Introduction to Geography: Industrial Location, High-Tech, and Service Sectors
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are the primary activities in economic geography?
Primary activities are locationally tied to natural resources.
What do secondary activities in economic development relate to?
Secondary activities are more closely related to cultural and economic factors than to physical circumstances.
Which regions account for about three-fifths of the world's manufacturing output?
Eastern Anglo America, Western and Central Europe, Eastern Europe, and Eastern Asia.
What is the significance of Newly Industrializing Countries (NICs) in manufacturing?
NICs have been significantly increasing their contribution to world manufacturing activity.
What are the assumptions of Industrial Location Theory?
People are economically rational, and producers and sellers aim to maximize profit, guided by supply, demand, and market equilibrium.
What is Weber's least cost industrial location model?
A model that determines industrial location decisions based on minimizing transport, labor, and agglomeration costs.
What factors are considered in Weber's Least Cost Location Model?
Agglomeration, transportation costs, material-oriented vs. market-oriented locations, and the substitution principle.
What are the characteristics of footloose industries?
Footloose industries have negligible transportation costs and can be located anywhere, often inseparable from markets.
What are agglomeration economies?
Savings to an individual firm that result from spatial association with other similar economic activities, such as shared infrastructure and labor pools.
What role do political considerations play in industrial location?
Political factors, such as land use, zoning controls, environmental standards, and government inducements, can significantly affect locational decisions.
What is Just-in-Time (JIT) production?
A production strategy that seeks to reduce inventories and reinforces spatial agglomeration tendencies.
What enables flexible production systems?
Reprogrammable computerized machine tools, computer-aided design, and computer-aided manufacturing systems.
How do classical location theories relate to high-tech industries?
Classical theories do not adequately explain the location of high-tech industries, which include electronics, communications, and pharmaceuticals.
What are the locational tendencies of high-tech industries?
Proximity to major universities, avoidance of strong unions, availability of venture capital, and favorable quality of life.
What impact do high-tech industries have on economic geography?
They are a major factor in employment growth and manufacturing output, often regionally concentrated with specialization.
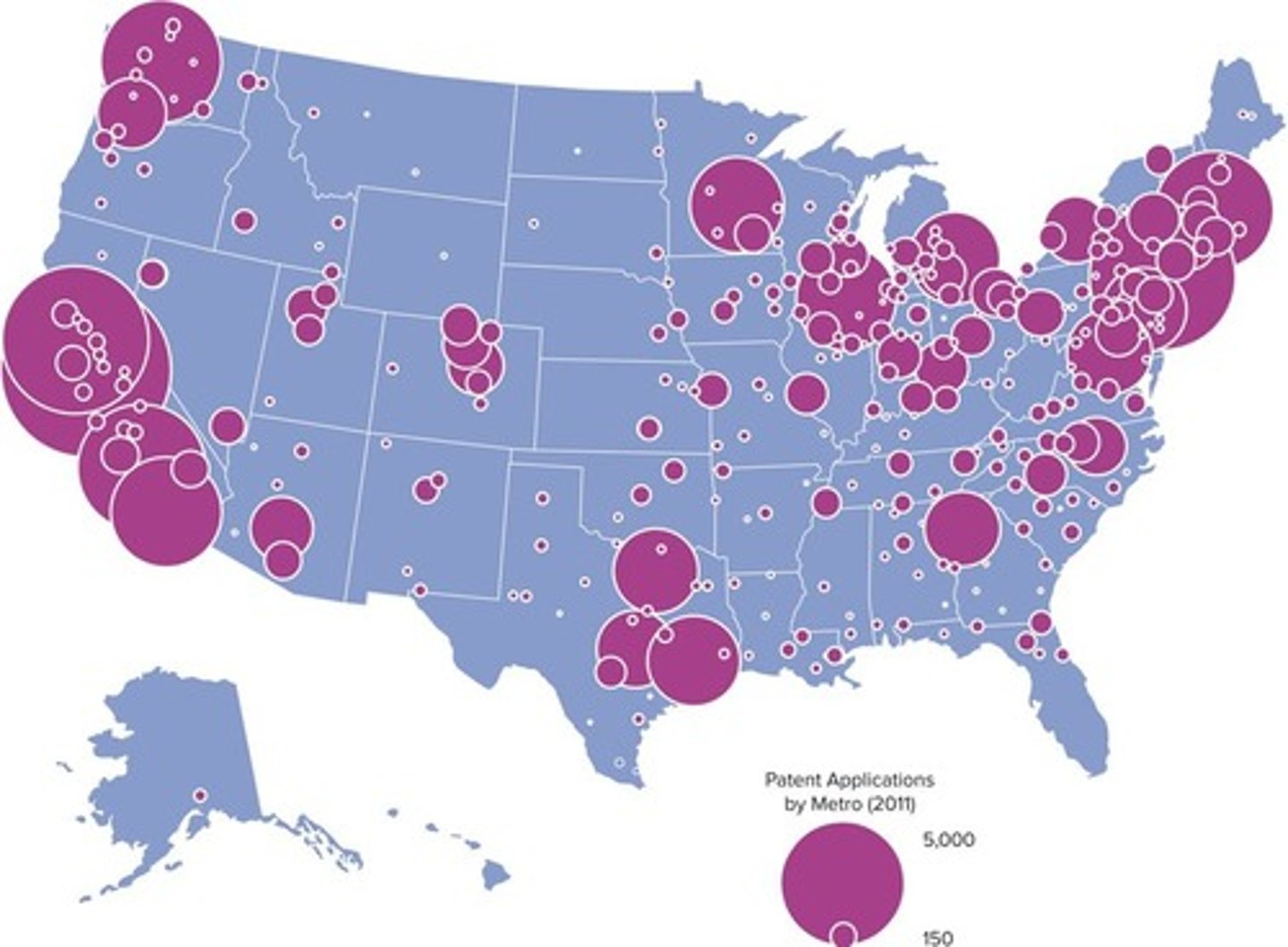
What is the significance of patent applications in technological innovation?
Patent applications tend to cluster in hubs of technological innovation, indicating concentrated development in specific regions.
What is the role of transportation in industrial location?
Transportation characteristics, such as the cost and mode, are crucial in determining the optimal location for industries.
What is the relationship between innovation and manufacturing processes?
Innovation in manufacturing processes leads to flexible production and the ability to shift between different outputs and processes.
What are the implications of declining transport costs for industrial location?
Declining transport costs have made Weberian location theories less applicable, allowing for more flexibility in industrial placement.
What are agglomerating forces in high-tech industries?
Factors that influence the concentration of industries in specific locations, enhancing economic efficiency.
What is the significance of globalization in high-tech activities?
It facilitates the transfer and dispersion of high-tech activities across different regions.
What does the term 'footloose' refer to in production?
Phases of production that can be located anywhere without significant cost implications.
What role do Asian cities play in high-tech manufacturing?
Cities like Singapore, Shanghai, Seoul, and Bangalore are prominent centers for high-tech industries.
What is comparative advantage in the context of outsourcing?
The principle that areas or countries can improve their economies by specializing in the production of goods for which they have a relative advantage.
What is outsourcing?
The practice of producing parts or products abroad for domestic sale or subcontracting to domestic companies.
What defines a Transnational Corporation (TNC)?
A private firm that operates branches in countries foreign to its headquarters.
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
Investment involving the purchase or construction of foreign factories and assets, or merging with foreign companies.
What percentage of FDI flows to developing countries?
About one-third of FDI.
What is the contribution of the service sector to the U.S. workforce as of 2020?
77% of U.S. workers are employed in the service sector.
What are tertiary activities?
Services that provide support to primary and secondary activities, including consumer and business services.
What is the most important activity in the tertiary sector?
Tourism, which is the world's largest industry in terms of jobs and value generated.
Name examples of consumer services.
Retail, banking, hotels, healthcare, entertainment, and transportation services.
What characterizes business services?
Services that involve specialized knowledge and skills, often found in the knowledge sector.
What is meant by 'externalization' of specialized services?
The separation of production and consumption, requiring high-level personal contacts between clients and service firms.
What is the impact of information technology on service activities?
It has spurred growth in international trade flows and economic interdependence in services.
What are some leading international business and financial centers?
New York and London are prominent examples.
What is the significance of offshore banking havens?
They provide financial services with tax advantages and privacy, contributing to global finance.
How has the service sector's role changed in the global economy?
It has become an increasingly significant factor in international trade and economic integration.
What is the relationship between high-tech industries and national identity?
Many high-tech firms have lost their original national identities due to globalization and international operations.
What does the financial district of Shanghai symbolize?
The dramatic changes in the geography of secondary and tertiary activities in China.
What has contributed to China's growth as a manufacturing exporter?
An increasing role in financial services and advanced business services.
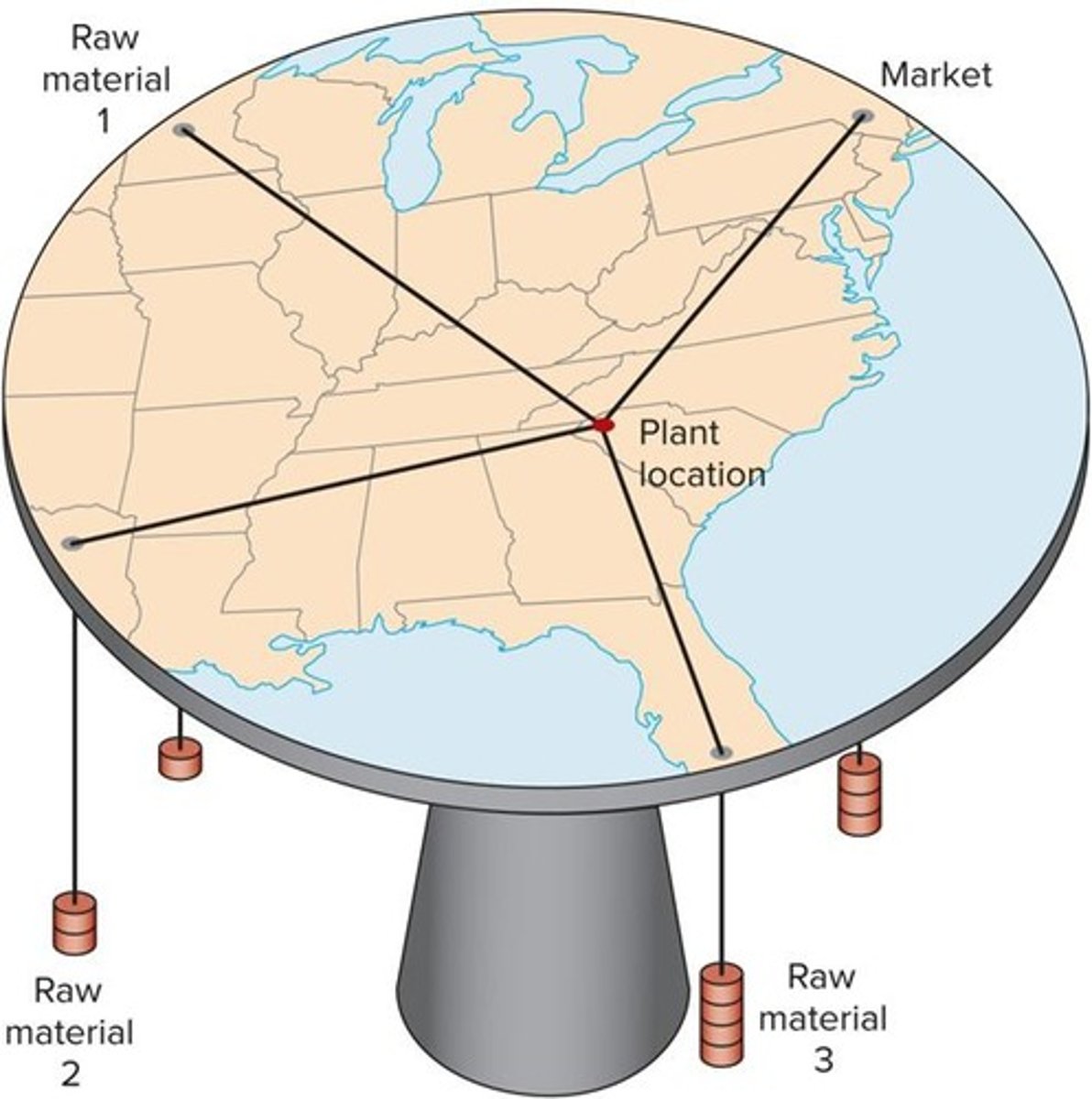
Who proposed the mechanical model for determining least-cost plant locations?
Alfred Weber.
What does the plane table solution demonstrate?
The least-transport-cost point for plant location based on raw material and market locations.
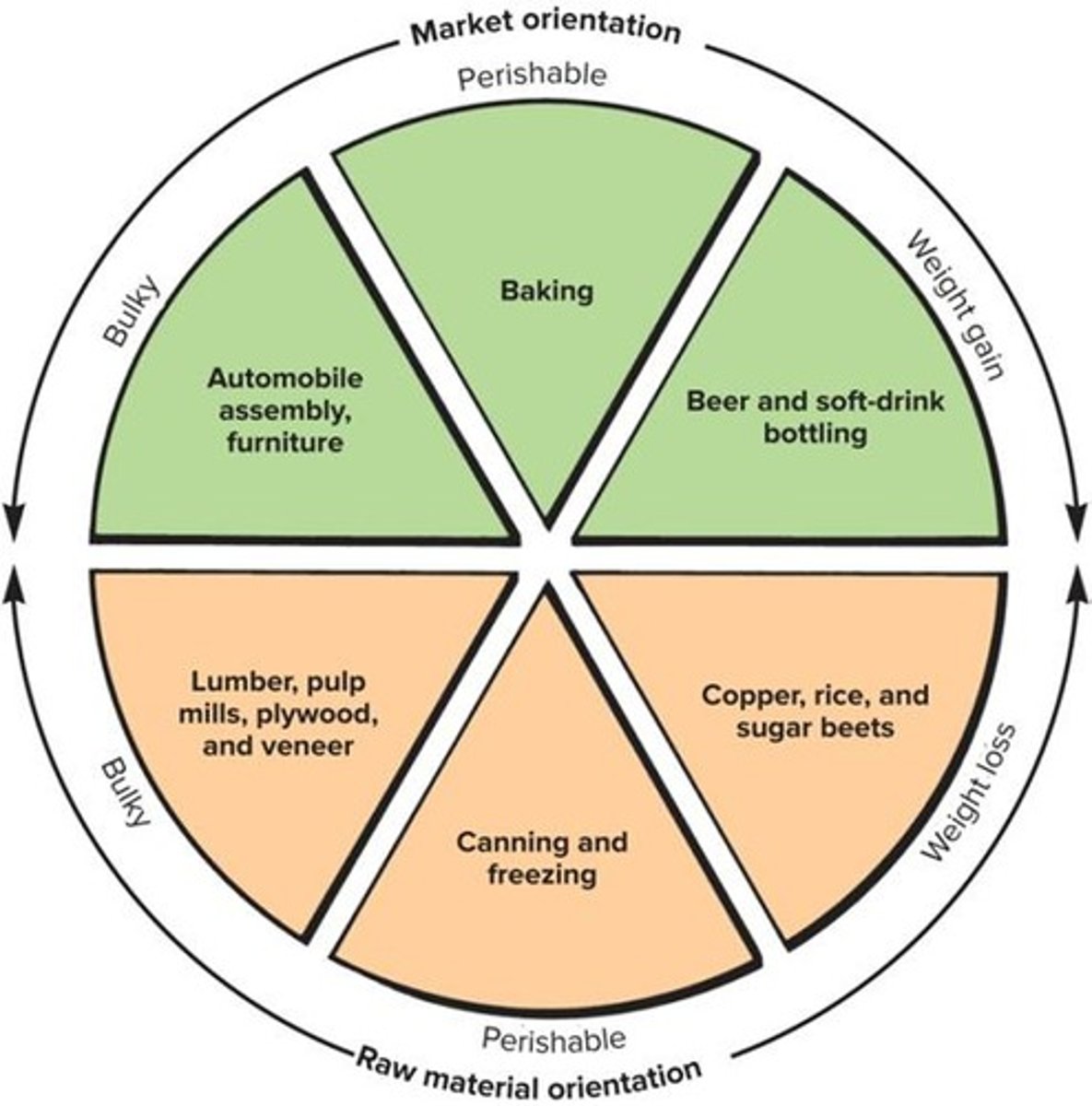
What is raw material orientation?
It occurs when there are limited alternative material sources or when materials are perishable.
What does market orientation represent in industrial processes?
The least-cost solution when manufacturing uses commonly available materials that add weight to the final product.
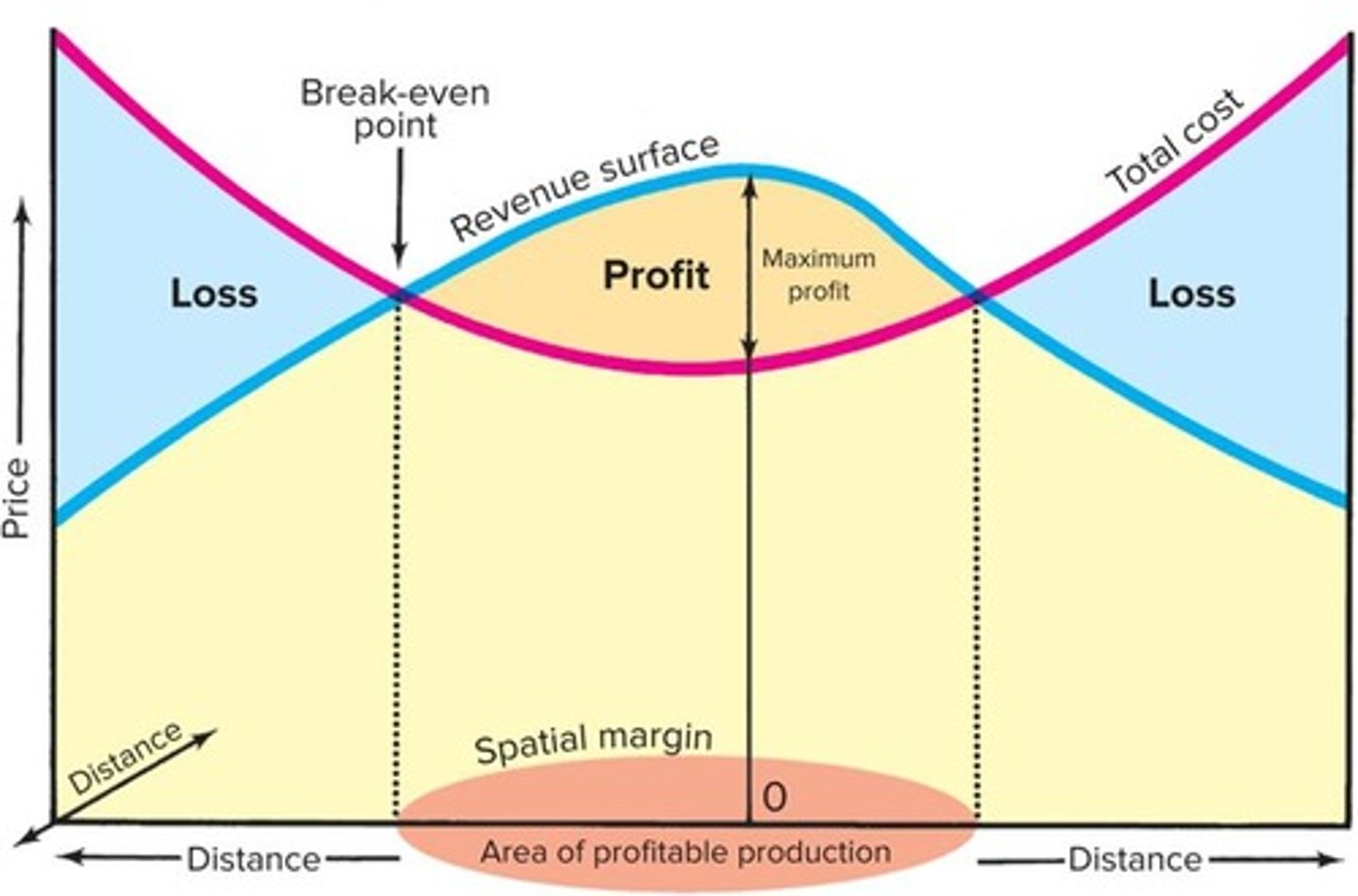
What is the spatial margin of profitability?
The area where profitable operation is possible, defined by the intersections of total-cost and total-revenue surfaces.
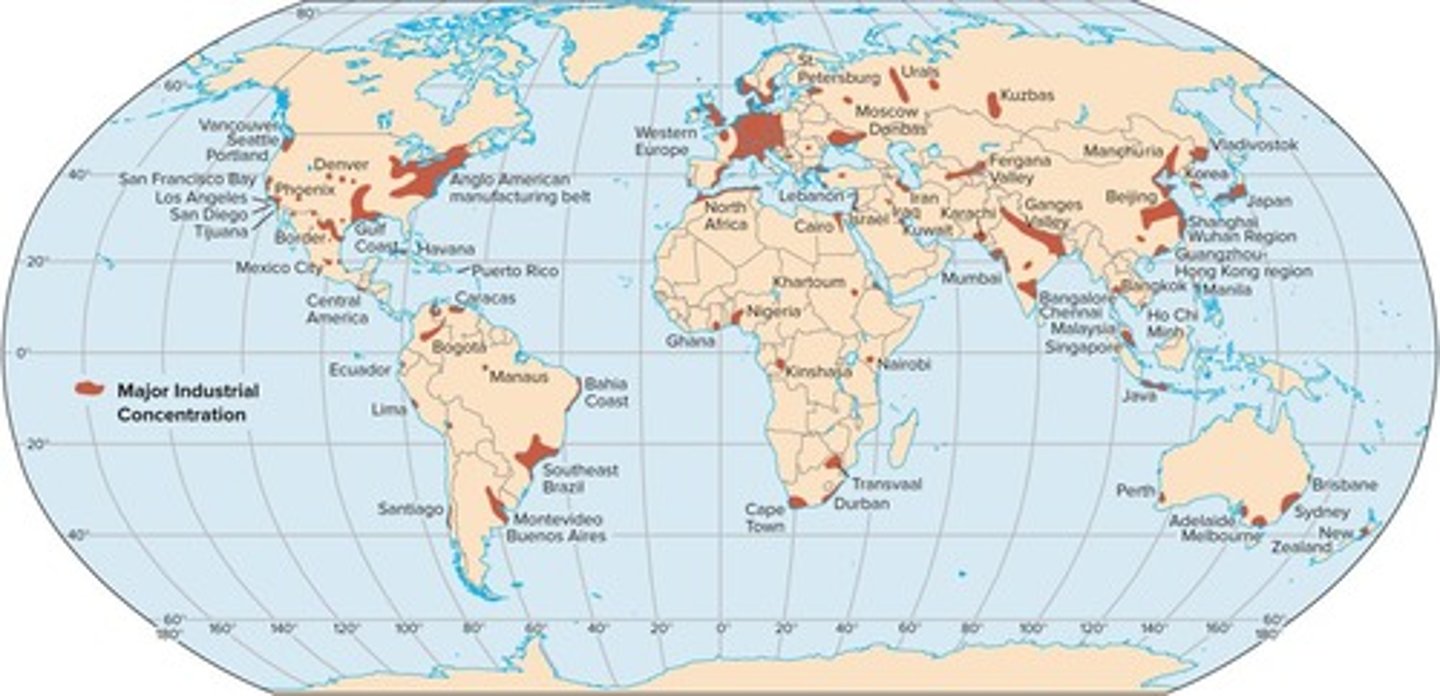
What are some key industrial regions in North America?
Vancouver, Seattle, San Francisco Bay, Los Angeles, and Mexico City.
Name a major industrial region in Asia.
Shanghai, Beijing, or Mumbai.
What characterizes hubs of technological innovation?
They are home to highly educated residents, research universities, and established technology companies.
What role do transnational corporations (TNCs) play in globalization?
They are engines of globalization, with their headquarters primarily in the U.S., Europe, China, and Japan.
How much did services account for global GDP in 2014?
Over 70%, up from about 55% in 1980.
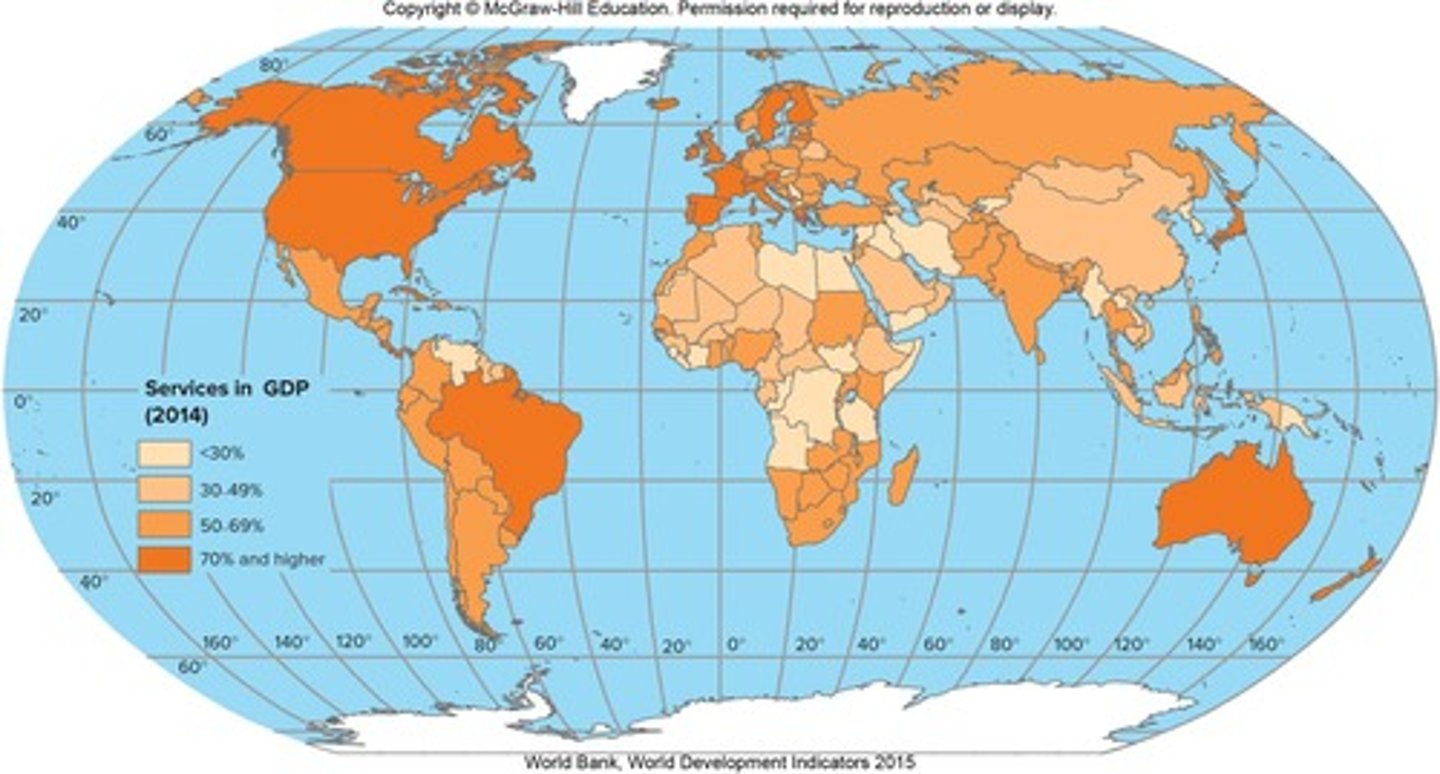
Where are low-level consumer services most effectively performed?
Where demand and purchasing power are concentrated.
What are some examples of offshore financial centers?
Bermuda, Bahamas, Cayman Islands, Luxembourg, and Switzerland.
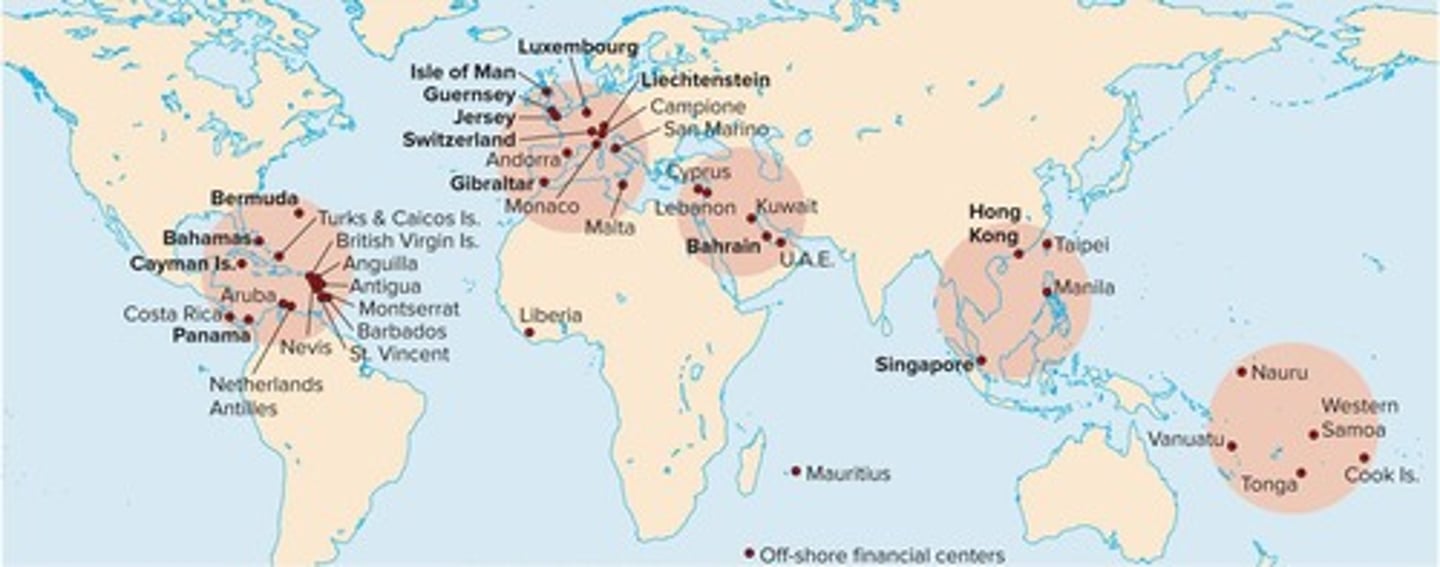
What is the significance of offshore banking?
It provides financial services in jurisdictions with favorable regulations and tax benefits.
What is the impact of technological innovation on patent applications?
Patent applications are clustered in hubs of technological innovation, indicating geographic unevenness.
What is the relationship between industrial location and raw materials?
Industries often locate near raw materials to minimize transportation costs.
What factors influence the choice of industrial location?
Availability of raw materials, market proximity, and transportation costs.