Human Factors and Ergonomics
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These notes cover key concepts in Human Factors and Ergonomics for IB Design Technology HL. Topics include anthropometrics, psychological and physiological factors, types of ergonomic data, environmental considerations, and sustainable design. They also explore the international implications of resource management and the role of technology in ergonomic design.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
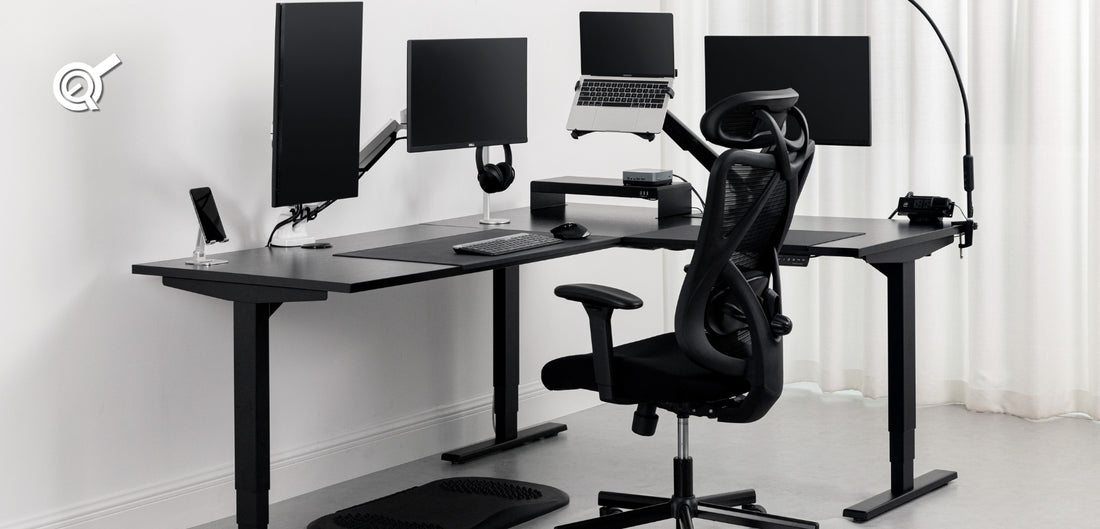

What is Ergonomics?
The scientific discipline studies interactions among humans and other elements of a system, aiming to design for optimal human well-being and system performance.
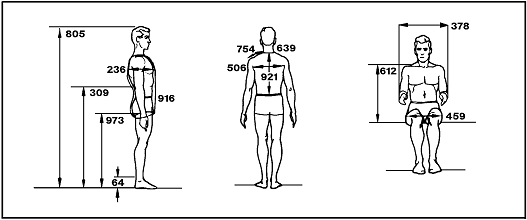
What is Anthropometrics?
The study of human body measurements, focusing on strength and size to ensure user comfort and productivity in design.
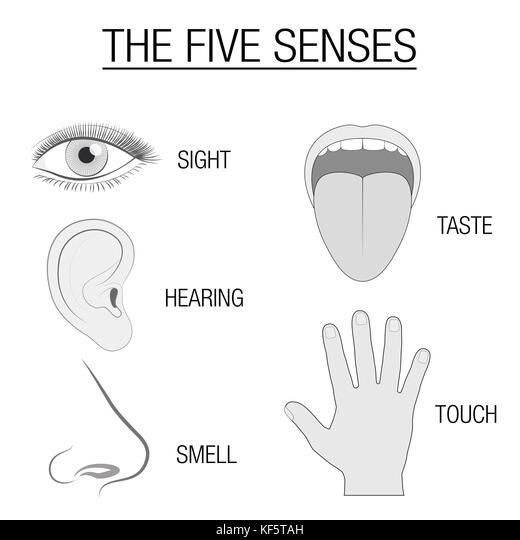
Define Psychological Factors in ergonomics.
The various psychological traits of people that have an impact on design, such as touch, taste, and scent, which are frequently arbitrary and subjective.

What are Physiological Factors?
Related to physical characteristics used to optimize the user’s safety, health, comfort, and performance, including aspects like adjustability, alertness, and biomechanics.
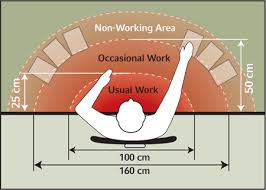
Functional Data
Data related to tasks and interactions, such as reaching, navigating, and space considerations in design.
Define Environmental Factors in the context of ergonomics.
Elements like management policies, physical environment, equipment design, job nature, social environment, and worker factors influencing ergonomics.
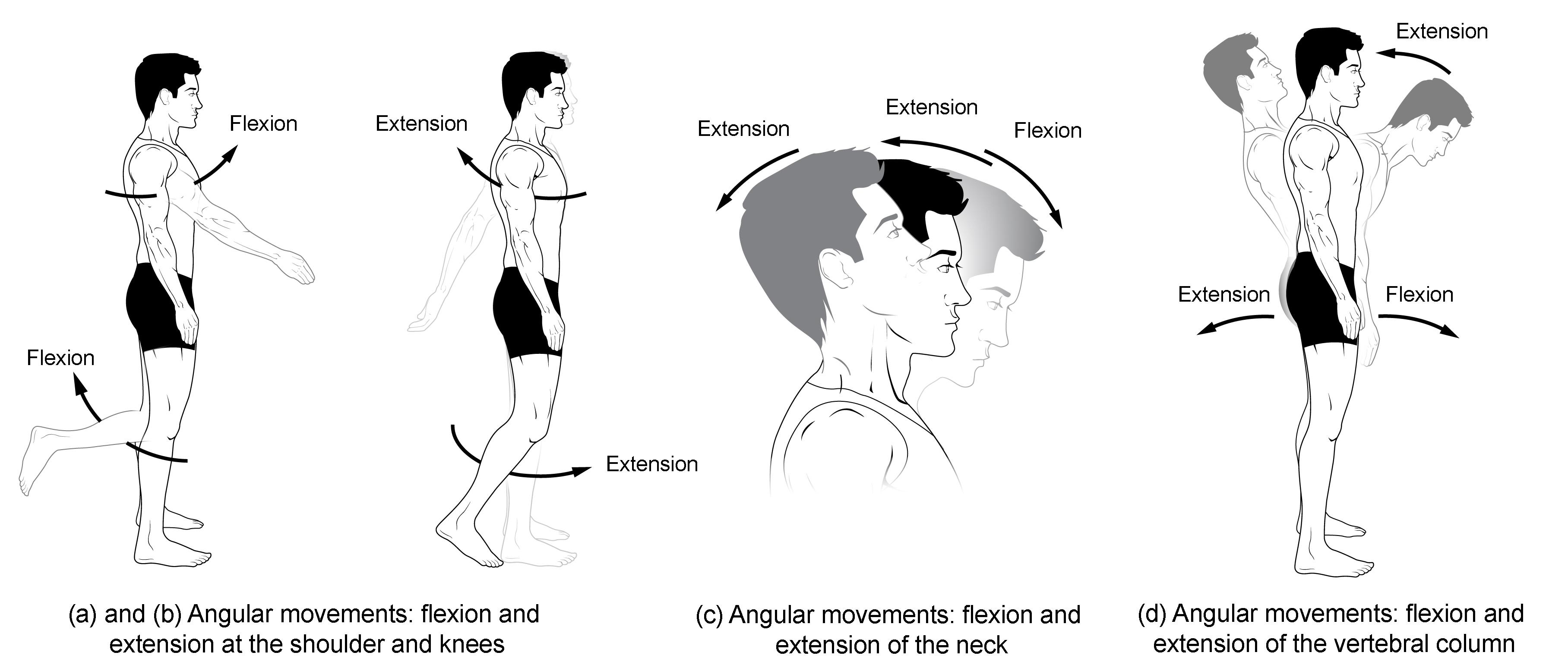
What is meant by Dynamic Data in ergonomics?
Human body measurements taken when the subject is in motion, related to the range and reach of various body movements.
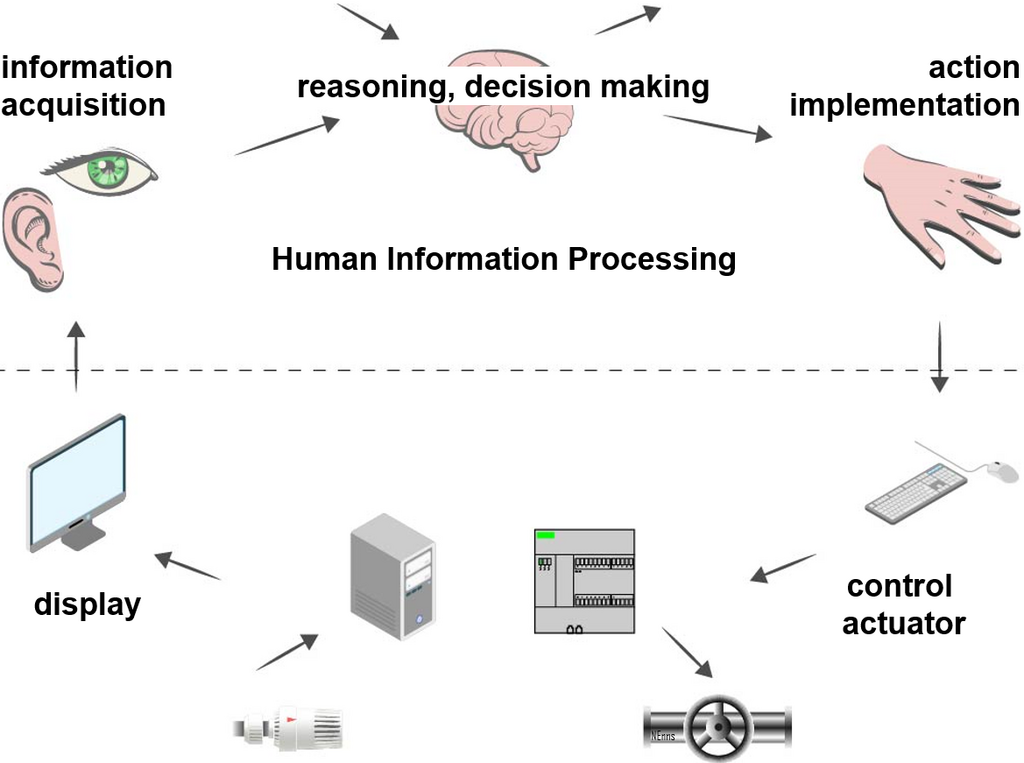
What is the significance of the Human Information Processing System?
An automatic system that a person uses to interpret information and react, comprising inputs, sensory processes, central processes, motor processes, and outputs.
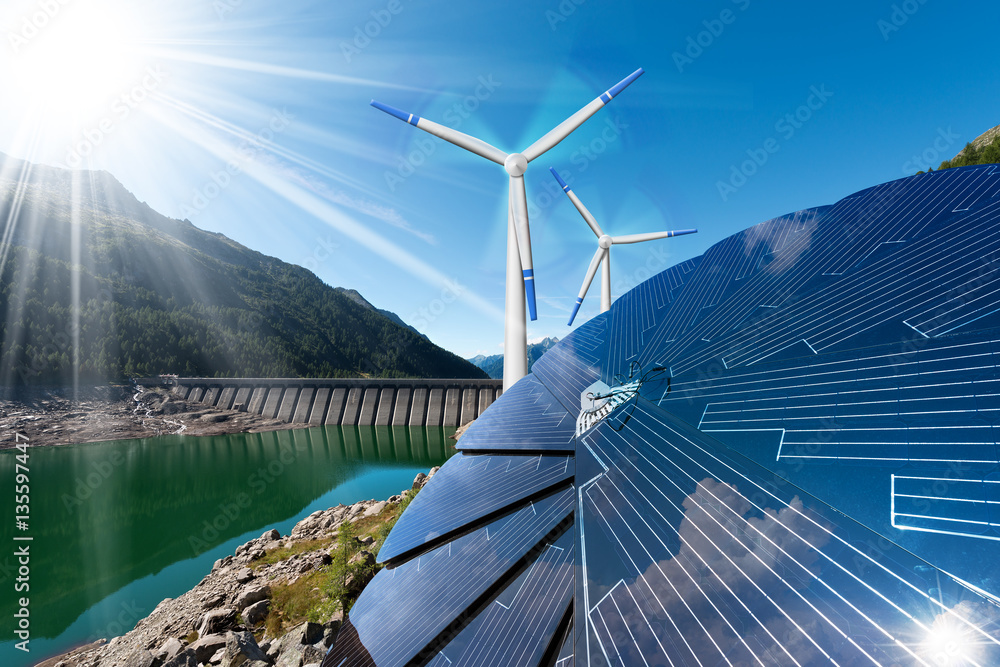

What are Renewable Resources?
Solar, wind, hydro, wave, tidal, thermal, and biofuels are examples of natural resources that can replenish over time or never run out.
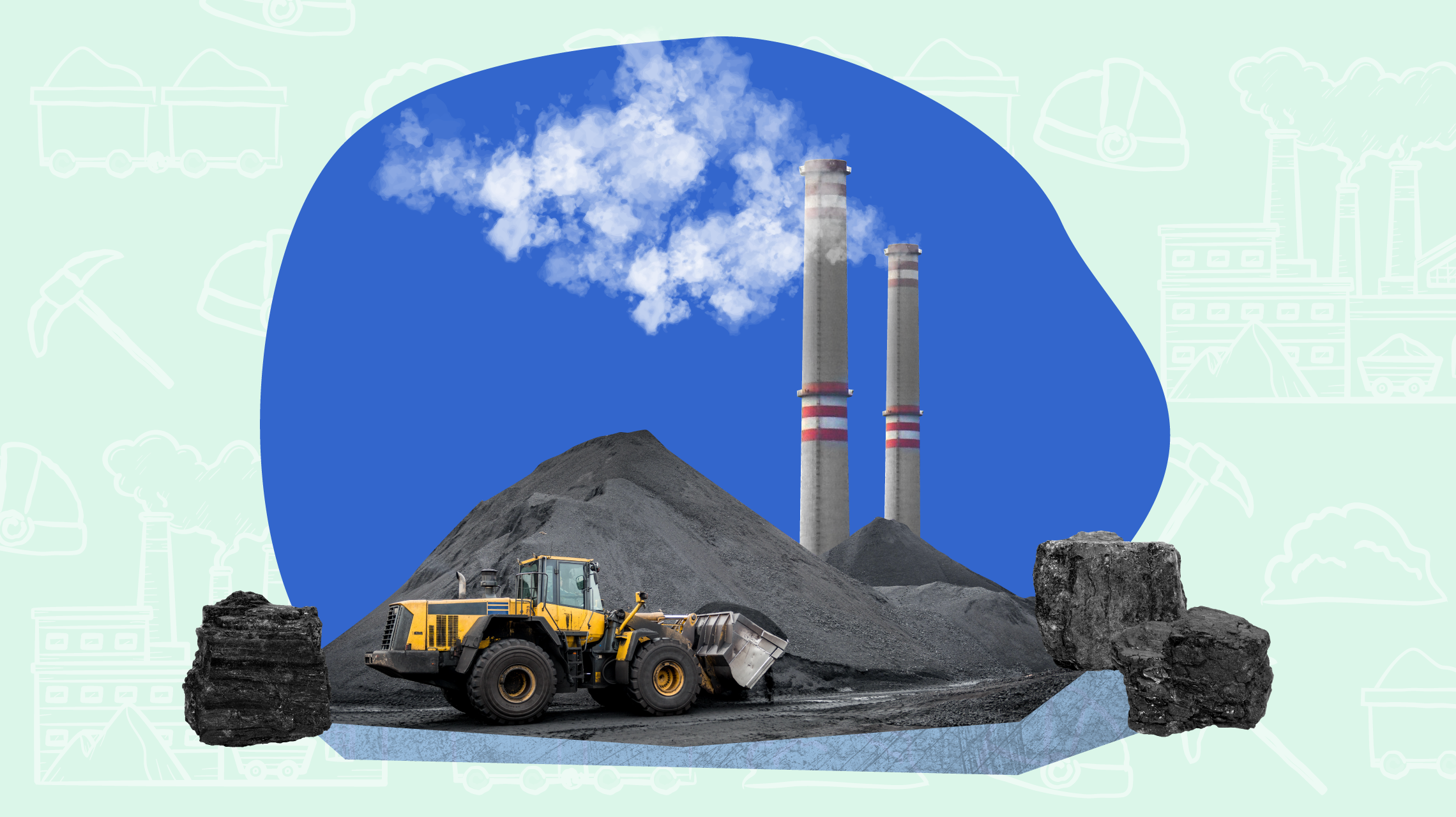

Define Non-renewable Resources.
Natural resources that do not replenish at a sustainable rate and will run out if the current harvesting rate is continued, such as natural gas, oil, coal, and nuclear energy.
What is the importance of International Mindedness in Design Technology?
Involves reacting to global issues and opportunities in resource management as well as comprehending the ethical, social, and environmental effects of resource management and extraction on a global scale.