Social Psych (Exam 1)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is Social Psych? (ch. 1)
“Scientific study of the ways in which people’s thoughts, feelings and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people.”
Diff from personality psych cuz personality psych doesn’t depend on a situation like social psych does.
Construals (ch.1)
ways in which we perceive, understand and interpret social events and social ques
Empirical Research (ch.2)
research where observations are translated into testable hypotheses
Methods of Gathering Data (ch.2)
self-report
observation
non-participant observation
Self-Report (ch.2)
survey
questionnaire
interview
Observation (ch.2)
participant observation
Ex: Robber’s Cave…
Researcher’s were counselors at the camp where participant’s were being observed
Ethnography
the data collected from participant observation. Description about those participants and some aspect of them, typically culture.
Non-Participant Observation (ch.2)
Naturalistic Observation
researchers don’t interfere or influence variables (just observe)
subjects are in real world settings
Archival Analysis
collecting data from existing sources
Unobtrusive (indirect) measures
a technique used by an observer to record or observe behavior in a way that doesn’t interfere with or change a participant's behavior
no direct contact
ex: hidden camera
Research Designs (ch.2)
Observational: Description
Correlational: Prediction
Experimental: Causality
Observational Research Design (ch.2)
what is the nature of the phenomenon
Correlational Research Design (ch.2)
From knowing X, can we predict Y?
Experimental Research Design (ch.2)
Is variable X the cause of variable Y?
only research design that can make statements of causality
Types of Experimental Designs (ch.2)
True experiment (lab or field)
Natural/Quasi experiment
True Experiment (ch.2)
Has representative random sample
random assignment to conditions
independent variable is changed, other variables remain the same
Natural/Quasi Experiment (ch.2)
no true random assignment
Natural Experiment: IV is not manipulated, groups are otherwise similar
Quasi-Experiment: Same treatment on naturally occurring (different) groups
Reliability (ch.2)
Interrater Reliability
Test-Retest Reliability
Interrater Reliability (ch.2)
consistency amongst judgments and findings from multiple raters
Test-Retest Reliability (ch.2)
same test more than once over time
Validity (ch.2)
construct validity
internal validity
external validity
population validity
ecological validity
Construct Validity (ch.2)
how well a test or tool measures the construct that it was designed to measure
Internal Validity (ch.2)
Experimental control
not influenced by other variables
Random assignment to condition
External Validity (ch.2)
Population Validity
is population representative
Ecological Validity
Psychological realism
activate same feelings that field environment would but not using same stimuli from field environment (in a lab)
mundane realism
Bring field into lab (in a lab)
Ethical Concerns (ch.2)
Informed Consent
Deception
Debriefing
Informed Consent (ch.2)
Informed of risks and benefits
Informed of right to leave at any time
Deception (ch.2)
Ethical only if it does not obscure or affect parameters of informed consent
Debriefing (ch.2)
steps taken to ensure no lasting negative effects from participation
Institutional Review Board [IRB] (ch.2)
ethics committee that ensures research studies and projects are ethical
APA Guidelines for Ethical Research (ch.2)
IRB approves in advance
benefits outweigh risks
confidentiality of data
informed consent
timely debriefing of study’s purpose and procedures
Social Cognition (ch.3)
how we think about, select, interpret and remember social information to make judgments and decisions
Two types of mental processing involved
Automatic
Controlled
Automatic Processing (ch.3)
Schemas: mental structures people use to organize their knowledge about the social world around themes or subjects
Self-reference effect
Chronic accessibility vs Temporary accessibility
Priming
Self-reference Effect (ch.3)
info related to the self is processed more efficiently than other info
The Best Way To Process Information(compared to phonetic, semantic
according to that study)
Chronic Accessibility vs Temporary Accessibility (ch.3)
Chronic Accessibility: no need to prime, info is readily accessible
Temporary Accessibility: requires priming to be accessed
Priming (ch.3)
process by which recent experiences increase the accessibility of a schema, trait or concept
Kulechov Effect: shown same video of actor with same facial expression but different priming videos caused different descriptions of actor’s expression
Kelley “Guest lecturer” Study (1950)
students are given different descriptions of lecturer prior to lecture, each group of students rates her differently
“Donald” Studies (1977 & 2009)
Impacts of Schemas on Social Judgment (ch.3)
Primacy Effect: first impressions are lasting
Halo Effect: one good trait implies others
opposite referred to as horns effect
Belief perseverance: once an individual has developed a belief system, have difficulty getting rid of it
Ross, Leper and Hubbar (1975)
Confirmation Bias: notice things that confirm our schema and ignore all else
illusory correlations: association between two variables that aren’t real
illusion of control: sense of control in uncontrollable outcome
Self-fulfilling Prophecy: behaving in manner that you believe others expect from you
“clever Hans” the horse
Heuristics (ch.3)
mental shortcuts used in decision making
used when…
situation is ambiguous
not enough info
don’t care enough
don’t have the mental resources
Availability Heuristic (ch.3)
How easily does it come to mind?
Schwartz et al (1991):“Self-rated assertiveness”, “Self-rated humor” study(s)
Simulation heuristic (ch.3)
tendency to judge the frequency or likelihood of an event by the ease with which you can imagine it’s occurrence
Counter factual Resoning
engages controlled processing
influenced by proximity to goal, ease wiht which we can mentally ‘undo’ outcome
upward counterfactuals (more common)
downward counterfactuals
Representativeness Heuristic (ch.3)
how similar is it to a typical case?
base-rate info
ignoring general relevant stats in favor of case-specific info
Gambler’s Fallacy/Hot Hand
if someone is winning a lot, they expect to keep winning
Anchoring and Adjustment Heuristic (ch.3)
mental shortcut whereby people use a number or value as a starting point and then adjust from that “anchor” to make their decision or judgment
Hamil, Wilson & Nisbet (1980): “Atypical” vs “Typical” Welfare
studyparticipants read book about women’s situation with welfare
told is typical or atypical
answer questions about welfare. and base responses on women’s situation
Controlled Processing (ch.3)
thinking that is conscious, voluntary, effortful
Gilbert’s Theory of Automatic believing: initial acceptance info, assess truthfulness, unaccept if necessary
Gilbert, Tafarodi, & Malone (1993): Criminal defendant study
being distracted affected the sentence that people suggested
Ironic Processing (ch.3)
What can interfere with thought suppression?
high cognitive load (distracted, too much info)
time pressure
Wegner, Erber & Bowman (1993): Don’t be Sexist
Thought Suppression (ch.3)
monitoring process (automatic)
checks for instances where suppression is needed
operating process (controlled)
process of suppression
Social Cognition & Culture (ch.3)
Holistic Thinking Style
Collectivist
Analytic Thinking Style
Individualist
Cultural Difference in Social Thinking
East vs West:
equally capable of using either style
environment primes to use one over the other
Ex: Chinese participants tended to focus on central image in incongruent setting
Social Perception (ch.4)
how we come to understand other people
decoding nonverbal behavior
applying schemas (implicit personality theories)
coming up with explanation for behaviors (attributions)
Attribution Theory (ch.4)
description of the way in which people explain the causes of their own and others’ behavior
Attribution Ex: The last time I did well on an exam, it was because…
Classify:
Locus of Causality: External vs Internal
Stability: Stable vs Unstable
Pervasiveness: Global vs Specific
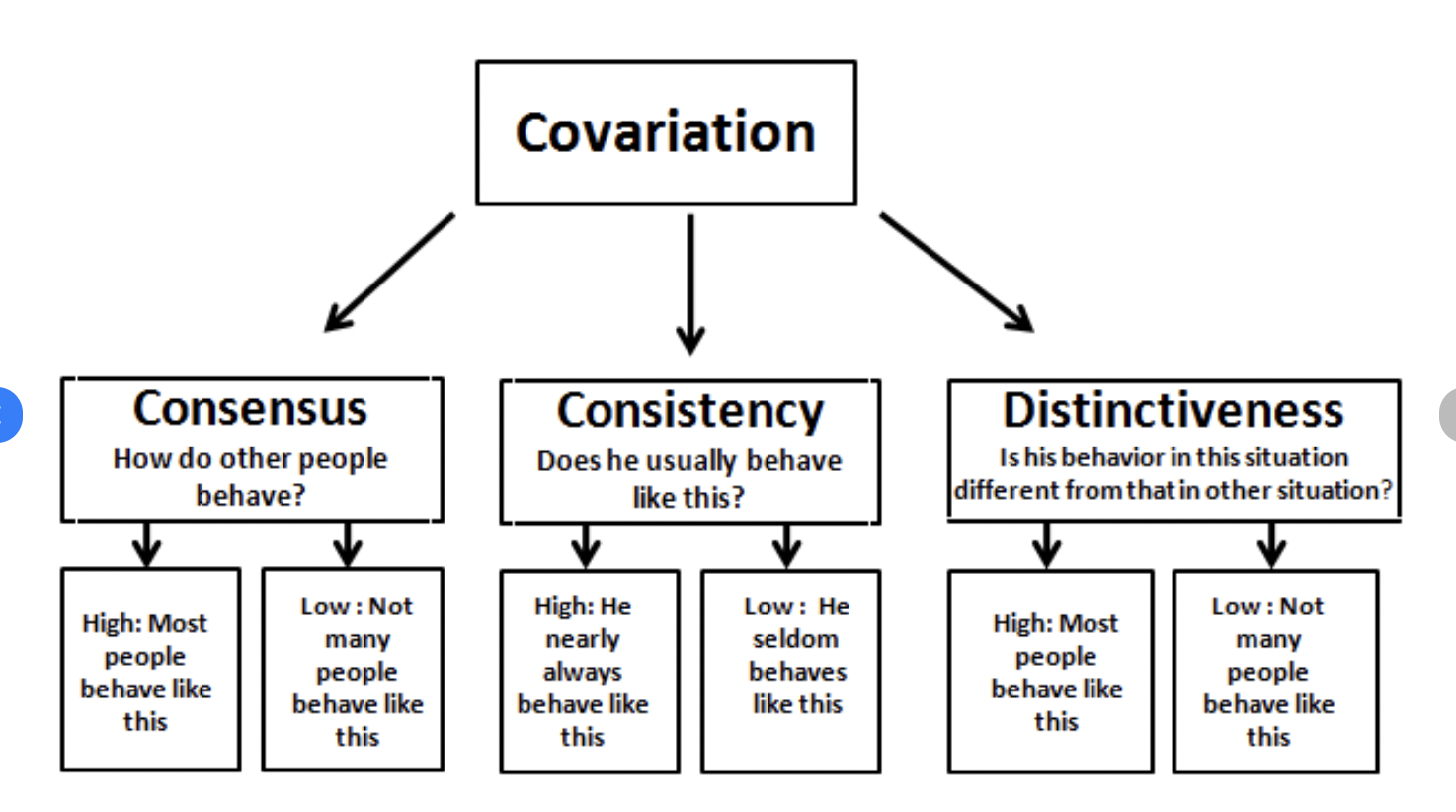
Kelley’s Covariation Model (ch.4)
model to explain the cognitive process used in deciding to make internal or external attribution’s for others behavior
3 factors
Consistency
Distinctiveness
Consensus
Actor/Observer Difference (ch.4)
see our own behaviors as caused by situational factors, see others’ behaviors as dispositionally motivated
Egocentric Bias (ch.4)
in a group, exaggerate amount & importance of our own contributions
Self-serving Bias (ch.4)
credit successes to internal/dispositional factors and credit failures to external/situational factors
Unrealistic Optimism
good things are more likely to happen to us and bad things aren’t
Defensive Attributions
explanations for other people’s situations/ outcomes that defend us from feelings of
vulnerability or mortality and protect self-esteem
Belief in a Just World
bad people get bad things, good people get good
Bias Blindspot (ch.4)
failure to recognize one’s own biases
Lau & Russell (1980):Players, coaches, and sportswriters study
Spontaneous Trait Interference (ch.4)
automatic inference of a trait after exposure to someone’s behavior
Fundamental Attribution Error (ch.4)
overestimating that other’s behavior is due to internal factors rather than situational factors
Perceptual Salience (ch.4)
the seeming importance of info that is the focus of people’s attention
Two-step Process of Attributions (ch.4)
automatic: make an internal attribution
controlled: adjust attribution by considering the situation
may still fail to make adjustment