Lesson 5: Understanding the Internet and the World Wide Web
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Internet
Largest global network connecting millions of computers.
Protocols
Rules governing data exchange over the Internet.
IP Address
Unique identifier for a device on a network.
Router
Device directing data packets across networks.
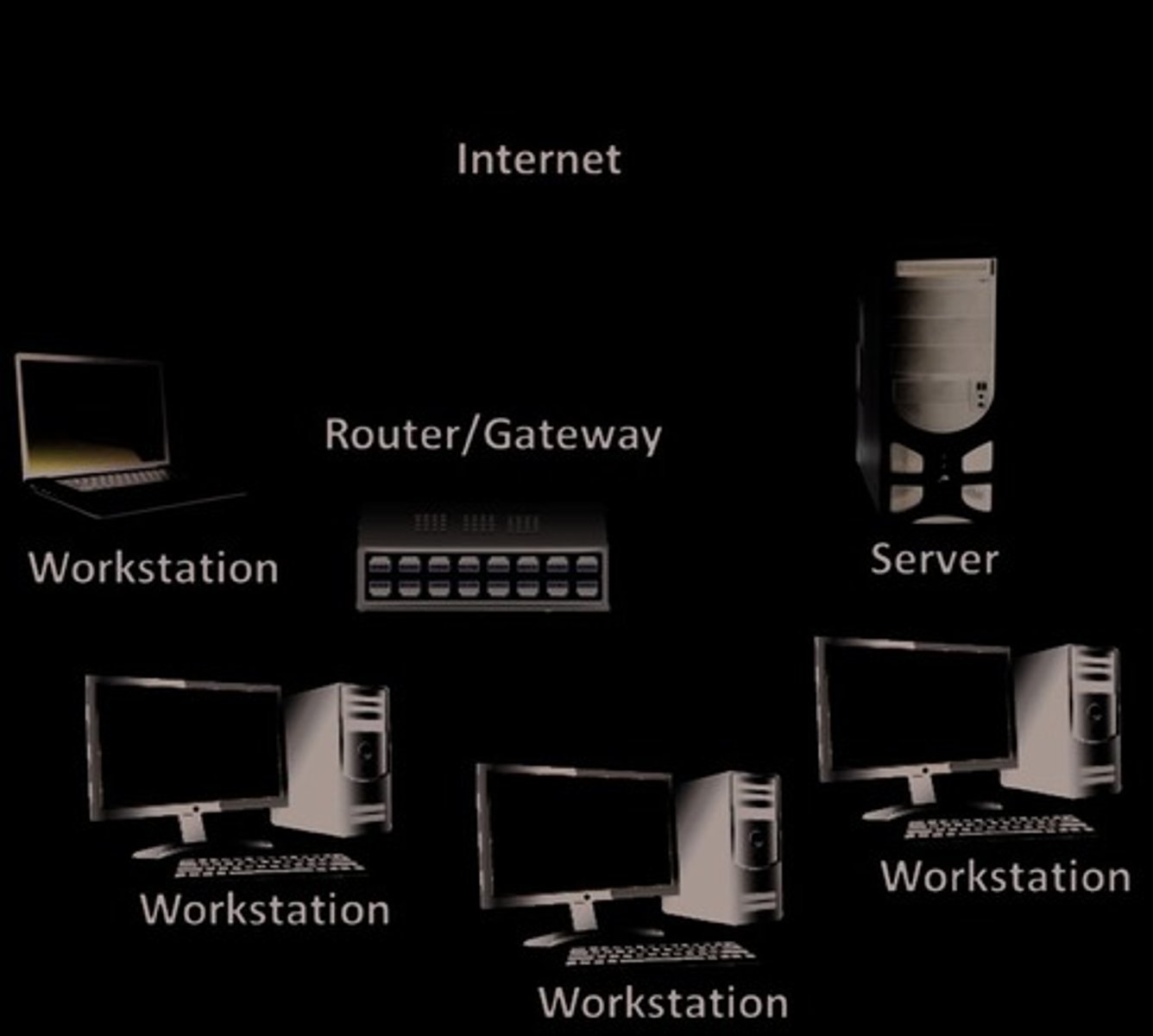
Client-Server Model
Architecture where clients request services from servers.
Domain Name Server
Translates domain names into IP addresses.
Email Protocols
Standards for sending and receiving email messages.
Cloud Computing
Internet-based computing providing shared resources.
E-commerce
Buying and selling goods/services online.

TCP/IP
Primary protocol for Internet communication.
ARPANET
First operational packet-switching network, precursor to Internet.
ISP
Company providing Internet access to users.
LAN
Local Area Network connecting computers in a limited area.
Packets
Small units of data transmitted over a network.
Node
Any active device on a network capable of communication.
Network
Group of interconnected computers sharing resources.
Information Superhighway
Metaphor for the Internet as a data transport system.
Data Compression
Reducing the size of data for transmission efficiency.
Point-to-Point Communication
Direct communication between two network endpoints.
Web Browser
Software for accessing and displaying web content.
Web Server
Server hosting websites and serving content to browsers.
NCP
Network Control Protocol, predecessor to TCP/IP.
Cyberspace
Virtual environment of the Internet and online activity.
Internet Architecture Board
Group overseeing technical development of the Internet.
ICANN
Organization managing domain names and IP addresses.
InterNIC
Network information center for domain registration.
National Science Foundation
U.S. agency supporting research and education in science.
Client/Server Model
A communication model where a computer user (client) requests a service from another computer (server) on the network.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Responsible for breaking data down into IP packets before they are sent, and for assembling the packets when they arrive.
Internet Protocol (IP)
Responsible for addressing each packet of data and sending and receiving data packets over the Internet.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
Takes care of the communication between a web server and a web browser, used for sending requests from a web client to a web server.
HTTPS (Secure HTTP)
Takes care of secure communication between a web server and a web browser, typically handling credit card transactions and other sensitive data.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Protocol used for encryption of data for secure data transmission.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Used for the transmission of emails.
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
Enables SMTP to transmit multimedia files including voice, audio, and binary data across TCP/IP networks.
Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
Used for storing and retrieving emails.
Post Office Protocol (POP)
Used for downloading emails from an email server to a personal computer.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Responsible for the transmission of files between computers.
Packet
The basic unit of information in network transmission; a collection of data that contains a segment of data and the address where the data are to be sent.
Packet Segmentation
The process of splitting packets of data when the data packet is larger than the maximum transmission allowed by the network.
Gateway
A node that allows you to gain entrance into a network, typically a router that links you to the Internet.
Domain Name Server (DNS)
Maintains a directory of domain names and translates them to Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
Octets
The four numbers in an IP address, each ranging from 0 through 255.
IPv4
The original IP addresses that use a 32-bit address, allowing for approximately 4.3 billion addresses.
IPv6
A newer version of IP developed to handle increasing Internet traffic, using a 128-bit address allowing for 340 trillion trillion trillion addresses.
Hexadecimal Characters
The characters used in an IPv6 address, consisting of both letters and numbers (0 through 9, and A through F).
Broadband
High-speed Internet access that is always on and faster than traditional dial-up access.
Always-On Connection
A connection that is always connected to the Internet, such as a cable connection.
Dial-Up Connection
A traditional method of connecting to the Internet using a modem to make the connection to an ISP.
Dial-Up Service
Affordable Internet access using existing phone lines.
Cable Access
Broadband Internet using cable television infrastructure.
Cable Modem
Device connecting coaxial cable to computer for Internet.
Satellite Access
Internet access via satellites for remote areas.
Fiber Optic (FiOS)
Internet access using light through optical fibers.
Wi-Fi
Wireless Internet connection using radio waves.
4G LTE
Fourth-generation cellular technology for fast Internet.
5G
Fifth-generation cellular technology with limited availability.
World Wide Web
System for accessing information over the Internet.
Hyperlink
Clickable link to another web page or resource.
Client
Computer requesting information from a server.
Downloading
Transferring files from server to computer.
Uploading
Transferring files from computer to server.
HTML
Language for developing and structuring web pages.
URL
Global address for resources on the Web.
Protocol
Standard for data exchange on the Internet.
Domain Name
Website's server name in a URL.
Path
Specific location of a resource on a server.
Resource Name
Name of the file or resource in a URL.
Ethernet Cable
Cable connecting modem to computer for Internet.
Coaxial Cable
Cable used for cable modem Internet connections.
Firewall
Security system blocking unauthorized network access.
Port
Numerical location for network services on a server.
DNS
Translates domain names into IP addresses.
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol, used for web communication.
Top-Level Domain (TLD)
Suffix indicating website type, e.g., .com, .gov.
Default Homepage
Page served when no resource name is specified.
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol, breaks data into packets.
Gateway Computer
Router connecting user to Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Web Crawler
Bot that indexes information on the web.
Search Engine
Software for finding information online.
Cookies
Stored data for user information and preferences.
Browser Cache
Temporary storage of web pages for faster access.
Browser History
List of recently visited web pages.
Bookmark
Saved link to revisit a web page later.
New Tab
Opens a new page within the same browser window.
New Window
Opens a completely independent browser window.
Refresh
Updates the current web page content.
Web 2.0
Current web state with user interactivity and collaboration.
Static Web
Original web with non-interactive, fixed pages.
Community-Based Input
User contributions and interactions on websites.
Data Packets
Small bits of data transmitted over the Internet.
Error Message
Indicates an invalid or non-existent domain request.
ID Number
Unique identifier stored in cookies for users.
Spyware
Malicious software that tracks user information.
Subfolders
Folders within a path on a server.
Data Transmission
Process of sending data over the Internet.
Wikis
Websites that enable users to contribute, collaborate, and edit site content.
Mobile devices
Devices such as smartphones and tablets that have helped to propel Web 2.0.
Social networking
The practice of expanding the number of one's business and/or social contacts by making connections through individuals.
Facebook (FB)
A social networking site launched in 2004, initially developed for students to maintain contact, now has billions of users worldwide.