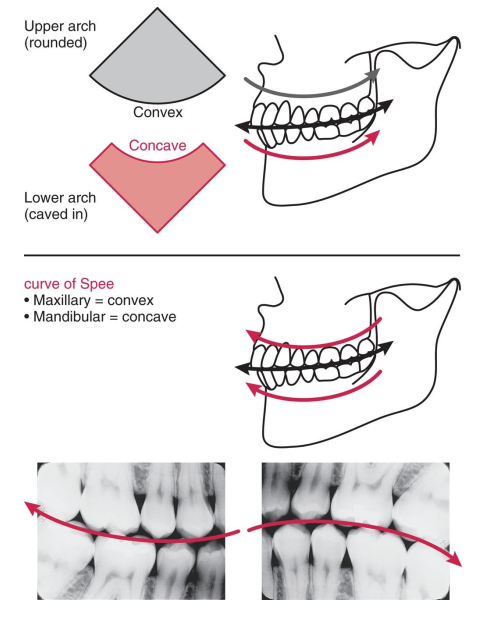
What is the curve of Spee? Why is it useful?
The curve of Spee is the convex nature of the maxilla and the concave nature of the mandible.
it is a useful landmark when mounting bite-wing radiographs.
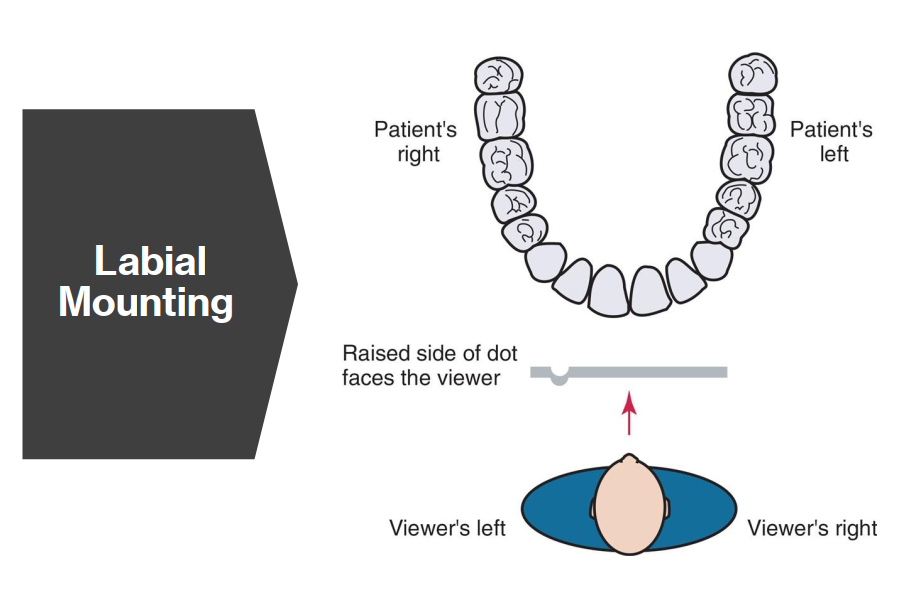
What is Labial Mounting?
Labial mounting is the standard (and preferred) method of mounting dental radiographs where:
The viewer’s perspective is as if looking at the patient face-to-face
The patient’s right side is on your left, and left is on your right
The raised dot on the film faces toward the viewer (convex side)
Used for both intraoral and extraoral film mounting to ensure consistent interpretation.
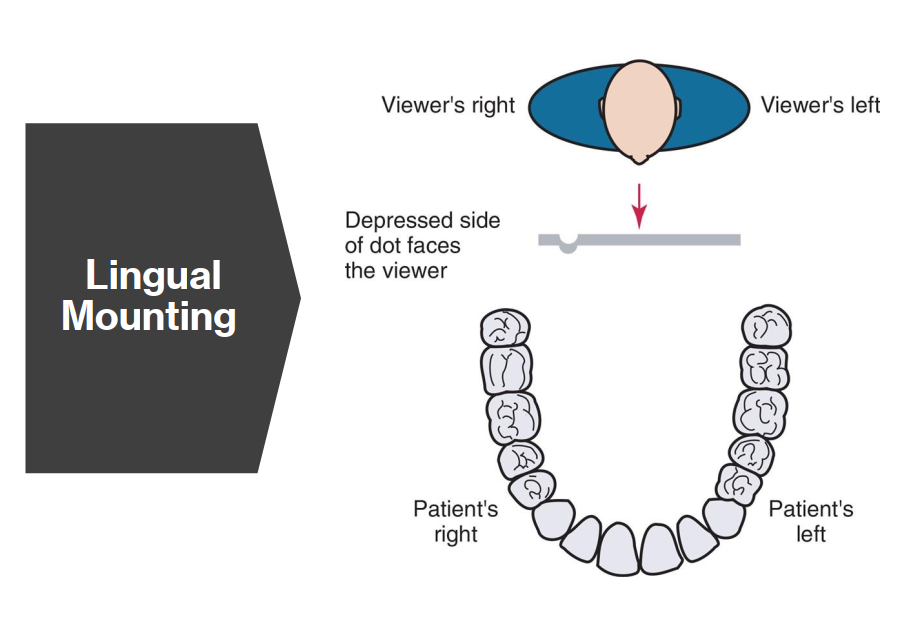
What is Lingual Mounting? How is this different to Labial Mounting?
Lingual mounting is a method of viewing dental radiographs as if you are behind the patient, looking out of their mouth.
The patient’s right side is on your right
The raised dot on the film is concave (faces away from viewer)
Less commonly used than labial mounting
Key difference to Labial Mount: Viewer’s perspective is from inside the patient’s mouth.
What equipment is necessary for Film viewing?
Light source → large enough to accommodate a variety of mounted films; Light should be uniform in intensity and evenly diffuse
Magnification → Magnifying glass may be useful for interpretation
What is the sequential order for film viewing?
Right side Maxillary PA → Left side maxillary PA
Left side Mandibular PA → Right side mandibular PA
Left side BW → right side BW
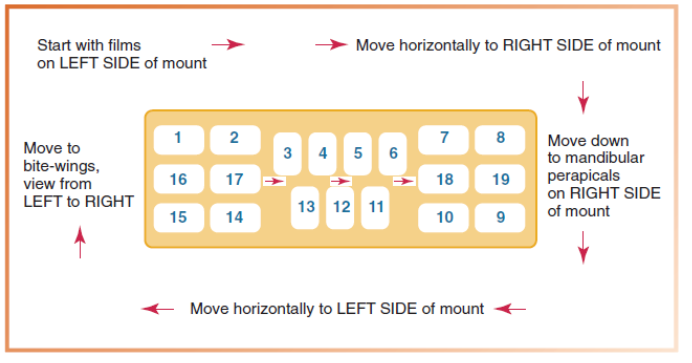
What do we look for when examining radiographic films? (5)
Unerupted, missing, impacted teeth
Dental caries
Size and shape of pulp cavities
Bony changes → level of alveolar bone, calculus
Root and periapical areas
Radiographic Error: Unexposed Film
Film appears clear
Reason: xray not on, electric failure, malfunctioning machine, user error
Fix: check that xray unit is on, and there is an audible exposure signal
Radiographic Error: Film exposed to light
Film appears black
Reason: film accidentally exposed to white light
Fix: check dark room for possible light leaks; make sure all lights are off before unwrapping film
Radiographic Error: Overexposed Film
Film appears dark in some areas; structures not clearly visible
Reason: excessive exposure time, high kVp or high mA
Fix: adjust control panel for appropriate exposure time/strength (ex. child, elderly) → reduce as needed
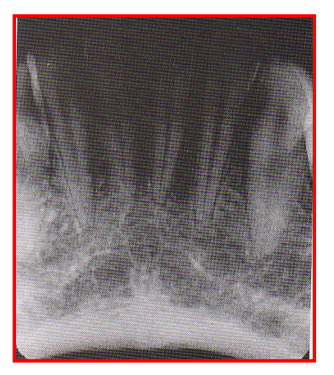
Radiographic Error: Underexposed Film
Film appears too light/bright; structures all look radiopaque.
Reason: insufficient exposure time, too low kVp, or low mA
Fix: check settings and increase as needed
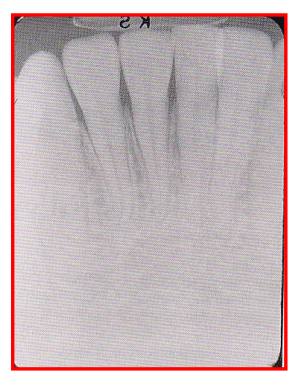
Radiographic Error: Inadequate Apical Coverage
Failure to see the apices on a PA radiograph → no root tips
Reason: Incorrect film placement
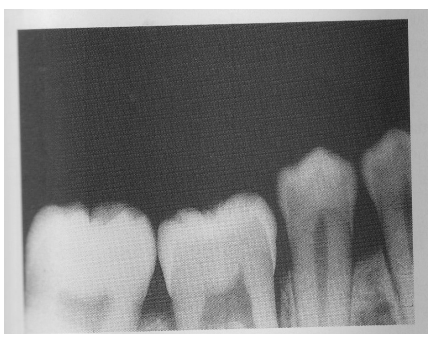
Radiographic Error: Line of occlusion
Occlusal plane appears tipped or tilted on a radiograph because the edge of the film was not placed PARALLEL to the incisal-occlusal surface of the teeth
Reason: Incorrect film placement → occurs when using digital method (folding film w fingers), and if client fails to close their mouth.
Fix: Client needs to hold film firmly against tooth to prevent film from dropping or slipping
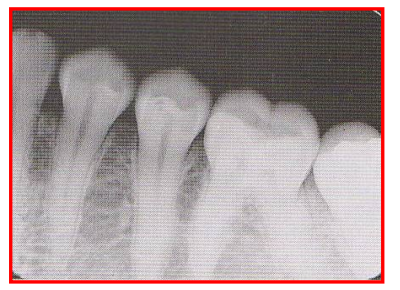
Radiographic Error: Overlapping
Film appears to have overlapping at the contact areas between teeth.
Reason: Incorrect HORIZONTAL angulation; central ray was not directed through interproximal spaces
Fix: Angle XCP more distally or mesially depending on direction of overlap
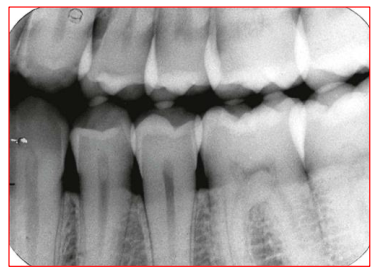
Radiographic Error: Foreshortening
Teeth appear short with blunted roots; image looks shorter than actual tooth
Reason: Excessive vertical angulation of the PID
Fix: Flatten the angle of the PID
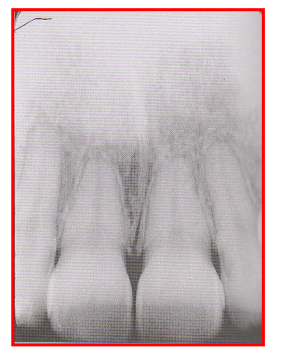
Radiographic Error: Elongation
Teeth appear long and distorted
Reason: insufficient vertical angulation (too flat)
Fix: Tilt PID up or down to increase vertical angulation
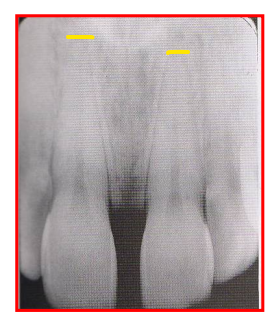
Radiographic Error: Incorrect vertical angulation (BW)
BW image appears distorted, you can see occlusal surfaces slightly.
Reason: Negative vertical angulation used
Fix: +10 deg vertical angulation when taking bisecting BW exposures → PID positioned downwards
compensates for the slight tilt of maxillary teeth and lingual bend of upper half of the film
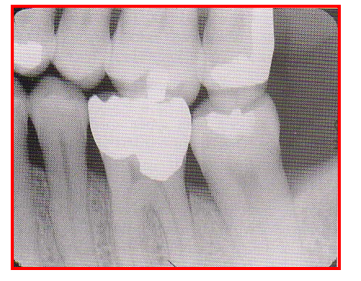
Radiographic Error: Cone Cut
A clear unexposed crescent appears on the film
Reason: PID was not properly aligned with the film holder and the xray beam did not expose the entire film.
Fix: Ensure central ray is centered over the film
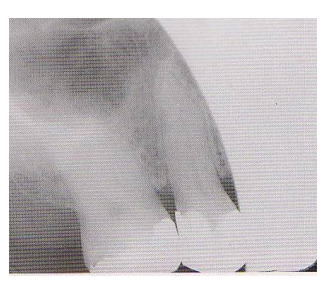
Radiographic Error: Film Bending
Image appears stretched and distorted
Fix: avoid bending film excessively either from heavy finger pressure or curvature of the palate → use cotton rolls to prevent too much bending.
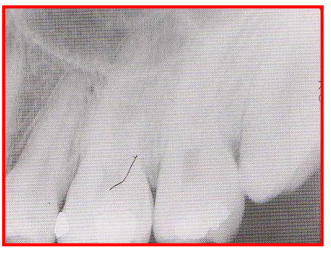
Radiographic Error: Film Creasing
Thin radiolucent line appears on processed films
Reason: crack in the film emulsion
Fix: use gentle pressure on the films when bending to fit into oral cavity/XCP holder
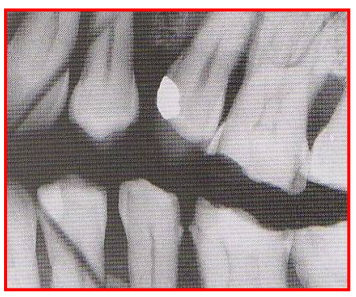
Radiographic Error: Phalangioma
Client’s finger was incorrectly positioned in front of the film instead of behind the film so bony finger appears on the film.
Reason: Finger-holding used in bisecting technique
Fix: have client position finger behind film.
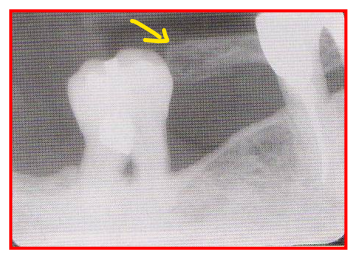
Radiographic Error: Double Exposure
2 images appear on the film
Reason: film was exposed twice
Fix: ensure working area is kept organized
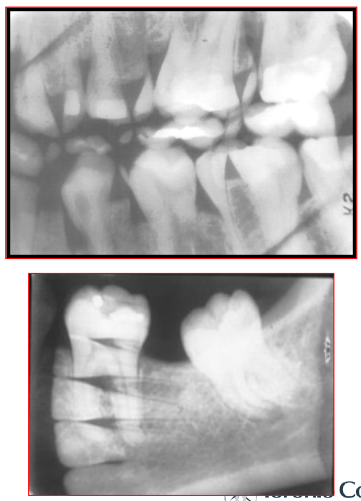
Radiographic Error: Penumbra
Blurred images appear on the film
Reason: client moving during exposure of the film
Fix: ensure client is stabilized and not moving during exposure
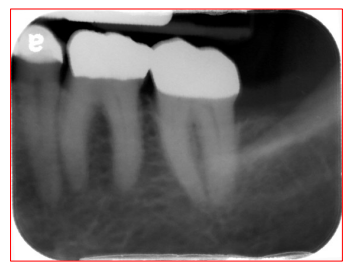
Radiographic Error: Reversed film
Image appears light with a HERRINGBONE pattern across the film (tire-tracks/waffle image)
Herringbone pattern is the actual pattern embossed on the lead foil.
Reason: Film was placed in the mouth backwards
Fix: ensure the proper side of the film is placed facing the PID
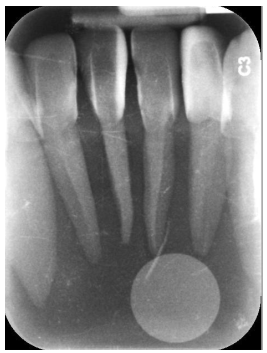
Radiographic Error: Reversed Phosphorus Plate
Radiopaque circle on the radiograph is the magnetic circle on the phosphorus plate
Reason: film placed backwards in mouth
Fix: ensure proper side of the film is placed facing the PID.
Radiographic Error: Static Electricity
Results from opening the film packet too quickly
Fix: ensure film is removed slowly from film packet

Radiographic Error: Poor Resolution/Poor Contrast
Aka Exposure Error
film appears too bright with many shades of grey.
Fix: check kVp on control panel