French Revolution
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Enlightenment
A period where people became smarter and used logic and scientific evidence rather than relying on religion.
Enlightenment challenges
Enlightenment challenged absolutism
Philosophers
Montesquieu
Voltaire
Rousseau
Montesquieu
Believed in constitutional monarchy, with the power of a monarch kept in check by a legislative assembly. This challenged the Ancien Regime as it made the King lose total power. Challenged divine right of kings.
Voltaire
Advocated freedom expression:
Freedom or speech, freedom of religious beliefs, freedom of political thought.
He also was a critic of the power and privilege of the Catholic Church.
This challenged the church and absolutism.
Rousseau
Argued that rights and responsibilities should be shared equally within a society and that everyone has the right to freedom.
This challenged both the estates system (unequal tax system). It challenged the ancien regime because many people weren’t completely free, the system of feudalism meant that the peasants could not acquire enough wealth to escape the lives they led. Also, the monarchy had the right to take away peoples freedom without trial using letters de cachet.
Reasons for Revolution
-Royal finances and the failure of financial reforms.
-Poverty in the countryside and towns.
-The Enlightenment.
-The American War of Independence.
-Harvest quality (1788-88)
-The rise of the bourgeois.
-Resentment of the tax system and corruption.
-That actions and character of Louis xvi.
-The decisions of the Assembly of Notables and the Parlememt or Paris

Topic 2
The Great Fear
A rumour that that in an attempt to overthrow revolution and defend their power the nobility were gathering military forces to suppress the peasants. This resulted in violence and peasants attacked their social superiors as they were seen to be the source of oppression.
To appease the peasants the noblemen were encouraged to appease feudalism.
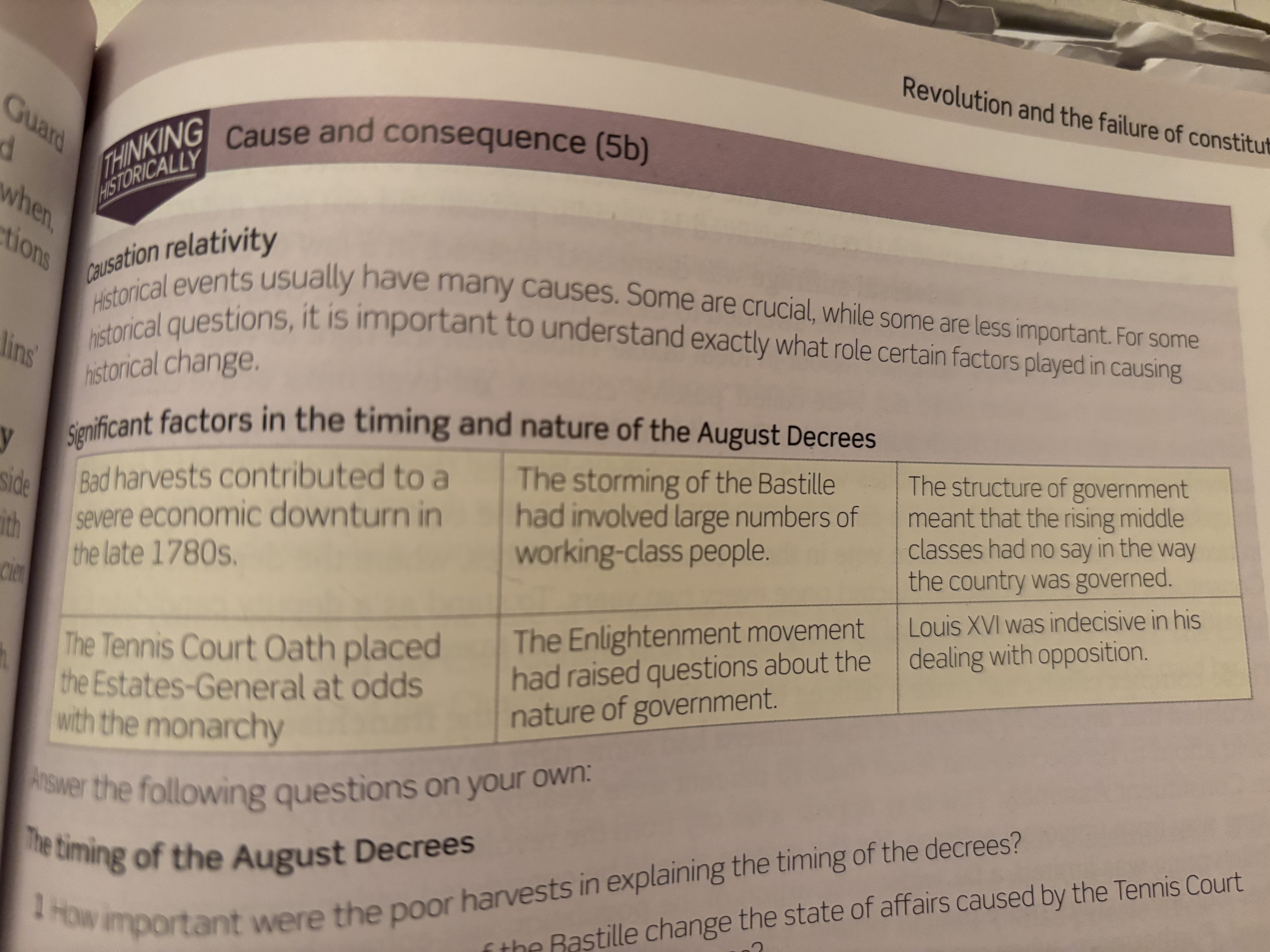
The August Decrees
They abolished many privileges that the nobility had including venality. Positions in the Church, military and civil became open to everyone. It also aimed to equally tax all 3 estates.
The significance of the August Decrees
The process of abolishing and making policies didn’t bring about sudden transformation as in practice few would see immediate or direct change. The Decrees were considered as more of a statement to cast aside the nobility’s privileges in the Ancien Regime.
The Declaration of Rights of Man
Was a death warrant to the systems privilege and the Ancien Regime. It is considered to be the most significant document in the French Revolution.
-Was issued by the Constituent assembly on the 26th August 1789.
-Lafayette and Jefferson were key authors.
-Men are born and remained equal in rights.
-Rights of liberty, property, security and resistance to oppression.
-Liberty consists in the freedom to do everything which doesn’t injure anyone.
-Law can only prohibit such actions as hurtful to society, nothing may be prevented which is not forbidden by law.
-Every citizen has the right to participate personally or through a representative. That rights are equal whether it protects or punishes.
- No one can be punished based on religion, provided that their manifestation of the beliefs doesn’t disturb public order established by law.
-The free communication of ideas and opinions to speak, write and print with freedom but abuse of this freedom will be defined by law.
-Taxes should be evenly distributed.
August 5th
Louis refused the August Decrees.
•This caused more agitation and anger in the Sans-Culottes.
•This caused Louis to hire Flanders to protect the Royal Family.
•Despite the discontent of the public, Louis voiced his objection of the Declaration of Rights of Man.
October Days
•A radical newspaper published a rumour that Louis’s officers trampled a revolutionary cockade (symbol) triggering a huge demonstration led largely by women to the Hotel de Ville in Paris. 6,000-7,000 people.
•When crowds reached Versailles, some broke in and killed guards. Marie Antoinette fled to Louis’s private apartment narrowly escaping death as her chamber was ransacked.
• The royal family were spared by Lafayette and the Royal Guard who convinced Louis to move the royal court to Paris. The National Guard escorted them to the Tuileries in Paris.
•Some deputies in the constituent assembly refused to attend meetings and left their positions, believing that they would be targeted next. The loss of deputies blew Louis’s support within the assembly.
Significance of the October Days
It had a symbolic significance as the event gave a sense of victory of the revolution over the Ancien regime
Significant factors of the October days
Reforms of the Constituent Assembly
•Though absolutism was over it was agreed that the monarch should remain.
•Louis retained the right to appoint ministers, ambassadors and military commanders. He was also granted 25 million livres to allow the royal family to live in a manner.
•Louis was stripped from legislative power so he could no longer initiate new laws or taxes.
Louis had some legislative power from suspensive veto allowing him to delay or suspend laws created for up to 4 years.