chemistry year 10-11 -> topic 6 rate and extent of chemical change
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
factors affecting the rate of a reaction
collision theory
for particles to react they must collide with enough energy.
activation energy = the minimum energy required
the more frequent the successful collisions are, the faster the rate of the reaction
what are the factors affecting the rate of a reaction (5)
increased temperature
increased surface area of solids
increased concentration of solutions
increased gas pressure
using a catalyst
factors affecting the rate of a reaction
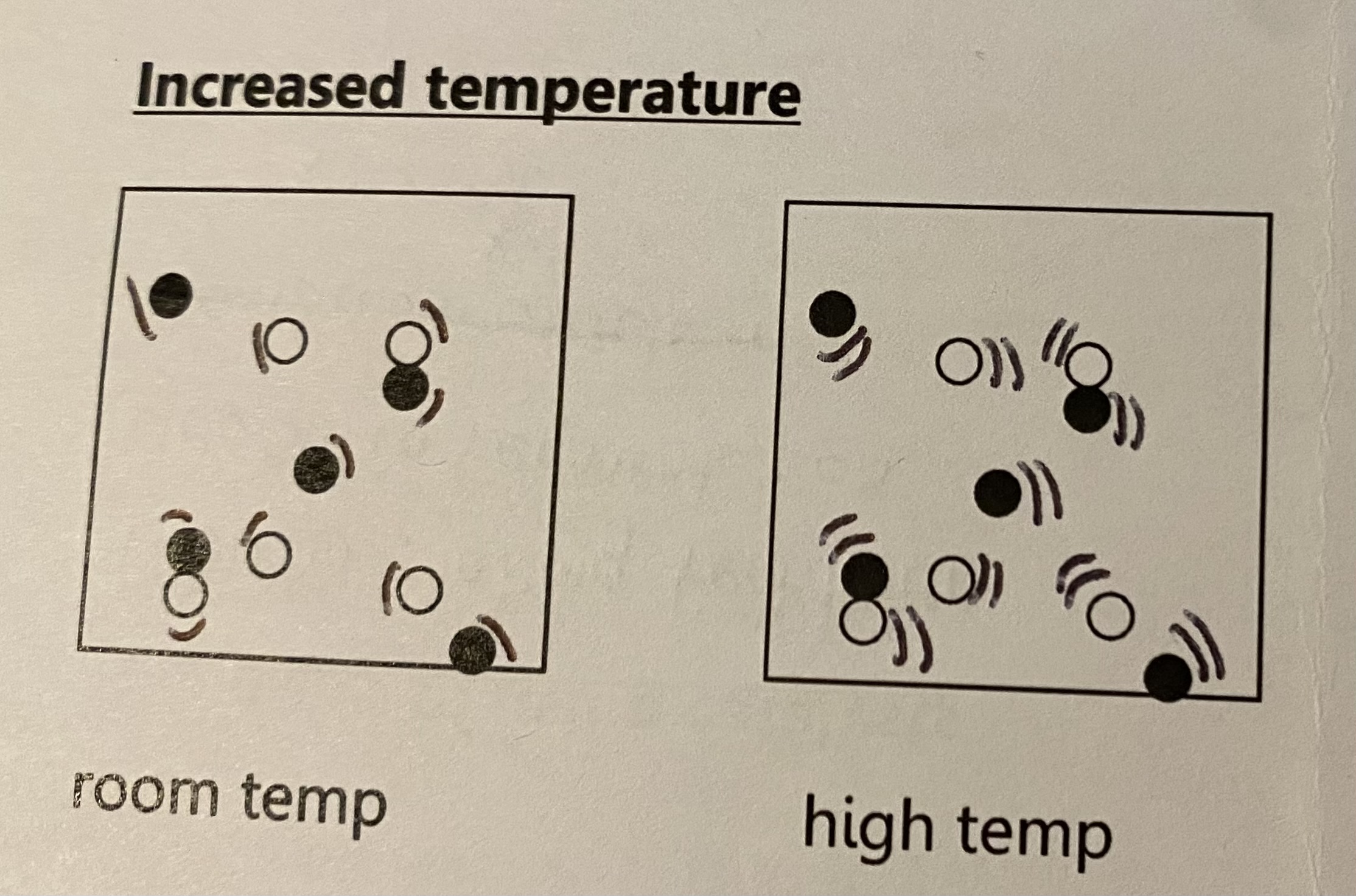
increased temp
as temp inc, reaction rate inc becayse the particles have more energy and move quicker and so particles collide more frequently
more of the collisions are successful because more of the particles have activation energy
factors affecting the rate of a reaction
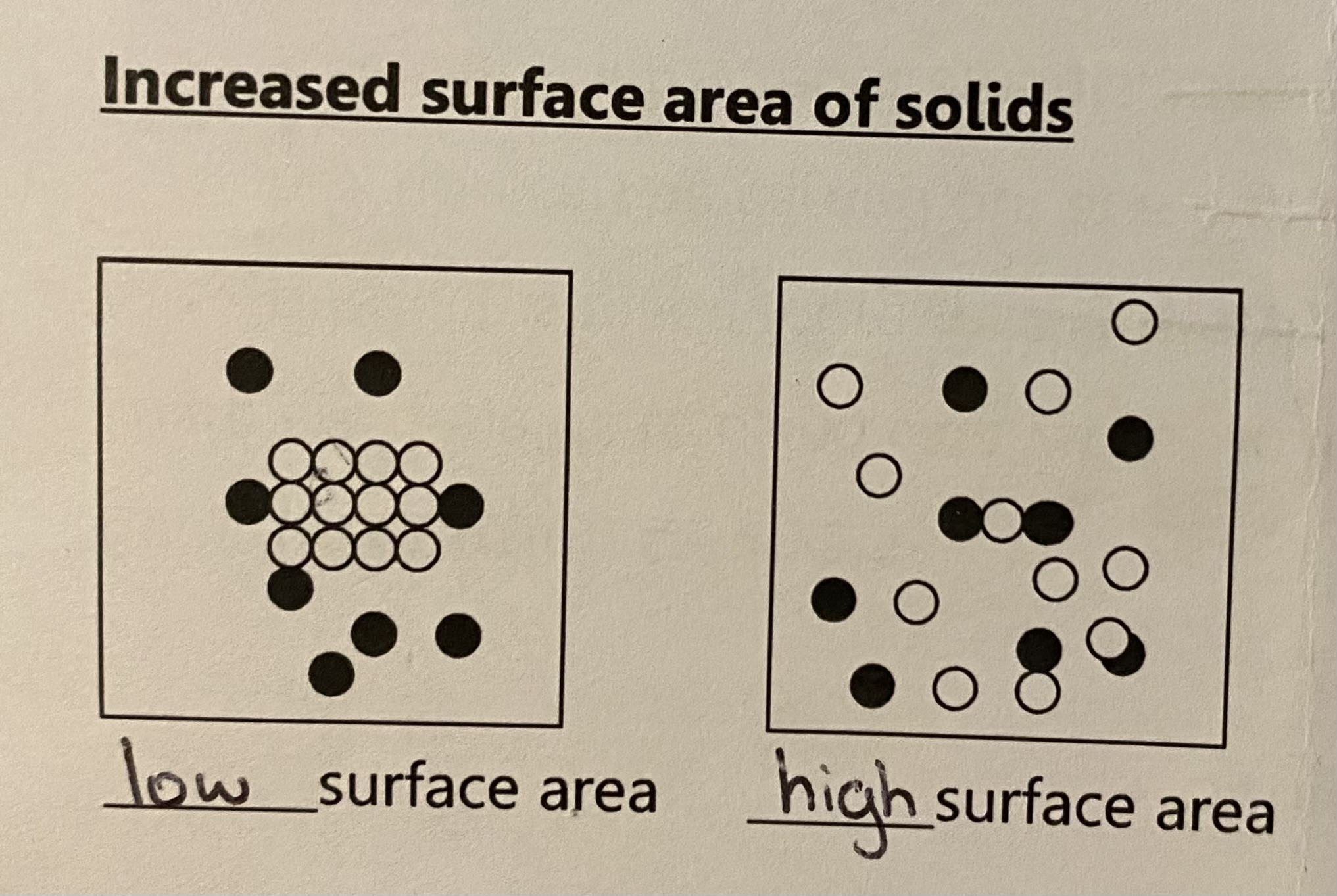
inc surface area of solids
does energy change
as surface area inc, reaction rate increases because there are more particles available to react and therefore an increase in the frequency of collisions between the reacting partcles
(energy doesnt change)
factors affecting the rate of a reaction
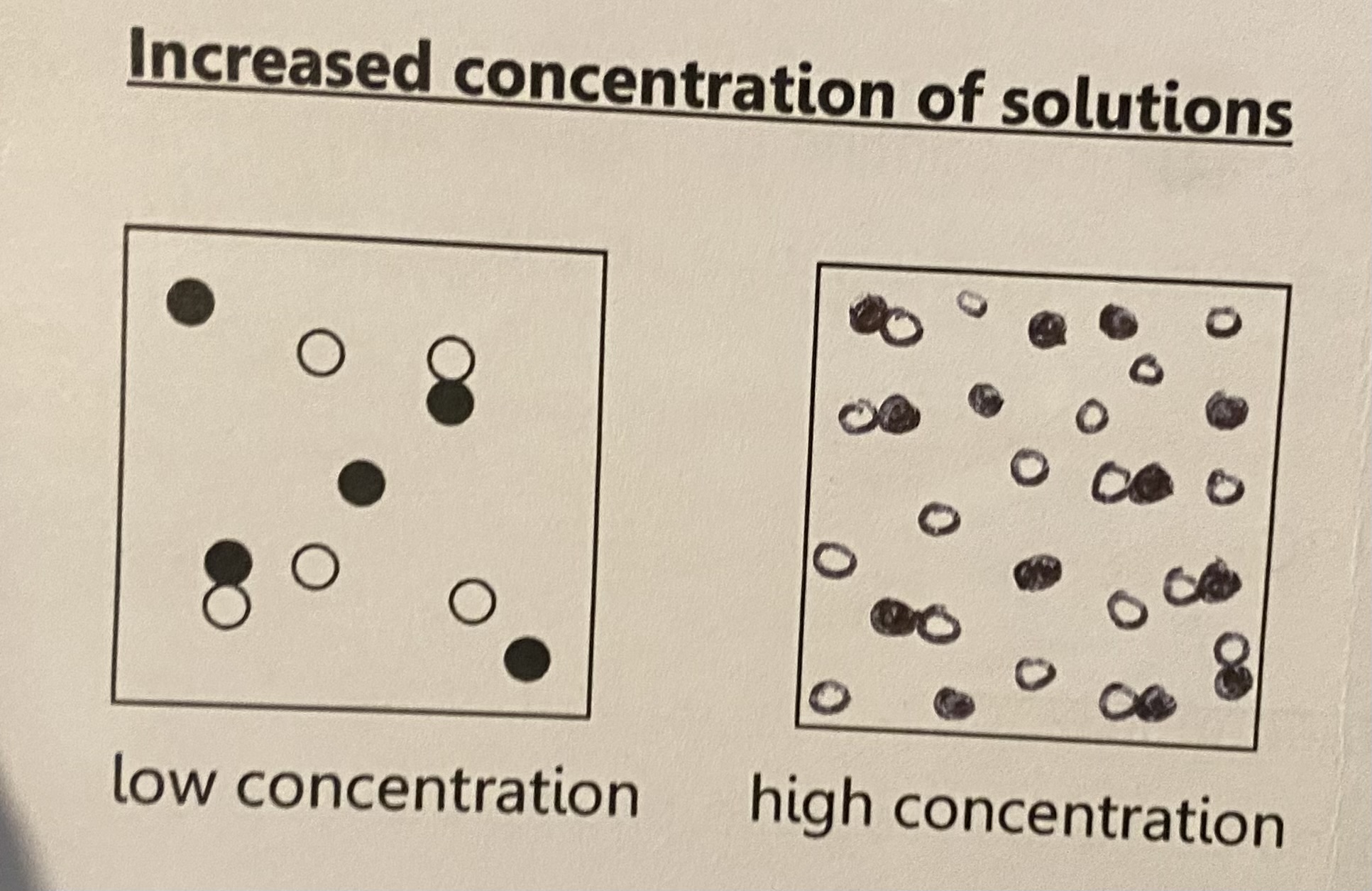
inc concentration of solutions
dpes energy change
as concentration increases reaction rate increases because there are more particles per unit volume and therefore an increase in the frequency of collisions between the reacting particles
(energy doesnt change)
factors affecting the rate of a reaction
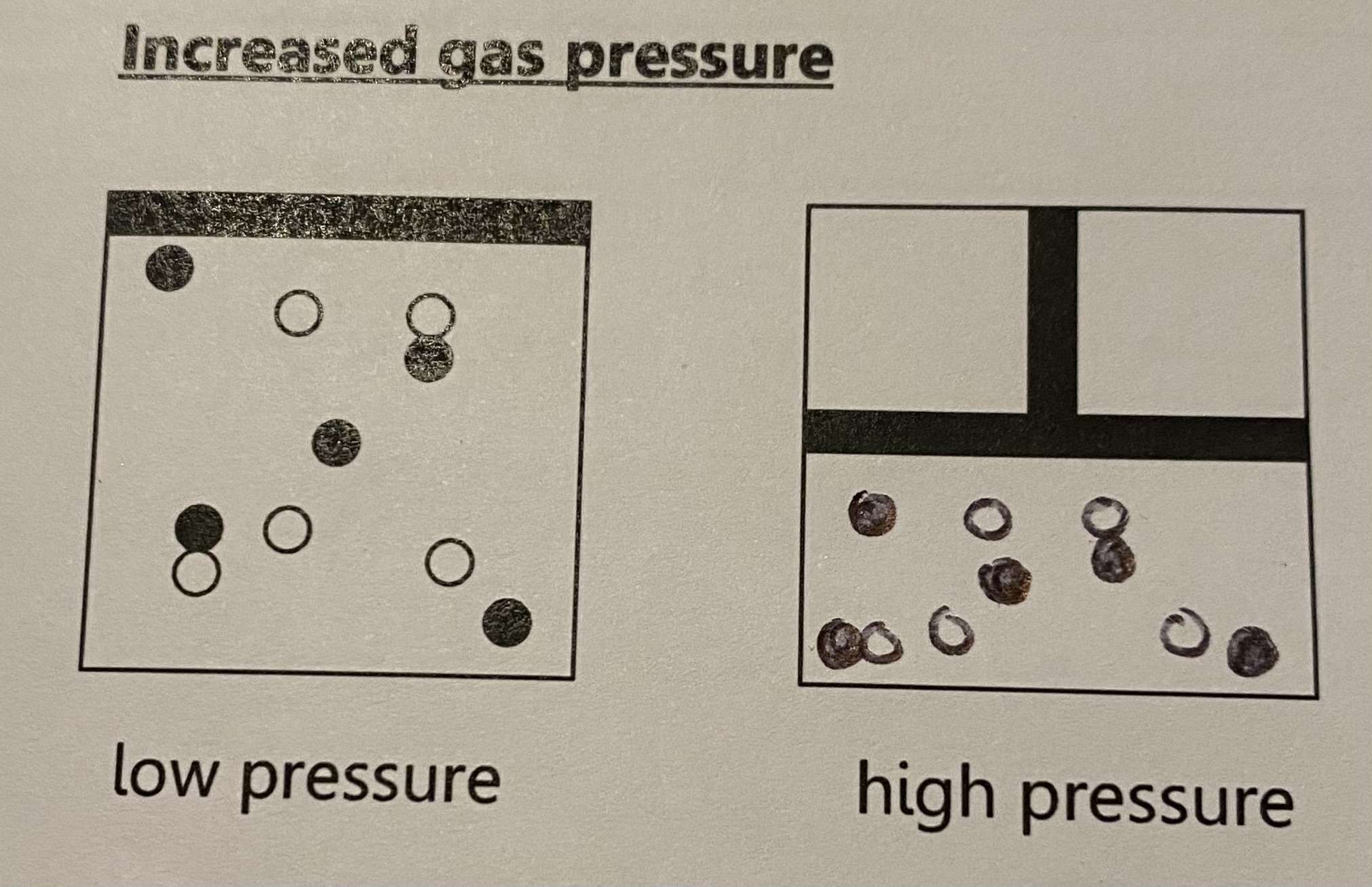
increased gas pressure
does energy change
increasing the pressure in a gas can be done by reducing the volume thsis squashes the particles together increasubg the pressure causing particles to collide more frequently, therefore inc rate of reaction
energy doesnt change
factors affecting the rate of a reaction
using a catalyst
catalsysts increase the rate of chemical reactions but are not run out during the reaction
different reactions need different catalysts
enzymes are catalysts in biological systems
catalysts increase the rate of reaction by providing a different pathway for the reaction that has a lower activation energy