Statistics - data collection
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Population definition
whole set of items that are of interest
sample definition
some subset of population intended to represent population
sampling unit
each individual thing in the population that can be sampled is known as sampling unit
sampling frame
often sampling units of a population are individually named / numbered to form list called sampling frame
Census - advantages + disadvantages
Advantages:
should give completely accurate result
Disadvantages:
time consuming and expensive
can not be used when testing involves destruction
large volume of data to process
Sample - advantages + disadvantages
Advantages:
cheaper
quicker
less data to process
Disadvantages:
data may not be accurate
data may not be large enough to represent small sub-groups
Simple random sampling - method:
number pop
use RNG to select a set amount of numbers w/ no repetition
find the ppl corresponding to numbers
Simple random sampling - advantages and disadvantages
advantages:
no bias
easy + cheap
Disadvantages:
sampling frame needed
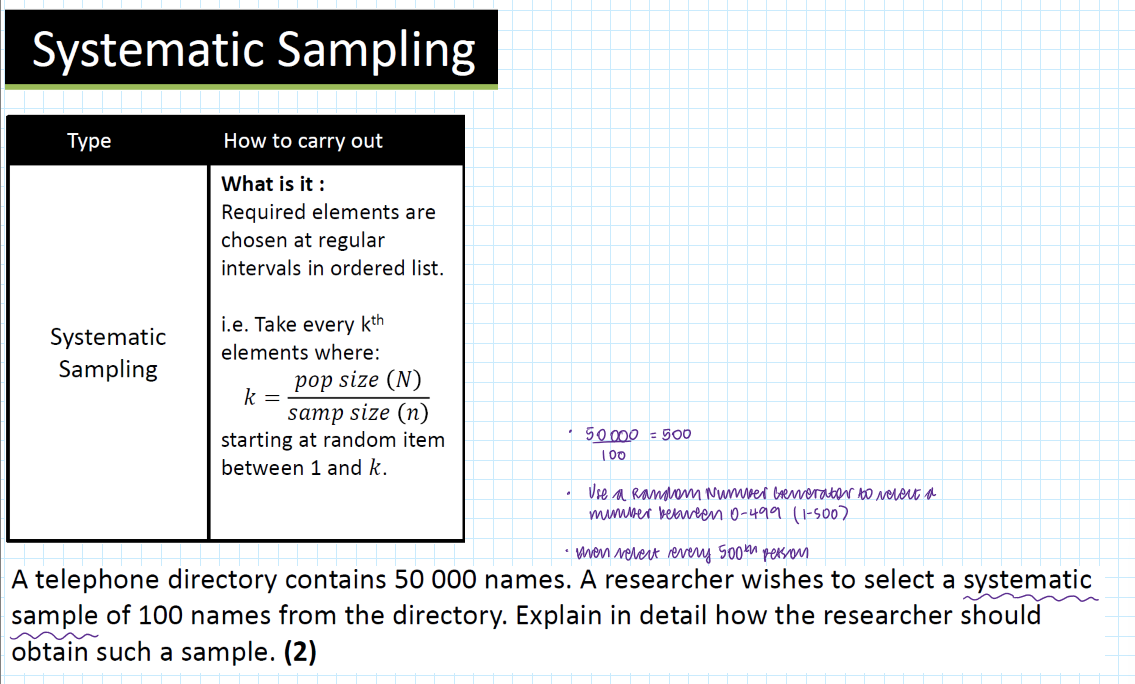
systematic sampling - method:
number pop
take every kth value where k=pop/sample
find the ppl corresponding to numbers
systematic sampling - advantages and disadvantages:
advantages:
easy
good for big pop
disadvantages:
can introduce bias
sampling frame needed
stratified sampling - method:
split pop into groups / strata
work out proportional sample for each group / strata
simple random sampling w/in each strata

stratified sampling - advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
proportional representation (mimics population)
Disadvantages:
good strata needs to be chosen
quota sampling - method:
divide pop by needed quality
then randomly sample
quota sampling - advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
quick
easy
allows for comparison between groups
Disadvantages:
bias
expensive
opportunity sampling - method:
anyone who is available + willing
opportunity sampling - advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
easy
cheap
Disadvantages:
unlikely to be representative
very dependent on the researcher
Types of Data - Qualitative:
non-numerical vales e.g. colour
Types of Data - Quantitative:
numerical values
Discrete vales
can only take specific values, e.g. shoe size, number of children
Continues values
can only take any decimal value (possible with a specific range)