Topic 3 Archaea
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Who first recognized Archaea as a separate domain?
Carl Woese & colleagues, via rRNA sequence comparisons (late 20th century).
What was archaea originally called?
Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria).
What were bacteria originally renamed to contrast archaebacteria?
Eubacteria (true bacteria).
How many domains of life are there today?
Three: Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya.
Why is capitalization important when writing Archaea vs archaea?
Capitalized = taxonomic rank; lowercase = organisms in general.
What type of chromosomes do archaea have?
Single, circular chromosomes (like bacteria).
How does archaeal DNA resemble eukaryotes?
DNA wraps around histone proteins
What type of bonds link archaeal membrane lipids?
Ether bonds.
Why do histones help archaea?
They stabilize DNA, especially in extreme environments.
What type of bonds link bacterial/eukaryotic lipids?
Ester bonds.
Why are ether bonds important for archaea?
More chemically stable in extreme conditions.
What special feature can archaeal membranes form under high heat?
Lipid monolayers (instead of bilayers).
What structural feature adds stability to archaeal lipids?
Branched isoprenoid side chains.
Do archaea have peptidoglycan cell walls?
No
What material forms many archaeal cell walls?
What molecules alternate in pseudomurein?
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) & N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid (NAT).
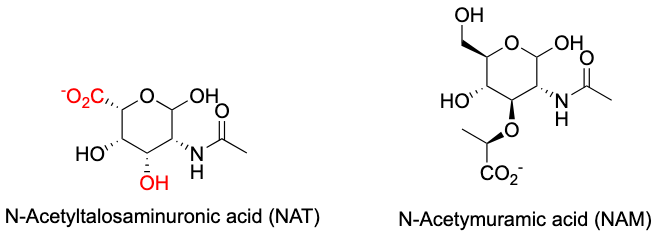
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) & N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid (NAT).
What type of glycosidic linkage is in pseudomurein?
β-1,3 linkages.
What linkage is in bacterial peptidoglycan?
β-1,4 linkages.
Why is pseudomurein resistant to lysozyme?
Lysozyme only breaks β-1,4 bonds
Name five shapes of archaeal cells.
Cocci, rods, filaments, lobed, square.
What is an example of a square-shaped archaeon?
Haloquadratum walsbyi.
What environments are Crenarchaeota often found in?
Thermophilic, hyperthermophilic, and acidophilic environments.
What membrane adaptation do many crenarchaeotes have?
Lipid monolayers.
What proteins protect crenarchaeotes from heat?
Thermostable proteins.
What role do molecular chaperones play in hyperthermophiles?
Refold denatured proteins.
What does halophile mean?
Salt-loving.
What NaCl concentration do halophiles require?
≥ 1.5 M NaCl.
What is the main risk of high-salt environments for cells?
Osmotic shock (water loss).
How does Halobacterium salinarum avoid osmotic shock?
Maintains high internal K+ concentration.
Do halophiles use chlorophyll for phototrophy?
NO.
Bacteriorhodopsin.
What does bacteriorhodopsin generate?
Proton motive force → ATP.
How do halophiles switch metabolism when O₂ is high?
Grow on organic carbon.
How do halophiles adapt when O₂ is low?
Use bacteriorhodopsin phototrophy.
What unique metabolic process do methanogens perform?
Methanogenesis (methane production).
Are methanogens bacteria or archaea?
Only archaea.
What environmental condition do methanogens require?
Strictly anoxic (no oxygen).
Where are methanogens commonly found?
Lake sediments, wetlands, ruminant guts, human colon.
What gas do methanogens release?
Methane (CH₄)
What superphylum do Thaumarchaeota belong to?
TACK superphylum.
What temperatures do Thaumarchaeota prefer?
Mesophiles (15–40 °C) & psychrophiles (<15 °C).
Where are Thaumarchaeota abundant?
Oceans (especially marine environments).
What role do Thaumarchaeota play in carbon cycling?
Assimilate inorganic carbon autotrophically.
What role do they play in nitrogen cycling?
Ammonia oxidation (first step of nitrification).
What key enzyme do ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) contain?
Ammonia monooxygenase (amoA gene).
What does ammonia monooxygenase do?
Converts ammonia → hydroxylamine (first nitrification step).
What important species is a model Thaumarchaeote?
Nitrosopumilus maritimus.
What psychrophilic Thaumarchaeote genome was sequenced in 2006?
Cenarchaeum symbiosum (from marine sponge).
Where are Korarchaeota typically found?
Hot springs
Why are Korarchaeota poorly understood?
Very difficult to culture.
What is the best-known Nanoarchaeote?
Nanoarchaeum equitans.
What is unusual about N. equitans’ genome?
Extremely small; lacks genes for essential functions.
What does N. equitans depend on for survival?
Its host Ignicoccus hospitalis.
What functions is N. equitans missing genes for?
Nucleotides, lipids, cofactors, amino acids.
What kind of relationship exists between N. equitans and I. hospitalis?
Obligate symbiosis (possibly parasitism). N. equitans is nearly completely dependent on its host.
Where are N. equitans-like organisms found?
High temperature environments
When was the Asgard superphylum proposed and what are the groups?
2017
Lokiarchaeota
Thorarchaeota
Odinarchaeota
Heimdallarchaeota
Why are they named after Norse gods?
First DNA found near “Loki’s Castle” hydrothermal vents.
Where else have Asgard archaea been detected?
US rivers, NZ hot springs, deep-sea sediments.
Why are Asgard archaea significant evolutionarily?
Closest known relatives of eukaryotes.
What type of genes do Asgard genomes contain?
Eukaryotic signature proteins (ESPs).
What do ESPs suggest about Asgard archaea?
Early steps toward eukaryotic complexity.
What is one proposed evolutionary model from Asgard?
Two-domain tree of life: Bacteria + Archaea (Eukarya evolved from Asgard).
What was the first cultivated Asgard archaeon?
Candidatus Prometheoarchaeum syntrophicum (2020, Lokiarchaeota).
Why is Asgard significance still debated?
Few have been cultured; physiology largely unknown.
What enzyme is unique to all hyperthermophiles?
Reverse DNA gyrase.
What does reverse DNA gyrase do?
Increases DNA supercoiling → raises DNA melting temp.
Why is DNA supercoiling important for hyperthermophiles?
Prevents denaturation at extreme heat.
What other proteins stabilize hyperthermophile DNA?
Thermostable DNA-binding proteins.
Where are methanogens found?
Anoxic environments (lakes, sediments, animal guts).
Where are halophiles found?
Hypersaline lakes, salt ponds, brines.
Where are hyperthermophiles found?
Hot springs, hydrothermal vents.
Where are acidophiles found?
Acidic hot springs, mine drainage.
Where are Thaumarchaeota especially abundant?
Oceans.
Are archaea only extremophiles?
No, many are mesophiles in soils and oceans.
What are the two earliest recognized archaeal phyla?
Crenarchaeota and Euryarchaeota.
What superphylum includes Thaumarchaeota and Korarchaeota?
TACK superphylum.
What superphylum includes very small, parasitic archaea?
DPANN superphylum.
What superphylum is closest to eukaryotes?
Asgard superphylum.
What is archaeal taxonomy described as?
Rapidly changing; constantly updated with new discoveries.
What makes archaeal lipids more stable than bacterial ones?
Ether linkages and branched chains.
What is the bizarre host-symbiont archaeal pair?
Nanoarchaeum equitans + Ignicoccus hospitalis.
What archaeon oxidizes ammonia in oceans?
Nitrosopumilus maritimus.
What marine sponge symbiont’s genome was sequenced in 2006?
Cenarchaeum symbiosum.
What Asgard archaeon was cultivated in 2020?
Candidatus Prometheoarchaeum syntrophicum.
What is the function of bacteriorhodopsin in halophiles?
Generates proton motive force for ATP.
What archaea live in animal digestive systems?
Methanogens.
What archaea may hold the key to eukaryotic origins?
Asgard archaea.