exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Last updated 10:31 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Ototoxicity
•Damage to the organ of hearing resulting
from:
•Noxious substances
•Therapeutic agents
•Chemotherapy drugs
•Aminoglycosides
•Loop diuretics
•Salicylates (aspirin)
•Anti-malaria drugs (quinine)
•Many can damage other organ systems
besides the ear
from:
•Noxious substances
•Therapeutic agents
•Chemotherapy drugs
•Aminoglycosides
•Loop diuretics
•Salicylates (aspirin)
•Anti-malaria drugs (quinine)
•Many can damage other organ systems
besides the ear
2
New cards
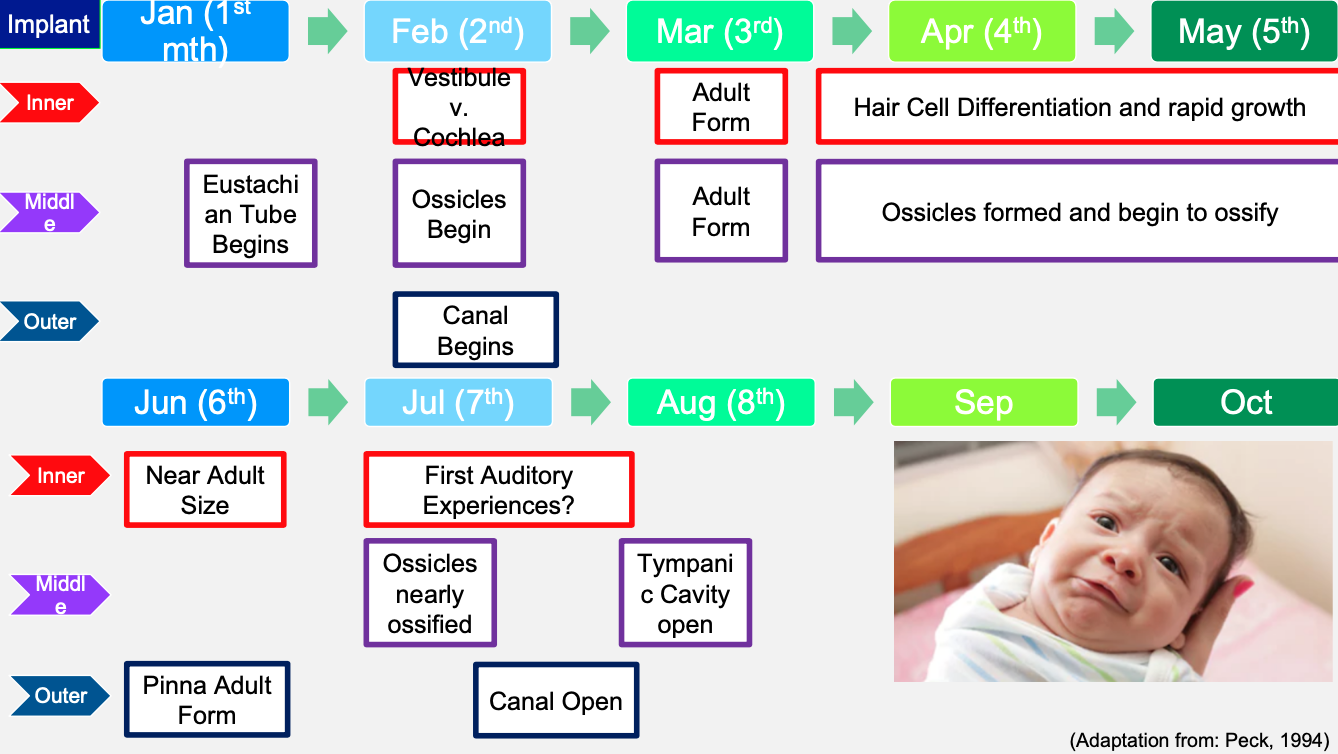
Timeline of embryology
3
New cards
genetic disorders
key features
4
New cards
usher syndrome
• One of most common syndromic hearing losses
• Affects retinas in both eyes (retinitis pigmentosa) causes night blindness and vision
loss
• Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
• Affects retinas in both eyes (retinitis pigmentosa) causes night blindness and vision
loss
• Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
5
New cards
Waardenburg syndrome
• Autosomal Dominant Inheritance, 1-3% of all congenital hearing losses
• Disorder of pigmentation of various parts of the body including:
• Eyes
• Hair
• Skin
• Stria vascularis in the cochlea
• 4 Classifications: Pigmentation may vary, often blue eyes and white
forelock
• W1 60% will have SNHL, dystopia canthourm (eyes appear wide-set)
• W2 90% will have SNHL
• W3: SNHL, dystopia canthorum and musculoskeletal abnormalities of the upper
limbs
• Disorder of pigmentation of various parts of the body including:
• Eyes
• Hair
• Skin
• Stria vascularis in the cochlea
• 4 Classifications: Pigmentation may vary, often blue eyes and white
forelock
• W1 60% will have SNHL, dystopia canthourm (eyes appear wide-set)
• W2 90% will have SNHL
• W3: SNHL, dystopia canthorum and musculoskeletal abnormalities of the upper
limbs
6
New cards
Pendred syndrome
• Most common cause of autosomal recessive syndromic HL
• Associated with broad range of hearing loss
• Often includes Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct (EVA)
• Progressive hearing loss – at times sudden
• Progressive vestibular dysfunction possible (65%)
• May include Mondini malformation
• Not enough turns in the cochlea
• Goiter is a hallmark
• Thyroid dysfunction Mondini’s
• Associated with broad range of hearing loss
• Often includes Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct (EVA)
• Progressive hearing loss – at times sudden
• Progressive vestibular dysfunction possible (65%)
• May include Mondini malformation
• Not enough turns in the cochlea
• Goiter is a hallmark
• Thyroid dysfunction Mondini’s
7
New cards
branchio-oto-renal
• Autosomal dominant inheritance
• Disruption of the development of tissues in the neck and malformations
of the ears and kidneys
• Branchio – Refers to the second branchial arch
• May result in cleft cysts or pits near the collar bone
• Oto – Hearing loss can be any of the three types
• May have pre-auricular pits or tags
• Renal – Kidney structure abnormalities
• Can result in end-stage renal disease in later life
• Disruption of the development of tissues in the neck and malformations
of the ears and kidneys
• Branchio – Refers to the second branchial arch
• May result in cleft cysts or pits near the collar bone
• Oto – Hearing loss can be any of the three types
• May have pre-auricular pits or tags
• Renal – Kidney structure abnormalities
• Can result in end-stage renal disease in later life
8
New cards
charge syndrome
C – Coloboma (gap or hole in the iris/eyelid)
H – Heart defects (varies)
A - Choanal Atresia (narrowing of the nasal passages)
R - Restriction in growth and development (varies)
G - Genital Abnormalities (varies)
E - Ear Abnormalities (middle and inner ear problems
including hearing and balance)
• Autosomal dominant inheritance
• Presentation varies widely from patient to patient
H – Heart defects (varies)
A - Choanal Atresia (narrowing of the nasal passages)
R - Restriction in growth and development (varies)
G - Genital Abnormalities (varies)
E - Ear Abnormalities (middle and inner ear problems
including hearing and balance)
• Autosomal dominant inheritance
• Presentation varies widely from patient to patient
9
New cards
alport syndrome
• 80% of cases are X-Linked
• Causes progressive kidney failure leading to end-stage renal
disease
• May need dialysis and kidney transplant
• Progressive SNHL hearing loss which can progress to
profound
• Usually identified in late childhood (school age)
• May require cochlear implantation
• Causes progressive kidney failure leading to end-stage renal
disease
• May need dialysis and kidney transplant
• Progressive SNHL hearing loss which can progress to
profound
• Usually identified in late childhood (school age)
• May require cochlear implantation
10
New cards
jervell and lange-nielsen
• Autosomal recessive inheritance
• Congenital SNHL
• Arrhythmia
• Prolongation of the QTc interval resulting
in fainting/and or sudden death
• Congenital SNHL
• Arrhythmia
• Prolongation of the QTc interval resulting
in fainting/and or sudden death
11
New cards
stickler syndrome
• Can be both dominant or
recessive
• Includes differences in:
• Eyes (severe myopia)
• Musculoskeletal (joint laxity)
• Orofacial structures
• Ears and hearing
• 5 different subsets depending
on genes encoding different
collagen types
recessive
• Includes differences in:
• Eyes (severe myopia)
• Musculoskeletal (joint laxity)
• Orofacial structures
• Ears and hearing
• 5 different subsets depending
on genes encoding different
collagen types
12
New cards
teacher-collins syndrome
• Autosomal Dominant
inheritance
• Effects development of the
bones and tissues of the face –
midface
• Often affects jaw which can
impact airway, feeding, and
speech
• Roughly half have hearing loss
• Generally conductive hearing
loss
• Due to abnormalities of the
outer and middle ear
inheritance
• Effects development of the
bones and tissues of the face –
midface
• Often affects jaw which can
impact airway, feeding, and
speech
• Roughly half have hearing loss
• Generally conductive hearing
loss
• Due to abnormalities of the
outer and middle ear
13
New cards
otitis externa
outer ear --- viral, bacterial, or fungal infection of the ear canal
14
New cards
otitis media
middle ear
15
New cards
Vea
Volume in ear canal
16
New cards
Ytm
admittance/compliance --- Y axis
17
New cards
TPP
tympanic peak pressure --- x axis
18
New cards
TW
tympanic width
-the pressure range of a tympanogram at a defined point
-calculated at half of Ytm value
-Reported as the absolute value of the range between the two
frequencies
-the pressure range of a tympanogram at a defined point
-calculated at half of Ytm value
-Reported as the absolute value of the range between the two
frequencies
19
New cards
CAPD
central auditory processing disorder
-We use a battery of listening tests to identify patterns of listening difficulty and develop skill profiles
- If someone has a diagnosis involving another neurologic process, we do not assess CAPD
- It is much more likely that the other diagnosis is responsible for any processing deficits
-We use a battery of listening tests to identify patterns of listening difficulty and develop skill profiles
- If someone has a diagnosis involving another neurologic process, we do not assess CAPD
- It is much more likely that the other diagnosis is responsible for any processing deficits
20
New cards
ABR
auditory brainstem response test
Objective measurement of the auditory system including the nerves up to the
brainstem
Objective measurement of the auditory system including the nerves up to the
brainstem
21
New cards
Tone burst
• Tone bursts are not technically tones
• They are filtered noise that mimics the effects of a tone
• Work to identify the 5th wave of the auditory pathway
• Trace the 5th wave down until we find the quietest level we can see a response
• They are filtered noise that mimics the effects of a tone
• Work to identify the 5th wave of the auditory pathway
• Trace the 5th wave down until we find the quietest level we can see a response
22
New cards
Clicks
Used for Neural Assessment
• Broadband noises that includes many many frequencies
• Goal is to stimulate a large portion of the organ of hearing in order to make a very large response.
• We work to identify the 6 major waves created by the auditory pathway
• Broadband noises that includes many many frequencies
• Goal is to stimulate a large portion of the organ of hearing in order to make a very large response.
• We work to identify the 6 major waves created by the auditory pathway
23
New cards
wave 1
cochlea
24
New cards
wave 2
8th CN
25
New cards
wave 3
cochlear nucleus
26
New cards
wave 4
superior olivary complex
27
New cards
wave 5******
lateral lemniscus****
28
New cards
wave 6
inferior colliculus
29
New cards
Tone burst stimuli
loud tone bursts (look at wave 5)
30
New cards
ART
Acoustic Reflex Threshold (ART)
• Tympanogram performed to find TPP
• Ear is pressurized to TPP value (best movement of eardrum)
• Testing is performed with several different tones or noise (500 Hz)
• Sound is presented at a loud level and the contraction is measured
• Identify the softest sound the reflex is elicited (.02 or greater)
• Tympanogram performed to find TPP
• Ear is pressurized to TPP value (best movement of eardrum)
• Testing is performed with several different tones or noise (500 Hz)
• Sound is presented at a loud level and the contraction is measured
• Identify the softest sound the reflex is elicited (.02 or greater)
31
New cards
Suspected Otitis Media with Effusion
Type B
32
New cards
Resolving Otitis Media with Effusion
Type As
33
New cards
Negative Middle Ear Pressure
Type C (Eustachian tube malfunction)
34
New cards
Patent Pressure Equalization Tube
35
New cards
Perforation in the eardrum
36
New cards
Disarticulation of the Ossicles
37
New cards
TEOAEs Transient Evoked Otoacoustic Emissions
Noise stimulus
many sounds can be measured all at once
They will always show:
• The Reproducibility
• The level of loudness of the Emission
• The amount of noise
• The signal to noise ratio
many sounds can be measured all at once
They will always show:
• The Reproducibility
• The level of loudness of the Emission
• The amount of noise
• The signal to noise ratio
38
New cards
TEOAEs Test Frequencies and Norms
TEOAEs can test from: ~1000 to 4000 Hz
• SNR must be greater than greater than 6 dB
• 99% of ears will have TEOAEs if hearing is 20 dB
HL or better
• TEOAEs will be absent if hearing loss is greater
than 30 to 35 dB HL
• TEOAEs are always absent when hearing
thresholds are greater than 40 dB HL
• TEOAEs may or may not be present when
thresholds are 25 to 35 dB HL
• SNR must be greater than greater than 6 dB
• 99% of ears will have TEOAEs if hearing is 20 dB
HL or better
• TEOAEs will be absent if hearing loss is greater
than 30 to 35 dB HL
• TEOAEs are always absent when hearing
thresholds are greater than 40 dB HL
• TEOAEs may or may not be present when
thresholds are 25 to 35 dB HL
39
New cards
TEOAEs can test from
1000 to 4000 Hz
40
New cards
TEOAE Threshold level
TEOAE Present? Yes
41
New cards
TEOAE Threshold level 25 to 35 dB HL
TEOAE Present? Maybe
42
New cards
TEOAE Threshold Level >40 dB HL
TEOAE Present? Never
43
New cards
DPOAEs Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions
Tonal stimulus
one frequency assessed at a time
All machines will provide some
thing similar
• They will always show:
• The Reproducibility
• The level of loudness of the emission
• The amount of noise
• The signal to noise ratio
one frequency assessed at a time
All machines will provide some
thing similar
• They will always show:
• The Reproducibility
• The level of loudness of the emission
• The amount of noise
• The signal to noise ratio
44
New cards
DPOAEs can test from
1000 to 6000 Hz or higher in certain circumstances
45
New cards
Test Frequencies and Norms DOPAEs
DPOAEs can test from: ~1000 to 6000 Hz
or higher in certain circumstances
• SNR must be greater than greater than 6
dB
• DPOAEs will be present if hearing is 25
dB HL or better
• DPOAEs are generally absent when
hearing thresholds are greater than 40
dB HL
• DPOAEs may or may be present but low
amplitude (weak) between 40 to 60 dB
HL
or higher in certain circumstances
• SNR must be greater than greater than 6
dB
• DPOAEs will be present if hearing is 25
dB HL or better
• DPOAEs are generally absent when
hearing thresholds are greater than 40
dB HL
• DPOAEs may or may be present but low
amplitude (weak) between 40 to 60 dB
HL
46
New cards
DPOAEs Threshold level
DPOAE present? yes
47
New cards
DPOAE Threshold level >40 dB HL
DPOAE Present? Generally no
48
New cards
DPOAE Threshold level 40 to 60 dB HL
DPOAE present? Possible
49
New cards
CAPD Battery of tests
• Meant to overwork the systems in
order to evaluate breakdown
• Age-matched norms
• Evaluate patterns in test findings:
develop performance profiles
• Define specific nature of the problem
• Is it just binaural processing, a mix?
• Concern for other disorders
order to evaluate breakdown
• Age-matched norms
• Evaluate patterns in test findings:
develop performance profiles
• Define specific nature of the problem
• Is it just binaural processing, a mix?
• Concern for other disorders
50
New cards
Types of Behavioral Tests
-Temporal Processes – Pattern perception, gap detection
• Dichotic Listening (Speech Tests) – Different words or sentences presented to each ear, but patient listens only in one ear
• Monaural Low-Redundancy – Filtered speech, compressed speech
• Lateralization, localization, or binaural functions
• Auditory Discrimination Tests – Frequency, intensity, and duration of speech stimuli
• Dichotic Listening (Speech Tests) – Different words or sentences presented to each ear, but patient listens only in one ear
• Monaural Low-Redundancy – Filtered speech, compressed speech
• Lateralization, localization, or binaural functions
• Auditory Discrimination Tests – Frequency, intensity, and duration of speech stimuli
51
New cards
Temporal Processes
Pattern perception, gap detection
52
New cards
Dichotic Listening (Speech Tests)
Different words or sentences
presented to each ear, but patient listens only in one ear
presented to each ear, but patient listens only in one ear
53
New cards
Monaural Low-Redundancy
Filtered speech, compressed
speech
speech
54
New cards
Auditory Discrimination Tests
Frequency, intensity, and
duration of speech stimuli
duration of speech stimuli
55
New cards
Three major CAPD Profiles
Decoding deficits
Integration deficits
Prosodic deficits
Integration deficits
Prosodic deficits
56
New cards
Decoding deficits (true capd)
-System is unable to extract pitch,
loudness and timing cues
-Considered truest of all CAPDs because
it’s all auditory-based deficit
-Discrimination based problem,
-Located in left hemisphere and/or high
brainstem
loudness and timing cues
-Considered truest of all CAPDs because
it’s all auditory-based deficit
-Discrimination based problem,
-Located in left hemisphere and/or high
brainstem
57
New cards
Integration deficits
Deficit in the communication between the
right and left hemispheres (cortical)
Unable to combine information and synthesize
meaning (i.e. can’t put it all together)
Hard to process information quickly
System becomes easily overwhelmed when
lots of information is given
right and left hemispheres (cortical)
Unable to combine information and synthesize
meaning (i.e. can’t put it all together)
Hard to process information quickly
System becomes easily overwhelmed when
lots of information is given
58
New cards
Prosodic deficits
Unable to process the rise and fall in
pitch and loudness (syllabic
emphasis/intonation)
Right hemisphere problem (aka Right
Hemisphere APD)
Difficulty with analysis and synthesis of
prosodic features related to
communication
pitch and loudness (syllabic
emphasis/intonation)
Right hemisphere problem (aka Right
Hemisphere APD)
Difficulty with analysis and synthesis of
prosodic features related to
communication
59
New cards
Treatment for APD
bottom-up (stimulus driven)
tom-down (strategy driven)
tom-down (strategy driven)
60
New cards
Bottom-Up (stimulus driven)
Auditory training
Skills remediation
Environmental modifications including assistive
technologies
Skills remediation
Environmental modifications including assistive
technologies
61
New cards
Top-down (strategy driven)
• Language, cognitive, metacognitive strategies
• Educational interventions
• Workplace, recreational, and home accommodations
• Educational interventions
• Workplace, recreational, and home accommodations
62
New cards
Bottom-up examples
• You will listen to two sounds
• Tell me which sound is higher
pitch
• You will listen to two words, one
in each ear
• Tell me what word you heard in
the left ear only.
• Tell me which sound is higher
pitch
• You will listen to two words, one
in each ear
• Tell me what word you heard in
the left ear only.
63
New cards
top-down examples
• You are going to listen to a
sentence. There will be one word
missing.
• I want you to use the context from
the rest of the sentence to figure out
the missing word.
“Billy is going to the movie that
_____ at 4:30 this afternoon.”
sentence. There will be one word
missing.
• I want you to use the context from
the rest of the sentence to figure out
the missing word.
“Billy is going to the movie that
_____ at 4:30 this afternoon.”
64
New cards
Hearing aid fitting workflow
assessment, treatment planning, selection, development, verification, orientation, validation
65
New cards
assessment
Identify hearing loss and determine
candidacy for hearing aids
candidacy for hearing aids
66
New cards
treatment planning
Review results and options with
patient
patient
67
New cards
selection
Matching hearing aid features with patient’s
needs
needs
68
New cards
development
Formal gold standard prescriptive
methods to program hearing aids
methods to program hearing aids
69
New cards
verification
Ensure that hearing aids are functioning
properly and meeting expected prescriptive targets
properly and meeting expected prescriptive targets
70
New cards
Orientation
Instruct patient on hearing aid use and care,
as well as explain realistic expectations
as well as explain realistic expectations
71
New cards
validation
Measure patient’s subjective experience,
AND some objective measurements of benefit
AND some objective measurements of benefit
72
New cards
Candidacy for hearing aids
Assessment of hearing loss
Resolution/consideration of medical issues related to ear
Consideration of patient interest
Audiometric Candidacy:
• Minimum: Mild hearing loss in the 500 to 4000 Hz region
• Severity: If hearing loss is too great, may need cochlear implant
• Word Recognition Scores: Poor word recognition may impact benefit
• Speech in Noise Testing: Results may indicate the need for advanced
technologies to help in noise
• Loudness Discomfort Level (LDL)/Uncomfortable Level (UCL):
Patient may not be able to tolerate loud sounds
Resolution/consideration of medical issues related to ear
Consideration of patient interest
Audiometric Candidacy:
• Minimum: Mild hearing loss in the 500 to 4000 Hz region
• Severity: If hearing loss is too great, may need cochlear implant
• Word Recognition Scores: Poor word recognition may impact benefit
• Speech in Noise Testing: Results may indicate the need for advanced
technologies to help in noise
• Loudness Discomfort Level (LDL)/Uncomfortable Level (UCL):
Patient may not be able to tolerate loud sounds
73
New cards
Digital Features
multiple channels, multiple programs, compression (automatic gain control (AGC)): two functions, Wide Dynamic Range Compression, directional microphones, feedback reduction, linked hearing aids, data logging
74
New cards
multiple channels
Able to adjust hearing aid output in discrete frequency regions
75
New cards
multiple programs
Automatic or user-controlled programs based on patient’s needs in various settings
76
New cards
Compression (Automatic Gain Control (AGC)): Two functions
Limit how loud sounds get and minimize distortion
77
New cards
Wide Dynamic Range Compression (WDRC)
Preserve the experience of loudness
• When all sounds are amplified, how can you tell if what you hear is quiet, medium, or loud??
• When all sounds are amplified, how can you tell if what you hear is quiet, medium, or loud??
78
New cards
directional microphones
One forward facing and one rear facing
microphone
• Allows the hearing aid to determine the location of speech versus noise
• Processing allows for digital noise reduction
• Digital Noise Reduction: Reduces background noise based on it’s
frequency range and location
microphone
• Allows the hearing aid to determine the location of speech versus noise
• Processing allows for digital noise reduction
• Digital Noise Reduction: Reduces background noise based on it’s
frequency range and location
79
New cards
feedback reduction
Phase cancellation of feedback sounds
80
New cards
linked hearing aids
Sounds from one hearing aid can be transmitted
wirelessly to the opposite ear
wirelessly to the opposite ear
81
New cards
data logging
• How long hearing aids worn
• User adjustments to volume and programs
• Assessment of patient’s environments throughout the day
• User adjustments to volume and programs
• Assessment of patient’s environments throughout the day
82
New cards
validation - are the hearing aids helping?
Aided testing:
• In a soundfield with speech stimuli
• The Ling 6 Sounds for thresholds
• Word Recognition in Quiet
• Speech in noise testing
• DO NOT Use pure tone stimuli or narrowband
• Hearing aid processor may view as
feedback or noise
• The hearing aid would make them quieter
• In a soundfield with speech stimuli
• The Ling 6 Sounds for thresholds
• Word Recognition in Quiet
• Speech in noise testing
• DO NOT Use pure tone stimuli or narrowband
• Hearing aid processor may view as
feedback or noise
• The hearing aid would make them quieter
83
New cards
validation-continued
Self-report tools
• Standardized forms allow to track patient
perceptions and progress
• Client Oriented Scale of Improvement (COSI)
• Pre-test to define goals and manage expectations
• Filled out over time to determine if goals are met or
adjustments needed.
• Abbreviated Profile of Hearing Aid Benefit
(APHAB)
• Evaluate patient’s perception of benefit in different listening environments
• Can do pre and post test
• Lots of normative values
• Standardized forms allow to track patient
perceptions and progress
• Client Oriented Scale of Improvement (COSI)
• Pre-test to define goals and manage expectations
• Filled out over time to determine if goals are met or
adjustments needed.
• Abbreviated Profile of Hearing Aid Benefit
(APHAB)
• Evaluate patient’s perception of benefit in different listening environments
• Can do pre and post test
• Lots of normative values
84
New cards
verification
• Just because the programming software
says it’s programmed perfectly DOES NOT
mean it is set correctly in the real world!
• Ear acoustics can affect the output of the
hearing aid
• Could overamplify some sounds
• Could reduce amplitude of other sounds
• Two methods to verify:
• Test box
• Real ear measurement
says it’s programmed perfectly DOES NOT
mean it is set correctly in the real world!
• Ear acoustics can affect the output of the
hearing aid
• Could overamplify some sounds
• Could reduce amplitude of other sounds
• Two methods to verify:
• Test box
• Real ear measurement
85
New cards
Test Box Verification
• Hearing aids placed in
sound treated chamber
• Connected to ear
simulator (coupler)
• Speech sounds are
played into the hearing
aids
• Can ESTIMATE how
sounds are likely to
behave based on
programming
sound treated chamber
• Connected to ear
simulator (coupler)
• Speech sounds are
played into the hearing
aids
• Can ESTIMATE how
sounds are likely to
behave based on
programming
86
New cards
Real ear verification
• BEST way to measure hearing aid output
• Microphone placed in ear canal
• Hearing aid placed on ear and turned on
• Speech sounds are played from a speaker
• Can objectively measure EXACTLY how sounds are likely to behave based on programming
• Microphone placed in ear canal
• Hearing aid placed on ear and turned on
• Speech sounds are played from a speaker
• Can objectively measure EXACTLY how sounds are likely to behave based on programming
87
New cards
BAI - sound processor attachment
percutaneous, transcutaneous
88
New cards
percutaneous
an abutment is attached to implant and
comes through the skin (Direct Drive)
◦Provides best sound quality
◦More prone to infection
comes through the skin (Direct Drive)
◦Provides best sound quality
◦More prone to infection
89
New cards
transcutaneous
a magnet is attached to the implant and
is completely under the skin (Skin Drive)
◦Poorer sound quality (less access to high pitches)
◦Less likely for infection
◦Prone to fall/be knocked off of the head
is completely under the skin (Skin Drive)
◦Poorer sound quality (less access to high pitches)
◦Less likely for infection
◦Prone to fall/be knocked off of the head
90
New cards
hearing aids
Hearing Aids/BAI/MEI
Drive the natural hearing
system to create neural
responses in the cochlea
Drive the natural hearing
system to create neural
responses in the cochlea
91
New cards
Cochlear implants
Bypass the natural
hearing system to
stimulate the auditory
nerve directly
hearing system to
stimulate the auditory
nerve directly
92
New cards
Microtia
external ear is small and not formed properly
93
New cards
Atresia
born with no ear canal
94
New cards
pre-auricular tag
ear tag
95
New cards
pre-auricular sinus
ear pit
96
New cards
tympanometry
dynamic measure of the acoustic imminence in the external ear canal as a function of ear canal air pressure change
– Provides information regarding mobility
(compliance) of the tympanic membrane
– Guides us in determining the status of the ME
– Cross check assessment that aids in differential
diagnosis
– Provides information regarding mobility
(compliance) of the tympanic membrane
– Guides us in determining the status of the ME
– Cross check assessment that aids in differential
diagnosis
97
New cards
Immittance
assessment of middle ear function
98
New cards
Impedance
the opposition to the flow of energy
-blockage, resistance
-blockage, resistance
99
New cards
admittance
measure of how much energy passes through a system
100
New cards
high admittance
greater flow of energy through the system