Cycles of Matter in an Ecosystem
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
the ways in which and element-or compound such as water- moves between its various living and non-living forms and locations in the biosphere
biogeochemical cycle
involving gaseous materials such as oxygen, nitrogen and carbon dioxide
volatile cycles
materials such as phosphorous are transferred through the ecosystem in sedimentary cycles
non-volatile cycle
what are the 2 types of reservoirs
non-biological reservoirs and biological reservoirs (are the living organisms)
non-biological reservoirs include?
include air (atmosphere), water (hydrosphere) and soil (lithosphere)
2 types of pathways
biological process and physical processes
e.g absorption of nutrients by roots of plants or by aquatic organisms
biological processes
e.g removal of nutrients from land to aquatic bodies by erosion and expulsion of gases during volcanic eruptions
physical processes
the rate of movement of nutrients between two reservoirs along biological and physical pathways
flow rate or flux rate
period of time for which a nutrient stays withing a reservoir
residence time
is a key ingredient of living tissue
is a basic constituent of all organic compounds and is involved in the fixation of energy via photosynthesis
carbon
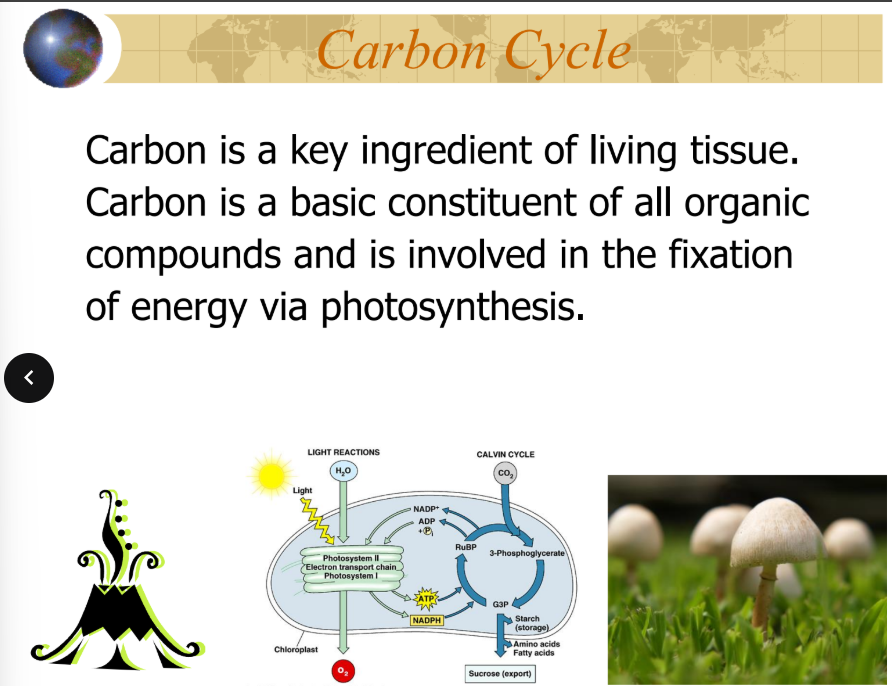
major reservoirs of carbon:

is the pivotal molecules in the carbon cycle
carbon dioxide
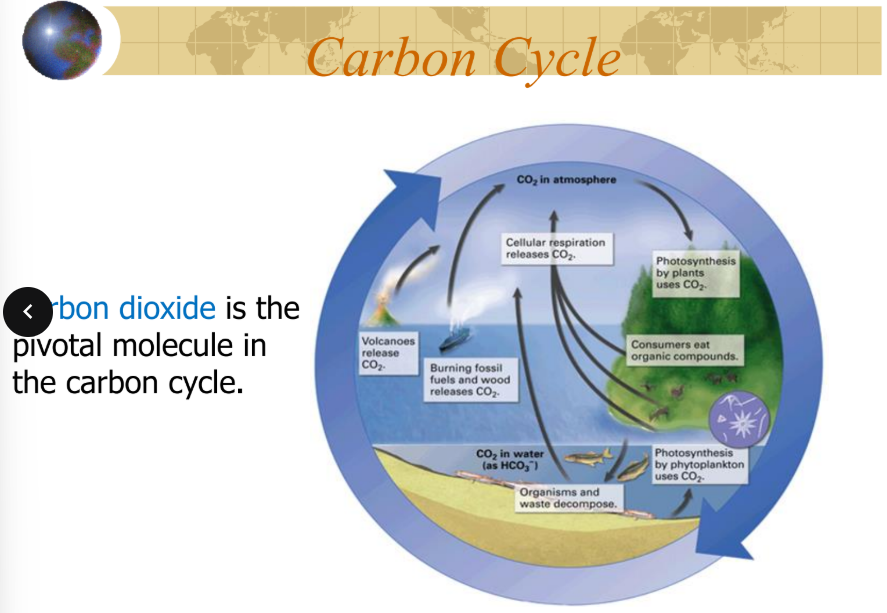
carbon dioxide is released into atmosphere by:
volcanic activity
respiration
human activities
the decomposition of organic matter
carbon moves between organisms and atmosphere as a consequences of two reciprocal biological processes:
photosynthesis and respiration
what is physical pump

driven mainly by autotrophic phytoplankton
photosynthesis is the initial method of bringing carbon into the biological pump
carbon stays in the food web or released from the food web in the form of defecation or dead tissues
tiny pieces of carbon-rich material sink under the force of gravity (marine snow)
biological pump
what is carbonate pump



complex mixture of carbon compounds and humic substances

is needed to build the most vital macromolecule of life- proteins and nucleic acids and forms the porphyrin rings of chlorophyll and hemoglobin
- most frequently deficient nutrient in crop production
nitrogen (nitrogen cycle)
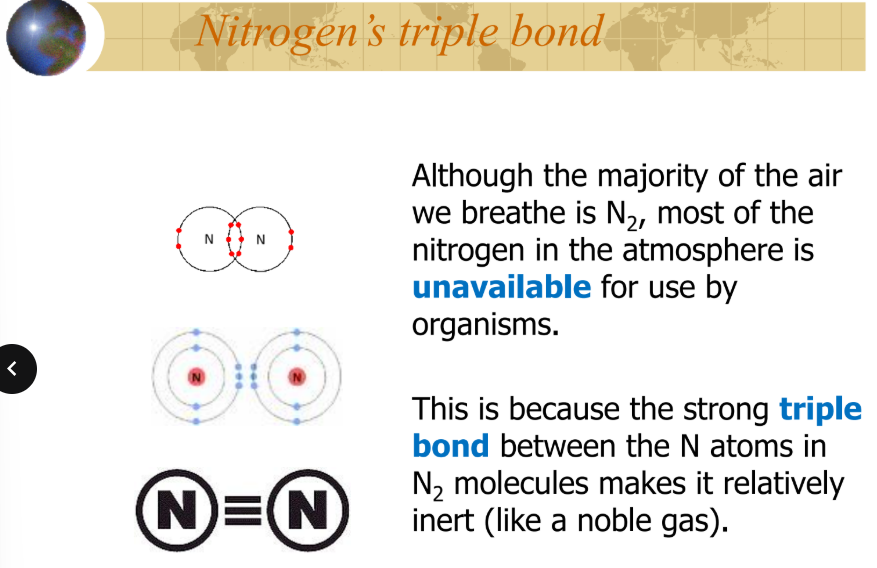
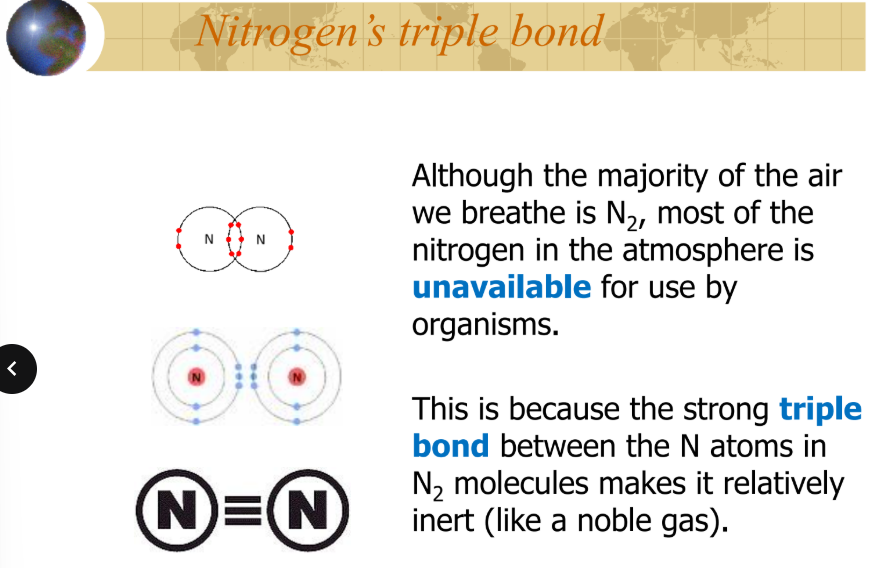
are capable of converting (N2) into ammonia (NH3) and ammonium (NH4+)

was the major source of soil nitrogen until recent times when the burning of fossil fuels became a major source of atmospheric deposition
atmospheric sources of soil nitrogen: lightning
nitrogen oxides come from a variety of combustion sources that use fossil fuels


are essential to the nitrogen cycle
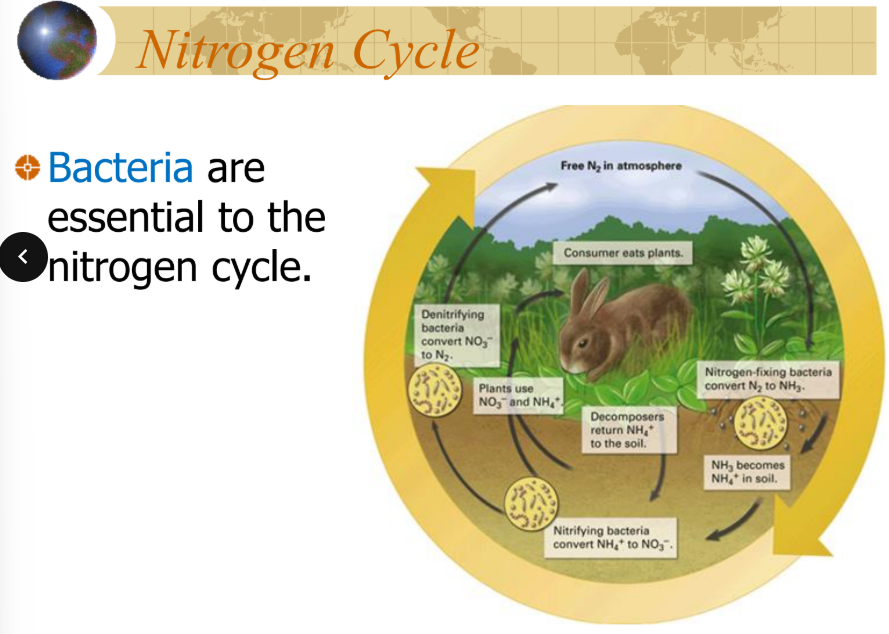
the most important source of fixed N is?
